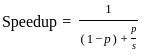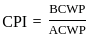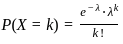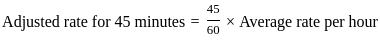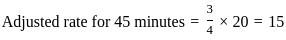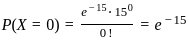UGC NET Paper 2: Computer Science 17th June 2023 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Which of the following is not a solution representation in a genetic algorithm?
1. Binary valued
2. Real valued
3. Permutation
4. Combinations
(a) Binary valued
(b) Real valued
(c) Permutation
(d) Combinations
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Combinations
In a genetic algorithm, solution representation refers to how the potential solutions (individuals in the population) are encoded. The given options can be categorized as follows:
- Binary valued: Represents solutions using binary encoding, where each gene is typically represented as either 0 or 1.
- Real valued: Represents solutions using real numbers, allowing for a more continuous representation.
- Permutation: Represents solutions as permutations of elements, where the order of elements matters.
- Combinations: This is not a standard representation in genetic algorithms. While permutations represent ordered arrangements, combinations represent unordered selections of elements. Genetic algorithms typically use representations that capture the structure and relationships among elements, and combinations may not be suitable for many optimization problems.
So, the correct answer is 4) Combinations.
Q2: Match List I with List II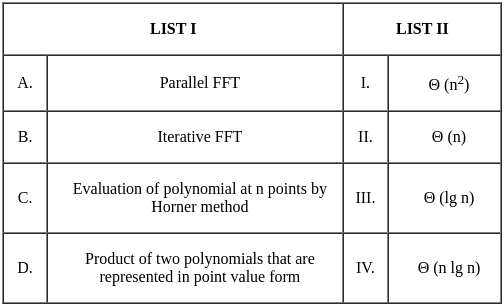
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
A - Parallel Fast Fourier Transform (FFT):
- The FFT can be executed in parallel, which reduces the time complexity from O(n log n) to O(log n) under ideal conditions, as the operations required to calculate the FFT can be effectively divided among multiple processors. Thus, it corresponds to III. Θ (lg n).
B - Iterative Fast Fourier Transform (FFT):
- The FFT, even when implemented iteratively, has a time complexity of O(n log n) because we divide the problem into smaller chunks recursively, and for each level of division, we do a constant amount of work. Hence it matches with IV. Θ (n lg n).
C - Evaluation of polynomial at n points by Horner method:
- If evaluated using the Horner method, a polynomial can be evaluated in O(n) operations. However, if we're evaluating the polynomial at n points, and the polynomial itself has degree n, the total complexity becomes O(n^2). Therefore, it corresponds to I. Θ (n^2).
D - Product of two polynomials that are represented in point value form:
- If the polynomials are represented in point-value form, their product can be computed pretty efficiently in O(n) time complexity. This is due to the fact that to compute the product polynomial at a point, you simply multiply the evaluations of the input polynomials at that point. However, a complete Fast Fourier Transform involves conversion back from point-value representation to coefficient representation, which takes O(n log n). As the question doesn't ask for this final conversion back, we'll go with II. Θ (n).
That's why the correct answer is option 3.
Q3: The following table shows the time between failures for a software:
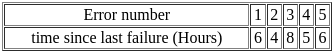
The reliability of the system for one hour operation assuming an exponential model is-
(a) 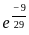
(b) 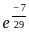
(c) 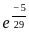
(d) 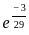
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 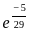
The reliability of a system in the context of reliability engineering is often modeled using the exponential distribution. The exponential reliability function is given by: 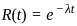
where:
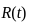 is the reliability at time t,
is the reliability at time t,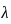 is the failure rate (reciprocal of the mean time between failures).
is the failure rate (reciprocal of the mean time between failures).
In this case, you are given the time between failures for the software:

To find the failure rate 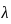 , you can use the formula:
, you can use the formula:
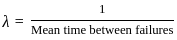
Mean time between failures (MTBF)is calculated as the average of the time between failures:
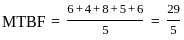
Now, the failure rate (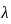 ) is:
) is:
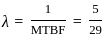
Substitute this into the reliability function:
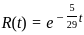
For one hour of operation ( ), the reliability becomes:
), the reliability becomes:
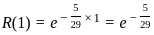
So, the correct answer is: 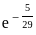
Therefore, the correct option is: 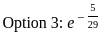
Q4: Given below are two statements:
Which of the following concurrency control protocol ensures both conflict serializability and freedom from deadlock?
Statement I: Two phase locking
Statement II: Timestamp ordering
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Two-phase locking (2PL):
- In this protocol, each transaction goes through two phases:
- The expanding (or growing) phase where locks are acquired, and the shrinking phase where locks are released.
- The name "two-phase" comes from the fact that all lock acquisitions occur before any lock is released.
- This ensures a level of consistency and conflict serializability, as two conflicting transactions can't be running at the same time.
- However, this method doesn't guarantee a deadlock-free environment.
- A deadlock situation can occur when two (or more) transactions each hold a resource the other needs, creating a standoff where neither can proceed.
Timestamp-based protocol:
- In timestamp-based protocols, each transaction is assigned a unique timestamp at the moment it is created.
- There are two types of timestamp protocols:
Thomas Write Rule and Basic Timestamp Ordering. The one that provides both conflict serializability and freedom from deadlock is the Basic Timestamp Ordering.
- This protocol ensures each transaction respects the chronological (timestamp) order of other transactions. When conflicts arise (for example if a later (younger) transaction tries to write data that an earlier (older) transaction is reading or writing), the conflicting transaction can be rolled back and restarted to prevent the scenario from causing inconsistency, thus ensuring conflict serializability.
- And since a younger transaction will always concede to an older one by being rolled back and restarted, there's no chance for deadlocks to occur, thus ensuring freedom from deadlock.
So, Statement I is incorrect because Two-phase locking (2PL) does not ensure freedom from deadlock, and Statement II is correct because Timestamp-based protocol ensures both conflict serializability and freedom from deadlock.
Q5: The clipping process in computer graphics is used for
(a) Adding graphics
(b) Copying
(c) Zooming
(d) Removing objects and lines
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Removing objects and lines
Clipping in computer graphics is the process of constraining the visibility of objects and lines within a defined view or volume, typically a rectangular window view. In simpler terms, it means cutting off areas of geometric shapes that lie outside the viewing volume.
This process is incredibly crucial in 2D and 3D graphics alike for several reasons:
- Performance Optimization: Rendering all elements in a given scene could be computationally intensive. By clipping objects that are not in the field of view, it significantly reduces the processing requirement, because these objects, despite being concealed, would still consume computational resources if not clipped.
- Visibility Maintenance: Clipping is also necessary for maintaining proper visibility of elements in the scene. For example, an object behind the viewer in a 3D scene doesn't need to be rendered. In complex scenes, this also accounts for different layers of objects, where objects in the foreground should block objects in the background.
- Correct perspectives in 3D spaces: 3D rendering involve translating three-dimensional coordinates to two-dimensional points to be displayed on the screen. Clipping ensures that the objects further away appear smaller and the ones closer look bigger, giving a sense of depth and maintaining correct perspective.
The primary types of clipping include Point Clipping, Line Clipping, Area Clipping (or Polygon Clipping), and Text Clipping. Each type has specific algorithms that work most efficiently for their respective tasks. The most well-known of these are the Cohen-Sutherland and the Liang-Barsky line-clipping algorithms.
Q6: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: I/O protection is ensured by a hardware trap
Reason R: I/O interrupt caused by the condition like I/O completion and device malfunction occurring within the I/O devices
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A is false but R is true
Assertion A:
- I/O protection is ensured by a hardware trap is not true because I/O protection is ensured by operating system routines.
- This is usually part of the kernel's responsibility, the core component of most operating systems. Kernel takes care of input/output (I/O) operations to ensure that they are performed safely, efficiently, and in accordance with the permissions of the active processes and users.
- This way, the operating system helps to prevent unauthorized access to I/O devices and maintains system integrity and security.
Reason R:
- I/O interrupt caused by the condition like I/O completion and device malfunction occurring within the I/O devices is true because an I/O interrupt can be triggered by events such as I/O completion and device malfunctions.
Q7: Let R = {x : x ∈ N, x is multiple of 3 and x ≤ 100} and S = {x : x ∈ N, x is a multiple of 5 and x < 100}. What is the number of elements in (R ∩ S) × (S ∩ R)?
(a) 36
(b) 33
(c) 20
(d) 6
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer 36
- The set R is the set of natural numbers less than or equal to 100 that are multiples of 3, while the set S is the set of natural numbers less than 100 that are multiples of 5.
- The intersection of these two sets, R ∩ S, would be multiples of both 3 and 5, or multiples of 15, that are less than 100. The multiples of 15 that are less than or equal to 100 are {15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90}, so there are 6 elements in the intersection of these sets.
- The cartesian product (R ∩ S) × (S ∩ R) would involve all ordered pairs where the first element is chosen from R ∩ S and the second element is chosen from S ∩ R. However, since the sets R ∩ S and S ∩ R are the same, this is basically choosing two elements from the set R ∩ S, which has 6 elements.
- The number of pairs we could form are 6 * 6 = 36.
So, the answer is: 36
Q8: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Fuzzifier is a part of a fuzzy system
Statement II: Inference engine is a part of fuzzy system
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
"Fuzzy" in this context refers to a systems or control method that smooths the harsh transitions of binary (on-off, true-false, yes-no) responses to more human-like spectrums of response. Fuzzy systems deal with degrees of truth, as opposed to binary logic which deals with true or false (1 or 0, on or off).
Fuzzifier:
- A Fuzzifier is a component of a fuzzy logic system that transforms crisp data inputs to fuzzy logic variables. In simpler terms, it takes a precise or specific input and decides the degree to which this input belongs to each of several predefined fuzzy sets.
- Fuzzy sets could be something like "Cold", "Warm", "Hot", when you're talking about expressing the temperature in a fuzzy system.
- For instance, If we input temperature data, a Fuzzifier will convert the exact temperature value to a degree of membership to the fuzzy sets of “Cold,” “Warm,” and “Hot.” For example, if the temperature is 25 degrees Celcius, the fuzzifier could interpret that as being "0% Cold", "50% Warm," and "50% Hot." This isn't a binary, it's a smooth transition between sets.
Inference Engine:
- Then we have the Fuzzy Inference Engine, which is also a part of any fuzzy system. The Fuzzy Inference Engine applies certain rules (which can be thought of as something similar to if-then clauses) to the fuzzy inputs after they've been calculated by the fuzzifier, to derive fuzzy outputs. This engine basically applies these rules to produce a new fuzzy set as a result.
- Continuing the temperature example, the fuzzy inference engine might apply rules like, "IF temperature is Warm THEN fan speed is Medium". These rules are usually set by the human designer of the system, based on some interpretation of what should happen under different circumstances.
- After the inference engine processes, a Defuzzifier then turns this fuzzy output back into a specific, crisp (clear and precise) value.
Both Fuzzifier and Inference Engine are indeed components of a fuzzy system, and they are pivotal in making any fuzzy logic model work. So, statement I and statement II are correct.
Q9: What will be the output of the following code?
#include <stdio.h>
int main ( ) {
int a, b, c;
a = 0x10;, b = 010;, c = a + b;
printf ("%d", c);
return 0;
}
(a) 20
(b) 24
(c) Garbage
(d) error
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 24
:
#include
int main() {
int a, b, c;
a = 0x10; // Hexadecimal notation for 16
b = 010; // Octal notation for 8
c = a + b;
printf("%d", c);
return 0;
}
0x10 is a hexadecimal representation which is equivalent to 16 in decimal and 010 is an octal representation which is equivalent to 8 in decimal.
So, c = a + b calculates as c = 16 + 8.
Hence, the output will be 24.
Q10: What is the output of following code?
#include <stdio.h>
main ()
struct s1
{char * z;
int i;
struct s1 * p;
}
static struct s1 a [ ] = {
{"Nagpur", 1, a + 1}
{"Raipur', 2, a + 2}
{"Kanpur', 3, a}
}:
struct s1* ptr = a:
printf (%s %s %s\n", a[0].z, ptr → z, a[2].p → z);
}
(a) Nagpur Raipur Kanpur
(b) Nagpur Nagpur Nagpur
(c) Kanpur Kanpur Kanpur
(d) Error
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Nagpur Nagpur Nagpur
In C programming, a structure (struct) is a user-defined data type that groups related variables of different data types together. A struct is used for packaging data where each element, known as a member, can have a different type.
#include
typedef struct s1 {
char * z;
int i;
struct s1 * p;
} s1;
int main() {
static s1 a[3] = {{"Nagpur", 1, a + 1}, {"Raipur", 2, a + 2}, {"Kanpur", 3, a}};
s1* ptr = a;
printf("%s %s %s\n", a[0].z, ptr -> z, a[2].p -> z);
return 0;
}
a[0].z refers to the string "Nagpur", which is the z value of the first structure.
ptr -> z also points to "Nagpur" because ptr was initialized to point to the first structure in the array.
a[2].p -> z also gives "Nagpur" because p of the third structure was initialized to point to the first structure in the array.
Therefore, the output of the corrected version of the provided code would be: Nagpur Nagpur Nagpur
This means the correct option from the given choices is 2) Nagpur Nagpur Nagpur.
Q11: Match List I with List II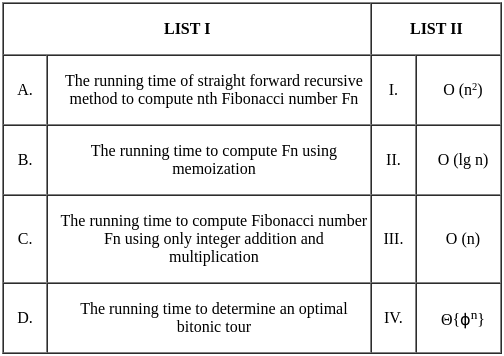
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(c) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
- A. The running time of a straightforward recursive algorithm to compute the nth Fibonacci number is exponential in the worst case, which can be represented as O(2^n) (this complexity is larger than any options provided). But, as an approximation, we can denote this as Θ{ϕn}, where ϕ is the golden ratio. So, A matches with IV.
- B. Using memoization (or dynamic programming), the time complexity of calculating the nth Fibonacci number will become linear, i.e., O(n), because we store and reuse the results of the sub-problems. So, B matches with III.
- C. When we use the matrix exponentiation method to compute Fibonacci numbers, the running time is O(log n), as it computes the nth Fibonacci number by performing only integer addition and multiplication using the matrix [[1,1], [1,0]]. So, C matches with II.
- D. The time complexity of determining an optimal bitonic tour is quadratic as it involves computations for each pair of points so Θ(n^2) is applicable. So, D matches with I.
Q12: Consider a disk system with 100 cylinders. The request to access the cylinders occurs in the following sequence:
4, 34, 10, 7, 19, 73, 2, 15, 6, 20
Assuming that the head is currently at cylinder 50, what is the time taken to satisfy all requests if it takes 1 ms to move from one cylinder to adjacent one and shortest seek time first policy is used?
(a) 119 ms
(b) 120 ms
(c) 142 ms
(d) 146 ms
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 119 ms
The Shortest Seek Time First (SSTF) Algorithm operates on the principle of servicing all requests in proximity to the current head location before moving further away. This strategy centralizes on serving requests that are nearest to the present location of the head, with the rationale being that the distance traversed by the head increases with the number of cylinders, so the SSTF algorithm prioritizes pending requests that are closest to the current position of the head.
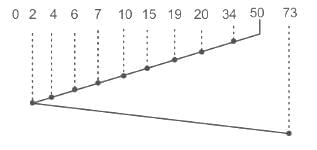
⇒ 50 - 2 = 48
⇒ 73 - 2 = 71
⇒ time taken to satisfy all requests = 48 + 71 = 119
Q13: Find the sum of all four digit numbers formed using the digits 1, 2, 4 and 6.
