Past Year Questions: Treatment of Wastewater | Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: A circular settling tank is to be designed for primary treatment of sewage of a flow rate of 10 million liters/day. Assume a detention period of 2.0 hours and surface loading rate of 40000 liters /m2/day. The height (in meters) of the water column in the tank is _____ (rounded off to 2 decimal places) (2024 SET-2)
Ans: 3 to 3.4
Sol: Given,
Discharge, Q = 10MLD
Detention period, td = 2hr
Over flow rate, V0 = 40,000 litres /m2/day
H = ?
As, Surface area of tank = Discharge/Over flow rate =Q/V0
So,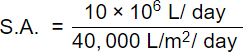
S.A = 250 m2
Volume of tank (V) = Q × td 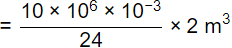
V = 833.33 m3
Hence, Height of water in tank or Height of setting zone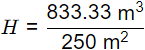
H = 3.33
Note: In reality, height of water in tank OR height of settling zone is estimated by above approach but if the bottom of sedimentation tank is assumed to be sloping or hoppered (i.e sludge zone is also considered) then height of water in tank is determined as follows:
Using, Volume of tank (V) = 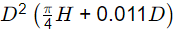
As,
S.A. = (π/4)D2 = 250 m2
D = 17.835 m
So, 833.33 = (17.835)2((π/4) H + 0.011(17.835))
So, H = 3.085 m
Q2: Activated carbon is used to remove a pollution from wastewater in a mixed batch reactor, which follows first-order reaction kinetics.
At a reaction rate of 0.38 /day, the time (in days) required to remove the pollutant by 95% is ______ (rounded off to 1 decimal place). (2024 SET-1)
Ans: 7.8 to 8
Sol: For first order kinetics,
Nt = N0e−kt
For efficiency of 95%,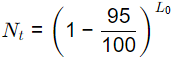
= 0.05N0
∴ 0.05 = e-0.38t
Taking In on both sides,
ln 0.05 = −0.38t × lne
⇒ t = 7.9 days
Q1: In the context of water and wastewater treatments, the correct statements are: (2023 SET-2)
(a) particulate matter may shield microorganisms during disinfection
(b) ammonia decreases chlorine demand
(c) phosphorous stimulates algal and aquatic growth
(d) calcium and magnesium increase hardness and total dissolved solids
Ans: a, c, d
Sol: Total dissolved solids comprise of inorganic salts, principally calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium bicarbonates, chlorides, sulfates and some small amount of organic matter that are dissolved in water.
Hardness is due to presence of multivalent cations. In most cases, it is due to the presence of soluble bicarbonates, chlorides and sulfates of calcium and magnesium.Too much phosphorous can cause increased growth of algae and large aquatic plants. It can result in decreased
levels of dissolved oxygen and the process is called 'Eutrophication'.
Ammonia creates a large chlorine demand, as the ammonia is converted to nitrogen gas and the chlorine becomes chloride during disinfection of water by chlorination.
Presence of particulate matter decreases the effectiveness of UV disinfection or chlorine disinfection by shielding the targeted microorganisms.
Q2: The wastewater inflow to an activated sludge plant is 0.5 m3/s, and the plant is to be operated with a food to microorganism ratio of 0.2mg/mg−d. The concentration of influent biodegradable organic matter of the wastewater to the plant (after primary settling) is 150mg/L, and the mixed liquor volatile suspended solids concentration to be maintained in the plant is 2000mg/L. Assuming that complete removal of biodegradable organic matter in the tank, the volume of aeration tank (in m3, in integer) required for the plant is _____. (2023 SET-1)
Ans: 16200 to 16200
Sol: Given,
Q1 = 6.5 m3/s
= 0.5 × 24 × 60 × 60
= 43200 m3/d
F/M = 0.2 (mg/mg−d)
S0 = 150 mg/l
X = 2000 mg/l
∴ 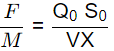
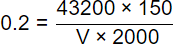
V = 16200 m3.
