UGC NET Paper 2: Economics 2nd Mar 2023 Shift 2 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: In case of two goods for which the MRS is zero or infinite, then the nature of goods is :
(a) Perfect substitutes
(b) Normal goods
(c) Perfect complements
(d) Close substitutes
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Perfect Complements
- In the context of consumer theory, the Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) helps describe the rate at which a consumer is willing to substitute one good for another while maintaining the same level of utility. If the MRS is zero or infinite, it reflects extreme preferences regarding the substitution between the two goods.
- MRS Zero or Infinite: When the MRS is zero, the consumer has no interest in substituting one good for the other; when it's infinite, the consumer would swap any amount of one good for even the smallest quantity of the other.
- Nature of Goods: This behavior is indicative of perfect complements. For perfect complements, consumers consume the goods in fixed proportions, and the indifference curves are right-angled, meaning the MRS can be zero or infinite because consumers only value specific combinations of the two goods.
- Solution: Option 3: Perfect complements
Q2: Which of the following is not true?
(a) Total effect of price change on consumption of a good is a combination of income effect and substitution effect
(b) For inferior goods, income effect is always larger than substitution effect, in absolute terms.
(c) For corner solution 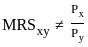
(d) For a normal good both the income and substitution effect hold
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is For inferior goods, income effect is always larger than substitution effect, in absolute terms.
- According to the inferior goods, the income effect is greater than the substitution effect, it is not always the case. The magnitude of each effect depends on the specific good and the consumer's budget constraint. In some cases, the substitution effect may even dominate the income effect, leading to a positive relationship between the price and consumption of inferior goods.
- The total effect of a price change on the consumption of a good is a combination of the income effect and substitution effect. The income effect is the change in consumption due to the change in the consumer's real income. The substitution effect is the change in consumption due to the change in the relative prices of goods.
Q3: The negative network externality in which a consumer wishes to own an exclusive or unique good such as specially designed sports car is:
(a) Bandwagon effect
(b) Tequila effect
(c) Snob effect
(d) Pigou effect
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Snob effect.
- Bandwagon effect: The bandwagon effect is a positive network externality that occurs when a consumer's demand for a good increases as more people consume it. This is because the consumer wants to be part of the crowd and feel like they are fitting in.
- Tequila effect: The tequila effect is a term used to describe the whole are more likely to engage in risky behavior when they are in a group. This is because people are less likely to be inhibited when they are surrounded by others who are also doing the same thing.
- Pigou effect: The Pigou effect is a term used to describe the way in which businesses will overproduce goods and services when there are negative externalities associated with production. This is because businesses do not take the negative externalities they create into account when making their production decisions.
- Important Points: The negative network externality in which a consumer wishes to own an exclusive or unique good such as a specially designed sports car is called the snob effect.
Here's why:
- Negative network externality: The value of the good to the consumer decreases as more people own it. In this case, the exclusivity and prestige associated with owning a unique sports car diminishes as more people own the same model.
- Exclusivity and uniqueness: Consumers who value the snob effect derive satisfaction from owning a good that few others possess. They want to stand out from the crowd and project an image of wealth, status, or individuality.
- Decreasing marginal utility: As more people acquire the good, its perceived exclusivity and social signaling power decline, making it less desirable for consumers who seek distinction.
Q4: When each player has chosen his or her optimal strategy given the strategy chosen by other player, the situation is referred to as.
(a) Nash Equilibrium
(b) Wicksel's Equilibrium
(c) Prisoner's dilemma
(d) Co-operative Game
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Nash Equilibrium.
- Nash equilibrium refers to the strategy in which the optimal strategy of each player, given other players' strategies, becomes the best possible response to those strategies. In other words, if all players adopt Nash equilibrium strategies, no player has an incentive to change their strategy unilaterally.
- This concept is fundamental in game theory and economics for analyzing situations where multiple players interact and make decisions that affect each other's outcomes.
- Wicksel's equilibrium is a concept in monetary economics that refers to the long-run equilibrium of the interest rate in a closed economy with a fixed exchange rate.
- Prisoner's dilemma is a classic game theory model that illustrates the conflict between individual rationality and cooperation.
- Co-operative game is a type of game in which players can form coalitions and make agreements to maximize their joint payoff.
Q5: The Keynes's animal spirits are closely associated with
(a) Past investment
(b) Current investment
(c) Aggregate income
(d) Aggregate expenditure
Ans: b
Sol: The correct response is Current investment.
- Keynes's Theory: John Maynard Keynes, a prominent economist of the 20th century, developed his theory during the Great Depression to explain the economic downturn and propose solutions to stimulate economic recovery.
- Animal Spirits: Keynes introduced the term "animal spirits" in his book "The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money" to describe the non-rational factors that influence economic decisions, particularly investment decisions. These animal spirits encompass emotions, instincts, and psychological factors that can't be easily quantified or predicted by traditional economic models.
- Relation to Investment: Keynes argued that investment decisions are not solely driven by rational calculations of expected returns and interest rates. Instead, they are heavily influenced by psychological factors such as confidence, optimism, pessimism, and risk aversion. These animal spirits can lead to fluctuations in investment levels, even in the absence of significant changes in economic fundamentals.
- Current Investment: When Keynes referred to animal spirits in the context of investment, he was primarily concerned with their impact on current investment decisions. This means that investors' sentiment and confidence levels at a given point in time can significantly influence their willingness to invest in new capital projects, expand businesses, or undertake entrepreneurial ventures.
- Implications: In times of optimism and confidence, investors may exhibit high levels of animal spirits, leading to increased investment activity and economic expansion. Conversely, during periods of pessimism or uncertainty, animal spirits may wane, resulting in reduced investment, economic contraction, and even recessions.
- Policy Response: Keynes argued that during economic downturns, when private investment is sluggish due to low animal spirits, government intervention through fiscal and monetary policies can help stimulate aggregate demand and restore confidence, thereby encouraging investment and economic recovery.
Q6: Which one of the following is not a component of M1 ?
(a) Currency
(b) Traveler's cheque
(c) Commercial paper
(d) Demand deposits
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is "Commercial paper."
M1 refers to a measure of the money supply that includes highly liquid assets that can be readily used for transactions. The components of M1 typically include:
- Currency: Physical cash in circulation, including coins and banknotes.
- Demand deposits: Funds held in checking accounts and other types of accounts that can be withdrawn on demand by the depositor, typically through checks, debit cards, or electronic transfers.
- Travelers' checks: These are prepaid checks that are widely accepted by merchants and banks and can be exchanged for local currency while traveling.
- "Commercial paper" refers to short-term debt instruments issued by corporations and financial institutions to raise funds for short-term financing needs. While commercial paper is an important financial instrument, it is not considered a component of M1 because it is not directly used for transactions by households and businesses in the same way as currency, demand deposits, and travelers' checks. Commercial paper falls under the category of M2 or M3, broader measures of the money supply that include less liquid assets.
M1 includes currency, demand deposits, and traveler’s checks, which are highly liquid assets used for transactions. Commercial paper, a short-term debt instrument issued by corporations, is not included in M1 (or M2/M3) as it is not a medium of exchange. Thus, the correct answer is (c) Commercial paper.
Q7: The condition of preferring a certain income to a risky income with same expected value is referred to as;
(a) Risk neutral
(b) Risk loving
(c) Risk averse
(d) Risk premium
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Risk averse.
The condition of preferring a certain income to a risky income with the same expected value is called risk aversion. Risk-averse individuals prefer certainty over uncertainty, even if it means forgoing potential gains.
- Risk-neutral individuals are indifferent between certain and risky outcomes with the same expected value.
- Risk-seeking (not risk-loving) individuals prefer risky outcomes for potential higher rewards.
- Risk premium is the additional return demanded for holding a risky asset.
Thus, the correct answer is (c) Risk averse.
Q8: A firm has the following total cost and demand functions: C = 1/3 Q3 - 7Q2 + 111Q + 50, Q = 100 - P, then find the profit maximizing level of output (Q*) and maximum profit of the firm.
(a) 50 and 100
(b) 111 and 2150
(c) 11 and 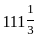
(d) 7 and 84
Ans: c
Sol: To find the profit-maximising output and maximum profit:
- First, rewrite the demand function as P = 100 - Q, so revenue is R = P × Q = 100Q - Q².
- Profit is R - C, where total cost is C = (1/3)Q³ - 7Q² + 111Q + 50.
- Set the derivative of profit with respect to Q to zero to find the maximum point.
- After solving, you get the profit-maximising output: Q* = 11.
- For the maximum profit, substitute Q = 11 into the profit formula. The result is:
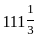
The correct answer is '11 and 111.3.
Q9: In the Mundell-Fleming model, the monetary policy will be more effective when there is
(a) Perfect capital mobility and flexible exchange rate
(b) Perfect capital mobility and fixed exchange rate
(c) Imperfect capital mobility and flexible exchange rate
(d) Imperfect capital mobility and fixed exchange rate
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Perfect capital mobility and flexible exchange rate.
- The Mundell-Fleming Model (MFM) describes the workings of a small economy open to international trade in goods and financial assets and provides a framework for monetary and fiscal policy analysis. The basic framework is a static, non-micro founded model extending the Keynesian IS-LM model. Indeed, the MFM shares with the IS-LM model the philosophical and methodological approach, and the basic features: the model is linear and the main assumption is that consumer prices are fixed. The MFM nests the IS-LM model as a special case, for a particular parameterization
- Perfect capital mobility means that there are no restrictions on the flow of capital across borders. This means that investors can freely move their money between countries in search of the highest returns. A flexible exchange rate means that the exchange rate is determined by market forces, rather than being pegged to a fixed rate.
Q10: The chain-weighted index is
(a) The total market value of goods and services produced in each year
(b) The percentage growth in real GDP
(c) A method for calculating changes in prices that used an average of base year from neighbouring years
(d) An Index that measures how the prices of goods and services included in GDP change.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is The total market value of goods and services produced in each year.
A chain index is an index number in which the value of any given period is related to the value of its immediately preceding period (resulting in an index for the given period expressed against the preceding period = 100); this is distinct from the fixed-base index, where the value of every period in a time series is directly related to the same value of one fixed base period.
- This index type is called a chain index because individual indices with a previous period = 100 can be chained together by multiplying (and dividing by 100) all consecutive indices, thus converting them into a series of indices with the first reference period = 100. This way, the consecutive values of the index numbers form a chain, as it were, from the first (reference) to the last period.
- Chain-weighted CPI takes real-word purchasing decisions into account to provide a more accurate picture of the cost of living.
- zChain-weighted CPI can capture both general changes in spending, as consumer preferences change, and substitution effects, when relative prices change.
- The adjustments in chain-weighted CPI make it a better measure of the cost of living, but a less accurate measure of inflation.
In 2017, chain-weighted CPI was substituted for regular CPI in setting federal income tax brackets.
The chain-weighted index is a method for calculating changes in prices that uses an average of base years from neighboring years to account for changes in consumption patterns and substitution effects. It provides a more accurate measure of price changes compared to fixed-base indices. Thus, the correct answer is (c).
Q11: If the two events A and B are not independent then which of the following is correct?
(a) P(A ∩ B) = P(A).P(B)
(b) P(A ∩ B) = P(A).P(B/A)
(c) P(A ∩ B) = P(A).P(A/B)
(d) P(A ∩ B) = 1 - P(AUB)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is P(A ∩ B) = P(A).P(B/A)
The formula P(A ∩ B) = P(A) . P(B/A) represents the probability of events A and B occurring simultaneously, given that event A has already occurred. It's based on the concept of conditional probability, which considers the likelihood of one event happening in relation to another
Let's break down the formula:
- P(A ∩ B): This represents the probability of both event A and event B occurring together.
- P(A): This represents the probability of event A occurring.
- P(B/A): This represents the conditional probability of event B occurring, given that event A has already occurred. In other words, it's the likelihood of event B happening after knowing that event A has happened.
Q12: If the consumption function passes through the origin and APC = MPC then it must be:
(a) Linear without any intercept
(b) Non linear without any intercept
(c) Linear with a negative intercept on the income axis
(d) Linear with a positive intercept on the consumption axis
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Linear without any intercept.
The consumption function is a concept from Keynesian economics that describes the relationship between total consumer spending and gross national income. It is used to determine the level of consumer expenditure that occurs in an economy for different levels of disposable income.
The difference between APC and MPC:
- APC (Average Propensity to Consume) is calculated by dividing total consumption expenditure by total disposable income.
- MPC (Marginal Propensity to Consume) is calculated by dividing the change in consumption expenditure by the change in disposable income.
- APC is a measure of the proportion of disposable income that is typically spent by households, while MPC is a measure of the responsiveness of consumption to changes in disposable income.
- APC is a static measure, while MPC is a dynamic measure.
- APC is always less than or equal to 1, as total consumption expenditure cannot exceed total disposable income.
- MPC can be greater than 1, if the change in consumption expenditure is greater than the change in disposable income.
- APC is useful for understanding the overall consumption behavior of households, while MPC is useful for understanding how changes in disposable income affect consumption.
Q13: Find the producer's surplus when
Pd = 3x2 - 20x + 5
Ps = 15 + 9x (x is the quantity)
(a) 400
(b) 350
(c) 450
(d) 500
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is '450'To find the producer's surplus:
First, set Pd = Ps to find the equilibrium quantity:
- 3x2 - 20x + 5 = 15 + 9x
- 3x2 - 29x - 10 = 0
- Solve for x (quantity): x = 10
At x = 10, equilibrium price: P = 15 + 9x = 105
Producer's surplus is area above supply curve and below equilibrium price:
Surplus = (Equilibrium price × quantity) - Area under supply curve
Area under supply curve: 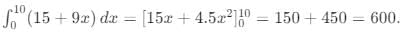
Surplus = (105 × 10) - 600 = 1050 - 600 = 450
The calculation is correct, and the answer (c) is correct.
Q14: Which of the following is true in case of the non-marketed environmental resources?
(a) Non excludable and non-rival in consumption
(b) Excludable but not rival in consumption
(c) Excludable and rival in consumption
(d) Non-excludable but rival in consumption
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Non excludable and non-rival in consumption.
Non-marketed environmental resources are typically non-excludable and non-rival in consumption. This means that it is difficult or impossible to prevent people from using these resources, and that one person's use of the resource does not diminish the availability of the resource for others.
- Excludability refers to the ability to prevent people from using a resource. Some environmental resources are excludable, such as national parks, which can be fenced in and visitors can be charged an entrance fee. However, many environmental resources are non-excludable, such as clean air and water. It is difficult or impossible to prevent people from breathing air or drinking water, even if they do not pay for it.
- Rivalry in consumption refers to the idea that one person's use of a resource diminishes the availability of the resource for others. Some environmental resources are rival in consumption, such as fish populations. If one person catches a fish, there is one fewer fish available for others to catch. However, many environmental resources are non-rival in consumption, such as clean air and water. One person's breathing of clean air does not diminish the availability of clean air for others.
Q15: Suppose 'X' places Rs. 8 value on one bread packet and 'Y' places Rs. 6 value on it. If there is no tax on bread, then price of bread packet is Rs. 5. so both X and Y choose to buy one packet each. Now suppose government levies a tax of Rs.. 2 per unit, the price of bread rises to Rs. 7. Then the deadweight loss and tax revenue collected respectively are :
(a) Rs. 1 and Rs. 2
(b) Rs. 2 and Rs. 4
(c) Rs. 2 and Rs. 2
(d) Rs. 1 and Rs. 4
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Rs. 1 and Rs. 2
In this type of problem, deadweight loss refers to the decrease in economic efficiency that occurs when a good for which the market outcome is not Pareto optimal is taxed. The tax revenue is simply the amount of money collected by the government from the tax.
