Types and Costs & Benefits of FDI to Home and Host Countries | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Meaning of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) |

|
| Types of FDI |

|
| Types of FDI in India |

|
| Costs and Benefits of FDI to Home and Host Countries |

|
Meaning of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)

- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) refers to the investment made by individuals, businesses, or entities from one country into businesses or assets located in another country.
- FDI typically involves acquiring direct ownership of assets or a significant stake in a foreign company, such as a subsidiary, branch, or joint venture.
- It is a long-term investment that provides the investor with some level of control or influence over the foreign business's operations and management.
- FDI is a key component of the global economy, facilitating the flow of capital, technology, and expertise across borders.
- It can take various forms, including equity investments, loans, reinvested earnings, or the establishment of new foreign enterprises.
- The primary goal of FDI is to earn a return on the investment, which may come from dividends, capital appreciation, or a share of the foreign company's profits.
- FDI brings numerous benefits to both the investing country and the host country.
- For the investing country, it offers opportunities for diversification, access to new markets, and potential for higher returns.
- For the host country, FDI can stimulate economic growth, create jobs, transfer technology, and increase foreign exchange reserves.
- However, it also raises concerns about national sovereignty, economic dependency, and the potential for profit repatriation.
- FDI is subject to regulations and policies set by both the investing and host countries, which can vary significantly.
- Many countries encourage FDI through incentives, tax breaks, and initiatives to attract foreign investors.
- While others may impose restrictions or conditions on foreign ownership in certain sectors to protect national interests.
Types of FDI
FDI can take several forms:
Greenfield Investment: This occurs when an investor establishes a new operation in the host country from the ground up, such as building new factories, offices, or R&D centers.
Mergers and Acquisitions: This involves acquiring partial or full ownership of an existing company in the host country through the purchase of shares or assets, providing a quick entry into the market.
Joint Ventures: Two or more companies form a new business entity in the host country, sharing ownership, control, profits, and losses.
Licensing and Franchising: An investor obtains rights to use intangible assets like trademarks, patents, trade secrets, or business models in the host country in exchange for fees or royalties.
Contract Production: An investor contracts a firm in the host country to produce goods and services according to specifications without acquiring ownership.
Privatization: Governments sell part or all of state-owned enterprises to foreign investors to raise funds and improve efficiency.
Brownfield Investment: An investor purchases existing operational assets like factories, real estate, or mines in the host country, which carries less risk than greenfield investments.
Types of FDI in India
In the Indian context, FDI takes several forms:
Greenfield Investment: Major global companies like Volkswagen, Hyundai, and Renault Nissan have set up new manufacturing facilities in India. Tech firms such as Samsung, Apple, and Nokia have also established new R&D and production centers.
Mergers and Acquisitions: Foreign acquisitions of Indian companies are common, with significant deals including Hindustan Unilever acquiring Hindustan Lever, ArcelorMittal acquiring Essar Steel, and Vodafone acquiring Hutchison Essar.
Joint Ventures: Joint ventures are prevalent, especially in the automotive industry, with examples like Maruti Suzuki (between Suzuki and the Government of India), Tata Motors’ JV with Fiat, and Ford’s JV with Mahindra & Mahindra.
Licensing and Franchising: Global brands like McDonald’s, KFC, and Pizza Hut have entered India through licensing and franchising agreements. Retailers like Marks & Spencer, Sephora, and IKEA also operate franchises in India.
Contract Production: Many global companies outsource manufacturing and services to Indian firms, including technology services, call centers, generic drug manufacturing, and automobile components.
Privatization: The Indian government has privatized many state-owned enterprises, attracting significant FDI, with companies like Vodafone, British Telecom, and Hindalco acquiring stakes in telecom and mineral firms.