(a) 86,658
(b) 88,858
(c) 91,958
(d) 93,358
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 86,658
We want to find the sum of all four-digit numbers that can be formed using the digits 1, 2, 4, and 6. Each distinct digit will occupy each place value (Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, and Units) the same number of times when we consider all possible permutations.
There are total 4! = 4*3*2*1 = 24 ways to permute 4 different digits in 4 places.
The sum of all 4-digit numbers can be found by calculating the sum for each of the 4 positions (Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, and Units), then summing those results.
For each position:
- Each of the 4 numbers (1, 2, 4, 6) will appear in each position 1/4th of the time in the total permutations, so 24 / 4 = 6 times for each.
- The sum of the digits is 1 + 2 + 4 + 6 = 13.
- So, the contribution for each position will be 13 * 6 = 78.
Now, we calculate the total sum taking into account the place value:
- The Thousands place contributes 78 * 1000 = 78,000.
- The Hundreds place contribute 78 * 100 = 7,800.
- The Tens place gives 78 * 10 = 780.
- The Units place contributes 78 * 1 = 78.
Adding those up, the total sum of all 4-digit numbers that can be made with the digits 1, 2, 4, and 6 is 78,000 + 7,800 + 780 + 78 = 86,658. So the answer is option 1) 86,658.
Q14: How will you free the memory allocated by the following program?
# include
#i nclude < stdio.h >
#define MAXROW 3
#define MAXCOL 4
int main()
{
int ** p, i, j;
p = (int **)malloc (MAXROW* size of (int*));
return 0:
}
(a) memfree (int p);
(b) dealloc (p);
(c) malloc (p, 0);
(d) free (p):
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is free(p);
The way to free the memory allocated by the given C program is option 4) free(p);.
The malloc function is used to dynamically allocate memory in the heap to store a 2D array (matrix) with MAXROW number of pointers to int.
#include
#include
#define MAXROW 3
#define MAXCOL 4
int main() {
int **p, i, j;
// Allocate memory for MAXROW pointers to int
p = (int **)malloc(MAXROW * sizeof(int*));
// Allocate memory for each row
for(i = 0; i < MAXROW; i++) {
p[i] = (int *)malloc(MAXCOL * sizeof(int));
}
// Free memory for each row
for(i = 0; i < MAXROW; i++) {
free(p[i]);
}
// Finally, free the memory for the pointers
free(p);
return 0;
}
The fixed version of the program allocates the memory for each row in the array and then frees it sequentially before at the end, releasing the memory used for the array of pointers itself.
Q15: If A = {4n + 2 | n is a natural number} and B = {3n | n is a natural number}. Which of the following is correct for A ⋂ B?
(a) {12n2 + 6n | n is a natural number}
(b) {24n - 12 | n is a natural number}
(c) {60n + 30 | n is a natural number}
(d) {12n - 6 | n is a natural number}
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is {12n - 6 | n is a natural number}
Set A generates numbers of the form 4n + 2, and set B generates numbers of the form 3n, both when n is a natural number. The intersection of the two sets will be numbers that can be generated by both formats.
Set A generates number:
n = 1, 2, 3, 4, ...
- 4*1 + 2 = 6
- 4*2 + 2 = 10
- 4*3 + 2 = 14
- 4*4 + 2 = 18
Set B generates number:
n = 1, 2, 3, 4, ...
- 3*1 = 3
- 3*2 = 6
- 3*3 = 9
- 3*4 = 12
- 3*5 = 15
- 3*5 = 18
A ⋂ B = (6, 10, 14, 18) ⋂ (3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18)
A ⋂ B = (6, 18)
Upon closer inspection, the option 4) {12n - 6 | n is a natural number} can indeed generate the sequence of numbers that belong to both A and B.
This sequence starts with ... when n = 1, 12*1 - 6 = 6 when n = 2, 12*2 - 6 = 18 when n = 3, 12*3 - 6 = 30 and so on.
These are indeed the terms that are common to sets A and B.
So, the correct answer is indeed option 4) {12n - 6 | n is a natural number}.
Q16: The total cost of retrieving records in sorted order using an unclustered B+ tree is
(P-Average number of records per data page
N-Data pages
F-Ratio of the size of a data entry to the size of a data record)
(a) (F*N) + P
(b) (F + P) * N
(c) F*N*P
(d) F + P/N
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is (F *NP) + P
Definitions from the question:
P = Average number of records per data page
N = Total number of data pages
F = Ratio of the size of a data entry (in the index) to the size of a data record
Key Concept – Unclustered B+ Tree Access in Sorted Order:
When a B+ tree is unclustered, the data entries (in the B+ tree) are stored separately from the actual data records.
If we retrieve records in sorted order:
We scan the leaf level of the B+ tree in order (cheap)
But for each data entry, we must fetch the corresponding data record from its data page
Since the index is unclustered, the records are not stored together — leading to many random I/Os.
Now, consider that for each data record, on average, 1 I/O is needed to fetch it from its own data page.
But here’s the twist: if each data page holds P records, and there are N data pages, then:
Total number of records = P × N
Total number of data entries = F × P × N
(Because F is the ratio of data entry size to data record size, so F times more entries than full records)
Now, in worst-case sorted retrieval:
We need to follow the order of data entries in B+ tree
For each entry, we access the corresponding record on a data page
Since it's unclustered, this can lead to up to F × N page reads (each of F records per page leads to a new page I/O)
Finally, for each page we retrieve, we may have to read multiple records on it (P per page), hence the P factor.
Final formula:
Total cost = F ⋅ N + P
Correct Answer: (a) (F × N) + P
Q17: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
A virtual memory system uses first-in first-out page replacement policy and allocates a fixed number of frames to a process
Assertion A: Increasing number of page frames allocated to a process sometimes increases the page fault rate.
Reason R: Some programs do not exhibit locality of reference.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct of A
Assertion A is true because of the phenomenon known asBelady's Anomaly-
- In some instances, increasing the number of page frames may result in an increased page fault rate.
- This unexpected result typically has to do with the specific page replacement algorithm being used not always behaving the way you'd expect as more and more page frames are added.
- In this case, the algorithm mentioned is First-In-First-Out (FIFO).
Reason R is also true, because some programs do not exhibit locality of reference.
- Locality of reference means that programs tend to request pages which are related to the pages they have already requested, or are likely to request pages they have requested recently. Not all programs follow this pattern.
However, R is not the correct of A. Belady's Anomaly isn't caused by a lack of locality of reference, rather it is related to the particular nuances of the replacement algorithm in question (in this case, FIFO). So while both statements are true, they aren't connected in the way the question implies. Hence the answer is option 2.
Q18: At a particular time of computation, the value of a counting semaphore is 7. Then 20 p operations and 'x' V operations were completed on this semaphore. If the final value of semaphore is 5. x will be
(a) 15
(b) 22
(c) 18
(d) 13
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 18
A counting semaphore is a synchronization mechanism used in concurrent programming to control access to a shared resource. It maintains a counter that can be incremented or decremented, allowing a specified number of threads or processes to access the resource simultaneously. The semaphore helps prevent race conditions and ensures orderly access to shared resources in a multithreaded or multiprocess environment.
- P stands for a wait operation. It reduces the value of counting semaphore by one for each wait operation.
- V stands for a signal operation. It increases the value of counting semaphore by one for each signal operation.
The current value of counting semaphore is 7. After performing 20P the value of counting semaphore becomes -13. Now 'n' V operations are to be performed, which makes the value of counting semaphore as 5.
The generated equation is like this: = -13 + n = 5
⇒ n = 5 + 13
⇒ n = 18
Q19: A processor chip is used for application in which 30% of execution time is spent on floating point addition. For the new model of the processor, the design team has come up with redesign of the floating point adder to make it twice as fast. What will be possible maximum speed up by this redesign?
(a) 2.0
(b) 1.06
(c) 1.18
(d) 2.5
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 1.18
To answer this question, we can use Amdahl's law, which is used to find the maximum improvement to an overall system when only part of the system is improved. The formula is:
where:
- p is the proportion of the execution time that the part to be improved contributes to the system and
- s is the speedup for that part.
In this problem, 30% of the execution time (or 0.30) is spent on floating point addition, so p = 0.30.
The floating point addition is being made twice as fast, so s = 2.
Let's plug these values into Amdahl's law to calculate the speedup.
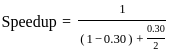
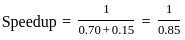
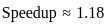
Thus, a maximum speedup of 1.18 could be achieved by making the floating point addition twice as fast. Therefore, the correct answer is option 3) 1.18.
Q20: Which of the following transforms in 2 dimension is used to resize a 2-dimensional object?
(a) Translation
(b) Rotation
(c) Scaling
(d) Shearing
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Scaling
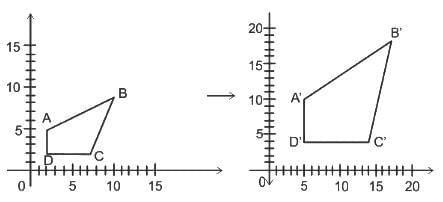
Scaling:
- Scaling is a geometric transformation that changes the size of a figure or a space, but not its shape.
- This transformation can either enlarge (scale up) or reduce (scale down) the dimensions of the object by a specific scale factor.
- This is the transform used to resize a 2D object.
Other Related Points
Translation:
- This is a geometric transformation that moves every point of a figure or a space by the same distance in a given direction. In 2D space, you can think of it as simply sliding the entire object either horizontally, vertically, or both.
Rotation:
- Rotation is a transformation that turns a figure or a space around a fixed point, called the center of rotation. The amount of rotation is typically specified in degrees.
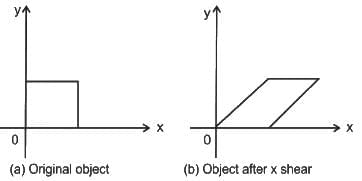
Shearing:
- Shearing is a transformation that distorts the shape of an object such that the angles between its points are changed, but not their collinearity or incidence relationships. You can think of it as a sort of "skew" transformation, slanting the object in a specific direction while keeping all points along a shear invariant parallel line in their original locations
Q21: A three dimensional array in C++ is declared as int A [a] [b] [c]. Consider that array elements are stored in row major order and indexing begins from 0. Here the address of an item at the location A [r] [s] [t] computed in terms of word length w of an integer is
(a) & A [0] [0] [0] + w (b*c*s + c*r + t)
(b) & A [0] [0] [0] + w (b*c*r* + c*s + t)
(c) & A [0] [0] [0] + w (a*b*r* + c*s + t)
(d) & A [0] [0] [0] + w (a*b*s + c*r + t)
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is & A [0] [0] [0] + w (b*c*r* + c*s + t)
In C++, for a 3-dimensional array declared as int A[a][b][c], the memory is allocated in a sequence such that it increases with 'c' first, then 'b', and finally 'a'. This is because the elements are stored in row-major order.
So, when we are trying to find the address of an element A[r][s][t]:
- 't' will contribute to its value directly, because we are moving in the 'c' dimension,
- 's' will have to consider all 'c' steps we have to take for every shift in the 'b' direction, hence 's' contributes 'c*s' shifts,
- 'r' will have to consider all 'bc' steps we have to take for every shift in the 'a' direction, hence 'r' contributes 'bc*r' shifts.
Therefore, the correct formula would be: & A[0][0][0] + w * (b*c*r + c*s + t)
So, the correct answer would be option 2: & A [0] [0] [0] + w (bcr + c*s + t)
Q22: Consider the following statements:
A. A database design is in BCNF if each member of the set of relation schemas that constitutes the design is in BCNF
B. A BCNF schema can have transitive dependency
C. It is always possible to obtain a 3NF design without sacrificing a lossless join
D. There are multivalued dependencies in 4NF
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A, C and D only
A. A database design is in BCNF if each member of the set of relation schemas that constitutes the design is in BCNF.
- This is true. BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form) applies at the relation schema level (a set of attributes); if all relation schemas are in BCNF, the database design can be said to be in BCNF.
B. A BCNF schema can have transitive dependency.
- This is false. The definition of BCNF is that for every dependency X -> Y in a relation, X must be a superkey. This disallows transitive dependencies, which would imply that there's a non-superkey attribute that determines another attribute.
C. It is always possible to obtain a 3NF design without sacrificing a lossless join.
- This is true. The process of normalizing a database schema to 3NF can be done in such a way that it does not lose the ability to perform a lossless join. This is ensured by taking care that when a functional dependency X -> Y causes a violation, the decomposition of the relation includes X in all decomposed relations.
D. There are multivalued dependencies in 4NF.
- This is True. 4NF (Fourth Normal Form) is specifically designed to handled multivalued dependencies. A multivalued dependency always requires at least three attributes because it consists of at least two attributes that are dependent on a third.
Based on these s, we can see that only statements A, C and D are true. Therefore, the correct option using the provided choices is: A, C, and D only
Q23: Consider a popular sports news site. At a given moment, 20,000 concurrent users submit a request (a transaction, T) once every 2 minutes on average. Each transaction requires the webapp to download a new article that on average has 3k bytes in length. What is the throughput?
(a) 8 megabits per second
(b) 4 megabits per second
(c) 6 megabits per second
(d) 2 megabits per second
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 4 megabits per second
First, we need to determine the amount of data transferred in one transaction.
The length of an average article is 3k bytes.
- In terms of bits, this would be 3000 bytes * 8 bits/byte = 24000 bits.
Next, let's calculate the total amount of data transferred in one minute.
- There are 20,000 users, each of whom submits a request once every 2 minutes.
- Therefore, in one minute, there will be 20,000 users / 2 = 10,000 transactions.
For each transaction, we've determined that there are 24,000 bits.
So, the total amount of data transferred in one minute is 10,000 transactions * 24,000 bits/transaction = 240 x 106 bits.
Since this question asked for throughput in megabits per second, we need to convert this quantity.
- 1 minute = 60 seconds,
- therefore, throughput = 240 x 106 bits/minute / 60 seconds/minute
- = 4 x 106 bits/second = 4 megabits/second. (megabits = 106)
So, the answer is: 4 megabits per second
Q24: A TCP server application is programmed to listen on port P on host S. A TCP client is connected to the TCP server over the network, Consider that while TCP connection is active the server is crashed and rebooted. Assume that the client does not use TCP keepalive timer. Which of the following behaviour/s is/are possible?
Statement I: The TCP application server on S can listen on P after reboot.
Statement II: If client sends a packet after the server reboot, it will receive the RST segment.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Statement I:
- After the server is rebooted, the TCP server application can indeed start listening again on the same port P.
- There is nothing technically preventing this. After a crash, provided there are no other issues (like issues with the OS, hardware, the network, etc.), the server software can start up again and bind to the same port it was listening on before the crash.
Statement II:
- When the client sends a packet after the server rebooted, it's very likely to receive a RST (reset) segment in response.
- This is because from the server's perspective, it has no knowledge of any prior connection that might have existed before it rebooted, so if it gets a packet from the client for what the client thinks is an ongoing connection, the server's response will be to send a RST to effectively tell the client "I don't know about any such connection."
Q25: Consider the following statements:
S1: LRU page replacement algorithm suffers from the belady's anomaly
S2: Shortest remaining time first scheduling may cause starvation
S3: Stack is shared by all threads in a process
(a) S1, S2 and S3 are true
(b) S1, S3 false and S2 is true
(c) S1, S2 are false and S3 is true
(d) S1, S2 and S3 are false
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is S1, S3 false and S2 is true
S1: LRU (Least Recently Used) page replacement algorithm suffers from belady's anomaly. False -
- The LRU (Least Recently Used) page replacement algorithm does not suffer from Belady's anomaly.
- Belady's anomaly is the phenomenon where increasing the number of page frames results in an increase in the number of page faults.
- This anomaly is typically associated with the FIFO (First-in, First-out) page replacement algorithm, not with LRU.
S2: Shortest remaining time first scheduling may cause starvations. True -
- The Shortest Remaining Time First (SRTF) scheduling algorithm can indeed cause starvation.
- This happens when short processes keep coming. This can indefinitely postpone the execution of longer processes, leading to their starvation.
