UGC NET Paper 2: Education 14th March 2023 Shift 1 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Which of the following Indian School of Philosophy rejects the Vedic Authority?
(a) Samkhya Philosophy
(b) Nyaya Philosophy
(c) Charvaka Philosophy
(d) Vaiśesika Philosophy
Ans: C
Sol: Charvaka Philosophy:
- Charvaka Philosophy, also known as Lokayata, is a school of Indian philosophy that originated around the 6th century BCE. It is known for its materialistic and atheistic approach, challenging the authority of the Vedas, the sacred texts of Hinduism.
- Charvaka's philosophy rejects the idea of a higher metaphysical reality, such as gods, the afterlife, or the concept of karma. Instead, it emphasizes empirical observation and direct sensory perception as the only valid sources of knowledge. According to Charvaka, knowledge can only be derived from what is immediately perceivable by the senses, and any claim beyond that is baseless.
- The philosophy promotes a hedonistic perspective, strongly emphasizing sensual pleasure and the pursuit of material wealth. It argues that the primary goal in life should be to maximize one's enjoyment and minimize suffering. In this view, there is no need for religious rituals, moral codes, or ethical obligations, as they are seen as mere social conventions or tools of manipulation by religious authorities.
- Other Indian schools often criticize Charvaka's philosophy for rejecting spiritual and moral values. However, it has significantly influenced the development of Indian philosophy by providing a contrasting perspective and stimulating intellectual debates.
- It is important to note that while Charvaka philosophy rejects the authority of the Vedas, it is still considered an important part of the Indian philosophical tradition. It represents a dissenting voice and contributes to India's rich diversity of philosophical perspectives.
Therefore it is clear that the Indian Charvaka School of Philosophy rejects the Vedic Authority.
Q2: Which of the following is not an Input function of the Structural Functional Analysis as specified by Gabriel Almond.
(a) Political socialisation and recruitment
(b) Rule-application
(c) Political Communication
(d) Interest articulation
Ans: B
Sol: Structural-Functional Analysis:
The structural-functional analysis, as developed by Gabriel Almond, examines the functions and dysfunctions of political systems. Almond identified several input functions that contribute to the functioning of political systems. These functions include political socialization and recruitment, political communication, and interest articulation.
Political socialization and recruitment:
- This input function focuses on how individuals acquire political attitudes, values, and beliefs. It involves the socialization of individuals into the political system and the recruitment of new members into political roles and positions.
Political communication:
- This input function refers to transmitting political information, ideas, and messages within a society. It encompasses various forms of communication, such as media, public speeches, and interpersonal communication, which shape political opinions and mobilize citizens.
Interest articulation:
- This input function involves expressing and representing various interests and demands within a political system. It includes the activities of interest groups, social movements, and other organizations that advocate for specific policy preferences and seek to influence political decision-making.
On the other hand, option 2) Rule application is not an input function specified by Gabriel Almond.
- Rule application generally pertains to implementing and enforcing laws, regulations, and policies within a political system. While it is an essential aspect of governance, it is not specifically categorized as an input function in the structural-functional analysis framework.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 2) Rule-application.
Q3: Which of the following is a non-recurring institutional cost in India?
(a) Furniture
(b) Laboratory Chemicals
(c) Salary
(d) Stipend
Ans: A
Sol: Non-recurring institutional costs:
- Non-recurring institutional costs refer to one-time expenses associated with the establishment or improvement of an institution or organization. These costs are not recurring and do not incur regularly.
- In the given options, furniture is a non-recurring institutional cost because it is typically purchased or acquired once for the initial setup or refurbishment of an institution. Once furniture is purchased, it can be used for an extended period without the need for regular expenditures.
On the other hand, options 2) Laboratory Chemicals, 3) Salary, and 4) Stipend are recurring institutional costs:
Laboratory Chemicals:
- Laboratory chemicals are required for scientific research, experiments, and analyses. These chemicals must be replenished periodically as they are consumed during laboratory activities.
Salary:
- Salary refers to the regular payment made to employees or staff members for their services. Salaries are recurring expenses and are typically paid on a monthly basis or at regular intervals.
Stipend:
- A stipend is a regular payment made to students or trainees to support their education or training endeavours. Stipends are usually provided on a predetermined schedule, such as monthly or quarterly, and are considered recurring costs.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 1) Furniture, which represents a non-recurring institutional cost in India.
Q4: Who introduced the method of Summated ratings in 1932 ?
(a) Thorndike, E.L.
(b) Likert, Rensis
(c) Thomson, A.
(d) Hull, Clark
Ans: B
Sol: Rensis Likert:
- Rensis Likert introduced the method of summated ratings in 1932. It is a psychometric scale commonly used in questionnaires and is the most widely used scale in attitude measurement.
- The scale is based on the idea that attitudes can be measured by asking respondents to rate a series of statements about an object or issue.
- The statements are typically worded in a positive or negative way, and respondents are asked to indicate their agreement or disagreement with each statement on a scale of 1 to 5, with 1 being strongly disagree and 5 being strongly agree. The scores on the individual items are then summed to create a total score for the scale.
The correct answer is 2) Likert, Rensis.
Q5: "Private speech leads to self regulated behaviour." Which Psychologist viewed this strongly ?
(a) Carl Rogers
(b) Lev Vygotsky
(c) Sigmund Freud
(d) Jean Piaget
Ans: B
Sol: Lev Vygotsky:
- Lev Vygotsky was a Russian psychologist who developed a sociocultural theory of cognitive development. He believed that children learn through social interaction with adults and other children. He also believed that private speech, or talking to oneself, is important to cognitive development. Vygotsky believed that private speech helps children to regulate their behaviour and to solve problems.
Here is a quote from Vygotsky:
- "Private speech is a transitional form between social speech and inner speech. It is a means of self-regulation that helps children to control their behaviour and to solve problems. As children mature, private speech becomes internalized and becomes inner speech."
- Vygotsky argued that private speech starts as externalized, audible speech during early childhood. Children engage in a private speech by talking aloud to themselves while engaging in activities or solving problems. Over time, this private speech becomes internalized and transforms into inner speech, where individuals think in words without vocalization.
- Vygotsky believed private speech is a cognitive tool that helps children regulate their thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. Through private speech, children can guide and direct their actions, solve problems, plan strategies, and monitor their thinking processes. It helps them to organize their thoughts and gain control over their behaviour.
- Vygotsky's view on private speech and self-regulated behaviour highlights the role of language and social interaction in cognitive development. He emphasized that children gradually internalize social interactions and cultural tools, such as language, to develop higher-order cognitive functions.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 2) Lev Vygotsky.
Q6: A Social process takes place when there is ________.
(a) an integration
(b) an assimilation
(c) a competition
(d) a conflict
Ans: B
Sol: Assimilation:
- Assimilation is a social process that occurs when individuals or groups adopt the cultural norms, values, and behaviours of a dominant or host society. It involves the integration of different cultural groups into a larger whole.
- Assimilation can happen in various contexts, such as when immigrants or minority communities adopt the majority population's language, customs, and practices. It often involves gradually blending cultural identities, where individuals or groups give up some aspects of their original culture and adopt those of the dominant culture.
- Social pressure, economic opportunities, and the desire for social acceptance or upward mobility can influence assimilation. It is often seen as a form of cultural integration or acculturation.
- However, it is important to note that assimilation is a complex and multifaceted process that can have positive and negative consequences. While it may lead to social cohesion and the sharing of common values, it can also result in the loss of cultural diversity and the marginalization of certain groups.
Hence it is clear that a Social process occurs when there is an assimilation.
Q7: 'Mental Health is the full Harmonious functioning of the Whole personality', who gave this meaning of Mental Health?
(a) Ladell Lee
(b) Kuppuswamy, B
(c) Hadfield J. A.
(d) Crow and Crow
Ans: C
Sol: Hadfield J. A.:
- James Arthur Hadfield, commonly known as J. A. Hadfield, was a prominent British psychiatrist. Who wrote extensively on the subject of mental health. He defined mental health as "the full and harmonious functioning of the whole personality." This definition emphasizes the importance of all aspects of the personality, including physical, emotional, social, and spiritual health.
- Hadfield's definition of mental health is still widely used today. It is a useful reminder that mental health is not simply the absence of mental illness. It is a state of well-being in which all aspects of the personality function harmonise.
- Hadfield viewed mental health as the optimal functioning and integration of the entire personality. According to her perspective, mental health involves the harmonious coordination and balance of various aspects of an individual's personality, including thoughts, emotions, behaviours, and relationships.
- Hadfield emphasized that mental health is not simply the absence of mental illness but a state of well-being where individuals can experience fulfilment, self-actualization, and positive interpersonal connections. She believed individuals could lead satisfying and meaningful lives when all personality components function harmoniously.
- His understanding of mental health as the full harmonious functioning of the whole personality highlights the importance of psychological well-being and the integration of various psychological processes.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 3) Hadfield J. A.
Q8: Which of the following perspective examines "how family members and intimate couples interact on a daily basis and arrive at a shared understanding of their situation?"
(a) Conflict Theory Perspective
(b) Functional Theory Perspective
(c) Social Interaction Theory Perspective
(d) Conversation Theory Perspective
Ans: C
Sol: The perspective that examines "how family members and intimate couples interact daily and arrive at a shared understanding of their situation" is the Social Interaction Theory Perspective.
Social Interaction Theory Perspective:
- The Social Interaction Theory Perspective focuses on the micro-level interactions and communication patterns between individuals within social groups, such as families or intimate couples. It explores how people interact face-to-face, interpret each other's actions and gestures, and create shared meanings.
- In the context of families and intimate couples, this perspective examines how family members and partners communicate, negotiate, and develop a shared understanding of their daily lives and situations. It emphasizes the importance of verbal and non-verbal communication, gestures, expressions, and other forms of social interaction.
- The Social Interaction Theory Perspective emphasizes that meaning is socially constructed through ongoing interactions and that individuals actively shape their social reality. It recognizes the role of social norms, roles, and expectations in guiding interactions within family and intimate relationships.
- By studying the social interactions and communication processes within families and intimate couples, this perspective provides insights into how shared understandings, meanings, and relationships are formed and maintained. It contributes to our understanding of the dynamics and functioning of these social units.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 3) Social Interaction Theory Perspective.
Other Related Points
Conflict Theory Perspective:
- The Conflict Theory Perspective examines society through conflict and social inequality. It focuses on the power struggles and resource competition between different social groups. In the context of families and intimate couples, this perspective analyzes how power dynamics, inequalities, and conflicting interests shape interactions and relationships.
Functional Theory Perspective:
- The Functional Theory Perspective, also known as functionalism, views society as a complex system with interconnected parts that work together to maintain social order and stability. It emphasizes the functions and roles performed by different social institutions, including families. Within this perspective, family and intimate relationships are seen as contributing to social cohesion, reproduction, and the socialization of individuals.
Conversation Theory Perspective:
- The Conversation Theory Perspective, the Coordinated Management of Meaning (CMM), focuses on how people co-create meanings through conversations and narratives. It examines the role of language and communication in shaping social realities and constructing shared understandings. In the context of families and intimate couples, this perspective explores how conversations and storytelling influence relationship dynamics, conflict resolution, and the development of shared meanings.
Q9: 'Care Education' has been focussed by:
(a) Paulo Freire
(b) Nel Noddings
(c) Mary Wollstonecraft
(d) Rabindranath Tagore
Ans: B
Sol: Nel Noddings:
- Nel Noddings is an influential educational philosopher who has extensively written about the philosophy of care in education. She is known for her work on the ethics of care and its application to education. Noddings emphasize the importance of relationships, empathy, and nurturing in education.
- According to Noddings, care should be at the core of education, and educators should prioritize the development of caring relationships with students. She argues that caring relationships foster trust, empathy, and a sense of security, essential for effective teaching and learning. Noddings emphasize the need to go beyond simply imparting knowledge and skills and address students' holistic well-being.
- Noddings' concept of care education focuses on nurturing students' moral and emotional development, encouraging them to become caring individuals who are sensitive to the needs and well-being of others. She suggests that care should be infused into the curriculum and pedagogy, creating an environment that values and promotes empathy, kindness, and compassion.
- Nel Noddings' work has significantly impacted education, inspiring educators and scholars to consider the moral and relational dimensions of teaching and learning. Her ideas have influenced the development of caring and compassionate educational practices, fostering a holistic approach to education that values students' well-being and ethical growth.
Hence. the focus on 'Care Education' has been given by Nel Noddings.
Q10: Which of the following has been proposed by the National Education Policy-2020 to frame the expected learning outcomes for Higher Education Programmes?
(a) General Education Council (GEC)
(b) Higher Education Grants Council (HEGC)
(c) National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF)
(d) Professional Standard Setting Bodies (PSSB)
Ans: c
Sol: Correct Answer is National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF)
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 proposes the National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF) to frame the expected learning outcomes for Higher Education Programmes. The NHEQF is designed to standardize and define learning outcomes, qualifications, and academic standards across higher education institutions in India, ensuring alignment with national and global educational goals. It provides a structured framework for curriculum design, assessment, and quality assurance.
- Option (a) General Education Council (GEC): The GEC, as per NEP-2020, is responsible for setting professional standards for teachers and education professionals, not for framing learning outcomes for higher education programs.
- Option (b) Higher Education Grants Council (HEGC): The HEGC focuses on funding and financial support for higher education institutions, not on defining learning outcomes.
- Option (d) Professional Standard Setting Bodies (PSSB): PSSBs are involved in setting standards for professional education and are part of the GEC, but they do not specifically frame learning outcomes for all higher education programs.
Q11: Which of the following is a tool used for analysing the development of a policy?
(a) Policy Decision
(b) Policy Assessment tool
(c) Policy Analysis Tool
(d) Policy Cycle
Ans: D
Sol: Policy Cycle: The policy cycle is a widely recognized framework used for analyzing the development and implementation of policies. It outlines the stages or phases a policy typically goes through, from its formulation to evaluation. The policy cycle can vary in the number of stages and their specific details, but the general stages often include the following:
- Agenda Setting: Identifying and defining the problem or issue that requires policy attention.
- Policy Formulation: Developing and shaping policy options or solutions to address the identified problem. This stage involves research, analysis, and consultation with stakeholders.
- Policy Adoption: The formal adoption or approval of the policy by the relevant decision-making authority or legislative body.
- Policy Implementation: The process of putting the policy into action, including the design and establishment of programs, regulations, and administrative procedures.
- Policy Evaluation: Assessing the policy's effectiveness, efficiency, and impact after its implementation. Evaluation helps to determine whether the policy objectives have been achieved and provides insights for potential adjustments or improvements.
- Policy Review: Conduct periodic reviews to re-examine the policy's relevance, effectiveness, and alignment with changing circumstances or new evidence. Policy review may lead to policy revision or termination.
The policy cycle is a helpful framework for analyzing and understanding the stages and processes involved in policy development. It provides a structured approach for policymakers, analysts, and stakeholders to assess policy options, monitor progress, and make informed decisions throughout the policy-making process.
Therefore, the tool used for analyzing policy development is Policy Cycle.
Q12: 'Collective Monologue leads to egocentric speech'. Which psychologist viewed this strongly ?
(a) Jean Piaget
(b) Lev Vygotsky
(c) Sigmund Freud
(d) Carl Rogers
Ans: A
Sol: Jean Piaget:
- Jean Piaget was a Swiss developmental psychologist who is best known for his theory of cognitive development. He believed children's cognitive development progresses through four stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational.
- Children are egocentric in the preoperational stage, which typically occurs between the ages of 2 and 7. This means that they are unable to see things from another person's perspective. As a result, they often talk to themselves or others without really communicating. This type of speech is called collective monologue.
- Piaget believed that collective monologue is a normal part of development and eventually disappears as children become more socially aware. However, some psychologists believe that collective monologue can be a sign of autism or other developmental disorders.
Therefore Jean Piaget is the correct option.
Q13: NCTE was established for which of the following objective?
(a) Universalisation of Education
(b) Uniting the teachers of India
(c) Increasing focus on research in Teacher Education
(d) Development of Teacher Education system
Ans: D
Sol: The National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE):
- It is a statutory body of the Government of India set up by an Act of Parliament in 1993. The NCTE is responsible for planning and coordinating teacher education in India. It also lays down norms and standards for teacher education institutions and awards recognition to these institutions. The NCTE also conducts research in teacher education and disseminates the results of its research.
Facts about NCTE:
- The NCTE was established on 17 August 1995 under the National Council for Teacher Education Act 1993.
- The NCTE is headquartered in New Delhi, India.
- The NCTE has a Governing Body, which the Chairperson of the NCTE heads.
- The NCTE has a Secretariat, which the Secretary of the NCTE heads.
- The NCTE has 10 Regional Committees located in different parts of India.
- The NCTE has several functions, including:
- Planning and coordinating teacher education in India.
- Laying down norms and standards for teacher education institutions.
- Awarding recognition to teacher education institutions.
- Conducting research in teacher education.
- Disseminating the results of its research.
- The NCTE is an important body in the Indian education system. It plays a vital role in ensuring that teachers are qualified and competent to teach in Indian schools. The NCTE's work is essential for the quality of education in India.
Therefore option 4 is the correct answer.
Q14: Inquiry Training model was given by:
(a) Deng
(b) Richard Suchman
(c) Luke
(d) Habermas
Ans: B
Sol: Inquiry Training Model:
- Richard Suchman, an American psychologist, developed the Inquiry Training model, also known as the Suchman Inquiry Model. This model is an instructional approach that emphasizes active inquiry, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills.
- The Inquiry Training model focuses on engaging learners in the inquiry process, where they actively explore, investigate, and seek answers to questions or problems. It encourages learners to ask questions, make observations, gather evidence, analyze data, and draw conclusions. The model promotes independent thinking, creativity, and self-directed learning.
- Suchman's Inquiry Training model provides a structured framework for educators to facilitate inquiry-based learning experiences. It encourages learners to develop their questions, conduct research or investigations, and collaborate with others to explore solutions or s.
- The model is often used in educational settings to foster higher-order thinking skills, scientific inquiry, and problem-solving abilities. It helps learners develop critical thinking, analytical reasoning, and the ability to apply knowledge to real-world situations.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 2) Richard Suchman.
Q15: Which one of the following is true about Reflective teaching?
(a) teaching via lecture method
(b) cyclic process of thinking about teaching
(c) process of thinking about research
(d) process of preaching
Ans: B
Sol: Reflective Teaching:
- Reflective teaching is a cyclic process of thinking about teaching. It involves planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. Teachers who engage in reflective teaching constantly think about how to improve their teaching practices. They are not afraid to experiment and try new things. They are also open to feedback from their students and colleagues.
Here are the four steps of reflective teaching:
- Planning: In this stage, the teacher plans their lesson. They consider the learning objectives, the content, the activities, and the assessment.
- Acting: In this stage, the teacher teaches the lesson. They implement the plan and interact with the students.
- Observing: In this stage, the teacher observes the students' learning. They look for evidence of student understanding and engagement.
- Reflecting: In this stage, the teacher reflects on the lesson. They consider what went well, what could be improved, and what they learned.
Reflective teaching is a valuable tool for teachers. It helps them to improve their teaching practices and to become more effective educators.
Hence, Reflective teaching is a cyclic process of thinking about teaching.