Q3: Identify the waterborne diseases caused by viral pathogens: (2023 SET-1)
(a) Acute anterior poliomyelitis
(b) Cholera
(c) Infectious hepatitis
(d) Typhoid fever
Ans: (a, c)
Sol: Water Borne Disease caused by
(i) Bacterial -- (a) Typhoid (b) Cholera
(ii) Virus -- (a) Jaundice (Hapatitis virus) (b) Poliomyetitis
(iii) Protozoa -- (a) Amoebic dysentry
Q1: A 2% sewage sample (in distilled water) was incubated for 3 days at 27ºC temperature. After incubation, a dissolved oxygen depletion of 10 mg/L was recorded. The biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) rate constant at 27ºC was found to be 0.23 day−1 (at base e).
The ultimate BOD (in mg/L) of the sewage will be_____________. (round off to the nearest integer) (2022 SET-1)
Ans: 1000 to 1005
Sol: Depletion of dissolved oxygen after 3 days incubation = 10 mg/L
Dilution factor = Vol. of diluted sample/Vol. of undiluted sewage sample = 100/2 = 50
BOD3 = DO consumed × dilution factor = 10 × 50 = 500mg/L
BOD3 = BODu(1−e−kt)
500 = BODu(1 − e−0.23 × 3)
BODu = 1003.162 mg/L
Q1: A grit chamber of rectangular cross-section is to be designed to remove particles with diameter of 0.25 mm and specific gravity of 2.70. The terminal settling velocity of the particles is estimated as 2.5 cm/s. The chamber is having a width of 0.50 m and has to carry a peak wastewater flow of 9720 m3/d giving the depth of flow as 0.75 m. If a flow-through velocity of 0.3 m/s has to be maintained using a proportional weir at the outlet end of the chamber, the minimum length of the chamber (in m,in integer) to remove 0.25 mm particles completely is _________ (2021 SET-2)
Ans: 9 to 9
Sol: Minimum length of chamber
Lmin = Vflow × td
Vfow = 0.30 m/s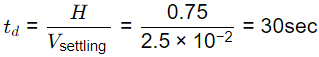
Lmin = 0.3 m/sec x 30 sec
= 9 m
Q2: An activated sludge process (ASP) is designed for secondary treatment of 7500 m3/day of municipal wastewater. After primary clarifier, the ultimate BOD of the influent, which enters into ASP reactor is 200 mg/L. Treated effluent after secondary clarifier is required to have an ultimate BOD of 20 mg/L. Mix liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS) concentration in the reactor and the underflow is maintained as 3000 mg/L and 12000 mg/L, respectively. The hydraulic retention time and mean cell residence time are 0.2 day and 10 days, respectively. A representative flow diagram of the ASP is shown below.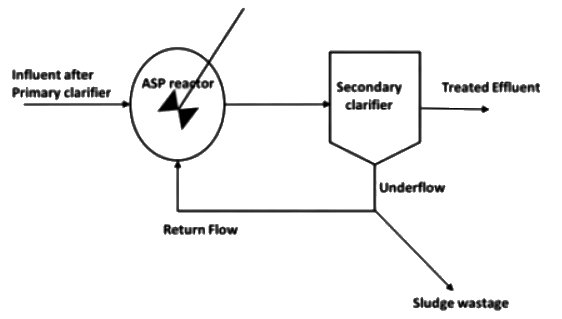
The underflow volume (in m3/day, round off to one decimal place) of sludge wastage is _________ (2021 SET-2)
Ans: 37 to 38
Sol: 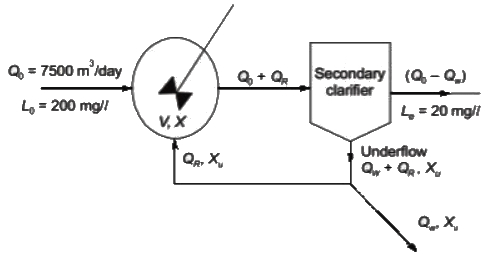 Given, X = 3000mg/l, Xu = 12000mg/l
Given, X = 3000mg/l, Xu = 12000mg/l
Since HRT = V/Q0
⇒ Volume of reactor,
V = Q0 × HRT
=7500 × 0.2 m3
=1500 m3
Sludge age,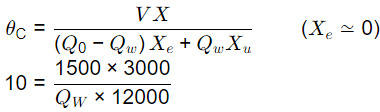
Qw = 37.5 m3/day
Q3: A secondary clarifier handles a total flow of 9600 m3/d from the aeration tank of a conventional activated-sludge treatment system. The concentration of solids in the flow from the aeration tank is 3000 mg/L. The clarifier is required to thicken the solids to 12000 mg/L, and hence it is to be designed for a solid flux of 3.2(kg/m2⋅h). The surface area of the designed clarifier for thickening (in m2, in integer) is ____________. (2021 SET-1)
Ans: 375 to 375
Sol: Q = 9600 m3/d
X = 3000mg/l
Xu = 12000mg/l
Solid flux = 3.2 kg/m2−h
Surface area, A = Total quantity of solids entering/Solid flux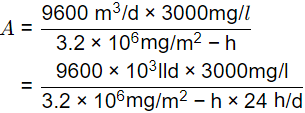
= 375 m2
