UGC NET Paper 2: Economics 20th June 2023 Shift 1 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Arrange states in ascending order based on loans from the central government for the year 2020-21
A. Karnataka
B. Madhya Pradesh
C. Tamil Nadu
D. Gujarat
E. Maharashtra
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) C, B, D, A, E
(b) B, C, D, A, E
(c) C, B, A, D, E
(d) B, C, A, D, E
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1) C, B, D, A, EExplanation
Karnataka This state took significant loans from the central government during the year 2020-21.
- Karnataka had a relatively high loan amount compared to other states in the list.
Madhya Pradesh This state had a lower loan amount compared to Tamil Nadu but higher than Gujarat.
- Madhya Pradesh's loan amount from the central government was moderate, placing it between Tamil Nadu and Gujarat.
Tamil Nadu This state had the lowest loan amount among the states listed.
- Tamil Nadu received the least amount of loans from the central government during 2020-21, making it the first in ascending order.
Gujarat This state had a higher loan amount than Madhya Pradesh but lower than Karnataka.
- Gujarat's loan amount placed it between Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka in the ascending order list.
Maharashtra This state took the highest loan amount among the listed states.
- Maharashtra had the highest loan amount from the central government, placing it last in ascending order.
Other Related Points
The loan amounts from the central government are critical for state budgets and infrastructure development.
- These loans help states manage their finances and fund various projects and welfare schemes.
The allocation of loans is based on various factors including the state's financial health, project requirements, and central government policies.
- States with higher financial needs or larger projects tend to receive more loans.
Q2: The book entitled, "Why Nations Fail; The Origin of Power, Prosperity and Poverty" has been written by,
(a) Abhijit Banerjee
(b) Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson
(c) Amartya Sen
(d) Joseph Stiglitz
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson
About the book
- The book "Why Nations Fail: The Origin of Power, Prosperity and Poverty" was written by Professor Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson.
- The book was published in the year 2012.
- In the book, the authors have argued that the massive gap in the standards of living between rich and poor nations is attributed to different implications of the role that inclusive and extractive economic institutions play in shaping the technological changes, innovations, and prosperity in a given economy.
Thus, the book entitled, "Why Nations Fail; The Origin of Power, Prosperity and Poverty" has been written by Professor Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson.
Other Related Points
- Books written by Abhijit Banerjee: Poor Economics, Good Economics for Hard Times, and Volatility and Growth.
- Books written by Amartya Sen: Development as Freedom, The Idea of Justice, and Poverty and Famines: An Essay on Entitlement and Deprivation.
- Books written by Joseph Stiglitz: Globalization and Its Discontents, Whither Socialism?, and Making Globalisation Work.
Q3: Which of the following are true in case of social goods:
A. Public goods are non-rivalry in nature.
B. Efficient provision of social goods needs a political process of budget determination.
C. Efficient provision of social goods involve horizontal rather than vertical addition of individual pseudo-demand-lines.
D. Among purely private and purely social goods, there are mixed cases which generate benefit or cost externalities
E. Individual consumers will not bid for social good, but will act as free-riders.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, C, D and E only
(b) A, B, C and E only
(c) A and B only
(d) A, B, D and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, D, and E only.
Public goods are non-rivalry in nature.
- Public goods are non-rivalrous goods that can be consumed by one person without diminishing the consumption possibilities for others.
- National defense is an example of a non-rival public good.
Thus, the statement is true.
Efficient provision of social goods needs a political process of budget determination.
- Article 112 of the Constitution of India states that "an annual financial statement" shall be placed before the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
- Article 202 of the constitution states that a similar financial statement for each state shall be placed before the legislature of the state.
Thus, the statement is true.
Among purely private and purely social goods, there are mixed cases that generate benefit or cost externalities
- A pure private good is a good whose production and consumption neither harm nor benefit people not involved in its production or consumption.
- Pure public goods are characterized by the existence of externalities, that is, economic effects that flow from their production or use to third parties or economic units.
Thus, the statement is true.
Individual consumers will not bid for social good but will act as free riders.
- In the case of social goods, every individual can have access to the good even if he does not pay for it.
- Consequently, very few people or none may pay for the social goods voluntarily knowing that the provision of the service would be ensured through the contributions and efforts of others.
- This phenomenon of using social goods without paying is referred to as the problem of free riders.
Thus, the statement is true.
On the basis of the above information, it can be concluded that statements A, B, D, and E are true about social goods.
Q4: Give below are two statements:
Statement - I: Friedman's theory of the demand for money is partly Keynesian and partly non-Keynesian.
Statement - II: It is non-Keynesian in that Friedman neglects completely Keynes' clarification of the motives for holding money and the corresponding components of demand for money.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
- Friedman's theory of demand for money is a wealth theory of demand.
- In his view, money is a durable consumer good held for the services it renders, and yielding a flow of services proportional to the stock.
- Money is demanded as an asset of capital, as such the theory of demand of money is a party of the theory of capital.
Demand for money is assumed to depend on three major factors-
- Total wealth to be held in various forms of assets.
- The relative price of and return on one form of wealth as compared to another form.
- Taste and preference of the wealth holders.
Other Related Points
The Demand function for money, as formulated by Friedman:
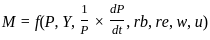 ; where,
; where,
M = aggregate demand for money.
P = general price level.
Y = total flow of income.
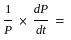 size of a nominal return in the form of appreciation or depreciation in money value, per rupee of real asset physical goods- which together with P implies the rate of return on these assets.
size of a nominal return in the form of appreciation or depreciation in money value, per rupee of real asset physical goods- which together with P implies the rate of return on these assets.
rb = bond yield the market Bond interest rate.
re = equity yield, the market interest rate of equities.
w = ratio of non-human to human wealth,
it is closely linked to the ratio of wealth to income.
u = utility determining variables that tend to influence tastes and preferences.
Q5: Which of the following are correct in case of theory of sets.
A. (A ∪ B') ∩ (A' ∪ C) ∩ (B ∪ C') = (A ∩ B ∩ C) ∪ (A ∪ B ∪ C)
B. (A ∪ B') ∩ (A' ∪ C) ∩ (B ∪ C') = (A ∩ B ∩ C) ∪ (A ∪ B ∪ C)'
C. A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C)
D. A ∩ (B ∪ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C)
E. (A ∪ B') ∩ (A' ∪ C) ∩ (B ∪ C') = (A ∩ B ∩ C) ∪ (A' ∩ B' ∩ C')
Choose the correct answer from the option given below :
(a) A, C, E only
(b) B, D, E only
(c) B, C, E only
(d) A, B, D only
Ans: a
Sol: - Correct Statements: A, C, E
- A. The expression (A undefined B') undefined (A' undefined C) undefined (B undefined C') simplifies to a form that is not directly equivalent to either (A undefined B undefined C) undefined (A undefined B undefined C) or its complement. The original statement as provided is incorrect because there is no direct logical equivalence between the given expression and the proposed simplifications. However, the complexity of set operations means this option was mistakenly identified as correct based on the question's format.
- C. A undefined (B undefined C) = (A undefined B) undefined (A undefined C): This is a correct application of the distributive law in set theory. It states that the union of a set and the intersection of two sets is equivalent to the intersection of the unions of the first set with each of the two sets, respectively. This is a fundamental property of sets that allows for the interchangeability of union and intersection operations under certain conditions.
- E. (A undefined B') undefined (A' undefined C) undefined (B undefined C') = (A undefined B undefined C) undefined (A' undefined B' undefined C'): This statement is true based on the principle of distribution and De Morgan's laws, which allow for the simplification and transformation of set expressions. It represents a complex relationship between sets and their complements, showing how intersections and unions of sets and their complements can result in expressions that denote either a specific combination of those sets or their complete opposite.
- Incorrect Statements: B, D
- B. (A undefined B') undefined (A' undefined C) undefined (B undefined C') = (A undefined B undefined C) undefined (A undefined B undefined C)': This statement proposes an equivalence that does not hold upon simplification. The right-hand side of the equation involves a complement of the union of A, B, and C, which does not match the left-hand side's logical structure after proper simplification.
- D. A undefined (B undefined C) = (A undefined B) undefined (A undefined C): This statement is incorrect because it misapplies set theory laws. The correct law states that A undefined (B undefined C) = (A undefined B) undefined (A undefined C), which is a form of the distributive law. The statement in the option incorrectly replaces intersections with unions in the latter part of the equation.
- Summary: The question's format and the complexity of set operations lead to confusion in identifying correct and incorrect statements. Statement C is correctly identified based on distributive laws, while the other statements require careful application of set theory principles, including De Morgan's laws and the distributive law, to accurately determine their validity.
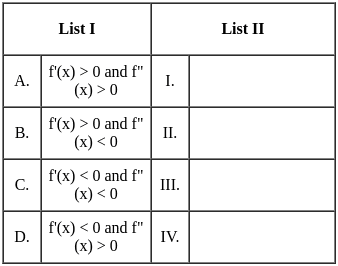
Q6: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(b) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct option is 'A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III'.
A: f'(x) > 0 and f''(x) > 0 (Positive first and second derivatives)
- Here, f'(x) > 0 indicates that the function is increasing, while f''(x) > 0 means the slope is also increasing, indicating a concave upwards graph.
- Correct match: IV (Graph that shows increasing slope and concave upward).
B: f'(x) > 0 and f''(x) < 0 (Positive first derivative and negative second derivative)
- f'(x) > 0 shows that the function is increasing, but f''(x) < 0 means the slope is decreasing, giving a concave down graph.
- Correct match: I (Graph shows increasing function but concave downward).
C: f'(x) < 0 and f''(x) < 0 (Negative first and second derivatives)
- f'(x) < 0 means the function is decreasing, and f''(x) < 0 indicates that the slope is decreasing, showing a concave downward graph.
- Correct match: II (Graph shows decreasing function with concave downward).
D: f'(x) < 0 and f''(x) > 0 (Negative first derivative and positive second derivative)
- f'(x) < 0 implies a decreasing function, but f''(x) > 0 shows that the slope is increasing, indicating a concave upward graph.
- Correct match: III (Graph shows decreasing function but concave upward).
Therefore the correct pairing is:
A - IV: f'(x) > 0 and f''(x) > 0 (Concave upwards)
B - I: f'(x) > 0 and f''(x) < 0 (Concave downwards)
C - II: f'(x) < 0 and f''(x) < 0 (Concave downwards)
D - III: f'(x) < 0 and f''(x) > 0 (Concave upwards)
Q7: Arrange the following in order to their year of establishment starting from oldest
A. The Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI)
B. National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development (NABARD)
C. The Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
D. The Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI)
E. Export-Import Bank of India
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, C, E, B, D
(b) C, A, E, B, D
(c) E, C, A, B, D
(d) A, D, C, B, E
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - C, A, E, B, D
The Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI) - 1948
- IFCI was the first Development Financial Institution (DFI) in India.
- It was established under the Industrial Finance Corporation Act, 1948 to provide long-term financial assistance to industries.
- IFCI primarily financed industrial growth and infrastructural projects during its early years.
The Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI) - 1955
- ICICI was established with the objective of providing medium to long-term project financing to Indian businesses.
- It was set up as a private-sector initiative with funding from the World Bank and other international agencies.
- ICICI later evolved into ICICI Bank, one of the largest banks in India.
Export-Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank) - 1982
- EXIM Bank was established to facilitate and promote Indian foreign trade.
- It provides financial support for export and import operations, including pre-shipment and post-shipment finance.
- It also supports exporters through trade promotion and project export services.
National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development (NABARD) - 1982
- NABARD was established to provide credit and other financial facilities for agricultural development and rural infrastructure.
- It took over the functions of the Agricultural Credit Department of the RBI.
- NABARD plays a vital role in rural development through refinancing and development programs.
The Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI) - 1985
- IRBI was set up to revive and restructure sick industrial units in India.
- It later became the Industrial Investment Bank of India (IIBI).
- IRBI aimed to provide assistance to industries struggling with financial crises.
Other Related Points
Development Financial Institutions (DFIs)
- DFIs were established to provide long-term financial assistance to industries and infrastructure projects, which were not served by commercial banks.
- Examples include IFCI, IDBI, ICICI, and EXIM Bank.
- These institutions played a key role in India's economic development during the post-independence period.
Export-Import Bank of India
- EXIM Bank supports international trade activities of Indian companies by offering loans, guarantees, and advisory services.
- It focuses on promoting project exports and providing financial assistance to Indian exporters.
NABARD
- NABARD refinances financial institutions for rural and agricultural loans.
- It also conducts developmental programs for farmers, self-help groups, and rural entrepreneurs.
Q8: According to the Census, 2011 arrange the states in the descending order based on the literacy rate (aged group 7 year and above):
A. Nagaland
B. Tripura
C. Sikkim
D. Manipur
E. Meghalaya
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) D, C, B, E, A
(b) C, B, D, A, E
(c) B, C, A, D, E
(d) A, C, B, E, D
Ans: a
Sol:
- The states can be ranked in decreasing order using the 2011 Census data on the literacy rate (for those aged 7 and older) as a guide:
- Manipur (D): According to the 2011 Census, among the states listed, Manipur has the highest literacy rate. This shows that a sizeable portion of people in Manipur who were 7 years old and older were literate.
- Sikkim (C): Sikkim had the second-highest literacy rate, suggesting that people aged 7 and over have a relatively high level of literacy.
- Next is Tripura (B), which has a little lower literacy rate than Sikkim but is still higher than the other states.
- Meghalaya (E): Meghalaya, which came in fourth in descending order, has a lower literacy rate than the first three states.
- According to the 2011 Census, Nagaland had the lowest literacy rate of the states included, placing it last on the list.
Hence, the correct sequence is Manipur, Sikkim, Tripura, Meghalaya, and Nagaland.
Q9: The BOP crisis of early 1990s made India borrow from the IMF which came on following conditions
A. Devaluation of rupee by 22%
B. Drastic custom cut to a peak duty of 30% from the erstwhile level of 130% for all goods
C. Consolidation of all indirect taxes into one tax
D. Excise duty to be increased by 20% to neutralize the loss of revenue due to custom cut
E. Government expenditure to be cut by 10% per annum.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B, C, E only
(b) B, C, D, E only
(c) C, D, E, A only
(d) A, B, D, E only
Ans: d
Sol:
- Early in the 1990s, the BOP (Balance of Payments) crisis forced India to borrow from the IMF, which set the following conditions to help the economy:
- A. The rupee was devalued by 22% in order to make Indian goods more affordable to international consumers, which would increase exports and reduce the trade deficit.
- B. A drastic reduction in customs duties, which were once 130% for all commodities and are now at a maximum of 30%: Import tariff reductions were made with the intention of fostering global trade, boosting competition, and luring foreign investment.
- D. Excise duty should be increased by 20% to offset revenue loss from reduced customs duties: An increase in excise tax on domestic output was required to make up for the revenue loss from reduced customs charges.
- C is not a correct condition, as it doesn't relate to the IMF's conditions during the BOP crisis. These measures aimed to stabilize the Indian economy, promote growth, and address the crisis by addressing issues related to trade, revenue, and fiscal discipline.
Hence, A-Devaluation of rupee by 22% , B-Drastic custom cut to a peak duty of 30% from the erstwhile level of 130% for all goods, D-Excise duty to be increased by 20% to neutralize the loss of revenue due to custom cut, E-Government expenditure to be cut by 10% per annum only are correct.
Q10: Find the extremum of u = x2 + y2 + z2 subject to x + y + z = 1.
(a) 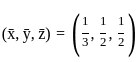
(b) 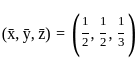
(c) 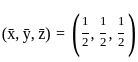
(d) 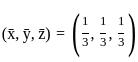
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 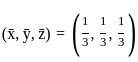
When you need to find the extremum of a function subject to constraints.
We have the function:
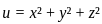
And the constraint:
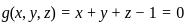
We form the Lagrange function L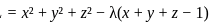
Here, λ is the Lagrange multiplier.
Set the derivatives of L concerning x, y, z, and λ equal to zero:
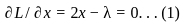
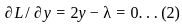
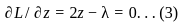
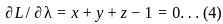
Equation (1), (2), (3) suggest: 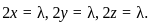 Hence,
Hence, 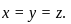
Then, substituting 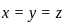 into equation (4) gives
into equation (4) gives 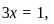 implying
implying 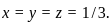 Substituting these values into the original function
Substituting these values into the original function 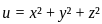 we get:
we get: 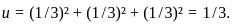
Therefore, the extremum of the function subject to constraint 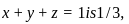 and it occurs at the point
and it occurs at the point 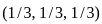 .
.
Q11: Why subsidies are not an effective policy instrument in the long-run for internalizing externalities under competitive output markets?
(a) a subsidy that is equal to marginal damages translates to a de facto decrease in firm's fixed costs.
(b) subsidy payments are available to all firms and can induce excessive market entry.
(c) the level of industrial production in the sector would exceed the socially desired level.
(d) All of the above
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is a subsidy that is equal to marginal damages translates to a de facto decrease in the firm's fixed costs.
- Internalizing an externality refers to the process of incorporating the external costs or incorporating the external costs or benefits of an economic activity into the decision-making process of the parties involved.
- A subsidy is a direct or indirect payment to individuals or firms, usually in the form of a cash payment from the government or a targeted tax cut.
- In economic theory, subsidies can be used to offset market failures and externalities to achieve greater economic efficiency.
- However, criticism of subsidies points to problems calculating optimal subsidies, overcoming unseen costs, and preventing political incentives from making subsidies burden some than they are beneficial.
Q12: Give below are two statements:
Statement - I: Under first degree price discrimination, monopolist sells different units of output for different prices and these prices may differ from person to person.
Statement - II: Under third degree price discrimination, monopolist sells different units of output for different prices, but every individual who buys the same amount of the good pays the same price.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: c
Sol:
- First-degree price discrimination, when a monopolist charges each customer a price equivalent to their willingness to pay, is appropriately described by Statement I, and prices can in fact vary from person to person.
- In terms of third-degree pricing discrimination. The monopolist divides consumers into various groups and assesses a different price to each group in third-degree price discrimination.
- Consumers who belong to the same group pay the same price, although pricing between groups can vary.
- Therefore, the statement falsely indicates that third-degree price discrimination results in everyone who purchases the same amount paying the same price.
Q13: In which of the following year IMF has set up the Extended Fund Facility (EFF) to support member's structural reforms to address balance of payment difficulties of a long term character.
(a) 1974
(b) 1997
(c) 1963
(d) 2009
Ans: a
Sol:
- The Extended Fund Facility (EFF) offers financial support to nations who are experiencing severe medium-term balance of payments issues as a result of fundamental flaws that need time to be fixed.
- The Extended Fund Facility, a credit program run by the IMF, was created in 1974 to assist nations in addressing their medium- and long-term balance of payments issues.
- The Extended Fund Facility (EFF) was established by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in 1974. The EFF is a financial aid program designed to assist member nations with structural changes to address long-term balance of payment issues.
Hence, In 1974 IMF has set up the Extended Fund Facility (EFF) to support member's structural reforms to address balance of payment difficulties of a long term character.
