UGC NET Official Paper 2: (Management) Held On - 2nd Sept 2024 Shift 2 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Which among the following characteristics influence consumer buying behavior strongly?
A. Cultural
B. Social
C. Personal
D. Psychological
E. Technological
(a) A, B, C and D Only
(b) B, C, D and E Only
(c) A, C, D and E Only
(d) A, B, D and E Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, C and D Only'
Consumer Buying Behavior:
- Consumer buying behavior refers to the actions and decision processes of individuals in purchasing and using products.
- It is influenced by multiple factors including cultural, social, personal, and psychological characteristics.
Cultural Factors:
- Cultural factors include the set of values, perceptions, preferences, and behaviors that are learned by members of a society from family and other important institutions.
- Culture affects what people buy, how they buy, and why they buy.
Social Factors:
- Social factors include the influence of family, friends, social networks, and other social interactions on buying behavior.
- Social status and roles within groups can significantly impact consumer choices.
Personal Factors:
- Personal factors include an individual's age, occupation, lifestyle, economic situation, and personality.
- These factors can influence preferences and purchasing decisions.
Psychological Factors:
- Psychological factors encompass motivation, perception, learning, beliefs, and attitudes.
- These internal processes impact how consumers select, purchase, and use products.
Other Related Points
Technological Factors:
- Technological factors refer to the impact of technology on consumer behavior, such as the use of online shopping, mobile apps, and digital marketing.
- While technology plays a significant role, it is not traditionally categorized among the primary characteristics influencing consumer behavior in classical models.
Q2: Find the initial feasible solution of the following transportation problem by Vogel's Approximation Method (VAM). 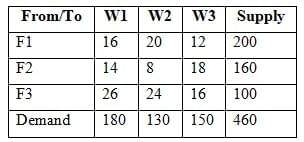
(a) ₹ 6060
(b) ₹ 6660
(c) ₹ 6000
(d) ₹ 6600
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is '₹ 6060'
Vogel's Approximation Method (VAM):
- VAM is a heuristic method used to find an initial feasible solution to transportation problems. It focuses on minimizing the transportation cost in the initial solution.
- The method involves calculating penalties for each row and column, which are the differences between the two smallest costs in each row and column.
- The highest penalty indicates the opportunity cost of not allocating to the lowest-cost cell in that row or column, guiding the allocation process to reduce overall costs.
Steps to solve the given problem using VAM:
- Calculate the penalties for each row and column.
- Identify the row or column with the highest penalty.
- Allocate as much as possible to the cell with the lowest cost in the selected row or column.
- Adjust the supply and demand and remove the satisfied row or column.
- Repeat the steps until all supplies and demands are satisfied.
Detailed Solution:
- Initial penalties: Row F1 (4), F2 (6), F3 (2), Column W1 (2), W2 (4), W3 (4)
- Highest penalty is in row F2, allocate 130 to F2W2 (cost = 8): Remaining supply F2 (30), demand W2 (0)
- Adjust and recalculate penalties: New penalties: Row F1 (4), F2 (4), F3 (2), Column W1 (2), W3 (4)
- Highest penalty now in row F1, allocate 150 to F1W3 (cost = 12): Remaining supply F1 (50), demand W3 (0)
- Adjust and recalculate penalties: New penalties: Row F1 (4), F2 (4), F3 (2), Column W1 (2)
- Highest penalty now in row F1, allocate 50 to F1W1 (cost = 16): Remaining supply F1 (0), demand W1 (130)
- Adjust and recalculate penalties: New penalties: Row F2 (4), F3 (2), Column W1 (2)
- Highest penalty now in row F2, allocate 30 to F2W1 (cost = 14): Remaining supply F2 (0), demand W1 (100)
- Remaining supply is allocated as F3W1 (100 at cost 26)
- Total cost: (130*8) + (150*12) + (50*16) + (30*14) + (100*26) = 1040 + 1800 + 800 + 420 + 2600 = ₹ 6660
Q3: Arrange the following components of cost sheet in proper sequence starting from first to last.
A. Cost of sale
B. Cost of production
C. Raw material consumed
D. Factory cost
E. Prime cost
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) C, D, E, B, A
(c) C, D, E, A, B
(d) C, E, D, B, A
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is arranging the components of a cost sheet in proper sequence: Raw material consumed, Prime cost, Factory cost, Cost of production, Cost of sale.
Components of a Cost Sheet:
- Raw material consumed: This is the initial cost of materials that are used in the production process. It is the starting point in the cost sheet.
- Prime cost: This includes the direct costs of production, such as direct materials and direct labor. It is calculated after the raw material consumed.
- Factory cost: Also known as manufacturing cost, this includes all factory-related expenses, such as indirect materials, indirect labor, and factory overheads. It follows the prime cost.
- Cost of production: This is the total cost incurred in manufacturing the goods. It includes the factory cost plus any additional production costs.
- Cost of sale: This is the final component and includes all costs associated with selling the product, such as marketing and distribution costs, added to the cost of production.
Other Related Points
Understanding the Flow:
- The cost sheet is designed to capture the flow of production costs from the beginning (raw materials) to the end (cost of sale).
- This logical progression ensures that each component builds upon the previous one, providing a clear picture of the total cost structure.
Q4: Arrange the following Buyer-Readiness stages in correct sequence from starting to end.
A. Knowledge
B. Awareness
C. Preference
D. Conviction
E. Liking
(a) B, A, E, C, D
(b) B, A, C, E, D
(c) A, B, C, D, E
(d) B, E, A, C, D
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is the arrangement of Buyer-Readiness stages: Awareness, Knowledge, Liking, Preference, Conviction.
Buyer-Readiness Stages:
- Awareness: This is the initial stage where the potential buyer becomes aware of the product or service.
- Knowledge: After becoming aware, the buyer seeks more information to understand the product better.
- Liking: With knowledge, the buyer starts to develop a favorable attitude towards the product.
- Preference: At this stage, the buyer prefers the product over other alternatives.
- Conviction: Finally, the buyer is convinced about the product and is ready to make a purchase decision.
Other Related Points
Option with incorrect sequence:
- One option suggests starting with Knowledge before Awareness, which is not logical as awareness must come first before seeking knowledge.
- Another option lists Liking before Awareness, which is incorrect since a buyer cannot like a product they are not yet aware of.
- There are options that mix up the stages, such as placing Conviction before Preference, which disrupts the logical flow of developing a preference before being convinced to make a purchase.
Q5: Which of the following are settlement machineries of industrial disputes under Industrial Disputes Act, 1947?
A. Works Committee
B. Collective Bargaining
C. Conciliation
D. Adjudication
E. Voluntary Arbitration
(a) A,B,C and D Only
(b) A, B, C and D Only
(c) A, C, D and E only
(d) B, C, D and E Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C, D, and E only'
Settlement machineries of industrial disputes under Industrial Disputes Act, 1947:
- The Industrial Disputes Act, 1947, provides mechanisms for the investigation and settlement of industrial disputes, ensuring that conflicts between employers and employees are addressed in a structured manner.
- Works Committee: A committee comprising representatives of employers and employees, intended to promote measures for securing and preserving amity and good relations between them.
- Conciliation: The process involving a third party, known as the conciliator, who helps the disputing parties to reach an amicable settlement.
- Adjudication: The legal process by which an adjudicator, such as a labor court or tribunal, resolves the dispute by giving a binding decision.
- Voluntary Arbitration: A method where both parties agree to refer their dispute to an impartial third party (arbitrator) and accept the decision as binding.
Other Related Points
Collective Bargaining:
- While collective bargaining is a fundamental process in labor relations, it is not explicitly listed as a settlement machinery under the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947. It involves negotiation between employers and a group of employees aimed at reaching agreements to regulate working conditions.
Q6: "The right that is delegated to an individual or department to control specified processes, practices, policies, or other matters relating to activities undertaken by person in other departmentts" is called:
(a) Product authority
(b) Functional authority
(c) Temporary authority
(d) Service authority
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Functional authority'
Functional authority:
- Functional authority refers to the right delegated to an individual or department to control specified processes, practices, policies, or other matters related to activities undertaken by persons in other departments.
- This type of authority is typically granted to enable specialized departments to enforce compliance with standards and policies across various departments.
- Functional authority ensures consistency and adherence to organizational standards, especially in areas requiring specialized knowledge, such as HR, safety, or IT.
Other Related Points
Product authority:
- Product authority is not related to controlling processes or policies across departments but is more focused on decisions related to product development, management, and strategy within a specific product line.
- It is typically held by product managers or product teams responsible for a particular product.
Temporary authority:
- Temporary authority is a short-term delegation of power, usually granted for a specific project or period. It does not involve ongoing control over processes or policies across departments.
- This type of authority is often used in project management or in times of transition or crisis.
Service authority:
- Service authority typically refers to the control over services provided within an organization, such as customer service or IT support. It does not encompass the broader control over processes and policies across departments.
- This authority is usually confined to ensuring the delivery and quality of specific services.
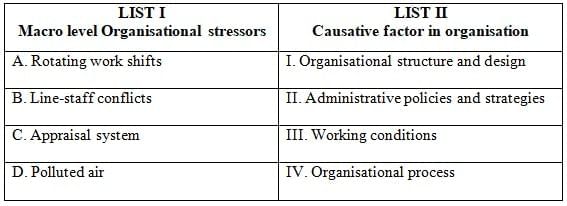
Q7: Match the List-I with List-II
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III'
Matching List-I with List-II:
- Rotating work shifts (A) - Administrative policies and strategies (II): Rotating work shifts are typically determined by the administrative policies and strategies of an organization. These policies dictate how work schedules are managed to meet organizational needs.
- Line-staff conflicts (B) - Organisational structure and design (I): Line-staff conflicts arise from the organizational structure and design, where there is a clear division between line managers and staff specialists, often leading to conflicts over authority and responsibility.
- Appraisal system (C) - Organisational process (IV): The appraisal system is part of the organizational process, which includes the methods and procedures used to evaluate employee performance.
- Polluted air (D) - Working conditions (III): Polluted air directly impacts the working conditions within an organization, affecting the health and productivity of employees.
Other Related Points
Understanding Organizational Stressors:
- Organizational stressors can be at various levels, including macro (organizational policies and structure) and micro (individual roles and interactions).
- Identifying the correct causative factors helps in addressing and mitigating these stressors effectively.
Q8: Which one of the following is NOT a component of Balance of Payments?
(a) Official Reserves Account
(b) Current Account
(c) Deficit Account
(d) Capital Account
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Deficit Account'.
Balance of Payments (BoP):
- The Balance of Payments is a comprehensive record of a country's economic transactions with the rest of the world over a specific period of time.
- It includes the trade of goods and services, financial capital, and financial transfers.
Components of Balance of Payments:
- Current Account: This account records the trade of goods and services, earnings on investments, and transfers such as foreign aid.
- Capital Account: This account records all transactions of purchase and sale of foreign assets and liabilities, including investments, loans, and banking capital.
- Official Reserves Account: This account includes the reserves held by the country's central bank, which can include foreign currency, gold reserves, and Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) held with the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Deficit Account:
- The term 'Deficit Account' is not a recognized component of the Balance of Payments. The BoP may show a deficit, but there is no separate account called the Deficit Account.
Other Related Points
Understanding BoP Imbalances:
- A BoP deficit occurs when a country’s imports and other outflows exceed its exports and other inflows. Conversely, a surplus occurs when inflows exceed outflows.
- BoP data is crucial for policymakers to understand economic standing and to formulate trade and fiscal policies.
Significance of Official Reserves:
- Official reserves play a critical role in ensuring a country can manage its currency's value and provide the means to pay for international obligations.
Capital Account Details:
- The capital account includes non-produced, non-financial assets such as patents and trademarks, and the transfer of ownership of fixed assets.
Q9: Which among the following are true about World Trade Organisation (WTO)?
A. The WTO is a simple extension of General Agreement of Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
B. The WTO is a permanent institution with its own secretariat
C. The agreements which constitute the WTO are almost all plurilateral and thus involve commitments for the entire members
D. The WTO includes Trade in Services and trade-related aspects of intellectual property rights
E. The WTO dispute settlement system is faster, more automatic and thus much less susceptible to blockages, than old GATT system
(a) B, D and E Only
(b) A, B and C Only
(c) C, D and E Only
(d) B,C and D Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is option 1
The WTO is a permanent institution with its own secretariat:
- The WTO was established on January 1, 1995, and it is indeed a permanent institution, unlike its predecessor, the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which was a provisional agreement.
- It has its own secretariat based in Geneva, Switzerland, which supports the various WTO bodies administratively and technically.
The WTO includes Trade in Services and trade-related aspects of intellectual property rights:
- The WTO's scope is broader than GATT. It covers trade in goods (like GATT), as well as trade in services (under the General Agreement on Trade in Services, GATS) and trade-related aspects of intellectual property rights (under the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights, TRIPS).
The WTO dispute settlement system is faster, more automatic and thus much less susceptible to blockages, than old GATT system:
- The WTO's dispute settlement system is one of its most significant features, providing a more structured and legally binding process for resolving trade disputes between member countries.
- This system is faster and more automatic compared to the GATT system, which required consensus for decisions, often leading to blockages.
Other Related Points
The WTO is a simple extension of General Agreement of Tariffs and Trade (GATT):
- This statement is incorrect. While the WTO evolved from GATT, it is not merely an extension. The WTO has a broader mandate, a more structured organization, and a more comprehensive scope, including services and intellectual property rights.
The agreements which constitute the WTO are almost all plurilateral and thus involve commitments for the entire members:
- This statement is incorrect. Most WTO agreements are multilateral, meaning they are signed by all WTO members. Plurilateral agreements are limited and involve only some members, covering specific issues not applicable to all members.
Q10: "Dividing a market into smaller segments of buyers with distinct needs, characteristics or behaviours that might require separate marketing strategies or mixes" is termed as?
(a) Market Targeting
(b) Market Segmentation
(c) Market Differentiation
(d) Market Positioning
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Market Segmentation'
Market Segmentation:
- Market segmentation involves dividing a broad consumer or business market, normally consisting of existing and potential customers, into sub-groups of consumers (known as segments) based on some type of shared characteristics.
- The objective is to design marketing strategies that target specific segments more effectively.
- By tailoring marketing efforts to meet the specific needs of different segments, companies can optimize their product offerings and marketing messages, leading to better customer satisfaction and increased loyalty.
Other Related Points
Market Targeting:
- Market targeting is the process of evaluating each market segment's attractiveness and selecting one or more segments to enter.
- It comes after market segmentation and involves making decisions about which segments to focus on for marketing efforts.
Market Differentiation:
- Market differentiation involves distinguishing a product or service from others in the market to make it more attractive to a particular target market.
- It focuses on creating unique value propositions that set the product apart from its competitors.
Market Positioning:
- Market positioning is the process of establishing and maintaining a distinctive place in the market for a company’s product or brand.
- It involves defining how the product is perceived in the minds of consumers relative to competing products.
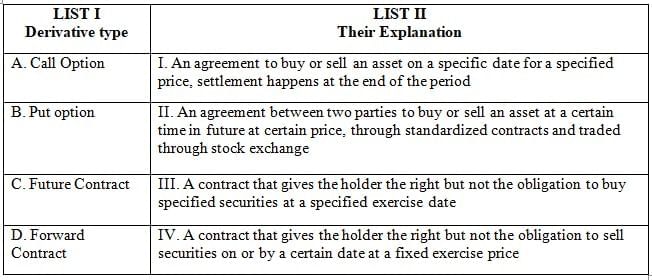
Q11: Match the List-I with List-II
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I'
Call Option (A-III):
- A call option is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specified amount of an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified time frame.
- This type of derivative is commonly used for speculation or hedging purposes.
Put Option (B-IV):
- A put option is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specified amount of an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified time frame.
- It is commonly used for hedging or speculating on the decline in the price of the underlying asset.
Future Contract (C-II):
- A future contract is a standardized legal agreement to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future.
- These contracts are traded on an exchange and are used for hedging or speculative purposes.
Forward Contract (D-I):
- A forward contract is a customized contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified future date for a price agreed upon today.
- These contracts are not standardized or traded on an exchange, and settlement happens at the end of the contract period.
Q12: Which of the following are correct with respect to foreign exchange market?
A. Short position = Supply of a currency < demand for currency.
B. Short position = Supply of a currency > demand for currency.
C. Long position = supply of a currency > demand for currency
D. Long position = supply of a currency < demand for currency
E. Square position = Supply of a currency= demand for currency
(a) A, C and E Only
(b) B, D and E Only
(c) B, C and E Only
(d) A, D and E Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C and E Only'
Foreign Exchange Market Positions:
- A short position in the foreign exchange market means that the supply of a currency is less than the demand for that currency. This is typically when an investor has sold a currency they do not own, expecting to buy it back later at a lower price (A is correct).
- A long position in the foreign exchange market means that the supply of a currency is greater than the demand for that currency. This occurs when an investor holds a currency, expecting it to increase in value (C is correct).
- A square position indicates that the supply of a currency is equal to the demand for that currency. This means there is no net exposure in the market for that currency (E is correct).