- Before the tax, 'X' and 'Y' both buy a packet of bread, each for Rs.5.
- After the tax of Rs.2 per unit is levied, the price of the bread rises to Rs.7.
After the tax is levied, 'X' still buys the bread because his value for it (Rs.8) is still more than the new price (Rs.7). However, 'Y' places a value of Rs.6 on the bread, which is less than the new price of Rs.7. Therefore, 'Y' chooses not to buy the bread.
- The tax revenue is the tax rate multiplied by the quantity sold. The tax rate is Rs.2 and one unit of bread is sold (to 'X'). Therefore, the tax revenue collected is Rs.2*1 = Rs.2.
The deadweight loss is the loss of economic activity caused by the tax. It's the value of the transaction that didn't happen because of the tax (the transaction involving 'Y'). 'Y' valued the bread at Rs.6 and the cost to produce the bread was Rs.5 (the original price before tax), so the deadweight loss is Rs.6 - Rs.5 = Rs.1.
To summarize, the tax revenue collected is Rs.2, and the deadweight loss is Rs.1
Q16: The component which distinguishes primary deficit from fiscal deficit is :
(a) Non-debt component of capital receipt
(b) Interest payment
(c) Debt component of capital receipt
(d) Revenue deficit
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Interest payment.
The primary deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue, excluding interest payments. The fiscal deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue, including interest payments.
Therefore, the component that distinguishes primary deficit from fiscal deficit is interest payment. The primary deficit is calculated by subtracting interest payments from the fiscal deficit.
Q17: Which of the following is not an assumption or conclusion of the inflation targeting approach ?
(a) Interest rate is the major instrument of monetary policy
(b) Higher interest rate controls aggregate demand
(c) Inflation is a supply side phenomenon
(d) Quantity of money supply is not very effective in controlling inflation
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Inflation is a supply-side phenomenon
- The inflation targeting approach is based on the assumption that inflation is primarily a demand-side phenomenon. It argues that inflation occurs when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply. In other words, when there is too much money chasing too few goods, prices will tend to rise.
Interest rate is the major instrument of monetary policy. This is a key assumption of the inflation-targeting approach. The central bank uses changes in interest rates to influence aggregate demand and control inflation.
A higher interest rate controls aggregate demand. This is a conclusion of the inflation-targeting approach. When the central bank raises interest rates, it becomes more expensive for businesses to borrow money. This can lead to a decrease in investment and hiring, which can slow down the economy and reduce aggregate demand.
Quantity of money supply is not very effective in controlling inflation. This is another conclusion of the inflation-targeting approach. While the quantity of money supply can have an impact on inflation, it is not a very precise or reliable tool for controlling inflation. The central bank has more direct control over inflation by using interest rates to influence aggregate demand.
Q18: In context of monetary policy, the sacrifice ratio refers to the _________
(a) Interest cost arising because of crowding out effect
(b) Loss of real value of money at the face of increasing inflation
(c) Output cost of reducing inflation
(d) Labour cost raising minimum wage
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Output cost of reducing inflation.
The sacrifice ratio is a measure of the economic output that must be forgone to reduce inflation by one percentage point. It is calculated by dividing the percentage point reduction in inflation by the percentage point decline in real GDP.
Monetary policy is used to control inflation by raising or lowering interest rates. When the central bank raises interest rates, it makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to a decrease in investment and economic growth. The sacrifice ratio is a way of measuring the trade-off between reducing inflation and maintaining economic growth.
Q19: Marx refers to the concept of organic composition of capital. Which one of the following ratios is used for this (where C is constant capital, V is variable capital and S is surplus value)?
(a) 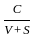
(b) 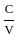
(c) 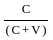
(d) 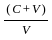
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is C/V
The organic composition of capital is the ratio of constant capital to variable capital, expressed as C/V. This ratio reflects the amount of capital invested in machinery, equipment, and raw materials (constant capital) compared to the amount invested in labor (variable capital).
Q20: Which of the following formula is used to calculate the yield of treasury bills (T-bills) where
Y = Discounted yield
P = Price
D = Days to maturity
(a) 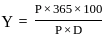
(b) 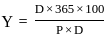
(c) 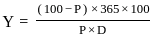
(d) 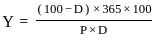
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 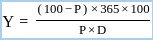
The discount yield is calculated and returned when it is sold at a discount to its face value, expressed as a percentage. Discount yield is commonly used to calculate the yield on municipal notes, commercial paper, and treasury bills sold at a discount.
- Discount yield computes the expected return of a bond purchased at a discount and held until maturity.
- Discount yield is computed using a standardized 30-day month and 360-day year.
- This calculation is commonly used for evaluating Treasury bills and zero-coupon bonds
Q21: The faster growth and more equal distribution of income can be examined simultaneously by
(a) Gini ratio
(b) Poverty-weighted growth rate
(c) Kuznet curve
(d) None of the above
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is poverty-weighted growth rate (PWGR
The poverty-weighted growth rate (PWGR)
- It is a measure of economic growth that takes into account the distribution of income. It is calculated by multiplying the growth rate of income for each income quintile (the 20% of the population with the lowest income, the next 20%, and so on) by the weight of that quintile in the total population. The weights are chosen so that the poverty-weighted growth rate gives more weight to the growth of income for the poorest quintiles.
- The Gini ratio: also known as the Gini index or Gini coefficient, is a measure of statistical dispersion intended to represent the inequality of distribution of wealth, income, or any other measure of welfare.
- Kuznet curve:
Income inequality is not a constant phenomenon. It can change over time, depending on the stage of economic development and other factors.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution to income inequality. The best way to reduce income inequality will vary depending on the specific circumstances of each country.\
Government policies can play a role in reducing income inequality. By investing in social safety nets, education, and other programs, governments can help to create a more equitable society.
Q22: Equivalent variation for a price increase of a good can be interpreted as:
(a) Willingness to pay
(b) Willingness to accept
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Willingness to pay
- Equivalent variation (EV) is a measure used in economics to quantify the change in income needed to restore a consumer to their original utility level after a change in prices. Specifically, for a price increase of a good, the equivalent variation represents the amount of money a consumer would be willing to pay beforehand to avoid the price increase.
- This concept essentially captures the consumer's willingness to pay to maintain their initial level of utility when faced with a potential increase in the price of a good. It is a forward-looking measure that assesses how much a consumer values their current consumption bundle enough to avoid a deterioration in their welfare due to higher prices.
- Willingness to pay in this context means the amount of money the consumer is ready to give up to prevent the price rise and maintain their initial utility.
- Willingness to accept would typically be used to describe how much money a consumer would require to accept a worsening of their situation, which is not what EV measures in this scenario.
Hence, for a price increase of a good, the equivalent variation aligns with the concept of the consumer's willingness to pay to avoid that price increase.
Q23: According to the specific factors model, which of the following is correct?
(a) Trade benefits the factor specific to the export sector of each country but hurts the factor specific to the import-competing sectors with ambiguous effects on mobile factors
(b) Trade hurts the factor specific to the export sector of each country and also hurts the factor specific to the import-competing sectors, with ambiguous effects on mobile factors.
(c) Trade benefits the factor specific to the import sector of each country but hurts the factor specific to the export-competing sectors, with ambiguous effects on mobile factors.
(d) Trade benefits the factor specific to the export sector as well as import-competing sector of each country, with ambiguous effects on mobile factors.
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Trade benefits the factor specific to the export sector of each country but hurts the factor specific to the import-competing sectors with ambiguous effects on mobile factors
- The benefits factors model is a variant of the Heckscher-Ohlin model that assumes that capital is specific to an industry, while labor is freely mobile between industries. In the specific factors model, trade benefits the factor specific to the export sector of each country.
Factors specific to the export sector: Trade benefits the factors specific to the export sector because it increases the demand for those factors. This is because the export sector expands as a result of trade. For example, if a country exports textiles, the demand for textile workers will increase as the country exports more textiles.
Factors specific to the import-competing sector: Trade hurts the factors specific to the import-competing sector because it decreases the demand for those factors. This is because the import-competing sector contracts as a result of trade. For example, if a country imports cars, the demand for car workers will decrease as the country imports more cars.
Mobile factors: The effects of trade on mobile factors are ambiguous. This is because mobile factors can move between industries in response to changes in demand. For example, if a country exports textiles and the demand for textile workers increases, textile workers can move from the import-competing sector to the export sector to take advantage of the higher wages.
Q24: ‘What does 'immiserising growth’ argued?
(a) Export-biased growth by poor nations would worsen their terms of trade so much that they would be worse off than if they had not grown at all
(b) Export-biased growth by rich nations would worsen their terms of trade so much that they would be worse off than if they had not grown at all
(c) Import-biased growth by poor nations would worsen their terms of trade so much that they would be worse off than If they had not grown at all
(d) Import-biased growth by Rich nations would worsen their terms of trade so much that they would be worsen off than if had not grown at all.
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Export-biased growth by poor nations would worsen their terms of trade so much that they would be worse off than if they had not grown at all.
Immiserizing growth is a theoretical concept in economics that suggests that economic growth can, under certain conditions, lead to a decrease in a country's overall welfare. This phenomenon is most likely to occur in poor countries that rely heavily on exports of primary goods.
When a poor country experiences export-biased growth, it produces more of its export goods and sells them on the international market. This increased supply of goods can drive down the prices of these goods, which in turn worsens the country's terms of trade. The terms of trade are a measure of how much a country's exports are worth in terms of its imports. A worsening of the terms of trade means that the country has to export more goods to buy the same amount of imports.
Q25: Compensating variation for a price decrease of a good can be interpreted as :
(a) Willingness to pay
(b) Willingness to accept
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is: Willingness to pay
Compensating variation is a concept in welfare economics used to measure the change in welfare or utility due to a change in prices. It represents the amount of money one would need to reach their initial level of utility after a price change.
Definition of Compensating Variation:
- Compensating variation (CV) is the amount of money that needs to be given to a consumer to compensate them for a change in the price of a good, keeping their utility level constant.
Price Decrease Interpretation:
- When the price of a good decreases, the compensating variation can be interpreted as the consumer's willingness to pay to maintain their initial level of utility despite the price change.
Willingness to Pay:
- Willingness to pay (WTP) is the maximum amount a consumer is willing to pay to acquire a good or to avoid a price increase.
- In the context of a price decrease, CV reflects how much the consumer would be willing to pay to return to the original price, indicating their preference for the lower price.
Other Related Points
Equivalent Variation:
- In contrast to compensating variation, equivalent variation (EV) measures the amount of money that would need to be taken away from a consumer before a price change to maintain their initial utility level.
Application in Policy Analysis:
- Compensating variation is often used in cost-benefit analysis and policy evaluations to assess the impact of price changes on consumer welfare.
Consumer Surplus:
- Compensating variation is related to consumer surplus, which measures the difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good and what they actually pay.
Q26: Which of the following is not true in the case of externality?
(a) It is related to human interactions
(b) It is tied to consumer sovereignty
(c) It is based on higher order judgements of right and wrong
(d) It is an amoral concept
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is It is related to human interactions
Externalities are costs or benefits affecting parties not directly involved in a transaction. They are:
- (a) True: Externalities arise from human interactions (e.g., pollution affecting others).
- (b) True: Externalities can conflict with consumer sovereignty, as one’s actions impact others.
- (c) False: Externalities are an amoral concept, not based on higher-order judgments of right and wrong.
- (d) True: Externalities are amoral, as they describe economic effects without moral judgment.
Thus, the correct answer is (c).
Q27: Which of the following is an example of depreciation of natural capital?
(a) Restoring rivers rendered unusable due to dumping of industrial effluents
(b) Representation of areas that have been cleared for years of open-cut mining
(c) Pollution-control activities by the public sector such as municipal waste treatment
(d) Detoxifying unusable soils for urban or rural development
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is ‘Representation of areas that have been cleared for years of open-cut mining’
Depreciation of natural capital refers to the depletion or degradation of natural resources, reducing their value and utility.
- (a) Restoring rivers is a remedial action, not depreciation.
- (b) Open-cut mining clears land, degrading natural capital (e.g., soil, ecosystems), making it a clear example of depreciation.
- (c) Pollution-control activities (e.g., municipal waste treatment) mitigate environmental damage, not cause depreciation.
- (d) Detoxifying soils is a restoration effort, not depreciation.
Thus, the correct answer is (b).
Q28: Which of the following postulates the Gravity Model correctly ?
(a) The smaller and the closer the two countries are, the smaller the volume of trade between them is expected to be
(b) The larger and the closer the two countries are, the larger the volume of trade between them is expected to be.
(c) The larger and the closer the two countries are, the smaller the volume of trade between them is expected to be
(d) The smaller and farther the two countries are, the larger the volume of trade between them is expected to be.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is The smaller and the closer the two countries are, the smaller the volume of trade between them is expected to be.
- The gravity model of trade is a simple economic model that predicts the volume of trade between two countries based on their economic sizes and the distance between them. The model is based on the idea that trade is like gravity.
- The gravity model is a simple but powerful tool that can be used to understand the patterns of trade between countries.
The gravity model predicts that the volume of trade between two countries is proportional to their economic sizes (GDP) and inversely proportional to the distance between them. Thus, larger and closer countries are expected to have larger trade volumes.
The correct answer is (b).
Q29: If the nominal tariff rate (t) on consumers of the final commodity is 10 per cent, the ratio of the cost of the imported put to the price of the final commodity in the absence of tariffs (ai) is = 0.8, and the nominal tariff rate on the imported input (ti) = 0, then find the rate of effective protection.
(a) 5%
(b) 8%
(c) 50%
(d) 10%
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is: 50%
The rate of effective protection measures the actual protection given to domestic producers by considering both the tariffs on final goods and the tariffs on imported inputs. It indicates the percentage by which the value-added in the domestic production process is increased due to the tariffs imposed on imported goods and inputs.
Nominal Tariff Rate (t):
- The nominal tariff rate on the final commodity is given as 10%.
Cost Ratio (ai):
- The ratio of the cost of the imported input to the price of the final commodity in the absence of tariffs is 0.8.
Tariff on Imported Input (ti):
- The nominal tariff rate on the imported input is 0%.
The formula for calculating the rate of effective protection (ERP) is:
ERP = (t - ai * ti) / (1 - ai)
Substituting the given values:
t = 0.10 (10%)
ai = 0.8
ti = 0.0 (0%)
ERP = (0.10 - 0.8 * 0) / (1 - 0.8) = 0.10 / 0.2 = 0.50 = 50%
Other Related Points
Understanding Effective Protection:
- Effective protection considers the impact of tariffs on both the final product and the inputs used in production, providing a more accurate measure of protection for domestic industries compared to nominal tariffs.
Value-Added Concept:
- Effective protection focuses on the value-added by domestic producers. If tariffs on inputs are lower than tariffs on the final product, domestic producers are effectively more protected.
Policy Implications:
- Governments use effective protection to assess the true level of protection provided to domestic industries and to design tariff structures that promote domestic production and economic development.
Q30: Match List I with List II
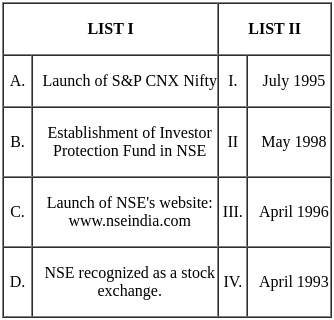
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(c) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
(d) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
Ans: b
Sol: A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV is correct answer.