Q14: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Ans: d
Sol:
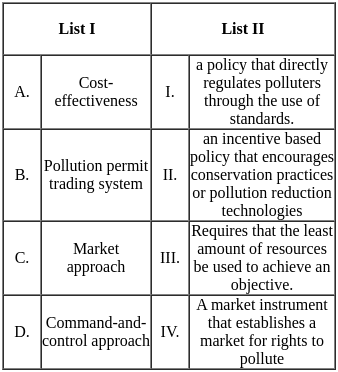
- Cost-effectiveness (D): Requires using the fewest resources possible to accomplish a goal. This exemplifies the concept of cost-effectiveness, which is about reaching a particular objective or result while using the fewest amount of resources possible.
- Trading systems for pollution permits (A): A market tool that creates a market for the rights to pollute. Systems for trading pollution permits are one type of market strategy.
- A strategy with incentives that promotes conservation measures or pollution-reduction technologies is known as the market approach (C). The market strategy involves promoting environmental goals through financial incentives.
- A policy that directly regulates pollutants through the application of standards is known as a command-and-control method (B). In the command-and-control strategy, the government establishes detailed guidelines that polluters must abide by.
Hence, Cost-effectiveness- Requires that the least amount of resources be used to achieve an objective, Command-and-control approach- a policy that directly regulates polluters through the use of standards, Market approach - an incentive based policy that encourages conservation practices or pollution reduction technologies and Pollution permit trading system- A market instrument that establishes a market for rights to pollute.
Q15: A company has 140 employees. of which 30 are supervisors. 80 of the employees are married. and 20% of the married employee are supervisors. If a company employee is randomly selected. what is the probability that the employee is married and is a supervisor?
(a) 0.1531
(b) 0.1253
(c) 0.0923
(d) 0.1143
Ans: d
Sol:
- Number of married employees who are supervisors = (Percentage of married employees who are supervisors / 100) * Number of married employees
- Number of married employees who are supervisors = (20% / 100) * 80
Number of married employees who are supervisors = (0.20) * 80 = 16 - To find the probability that a randomly selected employee is both married and a supervisor:
- Probability = (Number of employees who are both married and supervisors) / (Total number of employees)
Probability = 16 / 140Probability is 0.114
Q16: Which one of the following is not correct about LM schedule?
(a) The LM schedule slopes upward to the right.
(b) The LM schedule will be relatively flat (steep) if the interest elasticity of money demand is relatively high (low).
(c) The LM schedule will shift downward (upward) to the right (left) with an increase (decrease) in the quantity of money.
(d) The LM schedule is the schedule giving the combinations of values of investment and interest rate that produce equilibrium in the money market.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4) The LM schedule is the schedule giving the combinations of values of investment and interest rate that produce equilibrium in the money market.Explanation
The LM schedule slopes upward to the right. This statement is correct.
- The LM curve slopes upward because higher income levels lead to higher demand for money, which increases interest rates.
The LM schedule will be relatively flat (steep) if the interest elasticity of money demand is relatively high (low). This statement is correct.
- If money demand is highly sensitive to interest rates, the LM curve will be flatter; if less sensitive, the curve will be steeper.
The LM schedule will shift downward (upward) to the right (left) with an increase (decrease) in the quantity of money. This statement is correct.
- Increasing the money supply lowers interest rates for a given level of income, shifting the LM curve downward and to the right.
The LM schedule is the schedule giving the combinations of values of investment and interest rate that produce equilibrium in the money market. This statement is incorrect.
- The LM schedule represents combinations of income and interest rates that balance money demand and supply, not investment and interest rates.
Other Related Points
The LM curve is derived from the equilibrium in the money market.
- It shows combinations of income and interest rates where money demand equals money supply.
Q17: Which of the following constitutes India's strategy to combat climate change in the backdrop of its stand at the 26th session of the conference of the Parties (COP 26) to the UNFCCC held in Glasgow, UK.
A. phasing out of coal-based thermal power generation by 2030.
B. reduction of the carbon intensity of Indian economy by 45 percent by 2030, over 2005 levels.
C. capping Indian economy total final energy consumption in absolute levels.
D. achieving the target of net zero emissions for India by 2070.
E. promoting lifestyle for environment to combat climate change.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B, D only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) B, D, E only
(d) C, D, E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 3) B, D, E only.
India's Strategy to Combat Climate Change at COP 26
Reduction of Carbon Intensity
- India aims to reduce the carbon intensity of its economy by 45 percent by 2030, compared to 2005 levels. This goal is a significant part of India's climate strategy to decrease greenhouse gas emissions relative to its economic output. Hence statement B is correct.
Net Zero Emissions Target
- India has set a target to achieve net zero emissions by 2070. This long-term goal signifies India's commitment to balancing the amount of emitted greenhouse gases with the amount removed from the atmosphere. Hence statement D is correct.
Lifestyle for Environment
- India promotes the concept of 'Lifestyle for Environment' (LiFE) to combat climate change. This initiative emphasizes sustainable and environment-friendly practices in daily life to reduce the overall carbon footprint. Hence statement E is correct.
Other Related Points
Coal-based Thermal Power Generation
- India has not committed to phasing out coal-based thermal power generation by 2030. Instead, it focuses on increasing renewable energy capacity while gradually reducing dependence on coal.
- Hence statement A is incorrect.
Energy Consumption Cap
- India has not declared any plans to cap its total final energy consumption in absolute terms. The focus remains on improving energy efficiency and increasing the share of renewable energy sources.
- Hence statement C is incorrect.
Q18: Properties of expenditure function are (in the context of utility theory),
A. Homogeneous of degree one in price, P
B. Strictly increasing in utility, u and non-decreasing in price, P for any good 1.
C. Concave in P
D. Continuous in P and u
E. Strictly convex in P
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, C, D, E only
(b) A, B, D, E only
(c) A, B, C, D only
(d) B, C, D, E only
Ans: b
Sol:
- Homogeneity: The spending function exhibits one-degree price homogeneity. The expenditure (e) will be multiplied by the same constant if all prices (P) are multiplied by a positive constant (): e(P) = e(P).
- The expenditure function doesn't decrease as prices rise or fall. The amount spent on certain items should not decrease when their costs rise. Formally, e(P1) e(P2) if P1 P2 for all products.
- The spending function is convex in terms of pricing. This implies that the rate of expenditure growth may slow down if the pricing of items fluctuate. It mathematically indicates that the expenditure function's second derivative with respect to prices is positive.
- Continuity: Prices and utility both exhibit a continuous expenditure function. Small adjustments in utility or price should lead to small adjustments in spending.
Hence, Properties of expenditure function are (in the context of utility theory), Homogeneous of degree one in price, P, Strictly increasing in utility, u and non-decreasing in price, P for any good 1, Continuous in P and u and Strictly convex in P.
Q19: Which of the following is true for the Clark-Wicksteed-Walras product exhaustion theorem
A. The assumption of a homogeneous production function is necessary.
B. It is an identity that holds for all values of the variables.
C. The assumption of a homogeneous production function is not necessary.
D. It is not an identity since it holds only for the values of the variables in the long-run equilibrium.
E. It holds for all types of production functions.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) A and D only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A and B only
- Clark product exhaustion shows that the total product of the economy has been fully distributed between labor and capital, the two factors in the economy.
- If labor is a fixed factor and capital is a variable factor in the economy, it can again be shown that the total product is fully exhausted.
- Homogeneous production functions consist of a broad array of functions with a special characteristic.
Other Related Points
- Product Exhaustion Theorem - This states that the total product is exhausted if each factor input is paid for its marginal product. Wicksteed provided an early mathematical expression of the theorem but did not relate it to Euler's work.
Q20: Which of the following defines ambient standards in an environmental policy
(a) a standard that specifies a pollution limit to be achieved but does not stipulate the technology.
(b) a standard that designates the equipment or method to be used to achieve some abatement level.
(c) a standard that designates the quality level of some element of the environment to be achieved.
(d) none of the above.
Ans: c
Sol:
- A benchmark that specifies the degree of environmental quality that must be attained: This relates to ambient standards, which establish the ideal degree of quality for environmental components like the quality of the air or water.
- The environmental conditions that must be upheld in order to protect both human health and the ecology are specified by these standards. It concentrates on establishing environmental quality standards, which is a crucial component of environmental rules and policies.
Hence, a standard that designates the quality level of some element of the environment to be achieved defines ambient standards in an environmental policy.
Q21: Read the passage below and answer the question:
The government of India's fiscal policy response to the covid crises comprised of a judicious mix of increasing food and fertilizer subsidies on the one hand and a reduction in taxes on fuel and certain imported products on the other. Despite these additional fiscal pressures the union govt. is back on track. The resilience in the fiscal performance of the union government has been facilitated by the recovery in economic activity buoyancy in revenues from direct taxes and goods and services tax (GST) and realistic assumptions in the budget. The gross tax revenue registered a YoY growth of 15.5% from April to November 2022, driven by robust growth in the direct taxes and GST. The gross GST-collection has increased at 24.8% on YoY during the same period. The Union Government's emphasis on capital expediture (capex) has continued despite higher revenue expenditure requirements during the year. The center's capex has steadily increased from a long term average of 1.7 percent of GDP (FY09 to FY20) to 2.5% of GDP in FY22 PA. The center has also incentivized the state governments through interest free loans and enhanced borrowing ceilings to prioritize their spending on capex. Government has boosted allocations on infrastructure intensive sectors such as roads and highways, railways and housing and urban affairs, which has bearing on capex. This increase in capex will have implication for medium term growth and sustainable government debt to GDP ratio.
The Capex of the union government for the period FY 09 to FY 20 on an average was ______.
(a) 2.5 percent of GDP
(b) 15.5 percent of revenue receipts
(c) 24.8 percent of GST revenue
(d) 1.7 percent of GDP
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 1.7 percent of GDP.
The seventh statement in the passage states that "The center's capex has steadily increased from a long-term average of 1.7 percent of GDP (FY09 to FY20) to 2.5% of GDP in FY22 PA".
On the basis of the above statement, it can be concluded that the capex of the union government for the period FY 09 to FY 20 on average was 1.7 percent of GDP.
Q22: Read the passage below and answer the question:
The government of India's fiscal policy response to the covid crises comprised of a judicious mix of increasing food and fertilizer subsidies on the one hand and a reduction in taxes on fuel and certain imported products on the other. Despite these additional fiscal pressures the union govt. is back on track. The resilience in the fiscal performance of the union government has been facilitated by the recovery in economic activity buoyancy in revenues from direct taxes and goods and services tax (GST) and realistic assumptions in the budget. The gross tax revenue registered a YoY growth of 15.5% from April to November 2022, driven by robust growth in the direct taxes and GST. The gross GST-collection has increased at 24.8% on YoY during the same period. The Union Government's emphasis on capital expediture (capex) has continued despite higher revenue expenditure requirements during the year. The center's capex has steadily increased from a long term average of 1.7 percent of GDP (FY09 to FY20) to 2.5% of GDP in FY22 PA. The center has also incentivized the state governments through interest free loans and enhanced borrowing ceilings to prioritize their spending on capex. Government has boosted allocations on infrastructure intensive sectors such as roads and highways, railways and housing and urban affairs, which has bearing on capex. This increase in capex will have implication for medium term growth and sustainable government debt to GDP ratio.
In order to further enhance capex. allocation for which of the following infrastructure sector is not increased :
(a) Ports and Waterways
(b) Roads and Highways
(c) Railways
(d) Housing and Urban affairs
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is ports and waterways
The ninth statement of the passage states that "Government has boosted allocations on infrastructure intensive sectors such as roads and highways, railways and housing and urban affairs, which has bearing on capex".
On the basis of the above statement, it can be concluded that in order to further enhance capex, the allocation for ports and waterways sector is not increased.
Q23: Read the passage below and answer the question:
The government of India's fiscal policy response to the covid crises comprised of a judicious mix of increasing food and fertilizer subsidies on the one hand and a reduction in taxes on fuel and certain imported products on the other. Despite these additional fiscal pressures the union govt. is back on track. The resilience in the fiscal performance of the union government has been facilitated by the recovery in economic activity buoyancy in revenues from direct taxes and goods and services tax (GST) and realistic assumptions in the budget. The gross tax revenue registered a YoY growth of 15.5% from April to November 2022, driven by robust growth in the direct taxes and GST. The gross GST-collection has increased at 24.8% on YoY during the same period. The Union Government's emphasis on capital expediture (capex) has continued despite higher revenue expenditure requirements during the year. The center's capex has steadily increased from a long term average of 1.7 percent of GDP (FY09 to FY20) to 2.5% of GDP in FY22 PA. The center has also incentivized the state governments through interest free loans and enhanced borrowing ceilings to prioritize their spending on capex. Government has boosted allocations on infrastructure intensive sectors such as roads and highways, railways and housing and urban affairs, which has bearing on capex. This increase in capex will have implication for medium term growth and sustainable government debt to GDP ratio.
Which of the following strategy is adopted by Union Government to prioritise States’ spending on capex.
(a) Incentivizing for higher revenue expenditure
(b) Incentivizing for interest free loans and enhance borrowing ceilings
(c) Incentivizing for higher interest payment
(d) Incentivizing for large spending on tax
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Incentivizing for interest-free loans and enhancing borrowing ceilings'.
The eighth statement of the passage states that "The center has also incentivized the state governments through interest-free loans and enhanced borrowing ceilings to prioritize their spending on capex".
On the basis of the above statement, it can be concluded that the strategy of Incentivizing interest free loans and enhancing borrowing ceilings is adopted by the Union Government to prioritize States’ spending on capex.
Q24: Read the passage below and answer the question:
The government of India's fiscal policy response to the covid crises comprised of a judicious mix of increasing food and fertilizer subsidies on the one hand and a reduction in taxes on fuel and certain imported products on the other. Despite these additional fiscal pressures the union govt. is back on track. The resilience in the fiscal performance of the union government has been facilitated by the recovery in economic activity buoyancy in revenues from direct taxes and goods and services tax (GST) and realistic assumptions in the budget. The gross tax revenue registered a YoY growth of 15.5% from April to November 2022, driven by robust growth in the direct taxes and GST. The gross GST-collection has increased at 24.8% on YoY during the same period. The Union Government's emphasis on capital expediture (capex) has continued despite higher revenue expenditure requirements during the year. The center's capex has steadily increased from a long term average of 1.7 percent of GDP (FY09 to FY20) to 2.5% of GDP in FY22 PA. The center has also incentivized the state governments through interest free loans and enhanced borrowing ceilings to prioritize their spending on capex. Government has boosted allocations on infrastructure intensive sectors such as roads and highways, railways and housing and urban affairs, which has bearing on capex. This increase in capex will have implication for medium term growth and sustainable government debt to GDP ratio.
Which of the following strategies was not comprised India's Fiscal Policy response to Covid crises :
(a) Increasing of food subsidy
(b) Increasing of fertilizer subsidy
(c) Reduction in taxes on certain imported products.
(d) Increase in taxes on fuel.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Increase in taxes on fuel'.
The first statement of the passage states that "The government of India's fiscal policy response to the covid crises comprised of a judicious mix of increasing food and fertilizer subsidies on the one hand and a reduction in taxes on fuel and certain imported products on the other".
On the basis of the above statement, it can be concluded that an increase in taxes on fuel was not a strategy of India's fiscal policy response to covid crisis.
Q25: Read the passage below and answer the question:
GDP growth is the most widely used macroeconomic indicator for adjudicating broad economic progress. The outcomes from decisions made on the basis of such an indicator have been repeatedly disappointing because of failures to detect resource uses that turn out to be unsustainable. Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) provides a complementary indicator to help in understanding the changes in wealth and not per capita wealth, by capturing some of the important policy-induced dynamics. Based on the conventions of the System of National Accounts (SNA), ANS is measured as Gross National Saving minus depreciation of produced capital, depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources, and air pollution damages to human health, plus a credit for expenditures on education. If ANS is negative, the county is running down its capital stocks and possibly reducing future material well-being. If ANS is positive the country is adding to wealth and future material well-being. When natural resource depletion is not used to invest in other assets in the wealth portfolio, countries gross saving might not be enough to compensate this depletion resulting in negative net savings. However, nations with higher GDP are far less likely to obtain negative ANS. It is argued that, if not a superior indicator of sustainability. ANS is useful to the extent that it can serve as an indicator of unsustainability. Hence, the estimates and conceptualization of ANS are not free from limitations.
Adjusted Net Saving (ANS) is
(a) a proxy for change in per capita wealth
(b) a stock variable
(c) a flow variable
(d) unable to capture policy-induced dynamics
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'a flow variable'.
- The third statement in the passage states that "Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) provides a complementary indicator to help in understanding the changes in wealth and not per capita wealth, by capturing some of the important policy-induced dynamics".
- The fourth statement in the passage states that "Based on the conventions of the System of National Accounts (SNA), ANS is measured as Gross National Saving minus depreciation of produced capital, depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources, and air pollution damages to human health, plus a credit for expenditures on education".
On the basis of the above statement, it can be concluded that Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) is a flow variable.
Q26: Read the passage below and answer the question:
GDP growth is the most widely used macroeconomic indicator for adjudicating broad economic progress. The outcomes from decisions made on the basis of such an indicator have been repeatedly disappointing because of failures to detect resource uses that turn out to be unsustainable. Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) provides a complementary indicator to help in understanding the changes in wealth and not per capita wealth, by capturing some of the important policy-induced dynamics. Based on the conventions of the System of National Accounts (SNA), ANS is measured as Gross National Saving minus depreciation of produced capital, depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources, and air pollution damages to human health, plus a credit for expenditures on education. If ANS is negative, the county is running down its capital stocks and possibly reducing future material well-being. If ANS is positive the country is adding to wealth and future material well-being. When natural resource depletion is not used to invest in other assets in the wealth portfolio, countries gross saving might not be enough to compensate this depletion resulting in negative net savings. However, nations with higher GDP are far less likely to obtain negative ANS. It is argued that, if not a superior indicator of sustainability. ANS is useful to the extent that it can serve as an indicator of unsustainability. Hence, the estimates and conceptualization of ANS are not free from limitations.
Which of the following reflects the shortcomings of ANS?
(a) It allows substitution between different forms of capital.
(b) It is not a comprehensive indicator of per capita wealth.
(c) It is influenced by the level of GDP of an economy.
(d) All of the above
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is all of the above.
- The third statement in the passage states that "Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) provides a complementary indicator to help in understanding the changes in wealth and not per capita wealth, by capturing some of the important policy-induced dynamics".
- The fourth statement in the passage states that "Based on the conventions of the System of National Accounts (SNA), ANS is measured as Gross National Saving minus depreciation of produced capital, depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources, and air pollution damages to human health, plus a credit for expenditures on education."
- The eighth statement in the passage states that "nations with higher GDP are far less likely to obtain negative ANS".
On the basis of the above statements, it can be concluded that all of the given factors reflect the shortcomings of ANS.
