Treatment of Sewage | Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Sedimentation Tank
Settling Velocity
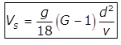
for d < 0.1 mm
Where,
Vs = The velocity of the settlement of particle or settling velocity in m/sec.
d = The diameter of the particle in the meter.
G = Specific gravity of the particle.
v = Kinematic viscosity of water in m2/sec.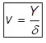 Y = Dynamic viscosity
Y = Dynamic viscosity
δ = Density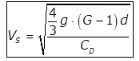
where,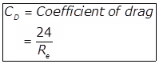
→ For laminar flow
Re = Reynolds number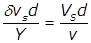
 for transition flow.
for transition flow.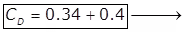 for turbulent flow.
for turbulent flow.
- Newtons Equation for Turbulent Settling
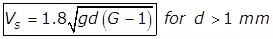
- Modified Hazen’s Equation for Transition Zone
(i)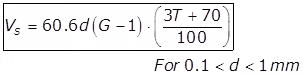
Where T = Temperature in oC.
(ii) Putting G = 2.65 for Inorganic Solids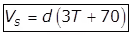
(iii) Putting G = 1.2 for Organic Solids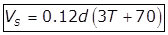
Critical Scour Velocity in Constant Velocity Horizontal Flow
Grit Chamber (VH)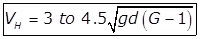
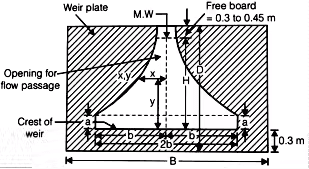
Proportional Flow Weir
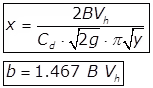
Where,
B = Width of the channel.
Vh = Horizontal flow velocity.
Cd = Coefficient of discharge.
x and y are coordinates on weir profile.
Parabolically or V-Shaped Grit Chamber Provided with a Parshall Flume
- Parshall Flume
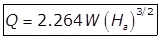
Where,
W = Width of the throat in the meter.
Flow in (m3/sec) through Parshall flume.
Ha = Depth of flow in the upstream leg of a flume of one-third portion in the meter.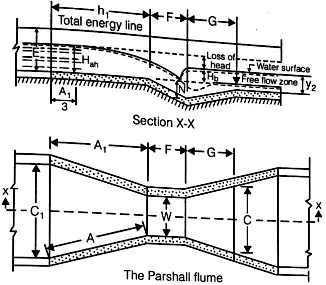
- Parabolic Grit Channel
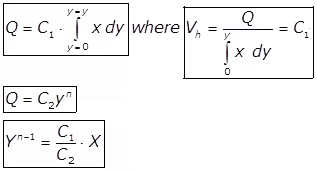
Where,
n = Discharge coefficients of the control section.
= 1.5 for partial flume.
= 1 for proportional flow weir.
(i) Aerated Grit Channels
(ii) Detritus Tank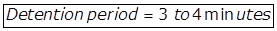
Skimming Tank
- Detention Period = 3 to 5 minutes.
- Amount of compressed air required = 300 to 6000 m3 per million liters of sewage.
- Surface Area,
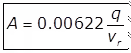
Where,
q = Rate of flow of sewage in m3/day.
Vr = Min. rising velocity of greasy material to be removed in m/min
= 0.25 m/min mostly.
Vacuators
Vacuum Pressure = 0 to 25 cm of Hg
For 10 to 15 minutes.
- Sedimentation Tank
(i) Overflow rate
= 40000 to 50000 lit/m2 day for plain sedimentation.
= 50000 to 60000 lit/m2 day for sedimentation with coagulation.
= 25000 to 35000 lit/m2 day for secondary sedimentation tank
(ii) Depth ~ 2.4 to 3.6 m.
(iii) Detention time = 1 to 2 hour.
(iv) width = 6.0 m
(v) Length = 4 to 5 times width.
(vi) Velocity of flow Vf = 0.3 m/min.
