UGC NET Paper 2: Commerce 13th June 2023 Shift 2 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: "Promise is an agreement"
Reason R: "An agreement is the sum total of offer and 'acceptance"
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is not correct
(d) A is not correct but R is correct
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Key Points
Promise:- A promise is a declaration or assurance that one will do something or that a particular thing will happen. It is often a unilateral declaration made by one party.
Agreement:- An agreement is a mutual understanding or arrangement between two or more parties. It often involves a 'meeting of the minds' where all involved parties agree to certain terms.
Assertion A: "Promise is an agreement"
- A promise to do something between two parties, or not, is said to form a sort of mutual understanding in pursuance of individual interests.
- For example If A promises to pay B a sum of Rs. 1000 to sell him 5 litres of oil and B accepts for the same, then Rs. 1000 is the consideration for a promise for B and vice versa.
Hence, Assertion A is correct.
Reason R: "An agreement is the sum total of offer and 'acceptance"
- The expression of the will of the person to another is called a proposal. This expression of interests with an intention to enter into a valid accord enforceable by law is termed is agreement.
- Every promise and every set of promises, forming the consideration for each other, is an agreement.
- A very essential element of proposal and subsequent agreement is the consideration for which the acceptor promises to do, or abstain from doing something, on the persuasion of the offerer.
- Without consideration, the promisor does not have any teeth to enter into a valid agreement.
- To sum up, we can represent the above information below: Agreement = Offer + Acceptance.
- Promises and commitments forming consideration for the parties to the same consent are known as an agreement. The agreement, which is legally enforceable, is known as a contract.
Hence, Reason R is correct.
Therefore we can say that Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Q2: The potential benefit of FDI to host countries include which of the following:
A. Access to superior technology and increased competition
B. Employment generation
C. Increase in domestic investments
D. Bridging host countries foreign exchange gaps
E. Reduction in income inequality
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, E only
(b) A, B, E only
(c) C, E, D only
(d) A, C, D only
Ans: D
Sol: Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an ownership stake in a foreign company or project made by an investor, company, or government from another country.
Key Points
Benefits of FDI in host countries
Access to superior technology and increased competition
- Recipient businesses get access to latest financing tools, technologies and operational practices from across the world. Over time, the introduction of newer, enhanced technologies and processes results in their diffusion into the local economy, resulting in enhanced efficiency and effectiveness of the industry.
Increase in domestic investments
- FDI assures a large quantity of domestic capital, production level, and job prospects, which is a crucial step toward the country's economic progress.
Improved Capital Flow
- Inflow of capital is particularly beneficial for countries with limited domestic resources, as well as for nations with restricted opportunities to raise funds in global capital markets.
Bridging host countries foreign exchange gaps
- FDI improves a country's balance of Payment as it causes an influx in foreign curency and helps in bridging host country's foreign exchange gaps.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is A, C, D only
Q3: Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs depicts human needs in the form of hierarchy ascending from the lowest to highest need. The correct order is.
(a) Esteem needs, Acceptance needs. Safety needs, Physiological needs, Need for Self-Actualization
(b) Physiological Needs, Safety needs. Acceptance needs, Need for Self-Actualization
(c) Safety needs, Esteem needs, Need for Self-Actualization. Physiological Needs, Acceptance Needs
(d) Physiological needs, Acceptance needs. Safety needs, Need for Self-Actualization, Esteem Needs
Ans: B
Sol: Maslow's hierarchy of needs
- It is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs
- Needs lower down in the hierarchy must be satisfied before individuals can attend to needs higher up.
- From the bottom of the hierarchy upwards, the needs are: physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem and self-actualization.
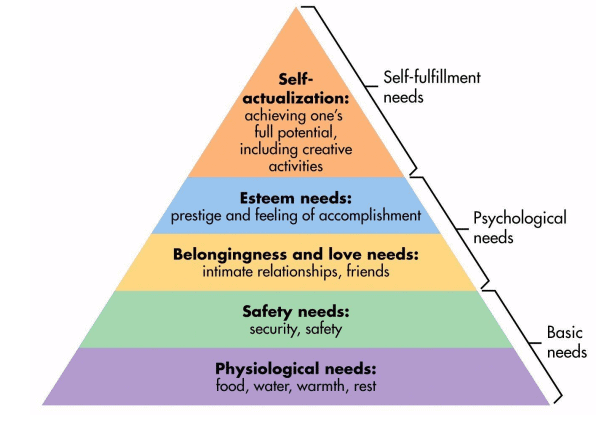
- Physiological needs - These are biological requirements for Human survival, e.g. air, food, drink, shelter, clothing, warmth, sex, sleep. If these needs are not satisfied the human body cannot function optimally
- Safety needs - protection from elements, security, order, law, stability, freedom from fear.
- Love and belongingness needs - after physiological and safety needs have been fulfilled, the third level of human needs is social and involves feelings of belongingness. The need for interpersonal relationships motivates behavior
- Esteem needs - which Maslow classified into two categories: (i) esteem for oneself (dignity, achievement, mastery, independence) and (ii) the desire for reputation or respect from others (e.g., status, prestige).
- Self-actualization needs - realizing personal potential, selffulfillment, seeking personal growth and peak experiences. A desire “to become everything one is capable of becoming”
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is Physiological Needs, Safety needs. Acceptance Needs, Need for Self-Actualization.
Q4: Which one of the below mentioned transaction is not a non-cash transaction?
(a) The acquision of assets by assuming directly related liabilities
(b) Conversion of debt into equity
(c) Interest on dividend received from investing activities
(d) The acquisition of an enterprise by means of issue of share
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Interest on dividends received from investing activities.
Non-cash expenses are those expenses that are recorded in the income statement but do not involve an actual cash transaction.
Some common noncash transactions include:
Depreciation:
- Depreciation means fall in the value of assets.
- The net result of an asset's depreciation is that sooner or later the asset will become useless. Depreciation does not result in outflow of cash and hence, it is a non-cash expenses.
Amortization:
- Amortization is an accounting technique used to periodically lower the book value of a loan or an intangible asset over a set period of time. Concerning a loan, amortization focuses on spreading out loan payments over time.
Unrealized gain:
- The term unrealized gain refers to an increase in the value of an asset, such as a stock position or a commodity like gold, that has yet to be sold for cash. As such, an unrealized gain is one that takes place on paper, as it has yet to be realized
Unrealized loss
Impairment expenses
Stock-based compensation:
- Stock Based Compensation (also called Share-Based Compensation or Equity Compensation) is a way of paying employees, executives, and directors of a company with equity in the business.
- Under US GAAP, stock based compensation (SBC) is recognized as a non-cash expense on the income statement.
- Provision for discount expenses
- Deferred income taxes
Q5: The adjusted present value model used by MNCs to evaluate capital budgeting decision is based on
(a) Gresham's principle
(b) Value additivity approach
(c) Law of one price
(d) Multilateral Netting approach
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Value Additivity Principle
Important Points
Value Additivity Principle
- The Value Additivity Principle in NPV states that the value of the total NPV of a bigger project is equal to the summation of all smaller NPVs of projects. In other words, the summation of all smaller NPVs provides the bigger NPV of an investment project. The NPV of a group of the independent projects will be equivalent to the NPV of all the independent projects.
- If A and B are two smaller projects, then the total NPV of the bigger project (A+B) would be −
- NPV (A+B) = NPV (A) + NPV (B)
- The adjusted present value model used by MNCs to evaluate capital budgeting decision is based on this method
Other Related Points
law of one price (LOOP) :
- The law of one price (LOOP) states that in the absence of trade frictions (such as transport costs and tariffs), and under conditions of free competition and price flexibility (where no individual sellers or buyers have power to manipulate prices and prices can freely adjust), identical goods sold in different locations must sell for the same price when prices are expressed in a common currency
Gresham's law:
- In economics, Gresham's law is a monetary principle stating that "bad money drives out good".
- For example, if there are two forms of commodity money in circulation, which are accepted by law as having similar face value, the more valuable commodity will gradually disappear from circulation
Multilateral netting:
- Netting is the process of consolidating payables against receivables between parties.
- Multilateral netting involves pooling the funds from two or more parties so that a more simplified invoicing and payment process can be achieved.
- It is a payment arrangement among multiple parties that transactions be summed, rather than settled individually. Multilateral netting can take place within a single organization or among two or more parties.
Q6: Which one of the following is an operational technique of hedging transaction exposure.
(a) Hedging through money market
(b) Hedging through forward
(c) Hedging through swap
(d) Hedging through leading & lagging
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Hedging through leading & lagging.
Hedging in stock market is a strategy used by investors to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in an asset. It involves taking an offsetting position in a related security or financial instrument, with the goal of minimizing potential losses from market volatility.
Types of Hedging:
Hedging through money market :
- It is a technique used to lock in the value of a foreign currency transaction in a company’s domestic currency.
- Therefore, a money market hedge can help a domestic company reduce its exchange rate or currency risk when conducting business transactions with a foreign company.
- It is called a money market hedge because the process involves depositing funds into a money market, which is the financial market of highly liquid and short-term instruments like Treasury bills, bankers’ acceptances, and commercial paper.
Hedging through forward :
- Forward contract is used for hedging the foreign exchange risk for future settlement.
- For example, An importer or exporter having FX contract limit may lock in current exchange rate by entering into forward contract with the bank to avoid adverse rate movement.
Hedging through swap:
- Currency swaps are a way to help hedge against that type of currency risk by swapping cash flows in the foreign currency with domestic at a pre-determined rate.
Leading and lagging:
- In this timing payments in foreign currencies and take advantage of currency movements.
- Leading is paying in advance, and lagging is paying later, sometimes after the due date. Businesses that use these techniques try to anticipate which way a currency will move and make their transactions accordingly.
- It is a type of operational hedging that is the course of action that hedges the firm's risk exposure by means of non-financial instruments, particularly through operational activities.
Q7: Which of the following factors influence the selection and construction of the scale?
A. Multicollinearity
B. Data properties
C. Number of dimensions
D. Level of Significance
E. Research objectives
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) D, E, B only
(c) C, E, B only
(d) A, E, D only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is C, E, B only.
Explanation
- Multicollinearity: Multicollinearity refers to a high degree of correlation between independent variables in a multiple regression model. If such a correlation is found, it makes it difficult to understand the effect of each individual variable. However, multicollinearity is generally a consideration in the model-building step, not in scale selection and construction. Scales are employed to structure responses and don't deal directly with the relationship between multiple predictors.
- Data properties: The nature of the data you are working with can greatly influence the choice and construction of scale. Data properties may include characteristics such as distribution (normal or non-normal), type of data (nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio), range of values, and the presence of outliers. For example, if you're working with ordinal data, certain scaling methods like Likert scales might be more appropriate.
- Number of dimensions: The number of dimensions in your data, or in other words, the number of variables or characteristics you are analyzing, can affect your scaling choice. In some instances, a unidimensional scaling is used when measurements reflect a single construct. However, when measurements reflect multiple characteristics, multidimensional scaling techniques are employed. These types of scales help to visualize patterns and relations in multi-attribute data sets.
- Level of Significance: The level of significance, often denoted by alpha (α), is a threshold set before the data collection for deciding whether to reject the null hypothesis. It determines the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. Mostly used in hypothesis testing, it doesn't fundamentally impact the selection and construction of the scale. In scale selection and construction, the focus is on the properties of the data and research objectives, not testing hypotheses.
- Research objectives: The goals of your research or analysis also play a crucial role in the choice of your scaling method. If your objective is to establish a hierarchy or ranking of data points, an ordinal scale would be suitable. On the other hand, if your goal is to establish distances or intervals between data points, an interval or ratio scale might be more appropriate.
Q8: Arrange the key steps in developing a perceptual map to determine the position of a brand in the market place in sequence:
A. Identify set of competing brands
B. Conduct qualitative research where customers score each brand on all key attributes
C. Put brands on two dimensional maps
D. Aggregate all brands belonging to that category
E. Identify important attributes that consumers use when choosing brands using qualitative research
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, E, D, A
(b) D, A, E, B, C
(c) A, C, D, B, E
(d) E, B, C, A, D
Ans: B
Sol: A perceptual map is a chart used to illustrate where a product or brand and its competitors are positioned according to consumer perception.
Steps in developing a perceptual map to determine the position of a brand in the market place
Select attributes
- Attributes are the variables the customer factors into their decision to purchase a product or service.
- Consider the most important aspects of a product and which aspects you'd like to study.
- For example, key attributes for a food product can be its taste, texture, smell and quality, and attributes for a vehicle can be its price, performance and model year
Set Dimentions:
- After attributes, this is the most crucial step to perform.
- Setting dimensions for map allows the customer’s perceptions to reflect clearly.
- This process involves giving numerical values on each axis. More numerical values will cause better mapping
Identify competition
Identify the company's top competition, which can be several businesses or organizations that provide similar products and services.
This step can help in developing a perceptual map showing where the company and its competitors rank in the thoughts and perceptions of customers
Decide Products/Brands
To Map and build a perceptual map for shoes, different shoes from different brands or varying styles need to be selected.
These brands can be competitors or a part of the product umbrella.
This step is crucial to increase the efficiency of map, as when choose the right products, customer perceptions from the map can lead to needed changes
Conduct A Survey
Perceptual maps thrive on data, and conducting surveys are the best way to do that.
The survey building process is as simple as it can get with SurveySparrow, which allows you to get to the analysis and actual mapping stage faster.
Plot the Results and Create The Map
Analyzing Map
Gaps in the grid could indicate new market opportunities, while heavily clustered quadrants could indicate that you need to work on communicating your product's USP.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is D, A, E, B, C.
Q9: For the interval-scale and ratio-scale data usually which of the following measure of association are used?
A. Kendall's tau b
B. Correlation ratio (eta)
C. Partial correlation
D. Spearman's rho
E. Product moment correlation
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, E only
(b) B, A, E only
(c) C, B, E only
(d) D, B, E only
Ans: C
Sol: An interval scale is one where there is order and the difference between two values is meaningful. Examples of interval variables include: temperature (Farenheit), temperature (Celcius),
A ratio variable, has all the properties of an interval variable, and also has a clear definition of 0.0. When the variable equals 0.0, there is none of that variable. Examples of ratio variables include: enzyme activity, dose amount, reaction rate,
Important Points
Correlation ratio (eta)
- A correlation ratio in statistics is a measure of the curvilinear relationship between the statistical variances within individual categories and the variances of the entire population or sample. Scales are defined as the ratio of two standard deviations representing these types of variation.
Partial correlation
- Partial correlation measures the strength of a relationship between two variables, while controlling for the effect of one or more other variables.
Product moment correlation
- Pearson's product moment correlation coefficient (sometimes known as PPMCC or PCC,) is a measure of the linear relationship between two variables that have been measured on interval or ratio scales. It can only be used to measure the relationship between two variables which are both normally distributed.
Other Related Points
Kendall’s Tau-b
- It is a useful measure of correlation because it does not assume any particular distribution for the variables being analyzed.
- Unlike Pearson’s correlation coefficient, Kendall’s Tau-b can be used with both continuous and ordinal variables. This makes it an ideal tool for researchers who are working with non-parametric data or data that does not meet the assumptions of other statistical tests.
- Kendall’s Tau-b is also useful because it is less sensitive to outliers than other
Spearman's rho
- It is a non-parametric statistical test of correlation that allows a researcher to determine the significance of their investigation. It is used in studies that are looking for a relationship, where the data is at least ordinal
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is C, B, E only.
Q10: Tax planning involves which of the following features?
A. It is an inherent right of the taxpayer
B. It has originated from the very existence of certain exemptions, deductions etc
C. Transactions take the form of colorable devices
D. It is legal and accepted by the judiciary
E. It is based on the principle of disclosure
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D only
(b) B, D, E only
(c) B, C, D only
(d) A, D, C only
Ans: B
Sol: Tax planning is the analysis of a financial situation or plan to ensure that all elements work together to allow us to pay the lowest taxes possible.
Features of Tax Planning
Object:
- The main object of tax planning is to reduce tax liability. This object is achieved by claiming deductions, reliefs and rebates allowed under the Act.
Ethical:
- Tax planning is ethical because it is an act within the four corners of the Act and it is not a colourable device to avoid the tax. It is based on the principle of disclosure
Basis:
- The basis of tax planning is claiming the deductions, rebates and reliefs which have been provided in the Act to achieve certain social and economic goals. It has originated from the very existence of certain exemptions, deductions etc
Study and analysis:
- Tax planning requires a thorough knowledge of the Act and analysis of its provisions so that tax liability may be reduced by fulfilling the conditions laid down in the Act.
Term:
- Tax planning can be short-term tax planning or long-term tax planning. When it is resorted to for the current year, it is called short-term tax planning but when it is resorted to availing tax benefits year after year, it is known as long-term tax planning.
It is legal and accepted by the judiciary:
- The Supreme Court of India delivered the first landmark judgement on the distinction between 'tax planning' and 'tax evasion' in the case of CTO Vs McDowell and Co Ltd in 1985, holding that "Tax planning may be acceptable provided it is done within the framework of law.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is B, D, E only.
Q11: Which expenses are expressly disallowed under profits from Business or Profession?
A. Salary paid out of India or to a non-resident in India
B. Wealth tax
C. Payment to any Rural Development Programme
D. Expenditure incurred by companies on notified skill development project
E. Interest, royalty or fees payable outside India
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, E only
(b) A, B, C only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) A, B, E only
Ans: D
Sol: Disallowed Expenditure are those expenses which are not allowed/ cannot be deducted while computing the taxable income under the head “Profits and Gains from Business or Profession”. It means such expenses will be added to the income on which tax needs to be remitted.
Expenses expressly disallowed under profits from Business or Profession are
Payments/ Credits made to Non- Resident, not being a Company or to a foreign Company
- If there is default in the TDS deduction or payment by the payer in respect of the payment/ credit of interest, Royalty, Fee for technical Services or any other sum chargeable under this Act (Other than Salary) to non-Resident, not being a Company or to a foreign Company, then 100% of such expenditure is disallowed in the hands of the payer.
Payment of Salary
- Any Salary payable — Outside India or — To a Non- Resident in India shall be disallowed, if tax has not been deducted or paid on or before the due date prescribed for such deductions
Payment made to State Government
- It includes Royalty, license fee, service fee, privilege fee, service charge or any other fee or charge
Disallowance of Income Tax, Wealth Tax, etc
- Payment of Income tax like TDS, Self Assessment Tax and Wealth tax is not allowed as deduction while computing Profits and Gains from Business or Profession
- Payment to Provident Fund and other Funds
- Any payment to a provident or other fund established for the benefit of the employees shall be disallowed unless the employer has made effective arrangements to secure that tax shall be deducted at source from any payments made from the fund which are chargeable to tax under the head “Salaries
Therefore we conclude that the correct answer is A, B, E only.
Q12: Match List I with List II.
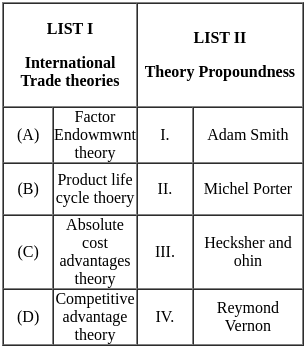
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
Ans: B
Sol: Explanation  Therefore we conclude that the correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II.
Therefore we conclude that the correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II.
Q13: _____ are the moral principles and values that guide behavior within the field of marketing and cover issues such as product safety. and truthfulness in marketing. communication. honesty in relationships with customers distributors, pricing issue,s and the impact of marketing decisions on the environment and society.
(a) Sustainable practices
(b) Marketing ethics
(c) Positioning principles
(d) Corporate social responsibility
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Marketing ethics .
Important Points
Marketing ethics
- It refers to the principles and values that guide the behavior of marketers, emphasizing honesty, responsibility, fairness, and respect for consumers and society
- Marketing ethics are a set of moral principles that guide a company's promotional activities.