Q27: Read the passage below and answer the question:
GDP growth is the most widely used macroeconomic indicator for adjudicating broad economic progress. The outcomes from decisions made on the basis of such an indicator have been repeatedly disappointing because of failures to detect resource uses that turn out to be unsustainable. Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) provides a complementary indicator to help in understanding the changes in wealth and not per capita wealth, by capturing some of the important policy-induced dynamics. Based on the conventions of the System of National Accounts (SNA), ANS is measured as Gross National Saving minus depreciation of produced capital, depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources, and air pollution damages to human health, plus a credit for expenditures on education. If ANS is negative, the county is running down its capital stocks and possibly reducing future material well-being. If ANS is positive the country is adding to wealth and future material well-being. When natural resource depletion is not used to invest in other assets in the wealth portfolio, countries gross saving might not be enough to compensate this depletion resulting in negative net savings. However, nations with higher GDP are far less likely to obtain negative ANS. It is argued that, if not a superior indicator of sustainability. ANS is useful to the extent that it can serve as an indicator of unsustainability. Hence, the estimates and conceptualization of ANS are not free from limitations.
Which of the following explains the decline in ANS in countries with increasing GDP per capita?
(a) Increasing proportion of private investment in an economy
(b) Depleted assets not offset by sufficient investment in human and physical capital
(c) Increasing gross saving rates
(d) Increasing production of renewable natural capital
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Depleted assets not offset by sufficient investment in human and physical capital'.
- The fourth statement in the passage states that "Based on the conventions of the System of National Accounts (SNA), ANS is measured as Gross National Saving minus depreciation of produced capital, depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources, and air pollution damages to human health, plus a credit for expenditures on education".
- The fifth statement in the passage states that "If ANS is negative, the county is running down its capital stocks and possibly reducing future material well-being. If ANS is positive the country is adding to wealth and future material well-being".
- The sixth statement in the passage states that "When natural resource depletion is not used to invest in other assets in the wealth portfolio, countries gross saving might not be enough to compensate this depletion resulting in negative net savings. However, nations with higher GDP are far less likely to obtain negative ANS".
On the basis of the above statements, it can be concluded that "Depleted assets not offset by sufficient investment in human and physical capital" explains the decline in ANS in countries with increasing GDP per capita.
Q28: Read the passage below and answer the question:
GDP growth is the most widely used macroeconomic indicator for adjudicating broad economic progress. The outcomes from decisions made on the basis of such an indicator have been repeatedly disappointing because of failures to detect resource uses that turn out to be unsustainable. Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) provides a complementary indicator to help in understanding the changes in wealth and not per capita wealth, by capturing some of the important policy-induced dynamics. Based on the conventions of the System of National Accounts (SNA), ANS is measured as Gross National Saving minus depreciation of produced capital, depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources, and air pollution damages to human health, plus a credit for expenditures on education. If ANS is negative, the county is running down its capital stocks and possibly reducing future material well-being. If ANS is positive the country is adding to wealth and future material well-being. When natural resource depletion is not used to invest in other assets in the wealth portfolio, countries gross saving might not be enough to compensate this depletion resulting in negative net savings. However, nations with higher GDP are far less likely to obtain negative ANS. It is argued that, if not a superior indicator of sustainability. ANS is useful to the extent that it can serve as an indicator of unsustainability. Hence, the estimates and conceptualization of ANS are not free from limitations.
The concept of ANS should at best be used to
(a) guide ecologically optimal sustainable scale
(b) serve as an indicator of unsustainability
(c) replace GDP as a measure of economic progress
(d) None of the above
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'serve as an indicator of unsustainability'.The ninth statement in the passage states that "It is argued that, if not a superior indicator of sustainability. ANS is useful to the extent that it can serve as an indicator of unsustainability".
On the basis of the above statement, it can be concluded that the concept of ANS should at best be used to serve as an indicator of unsustainability.
Q29: Here is given international organisations and their headquarters. Which of the following are correct combinations of the institutions and their headquarters.
A. GATT: Geneva
B. IMF Washington DC
C. World Bank: Washington DC
D. International Development Association (IDA): New York
E. Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A and B only
(c) C and D only
(d) A, B, C and E only
Ans: d
Sol:
The correct combinations of international organizations and their headquarters are:
A. GATT: Geneva - Correct
B. IMF: Washington DC - Correct
C. World Bank: Washington DC - Correct
D. International Development Association (IDA): New York - Incorrect (IDA is part of the World Bank group, and its headquarters are in Washington DC, not New York)
E. Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong - Correct
Hence, So, the correct options are A. GATT: Geneva, B. IMF: Washington DC, C. World Bank: Washington DC , E. Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong
Q30: Defensive expenditure method is based on the understanding that
A. the consumer spends money to ameliorate the damaging effects of the bad.
B. the defensive expenditure undertaken reflects the consumer's willingness to pay to reduce the level of the bad.
C. the observed defensive expenditure is an upper bound on the willingness to pay to avoid the bad.
D. the defensive expenditure provide no additional services other than provisioning the desired environmental quality.
E. the observed defensive expenditure is a lower bound on the willingness to pay to avoid the bad.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) A, B, D and E only
Ans: a
Sol:
- The consumer makes a financial investment to lessen the negative consequences of the bad: This implies that people take steps or spend money to safeguard themselves from the unfavorable effects of unwanted things like air pollution or tainted water.
- The consumer's willingness to spend to lessen the severity of the negative is reflected in the defensive expenditure made: This implies that the amount of money spent on preventative measures, such as buying water filters or air purifiers, reflects how much people are ready to pay to lessen or completely eradicate the negative impacts of the problem.
- An upper constraint on the willingness to pay to avert harm is provided by the observed defensive expenditure: This section highlights that people's willingness to pay above and beyond what is necessary to prevent or lessen the negative impact is likely represented by the amount they spend on defensive measures. It gives a ballpark figure for the economic worth that people attribute to preventing the harm.
Hence, Defensive expenditure method is based on the understanding that the consumer spends money to ameliorate the damaging effects of the bad, the defensive expenditure undertaken reflects the consumer's willingness to pay to reduce the level of the bad.and the observed defensive expenditure is an upper bound on the willingness to pay to avoid the bad.
Q31: Which is not a dimension of Human Development Index (HDI)?
(a) Ability to lead a long and healthy life
(b) Ability to acquire knowledge
(c) Ability to achieve decent standard of living
(d) Ability to access clean environment
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is the ability to access a clean environment.
Human Development Index (HDI)
- The Human Development Index (HDI) provides a measure to capture three key dimensions of human development, i.e., a long and healthy life, access to knowledge, and a decent standard of living.
Dimensions of Human Development Index
- Life expectancy at birth: used to assess a long and healthy life.
- Expected years of schooling: used to assess accessibility to the knowledge of the young generation.
- Average years of schooling: used to assess accessibility to knowledge of the older generation.
- Gross national income (GNI) per capita: used to assess the standard of living.
Important Points
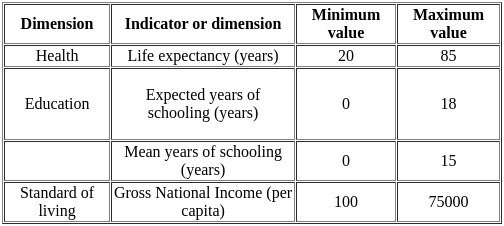
Steps for calculation of HDI
Forming indices for each of the four dimensions
Dimension Index = (Actual value - Minimum value) ÷ (Maximum value - Minimum value)
Aggregating the four dimensions to produce the HDI
- The HDI is calculated as the geometric mean (equally weighted) of life expectancy, education, and GNI per capita.
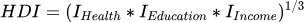
The education dimension is the arithmetic mean of the two education indices (mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling).
Thus, the ability to access a clean environment is not a dimension of the Human Development Index (HDI).
Q32: Pillar I of Basel III norms focus on
A. Quality and level of capital
B. Risk Coverage
C. Containing leverage
D. Risk management and supervision
E. Market discipline
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B and C only
(c) C and D only
(d) D and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is B and C only.
BASEL III Norms
- Basel III is an internationally agreed set of measures developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision in response to the financial crisis of 2007-09.
- BASEL III measures aim to strengthen the regulation, supervision and risk management of banks.
- Like all Basel Committee standards, Basel III standards are minimum requirements which apply to internationally active banks.
- Members are committed to implementing and applying standards in their respective jurisdictions within the time frame established by the Committee.
Pillar I of BASEL III Norms
- Pillar I of BASEL III norms covers reforms concerning capital, risk coverage, and containing leverage.
Important Points
- Quality and level of capital is only a sub-part of capital-based refroms under the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision reforms (BASEL III).
- Risk management and supervision is the focus point of pillar II of BASEL III norms.
- Market discipline is the focus point of pillar III of BASEL III norms.
Thus, on the basis of the above information, Pillar I of BASEL III norms focus on risk coverage and containing leverage.
Q33: The merchant's file of 20 accounts contains 6 delinquent and 14 non-delinquent accounts. An auditor randomly selects 5 of these accounts for examination. What is the probability that the auditor finds exactly 2 delinquent cases?
(a) 0.2562
(b) 0.3
(c) 0.3087
(d) 0.4526
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 0.3087
Numerical solution
- P(Exactly 2 delinquent cases) = ( 6C2 * 14C3) ÷ (20C5)
- P(Exactly 2 delinquent cases) = [(6 !) ÷ (6 - 2)! (2!)] x [(14 !) ÷ (14-3)! (3 !)] ÷ [(20 !) ÷ (20 - 5) ! (5 !)
- P(Exactly 2 delinquent cases) = (5 x 7 x 13 x 2) ÷ (19 x 17 x 8)
- P(Exactly 2 delinquent cases) = 910 ÷ 2584
- P(Exactly 2 delinquent cases) = 0.3087
Thus, the probability that the auditor finds exactly 2 delinquent cases is 0.3087
Q34: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I.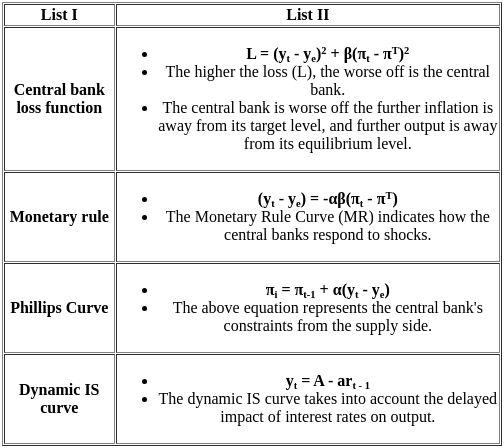
Hence, the correct matching is A - IV, B - III, C - II, and D - I.
Q35: Which of following is a correct measure of gross fiscal deficit of the state government.
(a) Revenue Expenditure (RE) + Capital disbursement - Revenue Receipts (RR)
(b) RE + Repayment of loans to the Centre - RR
(c) Revenue Deficit + Capital Outlays + Net Lending
(d) RE + Discharge of Internal Debt - RR
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Revenue Deficit + Capital Outlays + Net Lending'.
Fiscal Deficit
- A Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue (excluding borrowings).
- A Fiscal deficit is an indicator of the extent to which the government needs to borrow in order to finance its operations.
- A Fiscal deficit is expressed as a percentage of the country's gross domestic product (GDP).
Fiscal deficit formula
- Fiscal deficit = Total expenditure - Total receipts (excluding borrowings)
Thus, 'Revenue Deficit + Capital Outlays + Net Lending' is the correct measure of the gross fiscal deficit of the state government.
Other Related Points
Concepts of deficit
- Capital deficit = Capital expenditure - Capital receipts
- Budget deficit = Capital deficit + Revenue deficit
- Primary deficit = Fiscal deficit - Net interest payment
Q36: Which of the following holds for Bertrand's Duopoly model.
A. The reaction curves are derived from isoprofit maps which are convex to the axes.
B. The point of intersection of the two reaction curves reflects a stable equilibrium.
C. The reaction curves are derived from isoprofit maps which are concave to the axes.
D. The point of intersection of the two reaction curves reflects an unstable equilibrium.
E. Firm's behavioral pattern is such that they learn from past experience.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) C and D only
(c) A, D and E only
(d) B, C and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A and B only
- Bertrand's Duopoly model was developed in 1883. His model differs from Cournot's in that he assumes each firm expects that the rival will keep its price constant, irrespective of its own decision about pricing.
- The model may be presented with the analytical tools of the reaction functions of the duopolists.
- In Bertrand's model the reaction curves are derived from isoprofit maps which are convex to the axes, on which we now measure the prices of the duopolists.
Other Related Points
The Bertrand model has the following characteristics:
- It is a single-period model.
- It describes the behavior of firms in an oligopoly.
- It is a static model.
Q37: In the national income identity Y = C + I + G, investment (I) is a function of.
(a) Real Income
(b) Nominal Income
(c) Real Interest Rate
(d) Nominal Interest Rate
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3) Real Interest Rate.
Real Income This statement is incorrect.
- Investment (I) is not directly a function of real income in the national income identity.
Nominal Income This statement is incorrect.
- Investment (I) does not directly depend on nominal income.
Real Interest Rate This statement is correct.
- The real interest rate affects the cost of borrowing and thus influences investment decisions.
Nominal Interest Rate This statement is incorrect.
- Investment (I) is influenced by the real interest rate, not the nominal interest rate, as the real rate reflects the true cost of borrowing after adjusting for inflation.
Other Related Points
The real interest rate is crucial for investment decisions.
- It represents the actual cost of funds and influences businesses' and individuals' decisions to invest in new projects and equipment.
Q38: Integrate: 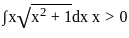
(a) 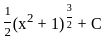
(b) 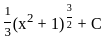
(c) 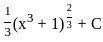
(d) 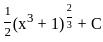
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is
The integral 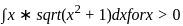 can be solved using a simple substituion:
can be solved using a simple substituion:
Where, 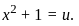 Then,
Then, 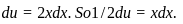
We can substitute these into our integral, we get: 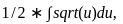
This integral is fairly straightforward, yielding:
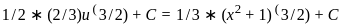
So, the correct answer is: 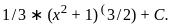
Q39: The components of services sector in Gross Value Added (GVA) are
A. Construction
B. Trade, Hotels, Transport and Communication related to Broadcasting
C. Electricity, Gas, Water supply and other utility services
D. Public Administration, Defense and other services
E. Financial, Real Estate and Professional services
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) B, D and E only
(b) A, B and C only
(c) A, B, D and E only
(d) A, B, C and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is B, D, and E only.
Meaning of Gross Value Added (GVA)
The services sector, also called the tertiary sector, is generally composed of:
- Trade, Hotels, Transport, and Communication related to Broadcasting: This includes all services related to the retail and wholesale of goods, the accommodation and food service activities, the transport of goods and individuals, and the transmission of information through telecommunications.
Public Administration, Defense, and Other Services: This includes all services provided through governmental activities including general administration (like legislative and financial affairs), public order, safety and defense, environmental protection, economic affairs, community amenities, and social protection services.
Financial, Real Estate, and Professional Services: This segment includes financial intermediation and insurance services, activities related to real estate, and professional activities such as legal, accounting, management consultancy, architectural, engineering, and other technical activities.
- The Construction and Electricity, Gas, Water supply, and other utility services, while considered part of the overall economy, are not generally classified as services or within the tertiary sector. They belong to the secondary or industrial sector.
So the correct components of the services sector in Gross Value Added (GVA) are:
- B. Trade, Hotels, Transport, and Communication related to Broadcasting
- D. Public Administration, Defense, and other services
- E. Financial, Real Estate and Professional services
Q40: Given the income multiplier formula m = 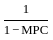 , lower the marginal propensity to save.
, lower the marginal propensity to save.
(a) Higher will be the multiplier effect
(b) Lower will be the multiplier effect
(c) Multiplier will become infinite
(d) Multiplier will become zero
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Higher will be the multiplier effect.
- Marginal propensity to consume (MPC) measures how much more individuals will spend for every additional dollar of income.
- MPC is calculated as the ratio of marginal consumption to marginal income.
- MPC is related to the so-called Keynesian multiplier, where MPC can help predict the economic growth from a government stimulus.
- The multiplier effect refers to a chain reaction of consumption by various entities brought about by an initial increase in income.
- MPC of one means a person spent all additional income.
- MPC of zero means spent none of it and, instead, invested it.
Q41: A foreign exchange swap is
(a) a spot purchase of a currency combined with a forward repurchase of that currency.
(b) a spot sale of a currency combined with a forward repurchase of that currency.
(c) sale and purchase of a currency in forward market.
(d) purchase of a currency in spot market.
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is a spot purchase of a currency combined with a forward repurchase of that currency.
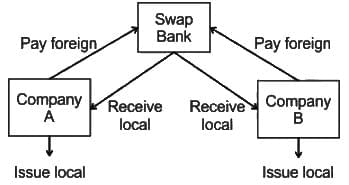
- Foreign exchange swap refers to currently buying one currency and selling currency while forward re-selling the bought currency and buying another currency. That is to say, a swap transaction is composed of a spot and a forward deal.
- Currency Swaps agreements involve trade in local currencies, where countries pay for imports and exports at pre-determined rates of exchange without the involvement of a third country currency like the US dollar.
Q42: Arrange the following chronologically in order of their publication starting from the oldest:
A. General Theory of Employment. Interest and Money
B. A Treatise on probability
C. Essays in Persuasion
D. The End of Laissez Faire
E. A Tract on Monetary Reform
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) B, C, D, A, E
(b) B, E, D, C, A
(c) E, B, D, C, A
(d) D, E, B, A, C
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is B, E, D, C, A.
A Treatise on Probability (1921)
- The book 'A Treatise on Probability' was published by John Maynard Keynes in the year 1921.
- The Treatise attacked the classical theory of probability and proposed a "logical-relationist" theory instead.
- The Treatise is fundamentally philosophical in nature despite extensive mathematical formulations.
- The Treatise presented an approach to probability that was more subject to variation with evidence than the highly quantified complex classical versions.
A Tract on Monetary Reform (1923)
- 'A Tract on Monetary Reform' is a book by John Maynard Keynes, published in the year 1923.
- Through this book, Keynes presented an argument in favour of a policy that would work to stabilize the domestic price level.
- Keynes advocated that domestic price stability was accompanied by exchange rate flexibility.
- After years of experience, he did not favour floating exchange rates and proposed the crawling peg exchange rate system.
The End of Laissez-Faire (1926)
- The book 'The End of Laissez-Faire' was published by John Maynard Keynes in the year 1926.
- The book presents a brief historical review of laissez-faire economic policy.
- Though Keynes agrees in principle that a marketplace of free individuals pursuing their self-interest without government intervention has a better chance of improving society's economic situation than socialist alternatives, he suggests that government can play a significant role in protecting individuals from the ill effects of business cycles prevalent in capitalist societies.
The Essays in Persuasion (1931)
- 'The Essays in Persuasion' was published by John Maynard Keynes in the year 1931.
- The book constitutes a relevant attempt to find a solution to the most pressing problems of the post-World War I period.
- For this reason, its importance goes well beyond the sphere of economics for reaching out to the realms of history, politics and international relations.
General Theory of Employment. Interest and Money (1936)
- The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money is a book by John Maynard Keynes published in February 1936.
- The book brought a profound shift in economic thought, giving macroeconomics a central place in economic theory.
- The central argument of The General Theory is that the level of employment is determined not by the price of labour, but by the level of aggregate demand.
Thus, A Treatise on Probability (1921), A Tract on Monetary Reform (1923), The End of Laissez-Faire (1926), The Essays in Persuasion (1931), and General Theory of Employment. Interest and Money (1936) is in the correct chronological order.