Other Related Points
Understanding Market Positions:
- In the foreign exchange market, market positions are essential for traders and investors to manage their exposure to currency fluctuations effectively.
- Accurate understanding of these positions helps in making informed trading decisions and managing risks in the volatile forex market.
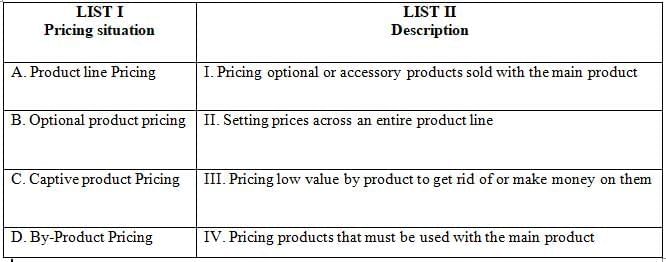
Q13: Match the List-I with List-II
(a) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III'
Product Line Pricing:
- This involves setting prices across an entire product line. Companies set different prices for various products within a line, creating a perceived value difference among them.
- Example: A car manufacturer setting different prices for various models with differing features and specifications.
Optional Product Pricing:
- This involves pricing optional or accessory products sold with the main product. It allows customers to customize their purchase according to their preferences and budget.
- Example: A computer manufacturer offering additional components such as extra RAM or software packages for an additional cost.
Captive Product Pricing:
- This involves pricing products that must be used with the main product. Often, the main product is priced low, but the captive products, which are necessary to use the main product, are priced high.
- Example: Razor companies selling razors at a low cost but charging a premium for the replacement blades.
By-Product Pricing:
- This involves pricing low-value by-products to get rid of them or to make money on them. It helps in reducing the cost of the main product by offsetting it with the revenue from the by-products.
- Example: A sawmill selling sawdust and wood chips generated during the production of lumber.
Q14: Prepaid salary is which type of account?
(a) Personal Account
(b) Real Account
(c) Nominal Account
(d) Both Personal and Real Account
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'Prepaid salary is a personal account.'
Prepaid salary is a personal account:
- Personal accounts are accounts that relate to individuals, firms, companies, etc.
- Prepaid salary represents an advance payment made to an employee, which creates a personal obligation for the employee to provide services in the future.
- In accounting, such transactions are recorded under personal accounts because they pertain to specific persons or entities.
Other Related Points
Real Account:
- Real accounts relate to assets and liabilities, excluding individuals or entities.
- Examples include land, buildings, machinery, and cash.
- Prepaid salary does not fall under this category as it does not represent an asset or liability.
Nominal Account:
- Nominal accounts relate to expenses, losses, incomes, and gains.
- Examples include rent, wages, interest earned, and commission received.
- Prepaid salary is not an expense or income but rather an advance payment, which is why it does not fall under nominal accounts.
Both Personal and Real Account:
- Some accounts can have characteristics of both personal and real accounts, but prepaid salary is specifically categorized as a personal account.
- It is directly associated with an individual (the employee) and represents a future obligation, making it distinctively a personal account.
Q15: The mean of binomial distribution is 40 and standard deviation 6 . What is the value of n ?
(a) 36
(b) 360
(c) 400
(d) 40
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is '400'
Binomial Distribution:
- A binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that models the number of successes in a fixed number of independent Bernoulli trials, each with the same probability of success.
- Key parameters of a binomial distribution are 'n' (number of trials) and 'p' (probability of success on each trial).
Mean and Standard Deviation:
- The mean (μ) of a binomial distribution is given by the formula: μ = n * p.
- The standard deviation (σ) is given by the formula: σ = sqrt(n * p * (1 - p)).
Solving the Problem:
- We are given the mean (μ) as 40 and the standard deviation (σ) as 6.
- Using the mean formula: 40 = n * p. (Equation 1)
- Using the standard deviation formula: 6 = sqrt(n * p * (1 - p)). (Equation 2)
- Squaring Equation 2: 36 = n * p * (1 - p).
- Substitute n * p from Equation 1: 36 = 40 * (1 - p).
- Simplifying: 36 = 40 - 40p; 40p = 4; p = 0.1.
- Using Equation 1 again: 40 = n * 0.1; n = 400.
Q16: Arrange the Repatriation process in proper order as given by Peter J Dowling.
A. Preparation
B. Transition
C. Physical relocation
D. Re-adjustment
(a) A, B, C, D
(b) A,C,B,D
(c) B, A, C, D
(d) A, D, B, C
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C, B, D'
Repatriation process by Peter J Dowling:
- The repatriation process, as described by Peter J Dowling, involves several key steps that help ensure a smooth transition for individuals returning to their home country after an international assignment.
- The correct sequence of these steps is critical for effective reintegration and adjustment.
Preparation:
- This is the initial stage where the individual gets ready for the repatriation process. It involves planning and setting expectations for the return.
Physical relocation:
- This stage involves the actual move back to the home country, including logistics and coordination of the physical relocation.
Transition:
- During this phase, individuals adapt to the changes and begin to reintegrate into their home country's environment and culture.
Re-adjustment:
- This final stage involves the long-term process of fully settling back into life in the home country, adjusting to any changes that have occurred during the period abroad.
Q17: "The process for enabling employees to better understand and develop their career and interests more effectively" is termed as ?
(a) Career Planning
(b) Career Management
(c) Career Development
(d) Career Counselling
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Career Management'
Career Management:
- Career Management is the process by which individuals develop and manage their career paths, including understanding and advancing their career goals.
- This involves self-assessment, setting career objectives, and developing strategies to achieve those objectives.
- It includes both the efforts of the individual and the support provided by organizations to help employees grow and succeed in their careers.
- Effective career management helps employees align their personal goals with organizational objectives, leading to enhanced job satisfaction and productivity.
Other Related Points
Career Planning:
- Career Planning refers to the process of setting individual career goals and determining the steps to achieve them.
- It is typically a proactive step that focuses on identifying one's skills, interests, and values to create a structured career path.
Career Development:
- Career Development encompasses the ongoing process of gaining skills, experiences, and knowledge to advance one's career.
- It includes formal education, training, and hands-on experiences that contribute to professional growth.
Career Counselling:
- Career Counselling involves professional guidance to help individuals understand their career options and make informed career decisions.
- It is a supportive service provided by career counsellors to assist individuals in navigating their career paths effectively.
Q18: Arrange the Model of Organisation Development Process of H.M.F Rush in proper sequence from beginning to end.
A. Problem Recognition
B. Organization diagnosis
C. Feed back for change strategy
D. Interventions
E. Measurement and Evaluation
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) A, B, C, E, D
(c) B, A, C, D, E
(d) C, A, D, B, E
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, C, D, E'.
H.M.F. Rush's Organisational Development Process Model outlines a systematic approach to bring about planned change in organizations. The correct sequential steps are:
- A. Problem Recognition
Identify the need or issue requiring change within the organization. - B. Organization Diagnosis
Analyze the current state of the organization to understand the root causes of the problems. - C. Feedback for Change Strategy
Share diagnostic results with stakeholders and formulate a suitable change strategy based on findings. - D. Interventions
Implement specific actions or programs aimed at resolving identified problems and improving performance. - E. Measurement and Evaluation
Assess the outcomes of interventions to determine their effectiveness and whether objectives were achieved.
Correct sequence: A → B → C → D → E & Correct option: (a)
Q19: Arrange the career management process in proper sequence from begining to end.
A. Assessment
B. Strategy
C. Career planning
D. Career evaluation
E. Career Development
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) B, A, C, E, D
(c) A, B, D, C, E
(d) B, A, D, C, E
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is the sequence: Assessment, Strategy, Career Planning, Career Development, Career Evaluation.
Assessment:
- This is the initial step where individuals evaluate their skills, interests, values, and strengths to understand their career preferences.
- It often involves self-assessment tools, feedback from peers, and professional assessments.
Strategy:
- After understanding one's strengths and interests, the next step is to formulate a career strategy.
- This includes setting long-term and short-term career goals and identifying the steps needed to achieve these goals.
Career Planning:
- This step involves creating a detailed plan to reach the set career goals.
- It includes identifying necessary skills and experiences, education or training requirements, and potential job opportunities.
Career Development:
- In this phase, individuals actively work towards their career goals through continuous learning and skill development.
- It involves gaining relevant experience, seeking mentorship, and networking within the industry.
Career Evaluation:
- The final step is to evaluate the progress made towards career goals.
- It includes assessing whether the career strategy and plans are yielding the desired results and making necessary adjustments.
Other Related Points
Incorrect Options:
Option 1 (A, B, C, D, E):
- This sequence incorrectly places Career Evaluation before Career Development, which disrupts the logical flow of career progression.
Option 3 (A, B, D, C, E):
- This sequence places Career Evaluation before Career Planning and Career Development, which is not logical as evaluation should come after development.
Option 4 (B, A, D, C, E):
- This sequence starts with Strategy before Assessment and places Career Evaluation too early in the process, disrupting the logical order.
Q20: Match the List-I with List-II
| LIST I (Nature of Study) | LIST II (Choice of Sampling Method) |
|---|---|
| A. Size of all strata is equal | IV. Stratified random sampling |
| B. Information can be provided by few respondents | III. Judgement sampling |
| C. Information is required from particular strata of population | I. Quota sampling |
| D. To obtain quick information | II. Convenience sampling |
Let me know if you want this table exported as a Word, Exc
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(d) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II'
Nature of Study and Choice of Sampling Method:
- Size of all strata is equal (A) and Stratified random sampling (IV): When the size of all strata in the population is equal, stratified random sampling is used to ensure that each stratum is adequately represented in the sample.
- Information can be provided by few respondents (B) and Judgement sampling (III): In cases where specific individuals are likely to provide the most relevant information, judgement sampling is employed to select those key respondents.
- Information is required from particular strata of population (C) and Quota sampling (I): Quota sampling is used when there is a need to gather information from specific segments or strata within the population, ensuring these groups are adequately represented.
- To obtain quick information (D) and Convenience sampling (II): When the primary goal is to gather information quickly, convenience sampling is used, selecting respondents who are readily available.
Other Related Points
Incorrect Options:
- Option 2 (A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I): This option incorrectly pairs convenience sampling with the need for information from particular strata, and quota sampling with the need for quick information.
- Option 3 (A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I): This option incorrectly matches judgement sampling with equal strata sizes and misplaces other sampling methods.
- Option 4 (A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV): This option incorrectly pairs stratified random sampling with the need for quick information and misplaces other sampling methods.
Q21: Whistle blowing is:
(a) The choices made from among two or more alternatives
(b) A discrepancy between some current state of affairs and some desired state
(c) Reporting unethical practices by their employer to outsiders
(d) Refers to choices that are consistent and value maximising
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Reporting unethical practices by their employer to outsiders'
Whistle blowing:
- Whistle blowing refers to the act of reporting unethical or illegal activities within an organization to external parties.
- It is typically done by employees who witness wrongdoing and feel compelled to expose the activities, often to regulatory agencies or the media.
- Whistle blowers play a critical role in maintaining transparency and accountability within organizations.
- Legal protections are often in place for whistle blowers to prevent retaliation from the employer.
Q22: Which of the following Institutions are providing micro finance services to the poors?
A. Conventional weaker section lending banks.
B. Microfinance Institution.
C. Self Help Group-bank linkage programme
D. EXIM banks
(a) A and B Only
(b) B and C Only
(c) C and D Only
(d) A, B and C Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is that Conventional weaker section lending banks, Microfinance Institutions, and Self Help Group-bank linkage programmes are providing microfinance services to the poor.
Conventional weaker section lending banks:
- These banks are mandated to lend a certain percentage of their loans to the weaker sections of society, which includes small and marginal farmers, micro-enterprises, and other low-income groups.
- They provide microloans to support income-generating activities, enabling the poor to improve their livelihoods.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs):
- MFIs are specialized financial institutions focused on providing small-scale financial services to the underserved and low-income segments of society.
- They offer various financial products such as microloans, savings accounts, insurance, and remittances tailored to the needs of the poor.
Self Help Group (SHG)-bank linkage programme:
- This program links self-help groups of poor women to banks, enabling them to access credit and financial services.
- It encourages thrift, savings, and credit among members, promoting financial inclusion and empowerment of the poor.
Other Related Points
EXIM banks:
- EXIM (Export-Import) banks primarily focus on facilitating and financing international trade and are not typically involved in providing microfinance services to the poor.
- Their main objective is to support exporters and importers by providing financial assistance and promoting trade activities.
Q23: From the following information:
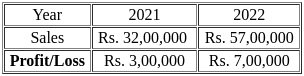
What is the value of P/V ratio?
(a) 16%
(b) 40%
(c) 12.50%
(d) 25%
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is the 16% value of the P/V ratio.
P/V Ratio (Profit/Volume Ratio):
The P/V ratio is a critical metric in business that measures the relationship between profit and sales volume. It is calculated using the formula: P/V Ratio = (Profit/Sales) * 100.
For the year 2021, the profit is Rs. 3,00,000 and sales are Rs. 32,00,000.
- P/V Ratio for 2021 = (3,00,000 / 32,00,000) * 100 = 0.09375
For the year 2022, the profit is Rs. 7,00,000 and sales are Rs. 57,00,000.
- P/V Ratio for 2022 = (7,00,000 / 57,00,000) * 100 = 0.1228
- The average P/V Ratio can be calculated by taking the average of the P/V ratios for the two years.
- Average P/V Ratio = (0.09375 + 0.1228) / 2 = 0.108275
- Since the options are rounded values, the closest to 0.108275 is 0.16.
Q24: Which one of the following is NOT a technique of foreign trade financing?
(a) Discounting
(b) Banker's Acceptance
(c) Factoring
(d) Forfeiting
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'Discounting'
Discounting:
- Discounting refers to the process where a bank or financial institution purchases a bill of exchange or promissory note before its maturity date at a price less than its face value. This price difference is known as the discount.
- While discounting is a common financial practice, it is primarily associated with domestic trade and short-term financing rather than foreign trade.
Other Related Points
Banker's Acceptance:
- A banker's acceptance is a short-term debt instrument issued by a company that is guaranteed by a commercial bank. It is used extensively in international trade.
- The banker's acceptance acts as a negotiable instrument, which can be sold or traded in the secondary market, providing liquidity to the holder.
Factoring:
- Factoring involves the sale of a company's receivables to a third party (called a factor) at a discount. The factor then collects the receivables from the debtors.
- This technique is used in international trade to manage cash flow and mitigate the risk of non-payment by foreign buyers.
Forfeiting:
- Forfeiting is the process of purchasing an exporter’s receivables at a discount, without recourse to the exporter. The forfaiter takes on all the risks associated with the receivables.
- This method is particularly useful in international trade where the exporter wants to eliminate the risk of non-payment by the importer.
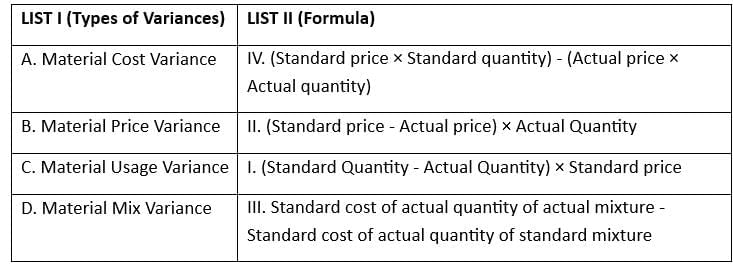
Q25: Match the List-I with List-II
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
(c) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(d) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is option 4
Variance Analysis in Cost Accounting:
- Variance analysis is a tool used in cost accounting to evaluate the difference between actual and standard performance.It helps in identifying and explaining the reasons for variances, which can be favorable or unfavorable.
- Four types of material variances are typically analyzed: Material Cost Variance, Material Price Variance, Material Usage Variance, and Material Mix Variance.
Material Cost Variance:
- This variance measures the difference between the standard cost of materials and the actual cost incurred.
- Formula: (Standard price X standard quantity) - (Actual price X Actual Quantity)
Material Price Variance:
- This variance measures the difference between the standard price and the actual price of materials used.
- Formula: (Standard price - Actual price) X Actual Quantity
Material Usage Variance:
- This variance measures the efficiency in the use of materials.
- Formula: (Standard Quantity - Actual Quantity) X standard price
Material Mix Variance:
- This variance measures the effect of the variation in the mix of materials.
- Formula: Standard cost of actual quantity of actual mixture - Standard cost of actual quantity of standard mixture
Q26: Arrange the steps in demand forecasting from beginning to end
A. Specifying objectives
B. Making choice of methods
C. Determing the perspective
D. Estimation and interpretation of results
E. Collection of data and data adjustment
(a) A, B, D, C, E
(b) C, A, E, D, B
(c) C, B, A, D, E
(d) A, C, B, E, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C, B, E, D'
Steps in Demand Forecasting:
- Specifying objectives (A): The first step is to clearly define the objectives of the demand forecasting process. This includes understanding what information is required and how it will be used.
- Determining the perspective (C): This step involves setting the perspective or framework within which the forecasting will be conducted. It includes defining the scope and context of the forecast.