S3: Stack is shared by all threads in a process. False -
- In a multithreaded process, each thread has its own separate stack space.
- This is necessary to keep track of the execution state for each individual thread.
- Other parts of the process such as the heap, global variables, and code segment are shared among all threads.
So, according to the given statements: S1: False S2: True S3: False
The appropriate choice is: 2) S1, S3 false and S2 is true.
Q26: Which of the following is used to determine the cost performance index?
(a) Budgeted cost of work performed - budget at completion
(b) Budgeted cost of work performed ÷ budget at completion
(c) Budgeted cost of work performed ÷ Actual cost of work performed
(d) Budgeted cost of work performed - Actual cost of work performed
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Budgeted cost of work performed ÷ Actual cost of work performed
The Cost Performance Index (CPI) is a key performance indicator in project management, particularly in the context of earned value management. It is used to assess the efficiency of cost performance on a project. The formula for calculating CPI is:
Where:
- BCWP (Budgeted Cost of Work Performed): The value of the work actually performed and completed according to the budget.
- ACWP (Actual Cost of Work Performed): The actual cost incurred for the work performed.
So, the CPI is essentially a ratio that helps you understand how well the project is performing in terms of cost efficiency. If the CPI is greater than 1, it indicates that the project is under budget, which is generally a positive sign. On the other hand, if the CPI is less than 1, it suggests that the project is over budget.
Now, let's relate this to the given options: 
This is the correct formula for calculating the Cost Performance Index (CPI) based on the above. It compares the budgeted cost of the work performed to the actual cost of the work performed. Therefore, option 3 is the correct choice for determining the Cost Performance Index.
Q27: Which is not a basic approach to the problem of conflict resolution in a production system?
(a) Assigning a preference based on the rule that matched
(b) Assigning a preference based the object that matched
(c) Assigning a preference based on the action that the matched rule would perform
(d) Assigning a preference based on the action that the matched object would perform
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Assigning a preference based on the action that the matched object would perform
In the context of conflict resolution in a production system, different rules may be applicable or relevant to a given situation, and there could be conflicts when multiple rules are triggered. Resolving these conflicts involves deciding which rule should take precedence or have a higher priority.
Assigning a preference based on the rule that matched:
- This approach involves giving priority to the rule itself. If multiple rules are triggered, the one with the highest priority or preference based on some criteria will be selected.
Assigning a preference based on the object that matched:
- This approach involves giving priority to the object (data, entity, etc.) that the rule is applied to. Depending on the characteristics or properties of the matched object, priority is assigned.
Assigning a preference based on the action that the matched rule would perform:
- This approach involves considering the action or operation that each rule would perform. The rule with the action that is deemed more critical or appropriate in the given context is given higher priority.
Assigning a preference based on the action that the matched object would perform:
- This option is not typically a basic approach in conflict resolution. Assigning preference based on the action that the matched object would perform is less common in traditional conflict resolution strategies. Usually, the focus is on rules, objects, or both.
In summary, assigning a preference based on the action that the matched object would perform (Option 4) is less common in the context of basic conflict resolution strategies in production systems. The more common approaches involve prioritizing rules, objects, or actions associated with the rules.
Q28: Let R (A, B, C, D, E, F) be a relational schema with following functional dependencies:
C → F, E → A, EC → D, A → B. Which of the following is a key for R?
(a) CD
(b) EC
(c) AE
(d) AC
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is EC
In order to find the key for a relational schema, we need to find a minimal set of attributes which can determine all other attributes. This is usually done by calculating the closure of each set of attributes.Given the functional dependencies:
- C → F, E → A, EC → D, A → B
Let's compute the closure of each candidate key:
- For CD closure: CD C gives F by the dependency C → F. But no other attributes can be determined. So, CD closure is CDF. It does not include all attributes.
- For EC closure: EC E gives A by the dependency E → A, and EC gives D by the dependency EC → D. Then, A gives B. Now we have ECABDF which includes all the attributes.
So, the key for R is EC.
Q29: Consider the following statements about heap sort algorithm:
A. The MAX-HEAPIFY procedure which runs in O(log n) time, is the key to maintaining the max heap property
B. The BUILD-MAX-HEAP procedure, which runs in O(log n) time, produces max-heap from an unordered input array
C. The MAX-HEAP-INSERT, which runs in O(log n) time, implements the insertion operation
D. The HEAP-INCREASE-KEY procedure runs in O(log n) time, to set the key of new node of its correct value
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B only
(b) A, C only
(c) B, D only
(d) A, B, C, D
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A, C only
A. The MAX-HEAPIFY procedure which runs in O(lg n) time, is the key to maintaining the max heap property.
- This statement is true. The MAX-HEAPIFY procedure is responsible for maintaining the max-heap property, and it indeed runs in O(log n) time.
B. The BUILD-MAX-HEAP procedure, which runs in O(lg n) time, produces a max-heap from an unordered input array.
- This statement is incorrect. The BUILD-MAX-HEAP procedure has a time complexity of O(n), not O(log n). It builds a max-heap from an unordered input array in linear time.
C. The MAX-HEAP-INSERT, which runs in O(lg n) time, implements the insertion operation.
- This statement is true. The MAX-HEAP-INSERT operation involves inserting a new element into the max-heap and then maintaining the max-heap property. Its time complexity is O(log n).
D. The HEAP-INCREASE-KEY procedure runs in O(n lg n) time to set the key of a new node to its correct value.
- This statement is incorrect. The time complexity of HEAP-INCREASE-KEY is O(log n), not O(n log n). It is used to increase the key of a node in a max-heap to its correct value.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 2) A, C only.
Q30: Consider the following statements about the software product line system:
Statement I: At the interaction level, components provide an operator display interface and an interface with the communication system used.
Statement II: At the I/O management level, components handle operator authentication, report generator and query manager.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Statement I: "At the interaction level, components provide an operator display interface and an interface with the communication system used." -
- It is true that at the interaction level, components often provide the user interface (which could include operator display) and the interface with the various other systems it needs to communicate with such as databases, files, other external systems, etc.
- Statement II: "At the I/O management level, components handle operator authentication, report generator and query manager." -
- The handling of operator authentication, report generation, and query management indeed seems to be the responsibilities of components at the I/O management level.
So, Option 1) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
Q31: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: The AVL trees are more balanced as compared to Red Black trees, but they may cause more rotations during insertion and deletion
Reason R: A Red Black tree with n nodes has height that is greater than 2 log2 (n + 1) and the AVL tree with n nodes has height less than logΦ (√5 (n+2)) -2 (where Φ is golden ratio)
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A is true but R is false
Assertion A: "AVL trees are more balanced as compared to Red Black trees, but they may cause more rotations during insertion and deletion."
- This assertion is correct. AVL trees are more strictly balanced than Red-Black trees, meaning that the height difference between the left and right subtrees of any node (called the balance factor) is at most 1 in AVL trees, whereas it can be up to 2 in Red-Black trees.
- However, this strict balancing in AVL trees can lead to more rotations during insertion and deletion operations compared to Red-Black trees.
Reason R: "A Red-Black tree with n nodes has a height that is greater than 2 log₂ (n + 1), and the AVL tree with n nodes has a height less than logΦ (√5 (n+2)) - 2 (where Φ is the golden ratio)."
- This reason is incorrect. The correct upper bound for the height of a Red-Black tree with n nodes is 2 log₂ (n + 1), not greater than.
- The statement for AVL trees is also incorrect; the correct upper bound for the height of an AVL tree with n nodes is approximately 1.44 * log₂(n+2) - 1.329.
Therefore, Assertion A is correct, but Reason R is incorrect. The correct answer is option 3: "A is true but R is false."
Q32: 256 Mb DRAM is organized as a 32M × 8 memory externally and as a 16K × 16K square array internally. Each row must be refreshed at least once every 50 milisecond to forestall loss of data; refreshing one row takes 100 nanoseconds. What fraction of the total memory bandwidth is lost to refresh cycles?
(a) 6.6%
(b) 3.3%
(c) 9.9%
(d) 4.3%
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 3.3%
To calculate the fraction of total memory bandwidth lost to refresh cycles, we need to consider the time spent on refreshing compared to the total time available.
First, let's find out how many rows are there in the DRAM:
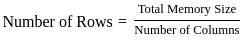

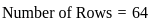
Now, let's calculate the time required to refresh all rows:
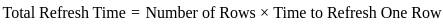
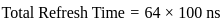
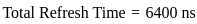
Now, let's find the time available for data access in one refresh cycle:
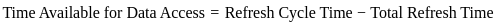
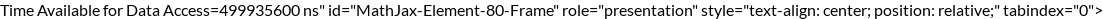
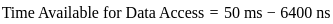
Finally, let's find the fraction of time lost to refresh cycles:
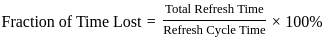
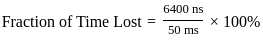
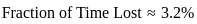
Now, let's compare this result with the given options:
The closest option is 3.3%, so the correct answer is: 2) 3.3%
Q33: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Validity checks real need of system users
Reason R: Completeness checks system user defined requirements.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct of A
- A validation check in software development ensures that the system is structured to meet the specified requirements and helps determine if the system meets the needs of the system users.
- The statement "Completeness checks system user-defined requirements," entails that a completeness check ensures all necessary parts of the system have been included and all requirements are fulfilled.
- Therefore, while both statements are true, Reason R does not directly explain Assertion A. They pertain to different aspects of system checks in software development. Validation is more about ensuring the system works as intended for the users, whereas completeness is about fulfilling all defined requirements, whether user-specific or functional.
Q34: Given the basic E R diagram and relational model, which of the following is incorrect?
(a) An attribute of an entity can have more than one value
(b) An attribute of an entity can be composite
(c) In a row of relational table, an attribute can have more than one value
(d) In a row of a relational table, an attribute can have exactly one value or a NULL value
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is In a row of relational table, an attribute can have more than one value
- In a relational database model, each attribute of a tuple (or row) must have only one value.
- This is a reflection of the atomicity property of the relational model.
- If more than one value is required, it should be represented as another row, or possibly in another table depending on the relationship.
- This is to maintain the integrity and simplicity of the design.
- However, it's worth mentioning that some modern DBMS do support multi-valued attributes, although this is outside the scope of the classical relational model.
Other Related Points
- An attribute in an ER diagram refers to a property or characteristic of an entity or relationship. In a relational model, it's equivalent is a table column.
- In ER modeling, an attribute can be single-valued or multi-valued. However, in a strict relational database model, each attribute of a row must have a single value (atomicity). If multiple values are needed, they can be normalized and placed in separate rows or tables.
- A composite attribute can be divided into smaller sub-attributes, which come together to represent a fuller concept. For example, an entity "Person" might have a composite attribute "Full Name", subdivided into "First Name" and "Last Name".
- In relational model, an attribute in a row can hold a single value or be marked as NULL, representing the absence of a value or unknown information.
Q35: Match List I with List II
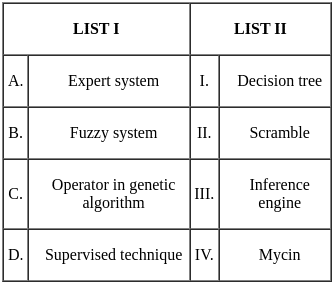
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
A. Expert system - IV. Mycin:
- An expert system is a computer program that emulates the decision-making ability of a human expert. It uses a knowledge base of human expertise and an inference engine to draw conclusions.
- Mycin is a classic example of an expert system designed for medical diagnosis. It used a rule-based system to analyze patient symptoms and recommend treatments.
B. Fuzzy system - III. Inference engine:
- Fuzzy systems deal with uncertainty and imprecision in data by using fuzzy logic, which allows for degrees of truth rather than strict true or false values.
- The inference engine is a component of an expert system that processes the rules and facts to draw conclusions. In the context of fuzzy systems, it handles the fuzzy logic rules.
C. Operator in genetic algorithm - II. Scramble:
- Genetic algorithms are optimization algorithms inspired by the process of natural selection. They use operators like mutation and crossover to evolve a population of solutions over generations.
- Scramble is a type of crossover operator in genetic algorithms. It involves randomly reordering segments of genetic information within individuals to create new offspring.
D. Supervised technique - I. Decision tree:
- Supervised learning involves training a model on a labeled dataset, where the algorithm learns from input-output pairs to make predictions on new, unseen data.
- Decision trees are a type of supervised learning technique used for both classification and regression tasks. They make decisions by recursively partitioning the data based on features.
Q36: In a multiuser operating system, 20 requests are made to use a particular resource per hour, on an average. The probability that no request is made in 45 minutes is
(a) e-15
(b) e-5
(c) 1 - e-5
(d) 1 - e-10
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is e-15:
To solve this problem, we can use the Poisson distribution, which is often used to model the number of events occurring in fixed intervals of time or space.
The Poisson distribution is given by the formula:
Where:
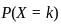 is the probability of observing k events,
is the probability of observing k events,- e is the base of the natural logarithm (approximately 2.71828),
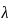 is the average rate of events per interval,
is the average rate of events per interval,- k is the actual number of events observed.
In this case, the average rate of requests per hour (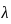 ) is 20. We want to find the probability of no requests in 45 minutes. We can adjust the rate for the given time interval:
) is 20. We want to find the probability of no requests in 45 minutes. We can adjust the rate for the given time interval:
Now, let 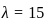 in the Poisson distribution formula to find the probability of no requests (
in the Poisson distribution formula to find the probability of no requests (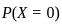 ):
):
Therefore, the correct answer is: 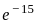
Q37: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: subsystem models show logical grouping of objects into coherent subsystem
Statement II: State machine models show how objects change their states in response to events.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Statement I: Subsystem models show logical grouping of objects into coherent subsystems.
- :
- This statement is correct. Object-oriented design often involves many different objects, each with their own attributes and methods.
- Subsystems are one way of managing this complexity by grouping related objects together.
- A subsystem model therefore shows these groups of objects that are related and interact closely with each other.
- For instance, in an online shopping system, all classes dealing with payment (like CreditCard, DebitCard, PayPal, etc.) could be grouped into a Payment subsystem.
Statement II: State machine models show how objects change their states in response to events.
- :
- This statement is also correct. In a substantial number of software applications, specifically those that deal with real-time systems, complex control systems, or certain types of business logic, objects can have different states.
- For instance, an 'Order' object might have states like "New", "Payment Processing", "Dispatched", "Delivered", etc.
- A state machine model represents the different states an object can have, and the ways (events or conditions) in which a transition happens from one state to another.
Q38: How many integral solutions are there to x + y + z + w = 29, where x ≥ 1, y ≥ 2, z ≥ 3 and w ≥ 0?
(a) 2400
(b) 2600
(c) 2800
(d) 3000
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 2600
This problem deals with integer partitions and combinations. A standard trick for these kinds of problems is to shift everything to the left side to make all the variables unconstrained.
Firstly, let's subtract the constraints from each variable:
- x' = x - 1
- y' = y - 2
- z' = z - 3
- w' = w - 0
- We can then express the equation in terms of the transformed variables:
- x' + y' + z' + w' = 29 - (1 + 2 + 3 + 0) => x' + y' + z' + w' = 23
- Instead of four positive integers x, y, z, and w satisfying the original equation, we are looking for four non-negative integers x', y', z', and w' satisfying the new equation.
- This amounts to partitioning 23 into four parts allowing that some of the parts could possibly be 0.
- The basic formula for combinations with repetitions (stars-and-bars method) is C(n + r - 1, r - 1), where "n" is the sum and "r" is the number of variables.
- So we have C(23 + 4 - 1, 4 - 1) = C(26, 3) = 26! / ((26-3)! * 3!) = 2600.
So the answer is: 2600
Q39: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Dendral is an expert system
Reason R: The rationality of an agent is not related to its reaction to the environment.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A is true but R is false
Dendral is an expert system. It was a groundbreaking AI project developed in the 1960s and 1970s aimed at automatically deducing the structure of organic molecules based on their mass spectrometry data. So, assertion A is correct.