Q16: Which of the following is not a Curriculum Approach?
(a) Behavioral Approach
(b) Managerial Approach
(c) Reconceptualist Approach
(d) Literature Approach
Ans: D
Sol: Literature Approach:
- Literature approach is a teaching method that uses literature to teach students about different subjects. This approach can be used to teach a variety of subjects, including history, science, and math.
- The literature approach is based on the idea that students learn best when they are engaged and interested in the material they are learning. By using literature, teachers can create a more engaging and interesting learning environment for their students.
- There are many different ways to use the literature approach in the classroom. One way is to use literature as a springboard for discussion and debate. Teachers can use literature to introduce students to different perspectives and ideas. They can also use literature to help students develop their critical thinking skills.
- Another way to use the literature approach is to use literature as a way to teach students about different cultures and time periods. By reading literature from different cultures and time periods, students can gain a better understanding of the world around them.
- The literature approach is a versatile and effective teaching method that can be used to teach a variety of subjects. By using literature, teachers can create a more engaging and interesting learning environment for their students.
Here are some of the benefits of using the literature approach in the classroom:
- It can help students develop their critical thinking skills.
- It can help students learn about different cultures and time periods.
- It can help students develop their imaginations and creativity.
- It can help students learn to appreciate different forms of literature.
- It can help students develop their writing skills.
If you are a teacher who is looking for a way to make your lessons more engaging and interesting, the literature approach is a great option to consider.
Hence, the Literature Approach is not a Curriculum Approach but a teaching method.
The four major curriculum approaches are:
- Behavioral Approach. This approach focuses on the development of specific, measurable, and observable learning objectives.
- Managerial Approach. This approach focuses on the efficient and effective management of the curriculum.
- Reconceptualist Approach. This approach challenges the traditional view of the curriculum and emphasizes the importance of student experience and voice.
- Humanistic Approach. This approach focuses on the development of the whole child, including their social, emotional, and intellectual needs.
Q17: According to NCFTE- 2009, which of the following is not recommended for Teacher Education ?
(a) To critically examine school curriculum, syllabi, and textbooks
(b) To help prospective teachers to engage with field experiences for construction of knowledge
(c) To teach learners only through theories to understand psycho-social attributes.
(d) To help teachers in developing consciousness and finer human responsibilities through self- reflection
Ans: C
Sol: NCFTE-2009:
- The NCFTE-2009 was developed by the National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) in India.
- The NCFTE-2009 is a framework for teacher education that provides a vision for the development of teacher education in India.
- The NCFTE-2009 is based on the principles of lifelong learning, reflective practice, and professional development.
- The NCFTE-2009 emphasizes the importance of teacher education in preparing teachers to teach in diverse and inclusive classrooms.
- The NCFTE-2009 is a living document that will be updated as needed to reflect the changing needs of the education system.
- The NCFTE- 2009 emphasizes the importance of experiential learning and the need for teachers to be able to connect theory with practice. The framework also stresses the importance of teachers being able to develop their own professional identities and to reflect on their own practice.
- The NCFTE-2009 is an important document that will help to improve the quality of teacher education in India. It is a comprehensive framework that provides a vision for the development of teacher education in India.
- The NCFTE-2009 is based on the principles of lifelong learning, reflective practice, and professional development. It emphasizes the importance of teacher education in preparing teachers to teach in diverse and inclusive classrooms. The NCFTE-2009 is a living document that will be updated as needed to reflect the changing needs of the education system.
Here are some of the key recommendations of the NCFTE- 2009 for teacher education:
- Teacher education should be based on a sound understanding of the principles of learning and development.
- Teacher education should prepare teachers to teach in diverse and inclusive classrooms.
- Teacher education should emphasize the importance of reflective practice.
- Teacher education should provide opportunities for teachers to develop their own professional identities.
- Teacher education should be lifelong and continuous.
According to NCFTE- 2009, 3) To teach learners only through theories to understand psycho-social attributes is not recommended for Teacher Education.
Q18: According to the non-technical, non-scientific approach (flexible), the process of curriculum development is -
(a) highly objective
(b) Universal
(c) Logical
(d) Heuristic
Ans: D
Sol: Heuristic:
- A heuristic approach to curriculum development is a non-linear, iterative process that emphasizes the importance of trial and error, flexibility, and creativity. This approach is based on the idea that there is no one right way to develop a curriculum, and that the best curriculum is one that is tailored to the specific needs of the students and the community.
Here are some of the key features of a heuristic approach to curriculum development:
- It is based on the idea that there is no one right way to develop a curriculum.
- It allows for flexibility and creativity in the development of the curriculum.
- It allows for the curriculum to be tailored to the specific needs of the students and the community.
- It is an ongoing process, rather than a one-time event.
The heuristic approach to curriculum development typically involves the following steps:
- Identify the needs of the students and the community. This step involves gathering information about the students' interests, abilities, and needs, as well as the needs of the community.
- Develop a set of learning goals. The learning goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Identify resources. This step involves identifying the resources that will be needed to implement the curriculum, such as materials, time, and personnel.
- Plan the curriculum. This step involves developing a plan for how the curriculum will be implemented, including the sequence of lessons, the activities that will be used, and the assessments that will be used to measure student learning.
- Implement the curriculum. This step involves putting the plan into action and teaching the lessons.
- Assess student learning. This step involves using the assessments to measure student learning and to make adjustments to the curriculum as needed.
- Reflect on the curriculum. This step involves reflecting on the effectiveness of the curriculum and making changes as needed.
The heuristic approach to curriculum development is a flexible and adaptable approach that can be used to create a curriculum that is both effective and engaging. This approach is well-suited for use in a variety of settings, including schools, community organizations, and businesses.
Therefore, according to the non technical - non scientific approach (flexible), the process of curriculum development is heuristic.
Q19: Which of the following is not a suitable option when curriculum is viewed as non technical - non scientific (flexible) approach ?
(a) Curriculum is viewed as quality activities
(b) Curriculum is viewed as the delivery of mapped out content and experiences
(c) Curriculum is viewed as conversation
(d) Curriculum is viewed as an emerging phenomenon with which humans interact
Ans: B
Sol: Curriculum:
- A curriculum is a plan for the learning experiences that students will have in an educational setting. It includes the content, skills, and knowledge that students are expected to learn, as well as the methods that will be used to teach them. The curriculum is typically developed by a team of educators, and it is often based on the needs of the students, the community, and the state or country.
Curriculum is viewed as the delivery of mapped out content and experiences:
- This is not a suitable option when curriculum is viewed as a non-technical, non-scientific (flexible) approach because it implies that the curriculum is fixed and predetermined. A flexible curriculum, on the other hand, is one that is constantly evolving and changing in response to the needs of the learners and the world around them.
- A flexible curriculum is more likely to be viewed as a conversation, an emerging phenomenon with which humans interact, or a set of quality activities. A conversation implies that the curriculum is dynamic and interactive, and that it is constantly being shaped by the participants in the learning process. An emerging phenomenon implies that the curriculum is constantly evo
- lving and changing, and that it is never fully complete. A set of quality activities implies that the curriculum is focused on providing learners with opportunities to learn and grow in a meaningful way.
- A flexible curriculum is more likely to be effective in meeting the needs of all learners, as it can be tailored to the individual needs and interests of each learner. It is also more likely to be relevant to the needs of the world around them, as it can be constantly updated to reflect the latest changes in society and technology.
Curriculum as a conversation:
- This view of the curriculum sees it as a dynamic and interactive process, where the participants in the learning process (teachers, students, and other stakeholders) are constantly shaping and reshaping the curriculum. This view is often associated with a learner-centered approach to learning, where the students are the primary agents of their own learning.
Curriculum as an emerging phenomenon with which humans interact
- This view of the curriculum sees it as a constantly evolving and changing process, which is never fully complete. This view is often associated with a constructivist approach to learning, where the students are actively involved in constructing their own understanding of the world.
Curriculum as a set of quality activities
- This view of the curriculum sees it as a collection of activities that are designed to help students learn and grow. This view is often associated with a competency-based approach to learning, where the focus is on ensuring that students have mastered the skills and knowledge they need to be successful.
Hence, the correct answer is 2. Curriculum is viewed as the delivery of mapped out content and experiences.
Q20: What will be the 't value' when 'between-groups variance' and 'within-groups variance' is 200 and 50 respectively ?
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 16
(d) 8
Ans: B
Sol: t-test:
- The t-test is a powerful tool for testing hypotheses about the difference between means. However, it is important to note that the t-test is only valid if the assumptions of the t-test are met. These assumptions include:
- The data is normally distributed.
- The data is independent.
- The data is homogeneous.
Here are the steps in detail on how to calculate the t-value:
- Calculate the between-groups variance. This is the variance of the means of the groups.
- Calculate the within-groups variance. This is the variance of the scores within each group.
- Divide the between-groups variance by the within-groups variance.
- Take the square root of the result.
To calculate the t-value in this context, we typically consider the ratio of between-groups variance to within-groups variance when dealing with a t-test or similar statistical analysis (e.g., in an ANOVA F-test, which is related to t-tests for two groups). The t-value can be approximated using the square root of the F-ratio when comparing two groups, where the F-ratio is the between-groups variance divided by the within-groups variance.
Given:
- Between-groups variance = 200
- Within-groups variance = 50
The F-ratio is: F= Between-groups variance / Within-groups variance =200 / 50 = 4
For a two-group comparison, the t-value is the square root of the F-ratio (assuming equal degrees of freedom and a two-tailed test):
t = √F = √4 = 2
Thus, the t-value is 2.
Therefore, the correct answer is 2.
Q21: Curriculum Design conceptualizes the curriculum and arranges its major components as -
(a) Objectives, Content, Learning Experiences and Evaluation
(b) Materials, Learning Experiences, Pedagogy and Examination
(c) Students, Teachers, Syllabus and Evaluation
(d) Family, School, Work Place and Records
Ans: A
Sol: The major components of curriculum design are:
- Objectives: The objectives of a curriculum are the goals that it is designed to achieve. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Content: The content of a curriculum is the knowledge, skills, and understanding that students are expected to learn. Content should be aligned with the objectives of the curriculum and should be relevant to the students' needs and interests.
- Learning experiences: Learning experiences are the activities that students engage in to learn the content of the curriculum. Learning experiences should be active and engaging and should provide students with opportunities to apply what they are learning.
- Evaluation: Evaluation is the process of assessing student learning. Evaluation should be used to track student progress, identify areas where students need additional support, and make necessary adjustments to the curriculum.
The four components of curriculum design are interrelated and should be considered together when designing a curriculum. For example, the objectives of the curriculum will inform the selection of content, the learning experiences will be designed to help students achieve the objectives, and the evaluation will be used to assess student learning and make necessary adjustments to the curriculum.
Hence, Curriculum Design conceptualizes the curriculum and arranges its major components as Objectives, Content, Learning Experiences and Evaluation.
Q22: The correlation coefficient between scores on two parts of a given test is 0.50. What is the reliability coefficient of the total test?
(a) +1.00
(b) 0.67
(c) -1.00
(d) 0.76
Ans: B
Sol:
The reliability coefficient of a test is a measure of how well the test measures what it is supposed to measure. It is calculated by correlating the scores on two different forms of the test or by correlating the scores on the test with some other measure of the same construct.
In this case, the correlation coefficient between scores on two parts of a given test is 0.50. This means that the two parts of the test are moderately correlated. The reliability coefficient of the total test can be calculated using the Spearman-Brown formula:
rxx = 2r/(1+r)
In this case, r = 0.50 and n = 2. So, the reliability coefficient of the total test is:
rxx = 2(0.50)/(1+0.50) = 0.67
Therefore, the correct answer is 0.67.
Q23: Parametric and non-parametric analyses commonly share the following:
(a) Testing of null hypotheses only
(b) Chain of reasoning based on inferential statistics
(c) Statistics as means and frequencies
(d) Ordinal and interval scale data
Ans: B
Sol:
- Parametric and non-parametric analyses are two broad categories of statistical analyses used in research and data analysis. While they differ in their underlying assumptions and techniques, they share some common aspects. One common aspect is the use of inferential statistics, which involves making inferences or conclusions about a population based on sample data.
1- Testing of null hypotheses only:
- This option is not correct because both parametric and non-parametric analyses can involve testing null hypotheses. In hypothesis testing, researchers formulate a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, and statistical tests are used to assess the evidence against the null hypothesis.
2. Chain of reasoning based on inferential statistics:
- This option is correct. Both parametric and non-parametric analyses follow a chain of reasoning based on inferential statistics. In both cases, researchers use statistical techniques to analyze the data, calculate test statistics, and make inferences about the population based on the sample data.
3. Statistics as means and frequencies:
- This option is not entirely accurate. While both parametric and non-parametric analyses involve using statistical measures such as means and frequencies, it is not something they commonly share. The choice of statistical measures used in the analysis depends on the nature of the data and the specific research question.
4. Ordinal and interval scale data:
- This option is not accurate in terms of what parametric and non-parametric analyses commonly share. Parametric analyses typically assume the data to follow a specific distribution and require interval or ratio scale data. Non-parametric analyses, on the other hand, do not rely on these assumptions and can be used with various types of data, including ordinal and interval scale data.
Hence option 2 is the correct answer.
Q24: Which of the example requires snowball sampling technique?
(a) Students with hearing impairments
(b) non-heterosexual individuals
(c) Untrained school teachers
(d) First generation learners
Ans: B
Sol: Snowball sampling technique:
- Snowball sampling technique is commonly used when the target population is difficult to reach or locate, and when the individuals in the population share a certain characteristic or trait that makes them hard to identify through traditional sampling methods. The technique involves starting with a small set of participants and then expanding the sample by asking those initial participants to refer other individuals who meet the criteria.
Based on this understanding, the example that would require snowball sampling technique is:
non-heterosexual individuals:
- Non-heterosexual individuals might be part of a population that is not easily identifiable or accessible through traditional sampling methods. Snowball sampling would be useful in reaching out to this population by starting with a few known non-heterosexual individuals and then asking them to refer other non-heterosexual individuals they know.
- This technique allows for the recruitment of participants who might not be openly identifiable or listed in conventional sampling frames or directories.
Therefore option 2 is the correct answer.
Q25: Which among the following is the correct sequence of the reflective level of teaching, as stated by Handal and Lauvas (1987) ?
(a) Planning and Reflection; Level of action; level of ethical consideration
(b) Level of ethical consideration; Planning and reflection; Level of action
(c) Planning and reflection; Level of ethical consideration; Level of action
(d) Level of action; Planning and reflection; Level of ethical consideration.
Ans: D
Sol: Handal and Lauvas define reflective teaching as "a process in which teachers systematically analyze their teaching practice to improve it." They identify three levels of reflective teaching:
The correct sequence of the reflective level of teaching, as stated by Handal and Lauvas (1987), is as follows:
Level of action:
- This stage involves actively engaging in teaching activities and implementing instructional strategies in the classroom.
- Teachers are focused on delivering lessons, facilitating student learning, and managing the classroom environment.
- During this stage, teachers are primarily concerned with the immediate actions and tasks related to teaching.
Planning and reflection:
- After the level of action, teachers enter the stage of planning and reflection. In this stage, teachers reflect on their teaching practices and evaluate their effectiveness.
- They analyze the outcomes of their instructional strategies, assess student learning, and consider the strengths and weaknesses of their teaching methods.
- Teachers also engage in self-reflection, identifying areas for improvement and setting goals for future teaching.
- This stage involves a thoughtful examination of teaching practices and the identification of strategies to enhance teaching effectiveness.
Level of ethical consideration:
- The final stage of the reflective level of teaching is the level of ethical consideration. In this stage, teachers reflect on the ethical implications of their actions and decisions in the teaching process.
- They consider the moral and ethical dimensions of teaching, such as treating students fairly, maintaining confidentiality, respecting diversity, and fostering a positive and inclusive classroom environment.
- Teachers critically evaluate the ethical consequences of their instructional decisions and strive to align their teaching practices with ethical principles.
Hence the correct sequence is Level of action; Planning and reflection; Level of ethical consideration.
Q26: A teacher maintains the collection of a student's work over a period of time. Which term is used for such type of collection ?
(a) Rubric
(b) Reflective journal
(c) Portfolio
(d) Anecdotal Record
Ans: C
Sol: Portfolio:
- A portfolio is a purposeful collection of students' work that exhibits the student's efforts, progress and achievement in one and more areas. It provides evidence of a learner's abilities, thoughts, and attitudes. It shows children's gradual progress and paves the way for development.
Portfolio can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Assessment: Portfolio can be used to assess student's learning over time. By looking at a student's portfolio, teachers can see how the student has progressed and what areas they still need to work on.
- Communication: Portfolio can be used to communicate with parents and other stakeholders about a student's learning. By sharing a student's portfolio, teachers can provide parents with a more comprehensive view of their child's progress.
- Self-reflection: Students can use portfolio to reflect on their own learning. By looking at their work over time, students can identify their strengths and weaknesses and set goals for their future learning.
There are many different ways to create a portfolio. The most important thing is to choose a format that will work best for the student and the purpose of the portfolio. Some common portfolio formats include:
- Traditional portfolio: A traditional portfolio is a physical collection of student work. This type of portfolio can be organized by topic, skill, or period.
- Digital portfolio: A digital portfolio is an electronic collection of student work. This type of portfolio can be accessed online and include various media, such as text, images, videos, and audio recordings.
- Web portfolio: A web portfolio is a website that showcases student work. This type of portfolio can be created using various software programs, such as WordPress or Wix.
Other Related Points
- A rubric is a set of scoring guidelines for evaluating students' work. These may include descriptive details of the work, which depend on the feasibility of learners' available time, the nature of the task, etc.
- A reflective journal is a record of a student's thoughts and feelings about their learning. It can be used to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and reflect on the learning process.
- An anecdotal record is an observation that is written in the form of story to provide information regarding a student's development over the period to be shared with parents.
Hence it can be concluded that through a portfolio teacher maintains the collection of a student's work over a period of time.
Q27: "Learners will be able to measure the correct volume of a chemical using a measuring flask". Above objective will fall under which category of educational objectives suggested by Anderson and Krathwohl ?
(a) Factual knowledge of analysis level
(b) Procedural knowledge of application level
(c) Conceptual knowledge of analysis level
(d) Meta cognitive knowledge of application level
Ans: B
Sol: The educational objective "Learners will be able to measure the correct volume of a chemical using a measuring flask" falls under the procedural knowledge of application level in Anderson and Krathwohl's taxonomy of educational objectives.
Procedural knowledge:
- Procedural knowledge is knowledge of how to do something. It is a type of knowledge that is often acquired through practice and experience. Procedural knowledge can be divided into two main categories:
- Concrete procedural knowledge is how to do something in a specific situation. For example, knowing how to drive a car is concrete procedural knowledge.
- Abstract procedural knowledge is knowledge of how to do something generally. For example, knowing how to solve a math problem is abstract procedural knowledge.
- It is knowledge of how to do something. In this case, the students need to know how to use a measuring flask to measure the correct volume of a chemical. This is a skill that can be learned through practice and experience.
- The application level of Bloom's taxonomy refers to the ability to use knowledge in new and concrete situations. In this case, the students need to be able to use their knowledge of how to use a measuring flask to measure the correct volume of a chemical in a real-world setting.