- Ethical marketing refers to a marketer’s obligation to ensure all marketing activities stick to core ethics principles, involving integrity, humility, and honesty — both internally and externally.
Other Related Points
Sustainability:
- As per UN World Commission on Environment and Development: “sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
Positioning:
- "Positioning" is the process that produces the product's image and places it in the consumer's mind. Positioning is the main process behind how consumers become aware of brands and their reputations
Corporate social responsibility:
- Corporate social responsibility or corporate social impact is a form of international private business self-regulation which aims to contribute to societal goals of a philanthropic, activist, or charitable institution.
Q14: A company's stock sells for Rs. 63. The company pays an annual dividend of Rs. 3 per share and has long established record of increasing its dividend by a constant 5% annually. For this company, the cost of equity (Ke) is ______.
(a) 13%
(b) 14%
(c) 10%
(d) 8%
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 10%
Cost of equity
- It is the return that a company requires for an investment or project, or the return that an individual requires for an equity investment.
- The formula used to calculate the cost of equity is either the dividend capitalization model or the CAPM.
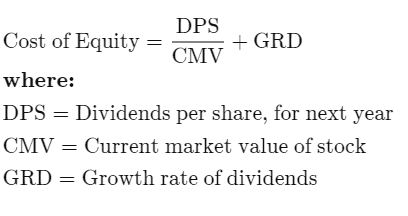
Here DPS=3 Rs
CMV=63 Rs
GRD=0.05
Putting values in above formula
=(3/63)=0.05
0.0976 ~ 10%
Q15: Which are the conditions in which unilateral relief is granted in cases where section 90 is not applicable in income tax?
A. a resident of India in the previous year", "accrues".
B. The income should have accrued out side India
C. The assessee should not have paid the tax in such foreign country by deduction
D. The income should not accrued outside India
E. The income should be taxed both in India and a foreign country with which India has no agreement for relief
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, E only
(b) B, C, E only
(c) A, D, E only
(d) A, C, E only
Ans: A
Sol: When there is no agreement between the home and resident countries, the home country is responsible for offering tax relief and preventing double taxation. Section 91 discusses the unilateral relief segment in detail.
Tax relief under Section 90
- Tax relief under Section 90 is for those who accrue income from global sources.
- This section also has provisions per which the Central government can enter into DTAA agreements with the government outside India.
- For tax relief under this a resident of India in the previous year", "accrues".
- Tax relief under Section 90A If India has entered into DTAA with the specified association, tax relief will be calculated as per the norms of Section 90 If the resident does not belong to India, they have to obtain a tax residence certificate (TRC) from the country to which they belong
- If India and a foreign country have a DTAA (Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement), relief is available under Section 90. If a DTAA exists with a particular association, there is tax relief under Section 90A. If India and a foreign country do not have a DTAA, relief is available under Section 91
Here are the basic rules for computing tax relief under Section 90
- Add both the income from India and foreign countries which is the global income Compute tax on the global income
- Calculate the average tax rate by dividing the computed tax by global income
- Calculate the amount of tax to be paid in a foreign country by diving the income accrued from the foreign country with the average tax rate computed above
- The tax relief that a taxpayer is subjected to get will be lower out of the amount computed above or the fixed value of tax to be paid.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is A, B, E only.
Q16: When technology allows many firms to operate efficiently in the markets, which market structure represents a better use of society's resources?
(a) Perfect competition
(b) Monopoly
(c) Monopolistic Competition
(d) Oligopoly
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Perfect competition .
There are four types of competition in a free market system: perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly.
Important Points
Perfect competition
- It occurs when all companies sell identical products, market share does not influence price, companies are able to enter or exit without barriers, buyers have perfect or full information, and companies cannot determine prices.
Following are the characteristics of perfect competition:
- Large numbers of buyers and sellers in the market.
- Free entry and exit of firms in the market.
- Each firm should be selling a homogeneous product. Buyers and sellers should possess complete knowledge of the market.
- No price control.
- When technology allows many firms to operate efficiently in the markets, this market structure represents a better use of society's resources
Other Related Points
- Under monopolistic competition, many sellers offer differentiated products—products that differ slightly but serve similar purposes. By making consumers aware of product differences, sellers exert some control over price.
- In an oligopoly, a few sellers supply a sizable portion of products in the market. They exert some control over price, but because their products are similar, when one company lowers prices, the others follow.
- In a monopoly, there is only one seller in the market. The market could be a geographical area, such as a city or a regional area, and does not necessarily have to be an entire country. The single seller is able to control prices.
Q17: Arrange the steps for verification and value of furniture and fixtures by an auditor.
Ensure that the amount and rate of
A. Depreciation charged on different items is based on fair estimate of their working life
B. Check that repair to furniture if any, during the current year is debited to Profit and loss Account
C. Verify with reference to the purchase invoice in case of the assets have been acquired during the current accounting period
D. See that payment made on account of purchases of any item of furniture and fixture through the invoices of the suppliers
E. Check that a stock register is maintained containing the details of the various items purchased
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, E, A, B, D
(b) A, B, C, D, E
(c) B, C, D, A, E
(d) A, E, C, D, B
Ans: A
Sol: Steps for verification and value of furniture and fixtures by an auditor.:
- 1. The auditor has to see that a proper record showing quantitative details of furniture and fixtures owned by the client is maintained.It is to be Verified with reference to the purchase invoice in case of the assets have been acquired during the current accounting period
- 2. The auditor has to see that all expenses incidental to the purchase of furniture and fixtures is capitalised along with the purchase price paid for it.He must Check that a stock register is maintained containing the details of the various items purchased
- 3. The auditor has to inquire whether the furniture and fixtures have been properly insured or not.
- 4. The auditor has to see that adequate provision for depreciation on furniture and fixtures is made. Depreciation charged on different items is based on fair estimate of their working life
- 5. The auditor if possible can go for physical verification of furniture on test check basis or he can rely on the management certificate to that effect.Check that repair to furniture if any, during the current year is debited to Profit and loss Account.
- 6.See that payment made on account of purchases of any item of furniture and fixture through the invoices of the suppliers
- 7. He has to further see that any damaged or unusable furniture, if existing, is fully written off in the books.
Therefore we can say that the correct sequence is C, E, A, B, D.
Q18: Which of the following are necessary characteristics of modern selling?
A. Database and knowledge management
B. Brand extension
C. Customer relationship management
D. Segmentation, targeting and positioning
E. Satisfying needs and adding value
Choose the most appropriate from the options given below:
(a) A, C, E only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) A, D, E only
Ans: A
Sol: Modern selling combines new tools and modern sales techniques, such as digital selling and social selling, to find, engage, and connect with potential customers.
Characteristics of modern selling
Customer maintenance and deletion:
- Many companies have discovered that 80 per cent of their sales come from 20 per cent of their customers. This means that it is very important to devote substantial resources to retaining existing high volume, high potential and highly profitable customers.
- Key account management has turn out to be an important form of sales organization because a salesperson or sales team can focus their efforts on one or a few chief customers.
Database and knowledge management:
- The modern sales force needs to be qualified in the Use and creation of customer databases, and how to use the internet to assist the sales task (e.g. finding customer and competitor information). In the past, sales people recorded customerinformation on cards and sent in the information through the post to head office.
Customer relationship management:
- Customer relationship management requires that the sales force focuses on the long term and not just on closing the next sale. The emphasis should be on creating win–win situations with customers so that both parties to the dealings gain and want to carry on the relationship.
Satisfying needs and adding value:
- Delivering added value for customers is all about understanding their circumstances, needs and preferences – at a specific moment in time. What customers perceive as a value add depends on who they are, what makes them tick and exactly what they need at a given moment.
Problem solving and system selling:
- Much of modern selling, mainly in business to business situations, is based upon the salesperson performing as a consultant working with the customer to spot problems, find out needs and propose and implement effective solutions.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is A, C, E only.
Q19: One factor Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) ______.
(a) is a perfect generalization of the t-test for paired observations.
(b) requires that the number of observations in each group be identical
(c) has less power when the number observations in each group is not identical
(d) is extremally sensitive to slight departure from normality
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is has less power when the number observations in each group is not identical
ANOVA:
- The one factorial analysis of variance tests whether there is a difference between the means of more than 2 groups. Thus, one-way ANOVA is the extension of the independent t-test to more than two groups or sample.
- It is most often employed when there are at least three groups of data, otherwise a t-test would be a sufficient statistical analysis.
- It has less power when the number observations in each group is not identical
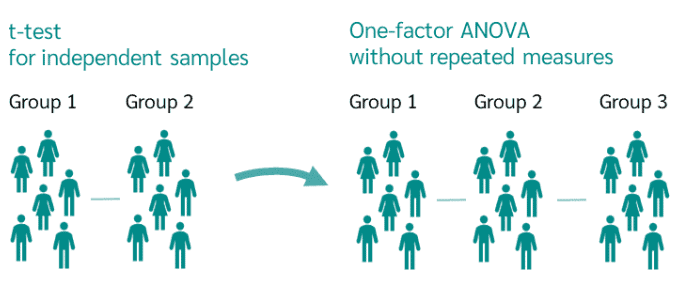
For a one-factor ANOVA to be calculated, the following conditions must be met:
1. Level of scale
- The scale level of the dependent variable should be metric, that of the independent variable nominally scaled.
2. Independence
- The measurements should be independent, i.e. the measured value of one group should not be influenced by the measured value of another group.
3. Homogeneity
- The variances in each group should be approximately equal. This can be checked with the Levene test.
4. Normal distribution
- The data within the groups should be normally distributed.
Q20: Blake and Mouton recognise four leadership styles. One of them is the autocratic task management style. The autocratic task manager 1s one who
(a) Concern themselves very little with either people or production and have minimum involvement in their jobs.
(b) Display in their actions, the highest possible dedication both to people and to production.
(c) are concerned only with developing an efficient operation who have little or no concern for people
(d) have little or no concern for production but are concerned only for people
Ans: C
Sol: The Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid
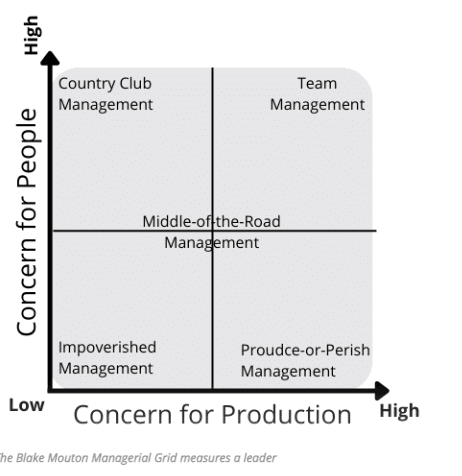
- It is a mental framework and graphic created by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton that can be used to help leaders identify their own leadership style and the style of their subordinates. The x-axis of the grid measures a leader's concern for production. The y-axis of the grid measures a leader's concern for people.
- The five leadership styles identified in the Blake Mouton Managerial resulting from a specific combination of a leader's concern for production and a leader's concern for people.
- These styles are known as country club management, impoverished management, middle-of-the-road management, produce or perish management, and team management.
Impoverished Management – Low Results/Low People
The Impoverished or "indifferent" manager is mostly ineffective. With a low regard for creating systems that get the job done, and with little interest in creating a satisfying or motivating team environment
- Produce-or-Perish Management – High Results/Low People Also known as "authoritarian" or "authority-compliance" managers, people in this category believe that their team members are simply a means to an end. The team's needs are always secondary to its productivity. This type of manager is autocratic, has strict work rules, policies and procedures, and can view punishment as an effective way of motivating team members.
Middle-of-the-Road Management – Medium Results/Medium People
- A Middle-of-the-Road or "status quo" manager tries to balance results and people, but this strategy is not as effective as it may sound. Through continual compromise, they fail to inspire high performance and also fail to meet people's needs fully.
- Country Club Management – High People/Low Results The Country Club or "accommodating" style of manager is most concerned about their team members' needs and feelings.
- Team Management – High Production/High People According to the Blake Mouton model, Team Management is the most effective leadership style. It reflects a leader who is passionate about their work and who does the best they can for the people they work with.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is are concerned only with developing an efficient operation who have little or no concern for people .
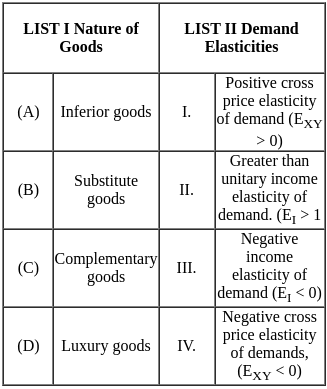
Q21: Match List I with List II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Important Points Inferior goods -
- Inferior goods are a type of good for which demand tends to decrease as consumer incomes rise and increase as consumer incomes fall.
- This is reflected in the concept of negative income elasticity of demand (Elasticity of Income, EI < 0).
- The negative income elasticity indicates that as consumers' incomes increase, which are likely to shift their consumption towards higher-quality or more desirable goods, leading to a decrease in demand for the inferior good.
Substitute goods -
- Substitute goods are products that can be used in place of each other, meaning that satisfy similar needs or desires.
- When the price of one substitute good increases, the demand for the other substitute tends to increase.
- This relationship is reflected in the concept of positive cross-price elasticity of demand (EXY > 0).
- Positive cross-price elasticity means that an increase in the price of one good leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of the other good.
Complementary goods -
- Complementary goods are products that are typically used together, so an increase in the price of one complementary good tends to lead to a decrease in the demand for the other, and vice versa.
- This is reflected in the concept of negative cross-price elasticity of demand (EXY < 0).
Luxury goods -
- Luxury goods typically have an income elasticity of demand (EI) greater than 1.
- This means that as consumer incomes rise, the demand for luxury goods increases at a proportionally higher rate.
- When people's incomes go up, they tend to spend a larger percentage of their income on luxury items.
- Conversely, if incomes fall, the demand for luxury goods tends to decrease at a higher rate.
- For luxury goods, this sensitivity is high, hence the value of EI > 1.
Q22: While using a recruiting yield pyramid, the managers are aware of which of the following while recruiting new hires?
A. The ratio of official needs to actual hires is 2 to 1
B. The ratio of places to the people called for an interview is 12 to 1
C. The ratio of offers male to new hires is 20 to 1
D. The ratio of candidates invited for interviews to candidates interviewed is about 4 to 3
E. The ratio of candidates interviewed to offers made is 3 to 2
Choose the most appropriate from the options given below:
(a) A, D, E only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) A, C, E only
(d) B, D, E only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A, D, E only.
- The recruiting yield pyramid is a visual representation used by human resource professionals and recruiters to illustrate the various stages of the hiring process and the conversion rates at each stage.
- It helps in analyzing the effectiveness and efficiency of the recruitment process.
Important PointsThe typical stages represented in a recruiting yield pyramid, along with their conversion rates -
- Total Applicants - This is the starting point of the recruitment process, where all potential candidates who apply for a job are considered.
- Screened Applicants - After initial application screening, some candidates may not meet the minimum qualifications and are screened out.
- Candidates Invited for Interview - From the screened applicants, a portion will be invited for an interview. This could be a phone interview, a video interview, or an in-person interview.
- Candidates Interviewed - This represents the number of candidates who actually go through the interview process.
- Offers Extended - After the interview process, some candidates will receive job offers.
- Offers Accepted - Out of the candidates who receive offers, some will accept and join the organization.
As per question,
- The ratio of official needs to actual hires is 2 to 1 - This means for every two positions that are officially needed, only one person is actually hired.
- The ratio of candidates invited for interviews to candidates interviewed is about 4 to 3 - This means for every four candidates invited for an interview, three are actually interviewed.
- The ratio of candidates interviewed to offers made is 3 to 2 - This means for every three candidates interviewed, two receive offers.
Thus, correct option 1 is A, D, and E only.
Q23: Sequence the following steps in the process of securitisation.
A. Special purpose vehicle (SPV) issue tradeable securities to find the purchase of pool of assets
B. SPV subcontracts (outsource) the originator for collection of interest and principle payments on the pool of assets
C. SPV repay the funds to the investor or cashflow arise on the pool of assets
D. Originator maker a pool of assets and sold it to the SPV
E. SPV pays the funds the orgination for the pool of assets
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, A, C, E
(b) D, E, B, A, C
(c) D, B, A, E, C
(d) E, A, B, D, C
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is - D, E, B, A, C
D: Originator creates a pool of assets and sells it to the SPV – First step, pooling and transferring assets.
E: SPV pays the funds to the originator for the pool of assets – SPV raises funds and pays the originator.
A: SPV issues tradeable securities to fund the purchase of assets – SPV issues securities to investors.
B: SPV subcontracts the originator for collection of interest and principal payments – SPV delegates collection to the originator.
C: SPV repays the funds to the investor as cash flow arises – Investors receive returns from asset cash flows.
Additional Information
Securitisation Process
- Securitisation is a financial process where assets are pooled together and then converted into tradeable securities.
- The SPV plays a critical role in isolating the pool of assets from the originator’s balance sheet, thus reducing risk and enabling easier access to capital.
Role of SPV
- The SPV is a legal entity created solely for the purpose of holding the asset pool and issuing the securities.
- It helps protect investors by ensuring that the underlying assets are legally separated from the originator.
Investors in Securitisation
- Investors in securitisation typically include institutions like banks, pension funds, and mutual funds that seek to invest in asset-backed securities.
- These investors receive periodic payments based on the cash flows generated by the underlying assets in the pool.
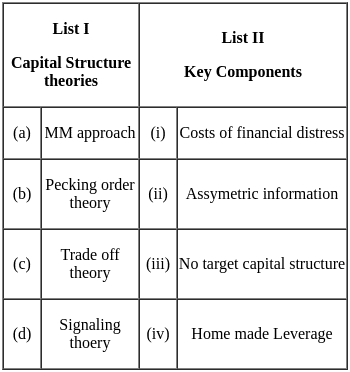
Q24: Match List I with List II.
Choose the correct answer answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II.
Important PointsMM approach - Home made Leverage
- Modigliani-Miller theorem - Investors can create their own leverage by borrowing and investing in risk-free assets.
- Homemade leverage- Investors can replicate the effects of corporate leverage by borrowing and investing in a firm's debt and equity.
Implications -
- Firms' capital structure is irrelevant to investors.
- Firms should focus on maximizing expected future cash flows and reducing risk, regardless of how they finance their operations.
In other words, investors can achieve the same level of risk and return regardless of the firm's capital structure. This is because they can always borrow or lend money to adjust their own leverage.
Pecking order theory - No target capital structure
- The Pecking Order Theory suggests that firms prioritize financing methods in a specific order.
- This begin with internal funds, followed by debt issuance, and finally, equity issuance.
- Unlike the traditional notion of a target capital structure, this theory contends that firms do not have a predetermined mix of debt and equity in mind.
- Instead, they rely on available funds and prefer internal financing due to the asymmetry of information between management and external investors.
- This theory emphasizes the pragmatic approach firms take in their financing decisions.
Trade off theory - Costs of financial distress
- Trade-off theory in finance suggests that companies must strike a balance between the tax benefits of debt financing and the costs associated with financial distress.
- The costs of financial distress include legal and administrative expenses related to bankruptcy proceedings, the loss of customer and supplier relationships, and the decline in the firm's value due to the uncertainty surrounding its financial health.
- Additionally, financial distress can lead to a reduced ability to invest in profitable projects, ultimately impacting the company's long-term viability.
Signaling theory - Asymmetric information
- Signaling theory addresses situations where one party possesses more or better information than another.
- In financial contexts, it often refers to a firm's ability to convey its quality or prospects to investors.
- For example, a company may issue a dividend to signal confidence in its future earnings or undertake a stock buyback to indicate undervaluation.
- These actions are intended to bridge the information gap and convey positive signals to investors, potentially affecting the firm's stock price.
Q25: Match List I with List II.