The given options refer to different milestones in the history of the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India. Let's match each event with its respective correct date:
Q31: Match List I with List II
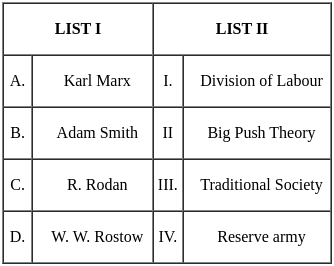
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(c) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
- The reserve army of labor is a crucial component of Marx's theory of surplus value. According to Marx, capitalists extract surplus value from workers by paying them less than the full value of their labor. This surplus value is what allows capitalists to accumulate profits.
- The concept of the division of labor has been explored by various thinkers throughout history, but it's widely attributed to Adam Smith, an 18th-century Scottish economist and philosopher. In his seminal work, "An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations," published in 1776, Smith elaborated on the division of labor and its role in economic advancement.
- The Big Push Theory was developed by Paul N. Rosenstein-Rodan, a Polish-American economist, in his 1943 paper titled "Notes on the Theory of the 'Big Push.'" The theory suggests that economic development in underdeveloped countries requires a significant initial investment to overcome the low levels of productivity and infrastructure that hinder growth.
- The term "traditional society" is a broad concept that has been used by various sociologists, anthropologists, and historians to describe societies that share certain characteristics.
Q32: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(b) A - IV, B - II, C - I, D - III
(c) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
- A census is a systematic procedure of acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given population. It is the official count of all people in a country or region. Censuses are conducted at regular intervals, typically every ten years, and provide detailed information about the population's age, sex, ethnicity, religion, occupation, education, housing, and other characteristics.
- In India, the first census was conducted in 1872 under Viceroy Lord Mayo. The first complete census was taken in 1881.
Q33: Match List I with List II
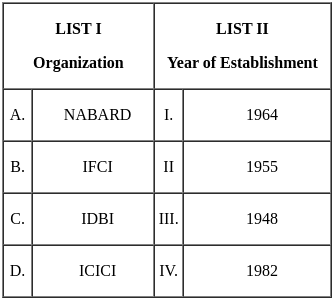
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(b) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is
- NABARD - The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development. It is an Indian governmental agency responsible for the policy, planning, and operations that promote agriculture and rural development in India. It provides financial and other support to farmers, small-scale industries, and other such businesses. Established on 12 July 1982.
- IFCI - The Industrial Finance Corporation of India. It's the first developed financial institution in India, established in 1948. The primary aim of IFCI is to provide medium and long-term financial assistance to large-scale industries, especially when normal banking institutions are unable to do so.
- IDBI - Industrial Development Bank of India. Established in 1964 by an Act of Parliament, IDBI was intended to provide credit and other financial facilities for the development of India's fledgling industrial sector. It is currently one of the main commercial banks owned by the Indian government.
- ICICI - The Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India. Established in 1955, ICICI Bank offers a wide range of banking products and services to corporate and retail customers. It is one of India's largest private-sector banks.
Q34: According to the IMF's World Economic Outlook report, arrange the estimated real GDP Growth rate (YOY) of the following countries for the year 2021 in descending order.
A. USA
B. Germany
C. United Kingdom
D. China
E. India
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, E, C, B, A
(b) E, D, C, A, B
(c) E, C, D, A, B
(d) D, E, B, C, A
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is E, D, C, A, B
According to the IMF’s World Economic Outlook (October 2021), the estimated real GDP growth rates for 2021 are: India (9.5%), China (8.0%), UK (7.4%), USA (5.9%), Germany (2.9%). Arranged in descending order: E, D, C, A, B. The correct answer is (b).
The global economic recovery is continuing, even as the pandemic resurges. The fault lines opened up by COVID-19 are looking more persistent—near-term divergences are expected to leave lasting imprints on medium-term performance. Vaccine access and early policy support are the principal drivers of the gaps.
The global economy is projected to grow 5.9 percent in 2021 and 4.9 percent in 2022, 0.1 percentage point lower for 2021 than in the July forecast. The downward revision for 2021 reflects a downgrade for advanced economies—in part due to supply disruptions—and for low-income developing countries, largely due to worsening pandemic dynamics. This is partially offset by stronger near-term prospects among some commodity-exporting emerging market and developing economies. Rapid spread of Delta and the threat of new variants have increased uncertainty about how quickly the pandemic can be overcome. Policy choices have become more difficult, with limited room to maneuver.
These figures have been published in the official report published by IMF for year 2021.
Q35: Arrange the Nobel laureates in Economics as per their year of receiving award in descending order.
A. Amartya Sen
B. Paul Krugman
C. James Tobin
D. Friedrich Hayek
E. Milton Friedman
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D, C, E
(b) E, C, A, B, D
(c) A, C, E, D, B
(d) B, A, C, E, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is B, A, C, E, D
- Amartya Sen was awarded the 1998 Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to welfare economics and social choice theory and for his interest in the problems of society's poorest members.
- Paul Krugman was awarded the 2008 Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences for his work associated with new trade theory and the New Economics Geography.
- James Tobin an American economist, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences in 1981.
- Friedrich Hayek an economist and philosopher, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences in 1974.
- Milton Friedman an American economist, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences in 1976.
Q36: Arrange the following in descending order on the basis of year of starting the scheme
A. Jal Jeevan mission
B. Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin)
C. Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Gramin)
D. Pradhan Mantri Sadak Yojana (Gramin)
E. Pradhan Mantri Koushal VikashYojana
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D,B,E,C,A
(b) C, A, D, B, E
(c) B, E, C, A, D
(d) C, D, B, E, A
Ans: a
Sol: According to official answer key, this question was dropped because none of the options matched correct chronology.
D,B,E,C,A is the correct answer.
Each of these schemes were initiated at different times by the government of India. Here they are arranged in descending order based on their start year:
- D. Pradhan Mantri Sadak Yojana (Gramin): This scheme was launched by the Government of India on December 25, 2000. It aims to provide all-weather road connectivity to unconnected villages.
- B. Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin): The Swachh Bharat Mission is a nation-wide campaign in India that aims to clean up the streets, roads and infrastructure of India's cities, towns, and rural areas. The campaign was officially launched on October 2, 2014.
- E. Pradhan Mantri Koushal Vikash Yojana: This was launched in July 2015 under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) with the aim of training over 40 crore individuals in different industry-relevant skills by 2022.
- C. Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Gramin): The mission was launched on November 20, 2016 with an aim to provide affordable housing to the rural poor.
- A. Jal Jeevan mission: The Jal Jeevan mission was launched on August 15, 2019 with the aim to provide tap water supply to rural households by 2024.
Q37: Arrange the followings in ascending order on the basis of Fund Allocation (Budget 2022-23)
A. Ministry of Railways
B. Ministry of Defence
C. Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare
D. Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
E. Ministry of Rural Development.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D, B, E
(b) E, B, C, D, A
(c) C, E, A, D, B
(d) B, C, D, E, A
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is C, E, A, D, B
A budget is a financial plan that outlines how a government, organization, or individual will spend their money over a specific period of time, typically a year. It is a crucial tool for allocating resources, ensuring financial stability, and tracking progress towards goals.
The ministries based on the fund allocation for the Budget 2022-23:
- Ministry of Rural Development - 160,000 crores
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways - 191,813 crores
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare - 200,000 crores
- Ministry of Defence - 523,600 crores
- Ministry of Railways - 1,400,000 crores
Based on the Union Budget 2022-23, fund allocations are: Defence (~₹5,25,166 crore), Road Transport and Highways (~₹1,99,108 crore), Railways (~₹1,40,367 crore), Rural Development (~₹1,38,204 crore), Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (~₹1,24,000 crore). Arranged in descending order: B, D, A, E, C. The correct answer is (c).
Q38: Arrange the following sources of revenue as per their share of contribution to total revenue in Union Budget 2022-23 in descending order.
A. Custom Duty
B. Income Tax
C. GST
D. Union Excise Duty
E. Non debt capital receipts.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) E, B, C, D, A
(b) E, C, B, D, A
(c) C, B, D, A, E
(d) C, B, A, D, E
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is C, B, D, A, E
Based on the Union Budget 2022-23, approximate revenue shares are: GST (~31%), Income Tax (~23%), Union Excise Duty (~12%), Customs Duty (~8%), Non-debt Capital Receipts (~3%). Arranged in descending order: C, B, D, A, E. The correct answer is (c).
Here's a breakdown of the revenue contribution of each source:
- GST: 17% - The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is the largest source of revenue for the Indian government, accounting for 17% of total revenue in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- Income Tax: 15% - Income Tax is the second-largest source of revenue, contributing 15% to the total revenue.
- Custom Duty: 4% - Custom Duty, levied on imported goods, contributes 4% to the total revenue.
- Union Excise Duty: 7% - Union Excise Duty, levied on domestically manufactured goods, contributes 7% to the total revenue.
- Non-debt Capital Receipts: 2% - Non-debt Capital Receipts, which include receipts from disinvestment, dividends, and external grants, contribute 2% to the total revenue
Q39: According to CMIE data (September 2022). arrange the states in descending order based on unemployment rate
A. Haryana
B. Rajasthan
C. Jammu Kashmir
D. Jharkhand
E. Tripura.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D, E, B
(b) B, C, A, D, E
(c) A, B, C, D, E
(d) B, C, A, E, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is B, C, A, E, D
The unemployment rate is the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. It is a measure of the health of an economy, as it reflects the number of people who are willing and able to work but are unable to find a job.
The unemployment rate can vary for a number of reasons, including:
- Economic conditions: When the economy is doing well, there are more jobs available and the unemployment rate is lower. When the economy is doing poorly, there are fewer jobs available and the unemployment rate is higher.
- Demographic factors: The unemployment rate can also be affected by demographic factors, such as the age and education level of the population. For example, young people and people with less education are typically more likely to be unemployed.
- Government policy: Government policies can also affect the unemployment rate. For example, policies that promote job creation can help to lower the unemployment rate, while policies that restrict immigration can make it harder for people to find work.
Other Related Points
- According to the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), India’s unemployment rate in March 2023 was 8.11%.
- The unemployment rate in urban India was 7.93%, while the unemployment rate in rural India was 7.44%.
- The states with the highest unemployment rates in India are Haryana, Rajasthan, Bihar, Jharkhand, Jammu & Kashmir.
- The state with the highest unemployment rate among union territories in India is Delhi.
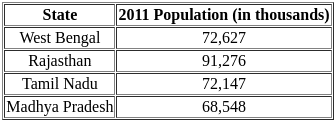
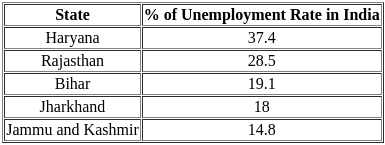
- The unemployment rate in India rose to 8.30% in December from 8.00% in November. This was the highest level in 16 months...
- Unemployment rate in India State-wise 2023:
Q40: Arrange the following policy rate (as on 31-12-2022) of the RBI in the descending order of their magnitude.
A. Repo rate
B. Bank rate
C. CRR
D. SLR
E. Reserve repo Rate.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D, C, E
(b) D, A, B, C, E
(c) B, D, A, E, C
(d) D, B, A, C, E
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is D, B, A, C, E.
As of 31-12-2022, RBI policy rates are:
SLR (18%),
Bank Rate (6.75%),
Repo Rate (6.5%),
CRR (4.5%),
Reverse Repo Rate (3.35%).
Arranged in descending order: D, B, A, C, E. The correct answer is (d).
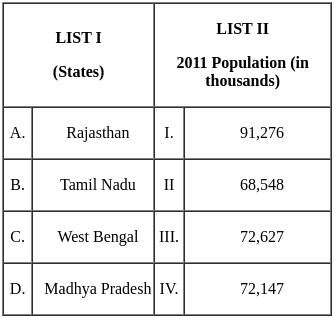
Q41: Arrange the states in ascending order based on population who are multidimensionally poor as per NITI Aayog Report 2021.
A. Punjab
B. Kerala
C. Sikkim
D. Goa
E. Tamil Nadu.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, C, E, A
(b) D, E, B, C, A
(c) A, E, D, B, C
(d) C, B, A, D, E
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is B, D, C, E, A
NITI Aayog, or the National Institution for Transforming India, is a think tank of the Government of India. It was established in 2015 as a replacement for the Planning Commission. NITI Aayog's mission is to provide strategic and policy advice to the Government of India. It also serves as a platform for coordination between the central and state governments.
According to the NITI Aayog National MPI Baseline Report 2021, the percentage of the population that is multidimensionally poor is: Kerala (0.71%), Goa (3.76%), Sikkim (3.82%), Tamil Nadu (4.89%), Punjab (5.59%). Arranged in ascending order: B, D, C, E, A. The correct answer is (a).
Q42: Arrange the following chronologically in order to their year of first occurrence starting from oldest:
A. Liquidity Preference Theory
B. Multiplier by R.F. Kahn
C. Division of Labour. Adam Smith
D. Quantity theory of Money, Fisher
E. Great Depression.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, E, B, A, D
(b) E, D, C, B, A
(c) B, C, D, E, A
(d) B, A, D, C, E
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is option 1) C, E, B, A, D.
Chronological Order of Economic Theories and Events
Division of Labour by Adam Smith Hence, C is the oldest event.
- Adam Smith's concept of the Division of Labour was introduced in his seminal work "The Wealth of Nations," published in 1776.
Quantity Theory of Money by Fisher Hence, D comes after C.
- Irving Fisher formulated the Quantity Theory of Money, which was extensively developed and popularized in the early 20th century, particularly around 1911.
Multiplier by R.F. Kahn Hence, B follows D.
- R.F. Kahn introduced the concept of the Multiplier in 1931, which was further developed by Keynes.
Liquidity Preference Theory by Keynes Hence, A comes after B.
- John Maynard Keynes introduced the Liquidity Preference Theory in 1936 in his work "The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money."
Great Depression Hence, E comes last in the chronological order provided.
- The Great Depression was a severe global economic depression that took place mostly during the 1930s, beginning in the United States in 1929.
Other Related Points
Division of Labour
- This concept refers to the separation of tasks in any system so that participants may specialize.
- It is a key element in the work of Adam Smith and remains a foundational principle in economics.
Quantity Theory of Money
- This theory suggests that the general price level of goods and services is directly proportional to the amount of money in circulation.
Multiplier
- The multiplier effect explains how an initial change in spending leads to a larger change in overall economic activity.
Liquidity Preference Theory
- This theory explains the relationship between the interest rate and the demand for money, arguing that people prefer to hold their wealth in liquid form.
Great Depression
- The Great Depression was a period of worldwide economic downturn, with widespread unemployment, poverty, and significant economic disruption.
Q43: Arrange the following organizations as per their years of establishment starting from the oldest.
A. WTO
B. ADB
C. UNCTAD
D. World Bank
E. WIPO.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, C, B, E, A
(b) D, B, C, E, A
(c) D, B, C, A, E
(d) D, B, A, C, E
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is D, C, B, E, A
- The World Bank was established in 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference along with the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The World Bank's most recent stated goal is the reduction of poverty. The World Bank helps developing nations implement development projects. World Bank headquarters is in Washington, D.C., United States.