Here are some examples of how the objective could be assessed:
- The students could be given a measuring flask and a set of chemicals and asked to measure the correct volume of each chemical.
- The students could be given a problem to solve that requires them to use their knowledge of how to use a measuring flask.
- The students could be asked to write a procedure for using a measuring flask.
By assessing the student's ability to measure the correct volume of a chemical using a measuring flask, the teacher can determine if the students have met the objective.
Q28: Which among the following is the correct sequence of career stages and professional standards for teachers?
(a) Expert Teacher, Lead Teacher, Beginner Teacher, Proficient Teacher
(b) Proficient Teacher, Beginner Teacher, Expert Teacher, Lead Teacher
(c) Beginner Teacher, Expert Teacher, Lead Teacher, Proficient Teacher
(d) Beginner Teacher, Proficient Teacher, Expert Teacher, Lead Teacher
Ans: D
Sol:
- The career stages for teachers generally follow a progression where teachers start as beginners, gain proficiency, develop expertise, and potentially take on leadership roles. This sequence reflects the growth and development of teachers throughout their careers.
A detailed of the career stages and professional standards for teachers.
- Beginner Teacher: This stage represents the initial phase of a teacher's career. Beginner teachers are typically new to the profession and are in the early stages of gaining experience and developing their teaching skills. They may require guidance and support from more experienced colleagues or mentors. Teachers are focused on learning classroom management techniques, lesson planning, and implementing instructional strategies at this stage.
- Proficient Teacher: As teachers gain experience and become more confident in their teaching abilities, they progress to the Proficient Teacher stage. Proficient teachers have developed a solid foundation of pedagogical knowledge and skills. They can plan and deliver effective lessons, manage classroom dynamics, assess student learning, and provide appropriate feedback. Proficient teachers can often differentiate instruction to meet the diverse needs of their students.
- Expert Teacher: The Expert Teacher stage represents a high level of mastery and expertise in teaching. Teachers at this stage have accumulated years of experience and deeply understand teaching methodologies, curriculum content, and effective instructional practices. Expert teachers consistently demonstrate exemplary teaching skills and are often sought for knowledge and expertise. They may contribute to the profession by mentoring other teachers, conducting research, or leading professional development initiatives.
- Lead Teacher: The Lead Teacher stage represents a leadership role within the teaching profession. Lead teachers may take on additional responsibilities such as curriculum development, instructional coaching, or coordination of school-wide initiatives. They often serve as instructional leaders, providing guidance and support to other teachers. Lead teachers may collaborate professionally, participate in policy development, and advocate for educational improvement.
It's important to note that the progression through these career stages may vary depending on the context, educational system, and individual professional goals. Additionally, teachers may continuously engage in professional development activities and refine their career skills.
Therefore the correct sequence of career stages and professional standards for teachers is Beginner Teacher, Proficient Teacher, Expert Teacher, and Lead Teacher.
Q29: Which of the following is a tool being used to create e-portfolio of learners?
(a) MS-Word
(b) Fekara
(c) Mahara
(d) Fedena
Ans: C
Sol: Mahara:
- Mahara is a free and open-source e-portfolio system that allows users to create, collect, and reflect on their work.
- It is a web-based application that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Mahara is used by students, teachers, professionals, and others to showcase their work, reflect on their learning, and connect with others.
Mahara offers a variety of features that make it a powerful e-portfolio tool. These features include:
- Rich media support: Mahara supports various rich media formats, including text, images, audio, and video. This allows users to create portfolios that are engaging and informative.
- Collaboration tools: Mahara includes various collaboration tools that allow users to share their work with others and get feedback. This can be helpful for students, teachers, and professionals looking to get feedback on their work.
- Assessment tools: Mahara includes various assessment tools that can be used to assess student learning. This can be helpful for teachers who are looking to assess student learning more authentically.
Hence, Mahara is the tool being used to create e-portfolios for learners.
Q30: Which among the following is not a Learning Management System (LMS)?
(a) Angira
(b) Blackboard
(c) Canvas
(d) Swayam Prabha
Ans: D
Sol: Angira:
Angira is an open-source Learning Management System (LMS) developed by India's National Informatics Centre (NIC). It is designed to be used by educational institutions in India. Angira is a free and customizable LMS that can deliver educational content, track progress, and provide a learning experience for the end user.
Angira offers a variety of features that make it a powerful LMS, including:
- Content management: Creating, storing, and managing training content.
- Course management: The ability to create and manage courses, including setting up assessments and tracking progress.
- User management: The ability to create and manage users, including setting up permissions and tracking activity.
- Reporting: The ability to generate reports on training activity, such as completion rates and course time.
- Integration with other systems: Angira can be integrated with other systems, such as student information systems (SIS) and human resources (HR) systems.
Blackboard:
It is a commercial LMS that educational institutions and businesses worldwide use.It is one of the most popular LMSs on the market. Blackboard offers a variety of features that make it a powerful LMS, including:
- Content management: Creating, storing, and managing training content.
- Course management: The ability to create and manage courses, including setting up assessments and tracking progress.
- User management: The ability to create and manage users, including setting up permissions and tracking activity.
- Reporting: The ability to generate reports on training activity, such as completion rates and course time.
- Integration with other systems: Blackboard can be integrated with other systems, such as student information systems (SIS) and human resources (HR) systems.
Canvas:
It is a commercial LMS that educational institutions around the world use. It is known for its user-friendly interface and integration with other Google products. Canvas offers a variety of features that make it a powerful LMS, including:
- Content management: Creating, storing, and managing training content.
- Course management: The ability to create and manage courses, including setting up assessments and tracking progress.
- User management: The ability to create and manage users, including setting up permissions and tracking activity.
- Reporting: The ability to generate reports on training activity, such as completion rates and course time.
- Integration with other systems: Canvas can be integrated with other systems, such as student information systems (SIS) and human resources (HR) systems.
Swayam Prabha:
- Swayam Prabha is not a Learning Management System (LMS) but rather an initiative by the Indian government. It aims to provide educational content to learners through direct-to-home (DTH) television channels.
- Swayam Prabha broadcasts educational videos and lectures on various subjects, enabling access to educational resources for learners across India. However, it does not typically offer interactive and comprehensive features in an LMS.
Hence, SWAYAM PRABHA is not a Learning Management System (LMS).
Q31: Which of the following is a distinguished characteristic of Web 2.0 tools?
(a) Static web pages
(b) Internet of Things (IoT)
(c) Interactive Social Media
(d) Block chain
Ans: C
Sol: Web 2.0:
- Web 2.0 is the second generation of the World Wide Web, characterized by user-generated content and collaboration. Interactive social media is a key component of Web 2.0, as it allows users to interact with each other and share information in a way that was not possible with static web pages.
Some examples of interactive social media include:
- Social networking sites such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn
- Microblogging platforms such as Twitter and Tumblr
- Wikis such as Wikipedia and WikiHow
- Blogging platforms such as WordPress and Blogger
- Social bookmarking sites such as Delicious and Pinterest
- Online forums
- Chat rooms
- Instant messaging
- Interactive social media has greatly impacted how we communicate, learn, and share information. It has made it easier for people to connect with others from all over the world and given us a platform to share our thoughts, ideas, and experiences with a wider audience.
Here are some of the benefits of interactive social media:
- Collaboration: Interactive social media makes it easy for people to collaborate on projects and share ideas. This can lead to new and innovative solutions to problems.
- Communication: Interactive social media makes it easy for people to stay connected with friends and family, regardless of location. This can help to strengthen relationships.
- Learning: Interactive social media can be a great way to learn new things. Many educational resources are available on social media, and you can also connect with experts in your field to get advice and guidance.
- Creativity: Interactive social media can be a great way to express creativity. You can share your thoughts, ideas, and experiences with others and collaborate with others to create new things.
Overall, interactive social media is a powerful tool that can be used for various purposes. It can help us connect, learn new things, and express our creativity.
Hence, the distinguished characteristic of Web 2.0 tools is interactive social media.
Q32: Which one of the following basic elements of administrative process suggested by H.Fayol are not a part of POSDCORB?
(a) Coordinating and controlling
(b) Commanding and coordinating
(c) Controlling and Commanding
(d) Commanding and Cooperating
Ans: D
Sol: Fayol administration:
Fayol administration refers to the administrative principles and concepts formulated by Henri Fayol, a prominent French management theorist and practitioner. Fayol is often regarded as one of the pioneers of modern management theory, and his ideas have significantly impacted the field of management.
- H. Fayol's administrative process includes several basic elements essential for effective management. These elements are:
- Planning involves setting objectives, determining the best course of action to achieve those objectives, and developing strategies and plans to guide the organization.
- Organizing: This refers to arranging and structuring the resources and activities of the organization in a way that supports the achievement of goals. It includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing hierarchies, and allocating resources.
- Staffing: This involves recruiting, selecting, and training employees who are competent of performing their assigned tasks. It also includes activities related to employee development, performance appraisal, and maintaining a suitable work environment.
- Directing: This element focuses on providing employees guidance, leadership, and motivation to understand their roles and responsibilities and perform their tasks effectively. It includes giving instructions, issuing orders, and providing feedback.
- Coordinating involves harmonizing and integrating the activities and efforts of different individuals, departments, and teams within the organization to achieve common goals. It includes activities such as communication, collaboration, and resolving conflicts.
- Reporting: This element involves establishing systems and processes for collecting and disseminating information within the organization. It includes reporting progress, sharing updates, and maintaining transparency.
- Budgeting: Budgeting involves preparing and managing the financial resources of the organization. It includes financial planning, budget allocation, cost control, and financial analysis.
Of the options provided, "Commanding and Cooperating" is not explicitly mentioned in Fayol's administrative process.
Q33: National Education Policy-2020 recommended which of the following functioning for the General Education Council?
(a) Accreditation
(b) Academic Standard Setting
(c) Funding
(d) Regulation
Ans: B
Sol: General Education Council (GEC):
- The National Education Policy 2020 (NEP 2020) recommended the establishment of a General Education Council (GEC) to oversee and regulate school education in India.
- The GEC will be responsible for setting academic standards, curriculum frameworks, and assessment procedures for school education. It will also be responsible for accrediting schools and teacher education programs.
- The GEC will be a statutory body, independent of the government. It will be composed of experts from the fields of education, research, and industry. The GEC will be funded by the government, but it will have operational autonomy.
- The GEC is expected to play a key role in improving the quality of school education in India. It will be responsible for ensuring that all schools meet the same high standards, regardless of their location or affiliation. The GEC will also be responsible for promoting innovation and creativity in school education.
- The establishment of the GEC is a major step forward in the reform of school education in India. The GEC has the potential to transform school education in India and make it more relevant to the needs of the 21st century.
Here are some additional details about the GEC's role in academic standard setting:
- The GEC will develop a national curriculum framework for school education. This framework will be based on the principles of equity, relevance, and quality.
- The GEC will set academic standards for all subjects at all levels of school education. These standards will be based on the national curriculum framework.
- The GEC will develop assessment procedures to ensure that all students meet the academic standards. These assessment procedures will be aligned with the national curriculum framework.
- The GEC will accredit schools and teacher education programs to ensure that they meet the required standards.
- The GEC's role in academic standard setting is essential to ensure that all students in India have access to a high-quality education. The GEC's work will help to ensure that all students have the opportunity to reach their full potential.
Hence option 2 is the correct answer.
Q34: The ICF model focusses on which of the following components of Disability?
(a) Activities and Participation
(b) Medical descriptions
(c) Doctors Prescription
(d) Psychiatrists Prescription
Ans: A
Sol: ICF Model:
- The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) is a biopsychosocial model of disability that was developed by the World Health Organization (WHO). The ICF is a framework for understanding and measuring disability that emphasizes the interaction between health conditions, personal factors, and environmental factors.
The ICF model focuses on three components of disability: body functions and structures, activities and participation, and environmental factors.
- Body functions and structures refer to the physiological functions of body systems (such as vision, hearing, movement, and cognition) and the anatomical parts of the body (such as organs, limbs, and tissues).
- Activities and participation refer to the things that people do in their daily lives (such as walking, talking, working, and socializing).
- Environmental factors refer to the physical, social, and attitudinal contexts in which people live and conduct their activities (such as the built environment, transportation systems, social attitudes, and policies).
The ICF model is a biopsychosocial model of disability, which means that it recognizes that disability is not just a medical condition, but also a social and environmental issue. The model emphasizes the importance of considering all three components of disability when assessing and addressing the needs of people with disabilities.
The ICF model is used by health professionals, rehabilitation professionals, and policymakers to understand disability and to develop interventions that can help people with disabilities to live full and productive lives.
Therefore The ICF model focusses on Activities and Participationcomponents of Disability.
Q35: A child from culturally backward family background has been admitted to your school. As a school Head, you will:
(a) Keep him in a class in which, there are many more students from culturally backward background.
(b) Ask a teacher to know more about the cultural background of the child.
(c) Keep him in a normal class but will make special arrangement for teaching him, keeping his special needs in view.
(d) Advise him to take up vocational education.
Ans: C
Sol: As a school head, I would choose option 3. I would keep the child in a normal class but would make special arrangements for teaching him, keeping his special needs in view. This would include providing him with extra help and support, such as tutoring, remedial classes, and one-on-one attention from teachers. I would also make sure to create a welcoming and inclusive environment for the child, so that he feels comfortable and supported.
Here are some specific things I would do to help the child:
- I would meet with the child and his parents to learn more about his background and his needs.
- I would assign a teacher to work closely with the child and provide him with extra help and support.
- I would create a welcoming and inclusive environment for the child, so that he feels comfortable and supported.
- I would provide the child with opportunities to learn about different cultures and backgrounds.
- I would encourage the child to participate in extracurricular activities and clubs.
- I would work with the child's parents to ensure that he is getting the support he needs at home.
I believe that all children deserve the opportunity to succeed, regardless of their background. By providing the child with extra help and support, I can help him reach his full potential.
Here are some additional things to consider:
- It is important to be sensitive to the child's cultural background and to avoid making assumptions about his needs.
- It is also important to work with the child's parents to ensure that they are supportive of his education.
- By providing the child with the support he needs, we can help him succeed in school and in life.
Q36: According to Michael Spence (1973), which among the following assumptions of Signalling theory are true?
A. Individuals differ in productivity
B. Productivity is fully person specific
C. Individuals do not know their productivity, but their employers do.
D. Schooling levels can be observed without incurring a cost
E. The productivity of individual is affected by schooling
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, and D Only
(b) A, C and E Only
(c) A, B and D Only
(d) C, D and E Only
Ans: C
Sol: Signalling Theory:
- Signalling theory is a branch of economics that studies how information asymmetry affects economic decisions. Signaling theory was first developed by Michael Spence in 1973 to explain how firms and workers can overcome the problem of asymmetric information in the labour market.
- Signaling theory is based on the idea that workers can use signals to communicate their productivity to firms. Signals are observable characteristics that are correlated with productivity. For example, education is a signal of productivity because it is correlated with productivity. More productive workers are more likely to invest in education.
According to Michael Spence (1973), the following assumptions of Signalling theory are true:
- Individuals differ in productivity: This assumption is based on the idea that not all individuals are created equal. Some individuals are more productive than others. This productivity can be due to factors such as innate ability, motivation, and work ethic.
- Productivity is fully person specific: Productivity can be affected by several factors, including individual characteristics, such as innate ability and motivation, and environmental factors, such as family income and parental education. However, it is also true that some people are naturally more productive than others. This is due to a combination of factors, including their innate ability, motivation, and work ethic.
- Schooling levels can be observed without incurring a cost: This assumption is based on the idea that schooling levels are publicly available information. Employers can easily find out what level of education an individual has by looking at their resume or conducting a background check.
Therefore the correct answer is A, B and D Only.
Q37: For curriculum development, Ronald Doll identifies the following aims:
A. Intellectual aims
B. Social-personal aims
C. Productive aims
D. Aesthetic aims
E. Spiritual aims
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Only A, B and C
(b) Only B, C and D
(c) Only C, D and E
(d) Only A, C and E
Ans: A
Sol: Ronald C. Doll:
- Ronald C. Doll was an American educator and author. He was born in Mehoopany, Pennsylvania, in 1913. He received his bachelor's degree from Columbia University in 1934, his master's degree in 1935, and his doctorate in 1951.
- Doll taught and served as a counselor and an administrator in a number of public schools. He eventually began teaching in the education departments of New York City area universities. He was a professor of education at Teachers College, Columbia University, from 1951 to 1978. He was also a visiting professor at a number of other universities, including Harvard University, the University of Chicago, and the University of California, Berkeley.
- Doll was a prolific author. He wrote over 20 books and numerous articles on curriculum development, educational philosophy, and educational administration. His most famous book is "Curriculum Improvement: Decision Making and Process," which was first published in 1964.
- Doll was a major figure in the field of curriculum development. His work has had a profound impact on the way that curriculum is taught and implemented in schools around the world. He was a recipient of the Distinguished Service Award from the American Association of School Administrators and the Distinguished Research Award from the American Educational Research Association. He died in 1998.
Ronald Doll identifies the following aims for curriculum development:
- Intellectual aims: These aims are concerned with the development of students' thinking abilities. They include the ability to think critically, solve problems, and make decisions.
- Social-personal aims: These aims are concerned with the development of students' social and emotional skills. They include the ability to interact with others, resolve conflicts, and manage emotions.
- Productive aims: These aims are concerned with the development of students' skills and knowledge that will enable them to be productive members of society. They include the ability to find and keep a job, manage money, and care for themselves and their families.
Doll does not identify aesthetic or spiritual aims for curriculum development. Aesthetic aims are concerned with the development of students' appreciation for beauty and art. Spiritual aims are concerned with the development of students' understanding of their place in the world and their relationship to a higher power.
Thus the correct answer is 1) Only A, B and C.
Q38: NAAC methodology for Assessment and Accreditation of general higher education institutions is an example of :
(a) Quality control
(b) Quality management
(c) Quality assurance
(d) Quality inspection
Ans: C
Sol: The NAAC methodology for Assessment and Accreditation of general Higher Education institutions is an example of quality assurance.
Quality Assurance:
- Quality assurance is a systematic approach to ensuring that products, services, and processes meet customer expectations. It involves setting standards, monitoring performance, and taking corrective action when necessary.
- The NAAC methodology for Assessment and Accreditation of general Higher Education institutions is a comprehensive and systematic approach to ensuring the quality of higher education institutions in India. It involves a self-assessment by the institution, followed by an external peer review. The peer review team assesses the institution against a set of criteria and makes recommendations for improvement.
- The NAAC methodology for Assessment and Accreditation of general Higher Education institutions is an important tool for improving the quality of higher education in India. It helps institutions to identify their strengths and weaknesses and to make improvements to their programs and services. It also helps to ensure that students are receiving a high-quality education.
Here are some of the benefits of quality assurance:
- Improved quality: Quality assurance can help to improve the quality of products, services, and processes by identifying and addressing weaknesses.
- Increased customer satisfaction: Quality assurance can help to increase customer satisfaction by ensuring that products, services, and processes meet customer expectations.
- Reduced costs: Quality assurance can help to reduce costs by preventing defects and errors.