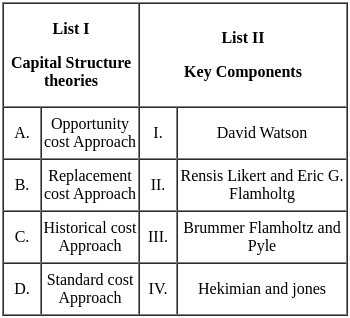
Choose the correct answer answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I.
Important PointsOpportunity cost Approach - Hekimian and jones
- Hekimian and Jones' Opportunity Cost Approach is a method for evaluating the cost of equity capital.
- It posits that the cost of equity is equivalent to the return that could be earned on an investment of similar risk elsewhere in the market.
- This approach considers the foregone returns an investor could have earned in alternative investments of comparable risk.
- By comparing the expected returns from different investment opportunities, it helps determine the appropriate cost of equity for a company.
Replacement cost Approach - Rensis Likert and Eric G. Flamholtz
- The Replacement Cost Approach was introduced by Rensis Likert and Eric G. Flamholtz.
- It is a method used in financial accounting that values assets based on the cost to replace them at current market prices.
- This approach provides a more accurate reflection of a company's true economic worth, especially in times of inflation or changing market conditions.
- By considering the cost of acquiring or replicating assets, it offers a more realistic assessment of a company's value compared to historical cost accounting methods.
- The Historical Cost Approach, associated with Brummer, Flamholtz, and Pyle, is an accounting method that values assets at their original purchase cost.
- This approach does not consider changes in market value or inflation over time.
- It is straightforward and easy to implement, providing a reliable record of transactions.
- However, critics argue that it may not reflect the true economic value of assets, especially in times of inflation or rapidly changing market conditions.
Standard cost Approach - David Watson
- The Standard Cost Approach, associated with David Watson, is a method used in managerial accounting to establish predetermined, standard costs for producing goods or services.
- These standard costs are based on a detailed analysis of past performance, industry benchmarks, and other relevant factors.
- Deviations from the standard costs can indicate areas where operations may need improvement or where there may be unexpected efficiencies.
- This approach helps in cost control and performance evaluation within an organization.
Q26: The utilitarian view of ethics is one of the few perspectives on business ethics and it includes:
A. Respecting and protecting individual liberties and privileges
B. Imposing and enforcing rules fairly and impartially
C. Ethical decisions made solely on the basis of their outcomes or consequences
D. Encourages efficiency and productivity and is consistent with goal of profit maximisation
E. Ethical decisions be learned on existing ethical norms in industries and communities
Choose the most appropriate from the options given below:
(a) A, E only
(b) C, D only
(c) B, C only
(d) D, E only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is C, D only.
- Business ethics refers to the principles, values, and moral guidelines that guide the behavior and decision-making processes within a business or organizational context.
- It encompasses the standards of conduct and integrity that individuals and organizations should uphold while conducting their operations.
Important Points
- The utilitarian view of ethics in business holds that decisions should be based on maximizing overall happiness or utility.
- It prioritizes actions that lead to the greatest benefit for the greatest number of people involved, considering stakeholders' well-being.
- This perspective assesses ethical choices based on their outcomes and consequences rather than strict adherence to rules or norms.
- It encourages efficiency and productivity, aligning with the goal of profit maximization for the overall benefit of society.
- However, critics argue that it can sometimes overlook the rights and interests of minority stakeholders in pursuit of the greatest overall good.
- As per questions, point C and D,
- The utilitarian view of ethics emphasizes making ethical decisions solely based on their outcomes or consequences. This means that an action is considered ethical if it leads to the greatest overall happiness or utility for the greatest number of people.
- The utilitarian view encourages efficiency and productivity and is consistent with the goal of profit maximization. This is because, under utilitarianism, actions that lead to greater overall utility, which can include financial well-being, are considered ethically favorable.
Q27: The coexistence and cooperation between the formal and informed financial sector is commonly referred to as:
(a) Flexibility of operation
(b) Financial dualism
(c) Well regulated financial system
(d) Catering the financial needs of modern economy
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is financial dualism.
- The formal financial sector refers to regulated and organized institutions like banks, credit unions, and financial markets that operate under government supervision.
- On the other hand, the informal financial sector consists of unregulated and often community-based systems, like moneylenders, rotating savings and credit associations (ROSCAs), and microfinance groups.
Important Points
- Financial dualism refers to the coexistence of a formal and informal financial sector in an economy.
- The formal financial sector is regulated by the government and includes banks, microfinance institutions, and other financial institutions that offer a variety of financial services, such as savings accounts, loans, and insurance.
- The informal financial sector is unregulated and includes a variety of traditional financial institutions, such as money lenders, rotating savings and credit associations (ROSCAs), and pawnbrokers.
- Financial dualism may exist because of cultural factors. Some people may prefer to use the informal financial sector because it is more familiar to them or because they do not trust the formal financial sector.
- There are a number of benefits to financial dualism.
- The informal financial sector can provide financial services to people who would not otherwise have access to them.
- This can help to promote economic growth and development. The informal financial sector can also help to reduce poverty by providing people with the financial resources they need to start or grow a business.
some examples of cooperation between the formal and informal financial sectors -
- Banks may offer mobile banking services to reach customers in rural areas.
- Insurance companies may offer micro-insurance products to low-income people.
- Governments may provide training and financial support to informal financial institutions.
Q28: Identify the correct sequence of the leadership development process as adopted by Anderson Consulting.
A. Coach executive terms on individual leadership and effective teamwork
B. Assess organisation's direction and current strategies speed at which successful results he achieved
C. Create effective communication strategies for key influences directors shareholder employees etc
D. coach individual executives performed behavior along communications
E. Assessing the organization's culture, defining expected shifts, and developing an action plan for change in the work culture by the person leading the charge.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, D, B, A, E
(b) E, B, A, C, D
(c) D, A, B, E, C
(d) B, E, D, A, C
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is B, E, D, A, C.
- Leadership development process refers to a structured and intentional approach to nurturing and enhancing leadership skills and qualities in individuals.
- It involves activities, training, and experiences aimed at cultivating traits like communication, decision-making, and team building.
Important Points
- Anderson Consulting's leadership development process is based on the belief that leadership is a skill that can be learned and developed.
- The process is designed to help employees to develop the skills and knowledge they need to be effective leaders.
- Anderson Consulting uses a variety of methods to identify the employees who have the potential to become leaders in the future.
The correct sequence of the leadership development process as adopted by Anderson Consulting is as follows -
- Identify the leadership talent pipeline - This involves identifying the employees who have the potential to become leaders in the future. Anderson Consulting uses a variety of methods to do this, including performance reviews, assessments, and feedback from managers.
- Develop a leadership development plan for each employee - This plan should be tailored to the individual's needs and goals, and it should identify the specific training and development activities that the employee needs to undertake.
- Provide leadership training and development opportunities - Anderson Consulting offers a variety of leadership training programs, including in-class training, online courses, and coaching.
- Provide mentorship and support - Anderson Consulting encourages its leaders to mentor and support their employees. This can help employees to develop their leadership skills and to prepare for more senior roles.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the leadership development process - Anderson Consulting regularly evaluates the effectiveness of its leadership development process to ensure that it is meeting the needs of the organization and its employees.
Q29: Which of the following enumerates the distinctive features of Management Audit?
A. It is an appraisal of both policies and actions
B. It is preventive as well as creative check of cost accounting data
C. It is organisation oriented
D. It is dynamic and result oriented rather than simply procedure bound
E. It ensures the sound and healthy growth of business organisation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D only
(b) A, C, E only
(c) B, D, E only
(d) A, D, E only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A, D, E only. Explanation
- A management audit is an independent and systematic evaluation of an organization's management system and processes.
- It is conducted to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of management in carrying out its responsibilities, and to identify areas for improvement.
- Management audits can be conducted by internal auditors, external auditors, or a combination of both.
- Internal auditors are employees of the organization, while external auditors are independent contractors.
Important Points
The distinctive features of management audit -
Comprehensive -
- Management audits involve a thorough assessment of various aspects of management practices, processes, and performance within an organization.
- It aims to provide a holistic view of how the organization is managed.
Objective -
- The audit is conducted with objectively and impartiality.
- The auditors or consultants conducting the management audit should not have any bias that could influence their findings and recommendations.
Systematic -
- Management audits follow a structured and systematic approach to gather relevant data, analyze information, and identify areas of improvement.
- It ensures that the audit is conducted in a methodical manner.
Appraisal of both policies and actions -
- Management audit is not just a review of the organization's policies and procedures.
- It also assesses how effectively these policies and procedures are being implemented.
Dynamic and result oriented -
- Management audit is not a static process.
- It must be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the organization's environment and to new challenges that the organization faces. Management audit is also focused on achieving results.
- It is not simply a compliance exercise.
Sound and healthy growth of the organization -
- The ultimate goal of management audit is to help the organization to grow and succeed.
- Management auditors identify areas where the organization can improve its performance and efficiency.
Thus, correct answer is A, D, E only.
Q30: Matrix structure is the realisation of two dimensional structure which emanates directly from two dimensions of authority. From which of the two, a is matrix structure is created?
(a) Functional and divisional
(b) Functional and project
(c) Functional and line
(d) Divisional and line
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Functional and project.Important Points
- A matrix structure is a combination of two or more organizational structures, such as functional and project management.
- In a matrix structure, employees report to both a functional manager and a project manager.
- The functional manager is responsible for the employee's day-to-day work, while the project manager is responsible for the employee's work on a specific project.
The two dimensions of authority in a matrix structure are -
- Functional authority - Functional authority is the authority to make decisions about the work of a department or function. Functional managers have functional authority over their employees.
- Project authority - Project authority is the authority to make decisions about the work of a specific project. Project managers have project authority over the employees assigned to their projects.
- The two-dimensional structure of a matrix structure is created by the intersection of functional authority and project authority.
- This can be visualized as a grid, with functional departments on one axis and projects on the other axis.
- Employees in a matrix structure are located at the intersection of their functional department and the project(s) they are assigned to.
Q31: The problem of persistent current account deficit can be avoided by pursuing which of the following polices?
A. Encouraging Savings
B. Controlling fiscal deficit
C. Devaluation of the domestic currency
D. Curtailing productivity
E. Reduced dependence in costly external commercial borrowings
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D only
(b) B, C, E only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) D, E, A only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is B, C, E only.
Explanation
- A current account deficit indicates that a nation is importing more goods, services, and capital than it is exporting.
- This deficit must be financed through borrowing or by using reserves.
- A sustained current account deficit can lead to a nation's increased indebtedness or a decrease in its foreign exchange reserves, which can have implications for its overall economic stability and long-term growth.
Important Points The problem of persistent current account deficit can be avoided by pursuing the following policies -
Controlling fiscal deficit -
- A fiscal deficit is when a government spends more money than it collects in taxes.
- This can lead to a current account deficit because the government needs to borrow money to finance its spending.
- By controlling the fiscal deficit, the government can reduce its need to borrow money and improve the current account balance.
Devaluation of the domestic currency -
- Devaluation of the domestic currency makes exports cheaper and imports more expensive.
- This can lead to an increase in exports and a decrease in imports, which can help to improve the current account balance.
Reduced dependence in costly external commercial borrowings -
- External commercial borrowings are loans that a country takes from foreign banks and other financial institutions.
- These loans can be expensive, and they can increase a country's debt burden.
- By reducing its dependence on external commercial borrowings, a country can improve its current account balance.
The other options are not effective ways to reduce a persistent current account deficit -
- Encouraging Savings - Encouraging savings can help to reduce the demand for imports, but it will not necessarily lead to an increase in exports.
- Curtailing productivity - Curtailing productivity will lead to a decrease in both exports and imports. However, it will also lead to a decline in economic growth.
Q32: One of the key assumptions of the Boston Consulting Group Growth Share matrix is
(a) Cash flow can be equated with profitability.
(b) Market share has a positive effect on cash flow as profits are related to market share.
(c) Market share acts as a proxy to competitive strength.
(d) Market growth rate cannot be used as a proxy to market attractiveness.
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Market share has a positive effect on cash flow as profits are related to market share.
- The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Growth-Share Matrix is a portfolio planning tool that helps businesses make strategic decisions about their product portfolio.
- It plots businesses into four quadrants based on market growth and relative market share: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs.
- The BCG Growth-Share Matrix can be used to make a variety of strategic decisions, such as which businesses to invest in, divest, or price differently.
Important PointsThe correct answer is Market share has a positive effect on cash flow as profits are related to market share.
- The BCG Growth-Share Matrix is based on the assumption that market share has a positive effect on cash flow.
- This is because businesses with a higher market share are more likely to have economies of scale, which can lead to lower costs and higher profits.
- Additionally, businesses with a higher market share are more likely to be able to charge higher prices for their products or services.
The other options are not assumptions of the BCG Growth-Share Matrix -
- Cash flow can be equated with profitability - Cash flow and profitability are not the same thing. Cash flow is the movement of money in and out of a business, while profitability is the amount of money that a business makes after all expenses have been paid.
- Market share acts as a proxy to competitive strength - Market share is not a perfect proxy for competitive strength. There are other factors that can contribute to competitive strength, such as customer loyalty, brand recognition, and product differentiation.
- Market growth rate cannot be used as a proxy to market attractiveness - Market growth rate can be used as a proxy for market attractiveness. A market with a high growth rate is likely to be more attractive to businesses than a market with a low growth rate.
Q33: Which one of the following is concerned with Endowment Policy?
(a) The issuer has advantage of receiving money at regular intervals of the policy with a specific sum of money at the expiry of the policy
(b) At the expiry of the policy. the insured receives the sum of insurance policy
(c) It covers the insured for the whole life. His nominee receives the assured sum with bonus after the death of insured
(d) The premium cost is high. If the insurer dies, the nominee receives the insurance amount
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is At the expiry of the policy. the insured receives the sum of insurance policy.
- An endowment policy is a type of life insurance contract that provides both a death benefit and a savings or investment component.
- It combines insurance coverage with a savings plan, allowing the policyholder to accumulate a lump sum amount over a specified period.
- If the policyholder survives the policy term, they receive the accumulated amount as a maturity benefit; in case of demise during the term, the beneficiary receives the death benefit.
- Additionally, endowment policies often offer bonuses or returns on investments, making them a popular choice for individuals seeking a combination of protection and savings.
- They are typically used for long-term financial goals like funding education or providing for retirement.
Important Points
Advantages for the Issuer in Receiving Regular Payments and a Specific Amount at Policy Expiry: This describes a scenario where the insurance company (issuer) benefits from receiving the regular premium payments from the policyholder and a certain sum of money at the end of the policy term. While the issuer does indeed receive regular payments in the form of premiums with most insurance policies, the end of the policy term usually involves a payout to the policyholder or their beneficiaries, not the issuer.
Sum of Insurance Paid to the Insured at Policy Expiry: This is a key characteristic of endowment policies. The policyholder, or "the insured," receives a lump sum payment at the end of the policy term if they are still alive. If the policyholder dies during the term, the death benefit is paid to the nominee.
Whole Life Coverage with Sum Assured Plus Bonus to the Nominee after the Policyholder’s Death: This statement is more characteristic of a whole life insurance policy as they are designed to provide lifelong coverage. The policyholder's beneficiaries (or "nominee") receive an assured sum along with any bonuses or dividends upon the policyholder's death.
High-Premium Cost, with the Insurance Amount Going to the Nominee upon the Insurer’s death: While it's true that insurance policies can have high premiums (such as whole life insurance), the receiving of the insurance amount by the nominee upon death of the insurer can be a characteristic of many life insurance policies, not just endowment policies. This statement describes life insurance in a broader sense, so it doesn't specifically pertain to endowment policies.
So, option 2 correctly pertains to the features and benefits of an Endowment Policy.
Q34: Which of the following elements cause problem in application of internal rate of return method while evaluating mutually exclusive projects?
A. Discount rate
B. Timing
C. Scale
D. Reversing flow
E. Leverage
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B only
(b) D, E only
(c) B, C only
(d) A, D only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is B, C only.
Let's analyze each statement:
Discount Rate
- This option is incorrect because:
- The internal rate of return (IRR) method itself doesn't directly focus on the discount rate; it determines the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) zero.
- When comparing mutually exclusive projects, IRR doesn't directly address differences caused by varying discount rates.
Timing
- This option is correct because:
- IRR may not accurately handle projects with different cash flow timings.
- Projects with early returns versus those with later returns can yield misleading IRR results, leading to potentially poor decision-making.
Scale
- This option is correct because:
- The IRR method doesn't consider the scale or size of projects.
- Comparing projects of different scales using IRR can be misleading, as a higher IRR on a small project might be less desirable than a lower IRR on a larger project.
Reversing Flow
- This option is incorrect because:
- Reversing flow (changes in the direction of cash flows) can complicate IRR calculations but isn't a fundamental problem in comparing mutually exclusive projects.
- Multiple IRRs can exist if cash flows change direction, but this issue isn't specific to project scale or timing differences.
Leverage
- This option is incorrect because:
- Leverage refers to the use of borrowed capital to finance a project, which isn't a direct concern when comparing the IRR of mutually exclusive projects.
- IRR analysis typically assumes project financing is separate from evaluation.
Based on the evaluation above, the correct answer is option 3: B and C, as these statements correctly describe aspects of the limitations of the IRR method when evaluating mutually exclusive projects.
Q35: Which of the following shapes are used to describe the long-run average cost curve?
A. S-shape
B. L-shape
C. V-shape
D. U-shape
E. W-shape
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B and D only
(c) C and E only
(d) C and D only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is B and D only.
- The long-run average cost (LRAC) curve is a graphical representation in economics that illustrates the lowest average cost per unit of output attainable when all factors of production, including capital, are variable.
- In other words, it shows the relationship between the scale of production and the average cost per unit in the long run.
Important Points
The long-run average cost curve (LAC) is a curve that shows the relationship between the average cost of producing a good or service and the quantity of output produced in the long run.
U-shape -
- The LAC curve is typically U-shaped, meaning that the average cost of production decreases as output increases to a certain point, and then begins to increase again.
- The LAC curve is U-shaped for a number of reasons. At low levels of output, firms may experience economies of scale.
- This means that the average cost of production decreases as output increases because the firm is able to spread its fixed costs over a larger number of units.
- However, at high levels of output, firms may experience diseconomies of scale.
- This means that the average cost of production increases as output increases because the firm becomes less efficient.
L-shape -
- The L-shaped LAC curve is a special case of the U-shaped LAC curve.
- It occurs when the firm reaches the minimum efficient scale of production.
- At this point, the average cost of production is the lowest possible and the LAC curve becomes horizontal.
Q36: The Model for Budget or "No frills" airlines was first developed in the USA by Southwest Airlines in the 1970s. The premise of this budget airline was to get passengers to their destination for less with an "adequate" level of service. This highly successful model has since been copied by airlines all over the world. The competitive advantage of budget airlines arises from the following.
(a) Sound Positioning
(b) Maintaining low operating costs while increasing revenue
(c) Effective market segmentation & Targetting
(d) Aggressive advertising
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Maintaining low operating costs while increasing revenue.
Explanation
- A budget refers to a detailed financial plan that outlines estimated revenues and expenses over a specific period, typically a fiscal year.
- It serves as a blueprint for managing and allocating resources, guiding an individual, organization, or government in achieving its financial goals.
- Budgets can cover various aspects, including income, expenditures, savings, and investments.
Important PointsBudget airlines offer lower fares than traditional airlines by maintaining low operating costs. This is achieved by -
- Using a single type of aircraft, which reduces training and maintenance costs.
- Operating from secondary airports, which have lower landing fees and other charges.
- Offering a limited range of services, such as no free baggage or meals.
- Having a high employee turnover rate, which keeps labor costs down.
Budget airlines also increase revenue by -
- Charging for additional services, such as checked baggage and seat assignments.
- Selling advertising space on their aircraft and websites.
- Partnering with other businesses, such as hotels and car rental companies, to offer discounts to their customers.