The second statement, however, is incorrect. The rationality of an agent in AI is very much related to its reaction to its environment. Rational agents should be able to make decisions based on their perceptions of the environment in order to achieve the best possible outcome or, in the case of uncertainty, the best expected outcome. Therefore, reason R is false.
Q40: Match List I with List II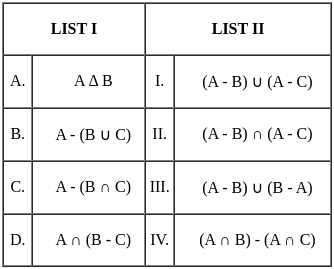
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
A Δ B:
- This represents the symmetric difference between sets A and B. It includes all those elements which are in A and B but not in their intersection. Mathematically, it can be represented as (A - B) ∪ (B - A). So, A matches with III.
A - (B ∪ C):
- This represents all elements in A not in (B or C). Another way to represent it would be (A - B) ∩ (A - C) because it is the intersection of elements that are only in A and not in B or C. So, B matches with II.
A - (B ∩ C):
- This represents all elements in A that are not common to both B and C, or equivalently, the elements just in A and not in the intersection of B and C. So, C matches with I.
A ∩ (B - C):
- This represents the intersection of A and the elements in B not in C. It is equivalent to (A ∩ B) - (A ∩ C) because you're taking all elements in both A and B, then removing any elements that are also in C. So, D matches with IV.
Therefore, the correct option is A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV. So, the correct option is 1).
Q41: Consider the following table of arrival time and burst time for three processes P0, P1, P2:

The pre-emptive shortest job first scheduling algorithm is used. Scheduling is carried out only at arrival or completion of a process. What is the average waiting time for the three processes?
(a) 3 ms
(b) 3.67 ms
(c) 4.47 ms
(d) 4 ms
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 3.67 ms
In Shortest Job First (SJF) scheduling, the process with the smallest burst time is processed next. In Preemptive SJF, if a new process arrives with CPU burst length less than remaining time of current executing process, CPU is preempted, and that new process starts execution.
Gantt chart
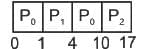
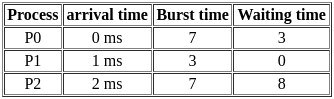
So, the average waiting time is:
(3ms + 0ms + 8ms) / 3 = 3.67ms (rounded to nearest hundredth)
So, the average waiting time for the processes under a preemptive SJF scheduling algorithm is approximately 3.67ms.
Q42: Which of the following scenario may lead to an irrecoverable error in a database system?
(a) A transaction writes a data item after it is read by an uncommitted transaction
(b) A transaction reads a data item after it is read by an uncommitted transaction
(c) A transaction reads a data item after it is written by a committed transactions
(d) A transaction reads a data item after it is written by an uncommitted transaction.
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A transaction reads a data item after it is written by an uncommitted transaction.
An irrecoverable error is an error that does not permit the database to return to a consistent state after a failure. They are primarily caused by inconsistencies that occur during transactions. Looking at the provided scenarios:
A transaction writes a data item after it is read by an uncommitted transaction-
- This is known as a Dirty Write. This is not necessarily an irrecoverable error, as a rollback operation can undo the changes if the uncommitted transaction fails.
A transaction reads a data item after it is read by an uncommitted transaction -
- This is known as a Dirty Read. This is not necessarily an irrecoverable error. Rollback operations can be implemented to maintain consistency.
A transaction reads a data item after it is written by a committed transaction -
- This is a normal operation within DBMS systems and doesn't lead to an irrecoverable error.
A transaction reads a data item after it is written by an uncommitted transaction -
This results in a Dirty Read, which can lead to an irrecoverable error under specific circumstances:
- if the transaction that issued the read operation commits before the transaction that issued the write operation, and then the system fails which causing the uncommitted transaction to abort.
- In this case, the committed transaction read and used uncommitted data, which can't be rolled back, leading to an irrecoverable state.
So, scenario 4 can cause an irrecoverable error, but it's worth noting that the specific set of circumstances to cause such an error is relatively rare in well-designed systems that use transaction isolation levels to avoid these types of issues.
Q43: Let 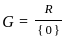 and H = {-1, 1} be groups under the multiplication. Then, the map ϕ : G → H defined by
and H = {-1, 1} be groups under the multiplication. Then, the map ϕ : G → H defined by 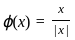 is
is
(a) Not a homomorphism
(b) A one-one homomorphism, which is not onto
(c) An onto homomorphism, which is not one to one
(d) An homomorphism
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is An onto homomorphism, which is not one to one
- The map ϕ: G → H is defined by ϕ(x) = x / |x|. G here is the set of non-zero real numbers and H is the set {-1, 1}. We are considering these groups under multiplication.
- Now, a mapping φ: G → H is called a homomorphism if for all a, b in G, we have ϕ(ab) = ϕ(a) * ϕ(b).
- Our mapping here, ϕ(x) = x / |x|, takes any positive number in G to 1 in H and any negative number in G to -1 in H. So, if we take two elements a and b in G, we have:
- ϕ(ab) = ab / |ab| ϕ(a) * ϕ(b) = (a / |a|) * (b / |b|)
- If a and b are both positive or both negative, |ab| = |a||b| so ϕ(ab) = ϕ(a) * ϕ(b). If a and b are of opposite signs, |ab| = |a||b| holds as well, therefore ϕ(ab) = ϕ(a) * ϕ(b) is true in this case, too.
This shows that the mapping ϕ is a homomorphism.
check whether it is one-one (injective) or onto (surjective).
- The function is not one-one, because multiple distinct elements in G (all positive numbers, for example) get mapped to the same element in H (1 in this case).
- The function is onto, because every element in H can be reached by some element in G (positive numbers map to 1 and negative numbers map to -1).
So, applying these conclusions to the options, the answer is:
3) An onto homomorphism, which is not one to one.
Q44: Which of the following parser is most powerful parser?
(a) Operator precedence
(b) SLR
(c) Canonical LR
(d) LALR
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Canonical LR
The Canonical LR parser is the most powerful among the ones you listed.
- Operator Precedence Parser: Only parses a certain subset of context-free grammars.
- Simple LR (SLR) Parser: This has more power than the Operator Precedence Parser and can parse a larger subset of context-free grammars.
- Lookahead LR (LALR) Parser: More powerful than SLR, it generates fewer states and is able to parse an even larger subset of context-free grammars.
- Canonical LR Parser: The most powerful of the four. It can parse all deterministic context-free grammars.
However, it's worth noting that although the Canonical LR parser is the most powerful, it also requires the most computational resources, which can make it less practical in some real-world scenarios. LALR parsers, for example, are widely used in various applications due to their balance of power and efficiency.
Q45: Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Ackermann's function is primitive recursive.
(b) L= {anbkcn+k : n ≥ 0, k ≥ 0} is regular language.
(c) L = {anbj : n = J2} is not context free language
(d) For every context sensitive language L not including λ, there exists some linear bounded automata M such that L ≠ L(M).
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is L = {anbj : n = J2} is not context free language
Ackermann's function is not primitive recursive.
- The primitive recursive functions form a subset of the total recursive functions or effectively calculable functions; however, there are total recursive functions which are not primitive recursive, such as the Ackermann function.
The language L= {anbkcn+k : n ≥ 0, k ≥ 0} is not regular.
- Regular languages adhere to the pumping lemma, which this language would violate. Given language is a Context free language.
L = {anbj : n = J2} is not context free language
- This is the correct statement. The language L isn't context-free as it represents a language where the number of 'a's is equal to the square of the number of 'b's.
- A context-free language wouldn't be able to generate or parse this kind of language, as it would require more context (like specific knowledge of numerical relationships) than a simple context-free grammar can provide. Because PDA can't able to calculation.
For any context sensitive language L, excluding λ (the empty string), there exists a linear bounded automaton M that recognizes the language such that L ≠ L(M).
- This is because a context-sensitive language is defined as a language that can be recognized by a linear bounded automaton. As such, the fourth statement as it stands is incorrect.
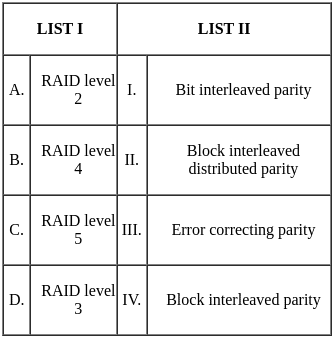
Q46: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(c) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
RAID level 2 ( III - Error correcting parity):
- RAID 2 uses an error-correcting code known as Hamming code, which is a set of parity bits for error detection and correction. Each bit of data is written to a separate disk drive in the array, and corresponding parity bits are written to additional drives, which allows the error correction to occur.
RAID level 4 (IV - Block interleaved parity):
- In RAID 4, data is split into blocks and written across multiple drives in an array (i.e., block-level striping). But unlike other RAID levels, RAID 4 has a dedicated disk for storing parity information. This configuration allows for high read data transaction rates because the data blocks and the parity are stored on different drives.
RAID level 5 (II - Block interleaved distributed parity):
- The parity information, which is used for data redundancy, is not written to a single, dedicated drive as in RAID 4. Instead, it is interspersed across all the drives in the array. This leads to a system where read and write operations can occur simultaneously on multiple drives, improving overall performance compared to RAID 4.
RAID level 3 (I - Bit interleaved parity):
- RAID 3 is similar to RAID 2 but it uses a simpler parity calculation. Data is split at the bit level and written across the drives in the array (i.e., bit-level striping) with parity being stored on a dedicated drive.
By matching RAID levels with their corresponding strategies, we get option 2 as the correct one: A - III, B - II, C - II, D - I.
Q47: Consider the following statements.
A. The identity is unique in any monoid.
B. A monoid is a group if there exists inverse of each element of monoid.
C. Semi group has closure, associative and identity properties.
D. Quasi group has closure property.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and D only
A. The identity is unique in any monoid.
- This is true. There is always exactly one identity element in any monoid structure.
B. A monoid is a group if there exists inverse of each element of monoid.
- This is true. A group must satisfy all the axioms of a monoid and additionally each element must have an inverse.
C. Semi group has closure, associative and identity properties.
- This is false. A semigroup only needs to have closure and associativity properties. The property of identity is not necessary for a structure to be considered a semigroup.
D. Quasi group has closure property.
- This is true. Quasigroups need to have an operation that is defined for every pair of group elements and which outputs an element from the group, providing closure property.
Q48: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: It is possible to create doubly linked list using only one pointer with every node.
Reason R: By storing the XOR of the addresses of the previous and next nodes.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are true and R is the correct of A
In a doubly linked list, each node typically maintains two references (or pointers): one to the next node and one to the previous node. However, it is indeed possible to create a doubly linked list using only one pointer per node. This can be achieved by storing the XOR of the addresses of the previous node and the next node in place of the two pointers. This technique is called XOR-linking.
Here's how it works:
- The XOR operation has a property whereby (A XOR B) XOR A equals B and (A XOR B) XOR B equals A.
- For each node, you are storing (address of previous node) XOR (address of next node). To traverse nodes in this list forward or backward, you start with a pointer to the current node and a pointer to its predecessor (for forward traversal) or its successor (for backward traversal). Then you can get the address of the next node or the previous node with XOR operations.
- So if you're traversing forward, your next node is (address of predecessor) XOR (current node's XOR value). To traverse backward, (address of successor) XOR (current node's XOR value) gives you the address of the previous node.
Using this technique you can successfully traverse both forward and backward in the list using only one pointer in each node. So, both the
Assertion A and the Reason R are true and R is indeed a correct of A.
Q49: Consider the following statements:
A. Dynamic metrics are collected by measurements made of a program in execution
B. Static metrics are collected by measurements made of representations of the system
C. The assessment of software quality is an objective process
D. An important part of quality assurance in the selection of standards that should apply to the software development process.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) A, B and D only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and D only
Statement C is not correct. While some aspects of software quality assessment can be measured objectively, like code efficiency or bug count, other aspects are often subjective and may vary based on individual needs and context. For example, usability, readability of code, or fitness for a particular purpose can be quite subjective.
Other options:
- A. Dynamic metrics are indeed collected by measuring a program while in execution.
- B. Static metrics are collected by analyzing representations of the system (such as source code, design documents, etc.) without executing the program.
- D. The selection of the appropriate standards and methodologies to apply during the software development process is a crucial part of software quality assurance.
Hence A, B and D only correct.
Q50: Consider a hash table of size seven with starting index zero and a hash function (6x + 3) mod 4. Assuming the hash table is initially empty. Which of the following is the content of the table when the sequence 1, 3, 8, 10, 5. is inserted into the table using closed hashing? Here "_______" denotes an empty location in the table.
(a) 1, 3, 8, 10, 5, _, _
(b) 3, 8, 1, _, 10, 5
(c) _,3, 8, 1, _, 10, 5
(d) _1, 3, 8, 10, 5, _
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is _1, 3, 8, 10, 5, _
To insert each element into the hash table using closed hashing, we can use the given hash function (6x + 3) mod 4. Let's go through each element in the sequence and insert them into the hash table:
- Insert 1:
- Hash value = (6 * 1 + 3) mod 4 = 9 mod 4 = 1
- The table becomes: _, 1, _, _, _, _, _
- Insert 3:
- Hash value = (6 * 3 + 3) mod 4 = 21 mod 4 = 1 (collision, linear probing)
- The table becomes: _, 1, 3, _, _, _, _
- Insert 8:
- Hash value = (6 * 8 + 3) mod 4 = 51 mod 4 = 3
- The table becomes: _, 1, 3, 8, _, _, _
- Insert 10:
- Hash value = (6 * 10 + 3) mod 4 = 63 mod 4 = 3 (collision, linear probing)
- The table becomes: _, 1, 3, 8, 10, _, _
- Insert 5:
- Hash value = (6 * 5 + 3) mod 4 = 33 mod 4 = 1 (collision, linear probing)
- The table becomes: _, 1, 3, 8, 10, 5, _
So, the correct answer is: 4) _, 1, 3, 8, 10, 5, _
Q51: Consider the following finite automata F1 that accepts a language L
 Let F2 be a finite automata which is obtained by reversal of F1. Then which of the following is correct?
Let F2 be a finite automata which is obtained by reversal of F1. Then which of the following is correct?
(a) L(F1) ≠ L(F2)
(b) L(F1) = L(F2)
(c) L(F1) ≤ L(F2)
(d) L(F1) ≥ L(F2)
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is L(F1) = L(F2)
Finite automata, also known as finite state machines, are abstract machines utilized in computer science and mathematical computations. They serve as a simple model for computation, providing a mathematical abstraction to describe and understand various systems' behaviors.
A finite automaton can be formally defined as a 5-tuple (Q, Σ, δ, q0, F) where:
- Q is a finite set of states.
- Σ (Sigma) is a finite set of symbols, called the alphabet of the automaton.
- δ (delta) is the transition function. It takes two arguments - a state and an input symbol, and returns the next state. δ : Q x Σ → Q
- q0 is the initial state from which any input is processed (q0 ∈ Q).
- F is a set of final state/states of Q (F ⊆ Q).
F1:
F2: Reversal of F1
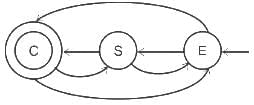
Both are accept same string so L(F1) = L(F2)
Q52: The maximum yield length of the following CNF CFG is
S → AB
A → CD
B → e
C → a
D → b
(a) 8
(b) 7
(c) 4
(d) 5
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 4
CFG stands for Context-Free Grammar. It is a formalism used in formal language theory and computer science to describe the syntax or structure of languages. In this CFG, S, A, B, C, D are non-terminal symbols, and a, b, and e are terminal symbols. These rules show that every non-terminal symbol eventually maps to a single terminal symbol.
- S → AB
- A → CD
- B → e
- C → a
- D → b
The production of S gives us AB, which can further be expanded as follows: A gives CD and B gives e.
So AB becomes CDe.
Further expanding C and D (which give a and b respectively), we obtain: CDe becomes ab and then e, leading to the string abe.