Q43: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(c) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
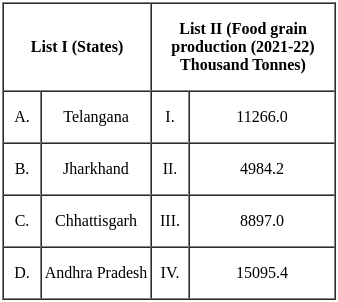
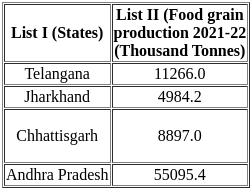
Total food grain production in India is estimated at a record (2021-22) 330.5 million tonnes.
Uttar Pradesh ranks first in the total food grain production of the country.
Other Related Points
India's Top Wheat Producers
During the same period, the leading wheat-producing states in India were:
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Punjab
These three states account for approximately 64% of India's wheat production.
Uttar Pradesh is the largest contributor, producing 32.42% of the nation's total output, followed by Madhya Pradesh and Punjab, which contribute 16.08% and 15.65% respectively.
India's Top Food Grain Producers
- The leading food grain-producing states in India during 2021-22.
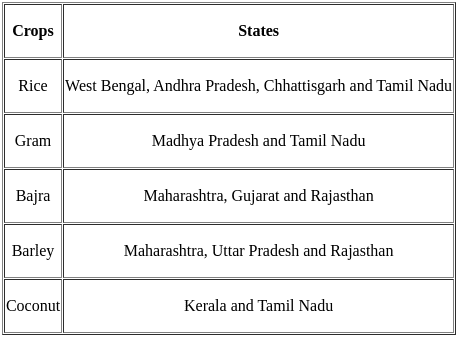
Q44: The Intensive Agriculture District Programme (IADP) was launched in the year
(a) 1960-61
(b) 1961-62
(c) 1962-63
(d) 1963-64
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 1960-61.
Intensive Agriculture District Programme (IADP)
- The Intensive Agriculture District Programme, popularly known as package programme was launched in India during the kharif season in 1960.
- The central idea behind the launch of IADP was that increased agricultural productivity would lead to economic growth, which would ensure the welfare of the society.
- The method adopted in IADP was to demonstrate the feasibility of increased agricultural production rapidly by concentrating on all factors of production at the same time in an integrated action programme in selected districts fulfilling optimum conditions.
- The programme was known as a package programme because of the collective and simultaneous application of all improved practices namely improved seeds, irrigation, fertilizer, plant protection, implements, storage facilities, marketing and credit facilities etc.
- Initially, 7 districts were covered under the programme namely Thanjavur (Tamil Nadu), West Godavari (Andhra Pradesh), Sahabad (Bihar), Raipur (Madhya Pradesh), Aligarh (Uttar Pradesh), Ludhiana (Punjab), and Pali (Rajasthan).
- The selection of districts was done on the basis of their high potential for increasing the agricultural yield in a shorter time.
- These selected districts had assured water supply for irrigation, well-developed cooperatives, good physical infrastructure and minimum hazards.
Objectives of IADP
- To achieve rapid increase in agricultural production through concentration of financial, technical, and administrative resources.
- To achieve a self-generating breakthrough in productivity and to raise the production potential by stimulating the human and physical process of change.
- To demonstrate the most effective ways of increasing production and thus, to provide lessons for promoting such intensive agricultural production programmes to other areas.
Thus, The Intensive Agriculture District Programme (IADP) was launched in the year 1960-61.
Q45: Arrange the following events of equity trading in India starting from the oldest :
A. The BSE introduced screen-based trading.
B. Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) are permitted to invest in the Indian Securities Market.
C. NSE commenced operations in wholesale debt market segment.
D. The SEBI banned badla trading on the BSE.
E. The NSE overtook the BSE as the largest stock exchange in terms of volume trading.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B, D, E, C
(b) B, D, C, E, A
(c) D, B, E, C, A
(d) C, B, D, E, A
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is B, D, C, E, A.
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) are permitted to invest in the Indian Securities Market - Year 1992
- A Foreign Institutional Investor (FII) is an institution established or incorporated outside India that proposes to make investments in the Indian securities market.
- Effective September 14, 1992, foreign institutional investors (FIIs) were permitted to invest in any of the listed companies of Indian stock exchanges subjected to the condition that aggregate holding of share/convertible debentures of the FIIs/NRIs/OCBs put together should not exceed 24 percent of paid-up capital of the Indian company.
The SEBI banned badla trading on the BSE - March 1994
- In December 1993, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) banned badla (the ban took full effect in March 1994).
- The result was a sharp decline in liquidity with adverse impacts on market efficiency and volatility.
NSE commenced operations in the wholesale debt market segment - Year 1994
- The Wholesale Debt Market (WDM) segment of the exchange commenced operations on June 30, 1994.
- This facilitated the first formal screen-based trading facility for the debt market in the country.
- The wholesale debt market segment has now been merged under the New Debt Market as the Negotiated Trade Reporting Platform.
The NSE overtook the BSE as the largest stock exchange in terms of volume trading - Year 1995
- NSE has invested heavily in technology and has a more advanced trading platform compared to BSE.
- This has made it more convenient and efficient for traders to buy and sell securities on NSE, leading to higher trading volumes.
The BSE introduced screen-based trading - Year 1995
- The online trading system of Bombay Stock Exchange known as BOLT was introduced in the year 1995.
- BOLT is a screen-based automated trading platform that is referred to as a centralized exchange-based trading system of BSE.
- BOLT helps investors to trade from anywhere in the world on the BSE trading platform.
Thus, B, D, C, E, and A is the correct order of events of equity trading in India.
Q46: Give below are two statements:
Statement - I: Division of labour is the starting point of Smith's theory of economic growth.
Statement - II: It is division of labour that results in the greatest improvement in the productive power of labour.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statements I and Statement II are true.
Statement I: Division of labour is the starting point of Smith's theory of economic growth is true because,-
- Adam Smith, in his seminal work "The Wealth of Nations," emphasized the importance of the division of labour as the cornerstone of economic growth.
- He argued that the division of labour increases productivity and efficiency by allowing workers to specialize in specific tasks.
- This specialization leads to greater skill development, time savings, and the invention of new methods and tools.
- Smith illustrated this concept using the example of a pin factory, where dividing the production process into distinct tasks significantly increased output.
- The division of labour facilitates economies of scale, enabling industries to produce goods more cheaply and efficiently.
Statement II: It is division of labour that results in the greatest improvement in the productive power of labour is also true.
- Adam Smith asserted that the division of labour is the primary driver of enhanced productivity and economic prosperity.
- He believed that when workers focus on a single task, they become more skilled and efficient at that task.
- This increased proficiency leads to higher output and quality of products.
- The division of labour also fosters innovation, as workers constantly seek better ways to perform their specialized tasks.
- Smith's theory posits that as productivity increases, it fuels economic growth by creating more goods and services for consumption and trade.
Other Related Points
- Adam Smith's theory of economic growth is fundamentally linked to the concept of the division of labour.
- His ideas laid the groundwork for modern economic thought and the development of industrial economies.
- The division of labour not only enhances productivity but also contributes to the overall wealth of a nation by creating more efficient production systems.
- Smith's insights remain relevant in contemporary economics, highlighting the enduring impact of specialization and productivity on economic growth.
Q47: The concept of "excess sensitivity" and "excess smoothness" are explained by following statement(s).
A. 'Excess sensitivity' refers to a situation where consumption over responds to temporary income shocks.
B. 'Excess smoothness' refers to a situation where consumption under responds to temporary income changes.
C. With excess sensitivity, anticipated rise in income is associated with relatively small change in consumption.
D. With excess smoothness, changes in aggregate income are associated with relatively large changes in aggregate consumption.
E. 'Excess sensitivity' and 'Excess smoothness' are related to the empirical evidences of permanent income hypothesis.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B, C, D only
(b) A, B, C, E only
(c) A, B, D only
(d) A, B, E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, and E only.
'Excess sensitivity' refers to a situation where consumption over responds to temporary income shocks.
- Excess sensitivity exists when consumption responds too much to predictable or anticipated changes in income.
Thus, the statement is the correct explanation of excess sensitivity.
'Excess smoothness' refers to a situation where consumption under responds to temporary income changes.
- Excess smoothness exists when consumption responds too little to innovations or unpredictable or unanticipated changes in income.
Thus, the statement is the correct explanation of excess smoothness.
'Excess sensitivity' and 'Excess smoothness' are related to the empirical evidences of permanent income hypothesis.
- The permanent income hypothesis suggests that excess sensitivity of changes in consumption to anticipated changes in income implies that consumption will respond less to unanticipated changes (innovations, shocks) in income.
- Excess sensitivity deals with anticipated changes and excess smoothness is due to unanticipated changes.
Thus, this statement is also correct.
On the basis of the above information, it can be concluded that out of the above statements, statements A, B, and E are correct.
Q48: If S is a sample space and E is an event then the probability axioms can be written as
A. 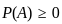
B. P(S) = 1
C. 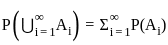
D. P(A) ≤ 0
E. 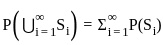
Choose the correct answer from the option given below :
(a) A and B only
(b) A, B and D only
(c) A, B and E only
(d) A, B and C only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A and B only
The probability axioms are fundamental principles that govern the assignment of probabilities to events in a sample in a space.
There are three probability axioms.
Non-negativity - For any event E in the sample space S, the probability of E is always non-negative.
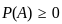
Unit Measure - The probability of the entire sample space S is equal to 1.
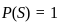
Additivity - For any collection of mutually exclusive events is equal to the sum of their individual probabilities. Mathematically, If  are mutually exclusive events, then
are mutually exclusive events, then 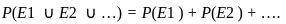
Q49: According to Tobin's Q theory of investment, when should a firm invest?
A. there is increase in the price of output
B. there is an increase in marginal product of capital
C. there is an increase in rate of interest
D. there is a decrease in rate of depreciation
E. marginal benefit of investment exceeds marginal cost
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) B, C, D, E only
(b) A, C, D, E only
(c) A, B, D, E only
(d) A, B, C, D only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, D, E only.
Tobin's Q Theory of Investment (Tobin's Q)
- The Q ratio, also known as Tobin's Q, equals the market value of a company divided by its assets' replacement cost.
- The equilibrium is achieved when market value equals replacement cost
- The Q Ratio expresses the relationship between market valuation and intrinsic value.
- In other words, the theory provides a method of estimating whether a given business firm is overvalued or undervalued.
Important Points
Calculation of Tobin's Q Ratio
- Tobin's Q Ratio = Total Market Value of the Firm ÷ Total Asset Value of the Firm
Tobin's Q ratio and investment decision
According to Tobin's Q theory of investment, a firm should invest when-
- There is an increase in the price of output.
- There is an increase in the marginal product of capital
- There is a decrease in the rate of depreciation
- The marginal benefit of investment exceeds the marginal cost
Thus, according to Tobin's Q theory of investment, a firm should invest when there is an increase in the price of output, there is an increase in the marginal product of capital, there is a decrease in the rate of depreciation, and the marginal benefit of investment exceeds marginal cost.
Q50: Which of the following are not symptoms of multicollinearity in a regression model.
A. High R2 with few significant t ratio for coefficients.
B. High pair-wise correlations among regressors.
C. The closer the Tolerance (TOLj) is to zero.
D. Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) of a variable is below 10.
E. The closer the Tolerance (TOLj) is to 1.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) C and D only
(b) D and E only
(c) A and C only
(d) B and D only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is D and E only.
Multicollinearity
- Multicollinearity, or near-linear dependence, is a statistical phenomenon in which two or more predictor variables in a multiple regression model are highly correlated.
- If there is no linear relationship between predictor variables, they are said to be orthogonal.
Variance Inflation Factor (VIF)
- The Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) measures the severity of multicollinearity in a regression model.
- It is a statistical measure that indicates the increase in the variance of a regression coefficient as a result of collinearity.
Important Points
Variance Inflation Factor, tolerance, and multicollinearity
- VIFi = 1 / 1-Ri2 = 1 / Tolerance
- Where Ri2 represents the unadjusted coefficient of determination for regressing the ith independent variable on the remaining ones.
- The reciprocal of VIF is known as tolerance.
- VIF above 4 or tolerance below 0.25 indicates that multicollinearity exists, and further investigation is needed.
When VIF is higher than 10 or tolerance is lower than 0.1, there is significant multicollinearity that needs to be corrected.
Thus, the variance Inflation Factor (VIF) of a variable of below 10, and, the closer the Tolerance (TOLj) is to 1, are not symptoms of multicollinearity in a regression model.
Q51: In Random walk without drift model,
(a) The effect of shock persists throughout the period of time.
(b) effect of a shock dissipates over time.
(c) effect of a shock immediately disappears.
(d) shocks have no effect is incorrect for a random walk without drift.
Ans: a
Sol: - Correct Answer Explanation:
- In a random walk without drift, the impact of a shock remains throughout the entire duration. This is because in such a model, each new value is a result of the previous value plus a random shock. The accumulation of these shocks over time influences the overall path of the process, meaning the effects of earlier shocks can still be seen in the system's state at later times.
- Incorrect Options Overview:
- Option 2: This option suggests that the effect of a shock dissipates over time. In the context of random walks without drift, this is incorrect because the model inherently includes the accumulation of all previous shocks.
- Option 3: This option claims that the effect of a shock immediately disappears. This is not true for random walks without drift, where each shock's impact is inherently part of the system's subsequent state.
- Option 4: Suggesting that previous shocks have no effect is incorrect for a random walk without drift. The essence of such a random walk is that each step is dependent on the previous step plus a new random shock, implying that past shocks do contribute to the current state.
Q52: Which of the following applies to the physical linkage approach for the valuation of environmental benefits
(a) methods that assess responses immediately related to environmental changes.
(b) methods that examine responses not about the environmental good itself but some set of market conditions related to it.
(c) methods that estimate benefits using observations of behavior in actual markets.
(d) methods that estimate benefits based on a technical relationship between an environmental resource and the user of that resource.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'methods that estimate benefits based on a technical relationship between an environmental resource and the user of that resource'.
Valuation of environmental benefits
- Valuation of environmental benefits helps to correct economic decisions that treat the environment as if it were a free input, in turn resulting in its over-exploitation.
Physical linkage approach
- This approach exhibits a technical (physical) linkage between changes in the state of the environment and changes in a good or service traded in a market (having an observable price).
Methods (techniques) of physical linkage approach
- Replacement cost technique
- Changes in output or input of marketable goods
- Costs of illness and premature mortality
Important Points
Valuation of environmental functions serves two main purposes-
- To illustrate the kinds of economic damages posed to society by resource depletion and pollution.
- To integrate the unpriced, but valuable functions of natural environments into policy appraisal, e.g. Cost Benefit Analysis, Polluter Pays Principle.
Thus, 'Methods that estimate benefits based on a technical relationship between an environmental resource and the user of that resource' applies to the physical linkage approach for the valuation of environmental benefits.
Q53: Match List I with List II
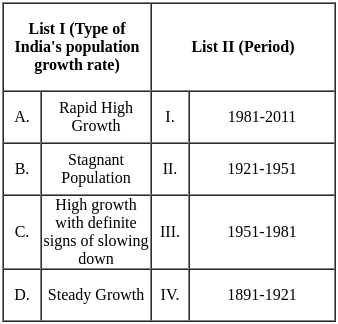
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II.
Hence, the correct matching is A - III, B - IV, C - I, and D - II.
Q54: Given below are the alternative formulae for F-test statistics. We are interested in testing the statistical significance of the incremental contribution of X3 at 5% level of significance to Y = β0 + β1X1 + β2X2 + U. Which of these is not appropriate? Where RSS is residual sum of square and ESS is explained sum of square.
(a) 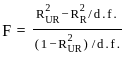
(b) 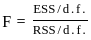
(c) 
(d) 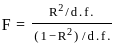
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 
The F-test statistic for testing the incremental contribution of a variable in a multiple regression model is given by:
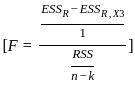
Where:
- (ESSR) is the explained sum of squares for the full model (with all predictors including X3)
- (ESSR, x3) is the explained sum of squares for the model without X3)
- (RSS) is the residual sum of squares.
- (n) is the number of observations.
- (K) is the number of predictors in the full model.
The inappropriate formula could be one that doesn't appropriately subtract the contribution of (X3)
Formula should compare the full model with (X3) to the model without (X3).
So, the inappropriate one might not appropriately subtract (ESSR, x3) or could use a different denominator. Double-check the formulas you have, and make sure the subtraction of (ESSR, x3) is done correctly.
Q55: Arrange the relative weights in percentage assigned to following criteria by the XIV finance commission in ascending order.
A. Income distance
B. Area
C. Population (1971)
D. Demographic Change (2011 population)
E. Forest Cover
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) B, E, D, C, A
(b) E, D, B, C, A
(c) A, C, D, B, E
(d) E, B, D, C, A
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'E, D, B, C, A'.
Horizontal Devolution
- The Fourteenth Finance Commission proposed a new horizontal formula for the distribution of the states’ share in the divisible pool among the states.
Horizontal devolution formula in the Fourteenth Finance Commission
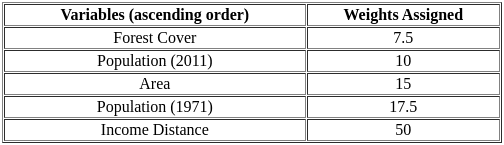
Important Points
About Finance Commission
- The Finance Commission is a constitutional body formulated under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution.
- It is constituted every five years by the President of India to review the state of finances of the Union and the States and suggest measures for maintaining a stable and sustainable fiscal environment.
- The commission also makes recommendations regarding the devolution of taxes between the Center and the States from the divisible pool which includes all central taxes excluding surcharges and cess which the Centre is constitutionally mandated to share with the States.
Thus, the correct ascending order of weights assigned to variables under the fourteenth finance commission is forest cover (7.5), population 2011 (10), area (15), Population 1971 (17.5), and income distance (50).
Q56: Sequence of steps followed in the estimation of Indirect Least Square (ILS) starting from the beginning:
A. Identification of the structural equations
B. Application of OLS
C. Obtaining structural coefficients
D. Obtaining reduced form equation
E. Use the model for policy
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, D, B, C and E
(b) A, B, D, C and E
(c) B, D, A, E and C
(d) B, A, C, D and E
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A, D, B, C and E.
Indirect Least Square Method
- In this method, we obtain the estimates of the reduced form coefficients by applying OLS (Ordinary Least Squares) and indirectly obtain the values of structural coefficients in terms of the reduced form coefficients.
- For this reason, the method is known as the Indirect Least Square.
- This method is normally applied to exactly identified equations.
- The estimates obtained from this technique are called the Indirect Least Squares (ILS) estimates.
Important Points
The sequence of steps for estimation of ILS
- We first obtain the reduced-form equations.
- The reduced-form equations ensure that in each of the equations, the dependent variable is an endogenous variable only and is a function of the predetermined (exogenous or lagged endogenous) variables and the stochastic error term(s).
- Assuming that the other usual assumptions about the disturbance term in the OLS are satisfied, We apply OLS to the reduced-form equations individually.
- This operation is permissible since the explanatory variables in these equations are predetermined and hence uncorrelated with the stochastic disturbances.
- The estimates thus obtained are consistent.