The other options are not as important to the competitive advantage of budget airlines -
- Effective market segmentation & Targeting - Budget airlines typically target price-sensitive travelers. They may also target specific markets, such as business travelers or leisure travelers.
- Aggressive advertising - Budget airlines often use aggressive advertising to promote their low fares. However, this is not as important to their competitive advantage as maintaining low operating costs and increasing revenue.
In conclusion, the competitive advantage of budget airlines arises from their ability to maintain low operating costs while increasing revenue. This allows them to offer lower fares than traditional airlines. Thus, option 2 is correct answer.
Q37: Sequence the following statistical distribution and tests in the increasing order of symmetry
A. Z-distribution
B. Chi-square distribution
C. T-distribution
D. F-distribution
E. Uniform distribution
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, B, E, A, C
(b) B, C, D, A, E
(c) E, B, D, C, A
(d) C, D, E, A, B
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is E, B, D, C, A.
- Symmetry means having two identical halves that are a mirror image of each other. In other words, if the object folded in half, the two halves will match perfectly.
- A statistical distribution is a description of how a set of data is spread out. It can be shown graphically as a histogram or a probability density function (PDF). The PDF shows the probability of each value in the data set occurring.
Important Points
Statistical distributions can be classified based on their symmetry are as follows-
Uniform distribution -
- The uniform distribution is a continuous distribution in which all values are equally likely.
- This means that the PDF is a flat line across the range of possible values.
Chi-square distribution -
- The chi-square distribution is a continuous distribution that is used to test goodness-of-fit and to compare observed and expected frequencies.
- It is right-skewed, meaning that most of the values are clustered towards the left and the tail of the distribution extends to the right.
F-distribution -
- The F-distribution is a continuous distribution that is used to compare the variances of two populations.
- It is right-skewed, similar to the chi-square distribution.
T-distribution -
- The T-distribution is a continuous distribution that is used to test hypotheses about population means when the population standard deviation is unknown.
- It is similar to the normal distribution, but with heavier tails.
- This means that the T-distribution is more likely to produce extreme values than the normal distribution.
Z-distribution -
- The Z-distribution is a continuous distribution that is also known as the standard normal distribution.
- It is symmetric, meaning that the PDF is the same on both sides of the mean.
- The Z-distribution is used to calculate z-scores, which can be used to compare values from different distributions.
Q38: Published by the UNDP. the HDI is summary measure of human development. It measures the average achievements of a country in three basic dimensions of human development and include the following.
(a) Standard of living. Income and Occupation
(b) Education. Occupation and Health
(c) Health. Education and Standard of living
(d) Poverty. Health and Standard of living
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Health. Education and Standard of living .
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite index published by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) that provides a summary measure of human development in different countries.
Important Points
It assesses a country's overall development by considering three fundamental dimensions -
- Health - This dimension is measured by life expectancy at birth. It reflects the average number of years a person is expected to live, indicating the overall health and well-being of a population.
- Education - This dimension is assessed using two indicators: mean years of schooling for adults aged 25 years or older, and expected years of schooling for children entering school. These indicators reflect the level of educational attainment in a country.
- Standard of Living- This dimension is represented by Gross National Income (GNI) per capita, adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP) to account for differences in the cost of living between countries. GNI per capita is a measure of a country's economic well-being.
- These three dimensions - health, education, and standard of living - are considered essential components of human development.
- By combining indicators from these dimensions, the HDI offers a comprehensive assessment of a country's overall development status.
- This allows for meaningful comparisons between countries and provides insights into the well-being and quality of life of their populations.
Q39: Match List I with List II Multiple purposes of performance assessment.
Choose the correct answer answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(d) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
These points are related to is "Performance Management". In the field of Human Resource Management, performance management includes activities that ensure goals are consistently met in an effective and efficient manner. It can focus on the performance of an organization, a department, an employee, or the processes in place to manage tasks. These activities involve performance assessment or review, training and development needs identification, administrative decision making based on performance data, and necessary documentation for legal and research purposes.
Here's an explanation for each point in the context of the matching points:
Development Uses - Identification of individual needs, strengths, and performance feedback. This refers to the use of performance assessment as a tool to identify a person's professional development needs, their strengths, and areas for improvement. The output from such an assessment can be used to provide constructive feedback for the individual, facilitate their growth, and improve their performance in their role. This can include identifying training needs or setting up a coaching or mentoring relationship.
Administrative Uses' Decisions - Identification for performance, recognition, individual performance, salary. promotion, termination. Here, performance assessment is used as a tool to make administrative decisions related to the employees. This includes decisions related to recognising their performance, adjusting their salary, considering them for promotions, or even employment termination in some cases. It ensures fair decision making in the organisation and helps to retain the best performers while letting go of poor performers.
Organisational Maintained Objectives - HR planning, Determining organisation training needs. Performance assessments can be implicitly linked to organisational goals and objectives. The outcomes of performance assessments can be used in HR planning, helping the organisation align its HR policies and strategies with the overall business objectives. Additionally, performance assessments can help determine the overall training and development needs of the organisation, guiding decisions about what training programs need to be implemented to improve overall organisational performance.
Documentation - Critics of validity research, Helping meet legal requirement. Documentation is a critical aspect of performance assessment. It serves as a record of an employee's performance over a certain period, which can be used for various purposes including legal requirements. It provides evidence of an employee's performance, abilities, and progress. The valid and supportive documentation can also help organizations respond to critics of validity research, showing that their assessments or tests are effective and unbiased.
Q40: Based on the relationship between marginal revenue product (MRP) and marginal resource cost (MRC), when it pays for the firm to expand the use of variable factor input?
(a) MRP > MRC
(b) MRP < MRC
(c) MRP = MRC
(d) MRP = MRC = 1
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is MRP > MRC.
- MRP (Marginal Revenue Product) is the additional amount of revenue that a firm earns as a result of hiring an additional unit of input (like labor).
- MRC (Marginal Resource Cost) is the additional cost incurred as a result of hiring that additional unit.
- When MRP is greater than MRC, this indicates that the extra revenue obtained from selling the product made by an additional unit of input is greater than the cost of hiring that extra unit.
- This is an ideal opportunity for firms to gain more profit, as the gains exceed the costs.
- As the firm increases its usage of a variable input, both MRP and MRC typically change.
- The MRP tends to decrease due to diminishing marginal productivity - extra inputs become less productive when used in combination with a fixed quantity of another resource.
- Meanwhile, MRC tends to increase due to increasing marginal cost - it becomes more expensive to hire extra inputs the more you already have.
- Ideally, the firm would continue to hire more inputs up until the point where MRP equals MRC, where any further hiring would not generate profits.
- Thus, when MRP > MRC, it still pays for the firm to expand the use of variable factor input.
Q41: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The price elasticity of demand is greater, more and better substitutes are available for the commodity
Statement II: Normal goods (EI > 0) for which EI > 1 are called luxuries while those normal goods for which EI is between zero and one are considered necessities
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: A
Sol: Explanation Statement I: The price elasticity of demand is greater, more and better substitutes are available for the commodity
- Price elasticity of demand is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded of a product to the percentage change in price.
- If price elasticity is greater than 1, the good is elastic; if less than 1, it is inelastic.
- If the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1, it is deemed elastic. That is, demand for the product is sensitive to an increase in price
Hence Statement I is correct.
Statement II: Normal goods (EI > O) for which EI > 1 are called luxuries while those normal goods for which EI is between zero and one are considered necessities
- A normal good is a good that experiences an increase in demand due to an increase in a consumer's income. Normal goods have a positive correlation between income and demand. Examples of normal goods include food, clothing, and household appliances.
- A normal good has an Income Elasticity of Demand > 0. This means the demand for a normal good will increase as the consumer’s income increases.
- Luxury goods usually have Income Elasticity of Demand > 1, which means they are income elastic. This implies that consumer demand is more responsive to a change in income. For example, diamonds are a luxury good that is income elastic
- A Giffen good has a negative income elasticity of demand and a relatively small substitution effect, i.e. the good does not have any close substitutes so when its price rises people find it difficult to switch to cheaper alternatives.
- Income Elasticity of Demand = 0 means that the demand for the good isn’t affected by a change in income and those normal goods for which EI is between zero and one are considered necessities
Hence Statement II is correct.
Therefore we can say that Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Q42: Which of the following are considered as off balance sheet activities of a commercial Bank.
A. Lending money to a depositor
B. Borrowing from RBI
C. Purchasing a future contract
D. Issuing letter of credit
E. Engaging in Swap Contract
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, E, D only
(b) B, C, E only
(c) B, D, C only
(d) A, C, E only
Ans: C
Sol: To protect themselves against interest rate increases, banks go off road, engaging in activities that do not appear on their balance sheets.These activities will appear on revenue statements, cash flow analyses, etc. Explanation
Off-Balance Activities:
Letters of Credit
- A letter of credit (LOC) is a document issued by a bank on behalf of its customer authorizing a third party to draw drafts on the bank up to a stipulated amount under specific terms and conditions. A letter of credit is a conditional commitment (except when prepaid by the account party) on the bank’s part to pay drafts drawn in accordance with the document’s terms
Loan Commitments
- A loan commitment is a written agreement, signed by the borrower and bank, detailing the terms and conditions under which the bank will fund a loan. The commitment will specify a funding limit and have an expiration date. For agreeing to make the accommodation, the bank may require a fee and/or maintenance of a stipulated compensating deposit balance from the customer
Borrowing from RBI:
- The commercial banks borrow money from the Reserve Bank of India by selling securities or bonds with an agreement to repurchase the securities on a certain date at a predetermined price.
Derivatives trading
- It can be used to hedge or reduce interest rate risks but can also be used by risky bankers or rogue traders to increase risk to the point of endangering a bank’s capital cushion and hence its economic existence.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is B, D, C only.
Q43: Before writing the research report (Pre-writing), a researcher usually considers
A. Purpose of study
B. Readers of report
C. Climax order of report
D. Visualization of report
E. Uses of report
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, D, E only
(b) A, C, E only
(c) E, B, A only
(d) D, B, A only
Ans: C
Sol: Explanation
- Before writing the research report (Pre-writing), a researcher usually considers
- Research Purpose:
- There always is a primary goal that the researcher is trying to achieve through a report. In the introduction section, he/she can cover answers related to this goal and establish a thesis which will be included to strive and answer it in detail.
- Uses of report:
- The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of research studies to a wider audience. The report should be clear, concise, and well-organised so that readers can easily understand the information presented.
- Readers of report:
- The target audience is the specific group of people to whom researchers seek to generalize their findings. It is critical to select a sample that appropriately represents the target audiences in order to generate robust and applicable results.
- Have a clear research objective:
- A researcher should read the entire proposal again, and make sure that the data they provide contributes to the objectives that were raised from the beginning. Remember that speculations are for conversations, not for research reports, if a researcher speculates, they directly question their own research.
- Establish a working model:
- Each study must have an internal logic, which will have to be established in the report and in the evidence. The researchers’ worst nightmare is to be required to write research reports and realize that key questions were not included.
- Research Purpose:
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is E, B, A only,
Q44: What are the different strategies firms resort to "pricing to capture ______
A. Challenge the cost route by identifying the inflection price point
B. Offering lower/aggressive price point
C. Penetration pricing
D. 'What the traffic can bear' pricing
E. Absorption cost pricing
Choose the most appropriate from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) D and E only
(c) A and B only
(d) B and E only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A and B only.
Key Points
Challenge the cost route
- This strategy involves a detailed understanding of the market's reaction to pricing.
- The firm identifies the price point at which sales volumes significantly increase or decrease.
- They aim to set the pricing at this 'inflection point' to maximize profitability and capture market share by attracting more customers.
Offering lower/aggressive price points
- This is a pricing strategy aimed at capturing a larger chunk of the market share quickly by offering prices significantly lower than the competitors.
- By doing so, more consumers will be inclined to try the product or service, boosting sales volume rapidly.
Penetration pricing
- This is very similar to option B. Penetration pricing involves setting a lower initial price to attract customers, penetrate the market quickly, and stimulate word of mouth.
- Once the consumer base is established, prices may rise as brand loyalty strengthens.
'What the traffic can bear' pricing
- This approach involves setting prices at a level that consumers are willing to pay, rather than pricing based on the cost of production or services.
- This strategy is more effective in markets where the firm's product or service is unique or when demand is incredibly high, and consumers are ready to pay more.
Absorption cost pricing
- This pricing strategy sets the product price to cover all variable and fixed costs, aiming to absorb all costs related to the product's production.
- This is achieved by dividing the total cost associated with creating the product by the total quantity produced, allowing firms to ensure all costs are covered.
- This can be a safer pricing strategy that ensures each unit sold contributes to the absorption of production costs.
Q45: Match List I with List II.
Choose the correct answer answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Explanation
The buyer-seller relationship is typically divided into several stages that describe the progression of the relationship over time. Here is a brief explanation of the four stages you've mentioned:
- Pre-relationship stage: This is the beginning stage where the seller is working on attracting the buyer's attention and the buyer is identifying their needs. The seller utilizes various marketing efforts to create awareness about their products or services. On the other hand, the buyer is recognizing their need for a product or service, and is conducting initial research, often by gathering information from multiple sources about potential sellers and solutions. This stage is pivotal for creating a strong, positive first impression that can lay the groundwork for a successful relationship.
- Early stage: Once the buyer's interest has been piqued, they may move on to a seller and start to develop a more in-depth understanding of how the seller's product or service can meet their needs. This stage often includes more focused information exchange, including sales presentations, product demonstrations, consultations, and the beginning of negotiations. Both parties will begin to explore the potential benefits of a relationship and assess whether or not it's a good fit.
- Development stage: In this stage, the buyer has already chosen the seller's product or service and the focus of the relationship shifts towards nurturing and development. The seller works to ensure that the product or service delivers on its promise and meets or exceeds the buyer's expectations. This can involve ongoing customer service, seeking out feedback, troubleshooting any issues that arise, and demonstrating consistent value. As trust and satisfaction build over time through repeated successful exchanges, the relationship strengthens and the buyer is likely to become a repeat customer.
- Long-term stage: This is the most mature stage of the buyer-seller relationship, where both parties have formed a strong and stable rapport. There is a high degree of mutual understanding, trust, and satisfaction. The seller considers the buyer to be a loyal customer and may make special efforts to maintain the relationship, such as providing special offers, anticipating future needs, or providing preferential treatment. The buyer, on the other hand, perceives the seller as a reliable supplier for their needs and often recommends the seller to others, hence becoming an advocate.
Q46: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The judgmental attribution error is the tendency to over estimate the of external factor and underestimate influence of external factor underestimate the influence of internal factors when making indgements about the behavior of others
Statement II: Self-seeing bias is the tendency for individual to attribute then own success to internal factors while pulling the blame for failures on external factors
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: D
Sol: Statement I: The judgmental attribution error is the tendency to over estimate the of external factor and underestimate influence of external factor underestimate the influence of internal factors when making judgments about the behavior of others
Fundamental attribution error :
- Fundamental attribution error — or “correspondence bias,” as it’s also called — essentially attributes a person’s behavior to their personality. It fails to consider any situational factors that may play a part.
- It makes people to overemphasize personal characteristics and ignore situational factors in judging others' behavior.
- It underestimates the influence of external factors and overestimate the influence of internal factors when making judgments about the behavior of others
Hence Statement I is incorrect.
Statement II: self-serving bias is the tendency for individual to attribute their own success to internal factors while putting the blame for failures on external factors
- Self-serving attributions.
- This bias gives all the credit of success to the individual, while all the failures are blamed on external circumstances.
- It refers to how we explain our behavior depending on whether the outcome of our behavior is positive or negative. For example, an athlete is more likely to attribute a good performance on their own ability, and a poor one on external causes like the event environment
Hence Statement II is correct.
Therefore we can say that Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Q47: Which of the following economic narratives relates the trade between any two countries to the sign of their economics?
(a) Phillips Curve
(b) Fisher effect
(c) Gravity model
(d) Kuznets Curve
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Gravity model.
Explanation
- The Theory of Comparative Advantage, first formulated by economist David Ricardo, argues that countries should specialize in producing goods and services in which they have a lower opportunity cost and then trade with other countries to obtain goods and services that they cannot produce as efficiently.
- This theory emphasizes that even if one country is less efficient in producing all goods compared to another country, there are still gains from trade for both parties.
Important Points Gravity model
- The gravity model of trade is a model that predicts the volume of trade between two countries based on their economic sizes and distance.
- The model is based on the analogy of Newton's law of gravity, which states that the force of gravity between two objects is proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- In the gravity model of trade, the economic size of a country is typically measured by its GDP.
- The distance between two countries is typically measured by the geographical distance between their capitals.
- The gravity model is a positive relationship, meaning that the trade between two countries is expected to increase as their economic sizes increase and the distance between them decreases.
The other options are not related to the sign of the economics of two countries -
- Phillips Curve - The Phillips curve is a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment.
- Fisher effect - The Fisher effect is a positive relationship between nominal interest rates and expected inflation.
- Kuznets Curve - The Kuznets curve is a negative relationship between income inequality and economic development.
Q48: A business has been discontinued in the previous year 2021-22. The business loss.
(a) Can be carried forward and set off against profit gain of business and profession
(b) Can be set off against income from business or profession or income under any other head
(c) Can be carried forward and set off for indefinite period. whether business is carried or discontinued
(d) Can be carried forward and set off for six years, whether business is carried or discontinued
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Can be carried forward and set off against profit gain of business and profession
Provisions for losses in IT Act:
Set off of losses
- Set off of losses means adjusting the losses against the profit or income of that particular year.
- Losses that are not set off against income in the same year can be carried forward to the subsequent years for set off against income of those years
Intra-head Set Off
- The losses from one source of income can be set off against income from another source under the same head of income.
- For eg: Loss from Business A can be set off against profit from Business B, where Business A is one source and Business B is another source and the common head of income is “Business”.
Inter-head Set Off
- After the intra-head adjustments, the taxpayers can set off remaining losses against income from other heads.
- Eg. Loss from house property can be set off against salary income.
Carry forward of losses
- After making the appropriate and permissible intra-head and inter-head adjustments, there could still be unadjusted losses.
- These unadjusted losses can be carried forward to future years for adjustments against income of these years.
- E.g A business has been discontinued in the previous year 2021-22.
- The business loss Can be carried forward and set off against profit gain of business and profession
Q49: What are the correct steps of procedures of e-filing of Income Tax Return?
A. Filing details and computation of tax
B. Generate XML file. filing income tax return and use of digital signature
C. Register and login on portal and select applicable return form
D. Use of ITR form V and sending ITR-V form to CPC
E. Making payment of balance tax and confirm the data provided
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, C, E, B
(b) C, A, E, B, D
(c) A, C, D, E, B
(d) A, B, C, D, E
Ans: B
Sol: Step by Step Guide on How to E-file ITR on Income Tax Portal
Step 1: Login
- Register and login on portal and select applicable return form
Step 2: Go to ‘File Income Tax Return’:
- File details and computation of tax
Step 3: Select the right ‘Assessment Year’
Step 4: Select status
Step 5: Select ITR type
Step 6: Choose the reason for filing ITR
Step 7: Add Bank Account Details and Other Information
- Making payment of balance tax and contain the data provided for
STEP 5. Fill form and upload
- If you choose to fill the form offline, after you have downloaded the form and filled all the details, click on 'generate XML'. Then go to the website again and click on the 'upload XML' button. You will have to first log in to upload the XML file saved on desktop and click on submit.
Step 8: e-Verify ITR:
- On submitting ITR form, an acknowledgement number is generated. In case the return is submitted using digital signature, you just have to preserve this number. If the return is submitted without a digital signature, an ITR-V is generated and is sent to your registered email ID.The tax filing process is incomplete and ITR is invalid unless your ITR V is verified.
Therefore we conclude that the correct answer is C, A, E, B, D.