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on December 19, 1966, with its headquarters in Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The bank aims to promote social and economic development in Asia and the Pacific through inclusive economic growth, environmentally sustainable growth, and regional integration. It provides loans, grants, and technical assistance to its members, which include 68 countries, 48 from Asia and the Pacific, and 20 from outside the region.
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the General Assembly of the United Nations to provide an institutional framework for international trade negotiations and to support developing countries in their efforts to trade more effectively on international markets.
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that plays a leading role in developing and promoting international intellectual property (IP) law. It was established in 1967 and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. It was established in 1995 and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. The WTO is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations.
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. It was established in 1995 and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. The WTO is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations
Q44: Given below are two statements :
Statement I : Countries always want to have foreign markets open for their exporters. But if a country limits access to its own market, foreign countries may take action to limit access to their own market.
Statement II : Trade agreement can help lower barrier to international commerce, but countries still have to believe that other countries are "playing fair".
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statements I and Statement II are true.
Let's analyze the Statement:
- Countries often seek to protect their markets while taking advantage of others, leading to trade protections like tariffs. If a country eliminates reciprocal trade concessions and restricts its market, other countries may react similarly to protect their interests, leading to retaliatory trade restrictions.
- Trade agreements aim to lower barriers to international trading. They establish rules to ensure fair treatment of all participants, but countries must trust that others are adhering to those rules -- i.e., "playing fair."
Q45: Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: A form of market failure results when products of different qualities are sold at a single price.
Reason R : A buyer and a seller possess different information about the product transacted.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Form a market failure indeed occurs when products of different qualities are sold at a single price. This phenomenon is known as adverse selection or the lemons problem. It arises when sellers have more information about the quality of their products than buyers do. This information asymmetry leads to a situation where buyers are unwilling to pay a high price for a product, even if it is of high quality, because they fear that they are more likely to get a low-quality product.
- As a result, the market is flooded with low-quality products, driving out high-quality ones, and causing market inefficiency.
Q46: Given below are two statements :
Statement I : Capital deepening is the process by which capital grows at a faster rate than labour and the capital labour ratio rises.
Statement II : The growth of output per worker is result of technological change which decreases output per worker for a given capital/labour ratio.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Let's analyze the both statements:
- Capital deepening refers to an increase in the amount of capital per worker in an economy. This happens when capital investment grows more rapidly than the labor force, leading to a rise in the capital-to-labor ratio.
- Technological change usually leads to an increase in output per worker, not a decrease. Technological advancements typically result in enhanced efficiency and productivity, allowing for a higher output per worker for a given capital/labor ratio.
Q47: Given below are two statements :
Statement I : When the level of investment is itself determined within the system then the effectiveness of monetary policy is enhanced by an elastic investment and inelastic liquidity preference schedule, whereas the opposite holds for the effectiveness of fiscal policy.
Statement II : Monetary policy, by accommodating fiscal policy may forestall the crowding out effect.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
- Statement I is true because an elastic investment schedule means that investment is sensitive to changes in interest rates. An inelastic liquidity preference schedule means that the demand for money is not sensitive to changes in interest rates. Therefore, when the level of investment is itself determined within the system, an elastic investment schedule and inelastic liquidity preference schedule will make monetary policy more effective, as changes in interest rates will have a greater impact on investment and a smaller impact on the demand for money. Conversely, fiscal policy will be less effective, as changes in government spending or taxes will have a smaller impact on investment.
- Statement II is also true because the crowding out effect is a phenomenon in which an increase in government spending leads to an increase in interest rates, which can then crowd out private investment. Monetary policy can accommodate fiscal policy by increasing the money supply, which can help to offset the increase in interest rates caused by the increase in government spending. Therefore, monetary policy can help to forestall the crowding out effect.
Q48: Given below are two statements :
Statement I : The IS curve is negatively sloped because an increase in the interest rate reduces planned investment spending and therefore reduces the equilibrium level of income.
Statement II : The smaller the multiplier and the less sensitive investment spending is to changes in the interest rate, the steeper is the IS curve.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
Let's analyze the statement:
- The IS (Investment-Saving) curve, part of the IS-LM model in macroeconomics, is indeed negatively sloped. Higher interest rates, all else being equal, make borrowing more expensive which tends to reduce investment spending, thus leading to lower overall income and output.
- This is also true. The steepness of the IS curve is determined by the responsiveness of investment to changes in the interest rate and the size of the multiplier. If the multiplier is small, or if the investment is less sensitive to interest rate changes, then changes in the interest rate will have a smaller effect on income. Therefore, the IS curve is steeper
Q49: The demand function for good A is given by QA = 100 - 2PA + 0.2 Y + 0.3 PB. Find the income elasticities of demand PA = 6, Y = 500, PB = 10
(a) 0.06
(b) 0.02
(c) 0.52
(d) -0.06
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is: 0.52.
The demand function for good A is expressed as QA = 100 - 2PA + 0.2Y + 0.3PB. To determine the income elasticity of demand, we need to calculate how the quantity demanded of good A (QA) responds to changes in income (Y). The income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in income, and it is calculated using the following formula:
Income Elasticity of Demand (EY) = (ΔQA / QA) / (ΔY / Y)
Where:
- ΔQA: Change in quantity demanded
- QA: Quantity demanded at a specific level of income
- ΔY: Change in income
- Y: Current income level
Let's calculate the income elasticity step by step.
Step 1: Calculate QA using the demand function:
- Substituting PA = 6, Y = 500, and PB = 10 into the demand function:
- QA = 100 - 2(6) + 0.2(500) + 0.3(10)
- QA = 100 - 12 + 100 + 3 = 191
Step 2: Calculate the change in QA with respect to a change in income (Y):
- The coefficient of Y in the demand function is 0.2, which means for every unit increase in income, QA increases by 0.2 units.
Step 3: Calculate Income Elasticity:
- Using the previously mentioned elasticity formula:
- EY = (ΔQA / QA) / (ΔY / Y)
- Assuming a small change in income (ΔY = 1):
- EY = (0.2 / 191) / (1 / 500)
- EY = (0.2 * 500) / 191 = 100 / 191 ≈ 0.52
Other Related Points
Understanding Income Elasticity:
- A positive income elasticity indicates that the good is a normal good; as income increases, the demand for good A increases.
- An elasticity of 0.52 suggests that demand for good A is relatively inelastic concerning income changes, meaning that demand increases at a lower rate than income.
Application of Elasticity:
- Income elasticity is crucial for businesses to understand market behavior and forecast demand changes based on economic trends.
- It aids in making informed pricing and production decisions to align with consumer income changes.
Market Implications:
- Policy-makers can use income elasticity insights to design economic policies that target low-income groups effectively and enhance welfare through appropriate interventions.
Q50: A player tosses two fair coins. He wins Rs. 5 if 2 heads occur, Rs 2 if 1 head occurs and Rs. 1 if no head occurs. Find his expected gain.
(a) Rs. 2
(b) Rs. 2.25
(c) Rs. 2.75
(d) Rs. 2.50
Ans: d
Sol: Expected gain is Rs. 2.50
To find the expected gain in this scenario, we first list all the possible outcomes of tossing two fair coins and then calculate the probability of each outcome.
We'll multiply each outcome's probability by the corresponding gain and sum these products to get the expected gain.
Let's denote the outcomes as follows:
HH = Both coins show heads
HT or TH = One coin shows heads, and the other shows tails
TT = Both coins show tails
Since the coins are fair, the probability of landing a head (H) or a tail (T) for any single toss is 0.5.
Now, let's calculate the probability of each outcome:
Probability of getting 2 heads (HH): (0.5 \times 0.5 = 0.25)
Probability of getting 1 head (HT or TH): There are two ways this can happen (HT or TH), so the probability is (0.5 \times 0.5 + 0.5 \times 0.5 = 0.5)
Probability of getting no heads (TT): (0.5 \times 0.5 = 0.25)
Next, we multiply each probability by the corresponding gain.
Gain for 2 heads = Rs. 5, Probability = 0.25. So, expected gain = (5 \times 0.25 = Rs.\ 1.25)
Gain for 1 head = Rs. 2, Probability = 0.5. So, expected gain = (2 \times 0.5 = Rs.\ 1.00)
Gain for no heads = Rs. 1, Probability = 0.25. So, expected gain = (1 \times 0.25 = Rs.\ 0.25)
Finally, to find the total expected gain, we sum these expected gains: [Rs.1.25 (for HH) + Rs. 1.00 (for HT or TH) + Rs. 0.25 (for TT) = Rs. 2.50.
Therefore, the player's expected gain from tossing two fair coins under the given conditions is Rs. 2.50.
Q51: A card is thrown from a well shuffled pack of playing cards. Find the probability that it is either a diamond or a king.
(a) 17/52
(b) 16/52
(c) 18/52
(d) 15/52
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 16/52
- A standard deck of playing cards contains 52 cards: 4 suits (hearts, diamonds, clubs, and spades) with 13 cards each (Ace through 10, and the face cards Jack, Queen, and King).
- To find the probability that a card drawn is either a diamond or a king from a well-shuffled pack of 52 playing cards, we'll follow these steps:
- Total number of possible outcomes: The deck has 52 cards.
- Favorable outcomes for a diamond: There are 13 diamonds in a deck.
- Favorable outcomes for a king: There are 4 kings in a deck.
- However, there's an overlap in our count since one of the kings is also a diamond (the King of Diamonds). To ensure we don't count this card twice, we need to subtract it from our total count of favorable outcomes.
- Total number of favorable outcomes = Number of diamonds + Number of kings - Overlap (King of Diamonds)
- Total favorable outcomes = 13 (diamonds) + 4 (kings) - 1 (King of Diamonds)
- Total favorable outcomes = 16
- The probability (P) of drawing either a diamond or a king is the total number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes. It becomes 16/52
Q52: Who was the chairman of 14th Finance Commission in India ?
(a) Dr. Vijay Kelkar
(b) Dr Y.V. Reddy
(c) Dr. C. Rangarajan
(d) Dr. N.K. Singh
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Dr Y.V. Reddy'
The 14th Finance Commission was constituted in January 2013, chaired by Dr. Y.V. Reddy, with recommendations for 2015–2020. Other options:
- (a) Dr. Vijay Kelkar: 13th Finance Commission (2010–2015).
- (c) Dr. C. Rangarajan: 12th Finance Commission (2005–2010).
- (d) Dr. N.K. Singh: 15th Finance Commission (2021–2026).
Correct answer: (b) Dr. Y.V. Reddy.
Other Related Points
Overview of Other Options:
Dr. Vijay Kelkar:
- He was the chairman of the 13th Finance Commission, which covered the period from 2010 to 2015.
Dr. C. Rangarajan:
- He was the chairman of the 12th Finance Commission, which covered the period from 2005 to 2010.
Dr. N.K. Singh:
- He was the chairman of the 15th Finance Commission, which covers the period from 2020 to 2025.
Q53: Zamindari Tenure was introduced by :
(a) Thomas Munro
(b) Lord Cornwallis
(c) H. Venkatasubbiah
(d) G. Myrdal
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Lord Cornwallis
- Zamindari Tenure was introduced by Lord Cornwallis in 1793 during British rule in India. The system aimed to streamline revenue collection by establishing landlords, known as zamindars, as intermediaries between the British government and the peasants.
- To simplify the process of revenue collection: The British administration sought to establish a stable and efficient system for collecting land revenue.
- To create a class of loyal intermediaries: The zamindars were expected to act as intermediaries between the British government and the peasants.
- To promote agriculture: The British believed that private ownership of land would incentivize investment in agriculture and increase productivity.
Q54: ‘Which of the followings are true about a fair game or fair bet ?
A. The entry of a fair bet is zero
B. The person who accepts fair bet is said to be risk lover
C. expected value of income from the bet is equal to the same amount of income with certainty
D. The person who refuses a fair bet is said to be risk neutral
E. The person who refuses a fair bet is said to be risk averse.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) B and E only
(c) C and D only
(d) C and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is C and E only
In discussing the characteristics and implications of participating in a fair game or bet, key definitions and personality types related to risk preferences are considered. A fair bet is defined as a gamble where the expected value of the net winnings is zero. Let's look at each statement:
A. This statement seems to intend to say "The expected value of a fair bet is zero," which is true for a fair bet since the expected value of winnings minus losses sums to zero. However, the phrasing "entry of a fair bet" is unclear but might be interpreted in context as referring to the expected value.
B. The statement that a person who accepts a fair bet is a risk lover is accurate. Risk lovers are individuals who derive utility from the gamble itself, beyond the expected monetary gain. They are willing to participate in a fair (or even unfair) bet because the gamble increases their utility.
C. True, the expected value from a fair bet is equal to the same amount of income with certainty, by the definition of a fair bet.
D. The statement incorrectly attributes risk neutrality to the refusal of a fair bet. A risk-neutral person is indifferent between a certain outcome and a gamble with the same expected value. Therefore, a risk-neutral person might or might not accept a fair bet based on factors other than risk preference, making this statement inaccurate for describing refusal of a fair bet.
E. True, a person who refuses a fair bet is said to be risk-averse. Risk-averse individuals prefer to avoid risk when possible, and they would decline a fair bet because they derive more utility from certainty than from the risk of the bet, even when the expected values are equal.
Given the analysis, the correct answer is:
Option 4) C and E only.
Q55: According to the modern theory of rent
A. All the factors may earn rent
B. Rent can only be earned in long-run
C. Transfer earning of an unused factor is zero
D. Only land can earn rent
E. Entire earning of an unused factor is economic rent.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, C, and E only
- According to the modern theory of rent, rent is not a unique feature of land, but rather it is a surplus that arises due to the difference between actual earnings and opportunity cost or transfer earnings. This means that any factor of production, including land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship, can earn rent if its marginal revenue product is greater than its opportunity cost.
- Rent may arise due to temporary factors such as market imperfections or technological innovation. In the long run, rent may persist due to more fundamental factors such as the scarcity of resources or the immobility of factors of production.
- The transfer earnings of an unused factor are not necessarily zero. The transfer earnings of an unused factor represent the value of the factor's output in its next best alternative use. If the factor's transfer earnings are positive, then it is earning rent in its current use.
- land is not the only factor of production that can earn rent. As mentioned above, any factor of production can earn rent if its marginal revenue product is greater than its opportunity cost.
- The entire earning of an unused factor is not necessarily economic rent. Economic rent is defined as the surplus that arises due to the difference between actual earnings and opportunity cost. If the factor's entire earning is equal to its opportunity cost, then it is not earning any economic rent.
Q56: How do adverse technology shocks affect labour demand and supply?
A. Decrease the demand for labour
B. Both real wage and employment fall
C. Real wage increases and employment falls
D. Real wage falls and employment increases
E. Adverse effect on market equilibrium.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) B, D and E only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: d
Sol: A, B and E only
A. Decrease the demand for labour
Adverse technology shocks, such as a decline in the productivity or the efficiency of technology, could decrease the demand for labor. This happens because firms and industries typically rely on technology to increase productivity, which allows them to employ fewer labor hours for the same level of output. If a technology shock makes technology less effective, firms might find that they require more labor hours to achieve the same output. However, because they're also now getting less output per unit of capital, firms may look for ways to cut costs—including through layoffs or hiring freezes. Hence, the demand for labor could decrease.
Real wage and employment may fall
The reduction in demand for labor due to an adverse technology shock likely leads to both a decrease in real wage and employment. The reasoning is straightforward—when the demand for labor decreases, there is downward pressure on wages (i.e., the price of labor) as firms seek to cut costs. Additionally, lower demand for labor means fewer jobs are available, causing employment to fall.