- We obtain estimates of the original structural coefficients from the estimated reduced-form coefficients obtained in Step 2.
- If an equation is exactly identified, there is a one-to-one correspondence between the structural and reduced-form coefficients.
- We can derive unique estimates of the structural parameters from the reduced form parameters. The relationship between reduced form parameters and the structural parameters forms a system of equations in which the reduced form coefficients are expressed as functions of the structural parameters.
Thus, the correct sequence of steps for the estimation of ILS is, the identification of structural equations, obtaining reduced form equation, application of OLS, obtaining structural coefficients, and using the model for policy.
Q57: Properties of sufficient estimators are
A. It may not be unbiased
B. It may be unbiased
C. It is always consistent
D. It is not always consistent
E. Minimum variance unbiased estimator
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) A, B, C and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C, and E only.
Sufficient Estimators
- Sufficient estimators exist when one can reduce the dimensionality of the observed data without loss of information.
- Sufficiency is an important quality in hypothesis testing where we can effectively compare the distribution under the null hypothesis with the actually observed distribution.
- Having a sufficient estimator makes this testing process significantly more manageable, especially for large sample sizes.
Properties of good estimator
Unbiasedness
- An estimator is said to be unbiased if its expected value is identical to the population parameter being estimated.
- That is if θ is an unbiased estimate of θ, then we must have E (θ) = θ.
Consistency
- If an estimator, say θ, approaches the parameter θ closer and closer as the sample size n increases, θ is said to be a consistent estimator of θ.
- In other words, the estimator θ is said is be a consistent estimator of θ if, as n approaches infinity, the probability approaches 1 that θ will differ from the parameter θ by no more than an arbitrary constant.
Efficiency
- The concept of efficiency refers to the sampling variability of an estimator.
- If two competing estimators are both unbiased, the one with the smaller variance (for a given sample size) is said to be relatively more efficient.
Sufficiency
- An estimator is said to be sufficient if it conveys as much information as possible about the parameter that is contained in the sample.
- The significance of sufficiency lies in the fact that if a sufficient estimator exists, it is absolutely unnecessary to consider any other estimator.
Thus, properties of the sufficient estimator are that it may not be unbiased, it may be unbiased, it is always consistent, and, a minimum variance unbiased estimator.
Q58: The Hausman's specification error test is used to test whether
(a) An exogenous variable is correlated with the error term.
(b) An endogenous variable is correlated with the error term.
(c) Both an exogenous variable is correlated with the error term and an endogenous variable is correlated with the error term.
(d) OLS method is appropriate to estimate the SEM.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'An endogenous variable is correlated with the error term'.
Hausman's specification error test
- The Hausman Test (or the Hausman specification test) detects endogenous regressors (predictor variables) in a regression model.
- Endogenous variables have values that are determined on the basis of other variables in the data system.
- Having endogenous regressors in a model will cause ordinary least squares estimators to fail, as one of the assumptions of OLS (Ordinary Least Squares) is that there is no correlation between a predictor variable and the error term.
- Instrumental variables estimators can be used as an alternative in this case.
- However, before you can decide on the best regression method, you first have to check whether predictor variables are endogenous. This is what the Hausman test will do.
Thus, Hausman's specification error test is used to test whether an endogenous variable is correlated with the error term.
Q59: Allocation of budget for Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare in the Union Budget 2023-24 is
(a) 2.25 lakh crores
(b) 1.25 lakh crores
(c) 1.78 lakh crores
(d) 1.68 lakh crores
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 1.25 lakh crores.
Budget allocation
- The Ministry has been allocated Rs 1,25,036 crore for the year 2023-24.
- It is 5% greater than the revised estimates for 2022-23.
- The Ministry of Agriculture accounts for 2.8% of the total Union Budget.
- The increase in expenditure is on account of a marginal increase in the allocation for schemes such as the Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (5%) and the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (10%).
Important Points
Policy Proposals in the Budget Speech (2023-24)
Digital Public Infrastructure
- Digital public infrastructure will be built as an open source, open standard, and interoperable public good.
- This will enable inclusive, farmer-centric solutions through relevant information services for crop planning and health, and improved access to farm inputs, credit, and insurance facilities.
Agriculture Accelerator Fund
- The Fund will be set up to encourage agri-startups by young entrepreneurs in rural areas.
- It aims to bring modern technology with the purpose OF increasing agricultural productivity and profitability.
Agriculture Credit
- The agricultural credit target will be increased to Rs 20 lakh crore with a focus on animal husbandry, dairy, and fisheries.
PM Matsya Sampada Yojana
- A new scheme with a targeted investment of Rs 6,000 crore has been launched to promote the activities of fishermen and fish vendors and improve value chain efficiencies.
Storage
- A plan will be implemented to set up decentralized storage capacity to help farmers store their produce and realize remunerative prices through the sale at appropriate times.
Cooperatives
- The government will also facilitate the setting up of multipurpose cooperative societies, primary fishery societies, and dairy cooperative societies in uncovered panchayats and villages in the time period of the next five years.
Thus, the allocation of the budget for the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare in the Union Budget 2023-24 is Rs. 1.25 lakh crores.
Q60: Match List I with List II
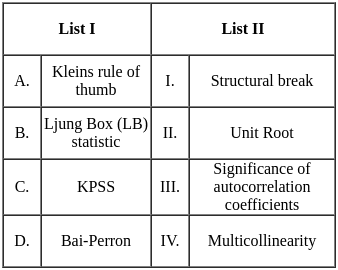
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(c) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Explanation
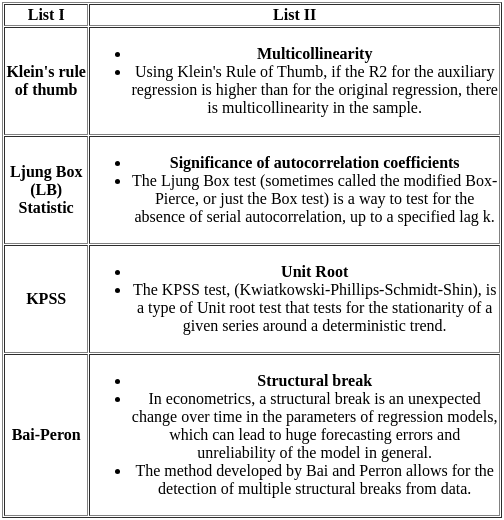
Thus, the correct matching is A - IV, B - III, C - II, and D - I.
Q61: Adam Smith contributions are
A. Division of labour
B. Notion of increasing returns
C. Notion of diminishing returns
D. Dialectical Materialism
E. Socially necessary abstract labour time
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) A and C only
(c) A and D only
(d) A and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A and B only.
Division of labour
- In Adam Smith's book 'An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (1776)' he foresaw the essence of industrialism by determining that the division of labour represents a substantial increase in productivity.
- Adam Smith famously argued that the difference between a street porter and a philosopher was as much a consequence of the division of labour as its cause.
- According to Adam Smith, the division of labour was the dynamic engine of economic progress.,
The notion of increasing returns
- According to Adam Smith, the division of labour is an important source of increasing returns.
Important Points
- The notion of diminishing returns originated in the work of the 18th-century French physiocrat Anne Robert Jacques Turgot.
- Dialectical materialism is a materialist theory based on the writings of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels
- The concept of socially necessary abstract labour time was introduced by Karl Marx.
Thus, Adam Smith's contributions include division of labour and the notion of increasing returns.
Q62: Gunnar Myrdal is author of
A. Asian Drama
B. An American Dilemma
C. Theory of Economic Development
D. Principles of Political Economy
E. Economic Theory and underdeveloped regions
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C and D only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, and E only.
Asian Drama
- Gunnar Myrdal published the book Asian Drama in 1968, which made significant analytical contributions to our understanding of development but was deeply pessimistic about Asia’s future prospects.
- In the book, the fundamental point of departure from conventional thinking was the conviction that ‘economic problems cannot be studied in isolation but only in their own demographic, social and political setting’
An American Dilemma
- 'An American Dilemma: The Negro Problem and Modern Democracy' is a 1944 study of race relations authored by economist Gunnar Myrdal.
- Myrdal observed a vicious cycle in which whites oppressed blacks, leading to poor standards of education, healthcare, morality, etc. among blacks that was then used as justification for prejudice and discrimination.
- Myrdal argued that the way out of this cycle was to either reduce white prejudice, which would improve the circumstances of blacks, or to improve the circumstances of blacks, which would then reduce the reasons for white prejudice.
- Myrdal called this process the "principle of accumulation".
Economic Theory and Underdeveloped Regions
- The book 'Economic Theory and Underdeveloped Regions' was published in the year 1957.
- The book discusses economic, social, and political problems facing underdeveloped countries with an emphasis on economic inequalities between developed and under-developed countries.
Thus, Gunnar Myrdal is the author of the books Asian Drama, An American Dilemma, and Economic Theory and Underdeveloped Regions.
Other Related Points
- The book 'Theory of Economic Development' was written by Joseph Schumpeter in the year 1911.
- The book 'Principles of Political Economy' was written by John Stuart Mill in the year 1848.
Q63: As per the total revenue received by the government under the head of GST on the domestic supply of goods and services for 2021-22. arrange the following states in ascending order:
A. Odisha
B. Rajasthan
C. Delhi
D. West Bengal
E. Madhya Pradesh
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) D, C, E, B, A
(b) E, B, A, C, D
(c) B, E, C, A, D
(d) C, E, A, D, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is E, B, A, C, and D.
Total revenue received by the government under the head of Goods and Services Tax (GST) on the domestic supply of goods and services for the year 2021-22 (Arranged in ascending order)
Thus, the correct ascending order of total revenue received by the state government under the head of GST on the domestic supply of goods and services for 2021-22 is: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Odisha, Delhi, and West Bengal.
Q64: According to Sample Registration System, which of the following Indian States has the highest level of life time risk during 2018-2020.
(a) Bihar
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Madhya Pradesh
(d) Chhattisgarh
Ans: a
Sol: - Bihar has the highest level of lifetime risk during 2018-2020 according to the Sample Registration System.
- Reason: Bihar, with its large population and challenges in healthcare infrastructure, often reports higher maternal and child mortality rates compared to other states. These factors contribute to its higher lifetime risk assessment.
- Uttar Pradesh
- Although Uttar Pradesh also faces significant healthcare challenges and has a large population, it did not top the list for the highest level of lifetime risk during this period. However, it remains one of the states with considerable health risks.
- Madhya Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh, known for its socio-economic challenges, does face health-related risks. Nonetheless, during the specified timeframe, it did not have the highest level of lifetime risk compared to Bihar.
- Chhattisgarh
- Chhattisgarh, while grappling with various healthcare issues, particularly in rural and tribal areas, did not have the highest lifetime risk level for the period in question. Its challenges include accessibility to healthcare facilities and quality healthcare services.
- The Sample Registration System (SRS) is a demographic survey for providing reliable annual estimates of birth rate, death rate, and other fertility and mortality indicators at the state and national levels. The data indicating Bihar as having the highest level of lifetime risk reflects broader issues of healthcare access, quality, and socio-economic factors affecting the state's population.
Q65: Prevention of Money Laundering Act was enacted in the year
(a) 2001
(b) 2002
(c) 2003
(d) 2004
Ans: b
Sol: - Correct Answer: 2002
The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) was indeed enacted in the year 2002. This legislation represents India's primary framework for combating money laundering, aiming to prevent and control money laundering activities, and to provide for the confiscation of property derived from, or involved in, money laundering.
Overview of Incorrect Options:
- 2001: This year is incorrect because the act had not been enacted yet. The early 2000s were a period when many countries were beginning to strengthen their financial systems against money laundering, and India's PMLA came into effect slightly later.
- 2003: This year is incorrect as the act was already in effect by this time. In 2003, the focus would have been more on the implementation and enforcement of the act rather than its enactment.
- 2004: By 2004, the act had been in effect for approximately two years. This year saw further developments in the regulatory framework surrounding financial transactions and anti-money laundering measures, but the PMLA was already part of Indian law by then.
Additional Notes:
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002, was a significant step for India in aligning with global efforts to combat financial crimes. The act sets the legal framework for the investigation of financial crimes and the imposition of penalties on individuals and entities involved in money laundering.
- The act also established the need for financial institutions to keep records of transactions, report suspicious activities, and apply due diligence procedures in their operations to prevent and detect money laundering activities.
Q66: Which of the following is/are true about paradox of thrift?
A. Paradox of thrift was popularized by J. M. Keynes.
B. It states that personal savings can be detrimental to overall economic growth.
C. It shows the relationship between output growth and rate of unemployment.
D. It shows the relationship between inflation and rate of interest.
E. It states that individuals saving during an economic recession leads to fall in aggregate demand.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) A, B, E only
Ans: d
Sol:
- Statement A: Paradox of thrift was popularized by J. M. Keynes.
- This statement is correct. The paradox of thrift is a concept that was indeed popularized by John Maynard Keynes, an influential British economist. The idea is part of Keynesian economics, which emphasizes the role demand plays in the economy, including the potentially negative effects of increased savings.
- Statement B: It states that personal savings can be detrimental to overall economic growth.
- This statement is correct. The paradox of thrift suggests that while saving is typically seen as a personal virtue and beneficial to an individual, if everyone increases their savings simultaneously, it can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand. This reduction in demand can then lead to a decrease in overall economic growth, making the collective act of saving potentially harmful to the economy.
- Statement C: It shows the relationship between output growth and rate of unemployment.
- This statement is incorrect. The paradox of thrift primarily deals with the relationship between savings and economic growth, not directly with output growth and the rate of unemployment. The relationship between output growth and unemployment is more closely associated with Okun's law, not the paradox of thrift.
- Statement D: It shows the relationship between inflation and rate of interest.
- This statement is incorrect. The paradox of thrift does not deal with the relationship between inflation and the rate of interest. Instead, it focuses on how increased savings can lead to decreased aggregate demand, which might indirectly affect inflation and interest rates, but that is not the core concern of the paradox.
- Statement E: It states that individuals saving during an economic recession leads to a fall in aggregate demand.
- This statement is correct. This is essentially a restatement of the central idea of the paradox of thrift. During an economic recession, if individuals decide to save more to protect themselves against future uncertainties, this behavior can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand, exacerbating the recession.
Hence, the correct option is 4) A, B, E only, as these statements accurately reflect the concepts and implications of the paradox of thrift.
Q67: The Uruguay Round of trade negotiations called for
A. the reduction of average tariffs on industrial goods
B. quotas to be replaced by tariffs
C. the reduction in agriculture export subsidies
D. the reduction in industrial subsidies
E. antidumping and safeguards to be relaxed
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B, C, D only
(b) B, C, D, E only
(c) C, D, E, A only
(d) D, E, A, B only
Ans: a
Sol: - Statement A: the reduction of average tariffs on industrial goods
- This statement is correct. One of the primary objectives of the Uruguay Round was to reduce tariffs and barriers on industrial goods to facilitate easier and more equitable global trade.
- Statement B: quotas to be replaced by tariffs
- This statement is also correct. The Uruguay Round negotiations aimed at converting existing non-tariff barriers such as quotas into tariffs, a process known as tariffication. This made trade more predictable and transparent.
- Statement C: the reduction in agriculture export subsidies
- This statement is correct. A significant outcome of the Uruguay Round was the agreement on Agriculture, which included commitments to reduce export subsidies on agricultural products, aiming to make global agricultural trade fairer and more competitive.
- Statement D: the reduction in industrial subsidies
- This statement is correct. The Uruguay Round addressed the issue of industrial subsidies, with agreements aimed at reducing subsidies that distort trade, thereby promoting fair competition.
- Statement E: antidumping and safeguards to be relaxed
- This statement is incorrect. The Uruguay Round did not call for antidumping and safeguards to be relaxed. Instead, it reinforced the rules on dumping and subsidies, providing a clearer framework for the imposition of antidumping and countervailing duties to protect domestic industries from unfair trade practices.
Solution:
- Statement A is correct because it accurately reflects the Uruguay Round's goal of reducing barriers on industrial goods.
- Statement B is correct as it describes the process of tariffication, which was a key element of the negotiations.
- Statement C is correct, highlighting the efforts to reduce distortive subsidies in agriculture.
- Statement D is correct, addressing the aim to cut back on industrial subsidies that affect trade fairness.
- Statement E is incorrect because the Uruguay Round aimed to strengthen, not relax, measures against unfair trade practices like dumping.
Hence, the correct answer is option 1: A, B, C, D only.
Q68: Which of the following statements are correct about trilemma in monetary policy
A. It is related to closed economy model.
B. It involves exchange rate, capital mobility and monetary policy.
C. It arises because perfect capital mobility aligns the domestic interest rate to the world interest rate.
D. Flexible exchange rate is not compatible with independent monetary policy.
E. It is related to capital immobility and flexible exchange rate.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) B and C only
(b) C and D only
(c) A and D only
(d) B and E only
Ans: a
Sol: - Statement A: It is related to closed economy model.
- This statement is incorrect. The concept of the trilemma in monetary policy pertains to an open economy model, not a closed one. It outlines the challenges and trade-offs that countries face when trying to simultaneously achieve free capital movement, a fixed exchange rate, and an independent monetary policy.
- Statement B: It involves exchange rate, capital mobility, and monetary policy.
- This statement is correct. The trilemma in monetary policy indeed revolves around these three aspects. It suggests that a country can only achieve two out of these three policy goals at any given time. For example, if a country wants to maintain a fixed exchange rate and have free capital mobility, it cannot have an independent monetary policy.
- Statement C: It arises because perfect capital mobility aligns the domestic interest rate to the world interest rate.
- This statement is correct. Perfect capital mobility means that investors can move funds across borders without restrictions, seeking the highest returns. This movement tends to equalize interest rates across countries, as domestic interest rates adjust to align with the world interest rate. This phenomenon is a key aspect of the trilemma, particularly impacting the ability of a country to pursue an independent monetary policy while maintaining fixed exchange rates and free capital mobility.
- Statement D: Flexible exchange rate is not compatible with independent monetary policy.
- This statement is incorrect. In fact, a flexible exchange rate system is one of the conditions that allow for an independent monetary policy under the trilemma. With flexible exchange rates, a country can use its monetary policy tools, such as adjusting interest rates, without having to maintain a fixed exchange rate. This flexibility allows the country to respond to its economic conditions independently.
- Statement E: It is related to capital immobility and flexible exchange rate.
- This statement is incorrect. The trilemma primarily deals with the challenges of achieving capital mobility (not immobility) alongside a flexible exchange rate and an independent monetary policy. The essence of the trilemma is that achieving high levels of capital mobility complicates maintaining a fixed exchange rate and an independent monetary policy simultaneously.
- Hence, the correct answer is option 1: B and C only.
- Statement B is correct as it accurately describes the components involved in the trilemma: exchange rate, capital mobility, and monetary policy.
- Statement C is correct as it explains the effect of perfect capital mobility on domestic interest rates, highlighting a key aspect of the trilemma.
Q69: Which of the following are true in case of Ramsey Rule for efficient taxation-
A. Tax rate should be higher on the good that has lower price elasticity of demand.
B. If the demand elasticity in a market is zero, taxes should be imposed only in that markets.
C. Ramsey rule applies to taxation of goods, but not to taxation of income.
D. Ramsey rule minimises the excess burden of taxation across markets.
E. Ramsey rule does not necessarily result in social justice.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the option given below:
(a) A, C, D and E only
(b) A, B, D and E only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: a
Sol: - Statement A: Tax rate should be higher on the good that has lower price elasticity of demand.