- Improved efficiency: Quality assurance can help to improve efficiency by streamlining processes and eliminating unnecessary steps.
- Increased compliance: Quality assurance can help to ensure compliance with regulations and standards.
- Improved reputation: Quality assurance can help improve an organisation's reputation by demonstrating its commitment to quality.
Q39: One of the accreditation schemes under NABET involves quality of:
(a) Pre-primary school governance
(b) Primary school governance
(c) Secondary school governance
(d) School governance
Ans: D
Sol: National Accreditation Board for Education and Training: The National Accreditation Board for Education and Training (NABET) is an autonomous body under the Quality Council of India (QCI) that is responsible for accrediting institutions and programs in the education and training sector. NABET has developed a number of accreditation schemes, one of which is the NABET Accreditation Scheme for School Governance.
The NABET Accreditation Scheme for School Governance is designed to assess the quality of school governance in terms of its effectiveness, efficiency, and sustainability. The scheme is based on the following criteria:
Leadership and management
- The leadership and management of a school should be effective and efficient. The school should have a clear vision and mission, and it should have a well-defined system for achieving its goals. The school should also have a strong management team that is capable of carrying out the school's vision and mission.
Governance and accountability
- The school should have a clear system of governance that ensures that the school is accountable to its stakeholders. The school should have a board of directors or trustees that is responsible for overseeing the school's operations. The school should also have a system for ensuring that the school is meeting the needs of its students and its stakeholders.
Human resources
- The school should have a qualified and competent workforce. The school should have a system for recruiting and selecting qualified staff. The school should also have a system for providing professional development for its staff.
Resources and infrastructure
- The school should have the resources and infrastructure it needs to provide a high-quality education. The school should have adequate facilities, equipment, and materials. The school should also have access to qualified staff and resources.
Curriculum and pedagogy
- The school should have a curriculum that is relevant to the needs of its students. The curriculum should be aligned with the national and state standards. The school should also have a pedagogy that is effective in teaching the curriculum.
Student learning and achievement
- The school should ensure that its students are learning and achieving at high levels. The school should have a system for assessing student learning and achievement. The school should also have a system for providing feedback to students and teachers.
Quality assurance
- The school should have a system for ensuring that it is meeting the highest standards of quality. The school should have a system for self-assessment and continuous improvement. The school should also be open to external scrutiny and evaluation.
The NABET Accreditation Scheme for School Governance is a valuable tool for schools that are committed to providing high-quality education and training. Accreditation provides schools with the recognition and support they need to achieve their goals and improve the lives of their students.
Hence option 4 is the correct answer.
Q40: Which of the following statements are not correct?
A. Social change is a local phenomenon
B. Speed of social change remains uniform
C. Social change occurs as an essential law
D. Definite prediction of social change is not possible
E. Social change is a global phenomenon
Choose the appropriate option:
(a) A and B Only
(b) B and C Only
(c) C and D Only
(d) D and E Only
Ans: A
Sol: Social change:
- It is a process that occurs at all levels of society, from the individual to the global. It is often driven by individual and collective action, and it can have a profound impact on the way people live and work. T
- he speed of social change varies depending on a number of factors, including the nature of the change, the level of resistance to change, and the resources available to support change.
- Social change is not a law, and it does not occur in a predictable or uniform way. It is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of factors, and it is not possible to predict with certainty how or when it will occur.
A. Social change is a local phenomenon. (Incorrect)
- Social change can occur at various levels, including local, regional, national, and global levels.)
B. Speed of social change remains uniform. (Incorrect)
- The speed of social change can vary depending on various factors and contexts. It is not necessarily uniform.)
C. Social change occurs as an essential law. (Correct)
- Social change is not an essential law but a result of complex interactions and dynamics within societies.)
D. Definite prediction of social change is not possible. (Correct)
- Social change is influenced by numerous factors and is difficult to predict with certainty.)
E. Social change is a Global Phenomenon. (Correct)
- Social change can occur at various scales, including global changes that impact societies worldwide.)
Therefore, the incorrect statements are A and B
Q41: Which of the following statements are true?
A. 'Veda' is not the name of any particular book
B. The hymns of Rig Veda are composed in the praise of gods
C. Vedic teachings belong to the 'Karma Marga'.
D. Upanishads are also called 'Vedanta'.
E. 'Vedanta' is the last part of Yajurveda.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C and D Only
(b) B, C, D and E Only
(c) C, D, E and A Only
(d) D, E, A and B Only
Ans: A
Sol: A. 'Veda' is not the name of any particular book. This is true.
- The Vedas are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda.
B. The hymns of Rig Veda are composed in the praise of God. This is also true.
- The Rigveda is a collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns counted among the four sacred Hindu texts known as the Vedas. It is the oldest Veda, and scholars consider it to be the foundational and oldest layer of Sanskrit literature. The Rigveda contains 1,028 Vedic Sanskrit hymns and 10,600 verses, organized into ten books (Mandalas). Each book is further organized into groups of hymns, with each hymn consisting of a series of verses. The hymns of the Rigveda are primarily composed in praise of the Vedic deities.
C. Vedic teachings belong to the 'Karma Marga'. This is also true.
- The Vedas are the oldest scriptures of Hinduism and are considered to be the foundation of Hindu philosophy. The Vedas teach that there are four paths to salvation, or moksha: karma marga, jnana marga, bhakti marga, and raja marga. Karma marga is the path of action, and it teaches that one can achieve salvation through selfless service and by following one's dharma, or duty.
D. Upanishads are also called 'Vedanta'. This is also true.
- The Upanishads are a collection of philosophical texts that are considered to be the culmination of the Vedas. The word "Upanishad" means "to sit near," and it refers to the practice of sitting near a teacher to receive instruction. The Upanishads are concerned with the nature of reality, the soul, and the relationship between the individual and the divine. They are also known as the Vedanta, which means "the end of the Vedas."
E. 'Vedanta' is the last part of Yajurveda. This is false.
- The Yajurveda is one of the four Vedas, and it is divided into two parts: the Shukla Yajurveda and the Krishna Yajurveda. The Shukla Yajurveda is the older of the two, and it is composed of hymns and sacrificial formulas. The Krishna Yajurveda is the younger of the two, and it is composed of hymns, sacrificial formulas, and prose s. The Vedanta is not a part of the Yajurveda.
Therefore the correct answer is 1) A, B, C, and D.
Q42: Which of the following statements are true in relation to values?
A. The term value is derived from Latin Word 'Valere'.
B. Value is defined as an enduring belief about the way things should be done or about the ends we desire.
C. Indian Constitution clearly enunciates the values of Justice, Liberty, Equity, Equality and Brotherhood in its Preamble.
D. The Parliamentary committee in Feb. 1999 identified five core universal values as : (a) Truth (b) Righteous conduct (c) Peace (d) Love (e) Non-violence
E. Values can only be taught at school level.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, and C
(b) A, B and D
(c) B, C and D
(d) C, D and E
Ans: B
Sol:
- A. The term value is derived from Latin Word 'Valere'. This is true. The word "value" comes from the Latin word "valere," which means "to be strong."
- B. Value is defined as an enduring belief about the way things should be done or about the ends we desire. This is also true. A value is a belief that guides our actions and decisions. It is something that we hold to be important, and it influences the way we live our lives.
- C. Indian Constitution clearly enunciates the values of Justice, Liberty, Equity, Equality and Brotherhood in its Preamble. This is false. The Indian Constitution does not mention the values of Justice, Liberty, Equity, Equality, and Brotherhood in its Preamble. The Preamble of the Indian Constitution mentions Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity, but not Equity. The correct term is "Fraternity," not "Brotherhood."
- D. The Parliamentary committee in Feb. 1999 identified five core universal values as : (a) Truth (b) Righteous conduct (c) Peace (d) Love (e) Non-violence. This is true. The Parliamentary committee in February 1999 identified five core universal values as: Truth, Righteous conduct, Peace, Love, and Non-violence.
- E. Values can only be taught at school level. This is false. Values can be taught at any age and in any setting. They can be taught at home, at school, in the workplace, and in the community.
Thus the correct answer is 2) A, B, and D.
Q43: For improving the quality of teachers, National Education Policy-2020 proposes:-
A. National Professional Standards for Teachers
B. 20 hours of Continuous Professional Development every year
C. National Mission for Mentoring
D. Horizontal Mobility of Teachers
E. Integrated Teacher Education Programme of four years
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C Only
(b) B, C and D Only
(c) A, C and E Only
(d) C, D and E Only
Ans: C
Sol: NEP 2020:
- The NEP 2020 is a comprehensive policy that aims to transform the education system in India. It is a bold and ambitious plan requiring significant investment and effort. However, if successful, it has the potential to make a real difference in the lives of millions of children and young people in India
The National Education Policy 2020 (NEP 2020) proposes the following measures for improving the quality of teachers:
National Professional Standards for Teachers:
The National Professional Standards for Teachers will set the minimum qualifications and competencies required for teachers. These standards will be based on the following six domains:
- Pedagogical content knowledge
- Pedagogical skills
- Assessment
- Communication
- Professional ethics
- Student and community engagement
The standards will be used to assess teachers during their recruitment, training, and professional development. They will also be used to provide teachers feedback and help them improve their practice.
National Mission for Mentoring:
- The National Mission for Mentoring will support new and experienced teachers through mentoring and coaching. Mentors will be experienced teachers who have been trained to provide support to their mentees. They will help mentees to develop their teaching skills, to reflect on their practice, and to overcome challenges.
Integrated Teacher Education Programme of Four Years
- The Integrated Teacher Education Programme of Four Years will provide teachers with the knowledge and skills they need to be effective in the classroom. The programme will cover various topics, including pedagogy, curriculum, assessment, and child development. It will also allow students to practice their teaching skills in real-world settings.
The NEP 2020's measures to improve the quality of teachers are ambitious and comprehensive. If implemented effectively, they can potentially transform India's education system.
Therefore, the correct answer is 3) A, C and E Only.
Q44: The distributive phase of Counselling focuses upon which problems of an individual?
A. Social
B. Educational
C. Vocational
D. Emotional
E. Occupational
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, and C only
(b) B, D and A only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: C
Sol: The distributive phase of Counseling focuses on the educational, vocational, and occupational problems of an individual. It is a process of helping individuals to make decisions about their future and to find the best fit for their skills and interests. The distributive phase of Counseling typically involves the following steps:
- Assessment: The counselor will assess the individual's interests, skills, and values.
- Exploration: The counselor will help the individual to explore different options and to identify potential career paths.
- Decision-making: The counselor will help the individual to make a decision about their future and to develop a plan to achieve their goals.
- Implementation: The counselor will help the individual to implement their plan and to make the transition to their new career.
- The distributive phase of Counseling can be a valuable resource for individuals who are facing educational, vocational, or occupational problems. It can help them to make informed decisions about their future and to find the best fit for their skills and interests.
A is incorrect because the distributive phase of Counseling does not focus on social problems. Social problems are typically addressed in the adjustive phase of Counseling.
D is incorrect because the distributive phase of Counseling does not focus on emotional problems. Emotional problems are typically addressed in the adjustive phase of Counseling.
Thus the correct answer is 3) B, C and E only.
Q45: Client - Centred Counselling hypothesizes that man is ________.
A. Rational
B. Self Centred
C. Socialized
D. Constructive
E. Forward moving
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D only
(b) A, C, D, E only
(c) A, B, D, E only
(d) B, C, E, D only
Ans: B
Sol: Client-centered counseling:
- Client-centered counseling, also known as person-centered counseling, is a humanistic approach to psychotherapy that was developed by Carl Rogers in the 1940s. It is based on the belief that people are inherently good and have the capacity to grow and change. The goal of client-centered counseling is to help clients become more self-aware and to develop a more positive self-concept.
Client-centered counseling hypothesizes that man is
- A. Rational: This means that individuals have the capacity for logical thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving.
- C. Socialized: People are influenced by their social environment and learn to conform to social norms.
- D. Constructive: This refers to the belief that individuals have an innate tendency toward growth, self-actualization, and becoming the best version of themselves. Client-Centered Counseling recognizes and supports this constructive and positive aspect of human nature.
- E. Forward Moving: Client-Centered Counseling views individuals as constantly striving to move forward, grow, and reach their full potential. It emphasizes the importance of facilitating this forward movement through the therapeutic relationship and creating conditions that support personal development.
Hence, A, C, D, E only includes the correct characteristics associated with Client-Centered Counseling's hypothesis about human nature.
Q46: Which among the following are the characteristics of Teaching profession?
A. It essentially involves an intellectual operation
B. It transforms into practice raw material
C. It tends towards self-organization
D. It does not bother much about autonomy
E. It has a common code of ethics
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) A, C and E Only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) D, C and E only
Ans: B
Sol: The characteristics of the teaching profession are: A. It essentially involves an intellectual operation
- Teaching is a profession that requires a high level of knowledge and expertise. Teachers must be able to understand and apply complex concepts, and they must be able to communicate these concepts to their students in a clear and concise way.
C. It tends towards self-organization
- Teachers are responsible for their own professional development. They must stay up-to-date on the latest research and best practices in education, and they must be able to adapt their teaching methods to meet the needs of their students.
E. It has a common code of Ethics
- Teachers are held to a high ethical standard. They must be honest, fair, and respectful of their students. They must also be able to maintain confidentiality and protect the privacy of their students.
- B is incorrect because teaching does not transform raw material into practice. Teaching is about imparting knowledge and skills to students, not about transforming raw materials into something new.
- D is incorrect because teaching does bother about autonomy. Teachers need to be able to make decisions about their own teaching practices and to be able to adapt their teaching to meet the needs of their students.
Thus the correct answer is 2) A, C and E only.
Q47: The verticals proposed by National Education Policy-2020, under the umbrella of Higher Education Commission of India are
A. Higher Education Grants Council
B. Professional Standard Setting Bodies
C. National Higher Education Regulatory Council
D. National Council for Teacher Education
E. National Accreditation Council
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and E only
(b) A, D and C only
(c) A, C and E Only
(d) C, D and B only
Ans: C
Sol: The National Education Policy 2020 (NEP 2020) proposes the following verticals under the umbrella of the Higher Education Commission of India (HECI):
- National Higher Education Regulatory Council (NHERC):
- This council will regulate higher education in India, including teacher education.
- National Accreditation Council (NAC):
- This council will be responsible for accrediting higher education institutions in India.
- Higher Education Grants Council (HEGC):
- This council will be responsible for funding higher education institutions in India.
The NEP 2020 also proposes several other measures to improve the quality of higher education in India, including:
- A new curriculum framework that emphasizes critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity
- A new assessment system that is more holistic and formative
- A new school governance system that gives more autonomy to schools
- A new teacher recruitment and training system that is more rigorous and selective
The NEP 2020 is a comprehensive policy that aims to transform the education system in India. It is a bold and ambitious plan requiring significant investment and effort. However, if successful, it has the potential to make a real difference in the lives of millions of children and young people in India.
Hence, the correct answer is 3) A, C and E Only.
Q48: Which is not the definition of disability as seen by the Human Rights and Equal opportunity Commission (1994) ?
(a) Loss of physical or mental function
(b) Loss of a part of the body
(c) Any condition which affects a person's thought processes
(d) Emotional stress
Ans: D
Sol:
- Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission (HREOC) defines disability as: "A physical or mental impairment that has a substantial and long-term adverse effect on a person's ability to carry out normal day-to-day activities."
Emotional stress is not included in this definition because it is not a physical or mental impairment. Emotional stress can be a symptom of a disability, but it is not a disability in itself.
- The HREOC's definition of disability is based on the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF), which is a global standard for understanding and measuring disability. The ICF defines disability as:
"A complex phenomenon, reflecting an interaction between impairments, activity limitations and participation restrictions. Impairments are problems in body functions or structures, such as significant deviation or loss of psychological, physiological or anatomical functions. Activity limitations are difficulties in executing activities in a manner or within the range considered normal for a human being. Participation restrictions are problems experienced by an individual in involvement in life situations."
- The ICF's definition of disability is more comprehensive than the HREOC's definition, as it includes impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. However, both definitions are based on the idea that disability is a complex phenomenon that is not limited to physical or mental impairments.
Hence Emotional stress is not the definition of disability as seen by the Human Rights and Equal opportunity Commission (1994).
Q49: Which of the following is not an essential activity of Instructional design?
(a) Identification of learners to enroll
(b) Analysis of learners' needs
(c) Development of learning material
(d) Summative Evaluation
Ans: A
Sol: Instructional design (ID):
- Instructional design (ID) is the systematic process of creating learning experiences that result in desired changes in learner knowledge, skills, and attitudes. The four essential activities of instructional design are
- Analysis of learners' needs. This is the first step in the instructional design process. It is important to understand the learners' prior knowledge, skills, and abilities, as well as their learning goals, to design instruction that is effective and relevant.
- Development of learning objectives. Once the learners' needs have been analyzed, developing learning objectives is next. Learning objectives specify what the learners should be able to do at the end of the instruction. They should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Development of learning material. The next step is to develop the learning material. This can include a variety of formats, such as text, audio, video, and interactive exercises. The learning material should be designed to meet the learning objectives and to be engaging and effective for the learners.
- Evaluation of learning. The final step in the instructional design process is to evaluate the learning. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as pre-tests, post-tests, and surveys. The evaluation should be used to determine whether the learners have met the learning objectives and to identify any areas where the instruction can be improved.
ID is a valuable tool for educators, trainers, and other professionals who want to create effective learning experiences. By following the steps of ID, you can ensure that your instruction is tailored to your learners' needs and that it effectively achieves your desired results.
Here are some of the benefits of instructional design:
- Effectiveness: ID can help you create more effective instruction in achieving your desired results.
- Efficiency: ID can help you save time and resources by ensuring your instruction is well-designed and efficient.
- Flexibility: ID can help you create flexible and adaptable instruction to your learners' needs.
- Scalability: ID can help you create scalable instruction that can be easily adapted to different audiences.
Therefore, the correct answer is the Identification of learners to enrol.
Q50: How many categories of disabilities are included in RPWD Act, 2016?
(a) 22
(b) 21
(c) 07
(d) 19
Ans: B
Sol: The Rights of Persons with disabilities Act, 2016:
- The Rights of Persons with disabilities Act, 2016 (RPwD Act) is a landmark piece of legislation that has the potential to improve the lives of millions of people with disabilities in India. The Act was passed by the Indian Parliament in December 2016 and came into force on April 19, 2017.
- The RPwD Act is a comprehensive piece of legislation that provides for a range of rights and entitlements for persons with disabilities. These rights include the right to equality, the right to non-discrimination, the right to education, the right to employment, the right to access to public places, the right to healthcare, and the right to rehabilitation.
The Rights of Persons with disabilities Act, 2016 (RPwD Act) includes 21 categories of disabilities. These are:
- Blindness
- Low vision
- Hearing impairment
- Speech and language impairment
- Locomotor disability
- Cerebral palsy
- Mental retardation
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Multiple disabilities
- Dwarfism
- Thalassemia
- Hemophilia
- Sickle cell anemia
- Muscular dystrophy
- Leprosy-cured
- Acid attack victims
- Burn victims
- Persons with chronic diseases
- Persons with HIV/AIDS
- Persons with mental illness
- The Act also includes a provision for "other disabilities" that are not specifically mentioned in the list. This provision is intended to ensure that all persons with disabilities are covered by the Act, regardless of the specific nature of their disability.
