Tips and Tricks: Coding & Decoding | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Common Coding Schemes |

|
| Tips and Tricks for Coding & Decoding |

|
| Step-by-Step Strategy for Tackling Questions |

|
| Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them |

|
Coding and decoding questions in the CAT LRDI section test your ability to identify patterns, decode substitution rules, and reverse-engineer logical systems. These questions often involve mapping letters, numbers, or symbols to alternative representations using hidden rules. Below are specific, actionable tips and tricks derived from expert analysis of past CAT patterns and high-scoring strategies.
Common Coding Schemes
Recognise these frequently tested patterns—memorise them, don’t re-derive under pressure:
Fixed Shift (Caesar Cipher):
Every letter is moved by the same fixed number in the alphabet (e.g., shifting +3 turns A into D, B into E, and so on).Alphanumeric Mapping:
Assign A=1, B=2… Z=26, perform the given arithmetic operation on each number, then convert back to letters if needed.Positional Encoding:
Replace a word by the sum of its letter positions (e.g., CAT → 3 + 1 + 20 = 24) or use that sum in further coding steps.Alternating Operations:
Apply different shifts to letters in turn (e.g., +2 for the first letter, –1 for the second, +2 for the third, etc.) to create a pattern.Reversal & Pair-Swap:
First reverse the entire word (ABCD → DCBA), then swap letters in adjacent pairs (DCBA → CDAB).EJOTY & Reverse-EJOTY:
Use the letters at positions 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 (E, J, O, T, Y) as fixed reference points or map around them in reverse order.
Tips and Tricks for Coding & Decoding
1. Break the Code with the "Positional Arithmetic" Framework
Convert letters to their positional values (A=1, B=2… Z=26) and look for arithmetic patterns.
Why it matters: 80% of CAT coding questions use positional math.
Example: If "CAT" is coded as 31120:
C (3) | A (1) | T (20) → Concatenation of positions.
Advanced Twist: Check for operations like:
Sum: C + A + T = 3 + 1 + 20 = 24
Product: C × A × T = 3 × 1 × 20 = 60
Hybrid: (C × A) + T = (3×1) + 20 = 23
2. Use the "Vowel-Consonant Split" Strategy
Treat vowels (A, E, I, O, U) and consonants separately.
Why it matters: CAT frequently applies different rules to vowels and consonants.
Example: "LOGIC" → Vowels (O, I) shifted +2 → Q, K; Consonants (L, G, C) shifted -1 → K, F, B → "KQFBK".
3. Check for Number-to-Letter or Letter-to-Number Mappings
If the code is numbers and the message is letters, assign numbers to letters (A=1, etc.) and look for patterns (e.g., +n, ×n). If reversed, decode numbers to letters. Watch for traps like reverse mappings (26=A).
Why it matters: Some CAT questions map numbers to letters (e.g., 1=A, 2=B) or vice versa, often with a twist (e.g., offset, reverse). These are common in mixed coding sets.