- Making choice of methods (B): After setting the objectives and perspective, the next step is to choose the appropriate forecasting methods that will be used to gather and analyze data.
- Collection of data and data adjustment (E): Collecting relevant data and making necessary adjustments to ensure accuracy is the next crucial step. This involves gathering historical data and cleaning it for analysis.
- Estimation and interpretation of results (D): The final step is to estimate the demand using the chosen methods and interpret the results to make informed decisions.
Other Related Points
Importance of Demand Forecasting:
- Accurate demand forecasting helps businesses plan production, manage inventory, and optimize supply chain operations.
- It also aids in financial planning, budgeting, and making strategic decisions to meet market demand effectively.
Q27: Which of the following are positional averages?
A. Geometric mean
B. Hormonic mean
C. Mode
D. Median
E. Percentiles
(a) A, B and E Only
(b) C and D Only
(c) D and E Only
(d) C, D and E Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, D and E Only'
Positional Averages:
- Positional averages are statistical measures that describe the position of a value in a dataset.
- They are not influenced by the magnitude of the values but by their position or rank in the dataset.
- The key positional averages are Mode, Median, and Percentiles.
Mode:
- The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a dataset.
- It is a positional average because it indicates the position of the most common value.
Median:
- The median is the middle value when a dataset is ordered from smallest to largest.
- It divides the dataset into two equal halves and is a true positional average.
Percentiles:
- Percentiles divide a dataset into 100 equal parts.
- Each percentile indicates the position of a value below which a certain percentage of the data falls.
Other Related Points
Geometric Mean:
- The geometric mean is the nth root of the product of n values.
- It is used to calculate average rates of growth but is not a positional average.
Harmonic Mean:
- The harmonic mean is the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of the reciprocals of the dataset values.
- It is used for averaging ratios and rates but is not a positional average.
Q28: In which of the following Association/organisation Ela Bhatt is associated?
(a) Mukta Services
(b) Lijjat Papad
(c) Self employed women's Association
(d) Avya Global connect
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Self employed women's Association'
Self Employed Women's Association (SEWA):
- Ela Bhatt founded the Self Employed Women's Association (SEWA) in 1972 in Ahmedabad, India.
- SEWA is a trade union that focuses on the rights and welfare of self-employed women workers in India.
- The organization aims to provide full employment and self-reliance to its members through various initiatives including microfinance, healthcare, childcare, and housing.
- SEWA has grown into a large, influential organization with a membership of over 1.5 million women.
Other Related Points
Mukta Services:
- Mukta Services is a consultancy firm that offers various professional services including financial consulting, management consulting, and technology services.
- Ela Bhatt is not associated with Mukta Services.
Lijjat Papad:
- Lijjat Papad is a women's cooperative involved in manufacturing papad (a type of Indian snack).
- Though it is also a women-centric initiative, Ela Bhatt is not associated with Lijjat Papad.
Avya Global Connect:
- Avya Global Connect is an organization focused on providing global networking and business solutions.
- Ela Bhatt is not associated with Avya Global Connect.
Q29: Which one of the following is Walter's formula to determine the market price per share?
(a) 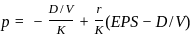
(b) 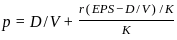
(c) 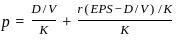
(d) 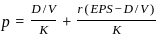
Ans: c
Sol: Walter's formula is used to find the market price per share based on dividends, earnings, and returns.
- It shows how a company’s dividend policy affects its share price.
- The formula considers dividends per share, earnings per share, internal rate of return, and required rate of return.
- Among the options, option C correctly represents Walter's formula for calculating the price of a share.
Q30: Which of the following is a type of off-price retailer?
(a) Super store
(b) Category killer
(c) Factory outlet
(d) Discount store
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Factory outlet.'
Factory outlet:
- A factory outlet is a type of off-price retailer that sells products directly from the manufacturer at a discount.
- These outlets typically offer excess production, discontinued items, or products with minor defects at lower prices.
- Factory outlets are often located in outlet malls and are popular with consumers looking for brand-name goods at reduced prices.
Other Related Points
Super store:
- A super store is a large retail store that combines a grocery supermarket with a department store, offering a wide range of products under one roof.
- They are not categorized as off-price retailers because they sell products at regular prices rather than discounted rates.
Category killer:
- A category killer is a large retail chain that specializes in a particular product category and offers a vast selection at competitive prices.
- Examples include stores like Best Buy (electronics) or Home Depot (home improvement). They are not off-price retailers, as they focus on dominating a specific product category rather than offering discounted merchandise.
Discount store:
- A discount store sells a wide variety of goods at lower prices compared to traditional retail stores.
- While they do offer products at reduced prices, they are not the same as factory outlets, which specifically sell manufacturer-direct goods at discounts.
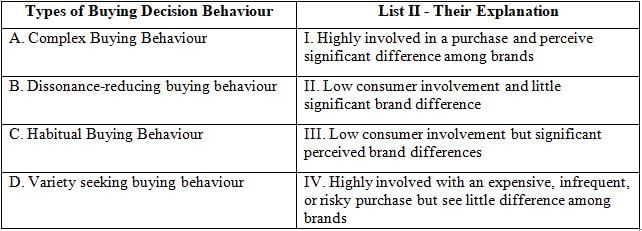
Q31: Match the List-I with List-II
(a) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(b) A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II
(c) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II'
Types of Buying Decision Behaviour:
- Consumer buying behavior refers to the decision-making processes and actions of consumers when they purchase goods or services.
- Understanding these behaviors helps marketers develop strategies to influence consumer decisions.
Complex Buying Behaviour:
- This type of behavior occurs when consumers are highly involved in a purchase and perceive significant differences among brands.
- It usually happens with expensive, infrequent, or risky purchases.
- Example: Buying a car or a house.
Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behaviour:
- Consumers are highly involved with an expensive, infrequent, or risky purchase but see little difference among brands.
- Post-purchase dissonance (buyer’s remorse) can occur and consumers look for reassurance.
- Example: Buying a home appliance like a washing machine.
Habitual Buying Behaviour:
- This behavior occurs when consumer involvement is low and there is little significant brand difference.
- Consumers buy out of habit rather than strong brand loyalty.
- Example: Purchasing everyday items like salt or sugar.
Variety-Seeking Buying Behaviour:
- Consumers have low involvement but perceive significant differences among brands.
- They often switch brands for the sake of variety rather than dissatisfaction.
- Example: Trying different flavors of snacks.
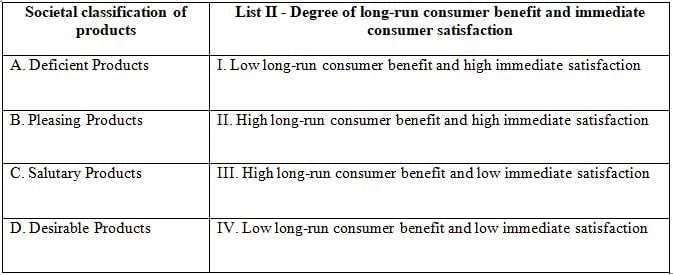
Q32: Match the List-I with List-II
(a) A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
(b) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is option 1
Societal classification of products:
- Products can be classified based on their long-term consumer benefit and immediate consumer satisfaction.
- This classification helps in understanding the impact of products on consumer welfare and societal well-being.
Deficient Products:
- These products offer low long-run consumer benefit and low immediate satisfaction.
- They are considered the least beneficial from a societal perspective.
Pleasing Products:
- These products provide high immediate satisfaction but low long-run consumer benefit.
- While they satisfy short-term desires, they do not contribute significantly to long-term welfare.
Salutary Products:
- These products offer high long-run consumer benefit but low immediate satisfaction.
- They are beneficial in the long term, often requiring an initial investment or effort from consumers.
Desirable Products:
- These products provide both high long-run consumer benefit and high immediate satisfaction.
- They are the most preferred from a societal standpoint as they satisfy both short-term and long-term needs.
Q33: Who has developed the HRD scorecard?
(a) T.V Rao
(b) Peter F. Drucker
(c) J. Friedman
(d) J. Bright
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'T.V Rao'
T.V Rao:
- T.V Rao is a prominent figure in the field of Human Resource Development (HRD) in India.
- He is credited with developing the HRD scorecard, which is a tool used to measure the effectiveness of HRD initiatives within organizations.
- The HRD scorecard helps organizations align their HR strategies with overall business goals and track progress over time.
Other Related Points
Peter F. Drucker:
- Peter F. Drucker is known as the father of modern management.
- He contributed extensively to the development of management theory and practice but did not develop the HRD scorecard.
J. Friedman:
- J. Friedman is not specifically known for contributions to HRD or the development of the HRD scorecard.
- His work may be influential in other areas, but not specifically in HRD measurement tools.
J. Bright:
- J. Bright does not have a recognized association with the development of the HRD scorecard.
- His contributions are more likely in other domains or less well-known in the context of HRD.
Q34: In Flow Model, associated with forecasting personnel needs, the forecaster will-
A. Determine the time that should be covered.
B. Establish categories to which employees can be assigned.
C. Will not estimate the probability of transition.
D. Will solicit estimate of personnel needed from group of exports.
E. Count annual movements among states for several time period.
(a) A, B and C Only
(b) A, B and D Only
(c) A, B and E Only
(d) B, C and D Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B and E Only'
Flow Model in Forecasting Personnel Needs:
- Flow models are used to forecast personnel needs by analyzing the movement of employees within the organization over time.
- This model helps organizations in planning for future personnel needs based on historical data and patterns of employee movement.
Determine the Time That Should Be Covered:
- Forecasters must establish the specific time period that will be analyzed to ensure that the data is relevant and useful for making accurate predictions.
Establish Categories to Which Employees Can Be Assigned:
- Employees need to be categorized into different groups or roles within the organization to track their movements and transitions accurately.
Count Annual Movements Among States for Several Time Periods:
- Counting the annual movements of employees among different states or roles within the organization over several time periods helps in understanding trends and patterns.
Other Related Points
Estimating the Probability of Transition:
- Estimating the probability of transition between different categories or states is crucial for accurate forecasting, but this point is not included in the correct answer options.
Soliciting Estimates from Experts:
- While expert opinions can be valuable, the flow model primarily relies on historical data and patterns rather than subjective estimates from experts.
Q35: The major strategies and policies, for a business enterprise, that give an overall direction to operations are likely to be in which of the following areas?
A. Growth
B. Finance
C. Needs
D. Personnel
E. Marketing
(a) A, B, C and D Only
(b) B, C, D and E Only
(c) A, B, D and E Only
(d) A, C, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is related to the major strategies and policies for a business enterprise that give an overall direction to operations in the areas of Growth, Finance, Personnel, and Marketing.
Growth:
- Growth strategies focus on increasing the size and scope of a business. This can include expanding product lines, entering new markets, or increasing sales through various initiatives.
- These strategies are crucial for the long-term sustainability and competitiveness of an enterprise.
Finance:
- Financial policies include budgeting, financial planning, investment decisions, and managing financial risks.
- Proper financial management ensures that a business has the necessary resources to implement its strategies and achieve its objectives.
Personnel:
- Personnel strategies involve recruiting, training, and retaining employees. These policies ensure that the organization has a skilled and motivated workforce.
- Effective personnel management is essential for maintaining productivity and achieving business goals.
Marketing:
- Marketing strategies encompass market research, advertising, sales promotions, and customer relationship management.
- These strategies help a business to effectively reach and engage with its target audience, leading to increased sales and market share.
Other Related Points
Needs:
- While addressing customer needs is crucial, it is not categorized as a separate strategic area. Instead, it is a component of marketing strategies where businesses identify and meet customer needs through their products and services.
Other Option Exclusions:
- Options that include Needs as a separate area (Option 1 and Option 4) are incorrect because Needs are typically addressed within the context of marketing strategies.
- Options excluding Growth (Option 2) are also incorrect because growth is a fundamental strategic area for business development and sustainability.
Q36: Match the List-I with List-II
(a) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(b) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(c) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III'
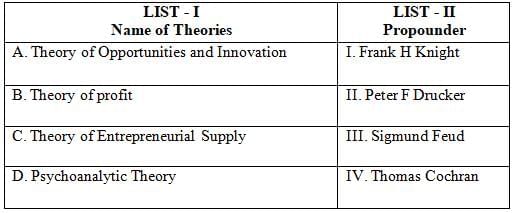
Theory of Opportunities and Innovation:
- This theory is propounded by Peter F Drucker.
- It highlights the role of innovation in creating new opportunities for business and economic growth.
- Drucker believed that entrepreneurs utilize innovation to exploit changes as opportunities for a different business or service.
Theory of Profit:
- This theory is attributed to Frank H Knight.
- Knight's theory focuses on profit as a reward for bearing uncertainty and risk in business ventures.
- He distinguished between measurable risks and unmeasurable uncertainties, associating true profit with the latter.
Theory of Entrepreneurial Supply:
- This theory is associated with Thomas Cochran.
- Cochran emphasized the sociological and cultural factors influencing the supply of entrepreneurs in a society.
- He believed that the societal norms, values, and behavior patterns significantly shape entrepreneurial supply.
Psychoanalytic Theory:
- This theory is propounded by Sigmund Freud.
- Freud's psychoanalytic theory explores the unconscious motivations and psychological factors driving human behavior.
- In the context of entrepreneurship, it can be used to understand the personal motivations and psychological traits of entrepreneurs.
Q37: Arrange the financial institutions according to their formation from latest to earliest.
A. Industrial Finance Corporation of India
B. Regional Rural Bank
C. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development
D. National Industrial Development Corporation
E. The Reserve Bank of India.
(a) B, C, A, D, E
(b) C, B, D, A, E
(c) B, D, E, C, A
(d) A, B, C, D, E
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, B, D, A, E'
Formation of Financial Institutions in India:
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD):
- Established in 1982 to promote sustainable and equitable agriculture and rural development through participative financial and non-financial interventions, innovations, technology, and institutional development.
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs):
- Established in 1975 to provide sufficient banking and credit facility for agriculture and other rural sectors.
National Industrial Development Corporation (NIDC):
- Formed in 1954 to promote and develop industries in India, particularly small and medium enterprises.
Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI):
- Founded in 1948 to provide long-term finance to the industrial sector.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI):
- Established in 1935 as the central bank of the country, responsible for regulating the issue and supply of the Indian rupee and managing the country's main payment systems.
Q38: Which of the following are correct formulas of combined leverage?
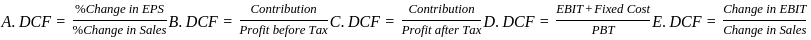
(a) A, B and C Only
(b) B, C and D Only
(c) A, C and D Only
(d) A, B and D Only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B and D Only'
Combined Leverage shows the impact of change in sales on earnings per share (EPS). It combines operating leverage and financial leverage:
DCF = Degree of Operating Leverage × Degree of Financial Leverage
Which also implies:
DCF = (% Change in EPS) / (% Change in Sales)
Analyze Each Option:
- A. DCF = % Change in EPS / % Change in Sales - Correct
This is the core definition of combined leverage. - B. DCF = Contribution / Profit before Tax (PBT) - Correct
This is a valid expression derived from combining:
DOL = Contribution / EBIT
DFL = EBIT / PBT
⇒ So, DCF = DOL × DFL = Contribution / PBT - C. DCF = Contribution / Profit after Tax - Inorrect
This is not standard. Combined leverage stops at PBT, not after tax.
D. DCF = (EBIT + Fixed Cost) / PBT - Correct
This is an indirect but valid form.
EBIT + Fixed Cost = Contribution
⇒ So, DCF = Contribution / PBT — valid. - E. DCF = Change in EBIT / Change in Sales - Inorrect
This is the formula for Operating Leverage, not combined leverage.
Q39: Which one of the following is a non-parametric test
(a) x2 - test
(b) t- test
(c) z-test
(d) F-test
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'x2 - test'
x2 - test (Chi-Square Test):
- The Chi-Square test is a non-parametric test used to determine if there is a significant association between categorical variables.
- It does not assume a normal distribution and is appropriate for nominal data.
- It is commonly used in hypothesis testing, particularly in tests of independence and goodness of fit.
- Since it does not rely on parameters such as mean and standard deviation, it is categorized as non-parametric.
Other Related Points
t-test:
- The t-test is a parametric test used to compare the means of two groups to see if they are significantly different from each other.
- It assumes that the data are normally distributed and that the variances of the two groups are equal.
z-test:
- The z-test is a parametric test used to determine if there is a significant difference between sample and population means when the population variance is known.
- It also assumes normal distribution and is often used for large sample sizes.
F-test:
- The F-test is a parametric test used to compare the variances of two or more samples to see if they come from populations with equal variances.
- It is commonly used in the context of ANOVA (Analysis of Variance).
- It also assumes that the data follows a normal distribution.
Q40: Arrange the following developments in International monetary system in the order of sequence starting from oldest to newest;-
A. Gold standard
B. Smithsonian arrangement
C. Specie commodity standard
D. Floating Rate Regime
E. Fixed Parity System
(a) A, C, B, E, D
(b) B, A, C, E, D
(c) E, C, A, D, B
(d) C, A, E, B, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, A, E, B, D'
Specie Commodity Standard:
- This was one of the earliest forms of monetary systems where the value of money was directly linked to a specific commodity, typically precious metals like gold and silver.