So, apparently, the yielded string has length three. However, note that the grammar rule B → e is part of Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) grammar, and although it appears to produce a single terminal symbol, it is considered to produce two symbols in terms of its yield length. This is because in CNF, each production either produces two non-terminals or one terminal.
With that understanding, we would have: S (yield length = 4) → A (yield length = 2) + B (yield length = 2)
This sums up to a total yield length of 4, which corresponds to option 3) 4.
Therefore, the maximum yield length of this CFG is 4, and the correct answer is 3) 4.
Q53: ___________ is intended to show that a system both conforms to its specifications and meets the expectations of the system customer.
(a) Software specification
(b) Software design
(c) Software evaluation
(d) software validation
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is software validation
Software Validation:
- This is the process to evaluate the system during or at the end of the development process to determine whether it satisfies the specified requirements. That is, to ensure that 'you built the right thing'. This often involves acceptance testing, where the customer themselves provide the final validation that the system meets their needs and expectations. So it is correct answer of the given question.
Other Related Points
Software Specification:
- This involves detailed documentation of the requirements and functionalities that the software is supposed to provide. It's essentially the 'what' - explaining what the software is intended to achieve, without detailing how it will do it. It includes elements like functional requirements, performance, interfaces, design constraints, etc.
Software Design:
- This the process of envisioning and defining the software solutions to one or more sets of problems. It is the 'how' in the process - covering how the software will achieve the goals set in the software specification. One might think about it as a blueprint that describes the parts and how they should interact with each other. It can have different levels like high-level (or architectural) design and detailed (or low-level) design.
Software Evaluation:
- This involves assessment or review of a software product during its development or after its completion to know its usability, quality, performance, etc. It also finds out whether the software meets its intended purpose and satisfies the predefined requirements or not.
Q54: Which is not the component of the natural language understanding process?
(a) Morphological analysis
(b) Semantic analysis
(c) Pragmatic analysis
(d) Meaning analysis
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Meaning analysis
Meaning analysis is not a conventional component in the process of Natural Language Understanding (NLU). The usual components include:
- Morphological analysis: This refers to the process of identifying and analyzing the structure of words. This is significant in NLU as words have different forms and these forms can have different meanings in different contexts.
- Semantic analysis: This is the process that determines the meaning of sentences by understanding the meaning of the individual words in the context that they are used within the sentence.
- Pragmatic analysis: It implies interpreting the intended meaning of the sentence. This can depend on context, the previous conversation, the speaker's intended meaning, and general world knowledge.
"Meaning Analysis" is not a conventionally distinguished step in the NLU process. It seems too broad and vague and potentially encompasses semantic analysis and/or pragmatic analysis.
Other Related PointsNatural Language Understanding (NLU) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence that focuses on machine reading comprehension. The goal of NLU is to create systems that understand input presented in natural language, including slang, jargon, or colloquial speech. The process typically involves several steps:
- Tokenization: This is the first step in NLU where the text input is broken down into 'tokens' or individual words. For example, the sentence "I love apples" would be tokenized into "I", "love", "apples".
- Morphological Analysis: Here, words are further broken down into their smallest meaningful components, called morphemes. This step considers prefixes, suffixes, and root words which may affect a word's meaning. For instance, "unhappiness" would be split into three morphemes: "un", "happi", "ness".
- Part of Speech Tagging (POS): Each token is categorized according to its part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, etc.). This analysis can help in understanding the grammatical structure of the sentence.
- Dependency Parsing/Syntactic Analysis: This step aims to analyze the grammatical structure of a sentence, establishing relationships between "head" words and words that modify or depend on them. For example, in the sentence "A cat chases a mouse", "cat" is the subject and "chases" is the verb with "mouse" as its object.
- Semantic Analysis: This step aims to understand the meaning of the words and how they combine to form the meaning of the sentence. It involves understanding aspects like named entities (people, organizations, locations), numerical entities (dates, times, numbers), and coreferences (linking pronouns to the entities they refer to).
- Pragmatic Analysis: Pragmatic Analysis goes beyond the literal meaning of the text to understand the context and intention behind the words. It can involve factors like the conversation history, the speaker's attitudes, and cultural knowledge.
- Discourse Integration: This step involves understanding the text in the context of the full conversation or textual context.
- Common Sense and World Knowledge: Often, understanding language requires more than just understanding the words and structure of the sentence. A system also needs to have some knowledge of the world and about what is common or likely in certain situations.
Q55: Suppose a circular queue of capacity (n - 1) elements is implemented with an array of n elements. Assume that the insertion and deletion operations are carried out using REAR and FRONT as array index variable respectively. Initially, REAR = FRONT = 0. The conditions to detect queue empty and queue full are
(a) EMPTY : REAR == FRONT
FULL : (REAR + 1) mod n == FRONT
(b) EMPTY : (FRONT + 1) mod n == REAR
FULL : (REAR + 1) mod n == FRONT
(c) EMPTY (REAR + 1) mod n == FRONT
FULL : REAR == FRONT
(d) EMPTY : REAR == FRONT
FULL : (FRONT + 1) mod n == REAR
Ans: A
Sol: The Correct answer is EMPTY : REAR == FRONT and FULL : (REAR + 1) mod n == FRONT
A circular queue is a queue whose last position is connected back to the first position.
- ENQUEUE – It is the operation to insert elements into the queue.
- DEQUEUE – It is the operation to delete elements from the queue.
After inserting an element in the last position, the next element again gets inserted into the first position.
- Given, Rear = Front = 0
- Here, the Rear is used to insert elements & the front is used to delete elements.
To check full condition in queue:
- (Rear + 1) % n == Front
- Example: Consider queue is full that means Rear = 6, front = 0, n = 7
- (6+1) % 7 = 7 % 7 = 0
To check empty condition in queue:
- Rear == Front
- Example: Consider queue is empty that means Rear = 0, front = 0, n = 7
- Rear = Front = 0
Hence, the correct answer is “option 1”.
Q56: Given below are two statements:
Let f(n) and g(n) be asymptotically positive functions. The following conjectures are given
Statement I: f(n) ≥ 1 and f(n) = O(g(n)) ⇒ g(n) = Ω(f(n))
Statement II: f(n) = O(g(n)) ⇒ Ig(f(n)) = O(1g(g(n))) where Ig(g(n)) ≥1 for all sufficient large n.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
In the asymptotic analysis, we refer to Big O notation (O) and Big Omega notation (Ω) to describe upper and lower bounds of functions respectively.
- Statement I is asserting that if f(n) ≥ 1 and f(n) is upper-bounded by g(n) (f(n) = O(g(n))), then g(n) should be lower-bounded by f(n) (g(n) = Ω(f(n))). In other words, if f(n) grows no faster than g(n), then g(n) grows at least as quickly as f(n). This statement is correct.
- Statement II, If f(n) = O(g(n)), then a function Ig(f(n)), which is presumably larger or equal to 1 for all sufficiently large n, would be bound by O(1g(g(n))). This seems to depend on the specific nature of the functions f(n) and g(n). This statement is correct.
Other Related Points
- Reflexivity: f(n) = (f(n)). Valid for O and 2.
- Transitivity: f(n) = (g(n)) and g(n) = (h(n)) = f(n) = (h(n)). Valid for O and Ω as well.
- Symmetry: f(n) = (g(n)) if and only if g(n) = (f(n)).
- Transpose symmetry: f(n) = O(g(n)) if and only if g(n) = (f(n)).
- If f(n) is in O(kg(n)) for any constant k > 0, then f(n) is in O(g(n)).
- If f₁(n) is in O(g₁(n)) and f₂(n) is in O(92(n)), then (f₁ + f2)(n) is in O(max(9₁(n)), (g₁(n))).
- If f₁(n) is in O(g₁(n)) and f₂(n) is in O(g₂(n)) then f₁(n) f₂(n) is in O(g₁(n) g₁(n)).
Q57: Consider following statements:
A. A context free language is generated by LR(o) grammar if and only if it is accepted by a deterministic pushdown automata and has prefix property
B. If M1 is the single tape TM simulating multilape TM M, then time taken by M1 to simulate n moves is (n3)
C. Push down automata behaves like a Turning machine when it has one auxiliary memory.
D. L= {anbncn : n ≥ 1} is not context free but context sensitive.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, B only
(c) D only
(d) B, C only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is D only
A. A context free language is generated by LR(0) grammar if and only if it is accepted by a deterministic pushdown automata and has prefix property:
- This statement is incorrect because a context-free language can be generated by an LR(0) grammar, but it does not need to be accepted by a deterministic pushdown automaton (DPDA).
- Moreover, LR(0) grammars don't necessarily generate languages with the prefix property; they can produce languages where a prefix of a valid string is also a valid string, which is not always handled well by a DPDA.
B. If M1 is the single tape TM simulating multilape TM M, then time taken by M1 to simulate n moves is (n3):
- This statement is incorrect because the best known upper bound for simulating a multi-tape Turing machine M on a single-tape Turing machine M1 is quadratic, i.e., O(n2), not cubic.
C. Push down automata behaves like a Turing machine when it has one auxiliary memory:
- This statement is incorrect. While a PDA with two or more stacks does have the same computational power as a Turing machine, the concepts are distinct, and a multi-stack PDA should not directly be referred to as a Turing machine.ed so far, effectively simulating the 'unbounded' nature of a Turing machine's tape.
D. L= L= {anbncn : n ≥ 1} is not context free but context sensitive:
- This statement is correct. The language L= {anbncn : n ≥ 1} is a context-sensitive language, not a context-free language.
- It cannot be represented by a context-free grammar (CFG) because it requires a mechanism to enforce that the number of a's, b's, and c's are equal, which is beyond the capabilities of a CFG.
- However, it can be represented by a context-sensitive grammar which has the power to enforce such constraints.
So, only Statement D is correct.
Q58: Match List I with List II
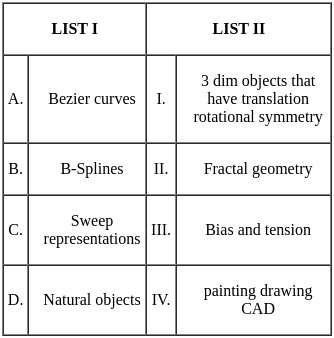
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(b) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
A. Bezier curves and IV (painting drawing CAD):
- Bezier curves are mathematical descriptions of curves that can accurately describe various shapes. They are widely used in computer graphics, including painting, drawing, and Computer-Aided Design (CAD), because of their power to model smooth and flexible curves with just a few parameters.
B. B-Splines and III (Bias and tension):
- B-splines, short for Basis Splines, are a highly generalized version of Bezier curves and can represent the same curves, but also provide more control over curves' shapes. The notion of bias and tension are key features of design layouts which B-Splines can often accommodate. They allow for control over how "tight" or "loose" a curve is and in which direction the curve tends to lean. Thus these tools can offer accurate control over graphical structures, matching the B-Splines with tense and biased controls.
C. Sweep representations and I (3 dim objects that have translation rotational symmetry):
- Sweep representations refer to the methods in computer graphics and solid modeling that represent a 3D object as a 2D profile swept along a path. These methods are capable of creating complex 3D objects with translation and rotational symmetry, as the same pattern is repeated in different orientations and positions.
D. Natural objects and II (Fractal geometry):
- Many natural objects - like mountain ranges, clouds, trees, and more - show a self-similar pattern: they have parts that resemble the whole, at many scales of magnification. Fractal geometry is a special form of graphical representation of mathematical functions or set of numbers generated by a mathematical function. This helps to explain structures in the world which have complexity, detail and hierarchy, such as those found in natural landscapes. As a result, fractal geometry has wide-ranging applications in many fields, including the representation of natural objects in computer graphics.
Q59: There are M points on one straight line AB and n points on another straight line AC none of them being A. How many triangles can be formed with these points as vertices?
(a) mn(m + n - 2)
(b) 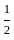 mn(m + n - 2)
mn(m + n - 2)
(c) 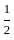 mn(m + n - 1)
mn(m + n - 1)
(d) mn(m + n - 1)
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is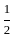 mn(m + n - 2)
mn(m + n - 2)
:
Let's consider a triangle with vertices B, C, and a point D on line AB. This way, we have two vertices from line AB (B and D) and one from line AC (C).
So, the vertices of the triangle would be B, C, and D.
This creates a triangle without using vertex A. If you have any specific requirements or constraints
= mC2 x nC1 + nC2 x mC1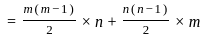
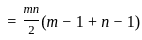
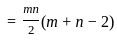
Q60: Which of the following is not a mutation operator in a genetic algorithm?
A. Random resetting
B. Scramble
C. Inversion
D. Difference
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B and D only
(c) C and D only
(d) D only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is D only
Mutation operators in a Genetic Algorithm are used for perturbing the genes in a solution. They help in keeping the diversity of the population and avoiding premature convergence on local optima. Here's a brief of the operators mentioned:
- A. Random Resetting: This is a type of mutation operator where a specific gene in a chromosome is randomly chosen and assigned a new value from the feasible parameter range.
- B. Scramble: This operator randomly selects two points in the chromosome and then shuffles the genes between those points.
- C. Inversion: Inversion mutation operators select a substring (i.e., a portion of the chromosome) and revert the order of genes within that.
- D. Difference: This is not a known mutation operator in the context of genetic algorithms.
Therefore, the answer is 4) D only.
Q61: A. The set of Turing machine codes for TM's that accept all inputs that are palindromes (possible along with some other inputs) is decidable
B. The language of codes for TM's M that when started with blank tape, eventually write a 1 somewhere on the tape is undecidable
C. The language accepted by a TM M is L (M) is always recursive
D. Post's correspondence problem is undecidable
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A and C only
(d) B and D only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is B and D only
A. The set of Turing machine codes for TMs that accept all inputs that are palindromes is decidable:
- A Turing machine accepts an input it if halts in an accept state. To say that a TM accepts all inputs that are palindromes means that every palindrome string needs to be an accepted input.
- This essentially needs us to determine the behavior of a Turing machine, which is generally undecidable due to the halting problem. The halting problem is a famous problem in computation which implies that there is no way to know with certainty whether a Turing machine will halt or continue forever.
- Therefore, a set of Turing Machine codes that accept palindromes is not decidable.
B. The language of codes for TM's M that when started with blank tape, eventually write a 1 somewhere on the tape is undecidable:
- This is a form of the halting problem, because in order to know if a Turing machine will eventually write '1' on the tape means we are asked to determine if a Turing machine will halt (write '1' and stop) or not. As we discussed earlier with point A, the halting problem is known to be undecidable.
C. The language accepted by a TM M is L(M) is always recursive:
- It's true that Turing machines recognize recursively enumerable languages, but it's not true that all languages a TM recognizes are recursive.
- A recursive language (also called a decidable language) is one where a TM will always halt with a 'yes' or 'no' answer - i.e., it will always accept or reject.
- However, there are languages where the TM might not halt for some strings — these are the recursively enumerable (r.e.) but not recursive languages. For this reason, statement C is false.
D. Post's correspondence problem is undecidable:
- Post's Correspondence Problem (PCP) is known to be undecidable, which means there is no algorithm that exists that can solve all instances of the PCP.
- Introduced by Emil Post in 1946 as a way of demonstrating that there were problems that were even impossible for a Turing Machine to solve, it serves as a classic example of the limits of computation.
So, the Option 4) B and D only remains the correct answer.