- The RPwD Act is a landmark piece of legislation that has the potential to improve the lives of millions of people with disabilities in India. By providing for a range of rights and entitlements, the Act seeks to ensure that persons with disabilities have equal opportunities and can participate fully in all aspects of society.
Therefore it is clear that The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (RPwD Act) includes 21 categories of disabilities.
Q51: Ralph Tyler and Hilda Taba grouped objectives of curriculum development into the following categories-
A. Knowledge acquisition
B. Psychomotor Domain
C. Intellectual Skills
D. Attitudes and Feelings
E. Academic skills or study habits
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C and D Only
(b) B, C, D and E only
(c) A, C, D and E only
(d) A, B, D and E only
Ans: C
Sol:
- Ralph Tyler and Hilda Taba were two of the most influential figures in the field of curriculum development. Tyler was a professor of education at the University of Chicago, and Taba was a professor of education at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Both Tyler and Taba were known for their work on curriculum theory and development, and their ideas have had a profound impact on the way that curriculum is taught and implemented in schools around the world.
Ralph Tyler and Hilda Taba grouped objectives of curriculum development into the following categories:
Knowledge acquisition:
- The goal of knowledge acquisition is to help students learn facts, concepts, and principles. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as lectures, readings, and discussions.
Intellectual skills:
- The goal of intellectual skills is to help students develop their thinking abilities. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and reasoning.
Attitudes and feelings:
- The goal of attitudes and feelings is to help students develop positive attitudes and feelings about themselves, others, and the world around them. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as role-playing, discussion, and experiential learning.
Academic skills or study habits:
- The goal of academic skills or study habits is to help students develop the skills they need to be successful in school. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as time management, note-taking, and test-taking strategies.
The psychomotor domain is not included in this categorization because it is concerned with the development of physical skills, such as those involved in sports, dance, and music. Tyler and Taba believed that these skills were important, but they did not consider them to be essential components of a well-rounded education.
Thus the correct answer is 3) A, C, D and E only.
Q52: Which of the following are Curriculum Implementation models?
A. Overcoming Resistance to Change (ORC) Model
B. Organizational Development (OD) Model
C. Concerns-Based Adoption (CBA) Model
D. Systems Model
E. Advance Organizer Model
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C and D Only
(b) B, C, D and E Only
(c) C, D, E and A Only
(d) D, E, A and B Only
Ans: A
Sol: The following are Curriculum Implementation models:
- Overcoming Resistance to Change (ORC) Model:
- The ORC Model is a framework for understanding and addressing the challenges of implementing change in organizations. It identifies five stages of change: awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, and adoption. The model suggests that change is more likely to be successful if it is planned and implemented in a way that takes into account the needs and concerns of those involved.
- Organizational Development (OD) Model:
- The OD Model is a systematic approach to improving organizational effectiveness. It focuses on the development of organizational structures, processes, and culture. The OD Model has been used to implement a wide range of changes, including curriculum changes.
- Concerns-Based Adoption (CBA) Model:
- The CBA Model is a framework for understanding the concerns of individuals who are implementing a new innovation. It identifies four stages of concern: personal, informational, management, and collaboration. The model suggests that it is important to address the concerns of individuals at each stage of implementation in order to ensure their success.
- Systems Model:
- The Systems Model is a framework for understanding the complex interactions between different elements of a system. It can be used to analyze the factors that influence the implementation of a new curriculum. The Systems Model suggests that it is important to consider the following factors when implementing a new curriculum: the goals of the curriculum, the resources available, the needs of the students, and the culture of the organization.
The Advance Organizer Model is a model of instruction that focuses on providing students with a framework for understanding new information. It does not address the challenges of implementing a new curriculum.
Therefore the correct answer is 1) A, B, C and D Only.
Q53: Which of the following are not true for ANCOVA ?
A. It uses partial correlation principles.
B. It transforms quasi-experiment into a true experiment.
C. It has two dependent variables.
D. It controls variance at analysis stage.
E. It controls variance at the time of structuring research design.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, E and B Only
(b) B, C and E only
(c) A, C and D Only
(d) D, B and C only
Ans: B
Sol:
- ANCOVA does not transform a quasi-experiment into a true experiment. A quasi-experiment is a study in which the researcher does not have full control over the independent variable. For example, a researcher might be interested in the effect of a new teaching method on student achievement. However, the researcher cannot randomly assign students to different teaching methods. Instead, the researcher might have to use existing classes or schools as the different treatment groups. This means that there may be other factors, such as the quality of the teachers or the students' prior knowledge, that could also affect the results.
- ANCOVA also does not have two dependent variables. ANCOVA is a statistical method that is used to compare the means of two or more groups on a single dependent variable, while controlling for the effects of one or more covariates.
- ANCOVA does not control variance at the time of structuring research design. ANCOVA is a statistical method that is used to control for the effects of covariates at the analysis stage.
- A and D are true for ANCOVA. ANCOVA uses partial correlation principles to control for the effects of covariates. ANCOVA also controls variance at the analysis stage.
Therefore the correct answer is B, C, and E.
Q54: When the size of the sample in a study increases:
A. The standard error approaches the standard deviation.
B. The magnitude of the error decreases.
C. Accuracy of prediction increases.
D. The sample mean moves away from the population mean
E. Generalization from the sample becomes more dependable.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D Only
(b) C, D and E Only
(c) B, D and C Only
(d) B, C and E Only
Ans: D
Sol:
- When the size of the sample in a study increases, the standard error decreases, the accuracy of prediction increases, and generalization from the sample becomes more dependable. This is because a larger sample size provides more information about the population, which allows for more accurate estimates of the population parameters.
- The standard error is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic. It is a measure of the variability of the statistic from sample to sample. The standard error decreases as the sample size increases because the sampling distribution becomes more narrow as the sample size increases. This means that the statistic is less likely to vary from sample to sample, and the estimates of the population parameters are more likely to be accurate.
- The accuracy of prediction is the degree to which the predictions made from a sample are accurate for the population. The accuracy of prediction increases as the sample size increases because the sampling distribution becomes more narrow as the sample size increases. This means that the predictions made from the sample are more likely to be accurate for the population.
- Generalization from the sample is the ability to make inferences about the population from the sample. Generalization from the sample becomes more dependable as the sample size increases because the sampling distribution becomes more narrow as the sample size increases. This means that the inferences made from the sample are more likely to be accurate for the population.
The following are incorrect statements:
- A. The standard error approaches the standard deviation. The standard error decreases as the sample size increases, while the standard deviation remains the same.
- D. The sample mean moves away from the population mean. The sample mean approaches the population mean as the sample size increases.
Therefore it can be concluded that, when the size of the sample in a study increases, the standard error decreases, the accuracy of prediction increases, and generalization from the sample becomes more dependable, hence the correct answer is 4.
Q55: On the basis of the procedure of inquiry, which of the following are types of case study?
A. Intrinsic case study
B. Descriptive case study
C. Evaluative case study
D. Instrumental case study
E. Interpretive case study
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and E only
(b) A, E and D Only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) C, D and E Only
Ans: A
Sol: Based on the procedure of inquiry, there are three types of case studies:
Descriptive case study:
- A descriptive case study is a detailed description of a particular situation or event. A descriptive case study aims to provide a rich and nuanced understanding of the case without making any judgments or interpretations.
- Descriptive case studies, such as anthropology, sociology, and education, are often used in the social sciences. They can be used to study a wide range of topics, such as a particular group's culture, a particular individual's behaviour, or the effectiveness of a particular program.
- To conduct a descriptive case study, the researcher will typically collect data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The data will then be analyzed to identify patterns and themes. The researcher will then write a detailed report that describes the case and its findings.
Evaluative case study:
- An evaluative case study is a study that evaluates the effectiveness of a particular program or intervention. An evaluative case study aims to determine whether the program or intervention is meeting its goals and objectives.
- Evaluative case studies are often used in education, social work, and public health. They can evaluate various programs and interventions, such as new teaching methods, social service programs, and public health campaigns.
- To conduct an evaluative case study, the researcher will typically collect data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The data will then be analyzed to identify the program's strengths and weaknesses. The researcher will then write a report describing the evaluation's findings.
Interpretative case study:
- An interpretative case study is a study that seeks to understand the meaning of a particular situation or event. An interpretative case study aims to understand how the case participants make sense of their world.
- Interpretative case studies are often used in anthropology, sociology, and education. They can be used to study a wide range of topics, such as the culture of a particular group, the behaviour of a particular individual, or the meaning of a particular event.
- To conduct an interpretative case study, the researcher will typically collect data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The data will then be analyzed to identify the participants' perspectives and interpretations. The researcher will then write a report describing the study's findings and their interpretation of the data.
The other two types of case studies, intrinsic and instrumental, are based on the purpose of the study, not the procedure of inquiry.
- Intrinsic case study: This type of case study is conducted, for its own sake, to understand a particular situation or event in depth.
- Instrumental case study: This type of case study is conducted to learn about something else, such as a particular theory or concept.
Hence, the correct answer is only 1) B, C and E.
Q56: Which among the following are not considered Assessment as Learning?
A. Teacher gives a unit test and assigns marks.
B. Teacher asks students to grade the assignment of their peers.
C. Teacher asks the students to do self assessment on a rubric
D. Teacher asks students to write a reflective journal.
E. Teacher gives grades and asks students to divide themselves into two groups based on their marks.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C Only
(b) B, C, D Only
(c) A, B, E Only
(d) C, D, E Only
Ans: C
Sol: Assessment as Learning: Assessment as learning is a formative assessment involving students in monitoring and gathering information about their own learning. They do this through self and/or peer- assessments to help understand how they are progressing in their learning and what, if anything, they can do to improve.
The following are not considered assessments as learning:
- A. Teacher gives a unit test and assigns marks. This is a summative assessment, which is used to measure student learning at the end of a unit or course.
- B. Teacher asks students to grade the assignment of their peers. This type of peer assessment is not considered assessment as learning because it does not involve students in monitoring their own learning.
- E. Teacher gives grades and asks students to divide themselves into two groups based on their marks. This is a type of summative assessment, and it does not involve students in monitoring their learning.
The following are considered assessments as learning:
- C. Teacher asks the students to do a self-assessment on a rubric. This is a type of self-assessment, which is a key component of assessment as learning.
- D. Teacher asks students to write a reflective journal. This is a type of self-assessment, which is a key component of assessment as learning.
Therefore the correct answer is option 3.
Q57: Which among the following should be the criteria to assess a teacher-made ICT resource?
A. Content validity
B. Language
C. Availability of app/application at learner's end
D. Time taken by teacher in development of the resource
E. Data/Bandwidth requirement
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D and E Only
(b) A, B, D and E Only
(c) B, C, D, and E Only
(d) A, B, C, and E Only
Ans: D
Sol: The criteria to assess a teacher-made ICT resource should include the following:
- A) Content validity is an important criterion to assess whether the information and materials included in the resource are accurate, relevant, and appropriate for the intended learning objectives. It ensures that the content aligns with the curriculum or educational standards.
- B) Language refers to the clarity, coherence, and appropriateness of the language used in the resource. It should be understandable to the target learners, free from ambiguity, and effectively convey the intended information.
- C) Availability of the app/application at the learner's end considers whether the technology or software needed to access and utilize the resource is accessible to the learners. It ensures learners have the tools or devices to use the resource effectively.
- E) Data/Bandwidth requirement is crucial to assess whether the resource requires a significant amount of data or a high-speed internet connection to function properly. Considering the limitations of learners' access to the internet or data availability, it is important to ensure that the resource can be used without imposing excessive data costs or relying on high-speed connections.
Option D, which states, "Time-taken by the teacher in the development of the resource," is not typically considered a criterion to assess the quality or effectiveness of an ICT resource because the time taken to develop a resource does not necessarily reflect its quality or suitability for learners. The effectiveness of an ICT resource is better assessed based on factors such as content validity, language, availability of necessary applications, and data/bandwidth requirements.
Therefore, the most appropriate answer is option 4) A, B, C, and E Only, as these criteria encompass the essential aspects to consider when assessing the quality and suitability of a teacher-made ICT resource.
Q58: Which among the following are Multisensory media?
A. Television
B. Graphs
C. Podcasts
D. Teleconferencing
E. Motion Picture Films
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, and E Only
(b) B, D and E Only
(c) B, C and D Only
(d) A, C and D Only
Ans: A
Sol: Multisensory Media:
- Multisensory media is a type of media that engages multiple senses, such as sight, hearing, touch, smell, and taste. Television, motion picture films, and teleconferencing are all examples of multisensory media because they engage multiple senses. Graphs and podcasts, on the other hand, are not multisensory media because they only engage one sense (sight and hearing, respectively).
- Multisensory media can be used for various purposes, such as education, entertainment, and marketing. For example, multisensory media can teach children about different cultures, provide entertainment for people of all ages, and promote products and services.
- Multisensory media is a powerful tool that can be used to engage and inform people. It can also be used to create immersive experiences that allow people to feel like they are part of the action.
Here are some examples of multisensory media:
- Television: Television is a multisensory medium because it engages both sight and hearing. Viewers can see the images on the screen and hear the broadcast sounds.
- Motion picture films: Motion picture films are multisensory media because they engage both sight and hearing. Viewers can see the images on the screen and hear the sounds being played.
- Tele-conferencing: Tele-conferencing is a multisensory medium because it engages sight and hearing. Participants can see each other on the screen and hear each other's voices.
- Virtual reality: Virtual reality is a multisensory medium because it engages sight, hearing, and touch. Users can see the virtual world, hear the sounds of the virtual world, and feel the objects in the virtual world.
- Augmented reality is a multisensory medium because it engages sight, hearing, and touch. Users can see the real world, hear the sounds of the real world, and feel the objects in the real world, as well as virtual objects that are superimposed on the real world.
Multisensory media is a growing field with many potential applications. As technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and immersive multisensory experiences in the future.
Hence the correct answer is 1.
Q59: Which of the following are the steps of Gagne's Nine step instructional design?
A. Gaining Attention
B. Creating content
C. Elicit Performance
D. Reviewing Performance
E. Providing Guidance
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and E only
(b) A, D and E Only
(c) A, C and E Only
(d) B, D and E Only
Ans: C
Sol: The nine steps of Gagne's Nine Events of Instruction are:
1.Gaining attention:
- The first step in Gagne's Nine Events of Instruction is to gain the attention of the learner. This can be done by using a variety of techniques, such as asking a question, telling a story, or showing a video. The goal is to get the learner's attention and focus on the learning material.
2. Informing the learner of the objective:
- The second step is to inform the learner of the objective of the lesson. This will help the learner to understand what they are expected to learn and why it is important. The objective should be clear, concise, and measurable.
3. Stimulating recall of prior learning:
- The third step is to stimulate recall of prior learning. This will help the learner to connect new information with what they already know. This can be done by asking questions, reviewing previous lessons, or providing a brief overview of the topic.
4. Presenting the content:
- The fourth step is to present the content of the lesson. This can be done in a variety of ways, such as through lectures, demonstrations, or hands-on activities. The goal is to present the information in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
5. Providing learning guidance:
- The fifth step is to provide learning guidance. This can be done by providing hints, feedback, or additional s. The goal is to help the learner to understand the material and to overcome any challenges they may be facing.
6. Eliciting the performance:
- The sixth step is to elicit the performance. This means giving the learner the opportunity to practice what they have learned. This can be done through a variety of activities, such as quizzes, tests, or projects. The goal is to assess the learner's understanding of the material and to provide feedback.
7. Providing feedback:
- The seventh step is to provide feedback. This is essential for helping the learner to improve their performance. The feedback should be specific, timely, and constructive.
8. Assessing the performance:
- The eighth step is to assess the performance. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as quizzes, tests, or projects. The goal is to measure the learner's mastery of the material.
9. Enhancing retention and transfer:
- The ninth and final step is to enhance retention and transfer. This means helping the learner to remember what they have learned and to apply it to new situations. This can be done through a variety of techniques, such as reviewing the material, providing practice opportunities, and encouraging the learner to apply the material to their own lives.
Gagne's Nine Events of Instruction is a powerful instructional design model that can be used to create effective learning experiences. By following these steps, you can help your learners to learn more effectively and efficiently.
Q60: Which among the following digital initiatives are being used by researchers/teachers for various research related activities?
A. e-Pathshala
B. Shodh Ganga
C. e-yantra
D. Shodh Gangotri
E. Shodh Sindhu
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D Only
(b) B, C and D Only
(c) B, D and E Only
(d) C, D and E Only
Ans: C
Sol: The following digital initiatives are being used by researchers/teachers for various research-related activities:
Shodh Ganga:
- Shodh Ganga is a repository of Indian theses and dissertations. It was launched in 2012 by the Indian Council of Social Science Research (ICSSR). The repository contains over 100,000 theses and dissertations in social sciences, humanities, and related disciplines. Shodh Ganga is a valuable resource for researchers, teachers, and students. It provides access to a wide range of research output, which can be used for research, teaching, and learning.
Shodh Gangotri:
- Shodh Gangotri is a database of research projects funded by the Indian government. It was launched in 2013 by the Department of Science and Technology (DST). The database contains over 100,000 science, engineering, and technology research projects. Shodh Gangotri is a valuable resource for researchers, teachers, and students. It provides information on ongoing and completed research projects, which can be used for research, teaching, and learning.
Shodh Sindhu:
- Shodh Sindhu is a database of research journals and e-books. It was launched in 2014 by the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD). The database contains over 100,000 research journals and e-books in various disciplines. Shodh Sindhu is a valuable resource for researchers, teachers, and students. It provides access to a wide range of scholarly literature, which can be used for research, teaching, and learning.
These digital initiatives are helping to make research more accessible and efficient. They provide researchers with the tools and resources to conduct high-quality research. They are also helping to promote collaboration and knowledge sharing among researchers.
Hence option 3 is the correct answer.
Q61: Which of the following are applicable to Quality Council of India ?
A. It is under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
B. It is operated by the Government of India only
C. It is under the Ministry of Education
D. It was formed in 1997.
E. It is a non-profit autonomous society.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, and E Only
(b) B, C and D Only
(c) A, B and C Only
(d) C, D and E Only
Ans: A
Sol: Quality Council of India:
- QCI is a non-profit autonomous society that was established in 1997.
- It is under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of the Government of India.
- QCI's mission is to promote total quality management (TQM) in India and to help Indian organizations achieve world-class standards of excellence.
- QCI offers a variety of services to organizations, including:
- Accreditation of certification bodies
- Training and development programs
- Consultancy services
- Information and dissemination services
- QCI is a member of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Asia-Pacific Quality Organization (APQO).
QCI has played a significant role in promoting TQM in India. It has helped to raise awareness of TQM among Indian organizations and has provided them with the tools and resources they need to implement TQM successfully. As a result of QCI's efforts, TQM has become increasingly popular in India and has helped to improve the quality of Indian products and services.
Here are some of the benefits of TQM:
- Improved quality of products and services
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Reduced costs
- Increased productivity
- Improved employee morale
- Enhanced competitive position
Therefore, the Quality Council of India (QCI) is a non-profit autonomous society formed in 1997. It is under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. So option 1) is the correct answer.