E. Adverse effect on market equilibrium.
Labor market equilibrium is reached when the supply of labor equals the demand for labor. An adverse technology shock disrupts this equilibrium because it reduces the demand for labor. As the demand curve shifts left, the equilibrium wage and the level of employment both decrease. At the same time, the supply of labor could change in response to lower real wages (though the direction of this change can depend on whether the income or substitution effect dominates).
To summarize, an adverse technology shock can have a range of negative impacts on the labor market, including a fall in the demand for labor, a decrease in real wages and employment, and a disruption to market equilibrium. These effects illustrate the intricate connections between technology, labor demand, wages, and market equilibrium. This detailed explanation aligns with options A, B, and E as the correct answers.
Q57: Which of the followings are correct conclusions without error in case of testing of Hypothesis ?
A. Reject null hypothesis (Ho), when it is true
B. Accept Ho, when it is true
C. Accept Ho, when Alternate hypothesis (H1) is true.
D. Reject Ho when H1 is true.
E. Accept Ho when H1 is false.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) B, D and E only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) A, C and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is B, D, and E only.
Testing of Hypothesis:
- Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to make decisions using experimental data.
- It involves making an assumption (null hypothesis) and determining whether there is enough evidence to reject it in favor of an alternative hypothesis.
Correct conclusions in hypothesis testing:
- B. Accept Ho, when it is true. This means that we have correctly identified that there is no effect or no difference as stated in the null hypothesis. It is one of the desired outcomes of hypothesis testing and indicates a true negative result. In other words, the sample data supports the null hypothesis, and this conclusion aligns with the actual state of nature. Hence, the Statement B is correct.
- D. Reject Ho when H1 is true. This outcome is crucial because it ensures that we are not mistakenly identifying an effect or difference that does not exist. By accepting Null Hypothesis Ho, when it is true, we avoid a Type I error, which can lead to incorrect conclusions and potential consequences in practical applications. Hence, the Statement D is correct.
- E. Accept Ho when H1 is false. Hence, the Statement E is correct.
Other Related Points
Explanation of incorrect statements:
- A. Rejecting the null hypothesis (Ho) when it is true is a Type I error, not a correct conclusion.
- C. Accepting the null hypothesis (Ho) when the alternative hypothesis (H1) is true is a Type II error, not a correct conclusion.
Additional key points:
- A Type I error occurs when the null hypothesis is true, but is incorrectly rejected.
- A Type II error occurs when the null hypothesis is false, but is incorrectly accepted.
- The goal in hypothesis testing is to minimize both Type I and Type II errors to make accurate conclusions.
Q58: Which of the following are correct for the Finance Commission ?
A. It is constituted under Article 380 of the Constitution
B. It is a statutory body
C. It is constituted under Article 280 of the Constitution
D. Prof. K C Pant was Chairman of 10th Finance Commission
E. Dr. Vijay Kelkar was Chairman of 14th Finance Commission.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) C and D only
(b) A, B and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) A, C and E only
Ans: a
Sol: C and D only is the right answer.
The Finance Commission is a constitutional body under Article 280 (C, true). K.C. Pant chaired the 10th Finance Commission (1992–1995) (D, true). Incorrect options:
- A: False; it’s Article 280, not 380.
- B: False; it’s a constitutional, not statutory, body.
- E: False; Dr. Y.V. Reddy chaired the 14th Finance Commission (2015–2020), not Vijay Kelkar (13th, 2010–2015).
Correct answer: (a) C and D only.
Q59: Which of the following are true ?
A. Product taxes will raise prices less under monopoly than under competition
B. A tax on capital income tends to be progressive, whereas tax on wage income tends to be regressive
C. The burden of tax will be distributed between sellers and buyers in the ratio of elasticity of demand to that of supply.
D. A unit tax enters through a parallel downward shift in the supply schedule
E. Imposition of tax raises price and quantity.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) A, B and C only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) A, B, C and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, and C only'
Product Taxes Under Monopoly and Competition:
- Under monopoly, the monopolist can set prices and may absorb some of the tax burden, leading to a smaller price increase compared to a competitive market where prices are set by market forces.
Progressive vs. Regressive Taxes:
- A tax on capital income tends to be progressive because it affects higher-income individuals more.
- A tax on wage income tends to be regressive because it affects lower-income individuals more.
Tax Burden Distribution:
- The burden of a tax is distributed between sellers and buyers based on the relative elasticities of demand and supply.
- If demand is more elastic than supply, producers bear a larger share of the tax burden, and vice versa.
Other Related Points
Effect of Unit Tax on Supply Schedule:
- A unit tax may not always cause a parallel downward shift in the supply schedule, meaning that the supply curve shifts vertically downwards by the amount of the tax.
- This effectively increases the cost of production for suppliers, leading to a higher price for consumers and a lower quantity supplied.
Imposition of Tax:
- Imposition of a tax generally raises the price of the good but reduces the quantity demanded and supplied. Therefore, statement E is incorrect because the quantity typically decreases, not increases.
Q60: Which of the followings are correct in case of money market in India?
A. Commercial bill is a short-term instrument with high risk
B. Treasury bill is an instrument of short-term borrowing by the government with absence of default risk
C. RBI uses refinance to relieve liquidity shortages in the system
D. The RBI has switched over from daily fixed rate repos auction system to discriminatory price auction repos.
E. SLR enables to impose secondary and supplementary reserve requirements on the banking system.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A, B and D only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'B, C and E only'
Treasury Bill (T-Bill):
- A treasury bill is a short-term government security with a maturity of less than one year.
- It is used by the government to raise short-term funds and is considered to have an absence of default risk due to government backing.
Refinance by RBI:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) uses refinance facilities to relieve liquidity shortages in the financial system.
- Refinance facilities provide banks with additional funds to meet short-term needs and manage liquidity.
Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR):
- SLR is the percentage of net demand and time liabilities that banks are required to maintain in the form of liquid assets.
- It enables the imposition of secondary and supplementary reserve requirements on the banking system, ensuring that banks have a buffer of liquid assets.
Other Related Points
Incorrect Options Explained:
A: Commercial Bill:
- A commercial bill is a short-term instrument but it generally has low risk compared to other financial instruments.
D: Repos Auction System:
- The RBI has adopted a fixed rate repo auction system, not a discriminatory price auction repo system. Therefore, statement D is incorrect.
Q61: Which of the following are the features of Environmental Economics as a field of study ?
A. It has its roots in the theory of externalities and public goods.
B. It is based on neoclassical welfare theory
C. It envisions human economy as a sub-system of the biosphere
D. It engages with the law of transformations of matter and energy
E. It focuses on finding the most efficient ways to reducing environmental damages.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, B and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct code is A, B, and E only.
It has its roots in the theory of externalities and public goods. This statement is correct.
- Environmental economics often deals with externalities (unintended side effects of economic activities) and public goods (goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous).
It is based on neoclassical welfare theory. This statement is correct.
- Environmental economics often uses concepts from neoclassical welfare theory to assess the economic impacts of environmental policies and regulations.
- It envisions human economy as a sub-system of the biosphere. This statement is incorrect.
- It engages with the law of transformations of matter and energy. This statement is incorrect.
It focuses on finding the most efficient ways to reducing environmental damages. This statement is correct.
- Environmental economics seeks to identify cost-effective measures to mitigate environmental harm.
Other Related Points
It envisions human economy as a sub-system of the biosphere.
- This statement is more characteristic of ecological economics rather than traditional environmental economics.
It engages with the law of transformations of matter and energy.
- This also aligns more closely with ecological economics, which integrates principles from ecology and thermodynamics.
Q62: Which of the following are the essential features of weak sustainability ?
A. It considers human-made capital and natural capital as close substitutes.
B. It puts emphasis on the initial size of an economy since the size of the initial capital stock is considered relevant.
C. It requires from each generation to ensure that their actions do not compromise the productive capacity of the generations to follow
D. the composition of the capital stock of an economy does not hold great significance
E. It renders natural capital as an absolute necessity for sustaining net national income over an indefinite period.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) A, B and C only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct code is A, C, and D only.
It considers human-made capital and natural capital as close substitutes. This statement is correct.
- Weak sustainability assumes that human-made capital can substitute for natural capital, meaning that as long as the total capital stock is maintained, it doesn't matter if natural capital is depleted.
- It puts emphasis on the initial size of an economy since the size of the initial capital stock is considered relevant. This statement is incorrect.
It requires from each generation to ensure that their actions do not compromise the productive capacity of the generations to follow. This statement is correct.
- This aligns with the principle of intergenerational equity, ensuring that future generations have the same opportunities and resources as the current generation.
The composition of the capital stock of an economy does not hold great significance. This statement is correct.
- Weak sustainability is concerned with the overall capital stock rather than the specific composition, allowing for substitution between natural and human-made capital.
- It renders natural capital as an absolute necessity for sustaining net national income over an indefinite period. This statement is incorrect.
Other Related Points
It puts emphasis on the initial size of an economy since the size of the initial capital stock is considered relevant.
- This statement does not typically align with the concept of weak sustainability, which focuses more on maintaining overall capital stock rather than the initial size of the economy.
It renders natural capital as an absolute necessity for sustaining net national income over an indefinite period.
- This concept is more aligned with strong sustainability, which emphasizes the irreplaceable nature of natural capital.
Q63: Marshall-Lerner condition states that:
A. Devaluation will improve the country's balance of payments if the sum of price elasticities of demand for exports and imports in absolute terms is greater than one.
B. Devaluation will increase the balance of payments deficit if the sum of the price elasticities of demand for exports and imports is less than one.
C. Devaluation will have no effect on the balance of payment situation if the sum of the price elasticises of demand for exports and imports is equal to one
D. In no case, devaluation can improve the balance of payment disequilibrium if either the price elasticities of demand for export or that of import is zero.
E. Marshall-Lerner condition has no relation with BOP situation.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and A only
(d) A, B and C only
Ans: d
Sol: A, B and C only
The Marshall-Lerner condition is a principle in international economics which states that currency devaluation will only lead to an improvement in the trade balance if the absolute sum of the long-term price elasticities of demand for imports and exports is greater than one. Below, each statement related to the Marshall-Lerner condition is explained:
Q64: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Detecting Serial Correlation (A):
- Serial correlation (or autocorrelation) occurs when the residuals (errors) in a regression model are correlated across observations. One common test to detect serial correlation is The Run's test.
Detection of Heteroscedasticity (B):
- Heteroscedasticity is a condition in which the variance of errors differs across observations in a regression model. The Goldfeld-Quandt test is a common method to detect heteroscedasticity.
Detection of Multicollinearity (C):
- Multicollinearity occurs when independent variables in a regression model are highly correlated. One way to detect multicollinearity is by calculating the Condition Index.
Test of Specification Error (D):
- Specification error occurs when the model is incorrectly specified, such as omitting a relevant variable or including an irrelevant one. Ramsay's RESET test (Regression Specification Error Test) is used to detect specification errors.
Q65: Match List I with List II
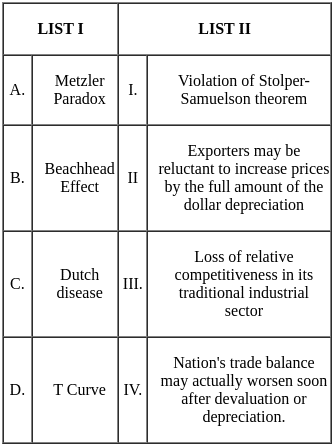
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(c) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct option is 'A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV'.
Metzler Paradox (A - I):
- The Metzler Paradox refers to a situation where a tariff on imports can lead to a decrease in the relative price of the import-competing good, which is a violation of the Stolper-Samuelson theorem. This paradox occurs under specific conditions in international trade theory.
Beachhead Effect (B - II):
- The Beachhead Effect suggests that exporters may be reluctant to increase prices by the full amount of the dollar depreciation. This effect occurs because firms established in a foreign market may prefer to maintain market share rather than fully adjust prices in response to currency fluctuations.
Dutch Disease (C - III):
- Dutch Disease describes the negative consequences that can arise from a rapid increase in a country's wealth, particularly from natural resources, leading to a loss of relative competitiveness in its traditional industrial sector. This effect can cause a decline in manufacturing and other export sectors.
T Curve (D - IV):
- The T Curve, also known as the J Curve, suggests that a nation's trade balance may actually worsen soon after a devaluation or depreciation of its currency before it starts to improve. This initial deterioration occurs due to the higher cost of imports and the delayed response in export volume.
Other Related Points
Metzler Paradox:
- This paradox demonstrates a counterintuitive outcome in international trade where protective tariffs may not always lead to expected increases in domestic prices.
Beachhead Effect:
- Firms may choose to absorb some of the currency depreciation impacts to maintain their competitive position and market share in the foreign market.
Dutch Disease:
- This phenomenon often affects countries with significant natural resource discoveries, leading to currency appreciation and making other export sectors less competitive.
T Curve (J Curve):
- The initial worsening of the trade balance is due to the higher cost of imports, which gradually improves as exports increase in response to the lower currency value.
Q66: Match List I with List II
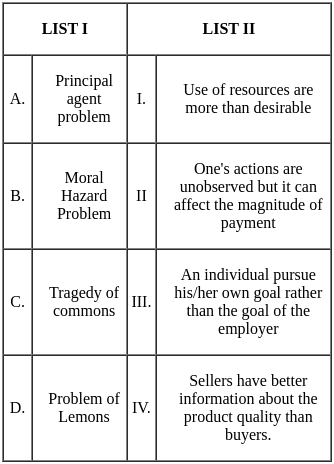
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
- Principal-agent problem: The principal-agent problem arises when one party (the principal) entrusts another party (the agent) to act on their behalf. The problem arises because the agent may not act in the best interests of the principal, but instead may pursue their own self-interest.
- Moral hazard problem: The moral hazard problem is a specific type of principal-agent problem that arises when the agent's actions are unobserved by the principal. This makes it difficult for the principal to ensure that the agent is acting in their best interests.
- Tragedy of the commons: The tragedy of the commons refers to a situation in which individuals overexploit a shared resource, leading to its depletion or degradation. This occurs because individuals act in their own self-interest, without considering the long-term consequences of their actions for the group as a whole.
- Problem of lemons: The problem of lemons refers to a situation in which there is asymmetric information in the market for a good. This means that sellers know more about the quality of the good than buyers do. As a result, buyers may be hesitant to purchase the good, even if it is of high quality because they fear that they may be buying a lemon (a low-quality good)
Q67: Read the following passage and answer the questions.
The Nobel Prize in Economics in 2022 has been awarded to Ben S. Bernanke, Douglas, W. Diamond and Philip H Dybvig "for research on banks and financial crisis". One of the important findings in their research is why avoiding bank collapses is vital. Saving must be channelled to investments for the functioning and growth of any economy. But there arises a conflict - while the savers want instant access to their money for unexpected outlays, the borrowers need to know they will not be forced to repay their loans prematurely. Diamond and Dybvig, show how banks offer an optimal solution to this problem. Banks may act as intermediaries, who accept deposits from savers and allow access to their money, when they wish and also offer long term loans to borrowers. But the analysis of these authors also shows banks are vulnerable to rumours and they may lead to their imminent collapse, when a large number of savers simultaneously, run to a bank to withdraw their money- a bank ran occurs and the bank collapses. such dangerous dynamics can be prevented through the government by providing deposit insurance and acting as a lender of last resort to banks. Diamond demonstrated another societally important function by a bank. Banks as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, are in a better position to assess a borrower's creditworthiness and ensure that loans are used for good investments. "The laureates insights have improved our ability to avoid both serious crisis and expensive bailouts."