Q62: Consider universe positive integer X= {1 ≤ n ≤ 8}, proposition P= "n is an even integer", Q = "(3 ≤ n ≤ 7) ^ (n ≠ 6)". Then truth set of P ↔ Q is
(a) {1, 4}
(b) {2, 6}
(c) {3, 4, 5}
(d) {1}
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is {1, 4}
SOLUTION:
X= {1 ≤ n ≤ 8} So, X = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
P= "n is an even integer" So, P = {2, 4, 6, 8}
Q = "(3 ≤ n ≤ 7) ^ (n ≠ 6)" So, Q = {3, 4, 5, 7}
P ↔ Q = (¬P v Q) ^ (P v ¬Q)
P ↔ Q = ({1, 3, 5, 7} v {{3, 4, 5, 7}) ^ ({2, 4, 6, 8} v {1, 2, 6, 8})
P ↔ Q = {1,3, 4, 5, 7} ^ {1, 2, 4, 6, 8}
P ↔ Q = {1, 4}
So, Correct answer is Option 1 {1, 4}
Q63: An observational technique that can be used to understand operational process and help to derive requirement for software to support operational process is known as
(a) Requirement specification
(b) Structural specification
(c) Ethnography
(d) Natural language specification
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Ethnography
- Understand the Environment: Ethnography requires an understanding of the environment where the software will be operational. This understanding is often achieved through immersion in the environment and observing processes directly.
- Observing Daily Routines: The researcher observes the day-to-day tasks, operations, and interactions of users within the system. This provides first-hand data about the activities that the software needs to support.
- Insights Into Behavior and Interaction: Ethnography doesn't just focus on the tasks to be done, but on how they are done, the interaction between different users, and the social aspects that could influence the software requirements.
- Cultural Understanding: Software isn't used in a vacuum but within a cultural context. Ethnography takes this into account, ultimately informing the design of a more user-friendly and efficient system.
- Identifying User Needs: Users may not always explicitly know or state what they need from a system. Ethnographic research can help identify these needs by observing how users perform tasks and handle processes.
- Informing Design and Functionality: The insights gained from ethnography inform the design and functionality of the software, focusing on real-life requirements of the users.
- Beneficial in Agile development: Ethnography is particularly beneficial in Agile development as it gives a chance to uncover hidden aspects of user needs and preferences which can be addressed in iterative development phases.
In conclusion, through ethnography, requirements for software can be derived organically from the environment in which it will be used, rather than being imposed based on assumptions or out-of-context criteria.
Other Related Points
- Requirement Specification: This refers to a document that describes what the software must do. It includes descriptions of system properties, functionalities, and constraints. Its role is to set the guidelines for the software development process, serving as a reference for developers and testers.
- Structural Specification: This defines the structure of software system components. It outlines how different parts of the system interact with each other and their individual responsibilities. The specification can manifest in the form of architectural diagrams, UML models, or API instructions.
- Natural Language Specification: This is a common method for communicating software requirements. They are written in natural, everyday language which makes it easy to understand for all stakeholders, including those who may not have a technical background. However, natural language specifications may lead to ambiguity and misunderstanding due to the inherent vagueness of languages and differences in interpretation, so they often need to be complemented with more formal methods of specification.
Q64: Southerland Hodgman method is used on
(a) Smooth curves
(b) Line segment
(c) Convex polygons
(d) Concave polygons
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Convex polygons
Smooth curves:
- The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is not designed for dealing with smooth curves. It works with polygons, and smooth curves typically involve mathematical representations like Bezier curves, which require different algorithms for processing.
Line segment:
- While the Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm can be adapted for clipping line segments, it is more commonly used for polygon clipping. There are other algorithms, like the Cohen-Sutherland or Liang-Barsky algorithms, that are specifically designed for clipping line segments.
Convex polygons:
- The primary use of the Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is for clipping convex polygons against a convex clipping window. Convex polygons are well-suited for this algorithm because the method relies on the convexity of the polygons to simplify the clipping process.
Concave polygons:
- The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is not well-suited for clipping concave polygons. The algorithm assumes convexity to simplify the process of finding the intersection points between the polygon edges and the clipping window.
So, the Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is mainly used for convex polygon clipping and is not intended for dealing with smooth curves or concave polygons. If you need to clip line segments or work with concave polygons, other algorithms may be more suitable for those specific tasks.
Q65: Let N denote the set of all natural numbers and R be the relation on NXN defined by (a, b) R(c, d), if ad(b + c) = bc(a + d). Then R is
(a) Symmetric only
(b) Reflexive only
(c) Transitive only
(d) An equivalence relation
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is An equivalence relation
We are given a relation R defined on pairs of natural numbers, where (a, b) R (c, d) if ad(b + c) = bc(a + d).
We can check whether R is symmetric, reflexive, transitive, or an equivalence relation by verifying the condition for each .
Symmetry:
- For a relation to be symmetric, if (a, b) R (c, d) then (c, d) R (a, b).
- Say we have (a, b) R (c, d), then we have ad(b + c) = bc(a + d).
- Swap a and b with c and d, then we get: cd(a + b) = ab(c + d) which is the original formula, therefore R is symmetric.
Reflexivity:
- For a relation to be reflexive, (a, b) R (a, b) must be true for all a, b.
- Let's plug (a, b) into the formula: ab(a + b) = ba(a + b) which is always true. Therefore R is reflexive.
Transitivity:
- For a relation to be transitive, if (a, b) R (c, d) and (c, d) R (e, f), then (a, b) R (e, f).
- However, checking the transitive property for this expression is
- ab/(a - d) = cd/(c - d) and cd/(c - d) = ef/(e - f)
- ab/(a - d) = ef/(e - f)
- af(b + e) = be(a + f)
- (a, b) R (e, f)
- Hence ,R is transitive
Above question follow all condition so it is an equivalence relation.
Q66: let R (A, B, C, D) be a relational schema with following function dependencies:
A → B, B → C
C → D and D → B
The decomposition of R into
(A, B) (B, C) (B, D)
(a) gives a lossless join, and is dependency preserving
(b) gives lossless join, but is not dependency preserving
(c) does not give a lossless join, but is dependency preserving
(d) does not give a lossless join and is not dependency preserving
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is gives a lossless join, and is dependency preserving
For the given relational schema R(A,B,C,D) with functional dependencies: A → B, B → C, C → D, D → B, it's decomposed into (A, B), (B, C), (B, D).
A decomposition is a lossless join if for every functional dependency X -> Y, at least one of these conditions holds:
- X ∩ Y ≠ Φ (The intersection of X and Y is not empty)
- X ∪ Y = R (The union of X and Y is equivalent to the original schema)
And it is dependency-preserving if for every dependency X -> Y in F, we have:
- a) X -> Y is in F' (The set of dependencies in the decomposed schema)
Analyzing the decomposed relations:
- Relation (A, B) covers A→B and D→B. The dependencies preserved are A→B and D→B.
- Relation (B, C) covers B→C. The dependencies preserved are B→C.
- Relation (B, D) covers C→D. The dependencies preserved are C→D.
- Notice all the functional dependencies are preserved after decomposition. Hence, it is dependency preserving.
- For the lossless join property, you should check if there's at least one common attribute in each pair of decomposed relations.
We have:
- (A, B) and (B, C) have 'B' attribute in common.
- (A, B) and (B, D) have 'B' attribute in common.
- (B, C) and (B, D) also have 'B' attribute in common.
- Therefore, this is a lossless join.
- The decomposition thus: gives a lossless join, and is dependency preserving
So the answer is option 1.
Q67: Given below are two statements:
Which of the following statement/s is/are correct with respect to virtual memory
Statement I: Address translation is performed for every logical address used during the execution of a program
Statement II: A program can execute only when all of its components are loaded in the memory
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Statement I is correct - Address translation is performed for every logical address used during the execution of a program
- Virtual memory systems use a process known as address translation to convert a program's logical addresses into physical addresses used to access the actual memory hardware. This translation is done for each logical address that is generated during the execution of a program.
Statement II is incorrect - A program can execute only when all of its components are loaded in the memory
- One of the significant advantages of virtual memory is that it allows programs to be executed even when all of its components are not loaded into memory. This is done by loading parts of the program that are currently needed, or pages, into physical memory while the rest of the program remains on the disk. This technique is also known as demand paging.
Q68: In the standard Ethernet with transmission rate of 10 Mbps, assume that the length of the medium is 2500 m and size of a frame is 512 bytes. The propagation speed of a signal in a cable is normally 2 × 108 m/s. The transmission delay and propagation delay are
(a) 25.25 μs and 51.2 μs
(b) 51.2 μs and 12.5 μs
(c) 10.24 μs and 50.12 μs
(d) 12.5 μs and 51.2 μs
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 51.2μs and 12.5μs
- The delay in Ethernet transmission, which is measured by the duration required to send a single frame over the physical medium, is determined by dividing the frame size by the speed of transmission. In this case, the transmission delay is:
- Transmission delay = Frame size / Transmission rate
512 bytes / 10 Mbps = 51.2 microseconds - In Ethernet, the propagation delay denotes the time duration for a single bit to traverse from source to destination over the physical network medium. It's assessed by dividing the medium's length by the transmission speed of the signal. In this case, the propagation delay is:
Propagation delay = Length of medium / Propagation speed
2500 m/2 x 108 m/s 12.5 microseconds
Consequently, in a standard Ethernet setup featuring a transmission rate of 10 Mbps, a medium length of 2500 m, and a frame size of 512 bytes, the correspondingly calculated transmission delay and propagation delay are 51.2μs and 12.5μs, respectively.
Q69: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(b) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
A. Critical region - II. Mutual exclusion:
- The critical region is a piece of code in a process where shared resources are accessed, and as such requires the principle of mutual exclusion to be followed so that race conditions are avoided.
B. Wait signal - I. Hoare's monitor:
- In the context of concurrent programming, a monitor is a synchronization construct that allows threads to have both mutual exclusion and the ability to wait (block) for a certain condition to become true.
C. Working set - III. Principle of locality:
- The working set of a process in a system typically refers to the set of pages in the most recent page references. The working set is based on the principle of locality, that suggests that most memory references within a process are localized to a few clusters in the memory space.
D. Deadlock - IV. Circular wait:
- Deadlock is a situation in computer systems where a set of processes or threads are each waiting for each other to release resources, causing a circular wait condition.
Q70: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
A. Physical layer -
- It is the lowest layer of the OSI model and it deals with the transmission and reception of the unstructured raw bit stream over a physical medium. So, it corresponds to III. Transmission of raw bits over communication channel.
B. Data Link Layer -
- It is responsible for the node-to-node delivery of the packet. It transforms raw bits into frames, so it corresponds to I. Transforming the raw bits in the form of frame for transmission.
C. Network layer -
- It decides which physical path the data will take based on the network conditions, the priority of service, and other factors. Thus, it corresponds to II. Control and monitoring of subnet.
D. Transport layer -
- It provides transparent transfer of data between devices and can use either connection oriented communication or connectionless, so it corresponds to IV. Datagrams transmission data through connection oriented or connectionless using datagram.
Q71: Consider the rectangle with vertices (0, 0), (0, 2), (3, 0), (3, 2). There is scaling of 2 towards x-axis and 3 towards y-axis. The new cordinates of the rectangle are
(a) (0, 0), (6, 0), (0, 4), (6, 4)
(b) (0, 0), (6, 0), (0, 4), (3, 2)
(c) (0, 0), (6, 0), (0, 6), (6, 6)
(d) (0, 0), (4, 0), (0, 6), (4, 6)
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (0, 0), (6, 0), (0, 6), (6, 6)
The scaling operation does not change the origin (0,0).
When you apply the scale of 2 towards the x-axis to a point (x,y), you get (2*x, y) because you're scaling only on the x-axis.
Similarly, when you apply the scale of 3 towards the y-axis to a point (x,y), you get (x, 3*y) because you're scaling only on the y-axis.
So:
- (0,0) remains (0,0) because 0*scale is still 0 on both axes
- (0,2) becomes (0,2*3) = (0,6) because the y coordinate is multiplied by 3
- (3,0) becomes (3*2,0) = (6,0) because the x coordinate is multiplied by 2
- (3,2) becomes (32,23) = (6,6) because both the coordinates are scaled
The new coordinates of the rectangle are (0, 0), (0, 6), (6, 0), (6, 6)
Q72: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(c) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - II
(d) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
A. PERT (Project Evaluation and Review Technique)
- PERT is a statistical tool used in project management, designed to analyze a range of tasks involved in completing a given project. It is used for non-repetitive work because of its ability to manage uncertainties.
- PERT involves identifying the longest path in a network of tasks based on their time estimates and dependencies. It allocates a time estimate to each phase of the project, making it possible to anticipate the time needed to complete the project.
B. Optimistic Time
- In project management, optimistic time is the best possible time in which an activity can be completed. It assumes that everything will go exactly as planned, with no interruptions or unforeseen delays. This scenario is quite ideal and often doesn’t occur.
- Optimistic time is used in three-point estimating techniques and PERT calculation. It helps project managers create a time cushion for uncertainties, adjusting the project timeline realistically.
C. CPM (Critical Path Method)
- CPM is a step-by-step project management technique to identify activities on the critical path. It is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities.
- The critical path method (CPM) is used for projects that are repetitive, involve activities that are related in a sequence. The primary goal of CPM is to calculate the longest path of planned activities to the end point, to determine key deadlines or schedule compression needs.
D. Pessimistic Time
- Pessimistic Time is a term used in project management to estimate the maximum amount of time that it would require to complete a project activity or task.
- It assumes situations where everything that could go wrong, does go wrong. Essentially, it's the longest time that you'd expect an activity to take. The pessimistic time is used in risk analysis and three-point estimates.
Q73: What is the output of following code?
main ( )
{static float a [ ] = {13.24, 1.5, 4.5, 5.4, 3.5}
float *j, *k;
j = a;
k = a + 4
j = j * 2;
k = k/2;
printf("% f% f', *j, *k):
}
(a) 13.25, 4.5
(b) 1.5, 3.5
(c) 13.24, 1.5, 4.5, 5.4, 3.5
(d) Illegal use of pointer in main function
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Illegal use of pointer in main function
The code as written would result in an error due to the illegal use of pointers, so the correct answer would be: Illegal use of pointer in main function
Here are the problems with the code:
- Pointers j and k are pointing to the addresses of elements in the array a. However, this line j = j * 2; and this k = k/2; are trying to perform the multiplication and division operations on these pointers, effectively trying to change the addresses they are pointing to.
- This is illegal in C as arithmetic operations other than addition and subtraction (for increment and decrement of pointer) are not allowed on pointers.
- The syntax of the printf function is incorrect. The correct syntax is with comma (,) instead of colon (:) and you also didn't close the first quotation mark.
The Correct Program is:
main ( )
{
static float a [ ] = {13.24, 1.5, 4.5, 5.4, 3.5};
float *j, *k;
j = a;
k = &a[4];
*j = *j * 2;
*k = *k / 2;
printf("%f, %f", *j, *k);
}
Q74: A. If some NP-complete problem P is in ℙ that P = NP
B. TSP is in ℕℙ
C. SAT is in ℕℙ
D. Hamilton circuit problem is not NP-complete
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and A only
(d) D, A and B only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and C only
Statement A: "If some NP-complete problem P is in P then P = NP" is correct.
- It states that if you can come up with a polynomial-time algorithm for a single NP-complete problem, then that would mean all NP problems have polynomial-time solutions -- that is, P would equal NP. This is the definition of NP-completeness.
Statement B: "TSP is in NP" is correct.
- The Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) is indeed an NP problem: given a list of cities and the distances between them, find the shortest possible route that visits each city and returns to the origin city. It can be verified quickly, but we do not have a quick solution on how to solve it.
Statement C: "SAT is in NP" is correct as well.
- The Boolean satisfiability problem (SAT) is a decision problem, whose instance is a Boolean expression written using only AND, OR, NOT, variables, and parentheses. The question is: given the expression, is there some assignment of TRUE and FALSE values to the variables that will make the entire expression true? A SAT instance can be checked quickly, but again, we have no quick algorithm to solve it.
Statement D: "Hamilton circuit problem is not NP-complete" is incorrect.
- The Hamiltonian circuit problem, which is finding a path in a graph that visits every vertex exactly once and returns to the original vertex, is a classic example of an NP-complete problem
Q75: Which one of the following is NOT a part of ACID properties of a database transaction?
(a) Atomicity
(b) Consistency
(c) Isolation
(d) Deadlock-freedom
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Deadlock-freedom
ACID properties of a database transaction
- Atomicity: It means that a transaction is treated as a single, indivisible logical unit of work, in which either all steps are performed or none are. If any step in a transaction fails, the entire transaction is rolled back, and the database is left unchanged.