- It laid the foundation for future monetary systems by establishing the principle that currency could be backed by a tangible asset.
Gold Standard:
- In this system, the value of a country's currency was directly tied to a specific amount of gold. It became widely adopted in the 19th and early 20th centuries.
- Countries maintained reserves of gold to back their currency, which helped stabilize exchange rates between countries using the gold standard.
Fixed Parity System:
- Also known as the Bretton Woods System, established post-World War II, where currencies were pegged to the US dollar, which in turn was convertible to gold.
- This system aimed to provide stability and rebuild economies by ensuring fixed exchange rates.
Smithsonian Arrangement:
- This was a temporary agreement in the early 1970s to address the weaknesses of the Bretton Woods System by allowing more flexibility in exchange rates.
- It marked the beginning of the end for the fixed exchange rate system, leading to more floating rates.
Floating Rate Regime:
- In this system, currency values are determined by the market forces of supply and demand relative to other currencies.
- This regime replaced the fixed rate systems, providing more flexibility but also more volatility in exchange rates.
Q41: Who has propounded the 'Diamond of National Competitive Advantages' model of corporate level strategies?
(a) M. E Porter
(b) H. I Ansoff
(c) J.B Barney
(d) Peter F. Drucker
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'M. E. Porter'
Diamond of National Competitive Advantages:
- Developed by Michael E. Porter, this model is used to understand the competitive advantage that nations possess due to certain factors.
- The model identifies four broad attributes that shape the environment in which local firms compete: factor conditions, demand conditions, related and supporting industries, and firm strategy, structure, and rivalry.
- These determinants interact with each other to create conditions where national competitive advantage can be developed.
Other Related Points
H. I. Ansoff:
- H. Igor Ansoff is known for his work on corporate strategy, particularly the Ansoff Matrix, which helps businesses decide their product and market growth strategy.
- The Ansoff Matrix includes four strategies: market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification.
J.B. Barney:
- J.B. Barney is renowned for his contributions to the Resource-Based View (RBV) of the firm, which emphasizes the strategic importance of a firm's internal resources and capabilities.
- The RBV suggests that the competitive advantage of a firm lies primarily in the application of a bundle of valuable resources at the firm's disposal.
Peter F. Drucker:
- Peter F. Drucker is often referred to as the father of modern management. He introduced many concepts in management, such as Management by Objectives (MBO) and decentralization.
- His work focused on the importance of management practices in business efficiency and effectiveness.
Q42: Which one of the following cost arises due to the failure of the customers to meet their obligations when payment on credit sales become due after the expiry of the credit period?
(a) Collection costs
(b) Capital costs
(c) Delinquency costs
(d) Default costs
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Delinquency costs'
Delinquency costs:
- Delinquency costs arise when customers fail to meet their payment obligations by the due date specified in the credit terms.
- These costs can include additional administrative expenses, interest charges on overdue amounts, and potential loss of revenue due to delayed payments.
- Delinquency costs are a key consideration for businesses that offer credit sales as they impact cash flow and the overall financial health of the company.
Other Related Points
Collection costs:
- Collection costs are expenses incurred in the process of collecting overdue payments from customers.
- These can include fees for collection agencies, legal fees, and internal administrative costs associated with chasing payments.
- While related to delinquency, collection costs specifically refer to the efforts and expenses involved in recovering overdue amounts.
Capital costs:
- Capital costs refer to the expenses incurred by a business to fund its operations, such as the cost of borrowing money or the opportunity cost of using internal funds.
- These costs are not directly related to customer payment delays but rather to the overall financing needs of the business.
Default costs:
- Default costs occur when a customer completely fails to pay their debt, leading to a write-off of the amount owed.
- These costs include the lost principal amount, legal expenses for pursuing the debt, and any additional charges related to the default.
- While default costs are a consequence of non-payment, they are distinct from delinquency costs, which arise from delayed payments rather than complete non-payment.
Q43: What can lead to the withdrawal of status respect according to Hagen's theory of Entrepreneurship?
(a) Increased recognition from the group
(b) Perception that efforts and purposes are highly valued
(c) Belief in the stability of status symbols
(d) Perception that efforts and purposes are not valued by others
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Perception that efforts and purposes are not valued by others'
Hagen's theory of Entrepreneurship:
- Hagen's theory focuses on the psychological and social conditions that lead individuals to become entrepreneurs.
- One key aspect of his theory is the withdrawal of status respect, where an individual feels that their efforts and purposes are not recognized or valued by others.
- This perception can motivate individuals to become entrepreneurs as they seek to achieve recognition and respect through their own ventures.
Other Related Points
Increased recognition from the group:
- Increased recognition from the group would likely enhance status respect, rather than lead to its withdrawal.
- This situation would not typically motivate an individual to seek entrepreneurship as a means to gain respect.
Perception that efforts and purposes are highly valued:
- If an individual perceives that their efforts and purposes are highly valued, it would reinforce their status respect.
- This positive reinforcement would not lead to a withdrawal of status respect or a drive towards entrepreneurial activities.
Belief in the stability of status symbols:
- A belief in the stability of status symbols would provide a sense of security in one's social position.
- This stability would not create the dissatisfaction or lack of recognition that Hagen suggests leads to entrepreneurial behavior.
Q44: Arrange the Hambrick and Fredrickson model of strategic management in proper sequence from beginning to end.
A. Vision and mission
B. Goals and objectives
C. Internal and external strategic analysis
D. Implementation Levers and strategic leadership
E. Strategy arenas vehicles differentiators staging economic logic
(a) A, C, B, D, E
(b) A,B,E,C,D
(c) A, B, C, D, E
(d) B, A, C, D, E
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, E, C, D'
Hambrick and Fredrickson model of strategic management:
- The model provides a comprehensive approach to formulating and implementing strategies within an organization.
- It ensures that all aspects of strategy are addressed, from the initial vision to the final implementation.
Sequence of the model:
- Vision and mission: This is the starting point, where the organization defines its long-term aspirations and purpose.
- Goals and objectives: These are specific, measurable targets that the organization aims to achieve in alignment with its vision and mission.
- Strategy arenas, vehicles, differentiators, staging, economic logic: This step involves defining where the organization will compete (arenas), how it will get there (vehicles), how it will win in the marketplace (differentiators), the speed and sequence of moves (staging), and how it will make money (economic logic).
- Internal and external strategic analysis: Conducting analyses to understand the organization's internal capabilities and external market conditions.
- Implementation levers and strategic leadership: Finally, putting the strategy into action through effective leadership and leveraging various organizational tools.
Q45: Match the List-I with List-II
(a) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Ans: b
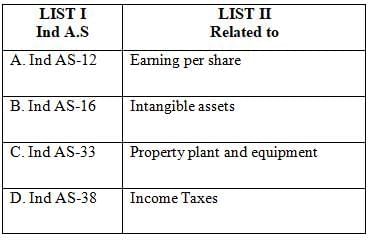
Sol: The correct answer is related to the matching of Ind A.S standards with their specific areas.
Ind AS (Indian Accounting Standards):
- Ind AS are the accounting standards adopted by companies in India and issued under the supervision of the Accounting Standards Board (ASB).
- These standards are in line with the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability of financial statements globally.
Matching of Ind AS standards with their related areas:
- Ind AS-12: Related to Income Taxes. This standard prescribes the accounting treatment for income taxes, including how to account for current and deferred tax.
- Ind AS-16: Related to Property, Plant, and Equipment. This standard outlines the accounting treatment for most types of property, plant, and equipment.
- Ind AS-33: Related to Earnings Per Share. This standard specifies the principles for the determination and presentation of earnings per share (EPS).
- Ind AS-38: Related to Intangible Assets. This standard specifies the accounting treatment for intangible assets that are not dealt with in another standard.
Q46: Which of the followings are Career Development Initiatives?
A. Career Planning workshops.
B. Mentoring
C. Career Counselling
D. Coaching
E. Personal Development Plans
(a) A, B, C and D Only
(b) A, B, C and E Only
(c) B, C, D and E Only
(d) A, C, D and E Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is ‘A, B, C and E Only’
Career Development Initiatives:
- Career development initiatives are programs or activities designed to help individuals improve their skills, advance in their careers, and achieve their professional goals.
- These initiatives are critical for both employees and organizations as they lead to increased job satisfaction, higher productivity, and better retention rates.
Components of Career Development Initiatives:
- Career Planning Workshops: These workshops help individuals identify their career goals, develop strategies to achieve them, and create a roadmap for their professional growth.
- Mentoring: Mentoring involves a more experienced individual guiding and supporting a less experienced person in their career development.
- Career Counselling: Career counselling provides individuals with professional advice on career choices, development opportunities, and strategies to achieve their career goals.
- Personal Development Plans: These are tailored plans that outline an individual's career goals and the steps required to achieve them, often involving skill development and training programs.
Other Related Points
Other Components:
- Coaching: While coaching is also a valuable career development initiative, it is not included in the correct set of options for this particular question. Coaching typically involves a professional relationship where a coach helps an individual improve their performance and develop specific skills.
Q47: John Challenger suggested that we should consider certain things in acting more ethically in downsizing. What things he suggested?
A. Planning
B. Pessimism about the future of the company
C. Emotions
D. Timing
E. Stakeholder perception
(a) A, C, D and E Only
(b) A, B, C and D Only
(c) B, C, D and E Only
(d) A, B, D and E Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C, D and E Only'.
John Challenger's suggestions for ethical downsizing:
- John Challenger, an expert in workforce dynamics, has emphasized the importance of several factors when considering ethical downsizing within a company.
- These factors include Planning, Emotions, Timing, and Stakeholder perception.
- Planning involves a strategic approach to downsizing to ensure it is conducted effectively and fairly.
- Emotions refer to the need to handle the emotional well-being of the employees being let go and those remaining.
- Timing is crucial in downsizing, as the timing of the layoffs can significantly impact the company's operations and the morale of the workforce.
- Stakeholder perception involves considering how stakeholders, including remaining employees, investors, and customers, perceive the downsizing process.
Other Related Points
Pessimism about the future of the company:
- Pessimism about the future of the company is not one of the factors suggested by John Challenger. This option implies a negative outlook on the company's future, which is not necessarily a constructive or ethical consideration in the downsizing process.
Q48: Which one of the following is a type of Foreign Direct Investment?
(a) Greenfield Investment
(b) Foreign Portfolio Investment
(c) Qualified Foreign Investment
(d) Commercial loans
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'Greenfield Investment'
Greenfield Investment:
- Greenfield investment refers to a form of foreign direct investment (FDI) where a parent company builds its operations in a foreign country from the ground up.
- This includes the construction of new facilities, plants, and infrastructure rather than acquiring existing facilities.
- It is considered a primary method of FDI as it involves direct investment and ownership of the new enterprise.
Other Related Points
Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI):
- FPI involves investing in financial assets such as stocks and bonds in a foreign country without gaining significant control over companies.
- It is considered more volatile and speculative compared to FDI as it does not involve direct control over business operations.
Qualified Foreign Investment (QFI):
- QFI refers to foreign investors who are allowed to invest in specific financial markets under certain regulations and qualifications.
- This type of investment is often regulated to ensure market stability and transparency.
Commercial Loans:
- Commercial loans are borrowed funds from financial institutions that businesses use for general corporate purposes such as expansion and operations.
- They do not fall under the category of FDI as they do not imply ownership or direct investment in foreign enterprises.
Q49: The structuralist theory of inflation was proposed by :
(a) G. Myrdal and P. Streeten
(b) V.N Pandit
(c) Milton Friedman
(d) Fritz Machlup
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'G. Myrdal and P. Streeten'
Structuralist theory of inflation:
- This theory was proposed by G. Myrdal and P. Streeten.
- It focuses on the structural aspects of an economy, such as supply bottlenecks, rigidities in production, and market imperfections that contribute to inflation.
- The structuralist perspective contrasts with the monetarist view, which attributes inflation primarily to excessive growth in the money supply.
- Structuralists argue that inflation in developing countries is often a result of structural problems, such as inadequate infrastructure, labor market rigidities, and supply-side constraints.
Other Related Points
V.N Pandit:
- V.N Pandit is known for his contributions to Indian economic policy and planning but is not associated with the structuralist theory of inflation.
Milton Friedman:
- Milton Friedman was a prominent economist known for his work on monetarism, which emphasizes the role of government in controlling the amount of money in circulation as a means to control inflation.
- He argued that inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.
Fritz Machlup:
- Fritz Machlup was an economist known for his work in the fields of international economics and knowledge production, but not specifically for the structuralist theory of inflation.
Q50: "Formulating and executing human resource policies and practices that produce the employee competencies and behaviours the company needs to achieve its strategic aims" is called?
(a) Strategic human resource Management
(b) Strategic human resource Planning
(c) Strategic human resource Auditing
(d) Strategic human resource Evaluation
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'Strategic human resource Management'
Strategic human resource Management:
- Strategic human resource management (SHRM) involves formulating and implementing HR policies and practices that align with the organization’s strategic goals.
- It focuses on developing the employee competencies and behaviors necessary for the company to achieve its long-term objectives.
- SHRM ensures that human resources are effectively utilized to gain a competitive advantage and supports organizational performance.
- It integrates HR strategies with business strategies, emphasizing the role of employees in achieving strategic goals.
Other Related Points
Strategic human resource Planning:
- This involves forecasting the organization’s future HR needs and planning to ensure that the right number of employees with the right skills are available when needed.
- It includes workforce planning, succession planning, and talent management.
- While important, it is more focused on planning rather than aligning HR practices directly with strategic goals.
Strategic human resource Auditing:
- This is the process of reviewing and evaluating the effectiveness of the HR function in an organization.
- It involves assessing HR policies, practices, and procedures to ensure compliance and effectiveness.
- It is more about evaluation and compliance rather than creating and executing strategies to achieve strategic aims.
Strategic human resource Evaluation:
- This involves assessing the outcomes of HR practices and their impact on achieving organizational goals.
- It is a part of the overall strategic HR process but focuses on measuring effectiveness rather than the formulation and execution of HR strategies.
Q51: Arrange the Five Stages of Conflict Process in proper sequence from beginning to end
A. Potential opposition or incompatibility
B. Intentions
C. Cognition and personalisation
D. Outcomes
E. Behaviour
(a) A, C, E, B, D
(b) A, C, B, E, D
(c) A, B, C, D, E
(d) A, D, E, C, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is the sequence "A, C, B, E, D" in the conflict process.
Conflict Process:
- The conflict process outlines the stages through which conflicts develop from their inception to their resolution.
- Understanding these stages helps in effectively managing and resolving conflicts.
Stages of Conflict Process:
Potential Opposition or Incompatibility (A):
- This initial stage involves the presence of conditions that create opportunities for conflict to arise, such as communication issues, structural disagreements, or personal variables.
Cognition and Personalisation (C):
- In this stage, the parties involved become aware of the conflict and begin to perceive it. Personalisation occurs when the conflict is felt and becomes emotionally charged.
Intentions (B):
- Here, the parties involved decide how to act in response to the conflict, determining their intentions and strategies, which may include competing, collaborating, compromising, avoiding, or accommodating.
Behaviour (E):
- This stage involves the actions taken by the parties in conflict, including verbal arguments, physical actions, or other behaviors that express their intentions.
Outcomes (D):
- The final stage involves the results of the conflict, which can be functional (positive outcomes like improved relationships and solutions) or dysfunctional (negative outcomes like further disputes and breakdowns in communication).
Q52: Which of the following are merits of Internal Rate of Return Method of Capital Budgeting?
A. Consider all cash flows
B. Satisfies the value additivity principle
C. Generally consistent with wealth maximization principle
D. It considers the time value of money
E. It never fails to indicate correct choice between mutually exclusive projects.
(a) A, B and E Only
(b) A, C and E Only
(c) B, C and D Only
(d) A, C, and D only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C, and D only'
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Method of Capital Budgeting:
- The IRR method is a popular capital budgeting technique that calculates the rate of return at which the net present value (NPV) of cash flows is zero.
- It is used to evaluate the profitability of potential investments or projects.
Consider all cash flows:
- The IRR method takes into account all cash inflows and outflows over the life of the project, ensuring a comprehensive analysis.
Generally consistent with wealth maximization principle:
- Projects with a higher IRR than the cost of capital are typically considered to add value to the firm, aligning with the principle of wealth maximization.
It considers the time value of money:
- The IRR method discounts future cash flows to their present value, recognizing the time value of money, which is essential for accurate investment appraisal.
Other Related Points
Satisfies the value additivity principle:
- The value additivity principle states that the value of a combination of projects should equal the sum of their individual values. The IRR method does not always satisfy this principle, which is why it is not included in the correct answer.
It never fails to indicate the correct choice between mutually exclusive projects:
- This statement is incorrect because the IRR method can sometimes give misleading results when comparing mutually exclusive projects, especially if they have different scales of investment or timing of cash flows.
Q53: Which one of the following is true about service marketing?
