Tribal Movements in India | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
Tribal Uprisings in India: A Historical Overview
Introduction: Tribal communities in India, known for their conservative values, have historically resisted changes that threatened the fabric of their societies. This resistance often manifested in tribal movements driven by revolutionary ideals, aiming to combat forces attempting to alter tribal structures. The following summary outlines key tribal rebellions during British rule in India.
Root Causes of Tribal Movements
Influx of Non-Tribals: The expansion of settled agriculture attracted non-tribals to tribal areas, leading to exploitation and loss of tribal land.
Government Control over Forest Land: Increasing demand for raw materials and railways resulted in the government's control over forest land, impacting tribal communities.
Forest Monopoly: The establishment of the Forest department and related acts established a complete government monopoly over Indian forest land.
Christian Missionaries: Viewed as extensions of colonialism, Christian missionaries were often targets of tribal rebels.
Land Revenue Settlement: Agricultural expansion by non-tribals eroded tribal traditions, leading to socio-economic differentiation.
Private Property Concept: Introduction of the notion of private property allowed the buying, selling, and mortgaging of land, causing land loss for tribals.
Timeline of Tribal Movements
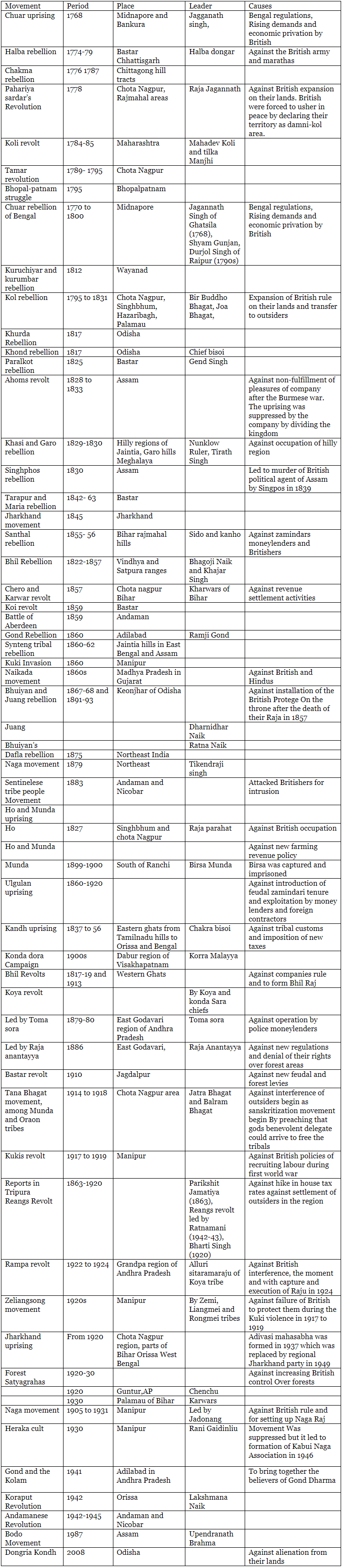
Conclusion
These tribal uprisings, fueled by a desire to preserve their cultural and socio-economic structures, significantly shaped India's history. While the rebellions weren't aimed at ending British rule, they played a crucial role in highlighting the struggles of tribal communities and resisting external influences. The timeline provides a glimpse into the diverse movements that arose across different regions, contributing to the broader narrative of India's fight against colonial forces.
|
1335 videos|1437 docs|834 tests
|
