- Consistency: This refers to ensuring that a transaction brings the database from one valid state to another. The database has integrity constraints, and it's the responsibility of the transaction to maintain these constraints. Hence, any transaction will take a database from one consistent state to another.
- Isolation: This property ensures that concurrent execution of transactions leaves the database in the same state as if the transactions were executed sequentially. It enables transactions to execute independently without interference.
- Durability: This property ensures that once a transaction has been committed, it will remain committed even in the presence of failures (system crash, power loss, etc.). The effects of an executed transaction are persistent and can survive any subsequent malfunction.
On the other hand, "deadlock-freedom" is not a part of ACID. Deadlocks are a condition where two or more transactions are unable to proceed because each holds a lock that the other needs. Deadlock prevention and detection are indeed crucial aspects of database management systems but are not included in the ACID properties.
Q76: Consider the following statements
A. Fuzzy C-means clustering is a supervised method of learning
B. PCA is used for dimension reduction
C. Apriori is not a supervised technique
D. When a machine learning model becomes so specially tuned to its exact input data that it fails to generalize to other similar data it is called underfitting
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) C and D
(d) D and A
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is B and C
A. C-Fuzzy means clustering is a supervised method of learning.
This statement is incorrect. Fuzzy C-means clustering is an unsupervised method, not a supervised one.
B. PCA is used for dimension reduction.
This statement is correct. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is commonly used for dimensionality reduction in machine learning.
C. Apriori is not a supervised technique.
This statement is correct. Apriori is an algorithm used for association rule mining in unsupervised learning.
D. When a machine learning model becomes so specially tuned to its exact input data that it fails to generalize to other similar data, it is called underfitting.
This statement is incorrect. The described scenario is an example of overfitting, not underfitting. Underfitting occurs when a model is too simple to capture the underlying patterns in the data.
The correct statements are B and C.
Q77: Which phase of compiler checks the grammar of programming?
(a) Code optimization
(b) Semantic analysis
(c) Code generators
(d) Syntax analysis
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Syntax analysis
Semantic Analysis:
- This phase checks whether the parse tree constructed follows the rules of the language.
- For example, it checks whether the variables used are declared, whether a variable is declared more than once, the compatibility of arguments in the function call and the function declaration, etc.
- Semantic analysis produces an annotated syntax tree as an output.
Other Related Points
Lexical Analysis:
- It is a first phase of a compiler, also known as scanning. This phase reads the source code and breaks it into a stream of tokens, which are the basic units of the programming language. The tokens are then passed on to the next phase for further processing.
Code Optimization:
- This phase of the compiler aims to improve the intermediate code so that the output program runs faster and takes less space. It attempts to minimize resource usage, such as memory or CPU time, and improve performance. This phase is often optional.
Code Generation:
- This is the final phase of compilation. It takes the optimized intermediate code as input and maps it to the target machine language. The code generator translates the intermediate code into the output language, which is typically the machine language of a computer.
Syntax Analysis or Parsing:
- This phase checks the program for grammatical errors, using the rules defined by the programming language. It receives a string of tokens from the lexical analyzer and arranges them in a way that shows the hierarchical structure of the program. This phase produces a parse tree as an output. This step is cr ucial in determining whether the code written by the user makes syntactical sense to the compiler.
Q78: Consider the following language:
L= {w ∈ { a, b, c }* : na(ω) + nb(ω) = nc(ω)}
L is
(a) Context free but not linear
(b) Not context free
(c) Context free and linear
(d) Linear
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Context free but not linear
The given language L={w ∈ { a, b, c }* : na(ω) + nb(ω) = nc(ω)} consists of strings over the alphabet {a, b, c} with the property that the total number of a's and b's in any string must be equal to the total number of c's.
This language is context-free.
- A context-free language (CFL) is typically one that can be generated by a context-free grammar (CFG) or recognized by a pushdown automaton (PDA). In this case, a PDA would have to simultaneously keep count of the number of 'a's and 'b's and compare this cumulative sum with the number of 'c's. Here the PDA can deterministically guess when to switch from pushing for 'a's/'b's to popping for 'c's. However, this is deterministic, and it can be done deterministically.
On the other hand, a linear language is a proper subset of context-free languages where the grammar generating the language never has more than one non-terminal in the right-hand side of any of its productions (can also be processed with a deterministic pushdown automaton).
Q79: The compiler for high level language that runs on one machine and produces code for other machine is called-
(a) Cross compiler
(b) Multipass compiler
(c) Optimizing Compiler
(d) One pass Compiler
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Cross compiler
Cross compiler
- A cross compiler is a type of compiler that is capable of creating executable code for a platform other than the one on which the compiler is running.
- For instance, you might be developing software on a Windows machine, but the target platform could be a different operating system or architecture, like Linux on ARM. The cross compiler allows the developer to compile the code on the Windows machine (the host machine), but the resulting executable is intended to be run on the different platform (the target machine).
- Cross compilers are especially necessary when the target platform is not capable of running a compiler, such as embedded systems with limited computational resources or specific hardware technologies such as gaming consoles. They are also useful when developing for different operating systems to ensure platform-specific optimization and compatibility.
That's why the statement "The compiler for a high-level language that runs on one machine and produces code for another machine" refers to a cross compiler.
The other options given like Multipass compiler, Optimizing Compiler, and One pass Compiler refer to different aspects of compilers:
- A Multipass compiler breaks down the process of translating source code into an executable form into multiple stages or "passes", each of which has its own specific task.
- An Optimizing compiler tries to enhance the performance of the output program, by reducing the execution time or the memory footprint of the program, or both.
- A One pass compiler scans the source code and generates the output code in a single pass over the source.
Q80: What is the (4 + 4) fit binary fixed point equivalent of -(3.72)10?
(a) 0011.1100
(b) 0011.1010
(c) 1100.0100
(d) 0011.1011
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 1100.0100
Fixed point representation is a way of storing real numbers in binary form. A 4 + 4 binary fixed point accommodates 4 bits for the integer part (one of them being the sign bit) and 4 bits for the fractional part.
Here is how we work out the binary equivalent of -3.72:
Integer part (-3):
- The binary representation of 3 is 0011.
- In the 2's complement system (which is used to represent negatives), flip the bits (1100) and then add 1 to get the representation of -3 which gives us 1101.
- Since we are representing a 4-bit binary number, we need to consider only 4 bits which is 1100 after discarding overflow bits. Why do we do that? While overflow is generally considered an error, in 2's complement binary arithmetic, an overflow is silently ignored.
- So the binary representation of -3 is 1100.
Fraction part (0.72): For the fractional part, we keep multiplying by 2:
- 0.72 * 2 = 1.44 => the first digit after decimal point is 1.
- 0.44 * 2 = 0.88 => the second digit after decimal point is 0.
- 0.88 * 2 = 1.76 => the third digit after decimal point is 1.
- 0.76 * 2 = 1.52 => the fourth digit after decimal point is 1. Therefore, the binary equivalent of 0.72 in 4-bit precision is .0100.
So the binary fixed point equivalent of -3.72 is -3 for the integer part, and 0.72 for the fractional part, combine them and we get answer: 1100.0100
Q81: Let ⊕ denote XOR operation. Let 1 and 0 denote the binary constants and F is the Boolean expression over two variables P and Q
F(P, Q) = ((1 ⊕ P) ⊕ (P ⊕ Q)) + ((P ⊕ Q) ⊕ (Q ⊕ 0))
Which of the following is equivalent expression to F?
(a) Ρ ⊕ Q
(b) P + Q
(c) 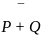
(d) 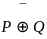
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 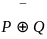
XOR operator ⊕ is both commutative and associative.
- A ⊕ B = AB̅ + A̅.B
- A ⊕ A = 0
- 1 ⊕ A = A̅
- 0 ⊕ A = A
CALCULATION:
- F(P, Q) = ((1 ⊕ P) ⊕(P⊕Q)) ⊕((P⊕Q) ⊕(Q⊕0) )
- F(P, Q) = 1 ⊕ (P ⊕ P) ⊕ Q ⊕ P⊕ (Q ⊕ Q) ⊕ 0
- F(P, Q) = (1 ⊕ 0) ⊕ Q ⊕ P⊕ (0 ⊕ 0)
- F(P, Q) = (1 ⊕ Q) ⊕ (P⊕ 0)
- F(P, Q) = Q̅ ⊕ P
- F(P, Q) = Q̅. P̅ + Q.P
- F(P, Q) = P ⊙ Q
- F(P, Q) =
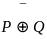
Q82: Let (Z, +) denote the group of all integers under addition. Then the number of all automorphisms of (Z, +) is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 2
In the group of all integers under addition, there are only two automorphisms. One is the identity map (each number maps to itself) and the other is the negation map (each number maps to its negative). This is because an automorphism in this group must preserve the group operation, which is addition, and these two functions are the only ones that do this.
- An automorphism is an isomorphism from a mathematical structure onto itself. In the context of groups, it's an isomorphism from a group to itself. In terms of the algebraic structure, an isomorphism preserves the group operation. For the group of integers under addition (Z, +), the operation is addition.
- In case of (Z, +), an automorphism must map 0 to 0 (as every group homomorphism preserves the identity) and must preserve addition. There are only two homomorphisms from (Z, +)to itself:
- The identity mapping (the function that maps every integer to itself), f(n) = n, and
- The negation function, f(n) = -n.
- This is because if τ: ℤ→ℤ is a group homomorphism, then τ(n) = nτ(1) for all n ∈ ℤ. As a result, the value of τ on any integer is determined by the image of 1.
Both of these homomorphisms are in fact automorphisms since they are bijective (one-to-one and onto).
So, the correct answer is 2) 2.
Q83: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
A. CDMA:
- CDMA or Code-Division Multiple Access is a digital cellular technology that uses spread spectrum techniques.
- The unique attribute that separates it from other technologies is its ability to allow several transmitters to send information simultaneously on a single communication channel.
- This is accomplished by assigning a code to every transmitter, consequently enabling multiple access, hence the term in its name "Multiple Access".
B. GSM:
- GSM is an abbreviation for Global System for Mobile communications (originally from Groupe Spécial Mobile).
- It is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. It's a cellular technology that employs a combination of two major multiple access schemes, FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) and TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access).
- In FDMA, each user is allocated a unique frequency band or channel while TDMA allows several users to share the same frequency band by dividing it into different time slots.
C. UMTS:
- UMTS which stands for Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, is a third-generation (3G) mobile cellular technology for networks based on the GSM standard.
- With advancements from previous technologies, UMTS is capable of providing higher data transfer rates and thus can contribute to a richer and more diverse range of services.
- It is known for offering a consistent set of services to mobile computer and phone users, irrespective of the fact that people are on the move.
D. WiFi:
- WiFi is a technology that allows an electronic device to exchange data or connect to the internet wirelessly using radio waves.
- It provides the underlying technology to create a home or business network (LAN) without physical wires or cables that is, a wireless network.
- On this network, users connect their devices to access the internet, share files, play games and many other things.
- This is convenient for devices like laptops, tablets, and smartphones that may frequently move throughout the space.
Q84: IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal)
45000054000300002006.....
What is the efficiency of this datagram?
(a) 76.19%
(b) 80.50%
(c) 82.24%
(d) 85.45%
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 76.19%
The header of the IP datagram given is in hexadecimal format.
 Size of the header is 20 to 60 Bytes
Size of the header is 20 to 60 Bytes
Version = 4 bits = (0100)2 (It is IPv4)
Header length = (0101)2 to (1111)2 = 5 bits to 15 bits
Total length = 216 bits
Identification = 216 bits
Fragment Offset = 216 bits
Time to live = 28 bits
Protocol = 28 bits
Header Checksum = 216 bits
SOLUTION:
IP Datagram = 45000054 00030000 2006.......
4 5 00 0054
The efficiency of an IP datagram can be determined by calculating the ratio of the payload (data) size to the total datagram size.
As we have determined above:
- The total size of the datagram is 84 bytes.
- The size of the header is 20 bytes.
Subtracting the header size from the total size gives us the payload size:
- Payload size = Total size - Header size Payload size = 84 bytes - 20 bytes = 64 bytes
The efficiency of the datagram is then:
- Efficiency = (Payload size / Total size) * 100%
So,
- Efficiency = (64 bytes / 84 bytes) * 100% ≈ 76.19%
Therefore, the efficiency of this datagram is approximately 76.19%.
Q85: IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal)
45000054000300002006.....
What is the protocol of the payload being carried by the packet?
(a) ICMP
(b) SCTP
(c) TCP protocol
(d) IGMP
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is TCP protocol
:
The header of the IP datagram given is in hexadecimal format.
Size of the header is 20 to 60 Bytes
Version = 4 bits = (0100)2 (It is IPv4)
Header length = (0101)2 to (1111)2 = 5 bits to 15 bits
Total length = 216 bits
Identification = 216 bits
Fragment Offset = 216 bits
Time to live = 28 bits
Protocol = 28 bits
Header Checksum = 216 bits
SOLUTION:
IP Datagram = 45000054 00030000 2006.......
20 06

The first byte of the IP header contains two fields: the version and the Internet Header Length (IHL). In your case, the first byte is "45" in hexadecimal.
The 9th byte (which is the 7th and 8th characters in the hexadecimal representation) identifies the protocol of the contained data.
In the given header, the protocol value is "06".
This value corresponds to the TCP protocol according to the Assigned Internet Protocol Numbers. Therefore,
The payload being carried by the packet is using the TCP protocol. So, the correct answer is: TCP protocol
Q86: IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal)
45000054000300002006.....
What is the size of datagram?
(a) 64 bytes
(b) 74 bytes
(c) 84 bytes
(d) 104 bytes
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 84 bytes
The header of the IP datagram given is in hexadecimal format.
 Size of the header is 20 to 60 Bytes
Size of the header is 20 to 60 Bytes
Version = 4 bits = (0100)2 (It is IPv4)
Header length = (0101)2 to (1111)2 = 5 bits to 15 bits
Total length = 216 bits
Identification = 216 bits
Fragment Offset = 216 bits
Time to live = 28 bits
Protocol = 28 bits
Header Checksum = 216 bits
SOLUTION:
IP Datagram = 45000054 00030000 2006.......
4 5 00 0054
The first byte of the IP header contains two fields: the version and the Internet Header Length (IHL). In your case, the first byte is "45" in hexadecimal.
The total length field is the second and third bytes of the IP header, "000054" in this case. These two bytes specify the total length of the whole IP datagram including the header and the data.
"000054" in hexadecimal is 84 in decimal. This value represents the total length of the datagram in bytes.
Therefore, the size of the datagram is 84 bytes.
Q87: IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal)
45000054000300002006.....
How many more routers can the packet travel to?
(a) 22
(b) 26
(c) 30
(d) 32
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 32
The header of the IP datagram given is in hexadecimal format.
Size of the header is 20 to 60 Bytes
Version = 4 bits = (0100)2 (It is IPv4)
Header length = (0101)2 to (1111)2 = 5 bits to 15 bits
Total length = 216 bits
Identification = 216 bits
Fragment Offset = 216 bits
Time to live = 28 bits
Protocol = 28 bits
Header Checksum = 216 bits
SOLUTION:
IP Datagram = 45000054 00030000 2006.......
20 06
 The first byte of the IP header contains two fields: the version and the Internet Header Length (IHL). In your case, the first byte is "45" in hexadecimal.
The first byte of the IP header contains two fields: the version and the Internet Header Length (IHL). In your case, the first byte is "45" in hexadecimal.
The hop limit (also known as the time-to-live limit in IPv4) is represented by the 8th byte, which in this case is "20" in hexadecimal. This value decrements by one each time the packet passes through a router. When it reaches zero, the packet is discarded.
"20" in hexadecimal translates to 32 in decimal. Therefore, the packet can travel through 32 more routers before it gets discarded.