Q1: A wastewater is to be disinfected with 35 mg/Lof chlorine to obtain 99% kill of micro-organisms. The number of micro-organisms remaining alive (Nt) at time t, is modelled by Nt = Noe−kt, where No is number of micro-organisms at t = 0, and k is the rate of kill. The wastewater flow rate is 36 m3/hr, and k = 0.23 min−1. If the depth and width of the chlorination tank are 1.5 m and 1.0 m, respectively, the length of the tank (in m, round off to 2 decimal places) is ________ (2019 SET-1)
Ans: 7.95 to 8.15
Sol: Nt = N0e-kt
∴ η = [1 - e-kt] 100
99 = [1 - e−0.23×t]100
∴ t = 20.22 min
Q = 36 m3/hr
V = Q x t
= (36/60) x 20.22 = 12.0132
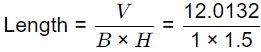
= 8.008 ≅ 8m
Q2: Consider the reactor shown in the figure. The flow rate through the reactor is Q m3/h. The concentrations (in mg/L) of a compound in the influent and effluent are C0 and C, respectively. The compound is degraded in the reactor following the first order reaction. The mixing condition of the reactor can be varied such that the reactor becomes either a completely mixed flow reactor (CMFR) or a plug-flow reactor (PFR). The length of the reactor can be adjusted in these two mixing conditions to LCMFR and LPFR while keeping the cross-section of the reactor constant. Assuming steady state and for C/C0 = 0.8, the value of Lcmfr/Lpfr ( round off to 2 decimalplaces ) [2019 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
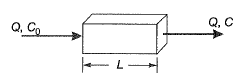 Ans: 1.12
Ans: 1.12Sol:
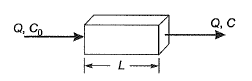 For (CMFR) completely mixed flow reactor
For (CMFR) completely mixed flow reactor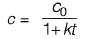
For (PFR) plug flow reactor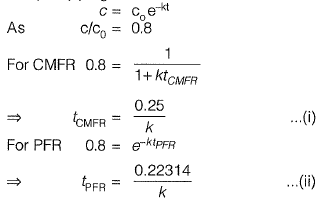
Now for steady state
v = constant and
L= vt
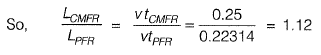
Q1: A schematic flow diagram of a completely mixed biological reactor with provision for recycling of solids is shown in the figure.
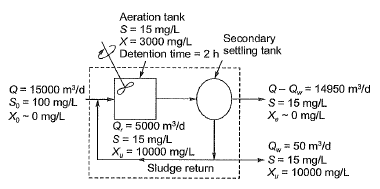
S0, S = readily biodegradable soluble BOD, mg/L
Q, Qr Qw = flow rates, m3/d
Xq, X, Xe, Xu = microorganism concentrations (mixed-liquor volatile suspended solids or MLVSS), mg/L
The mean cell residence time (in days, up to one decimal place) is _______ . [2018 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: 7.5 days
Sol: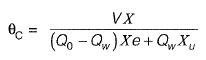
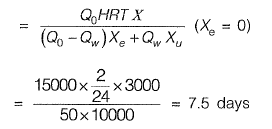
Q2: At a small water treatment plant which has 4 filters, the rates of filtration and backwashing are 200 m3/d/m2 and 1000 m3/d/m2, respectively. Backwashing is done for 15 min per day. The maturation, which occurs initially as the filter is put back into service after cleaning, takes 30 min. It is proposed to recover the water being wasted during backwashing and maturation. The percentage increase in the filtered water produced (up to two decimal places) would be ______ (2018 SET-2)
Ans: 7.75 to 7.95
Sol: Let total area of filters be 1m2
Water used for backwashing
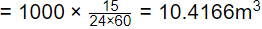
Water used for maturation
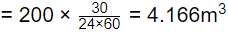
Total water wasted for backwashing and maturation
= 10.4166 + 4.166 = 14.58m3
Water to be treated by filtered
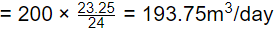
% increase in filtered water produced
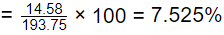
Q3: A waste activated sludge (WAS) is to be blended with green waste (GW). The carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) contents, per kg of WAS and GW, on dry basis are given in the table.