Q62: Match List I with List II
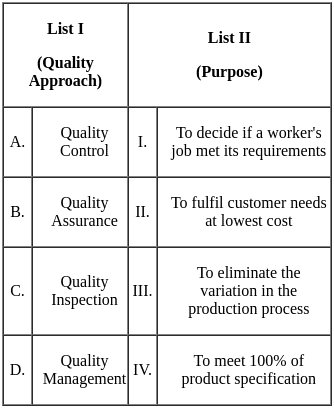
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(d) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
Ans: B
Sol: 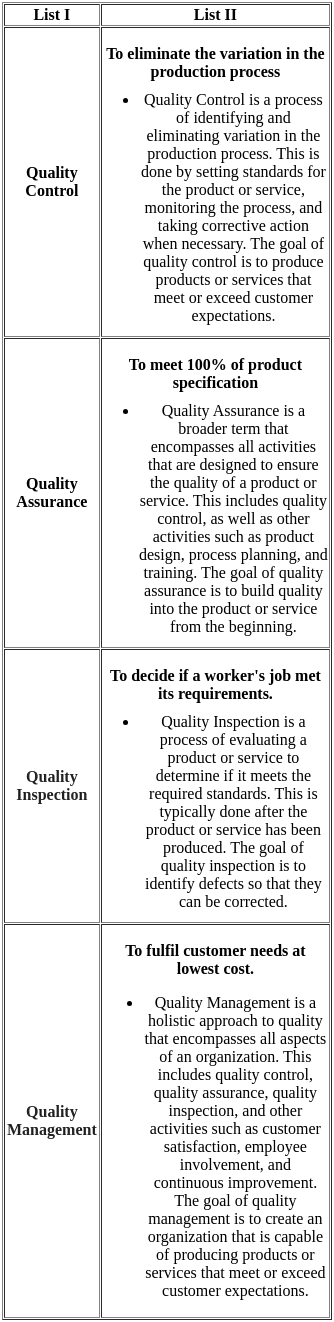
Hence the correct answer is 2) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II.
Q63: Match List I with List II
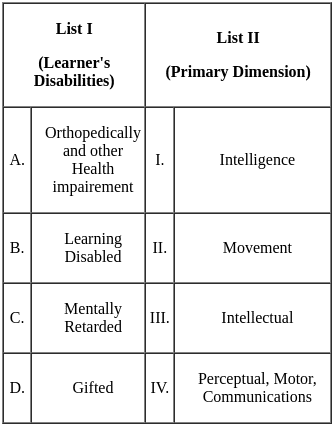
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: D
Sol: 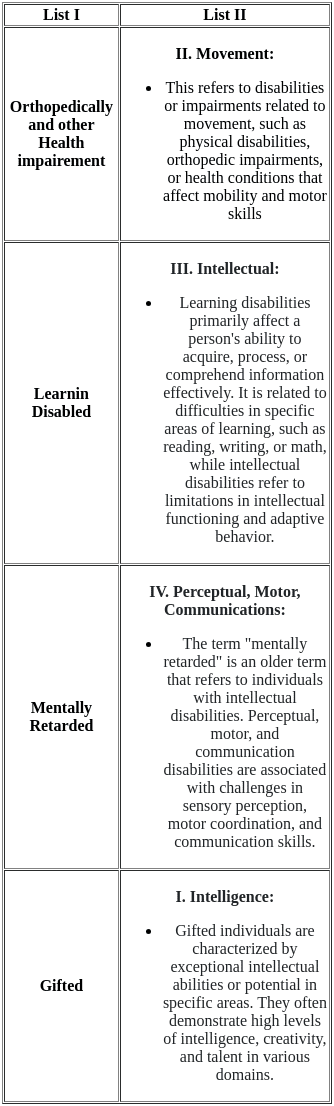
Therefore, the correct matching is A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I.
Q64: Sequence the last Five paths to liberation according to Buddha philosophy.
A. Right Concentration (Samyak Samadhi)
B. Right Effort (Samyak Vyayama)
C. Right mindfulness (Samyak Smrti)
D. Right livelihood (Samyak Ajiva)
E. Right conduct (Samyak Karmanta)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) E, C, D, B, A
(b) E, B, D, C, A
(c) E, D, B, C, A
(d) B, D, A, C, E
Ans: C
Sol: The last five paths to liberation according to Buddha philosophy are:
- Right conduct (Samyak Karmanta): This means behaving in a way that is ethical and compassionate. It includes abstaining from harming others, stealing, lying, sexual misconduct, and the use of intoxicants.
- Right livelihood (Samyak Ajiva): This means earning a living in a way that is ethical and does not harm others. It includes avoiding jobs that involve killing, stealing, lying, or the production or sale of intoxicants.
- Right effort (Samyak Vyayama): This means making an effort to overcome negative thoughts and emotions and to cultivate positive ones. It includes practicing mindfulness, meditation, and other techniques that help to develop concentration and equanimity.
- Right mindfulness (Samyak Smrti): This means being aware of the present moment and one's thoughts, feelings, and sensations without judgment. It includes practicing mindfulness meditation and other techniques that help to develop concentration and equanimity.
- Right concentration (Samyak Samadhi): This means achieving a state of deep concentration and tranquility. It includes practicing mindfulness meditation and other techniques that help to develop concentration and equanimity.
Therefore, the correct answer is 3) E, D, B, C, A.
Q65: Arrange the theorists in ascending order of their contribution to the theories of Learning:
A. E.L. Thorndike
B. Ivan P. Pavlov
C. Albert Bandura
D. Clark Hull
E. Edward C. Tolman
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, E, C, A
(b) C, A, B, D, E
(c) B, A, E, D, C
(d) E, C, A, B, D
Ans: C
Sol: The correct order of the theorists in ascending order of their contribution to the theories of Learning is:
Ivan P. Pavlov (1849-1936)
E.L. Thorndike (1874-1949)
Edward C. Tolman (1886-1959)
Clark Hull (1884-1952)
Albert Bandura (1925-
- Ivan P. Pavlov: Pavlov's work on classical conditioning laid the foundation for understanding how associations are formed between stimuli and responses. His experiments with dogs and the concept of conditioned reflexes are significant contributions to the field of learning.
- E.L. Thorndike: Thorndike's research focused on operant conditioning and the law of effect. He proposed the theory of instrumental learning, which emphasized the role of consequences in shaping behavior. Thorndike's work influenced later theories of behaviorism and learning.
- Edward C. Tolman: Tolman introduced the concept of cognitive maps and latent learning. He emphasized the importance of mental processes in learning and highlighted that behavior can be influenced by internal representations of the environment.
- Clark Hull: Hull's theories revolved around the concept of learning as a result of reinforcement. He developed the drive reduction theory and formulated mathematical models to explain learning processes. Hull's work contributed to the understanding of behavior and motivation.
- Albert Bandura: Bandura's social learning theory proposed that learning occurs through observation, imitation, and modeling. His research highlighted the role of social factors and cognitive processes in learning and emphasized the importance of vicarious reinforcement.
Therefore, the correct sequence is B, A, E, D, C.
Q66: Arrange the following in chronological order of their formation starting from the oldest to latest
A. Secondary Education Commission
B. Education Commission
C. National Knowledge Commission
D. University Education Commission
E. Justice Verma Commission
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, A, B, C, E
(b) B, D, A, E, C
(c) A, B, C, D, E
(d) D, C, E, B, A
Ans: A
Sol: The chronological order of the commissions is as follows:
- University Education Commission (1948-1949)
- Secondary Education Commission (1952-1953)
- Education Commission (1964-1966)
- National Knowledge Commission (2005-2009)
- Justice Verma Commission (2012-2013)
- The University Education Commission was the first education commission constituted in independent India. It was appointed in 1948 and submitted its report in 1949. The commission was headed by Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, who later became the President of India. The commission made a number of recommendations on the development of university education in India.
- The Secondary Education Commission was appointed in 1952 and submitted its report in 1953. The commission was headed by Dr. Lakshmanaswami Mudaliar. The commission made a number of recommendations on the development of secondary education in India.
- The Education Commission, also known as the Kothari Commission, was appointed in 1964 and submitted its report in 1966. The commission was headed by Dr. D.S. Kothari. The commission made a number of recommendations on the development of education in India at all levels.
- The National Knowledge Commission was appointed in 2005 by the Prime Minister of India, Dr. Manmohan Singh. The commission was headed by Mr. Sam Pitroda. The commission made a number of recommendations on the development of knowledge in India.
- The Justice Verma Commission was appointed in 2012 by the Prime Minister of India, Dr. Manmohan Singh, in the wake of the Nirbhaya gang rape case. The commission was headed by Justice J.S. Verma. The commission made a number of recommendations on the prevention of sexual violence against women in India.
The correct answer is 1) D, A, B, C, E.
Q67: Arrange the following chronologically:
A. The National Commission on Teachers - I
B. NCFTE : Towards preparing the Professional and Humane Teacher
C. The NPE review committee
D. National Advisory Committee on Learning without Burden
E. The Curriculum framework for Quality Teacher Education
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, A, C, D, E
(b) A, C, D, E, B
(c) C, A, B, E, D
(d) D, E, C, A, B
Ans: B
Sol: The chronological order is:
- A - The National Commission on Teachers - I (1983-85)
- C - The NPE review committee (1990)
- D - National Advisory Committee on Learning without Burden (1993)
- E - The Curriculum Framework for Quality Teacher Education (1998)
- B - NCFTE: Towards Preparing the Professional and Humane Teacher (2009)
Here are some more details about each of these:
The National Commission on Teachers - I (1983-85)
- Description: This commission, headed by Professor D.P. Chattopadhyaya, was established to review the status of teachers and teaching conditions in India. Its report aimed at improving teacher education and professional development.
The NPE review committee (1990)
- Description: This committee was set up to review the National Policy on Education (NPE) of 1986. It was headed by Acharya Ramamurti and provided recommendations for reforming various aspects of education, including teacher education.
National Advisory Committee on Learning without Burden (1993)
- Description: Headed by Professor Yash Pal, this committee was formed to address the issue of excessive academic burden on students. It recommended changes in curriculum and teaching methods to make learning more engaging and less stressful.
The Curriculum Framework for Quality Teacher Education (1998)
- Description: This framework was developed to provide guidelines for the quality improvement of teacher education programs in India. It emphasized professional competencies and continuous professional development for teachers.
NCFTE: Towards Preparing the Professional and Humane Teacher (2009)
- Description: The National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education (NCFTE) was formulated to guide the restructuring of teacher education. It aimed at preparing teachers who are not only professionally competent but also humane and sensitive to the diverse needs of learners.
Therefore, the correct answer is .A, C, D, E, B.
Q68: Arrange the steps of Wheeler's model for curriculum design in correct sequence:
A. Selection of Learning Experiences
B. Organization and Integration of Experiences
C. Aims, Goals and Objectives
D. Evaluation
E. Selection of Content
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, B, E, D
(b) C, B, A, E, D
(c) C, A, E, B, D
(d) E, C, B, A, D
Ans: C
Sol: Wheeler's model for curriculum design:
- Wheeler's model is a cyclical model, which means that it is an ongoing process. The curriculum should be evaluated on a regular basis and changes should be made as needed. This ensures that the curriculum is meeting the needs of the students and is relevant to the current world.
- Wheeler's model is a comprehensive model that takes into account all aspects of curriculum design. It is a useful tool for educators who are looking to develop a curriculum that is effective and meaningful.
Here are some of the advantages of using Wheeler's model for curriculum design:
- It is a comprehensive model that takes into account all aspects of curriculum design.
- It is a systematic approach to curriculum development that can help to ensure that the curriculum is effective and meaningful.
- It is a cyclical model that allows for continuous improvement and adaptation of the curriculum.
- Here are some of the disadvantages of using Wheeler's model for curriculum design:
- It can be a time-consuming and complex process.
- It requires a lot of input from a variety of stakeholders, which can be difficult to coordinate.
- It can be difficult to ensure that the curriculum is always meeting the needs of the students.
Wheeler's model for curriculum design is a cyclical model that consists of five steps:
1. Aims, goals, and objectives
- The first step is to identify the aims, goals, and objectives of the curriculum. This involves determining what the curriculum is trying to achieve and what students should be able to do after completing it.
2. Wheeler's model for curriculum design
- The next step is to select learning experiences that will help students achieve the aims, goals, and objectives of the curriculum. This involves choosing activities that are appropriate for the students' age, ability, and interests.
3. Selection of content
- The third step is to select the content that will be covered in the curriculum. This involves choosing topics that are relevant to the aims, goals, and objectives of the curriculum.
4. Organization and integration of experiences
- The fourth step is to organize and integrate the learning experiences and content into a coherent curriculum. This involves sequencing the activities and topics in a way that makes sense and provides a smooth flow of learning.
5. Evaluation
- The final step is to evaluate the curriculum. This involves assessing whether the curriculum is achieving its aims, goals, and objectives. It also involves identifying areas that can be improved.
Overall, Wheeler's model is a comprehensive and systematic approach to curriculum design that can be used to develop effective and meaningful curricula. However, it is important to be aware of the potential challenges involved in using this model.
Therefore, the correct order of the steps of Wheeler's model for curriculum design is: C, A, E, B, D.
Q69: Arrange the following research in an increasing order in terms of generalization of their respective findings:
A. Ethnographic research
B. Survey research
C. Experimental research
D. Action research
E. Case study research
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, E, B, C
(b) B, D, C, E, A
(c) D, E, A, C, B
(d) C, B, E, A, D
Ans: C
Sol: The correct order of research methods in terms of generalization of their respective findings is as follows:
- Action research
- Case study research
- Ethnographic research
- Experimental research
- Survey research
- Action research is not generalizable because it focuses on solving a specific problem in a particular setting. The action research results only apply to the specific setting in which the research was conducted.
- Case study research is the least generalizable type because it focuses on a single case or a small number of cases. This means that the results may not be applicable to other cases.
- Ethnographic research is also not generalizable because it involves an in-depth study of a particular culture or group. This means that the results may not be applicable to other cultures or groups of people.
- Experimental research is more generalizable than case studies or ethnographic research because it randomly assigns participants to different groups and manipulates an independent variable. This allows researchers to draw conclusions about cause-and-effect relationships.
- Survey research is the most generalizable type because it relies on self-reported data from many participants. This means that the results are less likely to be biased by participants' memories, perceptions, and social desirability bias.
Therefore, the correct order of research methods in terms of generalising their respective findings is D, E, A, C, B.
Q70: Gagne (1968) gave a sequence for cumulative learning for following learning types.
A. Concept
B. Multiple Discrimination
C. Stimulus-Response
D. Rules
E. Signal
Choose the correct sequence from the options given below:
(a) E, D, B, C, A
(b) E, D, A, B, C
(c) E, C, B, A, D
(d) C, A, B, E, D
Ans: C
Sol: Gagne's learning hierarchy is a theory of learning that proposes that new learning builds upon prior learning. To learn something new, you must first have mastered the prerequisite knowledge and skills. Gagne identified five levels of learning, each of which builds on the previous level:
- Signal learning: This is the simplest level of learning and involves learning to respond to a signal. For example, learning to stop when you see a red light.
- Stimulus-response learning: This level of learning involves learning to make a specific response to a specific stimulus. For example, learning to press a button when seeing a certain letter.
- Multiple discrimination learning: This level of learning involves learning to distinguish between different stimuli and appropriately respond to each one. For example, learning to identify different types of animals.
- Concept learning: This level of learning involves learning to group objects or events into categories based on common characteristics. For example, learning to classify animals as mammals, birds, reptiles, or amphibians.
- Rule learning: This level of learning involves learning to apply rules to solve problems. For example, learning to solve math problems using the rules of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Gagne's learning hierarchy is a useful tool for understanding how learning takes place. It can be used to design effective learning experiences tailored to the different levels of learning. For example, if you teach a class on animal classification, you would start by teaching students about the different types of animals. Once students have mastered the basic concepts, you can teach them about the classification rules.
- Gagne's learning hierarchy is a cumulative learning model, meaning that each learning level builds on the previous level. This means that you must first have mastered the lower levels to learn at a higher level. For example, to learn to solve math problems using rules, you must first be able to learn and understand the rules.
Therefore the correct sequence is E, C, B, A, D.
Q71: Arrange the following creative common licenses in the increasing order of restrictions.
A. CC-BY-SA
B. CC-BY-NC
C. CC-BY
D. CC-BY-ND
E. CC-BY-NC-ND
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D, C, E
(b) C, A, B, D, E
(c) D, C, B, A, E
(d) E, D, A, C, B
Ans: B
Sol: Creative Commons:
- Creative Commons is a nonprofit organization providing free, legally robust tools and licenses to enable creators to share their work while retaining certain rights. Creative Commons licenses are a set of standardized permissions that creators can apply to their creative works, such as text, images, music, videos, and more.
The arrangement of the Creative Commons licenses in increasing order of restrictions:
- CC-BY (Creative Commons Attribution): This license allows others to distribute, remix, tweak, and build upon the original work, even commercially, as long as they give appropriate credit to the original creator or licensor. This license has the fewest restrictions, allowing for the broadest use of the work.
- CC-BY-SA (Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike): This license includes the permissions of CC-BY, but it adds a requirement that any derivative works or adaptations of the original work must be released under the same or a compatible license. If someone modifies or builds upon the original work, they must share their derivative work under the same CC-BY-SA license.
- CC-BY-NC (Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial): This license allows others to remix, adapt, and build upon the original work as long as they give appropriate credit. However, this license prohibits commercial use of the work, so others cannot use it for commercial purposes without obtaining additional permission.
- CC-BY-ND (Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives): This license allows others to redistribute the original work commercially and non-commercially as long as it is unchanged and credited to the original creator. No derivative works or adaptations are allowed under this license.
- CC-BY-NC-ND (Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives): This license is the most restrictive as it combines the restrictions of CC-BY-NC and CC-BY-ND. It prohibits commercial use, does not allow derivative works, and requires proper attribution to the original creator.
Hence The correct answer is: option 2) C, A, B, D, E
Q72: Arrange in order the following stages of evolution of Organizational Quality Management.
A. Quality Management
B. Quality Assurance
C. Quality Inspection
D. Quality Control
E. Total Quality Management
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, B, A, E, C
(b) C, D, B, A, E
(c) B, A, D, E, C
(d) A, C, B, D, E
Ans: B
Sol: The stages of the evolution of Organizational Quality Management are as follows:
- Quality Inspection: This is the earliest stage of quality management, focusing on inspecting products or services after they have been produced.
- Quality Control: This stage focuses on controlling the quality of products or services during the production process.
- Quality Assurance: This stage focuses on assuring the quality of products or services before they are produced.
- Total Quality Management: This is the most comprehensive stage of quality management, and it focuses on the quality of all aspects of an organization, including its products, services, and processes.
Other Related Points
- The stages of evolution of Organizational Quality Management can be seen as a progression from a focus on inspecting products or services after they have been produced to a focus on controlling the quality of products or services during the production process, to a focus on assuring the quality of products or services before they are produced, and finally to a focus on the quality of all aspects of an organization.
- This progression reflects the increasing importance of quality management in organizations. In the early days of quality management, the focus was on inspecting products or services after they had been produced. This was because quality was seen as a problem that needed to be fixed after the fact. However, as quality management evolved, the focus shifted to controlling the quality of products or services during production. This was because it was realized that preventing problems from occurring in the first place was more efficient than fixing them after they had occurred.