Q88: A B-tree used as an index for a large database table has four levels including the root node. If a new key is inserted in this index, then maximum number of nodes that could be newly created in the process is
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 2
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 5
Formula:
- Considering all nodes are completely full means every node has N − 1 key.
- If a new key is inserted, then at every level there will be a new node created, and in the worst-case root node will also be broken into two parts. Since we have 4 levels, then 5 new nodes will be created
Other Related Points
- Diagram needs to be updated
- First, the overflow happens at the leaf, and second on the parent of that leaf, and so on until the last overflow happens at the root node.
- Therefore 4 nodes are created
If the database table has h levels and the level of the root node is 1 then on a new key insertion, the maximum number of nodes newly created is h + 1
Inserting a key into a full B-tree with 4 levels causes splits at each level (4 new nodes) and a new root (1 node), totaling 5 nodes.
Q89: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: If f and g are two functions and f = O(g) but g ≠ o(f), we say that the growth rate of g is smaller than that of f
Statement II: The class of all decision problems decided by a TM in exponential time, that is O(2k), k being a constant.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Statement I: This is incorrect.
- The notation f = O(g) means that the growth rate of function f is bounded by the growth rate of function g, up to a constant factor and beyond a certain point.
- If, in addition, g is not little o of f (meaning, g does not grow significantly slower than f beyond that certain point), then that doesn't bear on f growing faster than g. Instead it should mean that f does not grow faster than g and g does not grow significantly slower than f.
Statement II is incorrect.
- The class of decision problems decided by a Turing Machine (TM) in exponential time is typically denoted by EXP, and it is associated with O(2poly(n)), where "poly(n)" represents a polynomial in the input size n.
- The statement wrongly suggests that the class is O(2k), where k is a constant. In reality, the exponent in the exponential time complexity is a polynomial function of the input size.
Q90: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: A process involves a library function to create a thread.
Reason R: The threads make system calls to convey their resource and I/O requirement to the Kernel.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct of A
- Assertion A is true because a process can indeed use a library function to create a new thread. Libraries like the Pthreads library in C and Java's built-in multi-threading functionality offer such methods.
- Reason R is also true since threads, like processes, can make system calls to request services from the operating system's kernel, which include tasks related to resource allocation and I/O operations.
However, Reason R is not the correct of Assertion A. The reason for using a library function to create a thread doesn't directly relate to threads making system calls. In other words, threads making system calls to the kernel is a thread behavior and not a direct justification or for why a process would use a library function to create a thread.
Q91: IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal)
45000054000300002006.....
What is the header size ?
(a) 10 bytes
(b) 20 bytes
(c) 30 bytes
(d) 40 bytes
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 20 bytes
The header of the IP datagram given is in hexadecimal format.
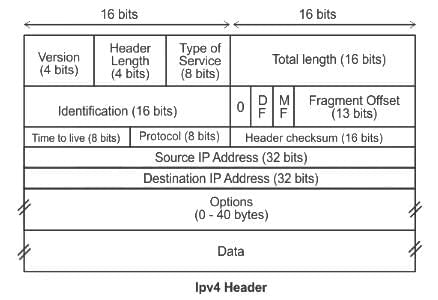
Size of the header is 20 to 60 Bytes
Version = 4 bits = (0100)2 (It is IPv4)
Header length = (0101)2 to (1111)2 = 5 bits to 15 bits
Total length = 216 bits
Identification = 216 bits
Fragment Offset = 216 bits
Time to live = 28 bits
Protocol = 28 bits
Header Checksum = 216 bits
SOLUTION:
IP Datagram = 45000054 00030000 2006.......
4 5 00 0054
The first byte of the IP header contains two fields: the version and the Internet Header Length (IHL). In your case, the first byte is "45" in hexadecimal.
The first digit '4' is the IP version i.e., IPv4. The second digit '5' represents the Internet Header Length (IHL).
The IHL field is 4 bits long and specifies the header length in 32-bit words. '5' in hexadecimal is 5 in decimal, which means the header length is 5 words (32-bit or 4 bytes each).
So, the size of the header is 5 * 4 = 20 bytes.
Q92: Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index):
for j = [0..... 1023]{
temp = 0;
for i = [0.... 16]:
temp = temp + T[i] [j];
print (temp/17.0); }
T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is paged and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is "least recently used ", If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format.
What is the main memory hit ratio?
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 0
To determine the number of page faults, let's analyze the memory accesses in the given program. Since the table T is stored in row-major format, the program accesses elements in a contiguous manner within rows. Each row has 1024 elements, and there are 17 rows.
The memory page size is 1024 words, and there are 16 pages. Each page can hold one row of the table.
Now, let's consider the nested loops:
for j in range(1024):
temp = 0
for i in range(17):
temp = temp + T[i][j]
print(temp/17.0)
The inner loop iterates over rows, so it sequentially accesses elements in a column (same column index j) for each iteration of the outer loop. This means that for each column, the inner loop will access 17 consecutive elements, which are located in 17 different rows.
Since each page can hold a full row (17 elements), accessing a column will result in a page fault for each iteration of the outer loop (for each column).
Therefore, the total number of page faults will be the number of columns multiplied by the number of page faults per column:
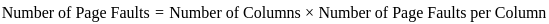
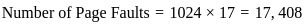
According to above solution no any page hit in the main memory
(17,408 - 17,408) / 17,408 = 0
So, the correct answer is: 1) 0
Q93: Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index):
for j = [0..... 1023]{
temp = 0;
for i = [0.... 16]:
temp = temp + T[i] [j];
print (temp/17.0); }
T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is paged and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is "least recently used ", If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format.
Consider again that T is stored in column-major format, what is the main memory hit ratio?
(a) 80%
(b) 95.6%
(c) 97.8%
(d) 99.9%
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 99.9%
In column-major format, each column contains 17 elements. The memory page size is 1024 words, and there are 16 pages. Each page can hold a complete column (60 elements) along with some remainder (4 elements).
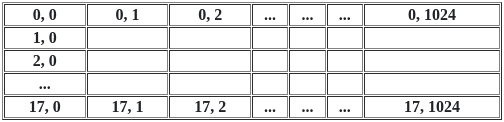
Now, let's calculate the main memory hit ratio.
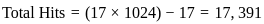
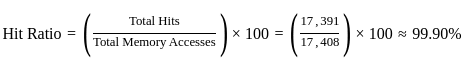
So, the correct answer is indeed: 4) 99.9%
Q94: Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index):
for j = [0..... 1023]{
temp = 0;
for i = [0.... 16]:
temp = temp + T[i] [j];
print (temp/17.0); }
T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is pages and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is "least recently used ", If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format.
Consider that T is stored in column major format, how many page faults will be encountered?
(a) 14
(b) 15
(c) 16
(d) 17
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 17
In column-major format, each column contains 17 elements. Given that the memory page size is 1024 words, we can calculate how many complete columns can fit into one page. .
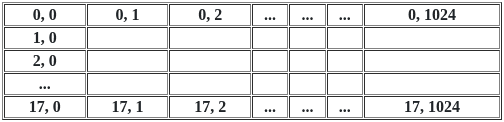

This means that each page can store 60 complete columns, along with 4 additional elements (the remainder). Therefore, for every 60 columns accessed, there will be a page fault for the next column, as it crosses the boundary of the page.
Now, we can determine the total number of page faults for the entire set of columns:
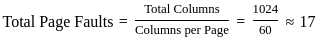
As in Q93, each column = 68 bytes, page = 4096 bytes,
so 60 columns per page.
Total columns = 1024, requiring 18 pages.
With 16 pages, faults occur for the first 16 columns (16 faults), plus one more fault when accessing the 17th page (columns 961–1024).
Total faults = 16 + 1 = 17.
The answer (d) is correct
So, the correct number of page faults, as per the provided , is 17.
Q95: Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index):
for j = [0..... 1023]{
temp = 0;
for i = [0.... 16]:
temp = temp + T[i] [j];
print (temp/17.0); }
T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is paged and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is "least recently used ", If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format.
How many page faults will be encountered?
(a) 16,402
(b) 17,408
(c) 18,208
(d) 18,608
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 17,408
To determine the number of page faults, let's analyze the memory accesses in the given program. Since the table T is stored in row-major format, the program accesses elements in a contiguous manner within rows. Each row has 1024 elements, and there are 17 rows.
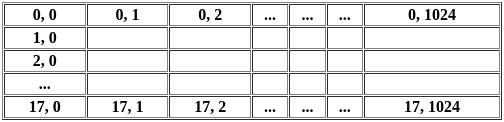
The memory page size is 1024 words, and there are 16 pages. Each page can hold one row of the table.
Now, let's consider the nested loops:
for j in range(1024):
temp = 0
for i in range(17):
temp = temp + T[i][j]
print(temp/17.0)
The inner loop iterates over rows, so it sequentially accesses elements in a column (same column index j) for each iteration of the outer loop. This means that for each column, the inner loop will access 17 consecutive elements, which are located in 17 different rows.
Since each page can hold a full row (17 elements), accessing a column will result in a page fault for each iteration of the outer loop (for each column).
Therefore, the total number of page faults will be the number of columns multiplied by the number of page faults per column:
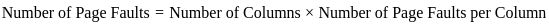
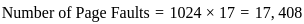
So, the correct answer is: 2) 17,408
Q96: Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index):
for j = [0..... 1023]{
temp = 0;
for i = [0.... 16]:
temp = temp + T[i] [j];
print (temp/17.0); }
T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is paged and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is "least recently used ", If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format.
What is fault ratio of row major to column major arrangements?
(a) 1024 ∶ 1
(b) 1301 ∶ 1
(c) 1240 ∶ 1
(d) 9107 ∶ 8
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 1024 ∶ 1
The fault ratio of row-major to column-major arrangements can be determined by comparing the number of page faults for each arrangement. In the row-major arrangement, as previously calculated, there are 17,408 page faults. In the column-major arrangement, there are also 17 page faults.
Now, let's find the fault ratio:

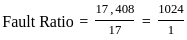
So, the correct answer is: 1) 1024 ∶ 1
Q97: Consider two hosts P and Q that are connected through a router R. The maximum transfer unit (MTU) value of the link between P and R is 1500 bytes and between R and Q is 820 bytes. A TCP segment of size 1400 bytes is transferred from P to Q through R with IP identification value of 0x1234. Assume that IP header size is 20 bytes. Further the packet is allowed to be fragmented that is Don't fragment (DF) flag in the IP Header is not set by P. Which of the following statement/s is/are true?
A. Two fragments are created at R and IP datagram size carrying the second fragment is 620 bytes
B. If the second fragment is lost, then R resends the fragment with IP identification value of 0x1234
C. If the second fragment lost, then P requires to resend the entire TCP segment.
D. TCP destination port can be determined by analyzing the second fragment only.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A and C only
(c) C and D only
(d) B and D only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A and C only
A) Two fragments are created at R and IP datagram size carrying the second fragment is 620 bytes:
- MTU between P-R = 1500 bytes. R should have received a full datagram of size 1400 bytes + 20 byte header = 1420 bytes. On R-Q link, the MTU = 820 bytes. So, R fragments the datagram received. One with 800 Bytes of data + 20 byte header = 820 bytes, and the other with the remaining data, thus 600 bytes of data + 20 byte header = 620 bytes. Fulfills condition (A).
B) If the second fragment is lost, then R resends the fragment with IP identification value of 0x1234:
- Incorrect. Routers, including R, do not resend failed fragments. The retransmission responsibility lies with the hosts.
C) If the second fragment lost, then P requires to resend the entire TCP segment:
- Correct. If the second fragment is lost, then the destination Q can't recognize the original TCP segment because any fragment loss leads to discarding all fragments. The destination then requests host P for a retransmission.
D) TCP destination port can be determined by analyzing the second fragment only:
- Incorrect. Only the first fragment contains the TCP header, as the IP fragmentation will occur after the TCP segmentation. The TCP header contains details like Source and destination ports. The second fragment does not contain the TCP header.
The answer is (2), A and C only.
Q98: Which of the following is not a property of a good system for representation of knowledge in a particular domain?
(a) Presentation adequacy
(b) infrential adequacy
(c) Infential efficiency
(d) acquisitional efficiency
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Presentation adequacy
Presentation Adequacy:
- This refers to how well the representation can convey the intended meaning to a user or another system. It involves the clarity and effectiveness of the representation for human understanding.
Inferential Adequacy:
- This property is about the representation's ability to support reasoning and inference. A good representation should allow for drawing conclusions and making inferences based on the knowledge it encapsulates.
Inferential Efficiency:
- This property relates to how quickly and effectively the system can perform inference operations. An efficient system can make logical deductions or draw conclusions in a timely manner.
Acquisitional Efficiency:
- This property is concerned with how well the system can acquire new knowledge or adapt to changes in the environment. An efficient system for knowledge representation should be able to incorporate new information easily.
So, in the context of knowledge representation systems, presentation adequacy might not be considered a primary property because the primary focus is often on the system's ability to represent, reason, and acquire knowledge efficiently. The effectiveness of presenting information to users is crucial but might be considered as a secondary aspect in comparison to the system's overall efficiency in handling knowledge.
Q99: What is x in the following program?
#include <stdio.h>
int main ( )
{typedef (* (*arrfptr [3]) ( ) ) [10];
arrfptr x;
return 0 ;
}
(a) x is a pointer
(b) x is a array of three pointer
(c) x is an array of three function pointer
(d) Error in x declaration
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is x is an array of three function pointer
The given program declares an array of three function pointers named x. Each function pointer is of type (* (*arrfptr [3]) ( ) ) [10].
typedef (* (*arrfptr[3])()) [10];
This declares arrfptr as an array of three pointers to functions with no parameters (specified by ()), and each function returns a pointer to an array of 10 elements. So, the correct answer is: x is an array of three function pointers
Other Related PointsAn array of pointers in C is essentially an array where each element is a pointer. This allows you to create an ordered collection of pointers, and each pointer can point to a different location in memory. The declaration of an array of pointers involves specifying the type of the elements that the pointers will point to.
Q100: Match List I with List II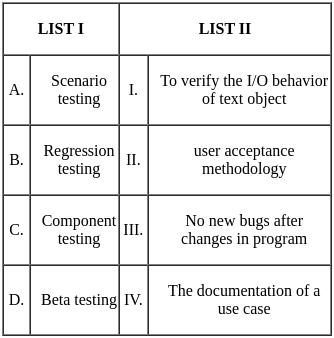
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(b) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Scenario Testing (A-IV):
- This type of testing is usually based on use cases or real-life scenarios that a software program might encounter.
- A scenario could be a specific sequence of actions a user might take when using an application.
- For example, a scenario for an e-commerce site might be "a user logs in, adds items to the shopping cart, removes one item, and then proceeds to checkout".
- The documentation of a use case or detailed user scenario is the basis for this kind of testing.
Regression Testing (B-III):
- Any time a change is made to software (like bug fixes, patches, or new functionality), there's a risk that other parts of the software that were previously working fine can unexpectedly break.
- To prevent such issues, testers perform regression testing, which aims to reveal any new bugs that might have been unknowingly introduced ("regressed") during the change. Essentially, the goal is to ensure there are "no new bugs after changes in the program."
Component Testing (C-I):
- This type of testing takes a deep look at specific parts (or "components") of the software.
- For example, it might focus on a specific feature or function. Testers might verify the input/output behavior of the component, which is why it is matching with "to verify the I/O behavior of a text object."
Beta Testing (D-II):
- This is a type of user acceptance testing that occurs after the software has passed initial stages of testing but before it is officially released. The software is typically provided to a small group of real-world users to get their feedback.
- This practice allows developers to catch any issues that might not have been caught during earlier testing phases. It is a type of "user acceptance methodology" as it is dependent on the feedback of actual, external users.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Computer Science 17th June 2023 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the structure and pattern of the UGC NET Paper 2 for Computer Science? |  |
| 2. How can candidates prepare effectively for the UGC NET Paper 2 in Computer Science? |  |
| 3. What are the common topics covered in the UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science syllabus? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET Paper 2 for Computer Science? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the UGC NET qualification in the field of Computer Science? |  |