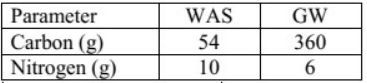 The ratio of WAS to GW required (up to two decimal places) to achieve a blended C:N ratio of 20:1 on dry basis is _____ (2018 SET-1)
The ratio of WAS to GW required (up to two decimal places) to achieve a blended C:N ratio of 20:1 on dry basis is _____ (2018 SET-1)Ans: 1.6 to 1.7
Sol: Let 20 kg of C and 1 kg of N is required
Let x kg of WAS is taken
∴ Carbon in xkg = 0.054 xkg
Nitrogen in xkg = 0.010 xkg
Let y kg of GW is taken
∴ Carbon in ykg = 0.360 ykg
Nitrogen in ykg = 0.006 ykg
Total Carbon,
0.054x + 0.36y = 20kg …(i)
Total Nitrogen,
0.01x + 0.006y = 1kg ...(ii)
x = 73.26 kg
y = 44.566 kg
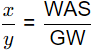
∴ = 1.6438
 1.64.
1.64.
Q1: The most important type of species involved in the degradation of organic matter in the case of activated sludge process is [2017 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
(a) autotrophs
(b) heterotrophs
(c) prototrophs
(d) photo-autotrophs
Ans: (b)
Sol: Activated sludge process is designed primarily for satisfaction of carbonaceous BOD which is done by heterotrophs.
Q2: The wastewater having an organic concentration of 54 mg/l is flowing at a steady rate of 0.8 m3/day through a detention tank of dimensions 2m x 4 m x 2 m. If the contents of the tank are well mixed and the decay contant is 0.1 per day, the outlet concentration (in mg/l, up to one decimal place) is _______ . [2017 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Ans: 18 mg/l
Sol: Q = 0.8 m3/d
Detention time,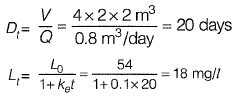
Q1: Match the items in Group-I with those in Group-ll and choose the right combination [2016 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
Group-I
P. Activated sludge process
Q. Rising of sludge
R. Conventional nitrification
S. Biological nitrogen removal
Group-ll
1. Nitrifiers and denitrifiers
2. Autotrophic bacteria
3. Heterotrophic bacteria
4. Denitrifiers
(a) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-1
(b) P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-1
(c) P-2, Q-2, R-4, S-1
(d) P-1, Q-4, R-2, S-3
Ans: (a)
Q1: In a wastewater treatment plant, Primary Sedimentation Tank (PST) designed at an overflow rate of 32.5 m3/day/m2 is 32.5 m long, 8.0 m wide and liquid depth of 2.25 m. If the length of the weir is 75 m, the weir loading rate (in m3/day/m) is __________ . [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: 112.67m3/d/m
Sol:
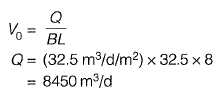
Weir length = 75 m
∴ Weir loading rate,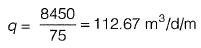
Q2: Total Kjcldahl Nitrogen ( IKN) concentration (mg/L as N) in domestic sewage is the sum of the concentration of [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) organic and inorganic nitrogen in sewage
(b) organic nitrogen and nitrate in sewage
(c) organic nitrogen and ammonia in sewage
(d) ammonia and nitrate in sewage
Ans: (c)
Sol: Kjehldahl Nitrogen = Organic nitrogen + free ammonia.