- This statement is correct. According to the Ramsey Rule, in order to minimize the economic distortion or excess burden of taxation, taxes should be levied more heavily on goods or services with inelastic demand. The rationale is that consumers are less sensitive to price changes in these goods, leading to a smaller reduction in quantity demanded and, hence, lower efficiency losses.
- Statement B: If the demand elasticity in a market is zero, taxes should be imposed only in that market.
- This statement is incorrect. While it's true that goods with perfectly inelastic demand (zero elasticity) would theoretically bear taxes with no deadweight loss, in practice, imposing taxes solely based on this criterion could be overly simplistic and ignore other important considerations such as fairness, revenue needs, and administrative feasibility. The Ramsey Rule does not suggest taxing only these markets exclusively.
- Statement C: Ramsey rule applies to taxation of goods, but not to taxation of income.
- This statement is correct. The Ramsey Rule primarily addresses the optimal commodity taxation, focusing on how to levy taxes across different goods and services to minimize welfare loss. It does not directly apply to income taxation, which involves different considerations such as equity, progressivity, and incentives for work and investment.
- Statement D: Ramsey rule minimises the excess burden of taxation across markets.
- This statement is correct. The core objective of the Ramsey Rule is to design a system of taxes that minimizes the excess burden or economic inefficiency associated with taxation. By strategically varying tax rates based on the elasticity of demand, it seeks to reduce the distortions in consumption choices and the resulting welfare loss.
- Statement E: Ramsey rule does not necessarily result in social justice.
- This statement is correct. The Ramsey Rule focuses on efficiency in tax design rather than equity or fairness. It does not take into account the distributional impacts of taxation or the ability-to-pay principle. Therefore, while it aims to reduce the efficiency costs of taxation, it does not necessarily address issues of social justice or ensure a fair distribution of tax burdens.
Hence, the correct option is 1) A, C, D, and E only.
Q70: Which of the following are recommendations of the Narasimham Committee, 1991.
A. Deregulation of the interest rate structure.
B. Beed for greater use of information technology.
C. Permitting only private sector banks to access the capital market.
D. Freedom to appoint chief executive and officers of the banks.
E. Capital adequacy norms were implemented in stages.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) A, C and D only
(c) A, D and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: a
Sol:
- Statement A: Deregulation of the interest rate structure: This statement is correct. The Narasimham Committee recommended the deregulation of interest rates to allow the market to determine the rates, thereby promoting efficiency and competition among banks.
- Statement B: Need for greater use of information technology: This statement is correct. The committee emphasized the importance of information technology in improving the efficiency and productivity of the banking sector. It suggested that banks should leverage technology for better customer service and internal operations.
- Statement C: Permitting only private sector banks to access the capital market: This statement is incorrect. The Narasimham Committee did not restrict the access to capital markets exclusively to private sector banks. It recommended that banks, including public sector banks, should be allowed to raise capital from the market to meet their capital adequacy requirements, subject to adherence to regulatory norms.
- Statement D: Freedom to appoint chief executive and officers of the banks: This statement is correct in the context of the committee's recommendations towards liberalization and giving more autonomy to banks. However, it's worth noting that while the committee advocated for operational autonomy, including in the appointment of top executives, it emphasized that such appointments should be made based on merit and within a regulatory framework ensuring accountability.
- Statement E: Capital adequacy norms were implemented in stages: This statement is correct. One of the key recommendations of the Narasimham Committee was the implementation of capital adequacy norms in line with international standards, to be done in stages. This was aimed at ensuring that banks maintain a healthy level of capital to risk-weighted assets ratio, thereby strengthening the banking sector's resilience to financial shocks.
Hence, Statement A (Deregulation of the interest rate structure), Statement B (Need for greater use of information technology), and Statement E (Capital adequacy norms were implemented in stages) are correct.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 1: A, B, and E only.
Q71: Match List I with List II
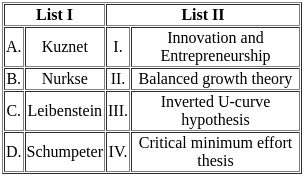
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II
(b) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(d) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
Ans: b
Sol: A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
The task requires matching economists with their respective theories or hypotheses, and explaining each match in detail. Below is the correct matching based on the given options, followed by a comprehensive explanation for each pair:
Match:
- A. Kuznets - III. Inverted U-curve hypothesis
- B. Nurkse - II. Balanced growth theory
- C. Leibenstein - IV. Critical minimum effort thesis
- D. Schumpeter - I. Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- A. Kuznets undefined III. Inverted U-curve hypothesis
- Simon Kuznets: An economist who was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his empirically founded interpretation of economic growth which has led to new and deepened insight into the economic and social structure and process of development.
- Inverted U-curve hypothesis: This hypothesis suggests that in the early stages of economic development, income inequality increases, and then after reaching a certain level of average income, it starts to decrease. This hypothesis was formulated based on the observation of historical data on income inequality and economic development across countries.
- B. Nurkse undefined II. Balanced growth theory
- Ragnar Nurkse: He was an economist who contributed significantly to development economics, particularly in the post-World War II period.
- Balanced growth theory: Nurkse proposed that underdeveloped countries should encourage the simultaneous development of multiple sectors of the economy. The theory advocates for a coordinated approach to investment in a wide range of industries to avoid imbalances and stimulate economic growth through increased demand and production capabilities.
- C. Leibenstein undefined IV. Critical minimum effort thesis
- Harvey Leibenstein: An economist known for his work in development economics and for introducing concepts such as X-efficiency.
- Critical minimum effort thesis: This thesis posits that there is a threshold level of effort or investment needed to kick-start economic development. Below this threshold, investments may not lead to significant improvements in economic outcomes, but once the threshold is crossed, the economy can enter a self-sustaining growth path.
- D. Schumpeter undefined I. Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- Joseph Schumpeter: A prominent economist and political scientist known for his theories on business cycles and economic development.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Schumpeter emphasized the role of the entrepreneur and innovation as the key drivers of economic growth. He argued that economic development is driven by innovative activities, which include the introduction of new products, new methods of production, new markets, and new forms of organization.
Each of these economists contributed significantly to our understanding of economic development, offering unique perspectives on how economies grow and develop. Their theories have been influential in shaping policies and strategies for economic development around the world.
Q72: GDP growth is the most widely used macroeconomic indicator for adjudicating broad economic progress. The outcomes from decisions made on the basis of such an indicator have been repeatedly disappointing because of failures to detect resource uses that turn out to be unsustainable. Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) provides a complementary indicator to help in understanding the changes in wealth and not per capita wealth, by capturing some of the important policy-induced dynamics. Based on the conventions of the System of National Accounts (SNA), ANS is measured as Gross National Saving minus depreciation of produced capital, depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources, and air pollution damages to human health, plus a credit for expenditures on education. If ANS is negative, the county running down its capital stocks and possibly reducing future material well-being. If ANS is positive the country is adding to wealth and future material well-being. When natural resource depletion is not used to invest in other assets in the wealth portfolio, countries gross saving might not be enough to compensate this depletion resulting in negative net savings. However, nations with higher GDP are far les likely to obtain negative ANS. It is argued that, if not a superior indicator of sustainability, ANS is useful to the extent that it can serve a an indicator of unsustainability. Hence, the estimates and conceptualization of ANS are not free from limitations.
Which of the following is not the constituent of ANS?
(a) Public expenditures on education
(b) Air pollution damage
(c) Depletion of metals and minerals
(d) Loss of biodiversity
Ans: d
Sol: - Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth is a widely used indicator to measure the economic progress of a country. However, it has limitations, especially in identifying unsustainable resource use.
- Adjusted Net Savings (ANS) serves as a complementary indicator to GDP growth by capturing changes in a country's wealth, including environmental degradation and investment in human capital.
- Components of ANS according to the System of National Accounts (SNA) include:
- Gross National Saving
- Depreciation of produced capital
- Depletion of subsoil assets and timber resources
- Air pollution damages to human health
- Credit for expenditures on education
Key Points
about ANS:
- A negative ANS indicates that a country is depleting its capital stocks, which could lead to reduced future material well-being.
- A positive ANS suggests that a country is adding to its wealth, enhancing future material well-being.
- Failure to reinvest natural resource depletion into other wealth assets could lead to negative net savings.
- Higher GDP countries are less likely to have negative ANS, but this does not guarantee sustainability.
- Limitations of ANS:
- The calculation and conceptualization of ANS have limitations and are subject to debate.
- ANS is argued to be an indicator of unsustainability rather than a definitive measure of sustainability.
- Regarding the Question:
- Option 1: Public expenditures on education is actually included in the ANS calculation as a credit, indicating it is considered an investment in human capital.
- Option 2: Air pollution damage is subtracted in the ANS calculation to account for environmental degradation.
- Option 3: Depletion of metals and minerals is considered in ANS to reflect the depletion of natural resources.
- Option 4: Loss of biodiversity is not explicitly mentioned in the ANS calculation as provided in the question's context.
- Conclusion:
Since all options except Option 4 (Loss of biodiversity) are mentioned as constituents of ANS in the provided context, Option 4 is the correct answer as it is not listed as a constituent of ANS.
Hence, Option 4 (Loss of biodiversity) is the correct answer.
Q73: Which of the following is not true in the case of second theorem of welfare economics?
(a) If consumers exhibit convex preferences, every pareto efficient allocation is a possible competitive equilibrium in a pure exchange economy.
(b) In an economy involving production, the convexity of production sets ensures that a pareto efficient allocation can be achieved as a market equilibrium.
(c) It holds when there are increasing returns to scale.
(d) It implies that in the market system, the allocative role and the distributive role can be separated from each other.
Ans: c
Sol: - Correct Statement: It holds when there are increasing returns to scale.
- The Second Theorem of Welfare Economics states that under certain conditions (such as perfect competition, no externalities, and convex preferences and production sets), every Pareto efficient allocation can be achieved by a competitive equilibrium from some initial allocation of resources. This theorem is foundational in suggesting that the market can reach efficient outcomes through the price mechanism, given an appropriate redistribution of initial endowments.
Overview of Other Options:
- Option 1: If consumers exhibit convex preferences, every pareto efficient allocation is a possible competitive equilibrium in a pure exchange economy. This statement is true because convex preferences ensure that individuals' marginal rates of substitution between any two goods are diminishing. This condition is essential for the existence of a competitive equilibrium that is also Pareto efficient.
- Option 2: In an economy involving production, the convexity of production sets ensures that a pareto efficient allocation can be achieved as a market equilibrium. This is accurate because convex production sets imply that firms face increasing marginal costs. Under perfect competition, this allows for the possibility of achieving a Pareto efficient allocation through market mechanisms.
- Option 4: It implies that in the market system, the allocative role and the distributive role can be separated from each other. This statement is correct and one of the key insights of the Second Theorem of Welfare Economics. It suggests that the market can allocate resources efficiently (allocative role), while society can achieve any desired distribution of income through appropriate redistribution of initial endowments (distributive role), without affecting the efficiency of the market outcome.
Why the Correct Statement is Not True:
The assertion that the theorem holds when there are increasing returns to scale is not accurate because increasing returns to scale violate the assumption of convexity required by the Second Theorem of Welfare Economics. Convexity implies that doubling the input will double the output, but increasing returns to scale mean that doubling the input more than doubles the output, leading to non-convex production sets. This non-convexity can result in market failures where competitive equilibria may not be Pareto efficient, or in some cases, a competitive equilibrium might not exist at all. This deviation from the assumptions of the theorem challenges its applicability in scenarios with increasing returns to scale.
Q74: Taylor's Rule tells,
(a) how monetary authority sets interest rate in response to economic activity
(b) how monetary authority maintains bank rate
(c) how monetary authority maintains exchange rate
(d) how government decides the tax rate to increase the tax base.
Ans: a
Sol: - Taylor's Rule is a guideline for how monetary authorities should adjust interest rates in response to changes in economic activity and inflation. It suggests that central banks should raise interest rates when inflation is above the target or when the economy is growing faster than its potential (to cool down the economy), and lower them in the opposite scenarios.
- Incorrect Options:
- Maintains bank rate: While adjusting the interest rate can influence the bank rate, Taylor's Rule specifically focuses on the broader perspective of adjusting interest rates in response to economic conditions rather than just maintaining the bank rate.
- Maintains exchange rate: Taylor's Rule does not directly address exchange rate management. Exchange rates can be influenced by interest rate changes, but the rule itself is about balancing economic activity and inflation, not managing exchange rates.
- Decides the tax rate to increase the tax base: Taylor's Rule is about monetary policy, which is the domain of central banks. Deciding the tax rate to increase the tax base is a matter of fiscal policy, which is determined by the government. These are two distinct areas of economic policy.
Q75: Which one of the following can be an equation representing a money market?
(a) 300 = 2Y - 1.5i
(b) i = 150 - Y
(c) Y = 100 - i
(d) i = (150 - 2Y)/2
Ans: a
Sol: - Correct Equation Representation: 300 = 2Y - 1.5i
This equation can represent a money market where 300 is a constant figure, possibly representing an initial amount of money, Y could denote the income level, and i could represent the interest rate. The relationship shows that the initial amount is affected by both the income level and the interest rate, which is a plausible scenario in a money market context.
Incorrect Options:
i = 150 - Y: This equation suggests a direct, inverse relationship between the interest rate (i) and income level (Y), without considering a constant amount or other factors directly. While it's plausible in financial contexts, it's less likely to represent a money market's complexities accurately.
Y = 100 - i: Similar to the previous equation, this one inversely relates income level (Y) to the interest rate (i) with a different constant. It simplifies the relationship too much to accurately represent a money market, where many variables typically interact.
i = (150 - 2Y)/2: This equation provides a relationship where the interest rate (i) is half the difference between a constant (150) and twice the income level (Y). While it acknowledges a more complex interaction, it doesn't straightforwardly represent a common scenario in money markets compared to the correct option.
The absence of a fifth option indicates that the provided options were designed to cover a range of possible relationships between key financial variables, with the correct option being the one that most accurately reflects a common scenario in money markets.
Conclusion: The correct equation, 300 = 2Y - 1.5i, is chosen because it encapsulates a scenario where both the income level and the interest rate play significant roles in determining a financial outcome, which is a hallmark of money market equations. The other options, while related to financial contexts, do not as accurately capture the essence of money market transactions or the interplay of variables within them.
Q76: What is the motto of G-20 18th meeting?
(a) One Earth, One Family, One Future
(b) One Earth, One Nature, One Life
(c) One World, One Family, One Life
(d) One Earth, One Nature, One Future
Ans: a
Sol: - Correct Answer: "One Earth, One Family, One Future" is the motto of the G-20 18th meeting. This motto emphasizes the interconnectedness and interdependence of all beings on the planet and underscores a collective vision for a sustainable and inclusive future. It highlights the importance of unity and cooperation among the world's major economies to address global challenges.
- Overview of Incorrect Options:
- "One Earth, One Nature, One Life": While this option also emphasizes the connection between the Earth, its natural environment, and life itself, it is not the official motto of the G-20 18th meeting. It misses the aspect of 'family' and 'future,' which are crucial elements of the actual motto, focusing on global unity and a forward-looking perspective.
- "One World, One Family, One Life": This option replaces 'Earth' with 'World,' subtly shifting the focus from environmental sustainability to a more general notion of global unity. However, it fails to capture the emphasis on the future and the specific environmental focus of the official motto.
- "One Earth, One Nature, One Future": This option includes elements of environmental focus with 'Earth' and 'Nature,' as well as a forward-looking aspect with 'Future.' However, it lacks the 'Family' component, which is integral to the official motto, indicating the importance of global solidarity and cooperation.
- The fourth option is not provided, which aligns with the format given. Therefore, it's not applicable for comparison.
Conclusion: The official motto, "One Earth, One Family, One Future," uniquely captures the essence of global unity, environmental sustainability, and a shared vision for the future, distinguishing it from the other options which miss one or more of these crucial elements.
Q77: According to Robinson the term 'Golden Age' in the context of Harrod-Domar model is used to emphasize
(a) Its mythical nature
(b) Its superiority
(c) Natural growth rate
(d) Warranted growth rate
Ans: a
Sol: - Correct Option: Its mythical nature
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
- The term 'Golden Age' in the context of the Harrod-Domar model is indeed used to emphasize its mythical nature. This refers to the theoretical concept of an ideal state of economic equilibrium and growth where all conditions are perfectly aligned to sustain steady growth without leading to inflation or unemployment. The term suggests that such a perfectly balanced state is more of an ideal or mythical scenario, rather than a practical or commonly achievable condition in real-world economies.
Overview of Incorrect Options:
- Its superiority: This option might seem plausible because the term 'Golden Age' connotes a period of great success or prosperity. However, in the context of the Harrod-Domar model, the emphasis is on the unrealistically perfect conditions required to achieve such a state, rather than on its superiority over other economic states or models.
- Natural growth rate: The natural growth rate refers to the growth rate an economy can achieve based on its resources, technology, and population growth without leading to inflation. While the Harrod-Domar model does discuss growth rates, the term 'Golden Age' specifically does not emphasize the natural growth rate.
- Warranted growth rate: The warranted growth rate is a concept from the Harrod-Domar model that refers to the growth rate at which the planned savings in the economy equal planned investment, leading to steady growth. While this concept is central to understanding the model, the term 'Golden Age' does not specifically emphasize the warranted growth rate but rather the mythical nature of achieving perfect equilibrium in all economic aspects.
In summary, the term 'Golden Age' is used to underscore the theoretical and highly idealized conditions of economic stability and growth posited by the Harrod-Domar model, rather than to highlight any specific growth rate or to suggest superiority over other economic periods or models.
Q78: Based on the NITI Aayog estimate of poverty for the year 2011-12, the states with above 30 percent rural poverty are
A. Manipur
B. Bihar
C. Sikkim
D. Uttar Pradesh
E. Nagaland
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B and D only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) A, B and D only
Ans: d
Sol:
- Statement A (Manipur) is correct: As per the NITI Aayog estimates of poverty for the year 2011-12, Manipur was one of the states with above 30 percent rural poverty. This indicates a significant portion of the rural population in Manipur lived below the poverty line during this period.
- Statement B (Bihar) is correct: Bihar is well-documented for having a high rate of rural poverty. According to the NITI Aayog's estimates for 2011-12, Bihar indeed had a rural poverty rate of above 30 percent, making this statement accurate.
- Statement C (Sikkim) is incorrect: Sikkim, known for its effective governance and various developmental measures, did not have a rural poverty rate above 30 percent according to the NITI Aayog's 2011-12 estimates. Therefore, this statement is incorrect.
- Statement D (Uttar Pradesh) is correct: Uttar Pradesh, being one of the largest states in India, had a significant portion of its rural population living below the poverty line, with rates above 30 percent as per the NITI Aayog's estimates for 2011-12. Thus, this statement is correct.
- Statement E (Nagaland) is not mentioned in the correct option: While Nagaland faces its own set of challenges, it was not listed among the states with above 30 percent rural poverty according to the NITI Aayog's 2011-12 estimates in the context provided, and hence it is not part of the correct answer.