Q50: Match List I with List II.
Choose the correct answer answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: Explanation 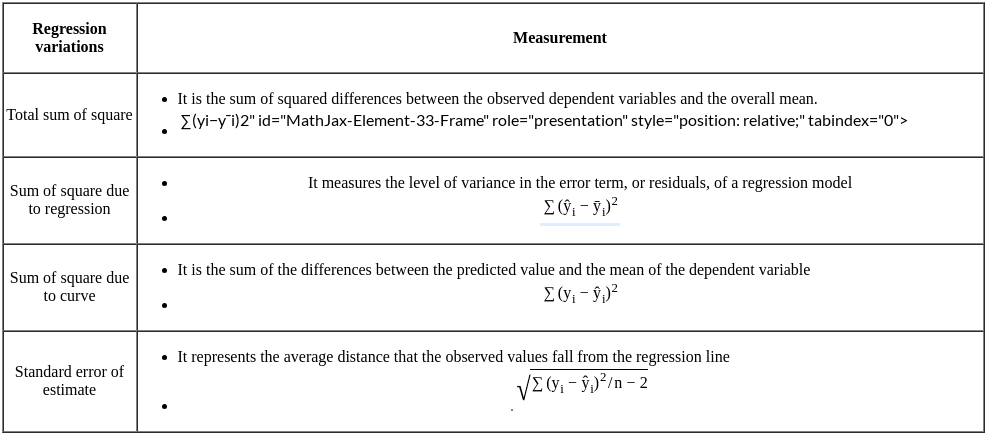 Therefore we can say that the correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV.
Q51: The following are the hallmarks of an effective marketing mix:
A. The marketing mix matches customer needs
B. The marketing mix ensures high probability
C. The marketing mix contain a competitive advantage
D. The marketing mix is well blended and matches corporate resources
E. The marketing mix adheres to ethical principles
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) A, C, D only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) B, C, D only
Ans: B
Sol: The four primary elements of a marketing mix are product, price, placement, and promotion. This framework aims to create a comprehensive plan to distinguish a product or service from competitors that creates value for the customer.
Following are the hallmarks of an effective marketing mix::
- The marketing mix should be well blended to form a consistent theme.
- If the product gives superior benefits to customers, the price which sends cues to customers regarding quality should reflect those extra benefits.
- All the elements of the promotional mix should be designed with the objective of communicating a consistent image.
- All the element of the marketing mix should reinforce each other to strengthen the positioning of the product in the marketplace.
- The marketing mix contains a competitive advantage to generate more business
- The marketing mix should match corporate resources.
- It is always tempting to provide to the customer the highest quality product at the lowest price, in a way most convenience to him, with the offering promoted in the most sophisticated way.
- But such a marketing mix would be very costly to provide. The choice of the marketing mix will be constrained by the financial resources and internal competencies of the company, and the customers willingness and ability to pay for such an exalted marketing mix.
- The marketing mix should be well blended and match corporate resources
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is A, C, D only.
Q52: The employer has provided the facility of a 1.8 litre (c.c) car. The car is used for private purposes also and all the expenses including the driver salary are borne by the employer. The expenses of employer during the previous year amounted to Rs. 60,000 and the employer has recovered Rs 1000 per month from the employee for this facility. What amount per year shall be reduced by the employer from actual amount of expenditure.
(a) 32,400
(b) 16,800
(c) 39,600
(d) 21,600
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 39,600.
- Under Section 17(2)(iii) of the Income Tax Act, 1961, the amount that can be deducted by an employer from an employee's salary is the amount paid by the employer to the employee as a contribution to a pension fund or provident fund.
- The maximum amount that can be deducted is 10% of the employee's salary.
some examples of contributions to a pension fund or provident fund that can be deducted by the employer under Section 17(2)(iii):
- Contributions to the Employees' Provident Fund (EPF)
- Contributions to the Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- Contributions to a superannuation fund
- Contributions to a gratuity fund
Important Points
The value of the perquisite provided by the employer is calculated as follows -
- Value of car used for personal purposes: Rs. 1800 per month.
- Value of driver salary: Rs. 900 per month.
- Therefore, the total value of the perquisite is Rs. 2700 per month.
- The employer has recovered Rs. 1000 per month from the employee. Therefore, the net value of the perquisite is Rs. 1700 per month.
- The annual value of the perquisite is Rs. 1700 x 12 = Rs. 20,400.
- However, the employer has incurred actual expenses of Rs. 60,000.
- Therefore, the amount that should be reduced by the employer from the actual amount of expenditure is Rs. 60,000 - Rs. 20,400 = Rs. 39,600.
- The deduction of Rs. 39,600 will reduce the employee's taxable income. This will result in a lower tax liability for the employee.
Q53: Arrange the procedure to make payment using electronic cash ledger.
A. Generation of challan Identification number (CIM) and Amount credited to electronic cash ledger
B. Form GST PMT-07 and correction in electronic cash ledger
C. Challan with CIN (challan identification number) and mandate form payment through NEFT or RTGS mode
D. Generate the challan in form GST PMT-6 from portal and enter the details
E. Amount as per payment rule can be deposited by using internet banking, debit credit card etc.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, B, C, E
(b) A, B, C, D, E
(c) D, C, E, B, A
(d) B, C, D, E, A
Ans: C
Sol: Procedure for Depositing GST Payment
- The correct procedure to make payment using electronic cash ledger is as follows:
Generate the challan in form GST PMT-6 from the portal and enter the details (D): This step involves creating a payment challan by providing the necessary details such as the tax amount, type of tax, and period for which the payment is being made.
Generation of challan Identification number (CIN) and mandate form payment through NEFT or RTGS mode (C): After generating the challan, you receive a Challan Identification Number (CIN), and you can choose to make the payment using NEFT or RTGS mode by filling out the mandate form.
Amount as per payment rule can be deposited by using internet banking, debit/credit card, etc. (E): Once you have the CIN and mandate form, you can proceed to deposit the required amount through various payment methods, such as internet banking, debit/credit card, etc.
Form GST PMT-07 and correction in electronic cash ledger (B): In this step, you may use Form GST PMT-07 to make corrections in your electronic cash ledger, if necessary, or address any issues related to the ledger.
Amount credited to electronic cash ledger (A): Finally, the amount is credited to your electronic cash ledger after a successful payment, and the transaction is recorded.
So, the correct order is: D, C, E, B, A.
Q54: Four schedule have been added at the end of the Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act. the second schedule entertains which one of the following?
(a) Provisions to conversion from private company into limited Liability Partnership
(b) Provisions regarding matters to mutual rights and duties of partners and limited Liability Partnership and its partners applicable in the absence of any agreement on such matters
(c) Provisions relating to conversion of a firm into limited Liability Partnership
(d) Provisions for conversion from unlisted public company into limited Liability Partnership
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Provisions relating to conversion of a firm into limited Liability Partnership
The Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act in India includes four schedules that cover different aspects of the applicability, conversion, and structure of LLPs.
Specifically, each of the schedules covers the following aspects:
The First Schedule includes provisions about the mutual rights and duties of partners and of the LLP and its partners in situations when there is no agreement on these matters.
The Second Schedule details provisions for the conversion of a traditional partnership firm into a Limited Liability Partnership.
The Third Schedule provides guidelines for the conversion of private companies into an LLP.
The Fourth Schedule prescribes rules for converting an unlisted public company into an LLP.
So according to these definitions, the correct answer would be: The second schedule in the LLP Act covers provisions corresponding to the conversion of a partnership firm into a Limited Liability Partnership. Hence the correct option is 3) Provisions relating to conversion of a firm into Limited Liability partnership.
Q55: When no liability for payment of tax in advance arise by an assessee on his income if tax payable is
(a) Less than 10,000
(b) Less than 50,000
(c) Less than 5,00,000
(d) Less than 7,50,000
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Less than 10,000
Advance tax:
- As per section 208, every person whose estimated tax liability for the year is Rs. 10,000 or more, shall pay his tax in advance, in the form of “advance tax”
- However, a resident senior citizen (i.e., an individual of the age of 60 years or above during the relevant financial year) not having any income from business or profession is not liable to pay advance tax
- Advance tax is to be paid in different instalments. The due dates for payment of different instalments of advance tax are as follows:
Q56: Which of the following drive growth of international business in digitally interconnected world?
A. Strong consumption in global south
B. Dynamic exchange, interest and inflation rates
C. Formation of trade promoting regional groups
D. Regulated capital and portfolio flows
E. Demographic dividend and low cost manufacturing
Choose the most appropriate from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) B, D and E only
(d) A, C and E only
Ans: D
Sol: Following drive growth of international business in digitally interconnected world:
Technological advancements:
- Rapid advancements in technology, especially in communication and transportation, have made it easier and faster for people, goods, and information to move across borders. This has led to an increase in international trade, investment, and cultural exchange.
Regional integration
- It is a process in which neighboring countries agree to improve cooperation through shared institutions and rules.Examples: European Union (EU), SAARC, NAFTA, ASEAN, EFTA, etc
Strong consumption in global south:
- The Global South is a term that broadly comprises countries in the regions of Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia (without Israel, Japan, and South Korea), and Oceania (without Australia and New Zealand), according to UNCTAD
Demographic dividend and low cost manufacturing
- Demographic Dividend helps in increasing the workforce, there will be rapid urbanisation and industrialisation. It leads to more investment in physical and human infrastructure. The productivity of the country's economy increases due to increased labour force.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is A, C and E only.
Q57: Match List I with List II.
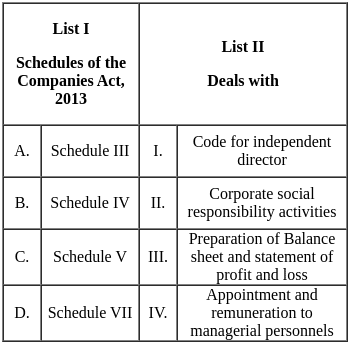
Choose the correct answer answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Ans: B
Sol: 
Explanation
Therefore we can say that correct matching code is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Q58: As the economy weakens, one would expect investment in ______ funds to increase and investment in ______ funds to decrease.
(a) long term : short term
(b) equity : bond
(c) money market mutual : equity
(d) municipal bonds: money market mutual funds
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is money market mutual : equity Explanation
Various Financial instruments:
Money market:
- A money market fund is a type of mutual fund that has relatively low risks compared to other mutual funds and most other investments and historically has had lower returns.
- Money market funds invest in high quality, short-term debt securities and pay dividends that generally reflect short-term interest rates.
Equity
- It represents the value that would be returned to a company's shareholders if all of the assets were liquidated and all of the company's debts were paid off.
- We can also think of equity as a degree of residual ownership in a firm or asset after subtracting all debts associated with that asset.
Municipal bonds (munis)
- These are debt securities issued by state and local governments.
- These can be thought of as loans that investors make to local governments, and are used to fund public works such as parks, libraries, bridges and roads, and other infrastructure.
- A bond is a loan that the bond purchaser, or bondholder, makes to the bond issuer. Governments, corporations and municipalities issue bonds when they need capital.
- An investor who buys a government bond is lending the government money. If an investor buys a corporate bond, the investor is lending the corporation money.
Q59: What are the positive attributes of mobile banking.
A. Negative experience in European countries
B. Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
C. Advanced Penetration of Mobile network
D. Less security
E. Faster data processing speed
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D only
(b) B, D, E only
(c) B, C, E only
(d) C, D, E only
Ans: C
Sol: Mobile Banking means the availability of banking services on mobile devices. A prominent mobile banking advantage is that it is akin to carrying a bank in our pocket.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Mobile Banking
WAP (wireless application protocol) based mobile banking
- It service wherein the customer can access the bank's website using the browser on their mobile phone
Time Saving
- Mobile Banking offers quick and instant banking services, eliminating dependence on banks for basic transactions
Monitoring Transactions
- Another mobile banking advantage is that it can track all your financial transactions. It can monitor your bank accounts and conveniently dispute fraudulent transactions simply by logging in to your mobile banking app.
Easy Access
- Whether some one wants to transfer funds, check account balances and statements, or apply for loans – you can do it all with mobile banking.
- We can order cheque books and apply for credit and debit cards, open fixed and recurring deposits, and more using your mobile banking app.
Faster data processing speed:
- Compared with other interfaces, mobile banking enables consumers to make faster payments across the greatest variety of uses, from bill payments to person-to-person transfers to in-person and online purchases
Security:
- Mobile apps are more likely to use multifactor authentication than an online banking website.These types of biometric logins can be especially helpful if your mobile phone is stolen as they’re harder to bypass than a password,
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is B, C, E only.
Q60: P, R and M are Partners in a firm. They shared profit and losses in the ratio of 3 ∶ 2 ∶ 1. On 1st April, R retired. The goodwill of the firm was valued at two years purchase based on the average of last three years profits. The Profits of the last three year were as under:
2020-21 Profit Rs 2,48,000
2021-22 Loss Rs 36,000
2022-23 Profit Rs 1,48,000
It was decided that share of goodwill be adjusted in the capital Accounts of P and M. What will be the amount of Goodwill of P and M?
(a) Rs. 60,000, Rs. 20,000
(b) Rs. 30,000, Rs. 50,000
(c) Rs. 30,000, Rs. 60,000
(d) Rs. 40,000, Rs. 70,000
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Rs. 60,000, Rs. 20,000
Step 1: Calculate Average Profit
- Sum of last three years' profits: Rs. 2,48,000 - Rs. 36,000 + Rs. 1,48,000 = Rs. 3,60,000
- Average Profit = Rs. 3,60,000 / 3 = Rs. 1,20,000
Step 2: Calculate Goodwill
- Goodwill = Average Profit × 2 Years Purchase
- Goodwill = Rs. 1,20,000 × 2 = Rs. 2,40,000
Step 3: Determine Old Ratio and New Ratio
- Old Ratio of P, R, and M: 3:2:1
- New Ratio of P and M after R's retirement: P:M = 3:1
- Therefore, P's new share = 3/4 and M's new share = 1/4
Step 4: Calculate P and M's Share of Goodwill Adjustment
- R's Goodwill Share = (Goodwill / Total Ratio) × R's Old Ratio
- R's Goodwill Share = (Rs. 2,40,000 / 6) × 2 = Rs. 80,000
- P and M will contribute to R's share of goodwill in their gaining ratio (which is same as their new ratio: 3:1)
- P's Contribution = Rs. 80,000 × 3/4 = Rs. 60,000
- M's Contribution = Rs. 80,000 × 1/4 = Rs. 20,000
Important Points
Further Clarifications:
- Goodwill Calculation: The process of calculating goodwill involves determining the average profit of the firm over a given period and multiplying it by a specific number of years purchase, as mentioned in the problem statement (2 years in this case).
- Adjustment of Goodwill: While adjusting the retiring partner's share of goodwill, the remaining partners bear the cost according to their new profit-sharing ratio.
- Old vs. New Ratio: Understanding the old ratio (3:2:1) and the new ratio (3:1) after the retirement is crucial for calculating individual contributions towards the retiring partner's share of the goodwill.
- Goodwill Distribution: The share of the retiring partner in the goodwill is distributed among the remaining partners based on their gaining ratio, which is determined by their new profit-sharing ratio.
- Equitable Distribution: This method ensures an equitable distribution of the retiring partner's share of goodwill, reflecting the increased stake and future profit rights of the remaining partners.
Q61: A company can issue shares at a discount subject to which of the following conditions?
A. Two year must have passed since the date at which the company was allowed to commence business
B. The shares to be issued must be of a class already issued
C. Issue must take place within three month after the date of the CLB approval
D. Issue of shares must be authorised by an ordinary resolution of the company
E. Resolution must specify the maximum rate of discount
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) B, D, E only
(d) C, D, E only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is B, D, E only.
Important Points Section 54 of the Companies Act, 2013, deals with the issue of shares at a discount. It states that a company can issue shares at a discount subject to the following conditions -
- The shares to be issued must be of a class already issued.
- Issue must take place within three months after the date of the CLB approval.
- Issue of shares must be authorized by an ordinary resolution of the company.
- Resolution must specify the maximum rate of discount.
- The maximum rate of discount is 10%, or such higher rate as may be fixed by the Central Government.
A company can issue shares at a discount only to its members, creditors, or employees.
The following are some of the reasons why a company may issue shares at a discount -
- To raise capital when the market value of the company's shares is below the par value.
- To reward employees or creditors for their loyalty or contributions to the company.
- To make the company's shares more affordable to small investors.
It is important to note that issuing shares at a discount can have some negative consequences, such as -
- It can dilute the earnings per share of existing shareholders.
- It can create a negative perception of the company in the market.
- It can make it more difficult for the company to raise capital in the future.
Therefore, companies should carefully consider the pros and cons of issuing shares at a discount before making a decision.
Q62: A T Kearney foreign Policy Globalization Index (2007) is a comprehensive framework to measure globalisation. It is based in 12
variables, grouped into which the following four baskets?
(a) Economic integration, Political integration, Knowledge Integration, Social Integration
(b) Personal Integration, Technological integration, Economic integration, Political integration
(c) Social integration, Political integration, Personal integration, Technological Integration
(d) Knowledge integration, Economic integration, Political integration Technological integration
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Personal Integration, Technological integration, Economic integration, Political integration.
Important Points
- The A.T. Kearney Foreign Policy Globalization Index (2007) is a comprehensive framework to measure globalization.
- It is based on 12 variables, grouped into the following four baskets -
- Personal integration - This basket measures the extent to which people around the world are connected to each other through travel, communication, and migration.
- Technological integration - This basket measures the extent to which people around the world are connected to each other through technology, such as the internet and telecommunications.
- Economic integration - This basket measures the extent to which people around the world are connected to each other through trade and investment.
- Political integration - This basket measures the extent to which people around the world are connected to each other through international organizations and agreements.
- The index is calculated by averaging the scores of the four baskets. The higher the index score, the more globalized a country is.
Q63: In a situation where the holding and subsidiary companies own shares in each other is known as-
(a) Partly owned subsidiary
(b) Cross holding
(c) Subsidiary company
(d) Wholly owned subsidiary
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Cross holding.
Important Points
- Cross holding refers to a situation where two companies, often a parent company and its subsidiary, own shares in each other.
- This creates a mutual ownership relationship. It's a complex ownership structure where both entities have a stake in one another.
- One of the main benefits of cross holding is that it can strengthen the relationship between the two companies.
- By owning shares in each other, the two companies are more likely to cooperate and work together.
- This can be beneficial to both companies, as it can lead to increased sales and profits.
Other Related Points
- Partly owned subsidiary - This term generally refers to a subsidiary company in which the parent company owns less than 100% of the shares, implying shared ownership with other parties.
- Subsidiary company - This is a company that is controlled by another company, referred to as the parent company. The parent company typically owns more than 50% of the subsidiary's shares.
- Wholly owned subsidiary - In this scenario, the parent company owns 100% of the shares of its subsidiary, providing full control and ownership. This is the most straightforward form of subsidiary ownership.
Q64: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: The return on capital invested is a concept that measures the profit which a firm earns on investing a unit of capital
Reason R: Yield on capital is another term employed to express the idea
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct but R NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is not correct
(d) A is not correct but R is correct
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are correct but R NOT the correct explanation of A.
- Return on capital (ROC) is a measure of how efficiently a company is using its capital to generate profits. It is calculated by dividing the company's net income by its total capital.
- Yield on capital is a measure of how much profit a company is generating on its capital investment. It is calculated by dividing the company's operating profit by its total capital.
Important Points
- Both Assertion A and Reason R are correct statements, but Reason R does not provide a correct explanation for Assertion A.
- Assertion A states that the return on capital invested is a concept that measures the profit which a firm earns on investing a unit of capital. This is true. The return on capital invested is a financial metric that evaluates the efficiency and profitability of a company's capital investments.
- Reason R states that Yield on capital is another term employed to express the idea. This is also true. "Yield on capital" is indeed another term used to refer to the return on capital invested. It represents the earnings generated from the capital invested.