What conflict do the bankers face while channeling saving into investment?
(a) While the borrowers want instant closing of the loan, the savers wants systematic withdrawals.
(b) While the savers want instant access to their money, the borrowers want to repay their loans, only when it matures.
(c) While the savers want instant closing of the loan, the borrowers demand more loan than their credit worthiness.
(d) Both the savers and borrowers want to close the loan immediately.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is While the savers want instant access to their money, the borrowers want to repay their loans, only when it matures.
Bankers face a fundamental conflict while channeling savings into investments. They must balance the competing demands of savers and borrowers. Savers desire immediate access to their funds to meet unexpected expenses or emergencies. In contrast, borrowers require assurance that their loans will not be prematurely demanded, allowing them to make long-term investments and generate returns. This inherent tension poses a challenge for bankers seeking to efficiently allocate savings towards productive investments.
Q68: Read the following passage and answer the questions.
The Nobel Prize in Economics in 2022 has been awarded to Ben S. Bernanke, Douglas, W. Diamond and Philip H Dybvig "for research on banks and financial crisis ". One of the important findings in their research is why avoiding bank collapses is vital. Saving must be channelled to investments for the functioning and growth of any economy. But there arises a conflict - while the savers want instant access to their money for unexpected outlays, the borrowers need to know they will not be forced to repay their loans prematurely. Diamond and Dybvig, show how banks offer an optimal solution to this problem. Banks may act as intermediaries, who accept deposits from savers and allow access to their money, when they wish and also offer long term loans to borrowers. But the analysis of these authors also shows banks are vulnerable to rumours and they may lead to their imminent collapse, when a large number of savers simultaneously, run to a bank to withdraw their money- a bank ran occurs and the bank collapses. such dangerous dynamics can be prevented through the government by providing deposit insurance and acting as a lender of last resort to banks. Diamond demonstrated another societally important function by a bank. Banks as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, are in a better position to assess a borrower's creditworthiness and ensure that loans are used for good investments. "The laureates insights have improved our ability to avoid both serious crisis and expensive bailouts."
What solution does the Diamond and Dybvig's theory offer to the conflict faced by the bankers while channeling savings into investments?
(a) Banks assure instant access to money to the savers and terminate long term project of borrowers
(b) Banks assure long-term finance to borrowers and terminate the savers’ accounts
(c) Banks act as intermediaries that accept deposits from savers and allow them access to their money when they wish, while also offering long term loans to borrowers
(d) All the above options were offered by Diamond and Dybvig's theory
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Banks act as intermediaries that accept deposits from savers and allow them access to their money when they wish, while also offering long term loans to borrowers
The Diamond-Dybvig model offers a solution to the conflict faced by bankers while channeling savings into investments by proposing the concept of deposit insurance. This mechanism provides a safety net for depositors, ensuring that a portion of their money remains protected even if the bank fails. This assurance helps to alleviate depositors' concerns about potential losses and reduces the likelihood of panic-driven withdrawals, which can destabilize banks and trigger financial crisis.
Q69: Read the following passage and answer the questions.
The Nobel Prize in Economics in 2022 has been awarded to Ben S. Bernanke, Douglas, W. Diamond and Philip H Dybvig "for research on banks and financial crisis". One of the important findings in their research is why avoiding bank collapses is vital. Saving must be channelled to investments for the functioning and growth of any economy. But there arises a conflict - while the savers want instant access to their money for unexpected outlays, the borrowers need to know they will not be forced to repay their loans prematurely. Diamond and Dybvig, show how banks offer an optimal solution to this problem. Banks may act as intermediaries, who accept deposits from savers and allow access to their money, when they wish and also offer long term loans to borrowers. But the analysis of these authors also shows banks are vulnerable to rumours and they may lead to their imminent collapse, when a large number of savers simultaneously, run to a bank to withdraw their money- a bank ran occurs and the bank collapses. such dangerous dynamics can be prevented through the government by providing deposit insurance and acting as a lender of last resort to banks. Diamond demonstrated another societally important function by a bank. Banks as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, are in a better position to assess a borrower's creditworthiness and ensure that loans are used for good investments. "The laureates insights have improved our ability to avoid both serious crisis and expensive bailouts."
According to the laureates, what leads to imminent collapse of banks?
(a) Fraudulent behaviour of the borrowers
(b) Increasing competition in the banking sector
(c) When a large number of savers simultaneously withdraw their money
(d) When a large number of borrowers simultaneously borrow money from the bank
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is When a large number of savers simultaneously withdraw their money
The laureates identify rumors as a primary factor contributing to the imminent collapse of banks. They explain that when rumors about a bank's stability spread, it can trigger a surge in depositors simultaneously withdrawing their funds, leading to a liquidity crisis and ultimately causing the bank's collapse. This phenomenon is known as a bank run.
Q70: Read the following passage and answer the questions.
The Nobel Prize in Economics in 2022 has been awarded to Ben S. Bernanke, Douglas, W. Diamond and Philip H Dybvig "for research on banks and financial crisis ". One of the important findings in their research is why avoiding bank collapses is vital. Saving must be channelled to investments for the functioning and growth of any economy. But there arises a conflict - while the savers want instant access to their money for unexpected outlays, the borrowers need to know they will not be forced to repay their loans prematurely. Diamond and Dybvig, show how banks offer an optimal solution to this problem. Banks may act as intermediaries, who accept deposits from savers and allow access to their money, when they wish and also offer long term loans to borrowers. But the analysis of these authors also shows banks are vulnerable to rumours and they may lead to their imminent collapse, when a large number of savers simultaneously, run to a bank to withdraw their money- a bank ran occurs and the bank collapses. such dangerous dynamics can be prevented through the government by providing deposit insurance and acting as a lender of last resort to banks. Diamond demonstrated another societally important function by a bank. Banks as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, are in a better position to assess a borrower's creditworthiness and ensure that loans are used for good investments. "The laureates insights have improved our ability to avoid both serious crisis and expensive bailouts."
What do the laureates suggest to prevent rumours-led bank collapses ?
(a) Reduce lending
(b) Increase lending
(c) Collaboration with other banks
(d) Government should provide deposit insurance and act as lender of last resort.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Government should provide deposit insurance and act as lender of last resort.
The laureates suggest two main ways to prevent rumor-led bank collapses:
- Deposit insurance: This would involve the government guaranteeing a certain amount of each depositor's money, even if the bank fails. This would help to prevent depositors from running to the bank to withdraw their money in a panic, as they would know that their money is safe.
- Lender of last resort: This would involve the government lending money to banks that are facing liquidity problems. This would help to prevent banks from failing, as they would know that they have a source of funding if they need it.
Q71: Read the following passage and answer the questions.
The Nobel Prize in Economics in 2022 has been awarded to Ben S. Bernanke, Douglas, W. Diamond and Philip H Dybvig "for research on banks and financial crisis". One of the important findings in their research is why avoiding bank collapses is vital. Saving must be channelled to investments for the functioning and growth of any economy. But there arises a conflict - while the savers want instant access to their money for unexpected outlays, the borrowers need to know they will not be forced to repay their loans prematurely. Diamond and Dybvig, show how banks offer an optimal solution to this problem. Banks may act as intermediaries, who accept deposits from savers and allow access to their money, when they wish and also offer long term loans to borrowers. But the analysis of these authors also shows banks are vulnerable to rumours and they may lead to their imminent collapse, when a large number of savers simultaneously, run to a bank to withdraw their money- a bank ran occurs and the bank collapses. such dangerous dynamics can be prevented through the government by providing deposit insurance and acting as a lender of last resort to banks. Diamond demonstrated another societally important function by a bank. Banks as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, are in a better position to assess a borrower's creditworthiness and ensure that loans are used for good investments. "The laureates insights have improved our ability to avoid both serious crisis and expensive bailouts."
According to Diamond, how do banks ensure that loans are used for good investments?
(a) Since banks act as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, they have better idea about the creditworthiness of the borrowers and hence can ensure loans are used for good investments.
(b) Since banks want to maximize profits, it can ensure loans are used for good investments
(c) Since bank want to benefit their customers, they can ensure that loans are used for good investment.
(d) Banks do not have enough information to ensure loans are used for good investment
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Since banks act as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, they have better idea about the creditworthiness of the borrowers and hence can ensure loans are used for good investments.
According to Diamond, banks ensure that loans are used for good investments by acting as intermediaries between savers and borrowers. This means that banks collect deposits from savers and then lend this money to borrowers. Banks are able to do this because they have a better understanding of the creditworthiness of borrowers than savers do. This is because banks have access to more information about borrowers, such as their financial history and business plans.
Q72: The Rural Landless Employment guarantee Programme (RLEGP) was launched on :
(a) 15th August 1947
(b) 15th August 1950
(c) 15th August 1983
(d) 15th August 2000
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 15th August 1983
- The Rural Landless Employment Guarantee Programme (RLEGP) was launched in India on August 15, 1983. It aimed to provide holds and those with marginal lands during the lean agricultural season.
- Guarantee of Employment: The RLEGP program guaranteed employment to at least one member of every landless laborer's family for up to 100 days in a year.
- Labour-Intensive Works: The program gave priority to labor-intensive works, especially those that would lead to the creation of durable assets in rural areas. The projects approved under the program included soil conservation, afforestation, rural connectivity, minor irrigation works, and the like, which would also aid in the overall development of the rural economy.
- Women Empowerment: The Programme aimed to provide at least 30% of the jobs to women to support gender equality and women's empowerment in rural areas.
- Building Infrastructure: The focus was also on infrastructural development of the rural regions, increasing overall productivity and facilitating economic growth.
Q73: In logit model, as the odds ratio decreases from 1 to 0, the logit becomes
(a) Negative
(b) Equal to 0
(c) Positive
(d) Fraction
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Negative.
- As the odds ratio (OR) decreases from 1 to 0, the logit, the natural log of the odds ratio, approaches negative infinity.
- to clarify this in a bit more detail:
- In a logistic regression model, the dependent variable is logged in a "logit" form, or the log-odds. If p denotes the probability of the event, then the logit is given by: Logit(p) = log(p/(1-p))
- As p slides from 1 towards 0, the odds p/(1-p) reduce from positive infinity to 0. When taking the natural log (log base e) of these odds to get the logit, as the odds decrease from 1 (the even odds point) to 0, the logit goes from 0 to negative infinity.
Q74: Rational expectations views include :
A. The market clearing rational expectations do not approach to the Phillips curve
B. Rational expectation as a theory of expectations
C. An emphasis on the credibility of policy makers
D. A preference for policy making rules rather than discretion
E. Generally insists that markets do not clear rapidly.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and D only
(b) A and E only
(c) A, B, C, D and E
(d) A, D and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is B, C and D only
- Rational expectations theory suggests that economic agents form expectations based on all available information, including past experience and knowledge of economic models. This implies that markets will not react quickly to policy changes, as agents will take time to understand and adjust their expectations.
- Rational expectations is an economic theory that states that individuals make decisions based on the best available information in the market and learn from past trends. Rational expectations suggest that people will be wrong sometimes, but that, on average, they will be correct,
- Standard models of policy credibility, defined as the expectation that an announced policy will be carried out, emphasize the preferences of the policymaker, and the role of tough policies in signalling toughness and raising credibility.
- A preference for policy-making rules rather than discretion. This is because rules are seen as more credible than discretion, and therefore more likely to be effective in influencing the expectations of economic agents.
Q75: In the budget at glance, which of the following items are included ?
A. budget estimate of the current year
B. Revised estimate of the current year
C. Actuals of the current year
D. Actuals for the preceding year
E. Budget estimate for the forthcoming year.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A and D only
(b) A, B, D and E only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) C and D only
Ans: b
Sol: A, B, D and E only
The Budget at a Glance includes:
- A: Budget estimate of the current year (planned allocations).
- B: Revised estimate of the current year (adjusted based on mid-year data).
- D: Actuals for the preceding year (final expenditure/revenue).
- E: Budget estimate for the forthcoming year (projected allocations).
- C: Actuals of the current year are not included, as they are finalized post-year.
Correct answer: (b) A, B, D, and E only.
Q76: Which of the followings are correct for OLS estimation in the presence of Heteroscedasticity ?
A. The estimated coefficients are linear
B. The estimated coefficients are unbiased
C. The estimated coefficients are biased
D. The estimated coefficients are consistent
E. The estimated coefficients are efficient.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and D only
(b) A, B and D only
(c) A, C and E only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: b
Sol: A, B and D only
In Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) estimation, when heteroscedasticity (i.e., a situation in which the variance of the error term, or residual, is not constant) is present:
Q77: Which of the following are correct ?
A. A competitive market can secure efficient resource use in the provision of private goods, but market failure occurs in that of social goods
B. Efficient provision of social goods involves horizontal rather than vertical addition of Individual pseudo-demand schedules
C. To seek efficient provision of social goods, a political process of budget determination is needed
D. Corrective action may be needed when consumer choice is based on false advertising
E. There are mixed cases between the extremes of purely private and purely social goods.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, B and E only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) A, C, D and E only
Ans: d
Sol: A, C, D and E only
A. A competitive market can secure efficient resource use in the provision of private goods, but market failure occurs in that of social goods
This is true. In a competitive market, resources are efficiently allocated in the provision of private goods due to the inherent self-interest of consumers and producers. However, for public or social goods (which are non-excludable and non-rival in consumption), free-market mechanisms often fail to achieve efficient provision, leading to so-called "market failures".
Q78: Measurement of income inequality is done by :
A. Gini coefficient
B. Lorenz curve
C. Palma Ratio
D. Deprivation ratio
E. Phillips Curve
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B and E only
(b) A and B only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) C and A only
Ans: c
Sol: A, B and C only.
A. Gini coefficient: The Gini coefficient is a measure of inequality of a distribution. It is defined as a ratio with values between 0 and 1: a low Gini coefficient indicates more equal income or distribution, while a high Gini coefficient indicates more unequal distribution.
B. Lorenz curve: The Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of the distribution of income or distribution of wealth. It shows the proportion of the total income or wealth assumed by the bottom x% of the people, although this is not rigorously true for a finite population. It is often used along with the Gini coefficient to provide a graphical illustration of income or wealth disparity.
C. Palma Ratio: Palma Ratio refers to the ratio of the richest 10% of the population's share of gross national income (GNI) divided by the poorest 40%'s share. It reflects the concept that changes in inequality are often due to changes at the ends of the distribution, focusing on the tails rather than the middle.
D. Deprivation Ratio: This isn't a standard term used in the measurement of income inequality. While deprivation indexes are used in some contexts, they are usually multi-dimensional, encompassing a range of factors like employment, health, or education. As such, they don't directly measure income inequality.
E. Phillips Curve: The Phillips curve is an economic concept that shows the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment in an economy, but it does not measure income inequality.
So, the correct options are A, B, and C.
Q79: Choose the correct statement for Schumpeter's theory of development.
A. Development is financed by real saving.
B. Capitalism keeps its character intact overtime
C. Development is evolutionary
D. Development creates inflation
E. Unlimited Supply of labour.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) C and D only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) None of the above
Ans: b
Sol: The correct option is: 2) C and D only
- A. Development is financed by real saving: Schumpeter's theory does not emphasize real savings for financing development. Instead, it highlights credit creation by banks to support entrepreneurial innovation.
- B. Capitalism keeps its character intact over time: Incorrect as per Schumpeter. He argued that capitalism is dynamic and changes through creative destruction, where new innovations replace old systems.