Other Segmentation of FDI
FDI can also be segmented into the following types:
Vertical FDI: This involves a company investing in another country to secure supplies of inputs or components for its production processes, such as automobile companies investing in tire factories or electronics firms investing in component manufacturers.
Horizontal FDI: This occurs when a company replicates its existing operations in another country to serve that foreign market, producing similar products in both the parent company and foreign subsidiary.
Conglomerate FDI: This happens when a company invests in unrelated businesses in another country, diversifying its business risks and leveraging managerial expertise across industries.
Costs and Benefits of FDI to Home and Host Countries
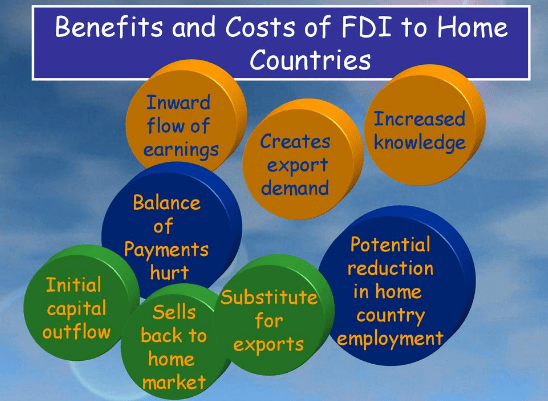
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) offers significant advantages for both host countries receiving the investments and home countries where the investing companies are based. However, FDI also brings associated costs and risks. Below are the key costs and benefits of FDI for both host and home countries.
For Host Countries
The costs and benefits of FDI for host countries are as follows:
Benefits:
- FDI can spur economic growth by creating jobs, injecting capital, and transferring technology. It also contributes to infrastructure development through investments in transportation, electricity, and telecommunications.
- FDI provides access to international markets and supply chains, boosting the competitiveness of local firms. Additionally, it can bring new capital that supports growth by expanding the productive capacity of the economy.
- Advanced technologies, managerial skills, and business practices brought by foreign companies can enhance the productivity and competitiveness of local firms through spillover effects.
- FDI can generate employment directly through foreign affiliates and indirectly by increasing demand for goods and services from local suppliers, thereby reducing unemployment.
- Local companies gain access to foreign markets by becoming part of global supply chains, expanding their customer base and sales.
- Host countries can impose technology transfer requirements and performance benchmarks on foreign investors to maximize the positive impacts.
Costs:
- FDI can lead to unfair competition, as small local firms may struggle to compete with large foreign multinationals.
- The influx of foreign firms may increase income inequality if these companies primarily employ skilled labor.
- There is a risk of environmental degradation if host countries have lax regulations.
- The economy may become exposed to external shocks and volatility due to global business cycles.
- Host countries may lose some policy autonomy, as they might need to conform to the demands of foreign investors.
For Home Countries
The costs and benefits of FDI for home countries are as follows:
Benefits:
- Companies can achieve higher profits and returns from their FDI projects, as well as gain access to cheaper resources, lower-cost production locations, and new markets for growth.
- FDI supports international expansion and the upgrading of skills and technology, enabling firms to expand production and sales to a larger global customer base, achieving economies of scale.
- Access to natural resources and lower-cost locations enhances the competitiveness of home country companies.
- FDI creates competitive pressure, forcing domestic firms to improve efficiency.
Costs:
- FDI can lead to job losses at home, especially in labor-intensive sectors that shift production abroad.
- There is a risk of strategic technology and intellectual property outflows to host countries, benefiting competitors.
- Firms are exposed to political and operational risks in foreign markets.
- Profits repatriated back to the home country may escape host country taxes, leading to a loss of potential tax revenue.
- FDI can lead to exchange rate appreciation, which may hurt the export competitiveness of the home country.
Conclusion
FDI presents numerous opportunities for economic development and growth, but it is essential for both host and home countries to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the associated costs and risks. By adopting well-considered policies and institutions, countries can optimize the gains from FDI while safeguarding their national interests. With the right approach, all parties involved can maximize the mutual benefits of FDI.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|




















