UGC NET Paper 2: Education 14th March 2023 Shift 2 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Match List I with List II
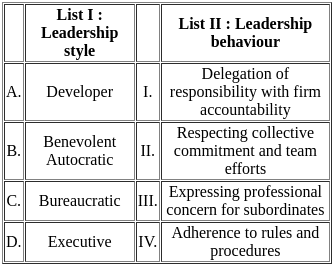
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
Ans: B
Sol: 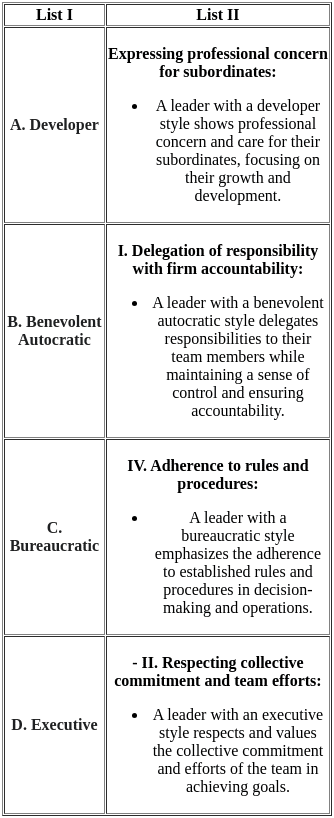 Therefore, the correct match is A - III, B - I, C - IV, and D - II.
Therefore, the correct match is A - III, B - I, C - IV, and D - II.
Q2: Match List I with List II
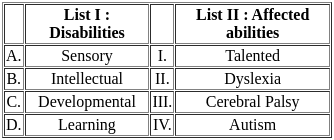
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
Ans: C
Sol: 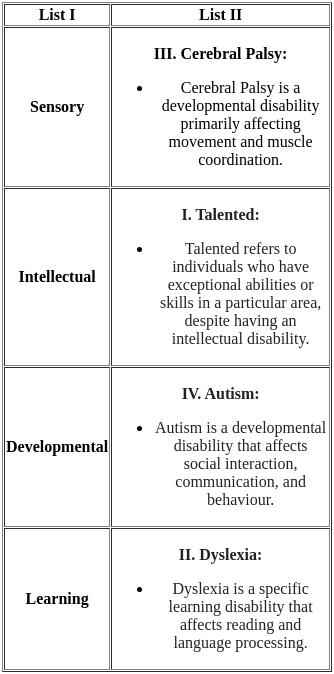 Therefore, the correct match is A - III, B - I, C - IV, and D - II.
Therefore, the correct match is A - III, B - I, C - IV, and D - II.
Q3: Arrange the following into the sequence for policy formulation
A. Need assessment according to objectives
B. Target setting based on trend projection
C. Finalization of themes and target areas
D. Determination of national objectives
E. Preparation of publication
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, B, C, E
(b) A, D, C, E, B
(c) D, A, C, B, E
(d) D, C, A, E, B
Ans: C
Sol: Policy formulation:
- Policy formulation is the process of developing and creating new policies or revising existing policies to address specific issues or achieve desired goals. It involves a series of steps and activities aimed at identifying problems, analyzing data and evidence, setting objectives, and designing strategies and interventions to guide decision-making and action.
The sequence for policy formulation is as follows:
- D. Determination of national objectives: This step involves identifying and determining the overarching objectives or goals that the policy aims to achieve at the national level. It sets the direction and purpose of the policy.
- A. Need assessment according to objectives: Once the national objectives are determined, a need assessment is conducted. This involves analyzing the current situation, identifying gaps or areas of improvement, and assessing the specific needs that should be addressed by the policy.
- C. Finalization of themes and target areas: Based on the need assessment, specific themes and target areas are identified. These are the key focus areas that the policy will address to achieve the national objectives. This step involves refining and finalizing the scope and coverage of the policy.
- B. Target setting based on trend projection: Once the themes and target areas are identified, targets are set based on trend projection. This involves analyzing relevant data and trends to determine specific measurable targets that need to be achieved within a given timeframe.
- E. Preparation of publication: After the policy has been formulated, a publication is prepared to communicate and disseminate the policy to relevant stakeholders. This publication serves as a comprehensive document that outlines the policy's objectives, strategies, targets, and implementation guidelines.
Therefore, the correct sequence for policy formulation is D, A, C, B, E.
Q4: Arrange the following in a chronological order of their formation from the earliest to the latest:
A. NAAC
B. NCTE
C. UGC
D. NCERT
E. NIEPA
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, E, A, B, C
(b) B, C, D, E, A
(c) C, D, E, A, B
(d) A, B, C, E, D
Ans: C
Sol:
Here is the correct for the chronological order of their formation: C, D, E, A, B
The correct chronological order of their formation is as follows:
C. UGC (University Grants Commission):
- It was established in 1956 as a statutory body to regulate and coordinate higher education in India.
- D. NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training): It was established in 1961 as an autonomous organization to assist and advise the central and state governments on school education and curriculum development.
E. NIEPA (National Institute of Educational Planning and Administration):
- It was established in 1962 as an autonomous organization to conduct research, training, and capacity-building in educational planning and administration.
A. NAAC (National Assessment and Accreditation Council):
- It was established in 1994 as an autonomous body to assess and accredit higher education institutions in India.
B. NCTE (National Council for Teacher Education):
- It was established in 1995 as a statutory body to oversee teacher education in India.
Therefore, the correct chronological order of their formation is C, D, E, A, and B.
Q5: Identify the sequence of data analysis steps in qualitative research.