- While both statements are accurate, Reason R does not directly explain or provide additional information about Assertion A. It essentially restates the concept using a different term, which doesn't serve as an explanation for Assertion A. Therefore, Option 2 is the correct choice.
Q65: Some bottles of soft drink were supplied by X to Y. Y got injured due to bursting of one of the bottles. Y claimed damages from X due to ?
(a) Condition as to fitness as quality
(b) Condition as to wholesomeness
(c) Condition as to merchantability
(d) Condition in a sale by description
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Condition as to merchantability.
Important Points
- In this scenario, the issue arises from a bottle of soft drink causing injury due to bursting.
- The legal concept that applies here is "merchantability," which is a condition in a contract of sale.
- Condition as to merchantability means that goods sold must be reasonably fit for the general purpose for which they are sold in the market.
- In simpler terms, when you buy a product, there is an implied condition that it should be suitable for normal use.
- In this case, when Y purchased the soft drink, there was an implied condition that it would be safe to consume and handle. Since the bottle burst and caused injury, it indicates a breach of the implied condition of merchantability.
- Y can claim damages from X based on this breach.
Options 1, 2, and 4 do not directly apply to the situation described -
- Condition as to fitness as quality generally relates to specific attributes or features of a product that a buyer may have specified and the seller has agreed to.
- Condition as to wholesomeness is more related to food products and implies that food products should be fit for human consumption.
- Condition in a sale by description refers to a situation where goods are sold based on a description, and the actual goods should correspond to that description.
In the given scenario, the most applicable condition is merchantability, as it pertains to the general suitability and safety of the product for its intended purpose, which was not met when the bottle burst and caused injury.
Q66: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: Cross listing can potentially increase the stock price and lower the cost of capital
Reason R: Cross listing facilitates wider stock ownership and expands investor base for a firm's stock
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options Given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: A
Sol: Assertion A: Cross listing can potentially increase the stock price and lower the cost of capital.
- Cross-listing is the listing of a company's common shares on a different exchange than its primary and original stock exchange. Companies must meet the exchange's listing requirements in order to be cross-listed.
- Advantages to cross-listing include having shares trade in multiple time zones, boosting liquidity and providing access to fresh capital.
- The international exposure provides companies with more liquidity, meaning there's a healthy amount of buyers and sellers in the market. The added liquidity provides companies with a greater ability to raise capital or new money to invest in the future of the company.
- Hence Assertion A is correct.
Reason R: Cross listing facilitates wider stock ownership and expands investor base for a firm's stock
- Companies that list shares across the globe attract varied investors belonging to different countries. This means more capital. But it also facilitates diversification advantages. MNCs that list globally are insulated from economic fluctuation occurring in a part of the world.
- Having shares in multiple exchanges buys the firm goodwill and a reputation in the international market. In addition, it adds to the firm’s international presence.
- Hence Reason R is correct,
Therefore we can say that Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A,
Q67: Which are correct regulatory provisions for foreign bank operations in India?
A. They are incorporated in India and have their head office in foreign country
B. Foreign banks since 2002 have been allowed to set up their subsidiaries in India
C. The foreign banks are allowed to operate in India even if they are not financially sound
D. They have to operate according to the banking regulations in India
E. RBI approved that foreign banks which are present in India could open their branches
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, E only
(b) A, B, C only
(c) B, D, E only
(d) C, D, E only
Ans: C
Sol: Explanation
- Foreign bank operations in India
- Foreign banks are those banking companies which open a branch in a different nation than the headquarters.
- They have their registered office in one country. These foreign banks open a branch in other countries. It is to provide better services and convenience to multinational customers.
- In the 2002–03 budget, foreign banks in India have been given more flexibility in their Indian operations wherein they are allowed to operate as branches of their overseas parent or as subsidiaries in India.
- The foreign banks are not allowed to operate in India if it they are not financially sound
- They have to operate according to the banking regulations in India
- Foreign banks do not require separate approval under FEMA, for opening branch office in India. Such banks are, however, required to obtain necessary approval under the provisions of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, from Department of Banking Operations & Development, Reserve Bank.
Therefore correct answer is B, D, E only.
Q68: Arrange the following legislations in primary and secondary market in ascending order of its enactment.
A. Mutual fund regulations
B. Credit rating agencies Regulations
C. Credit rating regulations
D. SEBI intermediaries regulations
E. Sweat equity regulations
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, A, D, E
(b) C, D, E, A, B
(c) A, B, C, D, E
(d) A, B, E, D, C
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, E, D, C'
Mutual Fund Regulations (A):
- SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) introduced the SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations in 1996 to regulate all mutual funds except those which are created and managed by the Reserve Bank of India or a banking company.
- These regulations were the earliest among the listed legislations and were aimed at safeguarding investor interests in mutual funds by ensuring transparency and accountability.
Credit Rating Agencies Regulations (B):
- The SEBI (Credit Rating Agencies) Regulations were enacted in 1999 to regulate the functioning of credit rating agencies in India.
- This regulation provided a framework to ensure the quality and integrity of the credit rating process, and to protect the interests of investors who rely on these ratings.
Sweat Equity Regulations (E):
- The SEBI (Issue of Sweat Equity) Regulations were implemented in 2002 to regulate the issue of sweat equity shares by companies to their employees and directors.
- This regulation helped in recognizing and rewarding valuable contributions by employees who contributed their know-how or intellectual property to the company.
SEBI Intermediaries Regulations (D):
- The SEBI (Intermediaries) Regulations came into effect in 2008 to provide a comprehensive set of guidelines for entities involved in the securities market.
- These regulations cover various market intermediaries such as brokers, sub-brokers, portfolio managers, and others, ensuring their proper functioning and protecting investor interests.
Credit Rating Regulations (C):
- The SEBI (Issue and Listing of Debt Securities) Regulations, known as Credit Rating Regulations, were enacted in 2008 to provide a framework for the issuance and listing of debt securities.
- These regulations ensure that the process of raising debt capital through the securities market is transparent and fair for all stakeholders involved.
Q69: Post-purchase consumers invariably experience cognitive dissonance which is referred to as-
(a) A feeling of happiness with the purchase
(b) Getting angry with the firm
(c) A feeling of uncertainty about making the right decision
(d) A state of extreme satisfaction
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A feeling of uncertainty about making the right decision.
Important Points
- Cognitive dissonance is a psychological theory developed by Leon Festinger in 1957.
- It refers to the discomfort or tension that arises when a person holds two contradictory beliefs, attitudes, or values, or when their behavior conflicts with their beliefs or values.
- In the context of post-purchase behavior, cognitive dissonance occurs when a consumer experiences uncertainty or doubt about whether they made the right decision in purchasing a product or service.
- This can happen because consumers are often faced with multiple options and making a decision can be challenging.
- For example, after making a significant purchase, such as a car or a computer, a consumer might question whether they made the right choice, especially if there were other appealing options available.
- This uncertainty is a common psychological response.
Other Related Points
- A feeling of happiness with the purchase - This statement does not align with cognitive dissonance, as it implies a positive and satisfied emotional state, whereas cognitive dissonance is characterized by a state of discomfort or uncertainty.
- Getting angry with the firm - This does not relate directly to cognitive dissonance. Cognitive dissonance is an internal psychological phenomenon, not an external emotional reaction towards a firm.
- A state of extreme satisfaction - Again, this statement suggests a high level of satisfaction, which contradicts the concept of cognitive dissonance.
Q70: One or more parties to a negotiable instrument is/ are discharged from liability in which of the following ways:
A. By giving the notice dishonour by the holder
B. By deliberately cancelling the name of party/parties
C. By taking qualified acceptance
D. By allowing drawee 24 hours to accept
E. By material alteration
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, D only
(b) D, A, C only
(c) E, C, B only
(d) A, B, C only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is E, C, B only.
- A negotiable instrument is a legally binding document that guarantees the unconditional payment of a specified amount of money either on-demand or at a specific time, to the holder or bearer of the instrument.
- It is a financial instrument that can be transferred from one person to another in such a way that the transferee (the person receiving it) acquires a legal right to the amount specified on the instrument.
Important PointsNegotiable instrument is/are discharged from liability in the following ways -
Material alteration -
- If the instrument is materially altered without the consent of all parties liable on it, all parties subsequent to the alteration are discharged from liability on the instrument.
Deliberately cancelling the name of party/parties -
- If the holder of a negotiable instrument deliberately cancels the name of any party liable on it, that party and all subsequent parties are discharged from liability on the instrument.
Taking qualified acceptance -
- If the holder of a bill of exchange takes a qualified acceptance, all parties subsequent to that holder are discharged from liability on the instrument.
Deliberately cancelling the name of party/parties -
- A person signs a promissory note as an endorser, guaranteeing the payment of the note if the maker fails to pay.
- If the holder of the note then deliberately cancels the name of the maker, the endorser is discharged from liability on the note.
Taking qualified acceptance -
- A person signs a bill of exchange as a drawer, directing the drawee to pay a certain sum of money to the payee on a certain date.
- If the payee then takes a qualified acceptance from the drawee, such as an acceptance that is conditional on the drawee having sufficient funds in their account,
- all parties subsequent to the payee are discharged from liability on the bill of exchange.
Thus, option 3 is E, C, B only correct.
Q71: Frederic W. Taylor is acknowledged as the father of scientific management. What is his major contribution to management.
(a) Theory of bureaucracy
(b) Identified characteristics of companies he considered excellent
(c) Application of psychology to industry and management
(d) How to raise productivity through greater efficiency in production and increased pay for workers
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is How to raise productivity through greater efficiency in production and increased pay for workers
Frederick Winslow Taylor, fondly remembered as the father of scientific management, introduced the concept of optimizing and simplifying jobs to boost productivity. He proposed that work should be studied scientifically to identify the most efficient way to perform specific tasks, thereby increasing productivity. He also believed that workers should be paid based on their production levels, a concept known as a "piece-rate system".
As a pioneer of the scientific management movement, Taylor aimed to maximize productivity by optimizing and simplifying jobs and tasks. Through systematic time and motion studies, he devised more efficient ways of working and highlighted the importance of breakdown and analysis of tasks to find the best method of doing work.
Furthermore, Taylor argued that workers should be incentivized to work more efficiently by linking pay directly to output. He introduced the idea of a "piece-rate system" where workers are paid based on the quantity they produce, rather than a flat wage irrespective of the work accomplished in a given time.
Q72: ______ is a most useful type of non probability sampling method when individuals with the desired characteristics experience or attitudes are difficult to identify or reach.
(a) Purposive Sampling
(b) Convenience Sampling
(c) Snowball Sampling
(d) Quota Sampling
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Snowball Sampling.
- Non-probability sampling is a type of sampling method in which the researcher does not select the sample in a random way.
- This means that some members of the population are more likely to be selected than others.
- Non-probability sampling methods are often used in qualitative research studies, where the goal is to learn about the experiences and perspectives of a particular group of people.
Important PointsThere are a number of different non-probability sampling methods, including -
- Convenience sampling - The researcher selects the sample from the population that is most convenient to them. For example, a researcher might survey students in their own class or interview people who walk by on the street.
- Purposive sampling - The researcher selects the sample based on their judgment about who is most likely to provide useful information. For example, a researcher might interview experts in a field or people who have experienced a particular event.
- Snowball sampling -
- The researcher asks existing study subjects to refer them to other potential subjects.
- This is often used to study hard-to-reach populations, such as people who are homeless or people who engage in illegal activities.
Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling technique commonly used in situations where it's challenging to identify or reach individuals with specific characteristics, experiences, or attitudes.
- It's particularly useful when the target population is small or hidden, such as in cases of rare diseases, sensitive issues, or marginalized communities.
- Quota sampling - The researcher sets quotas for different groups in the population and then selects a sample that meets those quotas. For example, a researcher might set a quota for 50% male and 50% female respondents.
Q73: A price ceiling below the equilibrium price leads to _______.
A. Black marketing
B. Shortage of commodity
C. Surplus of the commodity
D. Hoarding of commodity
E. Increased in consumption
Choose the most appropriate from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) B, D and E only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and D only.
- Price ceilings below the equilibrium price lead to shortages and black markets.
- This is because consumers want to buy more of the good or service at the price ceiling price than suppliers are willing to sell.
- Black markets arise when there is a shortage of a good or service, and people are willing to pay higher prices than the legal price ceiling in order to obtain it.
Important PointsPrice ceilings below the equilibrium price can have a number of negative consequences, including -
Shortages -
- Shortages can lead to higher prices for consumers, as well as decreased access to essential goods and services.
- Shortages occur because consumers want to buy more of the good or service at the price ceiling price than suppliers are willing to sell.
- This is because the price ceiling is below the equilibrium price, which is the price at which the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied are equal.
Black markets -
- Black markets can lead to crime, corruption, and a loss of tax revenue for the government.
- Black markets arise when there is a shortage of a good or service, and people are willing to pay higher prices than the legal price ceiling in order to obtain it.
- Black markets are illegal, but they can be very profitable for sellers.
Hoarding -
- Hoarding can reduce the quantity of goods or services that are available to other consumers, and it can also lead to higher prices.
- Hoarding is the accumulation of goods or services in the anticipation of a shortage or price increase.
- Hoarding can also contribute to shortages, as it reduces the quantity of goods or services that are available to other consumers.
Decreased quality - Suppliers may have to cut corners in order to meet the price ceiling, which can lead to a decrease in the quality of goods and services.
Q74: 'Pin Money' is used for ______
(a) Receipt on account of Dharmshala Goshala etc.
(b) Woman gets from her husband certain amount
(c) Income of non-residents from shipping business
(d) Income from building used for agriculture
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Woman gets from her husband certain amount .
- "Pin money" refers to a small amount of money that is set aside or allocated for personal spending, typically by a household, usually by the person who manages the finances.
- It's often used for discretionary or non-essential expenses, such as entertainment, personal care items, or small treats.
Important Points
The answer is option 2 -
Pin money is a small amount of money that a husband gives to his wife for her personal expenses.
It is not considered to be part of her household income and is not taxed.Pin money is a small amount of money that a husband gives to his wife for her personal expenses.
- It is not considered to be part of her household income and is not taxed. Pin money can be used for anything the wife wants, such as clothing, cosmetics, or entertainment.
- Pin money has been around for centuries, and its origins are unclear. However, it is thought to have originated in England during the Middle Ages.
- At that time, women were not allowed to own property or have their own income.
- Pin money was a way for husbands to provide their wives with a small amount of money that they could control themselves.
- Pin money is still common in many parts of the world today. In some cultures, it is seen as a sign of respect and love that a husband gives to his wife.
- In other cultures, it is simply seen as a way to help the wife pay for her personal expenses.
Other Related Points
- Option 1 is incorrect. Receipt on account of Dharmshala Goshala etc. is not considered to be pin money.
- Option 3 is incorrect. Income of non-residents from shipping business is not considered to be pin money.
- Option 4 is incorrect. Income from building used for agriculture is not considered to be pin money.
Q75: In order to protect domestic industries, trade restrictions are often been allowed and justified to counteract which of the following dumping practices?
(a) Persistent dumping
(b) Predatory dumping
(c) Sporadic dumping
(d) Reverse dumping
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Predatory dumping.
- Dumping is an international trade practice in which a country or company exports a product to another country at a price lower than the cost of production or below the price in its domestic market.
- This can be done either to gain market share in the importing country or to eliminate competition by driving domestic producers out of business.
Important Points
- Predatory dumping occurs when a foreign company intentionally sells its products in a foreign market at a price below its production cost or the market price in its home country.
- The goal of predatory dumping is to gain a competitive advantage, drive domestic producers out of business, and ultimately establish a monopoly or dominant market position.
- In response to predatory dumping, governments may impose trade restrictions such as tariffs or quotas to protect their domestic industries.
- These measures are implemented to counteract the unfair advantage gained by the foreign company engaging in predatory dumping.
Other Related Points
- Persistent dumping - This term is not a standard concept in trade economics. It may be a misnomer or a less common term, as it does not refer to a widely recognized form of dumping.
- Sporadic dumping - This refers to occasional instances of dumping, which are not consistently practiced by a foreign company. It may not require the same level of intervention as predatory dumping.
- Reverse dumping - This term is not a standard concept in trade economics. It may be a less common term, or a specific context not covered in the provided information.
Q76: Brewing financial stress endangering economic stability in developed economies is the immediate consequence of which of the following?
(a) Fiscal indispline
(b) Rising price level
(c) Over leverage
(d) Increased interest rates
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Increased interest rates.
Important Points
Increased interest rates can lead to financial stress in a number of ways, including -
Higher borrowing costs -
- When interest rates rise, it becomes more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money.
- This can make it difficult for businesses to invest and grow, and for consumers to buy homes and cars.
- It can also lead to higher debt payments for those who are already in debt, which can strain their finances.
Reduced lending -
- Banks and other financial institutions may also reduce lending when interest rates rise.
- This is because they are more likely to lose money on loans if borrowers default.
- This can make it even more difficult for businesses and consumers to access the financing they need.
Volatile markets -
- Rising interest rates can also lead to volatility in financial markets. This is because investors may sell off assets such as bonds and stocks in order to lock in higher yields.
- This volatility can make it difficult for businesses to raise capital and for investors to protect their savings.
Other Related Points
Fiscal indiscipline -
- This refers to a situation where a government is not adhering to sound fiscal policies, often characterized by excessive spending, large deficits, and growing public debt.
- While fiscal indiscipline can contribute to economic instability, it is not the immediate consequence mentioned in the question.
Rising price level (inflation) -
- While high inflation can have negative effects on an economy, such as reducing purchasing power and creating uncertainty,
- it is not directly related to financial stress endangering economic stability.
Over leverage -
- This occurs when individuals, businesses, or governments take on too much debt relative to their income or assets.
- Over leverage can indeed lead to financial stress, as debt obligations become harder to meet.
- However, it is not the immediate consequence mentioned in the question.
Q77: In which of the following cases, the agreement in void ab-initio
A. Mistake is caused by fraud or misrepresentation
B. Mistake as to the identify of person contracted with
C. Mistake as to the nature and character of a written document
D. Bilateral mistake
E. Unilateral mistake
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) C, D, E only
(b) A, C, E only
(c) B, A, C only
(d) D, E, B only
Ans: C
Sol: Void ab initio agreement :
- A void ab initio agreement is Latin for "void from the beginning." This means that legally, a contract was void as soon as it was created.
- The parties of the contract are not legally related based on what was written in the agreement because the agreement in question was never valid.
- Example: A contract with a minor would be void ab initio, as a minor is an incompetent party to the contract
- Where a Court declares an act to be void ab initio, the parties are returned to their respective places at the ab initio occasion, the agreement basically never occurred and therefore had no obligatory power over any parties to the contract.
- Contracts are void when one or more vitiating factors are present.
Characteristics of this type of contract include:
One or more parties has the option to enforce.
- This party must have been subject to undue influence, misrepresentation, coercion, or fraud.
- A party can receive compensation if he or she rightfully revokes the contract.
- The party whose consent is caused has the contract void option.
- Mistake is caused by fraud or misrepresentation
- Mistake as to the identify of person contracted with
- Mistake as to the nature and character of a written document
The correct answe r is B, A, C only.
Q78: Which of the following non-parametric test has no corresponding parametric test?
(a) Spearman rank correlation test
(b) Kruskal Wallis test
(c) Mann-Whitney test
(d) Ward-Wolfowitzone sample runs test
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Ward-Walfowitz one sample runs test .Explanation
- A parametric test is a statistical test that makes assumptions about the parameters of the population distribution from which the sample is drawn.
- A nonparametric test is a statistical test that does not make assumptions about the parameters of the population distribution from which the sample is drawn.
Important Points
- The Ward-Walfowitz one sample runs test is a non-parametric test that is used to test whether a sequence of observations is random.