(a) Services can be seen, tasted, felt, heard or smelled before purchase
(b) Services can be separated from the service providers
(c) Quality of services depends on who provides them and when, where and how
(d) Services can be stored for later sale or use
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Quality of services depends on who provides them and when, where and how'
Service marketing:
- Service marketing refers to the promotion and selling of intangible services as opposed to tangible products. Services are activities or benefits that one party can offer to another that are essentially intangible and do not result in the ownership of anything.
- The quality of services is highly variable and can depend on who provides them and when, where, and how they are provided. This variability is due to the human element involved in service delivery, making standardization challenging.
Q54: Match the List-I with List-II
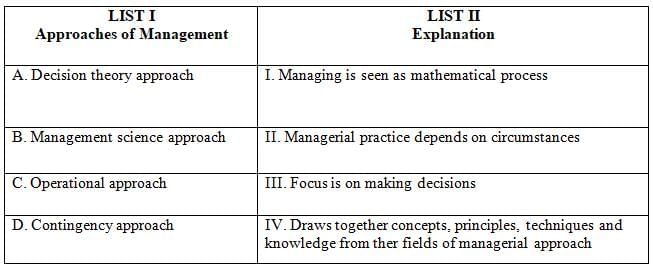
(a) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is the matching of List-I with List-II, specifically A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Decision theory approach:
- Focuses on making decisions.
- It involves the process of identifying and choosing alternatives based on values and preferences.
Management science approach:
- Managing is seen as a mathematical process.
- It uses mathematical models and statistical methods to aid in decision-making and problem-solving.
Operational approach:
- Draws together concepts, principles, techniques, and knowledge from various fields of managerial approach.
- It integrates different management principles and practices for effective management.
Contingency approach:
- Managerial practice depends on circumstances.
- It emphasizes that there is no one best way to manage; instead, the optimal course of action is contingent upon internal and external factors.
Q55: The procedure for determining the duties and skill requirements of a job and the kind of person who should be hired for it is :
(a) Job description
(b) Job analysis
(c) Job specification
(d) Job evaluation
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Job analysis'.
Job analysis:
- Job analysis is the process of determining the duties and skill requirements of a job and the type of person who should be hired for it.
- It involves collecting and analyzing information about the content and human requirements of jobs, as well as the context in which jobs are performed.
- Through job analysis, organizations gather detailed information about job responsibilities, necessary skills, outcomes, and work environment, which helps in creating job descriptions and job specifications.
Other Related Points
Job description:
- A job description provides a summary of the duties, responsibilities, and working conditions of a specific job.
- It focuses on what the job entails rather than the qualifications needed to perform it.
Job specification:
- A job specification outlines the qualifications, skills, and abilities required for a person to perform a specific job.
- It complements the job description by detailing the attributes a candidate must possess to be successful in the role.
Job evaluation:
- Job evaluation is a systematic process of determining the relative worth of jobs within an organization.
- It aims to establish a fair and equitable pay structure by assessing the value of each job in relation to others.
Q56: A sum total of ways in which an individual reacts and interacts with others is called:
(a) Perception
(b) Attitude
(c) Personality
(d) Values
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Personality'
Personality:
- Personality refers to the sum total of ways in which an individual reacts to and interacts with others.
- It encompasses a wide range of human behaviors and traits, including thoughts, emotions, attitudes, and actions.
- Personality is shaped by both genetic factors and environmental influences, such as experiences and social interactions.
- Understanding personality can help in predicting and explaining behaviors in various contexts, including the workplace, social settings, and personal relationships.
Other Related Points
Perception:
- Perception is the process by which individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions in order to give meaning to their environment.
- It is subjective and can be influenced by various factors such as past experiences, expectations, and cultural background.
- While perception affects how individuals see the world, it is not the same as personality, which is a broader concept encompassing overall behaviors and interactions.
Attitude:
- Attitude refers to a person's feelings, beliefs, and predispositions to behave in a particular way toward a specific object, person, or situation.
- Attitudes are more specific than personality traits and are often formed through experiences and social influences.
- While attitudes can influence behavior, they are just one component of a person's overall personality.
Values:
- Values are the core beliefs or standards that guide an individual's behavior and decision-making.
- They are deeply ingrained and can influence a person's actions and judgments over a long period of time.
- Values are an important aspect of personality but do not encompass the entire concept, which also includes traits, behaviors, and interactions.
Q57: Which of the following is true about the term "KAIZEN"?
(a) KAIZEN is dramatic, a real attention getter. It is like magma that appears in abrupt eruptions from time to time
(b) KAIZEN involves all the activities directed towards maintaining current technological, managerial and operating standards and improving current standards
(c) KAIZEN is subtle and its results are seldom immediately visible. It is an ongoing process and involves entire organisation
(d) KAIZEN is seen as major changes in the wake of technological break throughs or the introduction of latest management concepts or production techniques
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'KAIZEN is subtle and its results are seldom immediately visible. It is an ongoing process and involves entire organisation'
KAIZEN:
- KAIZEN is a Japanese term meaning "continuous improvement".
- It is a philosophy that focuses on continuous, incremental improvements in processes, products, or services.
- The approach involves everyone in the organization, from top management to workers on the shop floor.
- KAIZEN emphasizes small, ongoing positive changes that can lead to significant improvements over time.
- The changes are typically subtle, and their impact accumulates gradually, making them less dramatic or immediately noticeable.
Q58: In which of the following cases there will be Flow of Funds?
A. Purchase of Building for cash
B. Cash collection from debtors
C. Cash payment to creditors
D. Issue of share for cash
E. Payment of creditors by issue of shares
(a) A, B and C Only
(b) B and C Only
(c) A, C and D Only
(d) A, D and E Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, D and E Only'
Flow of Funds:
- Flow of funds refers to the movement of financial resources from one part of the economy to another. It typically involves transactions that result in changes in the financial position of entities involved.
Explanation of the correct answer:
- Purchase of Building for cash (A): This transaction involves using cash to acquire a building, resulting in a change in the financial position as cash is exchanged for a real asset.
- Issue of share for cash (D): When shares are issued for cash, it brings funds into the company, altering its financial position by increasing its cash reserves and equity.
- Payment of creditors by issue of shares (E): This transaction changes the financial structure by converting liabilities (creditors) into equity (shares), affecting the company's financial position.
Q59: Arrange the following procedures of testing hypotheses in proper sequence.
A. Making decisions
B. Setting a test criterion
C. Set up hypothesis
D. Set up suitable significance level
E. Doing computations
(a) C, D, B, E, A
(b) B, C , D, A, E
(c) C, D, A, B, E
(d) D, C , B, E, A
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, D, B, E, A'
Overview of Hypothesis Testing:
- Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that helps researchers make decisions using data.
- The process involves setting up a hypothesis, determining a significance level, setting a test criterion, performing computations, and making decisions based on the results.
Proper Sequence of Hypothesis Testing Procedures:
- Set up hypothesis: This is the initial step where you state the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Set up suitable significance level: This involves choosing a significance level (alpha), which is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true.
- Setting a test criterion: This involves determining the critical value or decision rule that defines the boundary for rejecting the null hypothesis.
- Doing computations: This involves calculating the test statistic from the sample data.
- Making decisions: The final step where you compare the test statistic to the critical value and decide whether to reject the null hypothesis.
Q60: Match the List-I with List-II
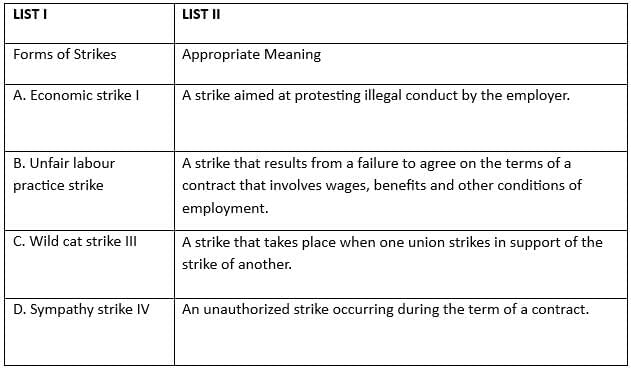
(a) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(c) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(d) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III'
Forms of Strikes and their Appropriate Meanings:
Economic Strike (A-II):
- An economic strike is one that results from a failure to agree on the terms of a contract that involves wages, benefits, and other conditions of employment.
Unfair Labour Practice Strike (B-I):
- This type of strike is aimed at protesting illegal conduct by the employer, such as violations of labor laws or unfair labor practices.
Wild Cat Strike (C-IV):
- A wild cat strike is an unauthorized strike that occurs during the term of a contract, without the approval of the union leadership.
Sympathy Strike (D-III):
- A sympathy strike takes place when one union strikes in support of the strike of another union, often to show solidarity.
Other Related Points
Understanding Types of Strikes:
- Strikes are a powerful tool used by labor unions and workers to negotiate better terms and conditions of employment, protest unfair practices, or show solidarity with other workers.
- Each type of strike has specific characteristics and legal implications, making it important to understand their definitions and appropriate contexts.
Q61: Match the List-I with List-II
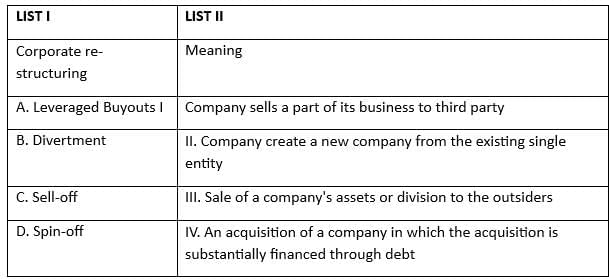
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(c) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II'
Corporate restructuring:
- Corporate restructuring refers to significant changes in a company's structure or operations aimed at improving efficiency, profitability, or adapting to market conditions.
- It includes various strategies such as mergers, acquisitions, divestments, and spin-offs.
Matching List-I with List-II:
A. Leveraged Buyouts (IV):
- Leveraged Buyouts involve the acquisition of a company, primarily financed through debt. The assets of the acquired company often serve as collateral for the loans.
B. Divestment (III):
- Divestment refers to the sale of a company's assets, divisions, or subsidiaries to outside parties. It is often done to focus on core operations or raise capital.
C. Sell-off (I):
- Sell-off occurs when a company sells a part of its business to a third party, usually to streamline operations or raise funds.
D. Spin-off (II):
- Spin-off is the process where a company creates a new, independent company by separating part of its business. The new entity operates independently but may retain a relationship with the parent company.
Q62: Robert L Katz identified three kinds of skills for administrators. Which among the following skills was NOT identified by Katz?
(a) Technical skill
(b) Human skill
(c) Design skill
(d) Conceptual skill
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Design skill'
Overview of Robert L. Katz's skills for administrators:
- Robert L. Katz, in his Harvard Business Review article in 1955, identified three core skills that managers need to be effective.
- These skills are crucial for different levels of management, and their importance varies depending on the managerial level.
Technical skill:
- Technical skill refers to the ability to perform specific tasks related to a particular field of work, such as engineering, accounting, or manufacturing.
- This skill is especially important for lower-level managers who directly oversee the day-to-day operations and technical work of their teams.
Human skill:
- Human skill involves the ability to work effectively with people and build cooperative team environments.
- It is crucial at all levels of management, as it facilitates communication, motivation, and leadership.
Conceptual skill:
- Conceptual skill refers to the ability to understand complex situations and develop creative solutions.
- This skill is particularly important for top-level managers who need to set the organization’s vision and strategy.
Other Related Points
Design skill:
- Design skill was not identified by Robert L. Katz as one of the core skills for administrators.
- While design thinking and innovation are valuable in modern management, they were not part of Katz’s original framework.
Q63: Arrange the following stages/elements of technology management in proper sequence starting from first to last;-
A. Technology Adaptation
B. Technology Abandonment
C. Technology Advancement
D. Technology Acquisition
E. Technology Awareness
(a) A, C, D, B, E
(b) B, C , D, A, E
(c) E, D, A, C, B
(d) D, C, A, B, E
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'E, D, A, C, B'
Technology Management:
- Technology management involves the planning, development, and implementation of technological capabilities to shape and accomplish the strategic and operational objectives of an organization.
- It encompasses various stages, from the initial awareness of technology to its eventual abandonment or replacement.
Stages of Technology Management:
- Technology Awareness: The first stage involves recognizing and understanding emerging technologies and their potential impact on the organization.
- Technology Acquisition: This stage involves obtaining the necessary technology through purchasing, licensing, or developing in-house.
- Technology Adaptation: After acquiring the technology, the organization customizes and integrates it into their operations to meet specific needs.
- Technology Advancement: This stage focuses on improving and upgrading the technology to enhance its performance and keep it up-to-date.
- Technology Abandonment: The final stage involves phasing out obsolete or less effective technology to make way for newer solutions.
Other Related Points
Importance of Sequence:
- Following the correct sequence ensures that organizations effectively manage the lifecycle of technology, from understanding and acquiring it to adapting, advancing, and eventually replacing it.
- This systematic approach helps in maximizing the technology’s benefits while minimizing risks and costs associated with its implementation and maintenance.
Q64: A company paid a dividend of ₹ 3.70 in the previous year. The dividends in the future are expected to grow perpetually at a rate of 8 per cent. What is the share price today if the market captalises dividend at 12 per cent?
(a) ₹. 40
(b) ₹. 33
(c) ₹. 100
(d) ₹. 200
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is the share price today is ₹ 100.
Understanding Share Price Calculation:
- The share price of a company can be calculated using the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), particularly the Gordon Growth Model for perpetually growing dividends.
- This model is given by the formula:
Price = Dividend per share / (Discount rate - Dividend growth rate)
Application of the Formula:
Given Data:
- Previous year's dividend (D₀) = ₹ 3.70
- Expected perpetual growth rate (g) = 8% or 0.08
- Market capitalization rate (r) = 12% or 0.12
- Next year's expected dividend (D₁) = D₀ * (1 + g) = ₹ 3.70 * 1.08 = ₹ 3.996
Using the Gordon Growth Model:
- Price = D₁ / (r - g) = ₹ 3.996 / (0.12 - 0.08) = ₹ 3.996 / 0.04 = ₹ 99.90 ≈ ₹ 100
Q65: Arrange the following Historical Events in operations management in the order of sequence starting from oldest to newest.
A. Quality Revolution
B. Scientific Management
C. Industrial Revolution
D. Operations Research
E. Human Relations
(a) C, B, E, D, A
(b) B, C, D, E, A
(c) A, B, D, C, E
(d) E, C, B, A, D
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is option 1: to arrange the historical events in operations management in the order of sequence starting from oldest to newest:
Industrial Revolution:
- The Industrial Revolution began in the late 18th century and marked the transition from agrarian economies to industrialized ones.
- It introduced mechanization and mass production, which significantly increased productivity and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Scientific Management:
- Developed by Frederick Taylor in the early 20th century, scientific management focused on improving labor productivity through systematic analysis and optimization of work processes.
- This approach emphasized standardization, time and motion studies, and the division of labor.
Human Relations:
- The Human Relations movement emerged in the 1930s, emphasizing the importance of social factors and employee well-being in the workplace.
- It highlighted the role of management in fostering positive relationships, employee motivation, and job satisfaction.
Operations Research:
- Operations Research developed during World War II, focusing on the application of mathematical models and analytical methods to decision-making and problem-solving in complex operations.
- It aimed to optimize resource allocation, logistics, and overall operational efficiency.
Quality Revolution:
- The Quality Revolution began in the latter half of the 20th century, emphasizing the importance of quality management and continuous improvement in organizations.
- Key principles included Total Quality Management (TQM), Six Sigma, and the use of statistical process control to ensure product and service quality.
Q66: Which of the following terms are associated with the VRIO framework of Internal Analysis?
A. Valuable
B. Rare
C. Inimitable
D. Organised for usage
E. Innovative
(a) A and B Only
(b) A, B and C Only
(c) A, B and E Only
(d) A, B, C and D Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, C and D Only'.
VRIO Framework:
- The VRIO framework is a tool for internal analysis used to evaluate an organization's resources and capabilities to determine their potential for sustained competitive advantage.
- VRIO stands for Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, and Organized for usage.
Valuable:
- Resources and capabilities must be valuable to enable the organization to exploit opportunities or neutralize threats in its environment.
Rare:
- Resources and capabilities must be rare among the firm's current and potential competition to provide a competitive advantage.
Inimitable:
- Resources and capabilities must be difficult to imitate or substitute by competitors.
Organized for Usage:
- The firm must be organized to capture the value from the resources and capabilities.
Other Related Points
Innovative:
- While innovation can be a significant factor for competitive advantage, it is not specifically part of the VRIO framework.
- Innovation would fall under being valuable, rare, and possibly difficult to imitate, but it is not a standalone criterion in the VRIO analysis.
Other Incorrect Options:
- Options listing combinations of valuable, rare, and innovative miss key elements of the VRIO framework such as Inimitable and organized for usage.
- These incorrect combinations do not fully encompass the criteria necessary for determining sustained competitive advantage as per the VRIO framework.
Q67: Which of the following are operational methodology of Self Help Group?
