Types of Puzzles | Reasoning Aptitude for Competitive Examinations - Bank Exams PDF Download
Reasoning Puzzles
Puzzles present information in a disordered manner, requiring systematic arrangement to accurately depict the details. This chapter focuses on questions presented in puzzle form, involving a specific number of items, which could be individuals or objects. The task involves analyzing provided information, organizing it logically, and responding to questions related to classification, arrangement, comparison, sequential order, or family-based scenarios.
Types of Puzzles
There are various categories of questions based on puzzles which are as follows
Type #1
Based on Classification
Certain items belonging to different groups or possessing different qualities are given along with some clues, with the help of which you are required to group the items having common properties and analyse the given items to answer the questions accordingly.
It is advisable to solve classification based puzzle by representing the given information in form of a table.
Example 1
1. Tom, Dick, and Harry are intelligent.
2. Tom, Brown, and Jack are hard working.
3. Brown, Harry and Jack are honest.
4. Tom, Dick and Jack are ambitious.
Q: Which of the following person is neither hard working not ambitious?
(a) Tom
(b) Dick
(c) Harry
(d) Jack
Ans: (c)
Sol: All the given information can be summarised in the tabular form as given below.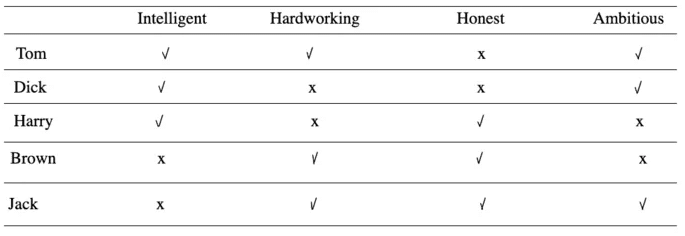
Clearly, Harry is neither hard working nor ambitious.
Type #2
Based on Seating/Placing Arrangement
In this type of puzzles, some clues regarding seating/placing arrangement (linear or circular) of some persons/objects along with additional information (like their profession, colour of wearing items, etc) are given. The candidates are required to form the proper sequence, arrange the persons using these clues and answer the questions accordingly.
Directions (Example Nos. 2-4) Read the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Five friends A, B, C, D and E are sitting on a bench and wearing different colours shirt, i.e. blue, red, yellow, white and green (not necessarily in this order).
I. A is sitting next to B and wearing red shirt.
II. C is sitting next to D and not wearing either blue or green shirt.
III. D is not sitting with E and E is wearing blue shirt.
IV. E is on the left end of the bench.
V. C is on the second position from the right.
VI. A is on the right of B and E.
VII. B is wearing green shirt.
VIII. A and C sitting together.
IX. D is not wearing white shirt.
Example 2. Where is A sitting?
(a) Between B and D
(b) Between D and C
(c) Between E and D
(d) Between B and C
Example 3. What is the colour of C's shirt?
(a) Blue
(b)Red
(c) White
(d) Yellow
Example 4. Who is sitting in the centre?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Sol: (Example Nos. 2-4) According to the given information, arrangement is as follows
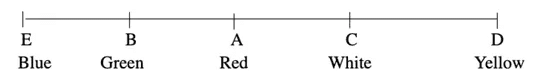
2. (d) A is sitting between B and C.
3. (c) The colour of C's shirt is white.
4. (a) A is sitting in the centre.
Type #3
Conditions, Grouping and Team Formation
In this type of puzzles, conditions regarding the selection or non-selection of persons or objects with respect to one another are given. On the basis of the given information, a team is to be formed and questions are answered accordingly.
Example 5. Four political parties W, X, Y, and Z decided to set up a joint candidate for the coming parliamentary elections.
The formula agreed by them was the acceptance of a candidate by most of the parties. Four aspiring candidate A, B, C and D approached the parties for the tickets.
A was acceptable to W but not Z.
B was acceptable to Y but not X.
C was acceptable to W and Y.
D was acceptable to W and X.
Q: When candidates B was preferred by W and Z, candidate C was preferred by X and Z and candidate A was acceptable to X but not to Y, who got the ticket?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Ans: (c)
Sol: (c) According to the given information, arrangement is as follows.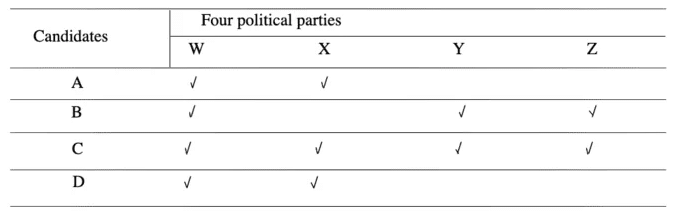
So, C is accepted by all the four parties.
Type #4
Based on Comparison
This type of puzzles are related to comparison. You are required to analyse all the given information, arrange the data in ascending/descending sequence and then answer the questions accordingly.
It is advisable to use the notation such as greater than (>), smaller than (<) and equal to (=) properly according to given condition/information.
Directions: Read the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
P, Q, R, S, T, V and W are the seven members of a family. There are three female members. Each of them has a different profession - Lawyer, Chartered Accountant (CA), Engineer, Teacher, Doctor, Architect and Pharmacist. No lady is either Pharmacist or Chartered Accountant. Each of them has a different monthly income. The Chartered Accountant earns the most. S, the Engineer earns less than V, the Doctor.
R, the Teacher, earns more than P and less than S. W's wife earns the least. T is an unmarried lady Lawyer and she earns less than P and more than only Q. The Pharmacist's income is not the lowest.
Example 6. Who earns the least?
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) P or Q
(d) R
Ans: (b) Q earns the least.