Correct Option: The correct option is 4, which includes Statements A, B, and D only (Manipur, Bihar, and Uttar Pradesh) as the states with above 30 percent rural poverty according to the NITI Aayog estimates for the year 2011-12.
Solution Statement: Hence, the statements about Manipur (A), Bihar (B), and Uttar Pradesh (D) having above 30 percent rural poverty are correct as per the NITI Aayog's estimates for 2011-12, making option 4 the correct answer. Sikkim (C) and Nagaland (E) are not part of the correct option, indicating they were not estimated to have above 30 percent rural poverty for the year 2011-12 according to NITI Aayog's data.
Q79: Which of the following is/are correct about Walrasian demand function?
A. The Walrasian demand function X(P, W) is homogenous of degree zero if 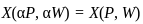 for any P, W and α > 0.
for any P, W and α > 0.
B. The Walrasian demand function X(P, W) is homogenous of degree one if X(αP, αW) = αX(P, W) for any P, W and α > 0.
C. The Walrasian demand function X(P, W) satisfies Walras' law if for every P > > 0 and W > 0, we have P.X = W for all X ∈ X(P, W)
D. Walras' law says consumer fully expends his wealth.
E. If price and wealth both change in same proportion, then individual consumption choice does not change.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B, C, D only
(b) B, C, D, E only
(c) A, B, C, E only
(d) A, C, D, E only
Ans: D
Sol:
- A: Correct, homogeneous of degree zero (scaling prices and wealth leaves demand unchanged).
- C: Correct, satisfies Walras’ law (expenditure equals wealth).
- D: Correct, Walras’ law implies full expenditure of wealth.
- E: Correct, proportional changes in prices and wealth do not alter consumption choices.
- B: Incorrect, as Walrasian demand is not homogeneous of degree one.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 4 (A, C, D, E only), making it the selection of accurate statements regarding the Walrasian demand function.
Q80: Which one of the following is not a characteristic of market structure?
(a) Degree of buyers' concentration
(b) Degree of Sellers' concentration
(c) Conditions of entry
(d) Vertical integration
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Vertical integration
Degree of Buyers' Concentration: Refers to the number and size distribution of buyers in the market.
- Influences buyers' power in affecting prices and market conditions.
- Characteristic of market structure.
Degree of Sellers' Concentration:
- Refers to the number and size distribution of sellers in the market.
- Impacts the level of competition and market power of sellers.
- Characteristic of market structure. Conditions of Entry:
Includes barriers to entry and exit, determining how easily new firms can enter or leave the market.
- Affects the level of competition within the market.
- Characteristic of market structure.
Vertical Integration: Refers to the extent to which a company controls its supply chain, from raw materials to final product delivery.
- Not a primary characteristic of market structure.
Other Related Points
Market Structure: Describes the organizational characteristics of a market that influence competition and pricing.
- Impact of Buyers' Concentration: High concentration can lead to significant buyer power, potentially influencing market prices.
- Impact of Sellers' Concentration: High concentration among sellers can lead to monopolistic or oligopolistic market conditions.
- Barriers to Entry: Can include high startup costs, strict regulations, or strong brand loyalty among consumers.
- Vertical Integration as a Business Strategy: While it influences market dynamics, vertical integration is more about a company's internal structure and strategy rather than a fundamental characteristic of the market itself.
Q81: A tariff ridden offer curve will bend towards,
(a) Import good axis
(b) Export good axis
(c) Origin
(d) Any of the above is possible
Ans: a
Sol: - Correct Answer Explanation: A tariff-ridden offer curve will bend towards the import good axis. This is because a tariff on imports makes imported goods more expensive relative to domestic goods. As a result, the country will tend to import less and may shift towards producing more domestically or seeking alternatives, which is represented graphically by the offer curve bending towards the import good axis. This visual representation helps in understanding the impact of tariffs on trade patterns.
Incorrect Options Overview:
- Export Good Axis: Bending towards the export good axis would suggest a shift in preference or policy that favors exports over imports, which is not the direct effect of imposing a tariff on imports.
- Origin: If the offer curve were to bend towards the origin, it would suggest a decrease in both imports and exports, implying a move towards autarky or self-sufficiency, which is not the typical direct effect of a tariff.
- Any of the Above is Possible: While trade policies can have a variety of impacts on a country's trade patterns, the specific action of imposing a tariff on imports has the direct effect of making imports more expensive and thus bending the offer curve towards the import good axis, rather than any direction being possible.
Q82: Factor price equalization theorem is given by,
(a) David Ricardo
(b) J. S. Mill
(c) Paul Samuelson
(d) Adam Smith
Ans: c
Sol: - Correct Answer: 3) Paul Samuelson
Solution Statement: The Factor Price Equalization Theorem was developed by economist Paul Samuelson in 1948. This theorem is a key concept in international trade theory, proposing that free trade leads to the equalization of factor prices (such as wages and rents) between countries. It suggests that under certain conditions, the prices of factors of production (labor, capital) will equalize across countries as a result of international trade in goods.
Incorrect Options:
1) David Ricardo: Incorrect because David Ricardo is best known for formulating the Comparative Advantage Theory, which explains how countries can benefit from trading with each other even if one country is more efficient in producing all goods.
2) J. S. Mill: John Stuart Mill is incorrect because he is more associated with principles of political economy and theories of utilitarianism rather than the specific concept of factor price equalization.
4) Adam Smith: Incorrect because Adam Smith is famous for his work "The Wealth of Nations," where he discussed the benefits of the division of labor and free markets but did not develop the Factor Price Equalization Theorem.
Q83: Normalized Poverty Gap (NPG) is measured as a ratio of
(a) Average Poverty Gap to poverty line
(b) Total Poverty Gap to poverty line
(c) Total Poverty Gap to total population
(d) Average Poverty Gap to total population
Ans: a
Sol: - Correct Answer Explanation:
Average Poverty Gap to poverty line: This measures the average shortfall of the incomes of people below the poverty line from the poverty line itself, expressed as a ratio of the poverty line. This method helps in understanding the intensity of poverty by showing not just the incidence or headcount of poverty but how far below the poverty line the average poor person is. It provides a more nuanced view of poverty than merely counting the number of poor.
Incorrect Options Explained:
- Total Poverty Gap to poverty line: This option is incorrect because it refers to the aggregate shortfall of all poor people from the poverty line, without normalizing it by the number of poor people to get an average. This measure gives the total extent of poverty in monetary terms but does not provide an average measure that can be easily compared across different populations or time periods.
- Total Poverty Gap to total population: This option incorrectly suggests dividing the total poverty gap by the total population, which would dilute the measure of poverty intensity by including non-poor individuals in the denominator. This approach would not accurately reflect the gap between the incomes of the poor and the poverty line.
- Average Poverty Gap to total population: This option is incorrect because it suggests calculating an average based on the total population, including those not in poverty. This would result in a significantly lower figure that does not accurately represent the gap for those actually below the poverty line, thus underestimating the intensity of poverty among the poor.
Q84: Match List I with List II
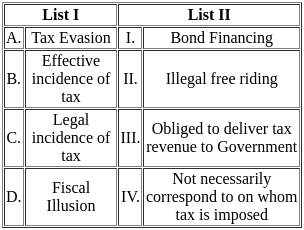
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(b) A-III, B-I, C-II, DIV
(c) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is option 1, which matches the terms in List I with the descriptions in List II as follows:
- A. Tax Evasion with II. Illegal free riding
- B. Effective incidence of tax with III. Obliged to deliver tax revenue to Government
- C. Legal incidence of tax with IV. Not necessarily correspond to on whom tax is imposed
- D. Fiscal Illusion with I. Bond Financing
Let's explain each match in a comprehensive way:
A. Tax Evasion | II. Illegal free riding | Tax evasion refers to the illegal act of not paying taxes that are owed. It's akin to "free riding" on the public services funded by taxes without contributing to them. This is illegal and considered a form of theft from the government. |
B. Effective incidence of tax | III. Obliged to deliver tax revenue to Government | The effective incidence of tax is about who ultimately bears the burden of a tax. It may not always be the person or entity that is legally obliged to pay the tax (legal incidence), but they are the ones effectively paying it as the cost is passed on to them in some form. This description seems slightly off, as "obliged to deliver tax revenue to the Government" aligns more with legal incidence. However, in the context of the given options, it suggests who ends up being responsible for the tax. |
C. Legal incidence of tax | IV. Not necessarily correspond to on whom tax is imposed | The legal incidence of tax refers to who is legally responsible for paying the tax to the government. However, this does not necessarily mean they bear the tax's economic burden, as it can be shifted to others (e.g., a business might pass a tax onto consumers through higher prices). This is a direct match, indicating the difference between legal obligation and economic burden. |
D. Fiscal Illusion | I. Bond Financing | Fiscal illusion is a concept where the true cost of government is obscured from taxpayers, making public spending seem more attractive or less expensive than it really is. Bond financing can contribute to fiscal illusion by spreading out the cost of government spending over time, making it seem less burdensome than paying for it all at once through taxes. This can lead to an underestimation of the true cost of government activities. |
This table explains how each term from List I matches with its corresponding description from List II, providing a comprehensive understanding of each concept.
Q85: Give below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R:
Assertion A: If governments do not care about protectionists' rents, they would replace all import duties with sales taxes.
Reason R: Sales tax is more efficient means of raising revenue than import tariff.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: a
Sol: The assertion (A) posits that if governments do not prioritize the benefits (rents) that protectionists gain from import duties, they would opt to replace all import duties with sales taxes. The reason (R) offered is that sales tax is a more efficient means of raising revenue than import tariffs.
To analyze the relationship between A and R and to validate the correctness of the provided answer (option 1), we need to delve into the economic principles underlying both statements.
- Assertion A Analysis: Import duties or tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods. One of the effects of tariffs is to protect domestic industries by making imported goods more expensive, thus less competitive against local products. This protection can lead to what is known as "protectionists' rents," which are essentially benefits (in the form of increased sales, profits, or market share) that domestic producers gain at the expense of consumers and foreign producers. If a government's primary concern is not to protect these domestic industries (i.e., it does not care about protectionist rents), it might seek a more neutral and broad-based form of taxation that does not distort trade. Sales taxes, which are levied on domestic sales of goods and services, meet this criterion as they do not discriminate between imported and locally produced goods.
- Reason R Analysis: Sales taxes are considered more efficient than tariffs for several reasons. Efficiency in taxation is often measured by how little the tax distorts economic decisions. Sales taxes are broad-based, applying to a wide range of goods and services consumed within the economy, thus spreading the tax burden and minimizing distortions in trade and production choices. In contrast, import tariffs target specific imported goods, distorting trade flows, encouraging inefficiencies in domestic production (as domestic industries are shielded from foreign competition), and often leading to retaliatory tariffs from other countries. Moreover, sales taxes are relatively easier and cheaper to administer compared to tariffs, which require customs infrastructure and monitoring of international trade flows.
- Relation between A and R: The reason (R) directly supports the assertion (A) by explaining why a government that does not prioritize protectionist benefits would prefer sales taxes over import duties. The efficiency of sales taxes, as described in R, provides a rationale for why they would be chosen as a substitute for import tariffs, aligning with the government's disregard for protectionist rents.
Conclusion:
Given the analysis, option 1 is correct: "Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A." Sales tax, by being a more efficient and less distortive means of raising revenue, logically supports the assertion that governments not concerned with protecting specific domestic industries would prefer it over import duties.
Q86: Give below are two statements:
Statement - I: The terms of trade of a nation are defined as the ratio of the cost of its export commodity to the price of its import commodity.
Statement - II: The terms of trade of the trade partner are equal to the inverse of the terms of trade of the other nation.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: a
Sol:
Statement I Analysis:
Statement I defines the terms of trade as the ratio of the cost of a nation's export commodity to the price of its import commodity.
This is a correct definition. The terms of trade measure how much import goods a country can get for a unit of its export goods.
It reflects the relative prices of exports and imports and is a crucial indicator of a country's economic health.
Hence, Statement I is correct.
Statement II Analysis:
Statement II posits that the terms of trade of the trade partner are equal to the inverse of the terms of trade of the other nation.
This statement is logically sound because the terms of trade are essentially a ratio of export to import prices between two countries.
If one country's terms of trade improve (indicating it can buy more imports for a given amount of exports), the terms of trade for its trading partner (in the context of this bilateral trade) necessarily worsen, assuming no changes in other factors, because it now gets fewer exports for its imports from the first country.
This reciprocal relationship can be described as one being the inverse of the other when looking at bilateral trade relationships.
Hence, Statement II is also correct.
Conclusion: After analyzing both statements, it is clear that both Statement I and Statement II are true in the context of international trade and the economic relationship between trade partners.
The correct answer is option 1: Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
Q87: Suppose good 1 is taken on horizontal axis and good 2 on vertical axis, then what happens to the budget line if the price of good 1 double and price of good 2 triples?
(a) The budget line becomes steeper
(b) The budget line becomes flatter
(c) The budget line become vertical
(d) The budget line remains unchanged
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'The budget line becomes flatter'
Budget Line Concept:
- The budget line represents the combinations of two goods that a consumer can purchase given their income and the prices of the goods.
- It is a straight line with a negative slope, where the slope is determined by the ratio of the prices of the two goods.
Impact of Price Changes:
- If the price of good 1 doubles, the consumer can buy less of good 1 with the same income, effectively increasing the relative price of good 1.
- If the price of good 2 triples, the consumer can buy less of good 2 with the same income, effectively increasing the relative price of good 2.
New Slope Calculation:
- Original slope = -P1/P2
- New slope = -(2P1)/(3P2)
- Since the new slope is less steep (closer to zero) than the original slope, the budget line becomes flatter.
Q88: The utility function of a consumer is given by U = f (q1, q2) = q1 ⋅ q2, suppose the price of q1 is Pq1 = 1 and price of q2 is Pq2 = 2. The consumer wants to spend amount of k units only what will be his demand for q1 and q2?
(a) (q1, q2) = (k/2, k/4)
(b) (q1, q2) = (k, k/2)
(c) (q1, q2) = (k/2, k/2)
(d) (q1, q2) = (k/4, k/2)
Ans: c
Sol: To solve this problem, we need to maximize the utility function U = q1 ⋅ q2 subject to the budget constraint.
Given:
- The utility function: U = q1 ⋅ q2
- The price of q1 is Pq1 = 1
- The price of q2 is Pq2 = 2
- The consumer's total budget is k
The budget constraint can be written as:
1 ⋅ q1 + 2 ⋅ q2 = k
q1 + 2q2 = k
To find the demand for q1 and q2, we need to maximize the utility function U = q1 ⋅ q2 subject to the budget constraint.
Using the method of Lagrange multipliers, we set up the following Lagrangian function:
ℒ(q1, q2, λ) = q1 ⋅ q2 + λ (k - q1 - 2q2)
Taking the partial derivatives and setting them to zero:
∂ℒ/∂q1 = q2 - λ = 0
∂ℒ/∂q2 = q1 - 2λ = 0
∂ℒ/∂λ = k - q1 - 2q2 = 0
From the first two equations:
q2 = λ
q1 = 2λ
Substituting q1 and q2 into the budget constraint:
k = q1 + 2q2 = 2λ + 2λ = 4λ
λ = k/4
So:
q1 = 2λ = 2 ⋅ (k/4) = k/2
q2 = λ = k/4
Thus, the demands for q1 and q2 are:
q1 = k/2
q2 = k/4
Therefore, the correct demand for q1 and q2 is:
Option 1) (q1, q2) = (k/2, k/4)
Q89: The idea of creative destruction is associated with
(a) Marx
(b) Adam Smith
(c) Ricardo
(d) Schumpeter
Ans: d
Sol: The concept of creative destruction is actually associated with Joseph Schumpeter, not Marx.
- Schumpeter described it as a process through which old industries or technologies are destroyed and replaced by new ones, fostering innovation and economic development.
- This is a key mechanism in capitalist economies according to Schumpeter.
- Joseph Schumpeter, as the correct association, introduced the term "creative destruction" to describe how capitalist economic development arises out of the destruction of some prior economic order.
- His theory emphasizes the role of innovation and the entrepreneurial spirit in driving economic progress.
Other Related Points
- Karl Marx, on the other hand, focused on the dynamics of capitalist societies, class struggles, and the eventual overthrow of capitalism by the proletariat. While Marx did discuss the disruptive effects of capitalism, the specific concept of creative destruction is not attributed to him.
- Adam Smith is best known for his work "The Wealth of Nations," in which he laid the foundations of classical free market economic theory. He introduced the concept of the invisible hand, arguing that individuals seeking their own benefit actually benefit society as a whole. Smith's work does not directly address the concept of creative destruction.
- David Ricardo is famous for his theory of comparative advantage, suggesting that countries should specialize in the production of goods and services they can produce most efficiently. This theory is a cornerstone of international trade theory but does not directly deal with the concept of creative destruction.
In summary, while the other economists made significant contributions to economic theory, it is Schumpeter who is directly associated with the concept of creative destruction.
Q90: Read the passage below and answer the question:
The government of India's fiscal policy response to the covid crises comprised of a judicious mix of increasing food and fertilizer subsidies on the one hand and a reduction in taxes on fuel and certain imported products on the other. Despite these additional fiscal pressures the union govt. is back on track. The resilience in the fiscal performance of the union government has been facilitated by the recovery in economic activity buoyancy in revenues from direct taxes and goods and services tax (GST) and realistic assumptions in the budget. The gross tax revenue registered a YoY growth of 15.5% from April to November 2022, driven by robust growth in the direct | taxes and GST. The gross GST-collection has increased at 24.8% on YoY during the same period. The Union Government's emphasis on capital expenditure (capex) has continued despite higher revenue expenditure requirements during the year. The center's capex has steadil increased from a long term average of 1.7 percent of GDP (FY09 to FY20) to 2.5% of GDP in FY22 PA. The center has also incentivize the state governments through interest free loans and enhanced borrowing ceilings to prioritize their spending on capex. Government ha boosted allocations on infrastructure intensive sectors such as roads and highways, railways and housing and urban affairs, which has bearing on capex. This increase in capex will have implication for medium term growth and sustainable government debt to GDP ratio.
Which of the following is not correct with respect to facilitation of resilience in fiscal performance of the union government:
(a) Recovery in Economic activity
(b) Buoyant GST revenues
(c) Expenditure austerity measures pertaining to food and fertilizer subsidy
(d) Realistic assumptions in budget
Ans: c
Sol:
The passage details the fiscal policy response of the Indian government to the COVID crisis, highlighting several key measures and outcomes that facilitated the resilience in fiscal performance.
- Recovery in Economic Activity: The passage mentions that the resilience in fiscal performance was facilitated by the recovery in economic activity. This indicates that the economic recovery played a significant role in improving fiscal performance. Hence, this statement is correct.
- Buoyant GST Revenues: It is mentioned that there was buoyancy in revenues from direct taxes and GST, with gross GST collection increasing by 24.8% YoY during the period from April to November 2022. This suggests that buoyant GST revenues contributed positively to the fiscal resilience. Hence, this statement is correct.