A. Village meeting of women in villages by MFI
B. Group formation
C. Group Training for 5-7 days on procedures and business development skills
D. Group meeting once in a week for mobilizing saving, disbursing and repaying loans.
E. Lending money for long term loans
(a) A, B and C Only
(b) B, C and D Only
(c) A, B, C and D Only
(d) B, C, D and E Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, C and D Only'
Operational Methodology of Self Help Group (SHG):
- Self Help Groups are small voluntary associations of people, typically women, who come together for the purpose of solving their common problems through self-help and mutual help.
- They play a crucial role in improving the socio-economic status of their members by promoting savings, providing access to credit, and facilitating income-generating activities.
Key Points:
- A. Village meeting of women in villages by MFI: Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) often conduct village meetings to introduce the concept of SHGs to women and motivate them to form groups.
- B. Group formation: The next step involves forming groups of 10-20 women who share similar socio-economic backgrounds and mutual trust.
- C. Group Training for 5-7 days on procedures and business development skills: Training sessions are conducted to educate the group members about the functioning of SHGs, savings, credit management, and business development skills.
- D. Group meeting once in a week for mobilizing saving, disbursing and repaying loans: Regular weekly meetings are held to collect savings from members, disburse loans, and ensure timely repayment.
Other Related Points
Lending money for long term loans:
- This option is not typically a primary operational methodology for SHGs. SHGs usually focus on short-term loans to meet immediate financial needs and facilitate quick repayment cycles to ensure sustainability and manage risk effectively.
Q68: If profit before interest and tax is Rs.10000, provision for Tax=Rs.5000, No. of Equity Share = 3000 , Preference dividend =2000, Dividend per equity share =0.40, what is the value of payout ratio?
(a) 10%
(b) 20%
(c) 50%
(d) 40%
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is option 4.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
Given:
Profit before interest and tax (PBIT) = ₹10,000
Provision for Tax = ₹5,000
Preference Dividend = ₹2,000
No. of Equity Shares = 3,000
Dividend per equity share = ₹0.40
Step 1: Calculate Net Profit after Tax (NPAT)
PBIT – Tax = ₹10,000 – ₹5,000 = ₹5,000
Step 2: Subtract Preference Dividend
Earnings available to equity shareholders = ₹5,000 – ₹2,000 = ₹3,000
Step 3: Calculate Total Equity Dividend
Dividend per share × Number of shares = ₹0.40 × 3,000 = ₹1,200
Step 4: Calculate Payout Ratio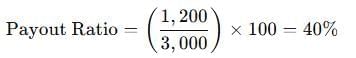
Q69: Under Brand Sponsorship, store brands are also known as which other names from the following?
A. National Brands
B. Generic Brands
C. Private Brands
D. Distributor Brands
E. Manufacturers Brands
(a) B, C and D Only
(b) A, B, and C Only
(c) C, D and E Only
(d) A, D and E Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is ‘B, C, and D Only’
Private Brands (Store Brands):
- Private brands, also known as store brands, are products that are manufactured and sold by a retailer under its own brand name.
- These brands are typically positioned as lower-cost alternatives to national brands and can only be found in the retailer's stores.
- Examples include Walmart's Great Value or Target's Up & Up.
Generic Brands:
- Generic brands are products that are not branded and are often sold at lower prices than branded products.
- These products usually have simple packaging and are intended to be low-cost alternatives to both national and private brands.
Distributor Brands:
- Distributor brands are another term for private or store brands, where the distributor, often a retailer, markets the product under its own label.
- These brands are managed and sold by the retailer, even if the actual manufacturing is outsourced.
Other Related Points
National Brands:
- National brands are products that are marketed under a manufacturer's own brand name and are widely distributed across various retail outlets.
- Examples include brands like Coca-Cola, Nike, and Apple.
Manufacturers Brands:
- Manufacturers brands, also known as national brands, are products created and marketed by the manufacturer who owns the brand.
- These brands are typically available in multiple retail locations and have widespread recognition.
Q70: What is the value of cost of capital after tax in a perpetual bond sold at par, coupon rate of interest being 7 per cent. Assuming that firm pay tax at a 50 per cent rate?
(a) 7%
(b) 35%
(c) 5%
(d) 3.50%
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is '0.035'
Cost of capital after tax in a perpetual bond:
- The cost of capital is the return rate that a company must earn on its investment to maintain its market value and attract funds.
- For perpetual bonds sold at par, the cost of capital is essentially the coupon rate adjusted for taxes.
- The formula to calculate the cost of capital after tax is: Cost of Capital = Coupon Rate × (1 - Tax Rate).
Calculation for the given data:
- Given the coupon rate of interest is 7% (0.07).
- The tax rate is 50% (0.50).
- Using the formula: Cost of Capital = 0.07 × (1 - 0.50) = 0.07 × 0.50 = 0.035.
Q71: Which of the following are the modes of strategic decision making according to Mintzberg?
A. Entrepreneurial Mode
B. Adaptive Mode
C. Planning Mode
D. Logical Incrementalism Mode
(a) A and B Only
(b) C and D Only
(c) A, B and C Only
(d) A, B, C and D Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B and C Only'
Modes of strategic decision making according to Mintzberg:
- Entrepreneurial Mode: This mode is characterized by the active search for new opportunities and a focus on growth and innovation. Decisions are made by a single individual or a small group, often the founder or top executives, based on intuition and vision for the future.
- Adaptive Mode: Also known as the incremental mode, this approach involves responding to changes in the environment in a piecemeal and reactive manner. Decision making is decentralized, and the organization adapts gradually to external pressures.
- Planning Mode: This mode involves a systematic analysis of the organization's environment and the formulation of comprehensive plans. It is characterized by the use of formal procedures, extensive data collection, and the involvement of multiple stakeholders in the decision-making process.
Other Related Points
Logical Incrementalisation Mode:
- This mode is not considered one of the primary modes of strategic decision making according to Mintzberg. It refers to an approach where decisions are made in small, logical steps rather than through comprehensive planning or radical changes.
- Although it shares some similarities with the adaptive mode, logical incrementalism is more about cautious and deliberate decision making, integrating feedback at each step to gradually shape the strategy.
Q72: Which of the following are the main objectives of establishment of International Monetary Fund (IMF)?
A. To provide long-term funds at concession rates to the poorest member countries.
B. To promote the development of Private enterprises in member countries.
C. To regulate the exchange rates and enforce the rules.
D. To promote exchange stability , maintaining orderly exchange arrangements and avoiding competitive exchange devaluation.
E. To assist in establishment of a multilateral system of payments in respect of current transaction between members.
(a) A, B and C Only
(b) B, C and D Only
(c) A, C and E Only
(d) C, D and E Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, D and E Only'
International Monetary Fund (IMF) Objectives:
- To regulate the exchange rates and enforce the rules: The IMF was established to oversee the international monetary system and ensure that exchange rates are stable and predictable.
- To promote exchange stability, maintaining orderly exchange arrangements, and avoiding competitive exchange devaluation: The IMF aims to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, and facilitate international trade, which helps in promoting high employment and sustainable economic growth.
- To assist in the establishment of a multilateral system of payments in respect of current transactions between members: The IMF supports member countries in establishing multilateral payment systems, ensuring smooth and stable currency transactions between nations.
Other Related Points
Other Options Explained:
- To provide long-term funds at concession rates to the poorest member countries: This is primarily the role of the International Development Association (IDA), not the IMF. The IMF typically provides short-term financial assistance to member countries facing balance of payments problems.
- To promote the development of Private enterprises in member countries: This is more aligned with the objectives of the International Finance Corporation (IFC), which is part of the World Bank Group, rather than the IMF.
Broader Context:
- The IMF was established in 1944 during the Bretton Woods Conference to provide a framework for international economic cooperation and to prevent the economic instability that had characterized the interwar period.
- It plays a crucial role in managing the international monetary system and providing financial support to countries in economic distress.
Q73: What is the primary objective of a feasibility study?
(a) To persuade investors to fund a project
(b) To assess the historical background of a business
(c) To uncover strength and weakness of a business idea
(d) To outline the technical development process
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'To uncover strength and weakness of a business idea'
To uncover strength and weakness of a business idea:
- The primary objective of a feasibility study is to evaluate the potential success of a business idea before significant resources are invested.
- This involves analyzing various aspects of the business idea including market demand, technical requirements, financial viability, and operational logistics.
- By identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the business idea, stakeholders can make informed decisions about whether to proceed, modify, or abandon the proposed project.
Other Related Points
To persuade investors to fund a project:
- While feasibility studies can be used to present a business case to potential investors, this is not their primary objective.
- The main goal is to determine the viability of the project itself, rather than focusing on securing funding.
To assess the historical background of a business:
- Assessing historical background may be part of a broader business analysis but is not the main focus of a feasibility study.
- Feasibility studies are forward-looking, aiming to predict future success rather than examining past performance.
To outline the technical development process:
- Outlining the technical development process can be one component of a feasibility study, especially in projects requiring significant technical resources.
- However, this is just one aspect and not the primary objective; the study is comprehensive, covering various factors like market, financial, operational, and legal aspects.
Q74: What is the belief among pluralists regarding conflict in organisation?
(a) Conflict is unnecessary and should be avoided at all cost
(b) Conflict is necessary and should be ignored
(c) Conflict is necessary but it can be managed and resolved
(d) Conflict should be eliminated through strict rules
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Conflict is necessary but it can be managed and resolved'
Belief among pluralists regarding conflict in organisations:
- Pluralists view conflict as an inherent and inevitable part of organisational life.
- According to pluralists, conflict arises due to the diverse interests, values, and perspectives of different groups within the organisation.
- They believe that rather than being something negative, conflict can be a source of growth and innovation if managed effectively.
- Pluralists advocate for mechanisms and processes that help manage and resolve conflicts constructively, such as dialogue, negotiation, and mediation.
Other Related Points
Conflict is unnecessary and should be avoided at all cost:
- This viewpoint is incorrect as it ignores the natural occurrence of conflict in organisations due to differing interests and goals.
- Avoiding conflict at all costs can lead to suppressed tensions, decreased innovation, and unresolved issues.
Conflict is necessary and should be ignored:
- Ignoring conflict is not a viable solution as it can escalate and lead to more significant issues within the organisation.
- Effective conflict management is crucial for maintaining a healthy organisational environment.
Conflict should be eliminated through strict rules:
- While rules and policies can provide a framework for managing conflict, they cannot eliminate it entirely.
- Strict rules may also stifle open communication and creativity, which are essential for organisational growth.
Q75: Arrange the major steps of Luthans O.B. Mod approach to behavioral performance management from earlier to later
A. Measure
B. Identity
C. Intervene
D. Analyse
E. Evaluate
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) B, C, D, E, A
(c) A, C, B, E, D
(d) B, A, D, C, E
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is option 4: to arrange the major steps of Luthans O.B. Mod approach to behavioral performance management from earlier to later.
Luthans O.B. Mod Approach:
- Luthans Organizational Behavior Modification (O.B. Mod) is a systematic application of reinforcement theory to influence employee behaviors in organizational settings.
- The approach involves a series of steps designed to change and manage behavior effectively through reinforcement and feedback.
Steps in the Correct Order:
- Identify: The first step involves identifying the critical behaviors that need to be changed or improved within the organization.
- Measure: In the second step, the frequency of these behaviors is measured to establish a baseline for comparison after the intervention.
- Analyze: The third step involves analyzing the antecedents and consequences of the behaviors to understand what triggers and reinforces them.
- Intervene: In the fourth step, interventions are implemented to modify the antecedents and consequences, aiming to encourage desired behaviors and discourage undesired ones.
- Evaluate: The final step involves evaluating the effectiveness of the intervention by comparing post-intervention behavior with the baseline measurement.
Q76: Which type of Intrapreneur is known for generating innovative ideas and seeking ways to improve process?
(a) Employee Intrapreneur
(b) Doers Intrapreneur
(c) Creator Intrapreneur
(d) Implementers Intrapreneur
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Creator Intrapreneur'
Creator Intrapreneur:
- A Creator Intrapreneur is characterized by their ability to generate innovative ideas and seek ways to improve processes within an organization.
- They focus on creativity and innovation, often thinking outside the box to come up with novel solutions to existing problems.
- These intrapreneurs play a crucial role in driving change and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the company.
Other Related Points
Employee Intrapreneur:
- While Employee Intrapreneurs are proactive and take initiative within their roles, they are not specifically focused on generating innovative ideas or improving processes. Their role is more about executing their responsibilities effectively.
Doers Intrapreneur:
- Doers Intrapreneurs are action-oriented and excel at implementing plans and strategies. They are critical for executing ideas but are not necessarily the source of innovative thinking.
Implementers Intrapreneur:
- Implementers Intrapreneurs focus on executing and bringing ideas to life. They are essential for the practical application of innovations but are not primarily responsible for generating the ideas themselves.
Q77: Match the List-I with List-II

(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(d) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV'
VRIO Framework:
- Developed by J.B. Barney.
- VRIO stands for Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization.
- This framework helps firms evaluate their resources and capabilities to achieve sustained competitive advantage.
Value Chain Analysis:
- Developed by M.E. Porter.
- It involves analyzing a company’s activities to identify primary and support activities that add value to the final product.
- The goal is to enhance efficiency and competitive advantage by optimizing these activities.
Product Market Matrix:
- Developed by H.I. Ansoff.
- Also known as Ansoff Matrix, it is used to identify and analyze growth strategies in terms of markets and products.
- It includes four strategies: Market Penetration, Market Development, Product Development, and Diversification.
PEST Analysis:
- Developed by Johnson and Scholes.
- PEST stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological analysis.
- This framework is used to assess the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization.
Q78: "Consumer buying behaviour in situations characterised by high consumer involvement in a purchase and significant prescribed differences among brands" is termed as:
(a) Complex buying behaviour
(b) Dissonance-reducing buying behaviour
(c) Habitual buying behaviour
(d) Variety-seeking buying behaviour
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'Complex buying behaviour'
Complex buying behaviour:
- This type of consumer behaviour occurs in situations where consumers are highly involved in the purchase decision and perceive significant differences among brands.
- Typically seen with high-value or infrequent purchases such as cars, houses, or expensive electronics.
- Consumers spend considerable time researching and evaluating before making a decision.
- Marketing strategies for products in this category often involve providing detailed information and emphasizing unique features to differentiate from competitors.
Other Related Points
Dissonance-reducing buying behaviour:
- Occurs when consumers are highly involved in a purchase but perceive little difference among brands.
- Common in situations where the purchase is expensive or infrequent, but the consumer does not see major differences among the options.
- Consumers may experience post-purchase dissonance (buyer's remorse) and seek reassurance after making a purchase.
Habitual buying behaviour:
- Involves low consumer involvement and little perceived differences among brands.
- Typical for routine purchases such as groceries or household items.
- Consumers do not spend much time in decision-making and tend to buy the same brand out of habit.
Variety-seeking buying behaviour:
- Occurs when consumers have low involvement but perceive significant differences among brands.
- Common in product categories where consumers frequently switch brands for the sake of variety, such as snacks or beverages.
- Brand switching is often driven by curiosity or the desire to try something new rather than dissatisfaction with the previous choice.
Q79: If Rf=10%,Rm=18% and Bi=1.35, What is the expected rate of return for security?
(a) 28.80%
(b) 18.80%
(c) 8.80%
(d) 20.80%
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer 20.80% is the expected rate of return for security
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM):
- The CAPM is a model used to determine the expected return on an asset based on its risk relative to the market.
- The formula for CAPM is: Expected Return = Risk-Free Rate + Beta * (Market Return - Risk-Free Rate).
- In this scenario, the given data includes: Risk-Free Rate (Rf) = 10%, Market Return (Rm) = 18%, and Beta (Bi) = 1.35.
- Using the CAPM formula: Expected Return = 10% + 1.35 * (18% - 10%) = 10% + 1.35 * 8% = 10% + 10.8% = 20.8%.
- Therefore, the expected rate of return for the security is 20.8%.
Q80: Which one of the following is true about the role of sales force/personal selling?
(a) Personal selling consists largely of non personal communication with large group of customers
(b) Personal selling is interpersonal arm of promotion mix
(c) Personal selling is less effective than advertising in more complex selling situations
(d) Personal selling sales force is not allowed to adjust marketing offer and presentation to fit each customer's special needs
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Personal selling is interpersonal arm of promotion mix'
Personal selling:
- Personal selling is a direct form of communication where a sales representative interacts one-on-one with potential customers.
- It is considered an interpersonal component of the promotion mix, meaning it involves face-to-face interaction.
- This interaction allows salespeople to tailor their messages and sales presentations to the specific needs and preferences of individual customers.
Other Related Points
Non personal communication:
- This refers to advertising, public relations, and other forms of mass communication that do not involve direct interaction with customers.
- Personal selling contrasts with this by involving direct, personal interaction.
Effectiveness in complex selling situations:
- In complex selling situations, personal selling is often more effective than advertising because it allows for detailed, customized communication.
- Sales representatives can address specific concerns and provide in-depth product information that advertising may not be able to convey.
Adjusting marketing offers:
- Personal selling allows sales representatives to adjust their marketing offers and presentations to fit each customer's unique needs and preferences.