- It does this by counting the number of runs in the sequence, where a run is defined as a consecutive sequence of observations that are all greater than or all less than the median value.
- The Ward-Walfowitz one sample runs test has no corresponding parametric test.
- This is because it is not possible to make assumptions about the distribution of the population data when using this test.
The other three options all have corresponding parametric tests -
- Spearman rank correlation test - Pearson correlation test
- Kruskal-Wallis test - One-way ANOVA
- Mann-Whitney test - Independent samples t-test
The Ward-Walfowitz one sample runs test is a non-parametric test that is used to test whether a sequence of observations is random. It has no corresponding parametric test.
Other Related PointsSparman rank correlation test -
- Spearman rank correlation coefficient is a nonparametric measure of the strength and direction of association between two ranked variables.
- It assesses how well the relationship between two variables can be described using a monotonic function.
- To calculate the Spearman rank correlation coefficient, the data is first ranked from lowest to highest for each variable.
Kruskal Wallir test -
- The Kruskal-Wallis test is a nonparametric test that is used to compare three or more independent groups on a continuous or ordinal variable.
- It is the nonparametric equivalent of the one-way ANOVA.
- The Kruskal-Wallis test works by ranking all of the data points in the sample, regardless of which group they belong to.
- The average rank is then calculated for each group.
Mann-Whitney test -
- The Mann-Whitney U test is a nonparametric test that is used to compare two independent groups on a continuous or ordinal variable.
- It is the nonparametric equivalent of the independent samples t-test.
- The Mann-Whitney U test works by ranking all of the data points in the sample, regardless of which group they belong to.
Q79: The coefficient of variation for a Poisson distribution with λ(mean) = 5 is ______.
(a) 31.1 percent
(b) 44.7 percent
(c) 35.2 percent
(d) 58.9 percent
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 44.7 percent.
Poisson distribution-
- The Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time or space if these events occur with a known constant mean rate and independently of the time since the last event.
- It is named after French mathematician Siméon Denis Poisson.
Important Points
- The coefficient of variation (CV) is a measure of the relative variability of a distribution.
- It is calculated by dividing the standard deviation by the mean.
- For a Poisson distribution, the standard deviation is equal to the square root of the mean.
- So, the CV for a Poisson distribution is calculated as follows -
CV = (√λ/λ) × 100 = (1/√λ) × 100."
For a Poisson distribution with mean = 5, the CV is therefore:
CV = 1/√λ = 0.4472
This is equal to 44.72 percent, rounded to two decimal places.
In other words, the coefficient of variation tells us that the standard deviation is 44.72% of the mean.
- This means that the distribution is relatively spread out, with a significant number of values that are above and below the mean.
- The coefficient of variation is a useful measure of variability because it is independent of the scale of the distribution.
- This means that it can be used to compare the variability of distributions with different means.
Q80: Sequence the conduct of following trade negotiation and facilitation rounds in chronological order.
A. Kennedy round
B. Doha round
C. Geneva round
D. Tokyo round
E. Uruguay round
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, C, A, E
(b) C, A, D, E, B
(c) A, B, D, C, E
(d) D, C, A, E, B
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is C, A, D, E, B.
Important Points
- The trade negotiation and facilitation rounds have played an important role in promoting global trade and economic growth.
- By reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers to trade, the rounds have made it easier for businesses to export their goods and services to new markets.
- This has led to increased competition and lower prices for consumers, as well as job creation and economic growth around the world.
The trade negotiation and facilitation rounds in chronological order are -
- Geneva round (1956-1957) - The Geneva round was the first round of multilateral trade negotiations under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). It resulted in the reduction of tariffs on a wide range of goods.
- Kennedy round (1964-1967) - The Kennedy round was the second round of multilateral trade negotiations under the GATT. It resulted in further reductions in tariffs, as well as the first agreement on non-tariff barriers to trade.
- Tokyo round (1973-1979) - The Tokyo round was the seventh round of multilateral trade negotiations under the GATT. It resulted in further reductions in tariffs and non-tariff barriers to trade, as well as agreements on new issues such as government procurement and technical barriers to trade.
- Uruguay round (1986-1994) - The Uruguay round was the eighth and most ambitious round of multilateral trade negotiations under the GATT. It resulted in the creation of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the conclusion of a number of agreements on trade in goods, services, and intellectual property.
- Doha round (2001-present) - The Doha round was launched in 2001 with the aim of further liberalizing trade and making it more inclusive. The round has been stalled for a number of years, but there is renewed hope that it may be concluded in the near future.
So, the correct chronological order is C, A, D, E, B, which corresponds to option 2.
Q81: Which one of the following subsidiary is not owned by the Reserve Bank of India.
(a) National Housing Bank (NHB)
(b) Industrial Development Finance Corporation (IDFC)
(c) National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
(d) Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporations of India (DICGC)
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Industrial Development Finance Corporation (IDFC) .
Important Points
A list of some of the major subsidiaries owned by the RBI -
- National Housing Bank (NHB) - NHB was established to promote and regulate housing finance institutions in India.
- Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) - DICGC provides insurance coverage to depositors in case a bank fails.
- Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Limited (BRBNMPL) - BRBNMPL is a wholly-owned subsidiary of RBI and is engaged in the production of banknotes.
- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI)- Although not directly owned by RBI, it is an umbrella organization for operating retail payments and settlement systems in India.
- Reserve Bank Information Technology Private Limited (ReBIT) - ReBIT is a wholly-owned subsidiary of RBI that focuses on research, innovation, and implementation of new technologies in the banking and financial sector.
- Indian Financial Technology and Allied Services (IFTAS) - IFTAS is another subsidiary of RBI that focuses on providing IT and technological services to banks and financial institutions.
- IDFC was founded in 1997 as a private sector enterprise. Over time, it has diversified its services and now operates in both infrastructure finance and asset management. IDFC operates independently and is not owned by the Reserve Bank of India. It was originally promoted by a consortium of public and private sector companies and government institutions.
Important Points
Subsidiaries of RBI:
- Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC)
- National Housing Bank (NHB) (since May 2019, previously an RBI subsidiary)
- Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Limited (BRBNMPL)
- Not a subsidiary of RBI:
- NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development)
- Therefore, your answer NABARD is indeed the correct one for the question about which subsidiary is not owned by the RBI.
Thus, Industrial Development Finance Corporation (IDFC) is not owned by the Reserve Bank of India.
Q82: Which of the following is not an essential characteristic of negotiable instrument?
(a) Sells little to a bonafide transferor for value.
(b) Flexibility in transfer
(c) Easy negotiability
(d) Transferor can sue in own name without giving notice to the debtor.
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Sells little to a bonafide transferor for value.
- A negotiable instrument is a legally binding document that guarantees the unconditional payment of a specified amount of money either on-demand or at a specific time, to the holder or bearer of the instrument.
- It is a financial instrument that can be transferred from one person to another in such a way that the transferee (the person receiving it) acquires a legal right to the amount specified on the instrument.
Important Points
Essential Characteristics of a Negotiable Instrument -
- In Writing - The instrument must be in written form.
- Unconditional Promise or Order - The promise or order to pay must be unconditional. There should be no conditions or contingencies attached.
- Fixed Amount - The amount to be paid must be specific and fixed, not subject to change.
- Payable to Bearer or to Order - It must be payable to the bearer or to a specific person or their order.
- Negotiability and Transferability - The instrument must be capable of being transferred from one person to another by delivery or endorsement.
- Date and Place of Payment - It should specify the date and place of payment.
- Given that Option 1 doesn't seem to relate to any known characteristic of a negotiable instrument, it's the correct answer for this question. It's possible that it's a partial or incomplete statement.
- Thus, Option 1 is Sells little to a bonafide transferor for value correct.
Q83: The dividend-irrelevance theory of Miller and Modigliani depends on which one of the following relationships between investment policy and dividend policy.
(a) Since dividend policy is irrelevant, there is no relationship between investment policy and dividend policy
(b) The level of investment does not influence or matter to the dividend decision
(c) Once dividend policy is set, the investment decision are residuals
(d) The investment policy is set ahead of time and not altered by change in dividend policy
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is The investment policy is set ahead of time and not altered by change in dividend policy
Dividend irrelevance theory :
- It proposes that a company’s dividend policy does not affect its overall value or stock price. It was introduced by Franco Modigliani and Merton Miller in 1961.
- It suggests that investors can create their desired income stream by buying or selling company shares as needed. This is regardless of whether the company pays dividends or retains its earnings.
- The theory aims to understand the relationship between dividends and a company’s value.
- This theory states that dividend patterns have no effect on share values.
- Broadly it suggests that if a dividend is cut now then the extra retained earnings reinvested will allow futures earnings and hence future dividends to grow.
- The investment policy is set ahead of time and not altered by change in dividend policy
- Dividend irrelevance theory holds that the markets perform efficiently so that any dividend payout will lead to a decline in the stock price by the amount of the dividend.
- In other words, if the stock price was $10, and a few days later, the company paid a dividend of $1, the stock would fall to $9 per share.
- As a result, holding the stock for the dividend achieves no gain since the stock price adjusts lower for the same amount of the payout
Q84: Match List I with List II.
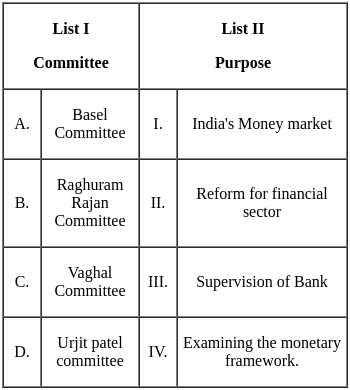
Choose the correct answer answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision
- The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) is an international regulatory framework established by central bank Governors from ten countries in 1974, following banking disturbances in the early 1970s.
- It formulates broad supervisory standards and guidelines and recommends statements of best practice in banking supervision with the aim to enhance the understanding of key supervisory issues and improve the quality of banking supervision worldwide.
- One of its most significant contributions is the Basel Accords (Basel I, Basel II, Basel III), which set international standards for banking regulations concerning capital adequacy, stress testing, and market liquidity risk.
Raghuram Rajan Committee
- The Raghuram Rajan Committee was constituted by the Government of India in 2007.
- Chaired by Raghuram Rajan, who later became the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, the committee was tasked with recommending steps to reform the Indian financial sector.
- This encompassed a broad range of topics from banking reform, consolidation of the sector, and enhancing the regulations to cover non-traditional financial entities and instruments.
- Its recommendations aimed at fostering financial inclusion, improving consumer protection, and enhancing the growth and development of the Indian financial market.
Vaghul Committee
- Formed in 1987, the Vaghul Committee focused on the Indian money market's workings.
- Chaired by Narayanan Vaghul, the then chairman of ICICI Bank, this committee aimed to analyze and suggest improvements for the efficiency, organization, and functioning of the Indian money market.
- The recommendations encompassed a wide range of suggestions, including developing a broader range of instruments and fostering an active secondary market to enhance liquidity and market depth.
- Matters such as deregulation of interest rates and paving the way for the introduction of new financial products were also covered.
Urjit Patel Committee
- The Urjit Patel Committee, officially known as the Expert Committee to Revise and Strengthen the Monetary Policy Framework, was constituted by the Reserve Bank of India in 2013.
- Chaired by Urjit Patel, the then Deputy Governor of the RBI (and later Governor), the committee was tasked with reviewing and strengthening the monetary policy framework.
- One of its pivotal recommendations was to adopt inflation targeting as the primary objective of the RBI's monetary policy framework.
- It advocated for a clear and explicit numeric inflation target and the establishment of a decision-making structure to ensure a more predictable and transparent monetary policy.
- This shift aimed at preserving the value of the currency and stabilizing inflation expectations, which are crucial for sustainable economic growth.
Q85: In order to maximise profits in oligopolistic markets, in which order firms addresses following strategic challenges?
A. Bargaining power of buyers
B. Competitive intensity of rival firms
C. Bargaining power of suppliers
D. Threat from substitute products
E. Threat of new entry
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, E, D, A
(b) D, E, A, C, B
(c) D, E, B, C, A
(d) E, B, C, A, D
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is D, E, A, C, B.
- An oligopoly is a type of market structure in which a small number of firms control a large share of the market.
- Oligopolistic firms are often interdependent, meaning that the actions of one firm can have a significant impact on the other firms in the market.
- Oligopoly markets are often characterized by high barriers to entry, which make it difficult for new firms to enter the market.
- These barriers to entry can include economies of scale, brand loyalty, and government regulations.
Important PointsIn order to maximize profits in oligopolistic markets, firms should address strategic challenges in the following order -
- Threat from substitute products - Substitute products are products or services that can satisfy the same need as the products or services offered by oligopolistic firms. The threat from substitute products is higher in markets where there are many close substitutes available.
- Threat of new entry - Oligopolistic markets are typically characterized by high barriers to entry, such as economies of scale, brand loyalty, and government regulations. However, new entrants can still pose a threat to existing firms, especially if they offer innovative products or services at lower prices.
- Bargaining power of buyers - Oligopolistic firms often sell to a small number of large buyers. This can give buyers a lot of bargaining power, which they can use to demand lower prices or better terms.
- Bargaining power of suppliers - Oligopolistic firms often rely on a small number of suppliers for their inputs. This can give suppliers a lot of bargaining power, which they can use to demand higher prices or better terms.
- Competitive intensity of rival firms - Oligopolistic markets are typically characterized by intense competition between a small number of firms. This competition can drive down prices and profits.
Q86: According to which concept. the life of the business is divided into appropriate segments for studying the results shown by the business in each of the segment?
(a) Periodic Matching Cost and Revenue Concept
(b) Dual Aspect Concept
(c) Accounting Period Concept
(d) Money Measurement Concept
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Accounting Period Concept.
- Accounting concepts, also known as accounting principles or accounting standards, are fundamental guidelines and rules that govern the field of accounting.
- These concepts provide a framework for recording, reporting, and interpreting financial transactions and events.
- They ensure consistency, reliability, and transparency in financial statements, making them understandable and comparable for users.
Important Points
- The Accounting Period Concept, also known as the Periodicity Concept, is a fundamental principle of accounting.
- According to this concept, the life of a business is divided into discrete and specific time periods, such as months, quarters, or years, for the purpose of preparing financial statements and analyzing the performance of the business.
- This concept recognizes that for meaningful financial analysis and decision-making, it's essential to have regular and timely financial reports.
- By breaking down the business's activities into specific time intervals, stakeholders can assess its performance, profitability, and financial position over those periods.
- The accounting period concept is important because it helps businesses to -
- Track their financial performance over time.
- Identify trends and patterns in their financial data.
- Make informed decisions about future operations.
- Compare their financial performance to other businesses in the same industry.
Other Related Points
- Option 1, "Periodic Matching Cost and Revenue Concept," is not a standard accounting concept. While matching costs and revenues is a key principle in accounting (the Matching Principle), it doesn't relate directly to the segmentation of time periods.
- Option 2, "Dual Aspect Concept," is another fundamental accounting concept, but it pertains to the idea that every transaction has at least two aspects (debit and credit) that affect different accounts. It's not directly related to dividing the life of a business into segments for analysis.
- Option 4, "Money Measurement Concept," is the principle that only transactions that can be expressed in monetary terms are recorded in accounting. It doesn't address the segmentation of time periods.
Q87: In the 'Category F' which companies are classified by the SEBI?
(a) Existing listed companies that are making a public issue
(b) New companies with less than 12 months in operation
(c) Companies having a good track record of profit
(d) Privately held companies
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Existing listed companies that are making a public issue.
Key Points
Existing listed companies that are making a public issue: As already mentioned above, these are companies that are currently trading on an exchange and are issuing additional shares to the public. They fall under Category F as per the SEBI guidelines.
New companies with less than 12 months in operation: These are typically startups, new businesses or business expansions that have been in operation for less than a year. These would not fit into Category F, as these companies often don't have a track record of public trading and are more commonly associated with initial public offerings (IPOs).
Companies having a good track record of profit: While a good track record of profit is generally a positive indicator for potential investors, it is not a distinguishing factor for Category F as per SEBI guidelines. Companies in Category F could have varying profit histories.
Privately held companies: These are businesses that are owned by non-governmental organizations or by a relatively small number of shareholders or company members. As private companies, they do not offer or trade their company stock (shares) to the general public on the stock market exchanges, but rather the stock is offered, owned and traded or exchanged privately. Hence, they would not come in Category F as they are not already listed.
Q88: Which of the following are likely to lead an appreciation in the value of a country's currency?
A. Higher real interest rate
B. Higher nominal interest rate
C. Lower inflation
D. Higher inflation
E. Large current account deficit
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C only
(b) A, C only
(c) D, B only
(d) E, A only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct option is A, C only.
Higher Real Interest Rate
- Higher real interest rates can attract foreign investors as they can get a higher return on their investment. This increases demand for the country's currency, which can lead to an appreciation in its value.
Higher Nominal Interest Rate
- Higher nominal interest rates might also attract foreign investors, but this scenario depends on relative inflation. If a country has high nominal interest rates but also high inflation, then the potential gain from higher nominal interest could be offset by the loss of purchasing power due to inflation.
Lower Inflation
- Lower inflation generally indicates a stable economy wherein the purchasing power of the currency is well maintained. Inflation erodes purchasing power, and hence, lower inflation rates are often desirable and attract foreign investors, potentially leading to an appreciation of the currency.
Higher Inflation
- Higher inflation can lead to a depreciation in the value of a currency because it erodes the purchasing power of money over time. This makes goods more expensive, and in turn, reduces the appeal for foreign investors, potentially leading to a depreciation of the currency.
Large Current Account Deficit
- Large current account deficits usually contribute to the depreciation of a currency. This is because a deficit means that the country is importing more goods, services, and capital than it is exporting. To pay for these imports, it sells its own currency, increasing supply and reducing its value. Therefore, a large current account deficit generally leads to depreciation, not appreciation, of the currency.
Q89: Which of the following notions objectively define an industry?
(a) Homogeneity of products
(b) High cross price elasticity of demand
(c) Use and consumption pattern
(d) Convention and market practices
Ans: B
Sol: The correct option is High cross-price elasticity of demand.
Each of the following notions can be used to define an industry, even though some are more relevant than others in certain contexts:
Homogeneity of Products: This suggests that an industry is characterized by the production of similar or identical products. For example, the automobile industry produces vehicles, while the food industry might produce a wide variety of food products that are related to their purpose, which is the nourishment of consumers.
High Cross Price Elasticity of Demand: Cross elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded of one good (say, Good A) responds to a change in the price of another good (Good B). If Goods A and B are substitutes, their cross elasticity will be positive because as the price of Good B rises, consumers will buy more of Good A. High cross-price elasticity often characterizes industries with close substitute products.
Use and Consumption Pattern: This view suggests that industries can be defined by how their products are used and consumed. For example, the fashion industry caters to the consumers' demand for clothing and related accessories. Similarly, the software industry caters to various digital needs that range from productivity to entertainment.
Convention and Market Practices: This implies that an industry can be defined based on predetermined standards, practices, or conventions that are widely accepted within a specific business sphere. Industries often develop their unique practices, conventions, and norms that set them apart.
Although other factors like the homogeneity of products, use, and consumption patterns, and convention and market practices also play a role in determining an industry, the concept of high cross-price elasticity of demand provides a more economic and market-based perspective on how industries can be defined. hence option 2 is correct.
Q90: Match List I with List II.
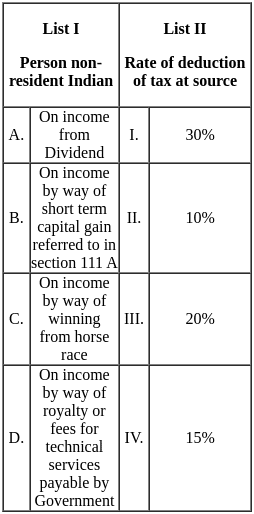
Choose the correct answer answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Ans: C
Sol: The correct option is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II.