- The next stage in the evolution of quality management focused on assuring the quality of products or services before they were produced. This was because it was realized that preventing problems from occurring in the first place was even more efficient than controlling them during the production process. The final stage in the evolution of quality management focuses on the quality of all aspects of an organization. This is because it is now realized that quality is not just a problem that needs to be fixed but an essential part of an organization's success.
The correct answer is 2. C, D, B, A, E.
Q73: Put the following laws in chronological order:
A. The Salamanca Declaration
B. The Biako Millennium Framework for Action for Asia and Pacific
C. UN Declaration on the Rights of Disabled Persons
D. The UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities
E. IEDSS
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D, B, E
(b) B, A, C, D, E
(c) C, A, B, D, E
(d) C, A, D, B, E
Ans: C
Sol: The chronological order of the laws is as follows:
- UN Declaration on the Rights of Disabled Persons (1975)
- The Salamanca Declaration (1994)
- The Bikawo Millennium Framework for Action for Asia and Pacific (2002)
- The UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (2006)
- IEDSS (2015)
- The United Nations General Assembly adopted the UN Declaration on the Rights of Disabled Persons on December 9, 1975. It was the first international instrument to address the rights of persons with disabilities specifically. The Declaration proclaims that persons with disabilities have the same fundamental rights as all other human beings and are entitled to the same opportunities to participate fully in society.
- The Salamanca Declaration was adopted by the World Conference on Special Needs Education in Salamanca, Spain, in June 1994. The Declaration calls for all children to be educated in regular schools, regardless of their disabilities or learning difficulties. It also calls for schools to be more inclusive so all children can learn together.
- The Biako Millennium Framework for Action for Asia and Pacific was adopted by the Asia-Pacific Decade of Disabled Persons 2003-2012 High-Level Intergovernmental Meeting in Beijing, China, in November 2002. The Framework calls for governments in the Asia-Pacific region to take action to improve the lives of persons with disabilities. It also calls for developing national plans of action to implement the Framework.
- The United Nations General Assembly adopted the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities on December 13, 2006. The Convention is the first international human rights treaty to address the rights of persons with disabilities specifically. It provides a comprehensive framework for protecting and promoting the rights of persons with disabilities.
- IEDSS stands for Inclusive Education for the Development of Sustainable Society. It is a global initiative that was launched in 2015. IEDSS aims to promote inclusive education and to ensure that all children, regardless of their disabilities or learning difficulties, have access to quality education.
Hence the correct answer is 3. C, A, B, D, E.
Q74: DISHA is a scheme of early intervention for which specified Disabilities?
A. Autism
B. ADHD
C. Cerebral Palsy
D. MR
E. Multiple Disabilities
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D Only
(b) B, C, D, E and A
(c) A, C, D and E only
(d) A, B, C and D Only
Ans: C
Sol: DISHA Scheme:
- The DISHA scheme is a government-funded scheme that aims to provide early intervention and school readiness for children with disabilities. The scheme was launched in 2017 and is currently available in all states and union territories of India except Jammu and Kashmir.
- The DISHA scheme is a valuable resource for children with disabilities and their families. It provides much-needed support and services that can help children with disabilities reach their full potential.
The DISHA scheme is a scheme of early intervention for children with the following disabilities:
- Autism
- Cerebral Palsy
- Mental Retardation
- Multiple Disabilities
The DISHA scheme provides a range of services to children with disabilities, including:
- Assessment and diagnosis of disabilities: The DISHA scheme provides free assessment and diagnosis of disabilities for children under the age of 6 years. This assessment is conducted by a team of experts, including doctors, psychologists, and therapists. The assessment helps to identify the child's specific needs and to develop an individualized plan of care.
- Early intervention services: The DISHA scheme provides a range of early intervention services for children with disabilities. These services are designed to help children develop their skills and abilities. Early intervention services can include speech therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy, and behavioral therapy.
- Training and counselling for parents and caregivers: The DISHA scheme provides training and counselling for parents and caregivers of children with disabilities. This training helps parents and caregivers to understand their child's disability and to develop strategies for supporting their child's development.
- Support for accessing education and other services: The DISHA scheme provides support for children with disabilities to access education and other services. This support can include help with transportation, financial assistance, and advocacy.
Therefore the correct answer is A, C, D and E only.
Q75: Match List I with List II
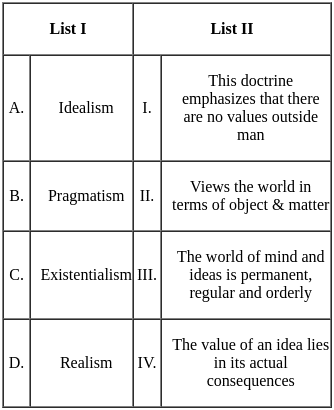
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D-I
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D-II
(c) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
Ans: B
Sol: 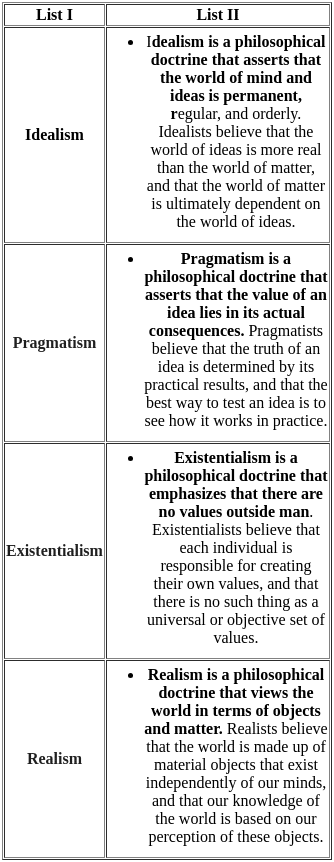 Hence the correct matching is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D-II.
Hence the correct matching is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D-II.
Q76: Match List I with List II
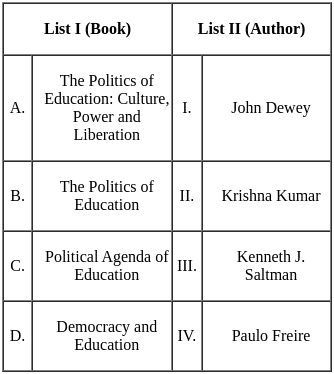
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(b) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Ans: C
Sol: 
Therefore the correct matching is A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Q77: Match List I with List II
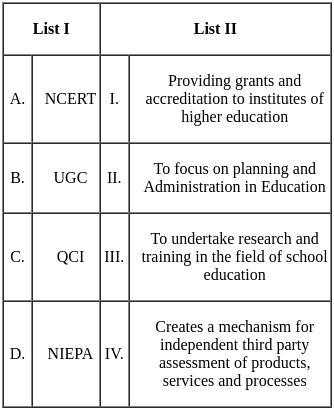
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(d) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
Ans: B
Sol: 
Therefore, the correct sequence is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Q78: Match List I with List II
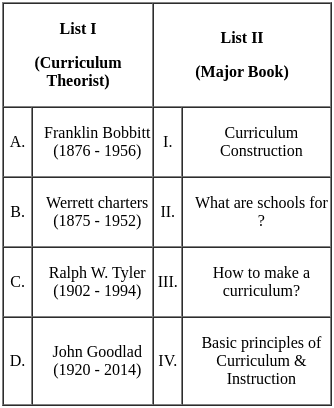
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: 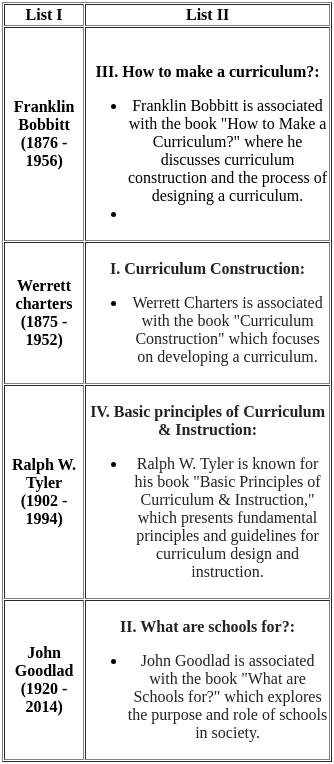
Hence the correct matching is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Q79: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
Ans: D
Sol: 
Hence the correct matching is A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III.
Q80: Which of the following statement(s) of Descartes relate him to the development of Idealism?
Statement I: That the self is the most immediate reality in the experience of each one of us.
Statement II: That the existence of God is evidenced in the experience of us by the fact that we have an idea of perfect being.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: A
Sol: Statement I: That the self is the most immediate reality in the experience of each one of us
- Descartes' famous statement "I think, therefore I am" is a statement of idealism. It states that the only thing that we can be sure of is our own existence, because we are the only thing that we can be sure of thinking.
- This is because we can doubt everything else, but we cannot doubt our own existence, because in order to doubt something, we must first exist in order to do the doubting.
Statement II: That the existence of God is evidenced in the experience of us by the fact that we have an idea of perfect being.
- Descartes' argument for the existence of God is also based on idealism. He argues that the idea of a perfect being is so great that it cannot have come from us, because we are imperfect beings. Therefore, the idea of a perfect being must have come from a perfect being, which is God.
- Idealism is the belief that reality is ultimately mental or ideal. It is opposed to realism, which is the belief that reality is ultimately material. Descartes' philosophy is often seen as a bridge between realism and idealism. He argued that the only thing that we can be sure of is our own existence, but he also argued that God exists and that the material world exists. This led some philosophers to see him as a realist, while others saw him as an idealist.
- Ultimately, whether Descartes is a realist or an idealist is a matter of interpretation. However, there is no doubt that his philosophy has had a profound influence on the development of idealism.
Hence, both Statement I and Statement II are true and relate Descartes to the development of Idealism.
Q81: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Learning outcomes are specific in nature.
Statement II: Learning outcomes are concerned with the product of learning.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: A
Sol: Statement I: Learning outcomes are specific in nature.
- This statement is true because learning outcomes should be clear, concise, and measurable. They should specify what students can do due to the learning experience. For example, a learning outcome for a math class might be "Students will be able to solve word problems involving fractions."
Statement II: Learning outcomes are concerned with the product of learning.
- This statement is also true because learning outcomes are about what students can do after learning something. They are not about the learning process, such as the activities or methods used to teach the content. For example, a learning outcome for a history class might be "Students will be able to identify the causes of the American Civil War."
Here are some examples of good learning outcomes:
- Students will be able to write a clear and concise essay.
- Students will be able to solve a quadratic equation.
- Students will be able to identify the main points of a persuasive speech.
- Students will be able to create a multimedia presentation.
- Students will be able to work effectively in a team.
By writing clear and specific learning outcomes, teachers can ensure their students learn what they need to know.
Hence, Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
Q82: Match List I with List II
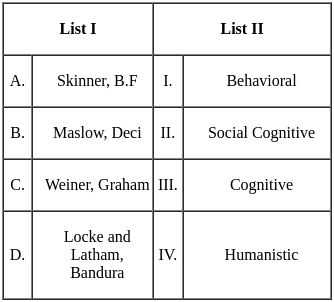
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(b) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(d) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
Ans: C
Sol: 
Hence the correct matching is A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II .
Q83: Which among the following are correct statements for the components of Critical Path Model (CPM)?
A. Events are represented by arrows.
B. The Earliest Start Time is the soonest time that an event can begin.
C. The Latest Start Time is calculated by working from the end of the diagram with the total time and subtracting the activity time from that.
D. Slack Event Time is the actual engagement time in an event.
E. The Slack Activity Time at node one should be zero.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) B, C and E only
(b) A, D and E Only
(c) C, D and A Only
(d) A, B and C Only
Ans: A
Sol: Critical Path Method (CPM):
- The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that helps to identify the tasks that are critical to the completion of a project. The CPM method uses a network diagram to represent the tasks in a project and the dependencies between them.
The following are some of the components of the Critical Path Method:
- Events: Events are represented by circles in a CPM network diagram. An event is a point in time when a task is completed.
- Activities: Activities are represented by arrows in a CPM network diagram. An activity is a task that takes time to complete.
- Earliest Start Time (EST): The EST is the soonest time that an event can begin. The EST is calculated by working from the beginning of the diagram and adding the activity times.
- Latest Start Time (LST): The LST is the latest time that an event can begin without delaying the project. The LST is calculated by working from the end of the diagram and subtracting the activity times.
- Slack Event Time: The slack event time is the amount of time that an event can be delayed without delaying the project. The slack event time is calculated by subtracting the EST from the LST.
- Slack Activity Time: The slack activity time is the amount of time that an activity can be delayed without delaying the project. The slack activity time is calculated by subtracting the EST of the successor event from the LST of the predecessor event.
Hence the correct answer is B, C and E only.
Q84: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(d) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
Ans: A
Sol: 
Hence the correct matching is A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III.
Q85: Given below are two statements :
Statement I: The ego ideal includes the rules and standards for good behavior.
Statement II: Conscience includes information about things that are viewed as bad by parents and society.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: A
Sol: Statement I: The ego ideal includes the rules and standards for good behavior.
- The ego ideal is a part of the superego, one of the three parts of the personality in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The superego is responsible for morality and conscience. It develops in early childhood due to the child's identification with their parents or other important caregivers. The superego contains the rules and standards for good behaviour that the child has learned from their parents. It also contains the child's ideal self, an image of what the child wants to be like.
Statement II: Conscience includes information about things that are viewed as bad by parents and society.
- The conscience is a part of the superego responsible for making the person feel guilty when they do something wrong. It contains information about things that are viewed as bad by parents and society. When the person does something considered bad by their conscience, they will feel guilty. This guilt can be a powerful motivator to change their behaviour.
So, both Statement I and Statement II are true. The ego ideal includes the rules and standards for good behaviour, and the conscience includes information about things that are viewed as bad by parents and society.
Q86: Given below are two statements :
Statement I: Behavioral approach of curriculum is logical and prescriptive and relies on technical and scientific principles
Statement II: Behavioral approach of curriculum is rooted in the works of John Dewey
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: C
Sol: Statement I: Behavioral approach of the curriculum is logical and prescriptive and relies on technical and scientific principles
- Statement I is true because the behavioural approach of curriculum is based on the idea that learning can be broken down into small, observable behaviours. These behaviours can then be taught and reinforced systematically. This approach relies on technical and scientific principles, such as reinforcement and shaping.
Statement II: Behavioral approach of curriculum is rooted in the works of John Dewey
- Statement II is false because the behavioural approach of curriculum is not rooted in the works of John Dewey. Dewey was a progressive educator who believed learning should be active, experiential, and problem-based. He did not believe in breaking down learning into small, observable behaviours.
- The behavioural approach of curriculum is associated with the work of B.F. Skinner, a psychologist who studied operant conditioning. Skinner believed that learning is a product of reinforcement and that behaviour can be shaped through trial and error.
- The behavioural approach of the curriculum has been criticized for being too mechanistic and for ignoring the importance of higher-order thinking skills. However, it has also been praised for its effectiveness in teaching basic skills.
Therefore the correct answer is Statement I is true, but Statement II is false.
Q87: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(b) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
Ans: B
Sol: 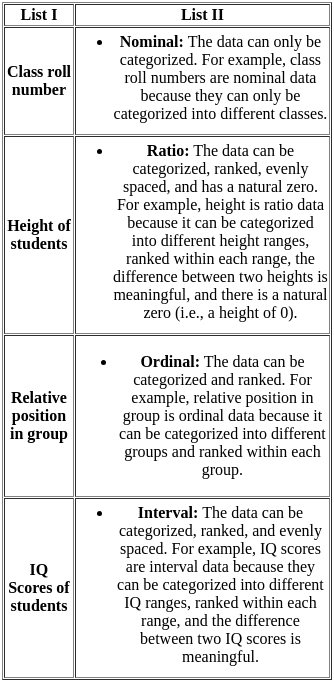
Hence the correct matching is A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I.
Q88: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Traditional pedagogical approaches would assume a teacher as an authoritarian figure, practising direct methods of instruction. Redefining this role around democratic principles involves rethinking both the concept of authority and forms of instruction used. In terms of the authority of the teacher educator, the issue is not one of somehow showing or neutralizing the power of teacher educator, since this is usually institutionally mandated, but how the authority is exercised at any moment in teacher education contexts. In other words, the focus becomes on how the teacher educator structures the teacher education context and uses their authority to enact democratic principles in doing so. The aim is to create a conceptual space for enacting a form of democracy when learners actively participate in a learning community that is richly connected and draws on funds of knowledge and expertise in a broader community. In terms of the forms of the instruction used, teaching becomes less oriented towards transmitting knowledge and principles of "best practices". Rather the forms of instruction become more dialogical and reflective as teacher candidates engage with a diversity of different viewpoints, beliefs, activities, policies and practices. Within this redefined role, teacher educator become facilitators of learning, provoking reflection on 'candidates' prior beliefs through discussion, joint problem solving, compromise and consensus. Positive, collaborative engaging relationships are crucial to non hierarchical pedagogical approaches, where students see each other as colloborators in the field of education rather than competitors.
Hierarchical pedagogical approaches promote
(a) Collaborative learning
(b) authoritarian learning
(c) Democratic teaching
(d) Reflective teaching
Ans: B
Sol: Hierarchical pedagogical approaches:
- Traditional or Hierarchical pedagogical approaches would assume a teacher is an authoritarian figure, practising direct methods of instruction.
- Hierarchical pedagogical approaches emphasize the authority and expertise of the teacher, with a primary focus on transmitting knowledge from the teacher to the students.
- These approaches limit student involvement and critical thinking, as students are expected to receive information and follow instruction passively. The teacher controls the learning process and makes decisions regarding content, pace, and evaluation.
Therefore Hierarchical pedagogical approaches promote authoritarian learning.
Q89: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Traditional pedagogical approaches would assume a teacher as an authoritarian figure, practising direct methods of instruction. Redefining this role around democratic principles involves rethinking both the concept of authority and forms of instruction used. In terms of the authority of the teacher educator, the issue is not one of somehow showing or neutralizing the power of teacher educator, since this is usually institutionally mandated, but how the authority is exercised at any moment in teacher education contexts. In other words, the focus becomes on how the teacher educator structures the teacher education context and uses their authority to enact democratic principles in doing so. The aim is to create a conceptual space for enacting a form of democracy when learners actively participate in a learning community that is richly connected and draws on funds of knowledge and expertise in a broader community. In terms of the forms of the instruction used, teaching becomes less oriented towards transmitting knowledge and principles of "best practices". Rather the forms of instruction become more dialogical and reflective as teacher candidates engage with a diversity of different viewpoints, beliefs, activities, policies and practices. Within this redefined role, teacher educator become facilitators of learning, provoking reflection on 'candidates' prior beliefs through discussion, joint problem solving, compromise and consensus. Positive, collaborative engaging relationships are crucial to non hierarchical pedagogical approaches, where students see each other as colloborators in the field of education rather than competitors.