(vii)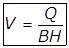 Where,V = Flow velocity
Where,V = Flow velocity
B = Width of the Basin
H = Depth of sewage in the tank.
(viii)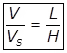
(ix)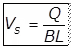
- Detention Time
(i)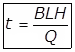
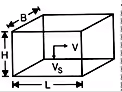
For rectangular Tank
(ii)
for circular tank
Where
d = Dia of the tank
H = Vertical depth of wall or side depth - Displacement Efficiency (η)

Trickling Filter
- Conventional Trickling Filter or Low Rate Trickling Filter
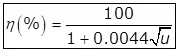
Where,
η = The efficiency of the filter and its secondary clarifier, in terms of % of applied BOD
u = Organic loading in kg/ha-m/day applied to the filter (called unit organic loading) - High Rate Trickling Filter
(i)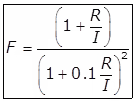
Where, F = Recirculation factor
Recirculation ratio
(ii)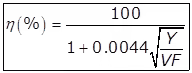
Where,
Y = Total organic loading in kg/day applied to the filter i.e. the total BOD in kg.
Y/VF = Unit organic loading in kg/Ha-m/day
V = Filter volume in Ha-m.
% efficiency of single-stage high rate trickling filter.
(iii)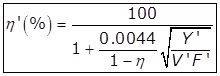
Where,
n' = Final efficiency in the two-stage filter.
Y' = Total BOD in the effluent from the first stage in kg/day.
F' = Recirculation factor for second stage filter
V' = Volume in second stage filter in ha-m.
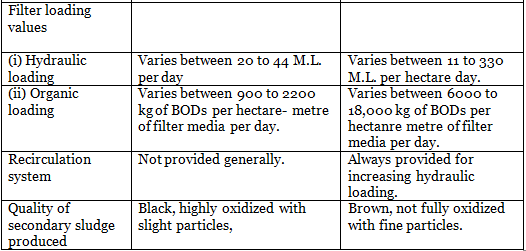
Dunbar Filter
Surface loading = 25000 MI/m2/day.
BOD removed = 85%
Sludge and its Moisture Content
The volume of sludge at moisture content P1%
The volume of sludge at moisture content P%
Sludge Digestion Tank
- When the change during digestion is linear.
(i)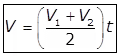
Where,
The volume of digestion in m3.
Raw sludge added per day (m./day)
Equivalent digested sludge produced per day on completion of digestion, m3/day.
Digestion period in the day.
(ii)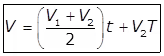
with monsoon storage
Where,
T = Number of days for which digested sludge (V2) is stored (monsoon) storage) - When the change during digestion is parabolic.
(i)
without monsoon storage
(ii)
without monsoon storage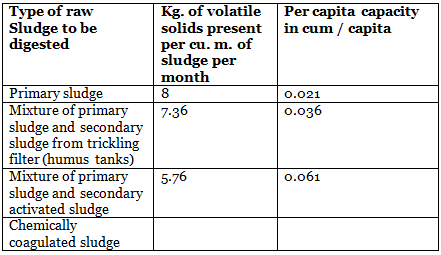
Destruction and Removal Efficiency (DRE)
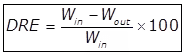
Where,
Win = The mass fill rate of one POHC (Principal organic Hazardous constituent) in the waste stream.
Wout = Mass emission rate of the same POHC present in the exhaust emission prior to release to the atmosphere.
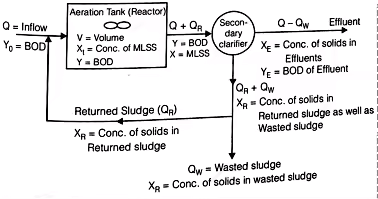
Aeration Tank (ASP)

- Detention period,
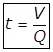
Where
V = Volume of the tank in m3.
Q = Quantity of wastewater flow into the aeration tank excluding the quantity of recycled sludge (m3/day) - Volumetric BOD Loading or Organic Loading, (U)
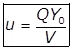
Where,
QYo = Mass of BOD applied per day to the aeration tank through influent sewage in gm.
