Thermodynamic Magic Square | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
Maxwell Thermodynamic Equations
In thermodynamics, the Maxwell equations are a set of equations derived by application of Euler's reciprocity relation to the thermodynamic characteristic functions.
The Maxwell relations, first derived by James Clerk Maxwell, are the following expressions:
- dH = TdS + VdP
- dG = –SdT + VdP
- dA = –PdV – SdT
- dV = TdS – PdV
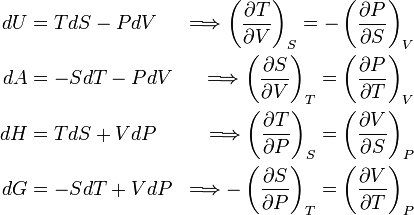
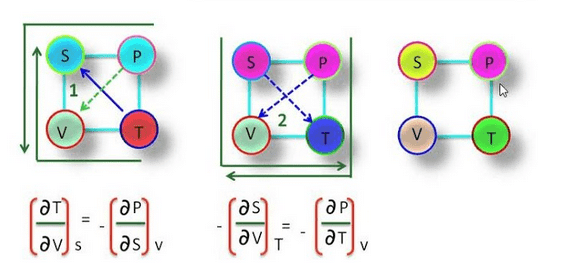
Thermodynamic Magic Square
The magic square plays a very important role in thermodynamic. By using magic square we find many important relationships between thermodynamic function or quantity.
These relations are known as Maxwell thermodynamic equations. S, P, V, T are at the corner of the square & known as thermodynamic coordinates.
We can find the Maxwell thermodynamic equation by using magic square.
dA = (–P)dV + (–S)dT
dA = –PdV – SdT …(3)
dG = VdP + (–S)dT
dG = VdP – SdT …(4) i.e.,
we can find the Maxwell thermodynamic equation by using magic square.
Maxwell Relationship between Thermodynamic Coordinates
i.e., S, P, V, T.
..........(2)
..............(3)
................(4)
We can find the relation between thermodynamic coordinates by using Euler’s theorem.
We know that if z s the function of x & y then z = f(x, y)
⇒
if z is a state function then it follows Euler’s theorem
i.e.
⇒
Four Maxwell thermodynamic equation are given below:
dH = TdS + VdP
dG = VdP – SdT
dA = –PdV – SdT
dV = TdS – PdV
We know that H, G, A & V are state function i.e., it follow the Euler’s theorem.
dH = TdS + VdP
⇒
i.e.
dG = VdP – SdT
⇒
dA = –PdV – SdT
⇒
i.e.
dV = TdS – PdV
⇒
Expansivity and Compressibility
The gas expands on heating through the expansion of gases is much more than that of liquids. Similar gas compressed on increasing the pressure.
“The variation of volume V with temperature T, keeping pressure P constant is called the coefficient of thermal expansion or expansivity. It is denoted by α. Thus
Similarly “the variation of V with P, keeping T constant, is called the coefficient of isothermal compressibility or compressibility. It is denoted by β
Another coefficient, isochoric thermal expansion coefficient, when the variation of P with T, keeping V constant is represented by γ
Q.1. Find the value of α, β, γ for an ideal gas?
Sol. Ideal gas equation is
PV = nRT (for n mole)
PV = RT (for 1 mole)
for ideal gas
PV = nRT
⇒
⇒
⇒ …(1)
for ideal gas
PV = nRT
PV = nRT
|
84 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Thermodynamic Magic Square - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What are Maxwell's thermodynamic equations? |  |
| 2. What is the thermodynamic magic square? |  |
| 3. What is expansivity in thermodynamics? |  |
| 4. What is compressibility in thermodynamics? |  |
| 5. How are the thermodynamic magic square and Maxwell's equations useful in practical applications? |  |

