Which of the following is not promoted by teacher following non-hierarchical approaches for facilitating learning among students:
(a) Collaboration
(b) Competition
(c) Discussion
(d) Best practices
Ans: B
Sol:
- The passage emphasizes that in non-hierarchical pedagogical approaches, teachers take on the role of facilitators of learning rather than being authoritative figures who preach or dictate knowledge to students. Instead, teachers provoke reflection, engage students in discussion, promote joint problem-solving, and encourage compromise and consensus-building.
- The focus is creating a collaborative learning environment where students actively participate and engage with diverse viewpoints, beliefs, activities, policies, and practices.
Therefore, teaching in non-hierarchical approaches does not promote Competition in facilitating student learning.
Q90: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Traditional pedagogical approaches would assume a teacher as an authoritarian figure, practising direct methods of instruction. Redefining this role around democratic principles involves rethinking both the concept of authority and forms of instruction used. In terms of the authority of the teacher educator, the issue is not one of somehow showing or neutralizing the power of teacher educator, since this is usually institutionally mandated, but how the authority is exercised at any moment in teacher education contexts. In other words, the focus becomes on how the teacher educator structures the teacher education context and uses their authority to enact democratic principles in doing so. The aim is to create a conceptual space for enacting a form of democracy when learners actively participate in a learning community that is richly connected and draws on funds of knowledge and expertise in a broader community. In terms of the forms of the instruction used, teaching becomes less oriented towards transmitting knowledge and principles of "best practices". Rather the forms of instruction become more dialogical and reflective as teacher candidates engage with a diversity of different viewpoints, beliefs, activities, policies and practices. Within this redefined role, teacher educator become facilitators of learning, provoking reflection on 'candidates' prior beliefs through discussion, joint problem solving, compromise and consensus. Positive, collaborative engaging relationships are crucial to non hierarchical pedagogical approaches, where students see each other as colloborators in the field of education rather than competitors.
Democratic principles in teaching learning are promoted by an educator through -
(a) Personal belief of teachers
(b) Authoritative teacher
(c) Discouraging dialogue
(d) Collaborative learning
Ans: D
Sol:
- Positive, collaborative engaging relationships are crucial to non-hierarchical pedagogical approaches, where students see each other as collaborators in the field of education rather than competitors.
- Collaborative learning is a specific approach to promoting democratic principles in teaching and learning. However, collaborative learning can be considered a strategy that aligns with the broader principles discussed in the passage, such as active student participation, dialogue, joint problem-solving, and collaboration.
Therefore, an educator clearly promotes Democratic principles in teaching-learning through collaborative learning.
Q91: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Traditional pedagogical approaches would assume a teacher as an authoritarian figure, practising direct methods of instruction. Redefining this role around democratic principles involves rethinking both the concept of authority and forms of instruction used. In terms of the authority of the teacher educator, the issue is not one of somehow showing or neutralizing the power of teacher educator, since this is usually institutionally mandated, but how the authority is exercised at any moment in teacher education contexts. In other words, the focus becomes on how the teacher educator structures the teacher education context and uses their authority to enact democratic principles in doing so. The aim is to create a conceptual space for enacting a form of democracy when learners actively participate in a learning community that is richly connected and draws on funds of knowledge and expertise in a broader community. In terms of the forms of the instruction used, teaching becomes less oriented towards transmitting knowledge and principles of "best practices". Rather the forms of instruction become more dialogical and reflective as teacher candidates engage with a diversity of different viewpoints, beliefs, activities, policies and practices. Within this redefined role, teacher educator become facilitators of learning, provoking reflection on 'candidates' prior beliefs through discussion, joint problem solving, compromise and consensus. Positive, collaborative engaging relationships are crucial to non hierarchical pedagogical approaches, where students see each other as colloborators in the field of education rather than competitors.
Which one of the following is not the institution mandated authority of the teacher ?
(a) Time table
(b) Time duration
(c) Medium of Instruction
(d) Methods of instruction
Ans: D
Sol:
- Methods of instruction s not the institution-mandated authority of the teacher. Because the institution may mandate certain aspects of a teacher's authority, such as curriculum requirements or assessment guidelines, the institution does not typically dictate the methods of instruction used.
- Teachers have autonomy in choosing instructional strategies and approaches that best suit their students' needs and align with their educational philosophy.
Q92: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Traditional pedagogical approaches would assume a teacher as an authoritarian figure, practising direct methods of instruction. Redefining this role around democratic principles involves rethinking both the concept of authority and forms of instruction used. In terms of the authority of the teacher educator, the issue is not one of somehow showing or neutralizing the power of teacher educator, since this is usually institutionally mandated, but how the authority is exercised at any moment in teacher education contexts. In other words, the focus becomes on how the teacher educator structures the teacher education context and uses their authority to enact democratic principles in doing so. The aim is to create a conceptual space for enacting a form of democracy when learners actively participate in a learning community that is richly connected and draws on funds of knowledge and expertise in a broader community. In terms of the forms of the instruction used, teaching becomes less oriented towards transmitting knowledge and principles of "best practices". Rather the forms of instruction become more dialogical and reflective as teacher candidates engage with a diversity of different viewpoints, beliefs, activities, policies and practices. Within this redefined role, teacher educator become facilitators of learning, provoking reflection on 'candidates' prior beliefs through discussion, joint problem solving, compromise and consensus. Positive, collaborative engaging relationships are crucial to non hierarchical pedagogical approaches, where students see each other as colloborators in the field of education rather than competitors.
For the pedagogical approaches centred around the democratic principles, which of the following is correct for the role of teachers with respect to teaching?
(a) The teaching become less oriented towards transmitting knowledge and principles of "best practice".
(b) Teaching does not engage learners with diversity
(c) Teaching focuses on preaching other than facilitating the learning
(d) Teaching is a hierarchical approach
Ans: A
Sol: Key Points
- In pedagogical approaches centred around democratic principles, teachers shift from simply transmitting knowledge and established practices to engaging learners in dialogical and reflective processes.
- The aim is to create a learning environment where teacher candidates actively participate, discuss different viewpoints, engage in joint problem-solving, and reflect on their beliefs. The role of the teacher becomes that of a facilitator of learning, provoking reflection and encouraging collaboration among students.
- This approach emphasizes a non-hierarchical relationship and learner collaboration rather than a top-down, authoritative teaching style.
Therefore the correct answer is option 1. The teaching becomes less oriented towards transmitting knowledge and principles of "best practice".
Q93: Which of the following are the guidelines of W. Edwards Deming for quality improvement of management?
A. Allocate huge sum of money
B. Eliminate fear
C. Use modern training methods on the job
D. Force employees to perform better
E. Stop depending on mass inspection
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D Only
(b) C, D and E Only
(c) A, D and E Only
(d) B, C and E Only
Ans: D
Sol: W. Edwards Deming:
- W. Edwards Deming was an American engineer, statistician, professor, author, lecturer, and management consultant. He is widely considered to be the father of the modern quality movement. Deming's 14 Points for Management are a set of principles that he believed were essential for improving quality and productivity.
The following are some of Deming's guidelines for quality improvement of management:
- Eliminate fear: Deming believed that fear is a major obstacle to quality improvement. He argued that employees need to feel safe in order to be creative and take risks.
- Use modern training methods on the job: Deming believed that training is essential for quality improvement. He argued that employees need to be trained in the latest methods and techniques in order to be effective.
- Stop depending on mass inspection: Deming believed that mass inspection is a waste of resources. He argued that it is better to focus on preventing defects in the first place.
Deming's 14 Points for Management have been widely adopted by businesses and organizations around the world. They have been credited with helping to improve quality and productivity in a variety of industries.
The correct answer is B, C and E Only.
Q94: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Now what is knowledge ? Is knowledge related to intelligence ? Intelligence uses knowledge, intelligence being the capacity to think clearly, objectively, safely and healthily. Intelligence is a state in which there is no personal emotion involved, no personal opinion, prejudice or inclination. Intelligence is the capacity for direct understanding. I am afraid this is rather difficult, but it is important, it is good for you to exercise your brain. So there is knowledge, which is the past continually being added to, and there is intelligence. Intelligence is the quality of the mind that is very sensitive, very alert, very aware. Intelligence does not hold on to any particular judgement or evaluation, but is capable of thinking very clearly, objectively. Intelligence has no involvement. Are you following? Now, how is this intelligence to be cultivated? What is the capacity of this intelligence? You are living here, being educated in all the various disciplines, in various branches of knowledge. Are you also being educated so that intelligence comes into being at the same time? You cannot think clearly if you are prejudiced, if you have opinions. You cannot think clearly if you are not sensitive; sensitive to nature, sensitive to all the things that are happening around you, sensitive not only to what is happening outside you but also inside you. If you are not sensitive, if you are not aware, you cannot think clearly. Intelligence implies that you see the beauty of the earth, the beauty of the trees, the beauty of the skies, the lovely sunset, the stars, the beauty of subtlety.
The paragraph is focussing upon -
(a) Discipline and Judgement
(b) Opinions and Prejudice
(c) Knowledge and Intelligence
(d) Thinking and Evaluation
Ans: C
Sol:
- According to the paragraph, knowledge refers to accumulating information over time. It is described as the past continually being added to.
- On the other hand, intelligence is defined as the capacity to think objectively, safely, and healthily. The absence of personal emotions, opinions, prejudices, or inclinations characterizes it. Intelligence is the ability to understand directly without being influenced by personal biases.
Therefore the paragraph focuses on Knowledge and Intelligence.
Q95: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Now what is knowledge ? Is knowledge related to intelligence ? Intelligence uses knowledge, intelligence being the capacity to think clearly, objectively, safely and healthily. Intelligence is a state in which there is no personal emotion involved, no personal opinion, prejudice or inclination. Intelligence is the capacity for direct understanding. I am afraid this is rather difficult, but it is important, it is good for you to exercise your brain. So there is knowledge, which is the past continually being added to, and there is intelligence. Intelligence is the quality of the mind that is very sensitive, very alert, very aware. Intelligence does not hold on to any particular judgement or evaluation, but is capable of thinking very clearly, objectively. Intelligence has no involvement. Are you following? Now, how is this intelligence to be cultivated? What is the capacity of this intelligence? You are living here, being educated in all the various disciplines, in various branches of knowledge. Are you also being educated so that intelligence comes into being at the same time? You cannot think clearly if you are prejudiced, if you have opinions. You cannot think clearly if you are not sensitive; sensitive to nature, sensitive to all the things that are happening around you, sensitive not only to what is happening outside you but also inside you. If you are not sensitive, if you are not aware, you cannot think clearly. Intelligence implies that you see the beauty of the earth, the beauty of the trees, the beauty of the skies, the lovely sunset, the stars, the beauty of subtlety.
The implication of intelligence is:
(a) One can see beauty around
(b) One can think critically always
(c) One can evaluate the surrounding
(d) One can judge properly always
Ans: A
Sol:
According to the paragraph, the implication of intelligence is that one can see the beauty of the earth, the beauty of the trees, the beauty of the skies, the lovely sunset, the stars, and the beauty of subtlety.
Therefore it can be concluded that intelligence implies that one can see the beauty around.
Q96: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Now what is knowledge ? Is knowledge related to intelligence ? Intelligence uses knowledge, intelligence being the capacity to think clearly, objectively, safely and healthily. Intelligence is a state in which there is no personal emotion involved, no personal opinion, prejudice or inclination. Intelligence is the capacity for direct understanding. I am afraid this is rather difficult, but it is important, it is good for you to exercise your brain. So there is knowledge, which is the past continually being added to, and there is intelligence. Intelligence is the quality of the mind that is very sensitive, very alert, very aware. Intelligence does not hold on to any particular judgement or evaluation, but is capable of thinking very clearly, objectively. Intelligence has no involvement. Are you following? Now, how is this intelligence to be cultivated? What is the capacity of this intelligence? You are living here, being educated in all the various disciplines, in various branches of knowledge. Are you also being educated so that intelligence comes into being at the same time? You cannot think clearly if you are prejudiced, if you have opinions. You cannot think clearly if you are not sensitive; sensitive to nature, sensitive to all the things that are happening around you, sensitive not only to what is happening outside you but also inside you. If you are not sensitive, if you are not aware, you cannot think clearly. Intelligence implies that you see the beauty of the earth, the beauty of the trees, the beauty of the skies, the lovely sunset, the stars, the beauty of subtlety.
Intelligence being the capacity to think clearly, objectively, safely and healthily, uses -
(a) Knowledge
(b) Comprehension
(c) Analysis
(d) Reflection
Ans: A
Sol:
- Intelligence is a state in which no personal emotion is involved, no personal opinion, prejudice or inclination. Intelligence is the capacity for direct understanding.
- Intelligence is the capacity to think objectively, safely and healthily. For this purpose, intelligence uses knowledge.
Q97: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Now what is knowledge ? Is knowledge related to intelligence ? Intelligence uses knowledge, intelligence being the capacity to think clearly, objectively, safely and healthily. Intelligence is a state in which there is no personal emotion involved, no personal opinion, prejudice or inclination. Intelligence is the capacity for direct understanding. I am afraid this is rather difficult, but it is important, it is good for you to exercise your brain. So there is knowledge, which is the past continually being added to, and there is intelligence. Intelligence is the quality of the mind that is very sensitive, very alert, very aware. Intelligence does not hold on to any particular judgement or evaluation, but is capable of thinking very clearly, objectively. Intelligence has no involvement. Are you following? Now, how is this intelligence to be cultivated? What is the capacity of this intelligence? You are living here, being educated in all the various disciplines, in various branches of knowledge. Are you also being educated so that intelligence comes into being at the same time? You cannot think clearly if you are prejudiced, if you have opinions. You cannot think clearly if you are not sensitive; sensitive to nature, sensitive to all the things that are happening around you, sensitive not only to what is happening outside you but also inside you. If you are not sensitive, if you are not aware, you cannot think clearly. Intelligence implies that you see the beauty of the earth, the beauty of the trees, the beauty of the skies, the lovely sunset, the stars, the beauty of subtlety.
A student can think clearly, if -
(a) he is sensitive to nature
(b) he is prejudiced
(c) he is not reflective
(d) he is not understanding
Ans: A
Sol:
- This passage illustrates that one can not think clearly if one is prejudiced in giving opinions.
- Moreover, sensitivity, especially sensitivity towards nature and all the things happening around us, is very important to think clearly.
Therefore it can be concluded that A student can think clearly if he is sensitive to nature.
Q98: Read the following passage and answer question based on it.
Now what is knowledge ? Is knowledge related to intelligence ? Intelligence uses knowledge, intelligence being the capacity to think clearly, objectively, safely and healthily. Intelligence is a state in which there is no personal emotion involved, no personal opinion, prejudice or inclination. Intelligence is the capacity for direct understanding. I am afraid this is rather difficult, but it is important, it is good for you to exercise your brain. So there is knowledge, which is the past continually being added to, and there is intelligence. Intelligence is the quality of the mind that is very sensitive, very alert, very aware. Intelligence does not hold on to any particular judgement or evaluation, but is capable of thinking very clearly, objectively. Intelligence has no involvement. Are you following? Now, how is this intelligence to be cultivated? What is the capacity of this intelligence? You are living here, being educated in all the various disciplines, in various branches of knowledge. Are you also being educated so that intelligence comes into being at the same time? You cannot think clearly if you are prejudiced, if you have opinions. You cannot think clearly if you are not sensitive; sensitive to nature, sensitive to all the things that are happening around you, sensitive not only to what is happening outside you but also inside you. If you are not sensitive, if you are not aware, you cannot think clearly. Intelligence implies that you see the beauty of the earth, the beauty of the trees, the beauty of the skies, the lovely sunset, the stars, the beauty of subtlety.
Intelligence is the quality of the mind that is -
(a) Very sensitive, very alert, very aware
(b) Thinking, Reflecting and Evaluating
(c) Prejudice, Bias, Sensitive
(d) Judgement, Evaluation, Thinking
Ans: A
Sol:
- Intelligence is the quality of the mind that is very sensitive, alert, and aware.
- Intelligence does not hold on to any particular judgement or evaluation but can think very clearly, and objectively. Intelligence has no involvement.
Hence option 1 is the correct answer.
Q99: Following benefits of inclusion are seen among children with disabilities :
A. High level of Social interaction with non disabled peers
B. Social competence and communication skills get improved
C. Children with diverse needs receive inferior standard of education in inclusive settings.
D. Social acceptance with diverse abilities is enhanced
E. Friendships develop more commonly between children with disabilities and those without disabilities
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D, E Only
(b) A, B, D, E Only
(c) B, C, D, E Only
(d) C, A, B, D Only
Ans: B
Sol: Here are some more details about the benefits of inclusion:
A. High level of Social interaction with non-disabled peers:
- Inclusion provides opportunities for children with disabilities to interact with their non-disabled peers. This can help them develop social skills and learn how to interact with others in various settings.
B. Social competence and communication skills get improved:
- Inclusion can help children with disabilities develop social competence and communication skills. They may learn how to initiate and maintain conversations, read social cues, and resolve conflict.
D. Social acceptance with diverse abilities is enhanced:
- Inclusion can help children with disabilities develop a sense of belonging and acceptance. They may feel more comfortable in their skin and more confident in their abilities.
E. Friendships develop more commonly between children with disabilities and those without disabilities:
- Inclusion can help children with disabilities develop friendships with their non-disabled peers. These friendships can provide them with social support and a sense of belonging.
Hence, the correct answer is 2. A, B, D, and E are all benefits of inclusion for children with disabilities.
C. Children with diverse needs receive an inferior standard of education in inclusive settings:
- C is not a benefit of inclusion, as children with diverse needs do not receive an inferior standard of education in inclusive settings. Research has shown that children with disabilities included in general education classrooms make greater academic progress than those placed in segregated settings.
Q100: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Change is the only constant in the contemporary society.
Statement II: Educational organizations' readiness for change management influences its policies and strategies.
In the light of the above statement, choose the correct answer from the options given below -
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: A
Sol: Statement I: Change is the only constant in the contemporary society.
- This statement is true because the world is constantly changing. New technologies are emerging, new ideas are being developed, and how we live and work is constantly evolving. Educational organizations need to be able to adapt to these changes to remain relevant and effective.
Statement II: Educational organizations' readiness for change management influences its policies and strategies.
- This statement is also true because how an educational organization manages change will directly impact its policies and strategies. If an organization is not prepared for change, it will likely experience difficulty implementing new initiatives and adapting to new challenges. On the other hand, if an organization is prepared for change, it is more likely to be successful in achieving its goals.
Here are some examples of how educational organizations can be more prepared for change:
- Create a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
- Encourage employees to think outside the box and come up with new ideas.
- Provide training on change management and leadership.
- Develop a process for managing change that is clear, concise, and easy to follow.
- Communicate effectively with employees about change and its impact on the organization.
- Be prepared to make adjustments to policies and strategies as needed.
By taking these steps, educational organizations can increase their readiness for change and improve their chances of success.
Hence, Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Education 14th March 2023 Shift 1 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the structure and format of the UGC NET Paper 2 in Education? |  |
| 2. What are the key topics covered in the UGC NET Paper 2 for Education? |  |
| 3. How can candidates prepare effectively for the UGC NET Paper 2 in Education? |  |
| 4. What is the marking scheme for the UGC NET Paper 2 in Education? |  |
| 5. Are there any eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET Paper 2 in Education? |  |





