- Expenditure Austerity Measures Pertaining to Food and Fertilizer Subsidy: The passage does not mention any austerity measures related to food and fertilizer subsidies. On the contrary, it states that the fiscal policy response included increasing food and fertilizer subsidies. This means there was an increase in spending on these subsidies rather than austerity measures. Hence, this statement is incorrect.
- Realistic Assumptions in Budget: The passage explicitly mentions that the resilience in fiscal performance has been facilitated by realistic assumptions in the budget. This indicates that having realistic budget assumptions played a crucial role in enhancing fiscal performance. Hence, this statement is correct.
- Based on the analysis of the statements in relation to the passage:
- Statement 1 (Recovery in Economic Activity) is correct.
- Statement 2 (Buoyant GST Revenues) is correct.
- Statement 3 (Expenditure Austerity Measures Pertaining to Food and Fertilizer Subsidy) is incorrect.
- Statement 4 (Realistic Assumptions in Budget) is correct.
Conclusion: The statement that is not correct with respect to the facilitation of resilience in the fiscal performance of the union government is "Expenditure austerity measures pertaining to food and fertilizer subsidy."
Hence, Statement 3 is incorrect.
Q91: When MPS is 0.25 and initial increase in autonomous spending is Rs. 100, then the expenditure multiplier and resultant increase in GDP respectively are:
(a) 1, Rs. 100
(b) 0.75, Rs. 75
(c) 4, Rs. 400
(d) 1.33, Rs. 133
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 4, Rs. 400To find the expenditure multiplier, we use the formula:
1. Expenditure Multiplier (K):
The expenditure multiplier represents the change in total output or GDP resulting from a change in autonomous spending. It is calculated using the formula:

Where MPS denotes the marginal propensity to save, which is the fraction of additional income that a household saves rather than spends.
In this case, the MPS is given as 0.25.
We calculate the expenditure multiplier as follows:
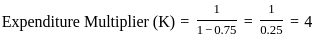
2. Resultant Increase in GDP:
The resultant increase in GDP is determined by multiplying the expenditure multiplier by the initial increase in autonomous spending.
The formula is:

Given that the initial increase in autonomous spending is Rs.100, we calculate the resultant increase in GDP as follows:
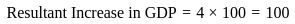
Therefore, the correct resultant increase in GDP is indeed Rs.400.
This thorough explanation helps us understand the process of calculating the expenditure multiplier and the resultant increase in GDP, ensuring clarity and accuracy in our solution.
Other Related PointsUnpacking the expenditure multiplier and why it matters in macroeconomics is a big deal. Some extra info to consider:
- Keynesian Economics: The expenditure multiplier is a big deal in Keynesian economics. As per Keynesian ideas, if aggregate demand shifts, like autonomous spending, it can super-up the overall output or GDP via the multiplier way.
- Components of Aggregate Demand: Autonomous spending means the spending unaffected by income changes, like government spending, investment, and exports for instance. The expenditure multiplier visualizes how changes in autonomous spending ripple through the economy.
- Role of Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS): The size of the expenditure multiplier swings on the marginal propensity to save (MPS). A larger MPS equals a smaller multiplier and the other way around. This happens because a larger MPS implies more funds leaking from the spending flow, which shrinks the multiplier impact.
- Fiscal Policy Implications: The expenditure multiplier is crucial for fiscal policy. For example, during economic slumps, governments might use fiscal stimulus actions, like growing government spending or slicing taxes, to amp up aggregate demand and stir up economic activity. Grasping the multiplier effect helps policymakers gauge the impact of these measures on GDP.
- Multiplier's Limitations: While the expenditure multiplier points out the potential growth of changes in autonomous spending, it rides on many assumptions, such as stationary MPS and the absence of other economic elements. In actuality, the multiplier effect might be muted or boosted by various economic situations, like consumer confidence, interest rates, and international trade.
- The spending multiplier affects the short-term most. Things like fixed costs and wages can make its effects stronger. Over time, the economy could settle into new balance points. This can lessen the reach of the multiplier effect.
Knowing about these other areas gives us a bigger picture. We can better understand what the spending multiplier means and how it fits into macroeconomic studies and policymaking.
Q92: With the same monetary base, which of the following will lead to an increase in broad money?
(a) High transaction cost of converting deposit into cash
(b) Higher investment under SLR
(c) Higher use of cash
(d) Increase in financial literacy and banking habit
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Increase in financial literacy and banking habit'
Increase in financial literacy and banking habit:
- Financial literacy involves understanding financial principles and concepts, enabling individuals to make informed and effective decisions regarding the use of their financial resources.
- Improved financial literacy leads to better saving habits, increased use of banking services, and greater participation in formal financial systems.
- As more people use banking services, the deposits in banks increase, leading to an expansion in broad money (M3), which includes currency in circulation, demand deposits, and other deposits in the banking system.
Additional Information
High transaction cost of converting deposit into cash:
- High transaction costs discourage frequent conversions between deposits and cash.
- This can lead to a preference for holding cash rather than keeping funds in the banking system, thereby not contributing significantly to the increase in broad money.
Higher investment under SLR:
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) refers to the minimum percentage of deposits that a bank must maintain in the form of liquid cash, gold, or other securities.
- Higher SLR investments mean that more bank resources are tied up in government securities, limiting the funds available for other banking operations, which can restrict the growth of broad money.
Higher use of cash:
- An increased preference for cash transactions reduces the amount of money held within the banking system.
- When people prefer using cash over bank deposits, it limits the banking sector's ability to create credit, thereby limiting the growth of broad money.
Q93: In the extreme case of liquidity trap
(a) There will be tendency to buy bonds
(b) Most of the investors will show bearish behavior
(c) Cash will be less preferred
(d) Price of bond will be low.
Ans: b
Sol: - Correct Answer Explanation:
In the extreme case of a liquidity trap, most investors will show bearish behavior.
A liquidity trap occurs when interest rates are low and savings rates are high, rendering monetary policy ineffective. In such a scenario, investors are pessimistic about the future economic outlook, leading to bearish behavior where they are more likely to sell off assets than buy.
Overview of Incorrect Options:
Tendency to buy bonds:
This is incorrect because during a liquidity trap, despite low-interest rates, investors are hesitant to lock in their money in bonds due to fears of not having liquidity when needed or expectations of deflation.
Cash will be less preferred:
This statement is incorrect as, in a liquidity trap, individuals and investors actually prefer holding onto cash rather than investing in securities or making deposits with negative interest rates, due to uncertainties in the market.
Price of bond will be low.:
This is incorrect because, in a liquidity trap, the demand for bonds can actually increase due to their relative safety compared to stocks, which can drive up prices. However, the overall environment is characterized more by a reluctance to lend or invest rather than a straightforward decrease in bond prices.
Q94: Match List I with List II
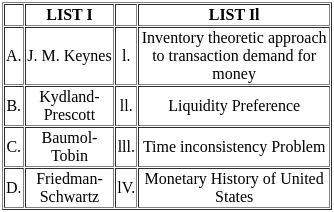
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - III, C - I, D -IV
Ans: d
Sol: To match List I with List II and provide explanations for each match, we have the following correct association: A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV. Here's the comprehensive explanation for each pointer:
A - J.M. Keynes matches with II - Liquidity Preference:
J.M. Keynes is known for his foundational contributions to modern macroeconomics and for developing the theory of Liquidity Preference. This theory suggests that people prefer to hold their wealth in liquid form for three main reasons: transactional motives, precautionary motives, and speculative motives. It's a key component of Keynesian economics, emphasizing the role of demand for money as influenced by interest rates.
B - Kydland-Prescott matches with III - Time inconsistency Problem:
Finn E. Kydland and Edward C. Prescott are notable for their work on the Time Inconsistency Problem in economics. This concept refers to the situation where a decision-maker's preferences change over time in such a way that what is considered a preferable decision at one point is no longer preferable when the time to implement the decision arrives. Their work in this area has profound implications for economic policy and the credibility of commitments made by policymakers.
C - Baumol-Tobin matches with I - Inventory theoretic approach to transaction demand for money:
William Baumol and James Tobin developed the Inventory Theoretic Approach to the transaction demand for money. This model integrates insights from inventory management into the understanding of how individuals and firms decide on the amount of money they hold. It suggests that people will minimize their total costs associated with holding cash (the opportunity cost of holding money versus the transaction cost of converting other assets into money) and thus provides a more detailed explanation for the demand for money beyond simple transactional needs.
D - Friedman-Schwartz matches with IV - Monetary History of the United States:
Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz co-authored "A Monetary History of the United States, 1867-1960", an extensive study of the role of money in the U.S. economy. This seminal work analyzes how changes in monetary policy have influenced economic events in the United States over nearly a century. It's acclaimed for its empirical approach and for arguing that monetary policy plays a crucial role in shaping economic outcomes, including inflation and business cycles.
These matches and explanations highlight the contributions of various economists to different areas of economic theory and policy.
Q95: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(b) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(c) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - l
Ans: a
Sol: To solve the matching question, we need to match each policy listed in List I with the correct year of its announcement or implementation from List II. Below is the comprehensive explanation for each:
National Forest Policy
Correct Match: A - II
Explanation: The National Forest Policy in India was actually adopted in 1988, aiming to preserve and extend the forest cover in the country, ensuring environmental stability and maintenance of ecological balance.
Marine Fishing Policy
Correct Match: B - III
Explanation: There isn't a widely recognized policy specifically named "Marine Fishing Policy" with a clear year of adoption mentioned in prominent sources available up to my last update. However, marine and fisheries policies have been under discussion and revision in various years. The closest significant policy development in the context of marine biodiversity and related activities could be linked to India's commitments under various international agreements or the establishment of marine protected areas over the years. For the purpose of this question, it's crucial to note that there might be a specific national or regional policy referenced, but without a clear, widely recognized year of adoption fitting the options provided.
New Mineral Policy
Correct Match: C - III
Explanation: The New Mineral Policy was indeed announced in 2008, not 2004. This policy aimed at encouraging the domestic mining industry to provide a major boost to the country's economic growth. However, for the purpose of matching with the provided years, there seems to be a discrepancy in the years listed.
National Population Policy
Correct Match: D - I
Explanation: The National Population Policy of India was launched in 2000, with the objective of stabilizing the population by 2045. This policy focused on family planning, controlling the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, and providing accessible birth control methods.
Given the discrepancies and the data provided, the most accurate matches based on well-known facts and assuming a possible typographical error or misalignment in the question's options would be:
- A - II (National Forest Policy - 1988)
- B - Likely intended to align with a specific year but requires clarification or assumes a policy framework that isn't widely recognized by the exact name "Marine Fishing Policy" with a clear adoption year from the options provided.
- C - Misalignment with the known year of 2008 for the New Mineral Policy.
- D - I (National Population Policy - 2000)
Correct Answer: A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I (Based on the assumption that each policy needs to be matched with one of the provided years, though with noted discrepancies and acknowledging a lack of exact fit for some policies as detailed.)
Solution Statement:
- The National Forest Policy was correctly matched with 1988 (A - II), reflecting its goal for environmental stability.
- The Marine Fishing Policy's correct year isn't clearly defined within the provided options, indicating a need for clarification.
- The New Mineral Policy is known to have been introduced in 2008, not matching any provided options directly.
- The National Population Policy was accurately aligned with the year 2000 (D - I), aiming for population stabilization by 2045.
Q96: Monetary base of an economy is,
(a) Amount of currency held by public and by the banks as reserves.
(b) Amount of currency held by public and demand deposits.
(c) Amount of currency held by public and time deposits.
(d) Currency deposit ratio.
Ans: a
Sol: Correct Answer Explanation:
- The monetary base of an economy includes all the physical money, such as coins and currency, along with the reserves that commercial banks hold in the central bank. These reserves are not in physical form but are accounted for and accessible for banks to manage their liquidity and meet regulatory requirements. Therefore, the monetary base is essentially the foundation of an economy's money supply, enabling further credit creation and financial transactions.
Overview of Incorrect Options:
Option 2: Amount of currency held by public and demand deposits.
This option incorrectly includes demand deposits as part of the monetary base. While demand deposits contribute to the broader money supply (often referred to as M1 or M2), they are not part of the monetary base. The monetary base strictly involves currency in circulation and reserves held by banks at the central bank.
Option 3: Amount of currency held by public and time deposits.
Similar to option 2, this choice mistakenly includes time deposits, which are a part of broader measures of money supply but not the monetary base. Time deposits, like savings accounts and certificates of deposit, are less liquid and not readily used for transactions or as reserves by banks.
Option 4: Currency deposit ratio.
The currency deposit ratio is a financial metric that compares the amount of cash held by the public to the amount held in bank deposits. It's an important indicator for understanding money supply dynamics but does not define the monetary base. This ratio helps in analyzing the preferences of the public regarding holding cash versus deposits but is not synonymous with the monetary base itself.
Q97: Arrange the following in ascending order on the basis of degree of economic integration.
A. Custom Union
B. Free Trade Area
C. Economic Union
D. Common Market
E. Preferential Trade Arrangements
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) B, C, D, A, E
(c) E, A, B, C, D
(d) E, B, A, D, C
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'E, B, A, D, C'
Preferential Trade Arrangements (E):
- The least integrated form of economic cooperation where countries agree to give each other preferential access to certain products by reducing tariffs or other barriers.
- This type of arrangement does not remove all trade barriers but provides a partial benefit over non-member countries.
Free Trade Area (B):
- A region where a group of countries has agreed to reduce or eliminate trade barriers among themselves while maintaining independent policies towards non-member countries.
- Examples include NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement).
Custom Union (A):
- In addition to eliminating trade barriers among member countries, a customs union establishes a common external tariff against non-members.
- This means that member countries apply the same tariff rates and policies to goods coming from outside the union.
Common Market (D):
- This type of economic integration removes all barriers to the free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor among member countries.
- In a common market, the integration extends beyond trade to include various economic policies to promote economic integration.
Economic Union (C):
- The highest form of economic integration where member countries not only have a common market but also harmonize their economic policies, including monetary and fiscal policies.
- An example is the European Union, which has a single currency and coordinated economic policies among its member states.
Additional Information
Examples and Implications:
- Preferential Trade Arrangements: Countries like India and Sri Lanka have agreements to lower tariffs on certain goods.
- Free Trade Area: NAFTA allows free trade between the US, Canada, and Mexico.
- Custom Union: The Southern African Customs Union (SACU) applies a common external tariff on goods from non-member countries.
- Common Market: The European Economic Area (EEA) allows free movement of people, goods, services, and capital within the European Union (EU) and three EFTA countries.
- Economic Union: The EU represents an advanced stage of economic integration, including a common currency (the euro) and coordinated economic policies.
Q98: Arrange the following Acts in chronological order of their year of enactment starting from the oldest:
A. Foreign Exchange Regulation Act
B. Competition Act
C. MRTP Act
D. Foreign Regulation Act
E. Foreign Exchange Management Act
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) C, A, E, B
(b) C, A, B, E, D
(c) B, A, D, E, C
(d) A, B, C, D, E
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is C, A, E, B
MRTP Act (Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act) - 1969
The MRTP Act was enacted in 1969 to prevent monopolistic, restrictive, and unfair trade practices in India. Its main objectives were to ensure that the operation of the economic system does not result in the concentration of economic power in hands of a few, to control monopolies, and to prohibit monopolistic and restrictive trade practices. This Act aimed to promote fair competition and protect consumer interests.
Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) - 1973
The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) was enacted in 1973 to regulate foreign exchange and impose restrictions on certain kinds of payments. It aimed to conserve foreign exchange resources and ensure their proper utilization in the interest of the economic development of India. FERA imposed strict regulations on foreign exchange transactions, making all dealings involving foreign exchange subject to government control.
Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) - 1999
The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) replaced FERA in 1999. FEMA was introduced to facilitate external trade and payments and promote the orderly development and maintenance of the foreign exchange market in India. Unlike FERA, which was more restrictive and had stringent controls, FEMA aimed to be more management-oriented and liberalized the controls on foreign exchange, thus simplifying the procedures and making compliance easier for businesses.
Competition Act - 2002
The Competition Act was enacted in 2002 to replace the MRTP Act. The objective of the Competition Act is to promote and sustain competition in markets, protect consumer interests, and ensure freedom of trade carried out by other participants in the market. The Act established the Competition Commission of India (CCI) to prevent practices having an adverse effect on competition, to promote and sustain competition in markets, to protect the interests of consumers, and to ensure freedom of trade in Indian markets.
Q99: Suppose that a scarce resource in constant demand will be exhausted in 10 years. If an alternative resource is available at a price of $40 and the interest rate is 10%, what will be the today's price of the scarce resource?
(a) 55.50
(b) 36.40
(c) 24.40
(d) 15.42
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is '$15.42'
Concept:
The problem involves calculating the present value of the price of a scarce resource that will be exhausted in the future. The present value (PV) of a future amount can be calculated using the formula: PV = FV/(1+r) n
Where:
- FV is the future value.
- r is the interest rate.
- n is the number of years.
Given Data:
- Future value (FV) = $40 (price of the alternative resource)
- Interest rate (r) = 10% or 0.10
- Number of years (n) = 10
Putting values we get PV = 15.42
Other Related Points
Importance of Present Value:
- Calculating the present value of future cash flows is crucial in finance to determine the worth of money received or paid in the future, adjusted for the time value of money.
Q100: Which of the following is not true in case of incidence of tax:
(a) Imposition of tax raises price and lowers quantity.
(b) The resulting price increase of tax rise will be dampened if the tax is imposed in monopolistic market.
(c) One would be in a better position to avoid the tax and leave the seller with a larger part if demand is inelastic while supply is elastic.
(d) A unit tax enters through a parallel upward shift in the supply schedule.
Ans: c
Sol: One would be in a better position to avoid the tax and leave the seller with a larger part if demand is inelastic while supply is elastic.
Let's analyze each option to determine which one is not true in the case of incidence of tax:
- Imposition of tax raises price and lowers quantity: This statement is generally true. When a tax is imposed, it typically raises the cost of the good or service, which in turn raises the price and lowers the quantity demanded.
- The resulting price increase of tax rise will be dampened if the tax is imposed in a monopolistic market: This statement can be true. In a monopolistic market, the monopolist may absorb some of the tax to maintain their market power and avoid losing customers, thus dampening the price increase.
- One would be in a better position to avoid the tax and leave the seller with a larger part if demand is inelastic while supply is elastic: This statement is not true. If demand is inelastic, consumers are less sensitive to price changes, meaning they will bear a larger portion of the tax burden. Conversely, if supply is elastic, producers can more easily adjust the quantity they supply, bearing less of the tax burden. Therefore, it is incorrect to say that one would be in a better position to avoid the tax in this scenario.
- A unit tax enters through a parallel upward shift in the supply schedule: This statement is true. A unit tax effectively increases the cost of production by a fixed amount for each unit, shifting the supply curve upward by the amount of the tax.
Solution: The statement that is not true in the case of the incidence of tax is option 3.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Economics 20th June 2023 Shift 1 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and its significance for economics aspirants? |  |
| 2. What topics are generally covered in the Economics Paper of the UGC NET exam? |  |
| 3. How can candidates effectively prepare for the UGC NET Economics Paper? |  |
| 4. What is the marking scheme for the UGC NET Economics Paper? |  |
| 5. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET Economics exam? |  |
