V = The volume of the aeration tank in m3.
Q = Sewage flows into the aeration tank in m3.
BOD5 in mg/lit (or gm/m3) of the influent sewage. 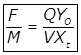
Where,
F/M = Food (F) to Microorganism (M) ratio QYo = Daily BOD applied to the aeration system in gm.
Yo = 5 day BOD of the influent sewage in mg/lit.
Q = The flow of influent sewage in m3/day.
MLSS (Mixed liquor suspended solids) in mg/lit.
V = The volume of the Aeration Tank (lit).
M = XtV = Total microbial mass in the system in gm.- Sludge Age (θc)
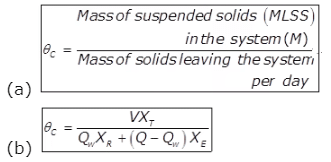
Where,
XT = The concentration of solids in the influent of the Aeration Tank called the MLSS i.e. mixed liquor suspended solids in mg/lit.
V = Volume of Aerator
Qw = The volume of waste sludge per day
The concentration of solids in the returned sludge or in the wasted sludge (both being equal) in mg/lit.
Q = Sewage inflow per day.
XE = The concentration of solids in the effluent in mg/lit. - Sludge Volume Index (S.V.I)
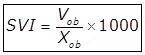
Where,
Xab = Concentration of suspended solids in the mixed liquor in mg/lit.
Vab = Settled sludge volume in ml/lit.
S.V.I = Sludge volume index in ml/gm. - Sludge Recycle and Rate of Return Sludge
QR·XR = (Q + QR) x R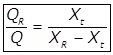
Where,
QR = Sludge recirculation rate in m3/day.
Xt = MLSS in the aeration tank in mg/lit.
XR = MLSS in the returned or wasted sludge in mg/lit.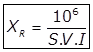
S.V.I = Sludge volume index in ml/gm.
(i) Specific substrate utilization rate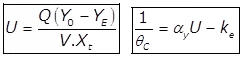
αy = 1 for MLSS and 0.6 for MLVSS, ke = 0.66
(ii) Oxygen Requirement of the Aeration Tank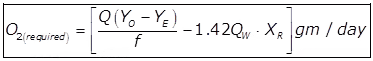
Where,
(iii) Oxygen Transfer Capacity (N)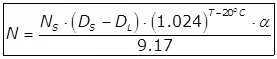
Where,
N = Oxygen transferred under field conditions in kg O2/k.wh (Or MJ)
Ns = Oxygen transfer capacity under standard conditions in kg O2/kwh (or MJ)
Ds = Dissolved oxygen-saturation value for sewage at operating temperature.
DL = Operation D.O level in Areation tank usually 1 to 2 mg/lit.
T = Temperature in oC
α = Correction factor for oxygen transfer for sewage usually 0.8 to 0.85.
Oxidation Ponds
- Depth → 1.0 to 1.8 m.
- Detention period → 2 to 6 weeks.
- Organic loading → 150 to 300 kg/ha/day.
- Under hot condition → 60 to 90 kg/ha/day.
Under cold conditions. - Length to width ratio = 2
- Sludge Accumulation = 2 to 5 cm/year
- Minimum depth to be kept = 0.3 m.
For Inlet Pipe Design
Assume V = 0.9 m/s
Assume flow for 8 hrs.
For Outlet Pipe Design
Dia of outlet = 1.5 dia of the inlet pipe
Septic Tank
- Detention time = 12 to 36 hr.
- Sludge accumulation rate = 30 lit/cap/year.
- Sewage flow = 90 to 150 lit/capita/day.
- Cleaning period = 6 to 12 months
- Length to width ratio = 2 to 3 m.
- Depth = 1.2 to 1.8 m
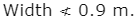
- Free board = 0.3 m.
Volume of Septic Tank = (Sewage flow x Detention time) + (Sludge accumulation rate) x Clearning rate
|
14 videos|142 docs|98 tests
|