Q1: The amount of CO2 generated (in kg ) while completely oxidizing one kg of CH4 to the end products is ___________ . [2014 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
Ans: 2.75kqCO2
Sol: 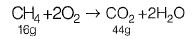
⇒ 16 g of CH4 when completely oxidized leads to 44 g of CO2
⇒ 1 kg of CH4 when completely oxidized leads to 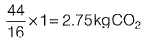
Q2: The dominating microorganisms in an activated sludge process reactor are [2014 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
(a) aerobic heterotrophs
(b) anaerobic heterotrophs
(d) autotrophs
(d) phototrophs
Ans: (a)
Q1: Direction: An activated sludge system (sketched below) is operating at equilibrium with the following information. Waste water related data : flow rate = 500 m3/hour, Influent BOD = 150 mg/L, effluent BOD = 10 mg/L. Aeration tank related data : hydraulic retention time = 8 hours, mean-cell-residence time = 240 hours, volume = 4000 m3, mixed liquor suspended solids = 2000 mg/L.
The mass (in kg/day) of solids wasted from the system is [2012 : 2 Marks]
(a) 24000
(b) 1000
(c) 800
(d) 33
Ans: (c)
Sol: Mean cell recidence time,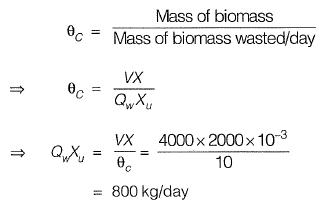
Q2: Direction: An activated sludge system (sketched below) is operating at equilibrium with the following information. Waste water related data : flow rate = 500 m3/hour, Influent BOD = 150 mg/L, effluent BOD = 10 mg/L. Aeration tank related data : hydraulic retention time = 8 hours, mean-cell-residence time = 240 hours, volume = 4000 m3, mixed liquor suspended solids = 2000 mg/L.
The food-to-biomass (F/M) ratio (in kg BOD per kg biomass per day) for the aeration tank is [2012 : 2 Marks]
(a) 0.015
(b) 0.210
(c) 0.225
(d) 0.240
Ans: (c)
Sol: Given,
Flow rate Q0 = 500 m3/hour
Influent BOD S0 = 150 mg/lit
effluent BOD, = 10 mg/lit.
Hydraulic retention time = 8 hour = 1/3 days
Mean - cell resistance time,
(θC) = 240 hour = 10 day
M . L . S . S, (X) = 2000 mg/lit.
Q1: Direction: The sludge from the aeration tank of the activated sludge process (ASP) has solids content (by weight) of 2%. This sludge is put in a sludge thickener, where sludge volume is reduced to half. Assume that the amount of solids in the supernatant from the thickener is negligible, the specific gravity of sludge solids is 2.2 and the density of water is 1000 kg/m3.
What is the solids content (by weight) of the thickened sludge? [2011 : 2 Marks]
(a) 3.96%
(b) 4.00%
(c) 4.04%
(d) 4.10%
Ans: (a)
Sol: Now,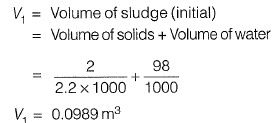
Volume of sludge after thickness
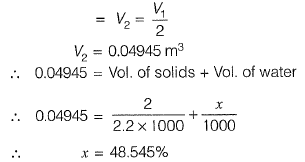
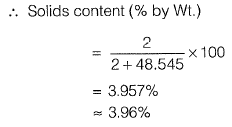
Q2: Direction: The sludge from the aeration tank of the activated sludge process (ASP) has solids content (by weight) of 2%. This sludge is put in a sludge thickener, where sludge volume is reduced to half. Assume that the amount of solids in the supernatant from the thickener is negligible, the specific gravity of sludge solids is 2.2 and the density of water is 1000 kg/m3.
What is the density of the sludge removed from the aeration tank? [2011 : 2 Marks]
(a) 990 kg/m3
(b) 1000 kg/m3
(c) 1011 kg/m3
(d) 1022 kg/m3
Ans: (c)
Sol: 2% of solids + 98% water→ 100% of sludge letx be the density of sludge.
|
14 videos|120 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Treatment of Wastewater - Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the primary methods for treating wastewater? |  |
| 2. Why is it important to treat wastewater before discharge? |  |
| 3. What are the stages of wastewater treatment? |  |
| 4. How does biological wastewater treatment work? |  |
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of untreated wastewater? |  |
