- This flexibility is a key advantage of personal selling over other forms of promotion.
Q81: Organizational culture refers to qualities of the workplace itself that influence its employees, whereas Organizational behavior refers to the resulting behavior of the people within it. Organizational culture includes factors such as core values, the company's mission statement and expectations of the employees. It defines the identity and how it wants to be perceived.
For the instance, if a company has a mission statement focused on providing the highest quality of customer service, then the core values may be centered around communication, professionalism and customer satisfaction. This will shape the employees expectations, such as expecting them to be willing and courteous to go the extra mile to serve the customer.
Organizational behavior is the resulting behavior of the people within the organization based on the culture they're immersed in. if the company culture is one that promotes customer service, then the employees are likely to display behavior such as friendliness and helpfulness when dealing with customers.
The opposite may be true if the company's culture revolves around a competitive environment and employees are expected to go above and beyond to be the most successful. In this case, employees may display behavior such as aggressiveness and competitiveness in order to achieve the highest results.
Organizational culture works as the foundation for the employee's behavioral exhibit, and the two are closely intertwined. If a company wishes to create a positive working environment, it is essential to establish an organizational culture that promotes a healthy behavioral environment among its employees.
Which statement best describes the relationship between organisational culture and organisational behavior?
(a) Organisational culture influences the resulting behavior of employees
(b) Organisational culture is the result of organisational behavior
(c) Organisational behavior is solely determined by external factors
(d) Organisational behavior is independent of organisational culture
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 1) Organisational culture influences the resulting behavior of employees.
- Organisational culture provides the foundation for how employees behave in the workplace.
- The mission statement and core values of the organisation directly shape employee behavior.
- A customer-focused organisational culture leads to behaviors such as friendliness and helpfulness.
- A competitive organisational culture may lead to aggressive and competitive behaviors among employees.
- Organisational culture sets the expectations and influences behavior patterns, creating a cohesive work environment.
Other Related Points
Organisational Culture:
- Defines the identity of the organisation through core values, mission statements, and expectations.
- Serves as a guide for the behavioral patterns employees are expected to exhibit.
Organisational Behavior:
- The resulting actions and attitudes of employees within the organisation.
- Heavily influenced by the culture employees are immersed in.
- Works as the reflection of the organisational culture in the workforce.
Q82: Organizational culture refers to qualities of the workplace itself that influence its employees, whereas Organizational behavior refers to the resulting behavior of the people within it. Organizational culture includes factors such as core values, the company's mission statement and expectations of the employees. It defines the identity and how it wants to be perceived.
For the instance, if a company has a mission statement focused on providing the highest quality of customer service, then the core values may be centered around communication, professionalism and customer satisfaction. This will shape the employees expectations, such as expecting them to be willing and courteous to go the extra mile to serve the customer.
Organizational behavior is the resulting behavior of the people within the organization based on the culture they're immersed in. if the company culture is one that promotes customer service, then the employees are likely to display behavior such as friendliness and helpfulness when dealing with customers.
The opposite may be true if the company's culture revolves around a competitive environment and employees are expected to go above and beyond to be the most successful. In this case, employees may display behavior such as aggressiveness and competitiveness in order to achieve the highest results.
Organizational culture works as the foundation for the employee's behavioral exhibit, and the two are closely intertwined. If a company wishes to create a positive working environment, it is essential to establish an organizational culture that promotes a healthy behavioral environment among its employees.
What role does organisational behavior play in the workplace?
(a) It defines organisational goals
(b) It represents resultant employee actions
(c) It determines managerial decisions
(d) It outlines employee training programmes
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is It represents resultant employee actions.
- Organizational behavior refers to the resulting actions and behaviors of employees based on the company’s culture and environment.
- It reflects how individuals and teams act in response to organizational values, goals, and practices.
- For example, a culture of customer service will lead to behaviors like helpfulness and friendliness.
- Organizational behavior helps managers understand, predict, and influence employee performance.
- It plays a critical role in shaping workplace productivity, morale, and overall success.
Other Related Points
Organizational Culture:
- It represents core values, mission statements, and workplace identity.
- It creates expectations for employees' attitudes and performance.
Resultant Behavior:
- Employee behavior aligns with the organization's culture.
- For example, customer-focused culture leads to courteous and helpful employee actions.
Organizational Goals:
- Defined separately but influenced by employee behavior.
- Behaviors contribute to achieving the company’s overall objectives.
Q83: Organizational culture refers to qualities of the workplace itself that influence its employees, whereas Organizational behavior refers to the resulting behavior of the people within it. Organizational culture includes factors such as core values, the company's mission statement and expectations of the employees. It defines the identity and how it wants to be perceived.
For the instance, if a company has a mission statement focused on providing the highest quality of customer service, then the core values may be centered around communication, professionalism and customer satisfaction. This will shape the employees expectations, such as expecting them to be willing and courteous to go the extra mile to serve the customer.
Organizational behavior is the resulting behavior of the people within the organization based on the culture they're immersed in. if the company culture is one that promotes customer service, then the employees are likely to display behavior such as friendliness and helpfulness when dealing with customers.
The opposite may be true if the company's culture revolves around a competitive environment and employees are expected to go above and beyond to be the most successful. In this case, employees may display behavior such as aggressiveness and competitiveness in order to achieve the highest results.
Organizational culture works as the foundation for the employee's behavioral exhibit, and the two are closely intertwined. If a company wishes to create a positive working environment, it is essential to establish an organizational culture that promotes a healthy behavioral environment among its employees.
In a company with a culture focused on customer service, employees are expected to demonstrate behaviors such as:
(a) Competitiveness and aggression
(b) Friendliness and helpfulness
(c) Independence and autonomy
(d) Innovation and Creativity
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Friendliness and helpfulness.
- In a customer service-focused culture, employees are encouraged to be courteous, friendly, and helpful.
- The organizational culture promotes behaviors that prioritize customer satisfaction and positive interactions.
- Employees are expected to “go the extra mile” to ensure customers' needs are met.
- Such behaviors align with values like professionalism, communication, and empathy.
- It leads to improved customer loyalty, trust, and overall business success.
Other Related Points
Customer Service Culture:
- Focuses on delivering exceptional service to customers.
- Values like empathy, professionalism, and courtesy are promoted.
Behavioral Outcomes:
- Employees display friendliness, patience, and helpfulness.
- Behavior reflects organizational culture and core values.
Contrasting Behaviors:
- Competitiveness and aggression align with competitive organizational cultures.
- Innovation and creativity align with R&D or technology-focused environments.
- Independence and autonomy fit decentralized or entrepreneurial settings.
Q84: Organizational culture refers to qualities of the workplace itself that influence its employees, whereas Organizational behavior refers to the resulting behavior of the people within it. Organizational culture includes factors such as core values, the company's mission statement and expectations of the employees. It defines the identity and how it wants to be perceived.
For the instance, if a company has a mission statement focused on providing the highest quality of customer service, then the core values may be centered around communication, professionalism and customer satisfaction. This will shape the employees expectations, such as expecting them to be willing and courteous to go the extra mile to serve the customer.
Organizational behavior is the resulting behavior of the people within the organization based on the culture they're immersed in. if the company culture is one that promotes customer service, then the employees are likely to display behavior such as friendliness and helpfulness when dealing with customers.
The opposite may be true if the company's culture revolves around a competitive environment and employees are expected to go above and beyond to be the most successful. In this case, employees may display behavior such as aggressiveness and competitiveness in order to achieve the highest results.
Organizational culture works as the foundation for the employee's behavioral exhibit, and the two are closely intertwined. If a company wishes to create a positive working environment, it is essential to establish an organizational culture that promotes a healthy behavioral environment among its employees.
Which of the following is NOT a factor included in organisational culture?
(a) Core values
(b) Company’s mission
(c) Employee's salary
(d) Expectations of employees
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Employee's salary.
- Organizational culture encompasses factors like core values, mission, and employee expectations.
- Core values refer to the guiding principles that define the company's identity and behavior.
- The company’s mission defines its purpose and goals, providing direction for employees.
- Employee expectations are shaped by the company culture, such as behavior and performance standards.
- Salary is a part of employee compensation and not a component of organizational culture.
Other Related Points
Components of Organizational Culture:
- Core Values: Fundamental principles guiding employee behavior.
- Mission Statement: Company’s vision and purpose.
- Expectations: Standards of behavior and performance expected from employees.
Employee Salary:
- Part of employee compensation and benefits.
- While important, it does not define the workplace culture.
Relationship Between Culture and Behavior:
- Culture influences employees' attitudes and behaviors at work.
- A strong organizational culture fosters productivity and job satisfaction.
Q85: Organizational culture refers to qualities of the workplace itself that influence its employees, whereas Organizational behavior refers to the resulting behavior of the people within it. Organizational culture includes factors such as core values, the company's mission statement and expectations of the employees. It defines the identity and how it wants to be perceived.
For the instance, if a company has a mission statement focused on providing the highest quality of customer service, then the core values may be centered around communication, professionalism and customer satisfaction. This will shape the employees expectations, such as expecting them to be willing and courteous to go the extra mile to serve the customer.
Organizational behavior is the resulting behavior of the people within the organization based on the culture they're immersed in. if the company culture is one that promotes customer service, then the employees are likely to display behavior such as friendliness and helpfulness when dealing with customers.
The opposite may be true if the company's culture revolves around a competitive environment and employees are expected to go above and beyond to be the most successful. In this case, employees may display behavior such as aggressiveness and competitiveness in order to achieve the highest results.
Organizational culture works as the foundation for the employee's behavioral exhibit, and the two are closely intertwined. If a company wishes to create a positive working environment, it is essential to establish an organizational culture that promotes a healthy behavioral environment among its employees.
What might employees in a competitive organisational culture display?
(a) Cooperation and teamwork
(b) Friendliness and helpfulness
(c) Indifference and passiveness
(d) Aggressiveness and Competitiveness
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Aggressiveness and Competitiveness.
- Competitive organizational culture focuses on achieving high performance and results.
- Employees are expected to outperform their peers, leading to behaviors such as competitiveness and aggressiveness.
- Team success is often measured by individual achievements, fostering a results-oriented work environment.
- Such a culture can drive productivity but may also increase stress levels among employees.
- Aggressiveness may manifest in striving to outperform colleagues or securing recognition and rewards.
Other Related Points
Characteristics of Competitive Organizational Culture:
- Performance-Oriented: Focus on individual and team achievements.
- High Pressure: Employees are often under pressure to meet goals and targets.
- Rewards-Based: Recognition and rewards are based on competitive results.
Impact on Behavior:
- Encourages aggressiveness to outperform colleagues.
- Drives competitiveness for achieving higher recognition.
- Can sometimes limit cooperation and teamwork among employees.
Comparison with Collaborative Cultures:
- Collaborative cultures focus on cooperation and teamwork.
- Employees in collaborative environments exhibit friendliness and helpfulness.
Q86: AI's impact on the workforce is multifaceted. It involves the automation of repetitive and routine tasks, changing skill requirements and job displacement. This can be beneficial for employees as it frees them up to focus on more complex and creative work, but it can also create concerns about job displacement and changes in the demand for certain types of jobs. However, AI is also creating new job opportunities, especially in data analytics machine learning and AI development.
Despite these potential benefits, there are also concerns about the drawbacks of implementing AI on a larger scale in the workforce. One potential concern is job displacement, which can lead to unemployment and the need for reskilling and upskilling. Another concern is the potential for bias and discrimination in algorithms, which can have negative consequences for marginalized individuals and communities.
Privacy and security are also major concerns regarding the impact of AI on the workforce. As AI becomes more advanced, it is important to ensure that personal data is protected, and AI system are secure against cyberattacks. Nonetheless, AI can also enhance efficiency and productivity, and its advancements may lead to new job opportunities for workers with the right skills and knowledge.
Which skill is likely to become increasingly important in light of AI's impact on the workforce?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) Creative thinking and problem-solving
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Creative thinking and problem-solving.
- AI automates repetitive and routine tasks, reducing the demand for manual labor and administrative work.
- With the increasing use of AI, human skills like creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving are becoming more valuable.
- Creative thinking enables employees to design solutions for complex problems that AI alone cannot solve.
- Problem-solving skills ensure humans remain adaptable and capable of addressing challenges posed by AI integration.
Other Related Points
Manual Labor and Routine Tasks
- AI can efficiently perform manual, repetitive, and administrative tasks, reducing reliance on human labor in these areas.
AI and Skill Shifts
- Automation increases demand for higher-order cognitive skills like critical thinking, innovation, and emotional intelligence.
AI-Enabled Workforce
- Workers need to focus on roles where human intervention adds value, such as strategic decision-making and problem-solving.
- Jobs in AI development, data analytics, and human-AI collaboration are becoming essential.
Q87: AI's impact on the workforce is multifaceted. It involves the automation of repetitive and routine tasks, changing skill requirements and job displacement. This can be beneficial for employees as it frees them up to focus on more complex and creative work, but it can also create concerns about job displacement and changes in the demand for certain types of jobs. However, AI is also creating new job opportunities, especially in data analytics machine learning and AI development.
Despite these potential benefits, there are also concerns about the drawbacks of implementing AI on a larger scale in the workforce. One potential concern is job displacement, which can lead to unemployment and the need for reskilling and upskilling. Another concern is the potential for bias and discrimination in algorithms, which can have negative consequences for marginalized individuals and communities.
Privacy and security are also major concerns regarding the impact of AI on the workforce. As AI becomes more advanced, it is important to ensure that personal data is protected, and AI system are secure against cyberattacks. Nonetheless, AI can also enhance efficiency and productivity, and its advancements may lead to new job opportunities for workers with the right skills and knowledge.
Which potential drawback of AI in the workforce is associated with algorithmic decisionmaking?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) Enhanced security measures
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Bias and Discrimination.
- Algorithmic decision-making in AI can unintentionally amplify biases present in the training data.
- Bias in AI systems can lead to unfair treatment and discrimination, particularly against marginalized individuals or communities.
- This drawback highlights a critical need for ethical AI development and regular audits of AI algorithms.
- Discrimination caused by AI algorithms can negatively affect hiring decisions, credit approvals, and other critical areas.
Other Related Points
Algorithmic Bias
- Bias occurs when AI algorithms make decisions based on historical or biased data, leading to discriminatory outcomes.
- Examples include biased hiring tools that favor certain demographics or facial recognition systems with lower accuracy for minority groups.
AI Ethics and Fairness
- Ensuring fairness in AI systems requires diverse datasets and regular testing to identify and eliminate bias.
- Organizations must implement guidelines to promote ethical AI development and decision-making.
Impact on Workforce
- Algorithmic bias can undermine trust in AI solutions, reducing their effectiveness in workforce management.
- Addressing these issues is crucial to ensure AI systems promote fairness, inclusivity, and transparency.
Q88: AI's impact on the workforce is multifaceted. It involves the automation of repetitive and routine tasks, changing skill requirements and job displacement. This can be beneficial for employees as it frees them up to focus on more complex and creative work, but it can also create concerns about job displacement and changes in the demand for certain types of jobs. However, AI is also creating new job opportunities, especially in data analytics machine learning and AI development.
Despite these potential benefits, there are also concerns about the drawbacks of implementing AI on a larger scale in the workforce. One potential concern is job displacement, which can lead to unemployment and the need for reskilling and upskilling. Another concern is the potential for bias and discrimination in algorithms, which can have negative consequences for marginalized individuals and communities.
Privacy and security are also major concerns regarding the impact of AI on the workforce. As AI becomes more advanced, it is important to ensure that personal data is protected, and AI system are secure against cyberattacks. Nonetheless, AI can also enhance efficiency and productivity, and its advancements may lead to new job opportunities for workers with the right skills and knowledge.
According to the passage, what must be ensured as AI becomes more advanced in the workforce?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) Decreased efficiency in operations
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Protection of personal data and cybersecurity.
- As AI becomes more advanced, protecting personal data from misuse is crucial to ensure privacy.
- Cybersecurity measures must be implemented to safeguard AI systems from cyberattacks.
- AI advancements come with the risk of data breaches, requiring stronger encryption and security protocols.
- Companies must comply with legal frameworks and data protection laws to secure sensitive information.
Other Related Points
Cybersecurity Concerns
- AI systems can become targets of cyberattacks, leading to compromised operations and data leaks.
- Strong security measures such as firewalls, data encryption, and AI monitoring are essential.
Data Privacy
- Personal and sensitive data used by AI must be stored securely and comply with privacy laws like GDPR.
- Failure to protect data can damage trust and lead to legal consequences.
AI and Efficiency
- AI enhances efficiency, but data breaches or cyberattacks can disrupt operations and reduce productivity.
- Ensuring cybersecurity safeguards the benefits AI provides to the workforce and organizations.
Q89: AI's impact on the workforce is multifaceted. It involves the automation of repetitive and routine tasks, changing skill requirements and job displacement. This can be beneficial for employees as it frees them up to focus on more complex and creative work, but it can also create concerns about job displacement and changes in the demand for certain types of jobs. However, AI is also creating new job opportunities, especially in data analytics machine learning and AI development.