- C. Development is evolutionary: This is correct. Schumpeter described development as an evolutionary process, driven by continual innovations and structural changes in the economy.
- D. Development creates inflation: This is also correct. According to Schumpeter, the innovation process and increased investment can lead to inflationary pressures.
- E. Unlimited supply of labour: Not part of Schumpeter's theory. This concept is related to the Lewis Model of development, which focuses on surplus labor in agrarian economies.
Other Related Points
- Schumpeter's theory emphasizes the role of entrepreneurs and innovation as key drivers of economic development.
- It introduces the concept of "creative destruction," where new industries and technologies replace outdated ones.
- The theory highlights the dynamic, non-linear nature of development, contrasting with static economic theories.
Q80: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - II, C - I, D - III
(b) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
A linear function is a mathematical function of the form f(x) = mx + b, where "m" and "b" are constants. In this equation:
- "x" is the independent variable.
- "f(x)" is the dependent variable, representing the output of the function.
- "m" is the slope of the line, indicating how steep it is.
- "b" is the y-intercept, the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
- Graphically, a linear function produces a straight line, hence the name. The slope determines the angle of the line, and the y-intercept determines where it intersects the y-axis. Linear functions are fundamental in mathematics and have various applications in science, engineering, economics, and more.
The exponential function is a mathematical function denoted as "e^x" or sometimes written as exp(x), where "e" is the base of the natural logarithm (approximately 2.71828), and "x" is the exponent. This function describes the growth or decay of a quantity at a rate proportional to its current value. It has applications in various fields such as physics, finance, and biology, and it plays a fundamental role in calculus and mathematical analysis.
A quadratic function is a type of polynomial function of degree 2, meaning the highest power of the variable is 2. Its general form is (f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c), where (a), (b), and (c) are constants, and (x) is the variable. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola, and its axis of symmetry is a vertical line that passes through the vertex of the parabola. Quadratic functions are commonly used to model various real-world phenomena and have applications in physics, engineering, and other fields.
A cubic function is a type of mathematical function that can be expressed in the form f(x) = ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d, where x is the variable, and a, b, c, and d are constants. The highest degree of the variable x in the function is 3, making it a cubic function.
Cubic functions often have a characteristic "S" or "wave" shape when graphed, and they can have up to three real roots (points where the function crosses the x-axis). The behavior of cubic functions can vary based on the coefficients a, b, c, and d, influencing factors such as the number of real roots, turning points, and overall shape of the graph.
Q81: In simultaneous equation models. OLS can be applied directly if
(a) It is a recursive model
(b) Order condition is satisfied
(c) Rank condition is satisfied
(d) Both order and rank conditions are satisfied
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is It is a recursive model
In simultaneous equation models, OLS can be applied directly if the model is recursive. A recursive model has a triangular structure where endogenous variables are determined sequentially, ensuring no simultaneous feedback loops. This eliminates the need for order and rank conditions (used for identification in non-recursive models). Correct answer: (a).
Q82: The Foreign Trade Policy (2015-2020) was announced on which date ?
(a) 1 August 2015
(b) 1 April 2015
(c) 30 August 2015
(d) 30 April 2015
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 1 April 2015.
The Union Commerce and Industry Ministry today announced changes in the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) of the Government of India. The present Policy which came into force on 1st April 2015, is for 5 years and has validity up to 31st March 2020.
Other Related Points
The highlights of the FTP:
- FTP 2015-20 provides a framework for increasing exports of goods and services as well as generation of employment and increasing value addition in the country, in line with the ‘Make in India’ program.
- The Policy aims to enable India to respond to the challenges of the external environment, keeping in step with a rapidly evolving international trading architecture and making trade a major contributor to the country’s economic growth and development.
- Measures have been taken to give a boost to exports of defense and hi-tech items.
- E-Commerce exports of handloom products, books/periodicals, leather footwear, toys and customised fashion garments through courier or foreign post office would also be able to get benefit of MEIS (for values up to INR 25,000).
- Manufacturers, who are also status holders, will now be able to self-certify their manufactured goods in phases, as originating from India with a view to qualifying for preferential treatment under various forms of bilateral and regional trade agreements. This ‘Approved Exporter System’ will help manufacturer exporters considerably in getting fast access to international markets.
- 108 MSME clusters have been identified for focused interventions to boost exports. Accordingly, the ‘Niryat Bandhu Scheme’ has been galvanized and repositioned to achieve the objectives of ‘Skill India’.
- Trade facilitation and enhancing the ease of doing business are the other major focus areas in this new FTP. One of the major objectives of the new FTP is to move towards paperless working in 24x7 environment
Q83: Which of the following are true for ridge lines?
A. they separate the relevant from the irrelevant portions of the isoquants
B. along the ridge lines, the slope of the isoquants is either zero or infinite
C. The relevant segment of the isoquants enclosed pertains to the stage II of production for labour and capital
D. Producers will never want to operate outside the region enclosed within the ridge lines.
E. The marginal product of both inputs-labour and capital is positive but declines for the portion of the isoquants within the ridge lines.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) B, C and E only
(c) A, C, D and E only
(d) A, B, C, D and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C, D, and E only.
Ridge lines define the economically viable region of isoquants:
- A: Separate relevant (efficient) from irrelevant portions.
- B: Slope is zero or infinite where one input’s marginal product is zero.
- C: Enclosed region is Stage II of production (diminishing returns).
- D: Producers avoid inefficient regions outside ridge lines.
- E: Marginal products are positive but declining within ridge lines.
Correct answer: (d).
Additional Information
Explanation of ridge lines and their significance:
- A. Ridge lines help in distinguishing the efficient and inefficient regions on an isoquant map. Outside these lines, increasing one input while keeping the other constant leads to no increase in output.
- B. The slope of the isoquants being zero or infinite along the ridge lines indicates boundary conditions where either labor or capital becomes non-productive.
- C. Stage II of production is characterized by diminishing marginal returns, where both inputs are used efficiently. The segments of isoquants within the ridge lines represent this stage.
- D. Operating outside the ridge lines means either labor or capital is being wasted, as one input would be in excess relative to the other.
- E. Within the ridge lines, the marginal products of both inputs are positive but declining, reflecting the realistic and efficient use of resources in production
Q84: Which of the following are correct in case of Poisson distribution ?
A. 'n' the number of trials is indefinitely large 1.e. n → ∞
B. 'p', the constant probability of success for each trial is indefinitely large
C. np =m is finite
D. μ3 = m + 2
E. μ4 = m + 3m2
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: b
Sol: A, C and E only
The Poisson distribution models events with:
- A: n→∞ (large trials).
- B: False; p→0 (small probability), not large.
- C: np = m is finite (mean of the distribution).
- D: False; μ3=m, not m+2.
- E: False; μ4 = m + 3m2 is a derived result, not a core assumption.
Q85: In multiple regression model, a hypothesis such as H0 : β2 = β3 = 0 can be tested using
(a) t-test
(b) Chi-square test
(c) ANOVA test
(d) F-test
Ans: d
Sol: To test whether two or more regression coefficients are equal to zero at the same time in a multiple regression model, you use the F-test. This method is preferred because:
- The F-test checks the joint significance of several coefficients together.
- It helps to determine if removing these variables would significantly reduce how well the model fits the data.
- The t-test is only used for testing a single coefficient at a time, not multiple ones together.
Q86: The causes and consequences of poverty include:
A. Unemployment
B. Low wages
C. Poor health
D. Low Population Growth
E. Low Literacy rates.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) B, D and E only
(c) B, C, D and E only
(d) A, B, C and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C and E only
The causes and consequences of poverty are complex and interrelated:
- Unemployment: When people are unable to find work, they are unable to earn an income and support themselves and their families.
- Low wages: Even if people are employed, they may not earn enough to meet their basic needs.
- Poor health: People who are poor are more likely to be in poor health, which can limit their ability to work and earn an income.
- Low literacy rates: People who are illiterate are less likely to be able to find good jobs, which can keep them trapped in poverty
Q87: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
- Cournot's model is a model of oligopoly where firms producing identical products compete in quantities. It is a static one-period model used to describe the behavior of firms in an oligopoly. In the Cournot model, firms independently decide on their output levels without considering any adjustments or dynamics over time.
- The Bertrand model is an economic theory named after Joseph Bertrand. It's used to analyze price competition between firms that produce similar or identical products. In this model, firms set their prices independently, assuming that if a firm's price is lower than its competitor's, it will capture the entire market demand. It contrasts with the Cournot model, where firms compete in quantities.
- Essentially, the Bertrand model explores the dynamics of price competition and how pricing strategies impact market outcomes.
- The Stackelberg Model is a concept in game theory and economics named after the German economist Heinrich von Stackelberg. It's a strategic interaction model where participants make decisions sequentially rather than simultaneously.
- The Sweezy Model, also known as the Sweezy-Kaldor model, is an economic model developed by Paul Sweezy and Nicholas Kaldor. It focuses on the dynamics of capitalist economies, particularly the behavior of firms and the role of investment in the business cycle.
Q88: India's Presidency of the Group Twenty (G-20) is a matter of great pride for all Indians. The G-20 is an intergovernmental forum consisting of 19 countries such as Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Kingdom and United States and the European Union. The G-20 was founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis as a forum for international economic cooperation. The size of G-20 indicates its relevance in the global economy. The G-20 members represent around 85% of the global GDP, over 75% of the global trade and 67% of world population. The G-20 summit is held annually under the leadership of a rotating presidency. India assumed the G-20 presidency from Indonesia on December 1, 2022 and will convene the G-20 leaders' summit for the first time in the country in 2023. The theme of India's G-20 presidency is "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam", that is, "One Earth, One family and One future" closely ties with LIFE (Lifestyle for Environment). The G-20 presidency steers the G-20 agenda for one year and hosts the summit. The G-20 consists of two parallel tracks: the Finance track and the Sherpa track. Finance ministers and Central Bank Governors lead the finance track, while Sherpas lead the Sherpa track. India's G-20 priorities are Green Development, Climate finance and life; Accelerated inclusive and resilient growth; Accelerating progress on SDGs; Technological transformation and Digital public infrastructure; Multilateral institutions for the 21st century; and Women Led development. India kickstarted its presidency term agenda with a series of initiatives and meetings. As a part of this, India will host over 200 meetings in over 50 cities across 32 different work streams before conducting the annual G-20 summit in Delhi in September 2023. The 43 Heads of Delegations, the largest ever in G-20 will be participating in the final summit. Conducting of this summit definitely increases India's standing in the global order. It is a great opportunity to showcase India's cultural heritage, culture and achievements to global leaders and India's commitment for global sustainable development.
For which purpose G-20 was originally founded ?
(a) to discuss international peace and counter-terrorism issues
(b) to discuss global economic and financial issues
(c) to discuss climate change and environmental issues
(d) to discuss resolving the war between Russia and Ukraine
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is to discuss global economic and financial issues
The G20 was originally founded in 1999 in response to the Asian financial crisis, as a forum for international economic cooperation to help prevent future crisis.
Q89: India's Presidency of the Group Twenty (G-20) is a matter of great pride for all Indians. The G-20 is an intergovernmental forum consisting of 19 countries such as Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Kingdom and United States and the European Union. The G-20 was founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis as a forum for international economic cooperation. The size of G-20 indicates its relevance in the global economy. The G-20 members represent around 85% of the global GDP, over 75% of the global trade and 67% of world population. The G-20 summit is held annually under the leadership of a rotating presidency. India assumed the G-20 presidency from Indonesia on December 1, 2022 and will convene the G-20 leaders' summit for the first time in the country in 2023. The theme of India's G-20 presidency is "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam", that is, "One Earth, One family and One future" closely ties with LIFE (Lifestyle for Environment). The G-20 presidency steers the G-20 agenda for one year and hosts the summit. The G-20 consists of two parallel tracks: the Finance track and the Sherpa track. Finance ministers and Central Bank Governors lead the finance track, while Sherpas lead the Sherpa track. India's G-20 priorities are Green Development, Climate finance and life; Accelerated inclusive and resilient growth; Accelerating progress on SDGs; Technological transformation and Digital public infrastructure; Multilateral institutions for the 21st century; and Women Led development. India kickstarted its presidency term agenda with a series of initiatives and meetings. As a part of this, India will host over 200 meetings in over 50 cities across 32 different work streams before conducting the annual G-20 summit in Delhi in September 2023. The 43 Heads of Delegations, the largest ever in G-20 will be participating in the final summit. Conducting of this summit definitely increases India's standing in the global order. It is a great opportunity to showcase India's cultural heritage, culture and achievements to global leaders and India's commitment for global sustainable development.
Which one of the followings is not India's G-20 priorities?
(a) Multilateral Institutions for 21st century
(b) Women-led development
(c) Development and sustained border
(d) Technological transformation and digital public infrastructure.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Development and sustained border
India’s G-20 priorities include Green Development, Climate Finance, and LiFE; Accelerated, Inclusive, and Resilient Growth; Progress on SDGs; Technological Transformation and Digital Public Infrastructure; Multilateral Institutions for the 21st Century; and Women-Led Development. "Development and sustained border" is not a priority. Correct answer: (c).
Q90: India's Presidency of the Group Twenty (G-20) is a matter of great pride for all Indians. The G-20 is an intergovernmental forum consisting of 19 countries such as Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Kingdom and United States and the European Union. The G-20 was founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis as a forum for international economic cooperation. The size of G-20 indicates its relevance in the global economy. The G-20 members represent around 85% of the global GDP, over 75% of the global trade and 67% of world population. The G-20 summit is held annually under the leadership of a rotating presidency. India assumed the G-20 presidency from Indonesia on December 1, 2022 and will convene the G-20 leaders' summit for the first time in the country in 2023. The theme of India's G-20 presidency is "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam", that is, "One Earth, One family and One future" closely ties with LIFE (Lifestyle for Environment). The G-20 presidency steers the G-20 agenda for one year and hosts the summit. The G-20 consists of two parallel tracks: the Finance track and the Sherpa track. Finance ministers and Central Bank Governors lead the finance track, while Sherpas lead the Sherpa track. India's G-20 priorities are Green Development, Climate finance and life; Accelerated inclusive and resilient growth; Accelerating progress on SDGs; Technological transformation and Digital public infrastructure; Multilateral institutions for the 21st century; and Women Led development. India kickstarted its presidency term agenda with a series of initiatives and meetings. As a part of this, India will host over 200 meetings in over 50 cities across 32 different work streams before conducting the annual G-20 summit in Delhi in September 2023. The 43 Heads of Delegations, the largest ever in G-20 will be participating in the final summit. Conducting of this summit definitely increases India's standing in the global order. It is a great opportunity to showcase India's cultural heritage, culture and achievements to global leaders and India's commitment for global sustainable development.