Sol: According to the given information, arrangement is as follows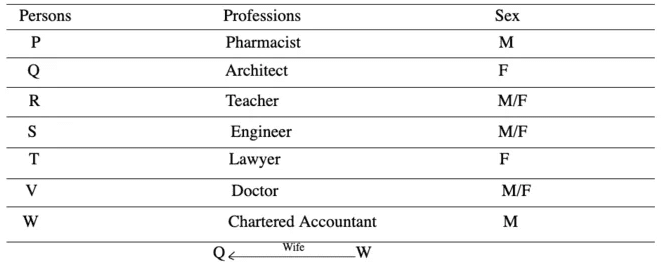
In terms of income, Q < T < P < R < S < V < W
Type #5
Sequential Order to Things
In this type of puzzles, some clues are given regarding the order of occurrence of certain events. The candidate is required to analyse the given information, frame the right sequence and then answer the questions accordingly.
Directions : Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Seven people J, K, L, M, N, O and P have to attend a seminar on seven different days of the same week starting from Monday and ending on Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. K has to attend a seminar on Wednesday. Only one person has to attend a seminar between K and P. J attends a seminar immediately after P.
The number of people who have to attend a seminar before J is same as who have to attend a seminar after L. Only one person has to attend a seminar between L and M. O has to attend a seminar immediately after M.
Example 7. On which of the following days does N have to attend a seminar?
(a) Sunday
(b) Thursday
(c) Saturday
(d) Wednesday
Ans: (a) N has to attend a seminar on Sunday.
Sol: According to the given information, arrangement is as follows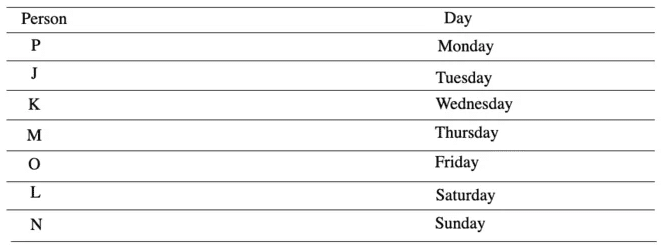
Type #6
Based on Family Problems
In this type of puzzles, some clues are provided regarding relationship amongst different members of a family, together with their professions, qualities, colours, dresses etc. You have to analyse the whole information and then answer the given questions accordingly.
Example 8. P, Q, R, S, T and U are 6 members of family in which there are two married couples. T, a teacher, is married to a doctor who is mother of R and U. Q, the lawyer, is married to P. P has one son and one grandson. Of the two married ladies one is a housewife. There is also one student and one male engineer in the family.
Q: Which of the following is true about the granddaughter of the family.
(a) She is a lawyer
(b) She is an engineer
(c) She is a student
(d) She is a doctor
Ans: (c)
Sol: According to the given information, arrangement is as follows
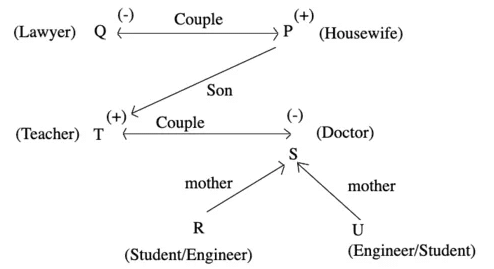
So, the granddaughter of the family is a student and either R or U is a student.
Type #7
Some Miscellaneous Puzzles
In this type of puzzles, some mixed clues regarding three or more conditions of persons/objects are given. It is required to analyse this mixed information with respect to different conditions and classify the objects accordingly to answer the questions asked.
Directions :Read the following information carefully and answer the questions mentioned below.
I. Five friends Amar, Kapil, Sarvesh, Rohan and Nagesh put on five shirts of different colours, i.e. Red, Yellow, Blue, White and Green, while they were going to attend a party. These colours are not in order.
II. They have different hobbies are reading, playing, outing, singing and writing.
III. Kapil, who likes singing, does not wear yellow shirt. Sarvesh wears red shirt and the does not like reading or writing. Nagesh likes playing and he does not wear blue or yellow shirt. Amar likes writing and Rohan does not wear yellow or green shirt.
Example 9. What is the colour of Kapil's shirt?
(a) White
(b) Green
(c) Blue
(d) Data inadequate
Ans: (d)
The colour of Kapil's shirt may be either blue or white or green Hence, data is inadequate to answer the question.
Sol: According to the given information, arrangement is as follows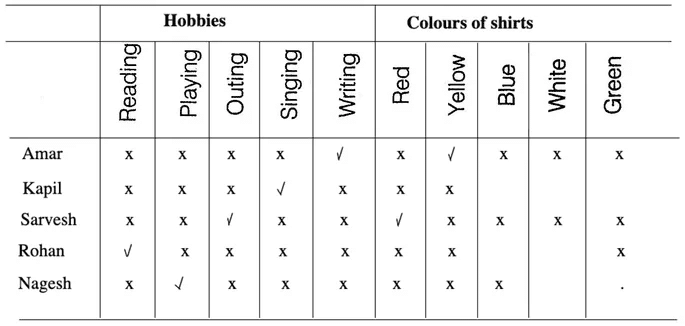
|
73 videos|86 docs|121 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Puzzles - Reasoning Aptitude for Competitive Examinations - Bank Exams
| 1. What are reasoning puzzles? |  |
| 2. What are some common types of reasoning puzzles? |  |
| 3. How can I improve my reasoning puzzle-solving skills? |  |
| 4. Are reasoning puzzles helpful for exams and cognitive development? |  |
| 5. How can I approach a reasoning puzzle with multiple possible solutions? |  |
