Despite these potential benefits, there are also concerns about the drawbacks of implementing AI on a larger scale in the workforce. One potential concern is job displacement, which can lead to unemployment and the need for reskilling and upskilling. Another concern is the potential for bias and discrimination in algorithms, which can have negative consequences for marginalized individuals and communities.
Privacy and security are also major concerns regarding the impact of AI on the workforce. As AI becomes more advanced, it is important to ensure that personal data is protected, and AI system are secure against cyberattacks. Nonetheless, AI can also enhance efficiency and productivity, and its advancements may lead to new job opportunities for workers with the right skills and knowledge.
What is one potential benefit of AI in the workforce mentioned in the passage?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) Decreased demand for data analysis
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Automation of repetitive tasks.
- AI automates routine and repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on complex and creative work.
- This improves workplace productivity and efficiency by eliminating manual tasks.
- Employees benefit by being able to engage in higher-value tasks that require problem-solving and innovation.
- Automation reduces human errors in repetitive processes, ensuring greater accuracy and consistency.
Other Related Points
Automation of Tasks
- AI helps automate tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and routine reporting.
- This allows businesses to save time, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
AI and Creativity
- With repetitive tasks automated, employees can focus on creative thinking, strategy, and innovation.
- This leads to greater job satisfaction and new growth opportunities within the workforce.
Job Transformation
- While AI automates certain jobs, it creates new opportunities in fields like data analytics, machine learning, and AI development.
- Reskilling and upskilling programs can help employees transition into
Q90: AI's impact on the workforce is multifaceted. It involves the automation of repetitive and routine tasks, changing skill requirements and job displacement. This can be beneficial for employees as it frees them up to focus on more complex and creative work, but it can also create concerns about job displacement and changes in the demand for certain types of jobs. However, AI is also creating new job opportunities, especially in data analytics machine learning and AI development.
Despite these potential benefits, there are also concerns about the drawbacks of implementing AI on a larger scale in the workforce. One potential concern is job displacement, which can lead to unemployment and the need for reskilling and upskilling. Another concern is the potential for bias and discrimination in algorithms, which can have negative consequences for marginalized individuals and communities.
Privacy and security are also major concerns regarding the impact of AI on the workforce. As AI becomes more advanced, it is important to ensure that personal data is protected, and AI system are secure against cyberattacks. Nonetheless, AI can also enhance efficiency and productivity, and its advancements may lead to new job opportunities for workers with the right skills and knowledge.
Which statement summarizes a potential outcome of advancement in workforce according to the passage?
(a) AI will eliminate all job roles that require creativity
(b) AI will benefit workers in specialised technical field
(c) AI advancement may create new job opportunities
(d) AI will lead to a decrease in overall workforce productivity
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is AI advancement may create new job opportunities.
- AI advancements are likely to create new job opportunities in fields such as data analytics, machine learning, and AI development.
- While AI automates repetitive tasks, it enables workers to focus on roles that require specialized technical skills.
- Industries embracing AI will require workers with skills in programming, AI integration, and systems management.
- The creation of these roles supports workforce transformation and opens new avenues for employment.
Other Related Points
AI and Job Opportunities
- AI advancements encourage job creation in emerging technical fields such as robotics, AI programming, and cybersecurity.
- There is an increased demand for roles involving AI supervision, ethical analysis, and decision-making systems.
AI in Technical Fields
- Workers specializing in machine learning, big data, and IoT (Internet of Things) benefit significantly from AI integration.
- This ensures economic growth by creating sustainable employment opportunities in modern industries.
Workforce Reskilling
- To adapt to AI advancements, reskilling and upskilling programs are critical for workers to transition into emerging roles.
- Fields such as digital marketing, cloud computing, and automation management see significant workforce demand.
Q91: Which of the following helps in Business decision making in ill-structured decision situations often using complex spreadsheets by creating "what if" models for managers?
(a) Management Information System (MIS)
(b) Decision Support System (DSS)
(c) Knowledge Work System (KWS)
(d) Executive Support System (ESS)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Decision Support System (DSS)'
Support System (DSS):
- A DSS is an information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities.
- It helps in analyzing large sets of data and compiling comprehensive information that managers use for decision-making purposes.
- DSS often uses complex spreadsheets and "what if" models to predict different outcomes based on various scenarios.
- They are particularly useful in ill-structured decision situations where the problem is not clear-cut and requires sophisticated analysis.
Other Related Points
Management Information System (MIS):
- An MIS provides information that organizations require to manage themselves efficiently and effectively.MIS typically deals with structured problems and provides routine reports, not suited for complex decision-making scenarios.
Knowledge Work System (KWS):
- KWS supports knowledge workers in the creation and integration of new knowledge into the organization.
- It is designed to handle specific tasks such as design, analysis, and engineering, rather than broad decision support.
Executive Support System (ESS):
- ESS is designed to help senior executives analyze, compare, and highlight trends in important variables.
- It supports strategic decision-making but does not focus on the detailed, analytical support provided by DSS for specific decision problems.
Q92: When we measure what type of demand we assume that effects of other variables is constant?
(a) Revenue and price elasticity of demand
(b) Gross elasticity of demand
(c) Income elasticity of demand
(d) Promotional elasticity of demand
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Income elasticity of demand'
Income elasticity of demand:
- Income elasticity of demand measures how the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in consumer income.
- While measuring income elasticity, it is assumed that the effects of other variables, such as the price of the good, prices of related goods, and consumer preferences, remain constant.
- This isolation of income changes helps in understanding the direct relationship between income levels and demand for a product.
Other Related Points
Revenue and price elasticity of demand:
- This elasticity measures how the quantity demanded of a good responds to changes in its price.
- While important, this type does not assume other variables are constant specifically in the context of income effects.
Gross elasticity of demand:
- This is not a standard economic term commonly used to describe demand relationships, and thus is not applicable in the context of this question.
Promotional elasticity of demand:
- This measures the sensitivity of demand in response to promotional efforts like advertising and sales promotions.
- It specifically focuses on how demand changes due to promotional activities, not assuming the constancy of other variables.
Q93: Arrange the Project Life Cycle phase in proper sequence from starting to end.
A. Definition phase
B. Conception phase
C. Implementation phase
D. Planning and organizing phase
E. Project clean-up phase
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D, E, C
(b) B, A, D, C, E
(c) B, A, C, D, E
(d) E, A, C, D, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'B, A, D, C, E'
Project Life Cycle Phases:
- Conception phase (B): This is the initial phase where the idea for the project is conceived. It involves identifying the need for the project and conducting a feasibility study to understand its viability.
- Definition phase (A): In this phase, the project's objectives, scope, and requirements are defined. It includes developing a project charter and defining the project's goals and deliverables.
- Planning and organizing phase (D): This phase involves detailed project planning, including creating schedules, budgets, resource allocation, and risk management plans. It sets the roadmap for project execution.
- Implementation phase (C): The project plan is put into action during this phase. It involves executing the tasks, managing resources, and monitoring progress to ensure the project stays on track.
- Project clean-up phase (E): This final phase involves closing out the project, ensuring all deliverables are completed, and conducting a post-project evaluation to learn from the experience and document lessons learned.
Q94: Which of the following are properties of regression coefficients?
A. 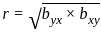
B. Change in origin are not affected
C. Change in scale are not affected
D. If both the regression coefficients have negative signs, the correlation coefficient will have a negative sign
E. If one regression coefficient is greater than one, then the other regression coefficient must be less than one.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, D and E Only
(b) A, D and E Only
(c) A, B, D and E Only
(d) A, B and C only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, D and E Only'
Properties of regression coefficients include:
- Regression coefficients are affected by a change in scale but not by a change in origin.
- If both regression coefficients are negative, their correlation coefficient will also be negative.
- If one regression coefficient is greater than one, the other must be less than one.
- Change in origin does not affect the regression coefficients, while a change in scale does.
Other Related Points
Change in scale:
- Change in scale affects the regression coefficients. If the scale of measurement of the variables changes, the regression coefficients will also change proportionally. Therefore, Property C, which states that changes in scale do not affect regression coefficients, is incorrect.
Q95: Which of the following movement of products clearly defines the term "Inbound Logistics"?
(a) Suppliers to company
(b) Company to Reseller
(c) Reseller to Customer
(d) Customers to Suppliers
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'Suppliers to company'
Inbound Logistics:
- Inbound logistics refers to the movement, storage, and receiving of goods into a business. It encompasses all the activities involved in the procurement and transportation of raw materials or products from suppliers to the company.
- This process is crucial for ensuring that the company has the necessary inputs to begin the production process or for reselling.
- Effective inbound logistics can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and ensure timely availability of materials, which in turn enhances overall operational performance.
Other Related Points
Company to Reseller:
- This movement involves the distribution of finished products from the company to resellers or distributors. This is part of outbound logistics, not inbound logistics.
- Outbound logistics focuses on delivering products to end-users or intermediaries, ensuring timely and efficient delivery.
Reseller to Customer:
- This movement is related to the supply chain process where resellers or distributors deliver products to customers. This is also part of outbound logistics.
- It ensures that the products reach the final consumer, facilitating the completion of the sales process.
Customers to Suppliers:
- This movement is typically not a part of standard logistics processes. It may refer to returns or reverse logistics, where customers return products to suppliers or manufacturers.
- Reverse logistics handles returns, recycling, and disposal, differing from inbound and outbound logistics.
Q96: A phenomenon in which the norm for consensus overrides that realistic appraisal of alternative course of action is:
(a) Groupshift
(b) Groupthink
(c) Brainstorming
(d) Nominal group technique
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Groupthink'
Groupthink:
- Groupthink is a psychological phenomenon that occurs within a group of people, in which the desire for harmony or conformity in the group results in an irrational or dysfunctional decision-making outcome.
- Members of the group strive for consensus to such an extent that they minimize conflict and avoid critical evaluation of alternative ideas and viewpoints.
- This leads to poor decision-making, as dissenting opinions and potential risks are not adequately considered.
- Key characteristics of groupthink include the illusion of invulnerability, collective rationalization, belief in inherent morality, stereotyping of outsiders, self-censorship, illusion of unanimity, direct pressure on dissenters, and self-appointed mindguards.
Other Related Points
Groupshift:
- Groupshift refers to a phenomenon where group members make decisions that are more extreme compared to their initial individual positions. This shift can be towards greater risk (risky shift) or greater caution (conservative shift).
- It is different from groupthink as it focuses on the direction and degree of decision changes rather than the suppression of dissent within the group.
Brainstorming:
- Brainstorming is a group creativity technique designed to generate a large number of ideas for the solution to a problem.
- The primary goal is to encourage free-flowing ideas and to avoid any criticism during the idea-generation phase to foster a creative atmosphere.
Nominal group technique:
- The nominal group technique (NGT) is a structured method for group brainstorming that encourages contributions from everyone.
- It involves individuals writing down their ideas independently, followed by a round-robin sharing session where ideas are discussed and prioritized.
- This technique helps to ensure that all group members have an equal opportunity to contribute.
Q97: Match the List-I with List-I

(a) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(c) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-I, B-III,1 C-II, D-IV
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III'.
Conflict Views:
- The Traditional View: This view holds that all conflict is harmful and must be avoided. It suggests that conflict disrupts the organization and prevents optimal performance. This is matched with 'A-II'.
- The Human Relations View: This perspective believes that conflict is a natural and inevitable outcome in any group. It sees conflict as an inherent part of human interaction, which can be managed and harnessed for positive outcomes. This is matched with 'B-I'.
- The Interactionist View: This view goes a step further by suggesting that conflict is not only inevitable but also necessary for a group to perform effectively. It sees conflict as a positive force that can stimulate innovation and improve group performance. This is matched with 'C-IV'.
- Functional Conflict: This type of conflict supports the goals of the group and improves its performance. It is considered beneficial as it encourages diversity of thought and can lead to better decision-making. This is matched with 'D-III'.
Q98: Match the List-I with List-II
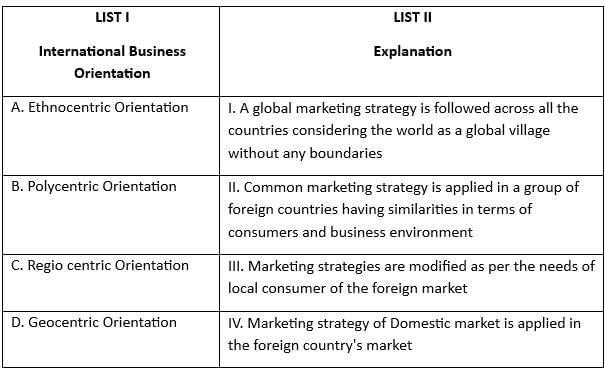
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(c) A-I, B-II, C-III. D-IV
(d) A-II, B-III,1 C-I, D-IV
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Option 2'
Ethnocentric Orientation (A-IV):
- In ethnocentric orientation, the marketing strategy that is effective in the domestic market is applied to the foreign market as well.
- This approach assumes that what works in the home country will also work abroad, without significant modifications.
Polycentric Orientation (B-III):
- Polycentric orientation involves customizing marketing strategies to meet the needs and preferences of local consumers in each foreign market.
- Companies adopting this approach treat each market as unique and develop strategies tailored specifically for each market.
Regio-centric Orientation (C-II):
- In regio-centric orientation, a common marketing strategy is applied within a specific region, where countries have similar characteristics in terms of consumer behavior and business environment.
- This approach allows for some level of standardization within a region, while still accommodating regional differences.
Geocentric Orientation (D-I):
- Geocentric orientation treats the world as a single market and develops a global marketing strategy that is consistent across all countries.
- This approach considers the world as a global village, with minimal modifications to the marketing strategy in different countries.
Q99: Arrange the following Trade Negotiation Rounds of World Trade Organisation in the order of their occurrence from oldest to latest:
A. Bali Conference
B. Geneva Conference
C. Hong Kong Conference
D. Cancun Conference
E. Doha Conference
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, E, D
(b) B, C, D, E, A
(c) A, B, C, D, E
(d) E, D, C, B, A
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'E, D, C, B, A'
World Trade Organisation (WTO) Trade Negotiation Rounds:
- The WTO is an international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations. Trade negotiation rounds are a key aspect of the WTO's efforts to enhance global trade.
- These rounds involve multiple meetings and conferences where member countries negotiate agreements to reduce trade barriers and establish fair trading practices.
Doha Conference (2001):
- Officially launched the Doha Development Agenda aimed at lowering trade barriers around the world, with a focus on improving trading prospects for developing countries.
Cancun Conference (2003):
- Held in Cancun, Mexico, this conference aimed to progress the Doha Development Agenda but ended without a final agreement due to disagreements among member countries.
Hong Kong Conference (2005):
- This conference was another attempt to advance the Doha Development Agenda, resulting in some progress, particularly on issues like agriculture and market access.
Geneva Conference (2008):
- An important meeting in Geneva focused on trying to break the deadlock in the Doha Round negotiations, though it ultimately ended without a conclusive agreement.
Bali Conference (2013):
- Known for the "Bali Package," which included measures to streamline trade, reduce agricultural subsidies, and improve food security in developing countries.
Other Related Points
Significance of Trade Negotiation Rounds:
- These rounds are crucial for global trade as they aim to create fairer trading conditions, reduce trade barriers, and address the concerns of developing nations.
- Each round builds on the previous ones, attempting to resolve outstanding issues and introduce new agreements to facilitate smoother international trade.
Q100: Who has suggested the 7-S framework for organisational change?
(a) McKinsey
(b) Peter Drucker
(c) Dale Yoder
(d) Mintzberg
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is the '7-S framework for organisational change'.
7-S Framework for Organisational Change:
- This framework was developed by McKinsey & Company, a global management consulting firm.
- The 7-S framework is a tool used to assess and monitor changes in the internal situation of an organization.
- The model includes seven interdependent factors: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Style, Staff, and Skills.
- These elements are divided into "hard" elements (Strategy, Structure, Systems) and "soft" elements (Shared Values, Style, Staff, Skills).
- The framework highlights the interconnectedness of these factors, emphasizing that a change in one area will likely affect the others.
Other Related Points
Peter Drucker:
- Peter Drucker was a management consultant, educator, and author, often referred to as the founder of modern management.
- He is known for concepts such as Management by Objectives (MBO) and the knowledge worker, but not for the 7-S framework.
Dale Yoder:
- Dale Yoder was a professor and author known for his contributions to the field of human resources and industrial relations.
- He did not develop the 7-S framework.
Mintzberg:
- Henry Mintzberg is an academic and author on business and management, known for his work on managerial roles and organizational structures.
- He did not create the 7-S framework but has made significant contributions to the study of management.
FAQs on UGC NET Official Paper 2: (Management) Held On - 2nd Sept 2024 Shift 2 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and its significance in the field of management? |  |
| 2. What are the main subjects covered in the UGC NET Paper 2 for management? |  |
| 3. How is the UGC NET exam structured, particularly for Paper 2 in management? |  |
| 4. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET exam for management? |  |
| 5. How can candidates prepare effectively for the UGC NET Paper 2 in management? |  |





