The size of G-20 in terms of world population, global GDP and global trade respectively is:
(a) 85%, 75% and 85%
(b) 67%, 75% and 85%
(c) 85%, 67% and 73%
(d) 67%, 85% and 75%
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 67%, 85% and 75%
The size of G-20 in terms of world population, global GDP and global trade:
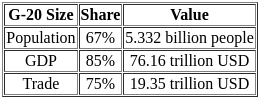
Q91: India's Presidency of the Group Twenty (G-20) is a matter of great pride for all Indians. The G-20 is an intergovernmental forum consisting of 19 countries such as Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Kingdom and United States and the European Union. The G-20 was founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis as a forum for international economic cooperation. The size of G-20 indicates its relevance in the global economy. The G-20 members represent around 85% of the global GDP, over 75% of the global trade and 67% of world population. The G-20 summit is held annually under the leadership of a rotating presidency. India assumed the G-20 presidency from Indonesia on December 1, 2022 and will convene the G-20 leaders' summit for the first time in the country in 2023. The theme of India's G-20 presidency is "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam", that is, "One Earth, One family and One future" closely ties with LIFE (Lifestyle for Environment). The G-20 presidency steers the G-20 agenda for one year and hosts the summit. The G-20 consists of two parallel tracks: the Finance track and the Sherpa track. Finance ministers and Central Bank Governors lead the finance track, while Sherpas lead the Sherpa track. India's G-20 priorities are Green Development, Climate finance and life; Accelerated inclusive and resilient growth; Accelerating progress on SDGs; Technological transformation and Digital public infrastructure; Multilateral institutions for the 21st century; and Women Led development. India kickstarted its presidency term agenda with a series of initiatives and meetings. As a part of this, India will host over 200 meetings in over 50 cities across 32 different work streams before conducting the annual G-20 summit in Delhi in September 2023. The 43 Heads of Delegations, the largest ever in G-20 will be participating in the final summit. Conducting of this summit definitely increases India's standing in the global order. It is a great opportunity to showcase India's cultural heritage, culture and achievements to global leaders and India's commitment for global sustainable development.
The theme of India's G-20 presidency is tied closely with -
(a) Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam
(b) One earth, one family and one future
(c) Technology, Infrastructure and SDG
(d) Life style for environment
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Life style for environment
The correct theme tied to India's G-20 presidency, according to your guidance, revolves around promoting a "Life style for environment" approach. This initiative endorses sustainable lifestyles globally and emphasizes the critical role individual and collective actions play in addressing environmental challenges. The "Life style for environment" (LiFE) concept underscores the importance of making environmentally conscious choices in daily life to mitigate climate change, reduce carbon footprints, and enhance biodiversity protection.
The theme of India’s G-20 presidency is "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam" ("One Earth, One Family, One Future"), closely tied to LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), which promotes sustainable living. Correct answer: (d).
Q92: India's Presidency of the Group Twenty (G-20) is a matter of great pride for all Indians. The G-20 is an intergovernmental forum consisting of 19 countries such as Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Kingdom and United States and the European Union. The G-20 was founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis as a forum for international economic cooperation. The size of G-20 indicates its relevance in the global economy. The G-20 members represent around 85% of the global GDP, over 75% of the global trade and 67% of world population. The G-20 summit is held annually under the leadership of a rotating presidency. India assumed the G-20 presidency from Indonesia on December 1, 2022 and will convene the G-20 leaders' summit for the first time in the country in 2023. The theme of India's G-20 presidency is "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam", that is, "One Earth, One family and One future" closely ties with LIFE (Lifestyle for Environment). The G-20 presidency steers the G-20 agenda for one year and hosts the summit. The G-20 consists of two parallel tracks: the Finance track and the Sherpa track. Finance ministers and Central Bank Governors lead the finance track, while Sherpas lead the Sherpa track. India's G-20 priorities are Green Development, Climate finance and life; Accelerated inclusive and resilient growth; Accelerating progress on SDGs; Technological transformation and Digital public infrastructure; Multilateral institutions for the 21st century; and Women Led development. India kickstarted its presidency term agenda with a series of initiatives and meetings. As a part of this, India will host over 200 meetings in over 50 cities across 32 different work streams before conducting the annual G-20 summit in Delhi in September 2023. The 43 Heads of Delegations, the largest ever in G-20 will be participating in the final summit. Conducting of this summit definitely increases India's standing in the global order. It is a great opportunity to showcase India's cultural heritage, culture and achievements to global leaders and India's commitment for global sustainable development.
The tracks in G-20 are :
(a) Finance track and Sherpa track
(b) Sherpa track and Economics track
(c) Climate track and Sherpa track
(d) Sherpa track and SDGs track
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Finance track and Sherpa track
- Finance Track: Led by Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors, this track focuses on economic and financial issues, including global economic growth, financial stability, and international trade.
- Sherpa Track: Led by Sherpas, who are senior government officials, this track coordinates the work of the various G-20 working groups and prepares for the G-20 leaders' summit.
Q93: Which of the following satisfy the assumptions of the classical linear regression model ?
A. Zero mean value of disturbance Ui
B. The explanatory variables and the error terms are not independent
C. Homoscedasticity or constant variance of Ui
D. No auto correlation between the disturbances
E. There is more than one exact linear relationship between explanatory variables.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C and D only
(b) A, C, D and E only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: A, C and D only
The assumptions of the classical linear regression model are:
- A. Zero mean value of disturbance Ui This is true. The expected value of the disturbance term (Ui), given the independent variables, is assumed to be zero.
- B. The explanatory variables and the error terms are not independent This is false. In the classical linear regression model, it is assumed that the explanatory variables and error terms are independent.
- C. Homoscedasticity or constant variance of Ui This is true. Homoscedasticity refers to the assumption that the variance of the disturbances are constant (i.e., the same) across all levels of the independent variables.
- D. No auto correlation between the disturbances This is true. The classical linear regression model assumes that the error terms (disturbances) for each observation are not related to the error terms of any other observation.
- E. There is more than one exact linear relationship between explanatory variables. This is false. This situation indicates the problem of perfect multicollinearity. Classical regression assumptions require that there is no exact linear relationship (perfect multicollinearity) among the independent variables.
Q94: If A, B and C are three different non-empty sets, then find which of the following are correct in laws of set operations ?
A. (A')' = A
B. (A U B) = 1 - (A ∩ B)
C. A U (B U C) = (A U B) UC
D. A U (B ∩ C) = (A ∩ B) U (A ∩ C)
E. A - B = A ∩ B'
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: b
Sol: Let’s check which set laws are correct:
- (A')' = A: This is correct. Taking the complement twice returns the original set.
- (A U B) = 1 - (A ∩ B): Incorrect. The complement of the intersection is not the same as the union.
- A U (B U C) = (A U B) U C: Correct due to the associative law for union.
- A U (B ∩ C) = (A ∩ B) U (A ∩ C): Incorrect. This is not a valid distributive law.
- A - B = A ∩ B': Correct. The difference of sets is the same as intersection with the complement.
The correct statements are A, C and E.
Q95: Which of the following are part of non-tariff barriers ?
A. Import quotas
B. Voluntary export restraint
C. Export subsidy
D. Compound tariff
E. Ad Valorem tariff.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) A, B and E only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: c
Sol: A, B and C only
A. Import quotas
An import quota is a non-tariff barrier. It is a type of protectionist trade restriction that sets a physical limit on the quantity of a good that can be imported during a specific period. By limiting the quantity of goods that can be imported, the government is able to protect domestic producers from foreign competition.
B. Voluntary export restraint (VER)
Voluntary export restraints are a form of non-tariff barrier. Each is a voluntary agreement between the exporting nation and the importing nation. The exporting country agrees to limit the quantity of certain goods that it exports to the importing country. Similar to import quotas, VERs are intended to protect domestic manufacturers from foreign competition.
C. Export subsidy
Export subsidies are government policies encouraging exports of goods and discourage sale of goods on the domestic market through direct payments, low-cost loans, tax relief for exporters, or government-financed international advertising. While they don't directly limit or restrict imports like quotas or VERs, they constitute a non-tariff measure as they indirectly affect trade by altering the competitive landscape.
D. Compound tariff
A compound tariff is a type of tariff, not a non-tariff barrier. It combines both an ad valorem duty and a specific duty. The aim of these tariffs is to protect domestic industries by increasing the cost of imported goods.
E. Ad Valorem tariff
An Ad Valorem tariff is a tariff levied as a proportion of the value of imported goods. This is a type of tariff, not non-tariff barrier.
Q96: Match List I with List II
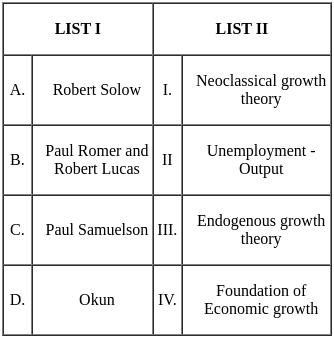
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(b) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
- Robert Solow: Solow is best known for his 1956 paper, "A Contribution to the Theory of Economic Growth," which laid the foundation for neoclassical growth theory. Solow's model showed that long-run economic growth could be achieved through the accumulation of capital and technological progress.
- Paul Romer and Robert Lucas: Romer and Lucas are among the leading figures in endogenous growth theory, which argues that economic growth is not simply determined by exogenous factors like population growth and technological progress, but is also influenced by endogenous factors like human capital, institutions, and government policies.
- Paul Samuelson: Samuelson is one of the most influential economists of the 20th century, and his contributions to neoclassical growth theory are significant. Samuelson's 1961 book, "Capital and Growth," is a classic in the field of growth economics.
- Okun: Okun is known for his "Okun's Law," which states that there is a negative relationship between the unemployment rate and the change in real GDP. Okun's Law is a useful tool for understanding the relationship between economic growth and unemployment.
Q97: Which of the following are the indicators of Human Development Index ?
A. Real GDP per capita
B. Adult literacy rate combined with enrolment ratio
C. Life expectancy at birth
D. Malnutrition under five
E. IMR under five.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: A, B and C only
- The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development". According to the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the HDI is calculated based on three key dimensions:
- A long and healthy life, measured by life expectancy at birth.
- Knowledge, measured by a combination of adult literacy rate and the combined primary, secondary, and tertiary gross enrollment ratio.
- A decent standard of living, measured by Gross National Income (GNI) per capita adjusted to purchasing power parity (PPP).
- Given these dimensions, let's evaluate the options:
- A. Real GDP per capita is similar but not exactly identical to the indicator used in HDI calculations. The indicator used is GNI per capita (PPP). However, GDP per capita is closely related and often used interchangeably in broader discussions of economic indicators. For the specific makeup of the HDI, GNI is the correct term, but the spirit of option A aligns with the third dimension of the HDI.
- B. Adult literacy rate combined with enrolment ratio fits the knowledge dimension of the HDI, indicating education levels.
- C. Life expectancy at birth is the exact measure used in the HDI for assessing health and longevity, aligning with the first dimension.
- D. Malnutrition under five and E. IMR (Infant Mortality Rate) under five are significant health indicators that influence and reflect a country's human development, especially in the aspect of health. However, neither of these specific indicators is used in the calculation of the HDI. Instead, life expectancy at birth serves as the comprehensive measure for the health dimension in the HDI.
- Therefore, the correct answer about the indicators of the Human Development Index (HDI) among the given options is:
- Option 3) A, B, and C only.
Q98: Which of the following monetary measure is used to control inflation ?
A. The Central Bank purchases government securities from Commercial Banks
B. The Central Bank sells the government securities to the Commercial Banks
C. The bank rate may be raised
D. The bank rate may be reduced
E. Raising of cash reserve ratio.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below"
(a) A, C and E only
(b) B, C and E only
(c) A, D and E only
(d) A and D only
Ans: b
Sol: B, C and E only
To control inflation, central banks employ various monetary policy tools to reduce the money supply or decrease the demand for money. Here's a look at each of the options provided:
- A . The Central Bank purchases government securities from Commercial Banks: This action actually increases the money supply in the economy, as it provides commercial banks with more money. This is typically done to combat deflation or stimulate economic growth, not to control inflation.
- B. The Central Bank sells government securities to the Commercial Banks: This action reduces the money supply in the economy because it takes money out of circulation and gives it to the central bank in exchange for the securities. This is a measure used to control inflation.
- C. The bank rate may be raised: Increasing the bank rate, the interest rate at which the central bank lends to commercial banks, makes borrowing more expensive. This reduces the amount of borrowing and spending, which can help control inflation.
- D. The bank rate may be reduced: Lowering the bank rate increases the money supply by making borrowing cheaper, which is not a measure to control inflation but to stimulate the economy.
- E. Raising of cash reserve ratio: The cash reserve ratio is the percentage of a bank's total deposits that must be kept on reserve at the central bank. Raising this ratio reduces the amount of funds that banks have available to lend, which can decrease the money supply and help control inflation.
Given the explanations above, the correct answer is:
Option 2) B, C, and E only.
Q99: Find the substitution parameter ρ(rho) of constant elasticity of substitution (CES) production function when the elasticity of substitution (σ) is greater than one
(a) ρ = 0
(b) ρ = 1
(c) -1 < ρ < 0
(d) 0 < ρ < ∞
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is -1 < ρ < 0
The elasticity of substitution (σ) is defined as the percentage change in the relative input proportions in response to a one percent change in the marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS). It is a measure of how easily one input can be substituted for another in the production process.
The CES production function is a neoclassical production function that exhibits constant elasticity of substitution. This means that the elasticity of substitution is the same for all levels of output. The CES production function is given by:
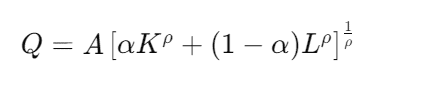
Where:
 is the total output.
is the total output.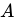 is a scale parameter (total factor productivity).
is a scale parameter (total factor productivity).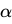 is the distribution parameter between capital
is the distribution parameter between capital  and labor
and labor  (with
(with 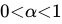 ).
).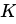 represents the input of capital.
represents the input of capital. represents the input of labor.
represents the input of labor. is a parameter that determines the elasticity of substitution between capital and labor. It is related to the elasticity of substitution (
is a parameter that determines the elasticity of substitution between capital and labor. It is related to the elasticity of substitution (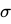 ) by the formula
) by the formula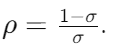
If σ > 1, then ρ < 0. Therefore, the substitution parameter ρ is negative when the elasticity of substitution is greater than one. So the answer is 3) -1 < ρ < 0.
Q100: Given regression model as Yi = α1 + β1 Xi + β2(Xi - X*)Di + Ui such a model is used to:
(a) Deseasonalise a quarterly time series data
(b) Seasonally adjust a monthly time series data
(c) To conduct chow test for structural break in time series data
(d) Test piecewise linear relationship in the data
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Test piecewise linear relationship in the data'
Piecewise Linear Relationship:
- A piecewise linear relationship is a type of relationship in which the data is divided into segments, with each segment having its own linear relationship.
- The given regression model (Yi = α1 + β1 Xi + β2(Xi - X*)Di + Ui) is designed to capture such piecewise linear relationships.
- In this model, (Di) is a dummy variable that indicates whether a certain condition is met (e.g., (Di = 1) if (Xi > X), and (Di = 0) otherwise).
- This allows the model to have different slopes for different segments of the data, thereby capturing the piecewise linear relationship.
Other Related Points
Overview of Other Options:
Deseasonalise a quarterly time series data:
- Deseasonalising involves removing seasonal effects from the data to analyze the underlying trend. The given model is not specifically designed for this purpose.
Seasonally adjust a monthly time series data:
- Seasonal adjustment aims to remove seasonal variations from the data. The given model is not aimed at seasonal adjustments.
Conduct Chow test for structural break in time series data:
- The Chow test is used to detect structural breaks in the data, indicating different regimes or periods. The given model does not directly facilitate the Chow test.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Economics 2nd Mar 2023 Shift 2 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and what subjects does it cover? |  |
| 2. How is the UGC NET Economics paper structured? |  |
| 3. What are the passing criteria for the UGC NET exam? |  |
| 4. How can candidates prepare effectively for the UGC NET Economics paper? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the UGC NET exam for aspiring researchers in economics? |  |




