Tax on dividend income:
- The Finance Act, 2020 also imposes a TDS on dividend distribution by companies and mutual funds on or after 1 April 2020.
- The normal rate of TDS is 10% on dividend income paid in excess of Rs 5,000 from a company or mutual fund. However, as a COVID-19 relief measure, the government reduced the TDS rate to 7.5% for distribution from 14 May 2020 until 31 March 2021.
Tax on short-term capital gains:
- Section 111A is applicable in the case of STCG on the purchase or sale of:
- equity shares or
- units of equity-oriented mutual funds or
- units of business trust
Tax rate on winnings from horse races:
- As per Section 194BB of the Income Tax Act, earnings from horse race winnings above Rs.10,000 is applicable for Tax Deduction at Source (TDS) at 30% + surcharge.
Q91: Government of India announced a medium-term fiscal deficit target of 4.5% of GDP by 2025-26, which involves a 2-percentage-point compression from current levels over the course of three financial years. Targets for the centre and states for 2023-24 are 5.9% and 3%. respectively, with half-a-percentage point leeway to the latter for power sector reforms. States have a steeper glide path for deficit reduction that is particularly vulnerable to political promises of free food and energy. Gol, on its part, is committed to a capital expenditure programme to nurse India economic recovery, and is nudging states towards fiscal balance.
India's ability to attain its pre-pandemic fiscal targets is also influenced by its need to keep credit flowing to small enterprises in an environment of globally high interest rates. Broad-based investment revival depends on keeping credit costs in check by better budgeting of government expenditure. States have additional requirement of cleaning up off-budget liabilities accumulated through political promises such as those on free electricity. Power distribution being the sole point of revenue injection, state utilities inability to pay is holding up investments in generation and transmission.
Apart from introducing imperfections in the market mechanism, sectarian political targeting of welfare perpetuates inequality. Universal wealth redistribution through cash transfers is a more robust approach. Promises to vote banks are essentially a zero-sum game where one segment benefit at the cost of another. India has unsuccessfully experimented with inclusive growth for much of its post-independence history. It has now corrected course to grow through clusters accompanied by even-handed welfare delivery. This approach has worked in steering the economy through multiple global economic crises. A return to competitive populism will be an unnecessary throwback the world's fastest-growing major economy can do without.
What is the medium term fiscal deficit target for the Govt of India for financial year 2023-24?
(a) 4.5 per cent of GDP
(b) 3.0 per cent of GDP
(c) 5.9 per cent of GDP
(d) 6.5 per cent of GDP
Ans: C
Sol: The correct option is 5.9 per cent of GDP.
As per the passage, "Targets for the centre and states for 2023-24 are 5.9% and 3%. respectively, with half-a-percentage point leeway to the latter for power sector reforms."
Other Related Points
- A fiscal deficit is a situation that occurs when a government's total expenditure exceeds its total revenue (excluding money from borrowings).
- In other words, it signifies the amount of money that the government has to raise by borrowing to completely meet its expenses.
- Fiscal deficit = Total Expenditure - Total Income (Excluding Borrowings)
Q92: Government of India announced a medium-term fiscal deficit target of 4.5% of GDP by 2025-26, which involves a 2-percentage-point compression from current levels over the course of three financial years. Targets for the centre and states for 2023-24 are 5.9% and 3%. respectively, with half-a-percentage point leeway to the latter for power sector reforms. States have a steeper glide path for deficit reduction that is particularly vulnerable to political promises of free food and energy. Gol, on its part, is committed to a capital expenditure programme to nurse India economic recovery, and is nudging states towards fiscal balance.
India's ability to attain its pre-pandemic fiscal targets is also influenced by its need to keep credit flowing to small enterprises in an environment of globally high interest rates. Broad-based investment revival depends on keeping credit costs in check by better budgeting of government expenditure. States have additional requirement of cleaning up off-budget liabilities accumulated through political promises such as those on free electricity. Power distribution being the sole point of revenue injection, state utilities inability to pay is holding up investments in generation and transmission.
Apart from introducing imperfections in the market mechanism, sectarian political targeting of welfare perpetuates inequality. Universal wealth redistribution through cash transfers is a more robust approach. Promises to vote banks are essentially a zero-sum game where one segment benefit at the cost of another. India has unsuccessfully experimented with inclusive growth for much of its post-independence history. It has now corrected course to grow through clusters accompanied by even-handed welfare delivery. This approach has worked in steering the economy through multiple global economic crises. A return to competitive populism will be an unnecessary throwback the world's fastest-growing major economy can do without.
Which of the following apt features of course corrected India growth story?
A. Redistributive growth
B. Cluster based growth
C. Inclusive growth
D. Even handed welfare delivery
E. Competitive populism
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A and C only
(d) B and D only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct option is B and D only.
As per passage
- India has unsuccessfully experimented with inclusive growth for much of its post-independence history.
- It has now corrected course to grow through clusters accompanied by even-handed welfare delivery
Q93: Government of India announced a medium-term fiscal deficit target of 4.5% of GDP by 2025-26, which involves a 2-percentage-point compression from current levels over the course of three financial years. Targets for the centre and states for 2023-24 are 5.9% and 3%. respectively, with half-a-percentage point leeway to the latter for power sector reforms. States have a steeper glide path for deficit reduction that is particularly vulnerable to political promises of free food and energy. Gol, on its part, is committed to a capital expenditure programme to nurse India economic recovery, and is nudging states towards fiscal balance.
India's ability to attain its pre-pandemic fiscal targets is also influenced by its need to keep credit flowing to small enterprises in an environment of globally high interest rates. Broad-based investment revival depends on keeping credit costs in check by better budgeting of government expenditure. States have additional requirement of cleaning up off-budget liabilities accumulated through political promises such as those on free electricity. Power distribution being the sole point of revenue injection, state utilities inability to pay is holding up investments in generation and transmission.
Apart from introducing imperfections in the market mechanism, sectarian political targeting of welfare perpetuates inequality. Universal wealth redistribution through cash transfers is a more robust approach. Promises to vote banks are essentially a zero-sum game where one segment benefit at the cost of another. India has unsuccessfully experimented with inclusive growth for much of its post-independence history. It has now corrected course to grow through clusters accompanied by even-handed welfare delivery. This approach has worked in steering the economy through multiple global economic crises. A return to competitive populism will be an unnecessary throwback the world's fastest-growing major economy can do without.
Which of the following is inferred ‘zero-sum game’ in the passage?
(a) Wealth redistribution
(b) Promises to vote banks
(c) Even handed welfare delivery
(d) Balanced budget
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Promises to vote banks.
As per passage, "Promises to vote banks are essentially a zero-sum game where one segment benefit at the cost of another."
Q94: Government of India announced a medium-term fiscal deficit target of 4.5% of GDP by 2025-26, which involves a 2-percentage-point compression from current levels over the course of three financial years. Targets for the centre and states for 2023-24 are 5.9% and 3%. respectively, with half-a-percentage point leeway to the latter for power sector reforms. States have a steeper glide path for deficit reduction that is particularly vulnerable to political promises of free food and energy. Gol, on its part, is committed to a capital expenditure programme to nurse India economic recovery, and is nudging states towards fiscal balance.
India's ability to attain its pre-pandemic fiscal targets is also influenced by its need to keep credit flowing to small enterprises in an environment of globally high interest rates. Broad-based investment revival depends on keeping credit costs in check by better budgeting of government expenditure. States have additional requirement of cleaning up off-budget liabilities accumulated through political promises such as those on free electricity. Power distribution being the sole point of revenue injection, state utilities inability to pay is holding up investments in generation and transmission.
Apart from introducing imperfections in the market mechanism, sectarian political targeting of welfare perpetuates inequality. Universal wealth redistribution through cash transfers is a more robust approach. Promises to vote banks are essentially a zero-sum game where one segment benefit at the cost of another. India has unsuccessfully experimented with inclusive growth for much of its post-independence history. It has now corrected course to grow through clusters accompanied by even-handed welfare delivery. This approach has worked in steering the economy through multiple global economic crises. A return to competitive populism will be an unnecessary throwback the world's fastest-growing major economy can do without.
India's roadmap to pre-pandemic level fiscal targets is primarily influenced by the considerations of _______.
A. Keeping competitive population in check
B. Urgency of broad-based investment revival in the economy
C. Need of universal wealth re-distribution
D. Need to maintain credit flow to small enterprises
E. Steering the economy through global economic crises
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A and C only
(d) A, B and D only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and D only.
- As per passage, "India's ability to attain its pre-pandemic fiscal targets is also influenced by its need to keep credit flowing to small enterprises in an environment of globally high-interest rates.
- Broad-based investment revival depends on keeping credit costs in check by better budgeting of government expenditure."
Q95: Government of India announced a medium-term fiscal deficit target of 4.5% of GDP by 2025-26, which involves a 2-percentage-point compression from current levels over the course of three financial years. Targets for the centre and states for 2023-24 are 5.9% and 3%. respectively, with half-a-percentage point leeway to the latter for power sector reforms. States have a steeper glide path for deficit reduction that is particularly vulnerable to political promises of free food and energy. Gol, on its part, is committed to a capital expenditure programme to nurse India economic recovery, and is nudging states towards fiscal balance.
India's ability to attain its pre-pandemic fiscal targets is also influenced by its need to keep credit flowing to small enterprises in an environment of globally high interest rates. Broad-based investment revival depends on keeping credit costs in check by better budgeting of government expenditure. States have additional requirement of cleaning up off-budget liabilities accumulated through political promises such as those on free electricity. Power distribution being the sole point of revenue injection, state utilities inability to pay is holding up investments in generation and transmission.
Apart from introducing imperfections in the market mechanism, sectarian political targeting of welfare perpetuates inequality. Universal wealth redistribution through cash transfers is a more robust approach. Promises to vote banks are essentially a zero-sum game where one segment benefit at the cost of another. India has unsuccessfully experimented with inclusive growth for much of its post-independence history. It has now corrected course to grow through clusters accompanied by even-handed welfare delivery. This approach has worked in steering the economy through multiple global economic crises. A return to competitive populism will be an unnecessary throwback the world's fastest-growing major economy can do without.
Sectarian political targeting of welfare, according to the passage will result into ______.
A. Inequality
B. Market imperfections
C. Profiteering
D. Inclusive growth
E. Decentralised growth
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B and C only
(c) C and D only
(d) D and E only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A and B only.
As per passage, "Apart from introducing imperfections in the market mechanism, sectarian political targeting of welfare perpetuates inequality."
Q96: The government's efforts to use technology to make ecommerce more competitive are beginning to show up in food delivery services. Customers are reporting noticeable price differences in orders placed on online apps using the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-market places that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online. Platform fees for food delivery using ONDC are being reported at a fifth of those charged by the market leaders. This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation. This also holds out the potential to break the dominance of Swiggy and Zomato, and eventually even that of retail platforms like Amazon and Flipkart. ONDC has the potential to dilute market concentration by increased consumer choice and lower entry barriers.
It could be a game-changer on the lines of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the infrastructure on which digital transactions are growing in this country exponentially. On its own, however, technology will not be a necessary and sufficient condition to make e- commerce more competitive. UPI has exposed those limits by being dominated by PhonePe and Google Pay, despite regulators seeking enhanced competition from among a wide field players. ONDC, designed by the commerce ministry to democratise e-commerce, could get around this by not being a platform, but it needs supporting regulation to break market silos.
A proposal to revive consumer protection rules that make e-market places liable for mis-selling by sellers could impede the progress of ONDC. Sellers should ideally be responsible for information about products, and platforms be accountable for communicating it to buyers. Consumer risks are, in some ways, magnified, in network of platforms ONDC intends to create. A mushrooming of gateways to facilitate digital purchases has to be accompanied by a set of rules that clearly delineates market risk from product risk.
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is getting increased traction because of
A. Strong consumer preferences and entry barriers
B. Considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation
C. A network of interconnected e-market places
D. Mushrooming growth of gateways to facilitate digital purchases
E. Proactive govt support and policy facilitation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) B, C and E only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct option is B, C and E only.
As per passage:
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-market places that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online
- This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation.
- The commerce ministry to democratise e-commerce, could get around this by not being a platform, but it needs supporting regulation to break market silos
Q97: The government's efforts to use technology to make ecommerce more competitive are beginning to show up in food delivery services. Customers are reporting noticeable price differences in orders placed on online apps using the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-market places that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online. Platform fees for food delivery using ONDC are being reported at a fifth of those charged by the market leaders. This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation. This also holds out the potential to break the dominance of Swiggy and Zomato, and eventually even that of retail platforms like Amazon and Flipkart. ONDC has the potential to dilute market concentration by increased consumer choice and lower entry barriers.
It could be a game-changer on the lines of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the infrastructure on which digital transactions are growing in this country exponentially. On its own, however, technology will not be a necessary and sufficient condition to make e- commerce more competitive. UPI has exposed those limits by being dominated by PhonePe and Google Pay, despite regulators seeking enhanced competition from among a wide field players. ONDC, designed by the commerce ministry to democratise e-commerce, could get around this by not being a platform, but it needs supporting regulation to break market silos.
A proposal to revive consumer protection rules that make e-market places liable for mis-selling by sellers could impede the progress of ONDC. Sellers should ideally be responsible for information about products, and platforms be accountable for communicating it to buyers. Consumer risks are, in some ways, magnified, in network of platforms ONDC intends to create. A mushrooming of gateways to facilitate digital purchases has to be accompanied by a set of rules that clearly delineates market risk from product risk.
After unified payment interface (UPI) success, which of the following government initiatives is making headlines to democratize e-commerce these days in India?
(a) Restraining e-commerce giants to follow inventory based business model
(b) Decentralized e-commerce payments infrastructure
(c) Proactive government facilitations of open network for digital commerce
(d) Prevention of market concentration and monopolies
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Proactive government facilitations of open network for digital commerce.
As per the passage, "UPI has exposed those limits by being dominated by PhonePe and Google Pay, despite regulators seeking enhanced competition from among a wide field players, ONDC, designed by the commerce ministry to democratise e-commerce"
Q98: The government's efforts to use technology to make ecommerce more competitive are beginning to show up in food delivery services. Customers are reporting noticeable price differences in orders placed on online apps using the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-market places that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online. Platform fees for food delivery using ONDC are being reported at a fifth of those charged by the market leaders. This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation. This also holds out the potential to break the dominance of Swiggy and Zomato, and eventually even that of retail platforms like Amazon and Flipkart. ONDC has the potential to dilute market concentration by increased consumer choice and lower entry barriers.
It could be a game-changer on the lines of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the infrastructure on which digital transactions are growing in this country exponentially. On its own, however, technology will not be a necessary and sufficient condition to make e- commerce more competitive. UPI has exposed those limits by being dominated by PhonePe and Google Pay, despite regulators seeking enhanced competition from among a wide field players. ONDC, designed by the commerce ministry to democratise e-commerce, could get around this by not being a platform, but it needs supporting regulation to break market silos.
A proposal to revive consumer protection rules that make e-market places liable for mis-selling by sellers could impede the progress of ONDC. Sellers should ideally be responsible for information about products, and platforms be accountable for communicating it to buyers. Consumer risks are, in some ways, magnified, in network of platforms ONDC intends to create. A mushrooming of gateways to facilitate digital purchases has to be accompanied by a set of rules that clearly delineates market risk from product risk.
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is expected to ________.
A. Lower consumer risk
B. Dilute market concentration
C. Reduce cost of intermediation
D. Increase competition
E. Increase market failure
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and E only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) A, B and C only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct option is B, C and D only.
As per passage:
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-market places that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online.
- Platform fees for food delivery using ONDC are being reported at a fifth of those charged by the market leaders.
- This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation.
- This also holds out the potential to break the dominance of Swiggy and Zomato, and eventually even that of retail platforms like Amazon and Flipkart.
- ONDC has the potential to dilute market concentration by increased consumer choice and lower entry barriers.
Q99: The government's efforts to use technology to make ecommerce more competitive are beginning to show up in food delivery services. Customers are reporting noticeable price differences in orders placed on online apps using the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-market places that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online. Platform fees for food delivery using ONDC are being reported at a fifth of those charged by the market leaders. This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation. This also holds out the potential to break the dominance of Swiggy and Zomato, and eventually even that of retail platforms like Amazon and Flipkart. ONDC has the potential to dilute market concentration by increased consumer choice and lower entry barriers.
It could be a game-changer on the lines of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the infrastructure on which digital transactions are growing in this country exponentially. On its own, however, technology will not be a necessary and sufficient condition to make e- commerce more competitive. UPI has exposed those limits by being dominated by PhonePe and Google Pay, despite regulators seeking enhanced competition from among a wide field players. ONDC, designed by the commerce ministry to democratise e-commerce, could get around this by not being a platform, but it needs supporting regulation to break market silos.
A proposal to revive consumer protection rules that make e-market places liable for mis-selling by sellers could impede the progress of ONDC. Sellers should ideally be responsible for information about products, and platforms be accountable for communicating it to buyers. Consumer risks are, in some ways, magnified, in network of platforms ONDC intends to create. A mushrooming of gateways to facilitate digital purchases has to be accompanied by a set of rules that clearly delineates market risk from product risk.
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Technology is a necessary and sufficient condition to make e-commerce more competitive
Statement II: Sellers are responsible and accountable for mis-selling on digital platforms
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options Given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: B
Sol: The correct option is Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
As per passage:
- On its own, however, technology will not be a necessary and sufficient condition to make e-commerce more competitive.
- A proposal to revive consumer protection rules that make e-market places liable for mis-selling by sellers could impede the progress of ONDC.
Q100: The government's efforts to use technology to make ecommerce more competitive are beginning to show up in food delivery services. Customers are reporting noticeable price differences in orders placed on online apps using the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-market places that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online. Platform fees for food delivery using ONDC are being reported at a fifth of those charged by the market leaders. This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation. This also holds out the potential to break the dominance of Swiggy and Zomato, and eventually even that of retail platforms like Amazon and Flipkart. ONDC has the potential to dilute market concentration by increased consumer choice and lower entry barriers.
It could be a game-changer on the lines of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the infrastructure on which digital transactions are growing in this country exponentially. On its own, however, technology will not be a necessary and sufficient condition to make e- commerce more competitive. UPI has exposed those limits by being dominated by PhonePe and Google Pay, despite regulators seeking enhanced competition from among a wide field players. ONDC, designed by the commerce ministry to democratise e-commerce, could get around this by not being a platform, but it needs supporting regulation to break market silos.
A proposal to revive consumer protection rules that make e-market places liable for mis-selling by sellers could impede the progress of ONDC. Sellers should ideally be responsible for information about products, and platforms be accountable for communicating it to buyers. Consumer risks are, in some ways, magnified, in network of platforms ONDC intends to create. A mushrooming of gateways to facilitate digital purchases has to be accompanied by a set of rules that clearly delineates market risk from product risk.
According to the passage which of the following is instrument in rapid growth of the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)?
(a) Network of interconnected market places
(b) Decentralised payment infrastructure
(c) Unified payment interface for digital commerce
(d) Mushrooming gateways facilitating digital purchases
Ans: A
Sol: The correct option is Network of interconnected market places.
As per passage:
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-market places that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online.
- Platform fees for food delivery using ONDC are being reported at a fifth of those charged by the market leaders.
- This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation. This also holds out the potential to break the dominance of Swiggy and Zomato, and eventually even that of retail platforms like Amazon and Flipkart.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Commerce 13th June 2023 Shift 2 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam, and what is its significance for candidates in the field of commerce? |  |
| 2. What subjects are generally covered in the UGC NET Paper 2 for commerce? |  |
| 3. How is the UGC NET exam structured in terms of marking and duration? |  |
| 4. What are some effective preparation strategies for UGC NET Paper 2 in commerce? |  |
| 5. What eligibility criteria must candidates meet to apply for the UGC NET exam in commerce? |  |
