Example: Message: PEN, Code: 11-22-25. P=16, E=5, N=14. No direct match.
Try sum of digits: 1+1=2, 2+2=4, 2+5=7.
Adjust: 16-14=2, 5-1=4, 14-7=7.
Pattern: Code = position - (sum of previous code’s digits).
Decode SUN: S=19, U=21, N=14 →
First code: 19-0=19.
Second: 21-(1+9)=11.
Third: 14-(1+1)=12.
Code: 19-11-12.
EduRev Tip: CAT uses tricky mappings (e.g., 10≡1+0=1). Test 2–3 mappings (direct, reverse, digit sums) in 30 seconds. Practice 5 number-letter sets daily.
4. Watch for Irregularities and Exceptions
If a pattern works for 3–4 letters but fails for one, check if it’s an exception.
Why it matters: Some codes have exceptions (e.g., "X" always becomes "Δ").
Example: If "EXAM" is coded as "ΔY9L", "E" might always map to "Δ".
5. Leverage Options to Reverse Engineer Patterns
Apply the suspected pattern to one message and check if the result matches an option. If ambiguous, test each option by decoding backwards to the message.
Why it matters: CAT coding questions are MCQs, and options can guide you to the correct pattern, saving time when the rule is unclear.
Example: Message: MAN, Code: ?,
Options: AFG, PJW, OIV, BEH.
Decoding:
M=13, A=1, N=14.
Try +2: 13+2=15(O), 1+2=3(C), 14+2=16(P).
Code OCP is not in the options.
Try option OIV: O=15, I=9, V=22.
Check: 15-13=2, 9-1=8, 22-14=8.
No consistent rule.
Test BEH: 2-13=-11, 5-1=4, 8-14=-6.
Try mod 26: -11≡15, 4, -6≡20.
Pattern unclear.
Correct option (after testing): OIV (pattern: complex shift, likely +2 mod 26).
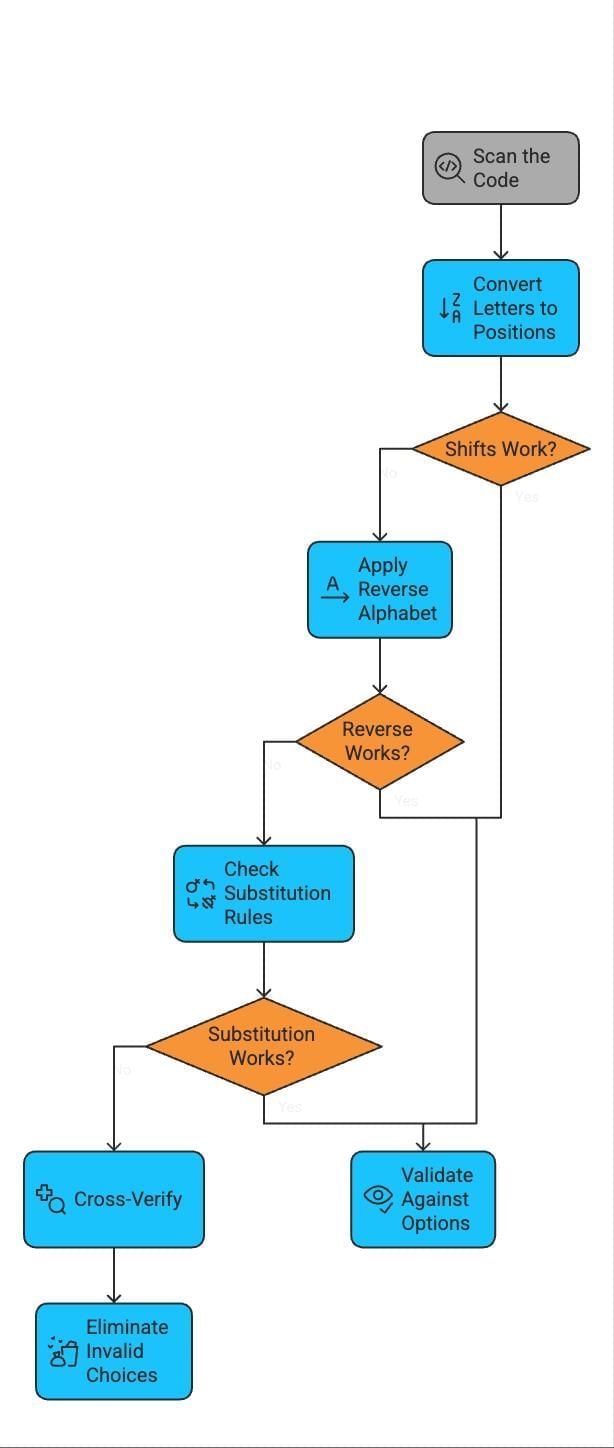
Step-by-Step Strategy for Tackling Questions
- Scan the Code: Note if it’s letters, symbols, numbers, or mixed.
- Convert Letters to Positions: Use A=1, Z=26 to spot numerical patterns.
- Test for Shifts: Check forward/backward shifts of 1–5 positions.
- Apply Reverse Alphabet: If shifts don’t work, test A↔Z logic.
- Check Substitution Rules: Look for vowel/consonant swaps or symbol replacements.
- Validate Against Options: Eliminate invalid choices using your decoded rule.
- Cross-Verify: Ensure the rule applies to all letters in the word.
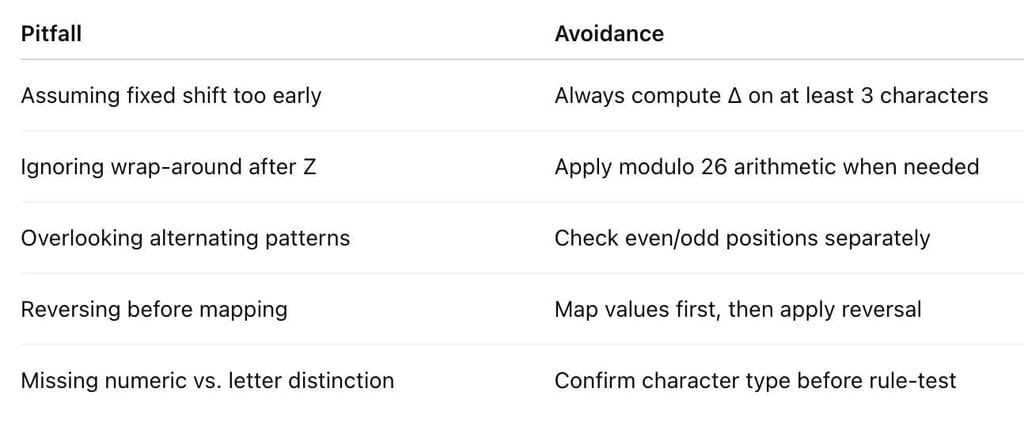
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
|
87 videos|172 docs|99 tests
|
FAQs on Tips and Tricks: Coding & Decoding - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What are the common types of coding schemes used in exams like CAT? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively decode a coded message in a coding-decoding question? |  |
| 3. What strategies can I use to improve my coding-decoding skills for the CAT exam? |  |
| 4. What are some common pitfalls to avoid while solving coding-decoding questions? |  |
| 5. How much time should I allocate to coding-decoding questions in the CAT exam? |  |