A. Labeling the segments with codes
B. Data transcription
C. Collapsing codes into themes
D. Reading through data
E. Dividing text to segments
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, E, A, C
(b) A, E, D, C, B
(c) B, C, E, D, A
(d) E, B, A, C, D
Ans: A
Sol: The correct sequence of data analysis steps in qualitative research is B, D, E, A, C.
- B. Data transcription: The first step in qualitative data analysis involves transcribing the data from audio or video recordings, interviews, or observations into written text. This step ensures that the data is readable and manageable for further analysis.
- D. Reading through data: Once the data is transcribed, the researcher reads it multiple times to become familiar with its content. This initial reading helps gain an overall understanding of the data and identify initial patterns, themes, or insights.
- E. Dividing text to segments: After reading through the data, the researcher divides the text into smaller segments or units, such as sentences, paragraphs, or sections. This step involves breaking the data into meaningful and manageable parts for further analysis.
- A. Labelling the segments with codes: Once the data is segmented, the researcher assigns codes or labels to each segment. Codes are tags or keywords that capture each segment's main ideas or concepts. This step helps organise and categorise the data based on themes or topics.
- C. Collapsing codes into themes: After coding the segments, the researcher examines the codes and identifies patterns or themes that emerge from the data. Themes represent broader categories or concepts that are derived from the coded segments. This step involves grouping similar codes together to develop meaningful themes.
Therefore, the correct sequence of data analysis steps in qualitative research is B, D, E, A, C.
Q6: Identify the correct order from the following process through six sigma quality initiative management strategy:
A. Finding the root causes of defects in the process and to reduce such defects
B. Collecting relevant data to measure the key aspects of the current process.
C. Implementing enhancement of the current process based upon data analysis.
D. Explaining the expectations of the customer
E. Ensuring the Sustenance of improvement of the current process.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, D, E, B, A
(b) B, E, A, C, D
(c) A, C, D, E, B
(d) D, B, A, C, E
Ans: D
Sol: The correct order of the process through the Six Sigma quality initiative management strategy is: D, B, A, C, E
- D. Explaining the expectations of the customer: The first step is to understand and clarify the expectations and requirements of the customer. This involves gathering information about customer needs and defining the critical-to-quality parameters.
- B. Collecting relevant data to measure the key aspects of the current process: Once the customer expectations are understood, relevant data is collected to measure the current process performance. This data helps in identifying the areas of improvement and potential sources of defects.
- A. Finding the root causes of defects in the process and reducing such defects: After collecting the data, analysis is conducted to identify the root causes of defects or variations in the process. This step involves using tools and techniques such as root cause analysis, statistical analysis, and process mapping to determine the underlying factors contributing to process inefficiencies.
- C. Implementing enhancement of the current process based upon data analysis: Based on the analysis and identification of root causes, improvements are implemented in the current process. This step involves making necessary modifications, redesigning processes, and implementing best practices to address the identified issues and improve process performance.
- E. Ensuring the sustainment of improvement of the current process: Once the enhancements are implemented, it is essential to ensure the sustainability of the improvements. This involves monitoring and controlling the process, setting up control mechanisms, and establishing continuous improvement practices to maintain improved performance over time.
Therefore, the correct order is D, B, A, C, E.
Q7: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The Samkkha theory that causation means a real transformation of the material cause into effect, it logically leads to the concept of evolution as the ultimate cause of the world of objects.
Statement II: The second type of utlimate reality admitted by the Samkhya is the self. The existence of the self must be admitted by all.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: a
Sol: Statement I: The Samkkha theory that causation means a real transformation of the material cause into effect, it logically leads to the concept of evolution as the ultimate cause of the world of objects.
- Samkhya's theory of Satkaryavada posits that the effect pre-exists in the cause (e.g., curd exists in milk), implying a transformation of the material cause (Prakriti) into the effect, not merely a relationship. Thus, Statement I is true, not false, as it aligns with Satkaryavada and the concept of evolution in Samkhya.
- Statement II is correct, as Samkhya recognizes Purusha (self) and Prakriti as two ultimate realities.
Q8: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: At the beginning of curriculum development, the very concept of the programme must be evaluated.
Statement II: Cognitive models of teaching can assist teachers in shaping their instructional approaches and evaluating students' learning.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: A
Sol: Statement I: At the beginning of curriculum development, the very concept of the programme must be evaluated.
- This is true because it is important to have a clear understanding of the goals of the curriculum before beginning to develop it. This will help to ensure that the curriculum is aligned with the needs of the students and the community.
Statement II: Cognitive models of teaching can assist teachers in shaping their instructional approaches and evaluating students' learning.
- This is also true because cognitive models of teaching provide a framework for understanding how students learn. This can help teachers to select the most effective instructional strategies and to assess students' learning in a meaningful way.
Thus, the correct answer is 1) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
Other Related Points Here are some of the benefits of using cognitive models of teaching:
- Improved instruction: Cognitive teaching models can help teachers select the most effective instructional strategies. This can lead to better learning for students.
- Increased student achievement: When teachers select the most effective instructional strategies, students are likelier to achieve at high levels.
- Improved assessment: Cognitive models of teaching can help teachers to assess student's learning in a more meaningful way. This can lead to a better understanding of student learning and more effective instruction.
There are a variety of cognitive models of teaching that teachers can use. Some common models include:
- The information processing model views learning as acquiring, storing, and retrieving information.
- The constructivist model views learning as a process of constructing meaning from experience.
- The social cognitive model: This model views learning as a process of observing and imitating others.
The best cognitive model for a particular teacher will depend on the teacher's style and the needs of the students.
Q9: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Teacher education is a continuous process, and its pre-service and in-service components are inseparable.
Statement II: In-service teacher education should take due care of future needs of the teacher's growth.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: A
Sol: Statement I: Teacher education is a continuous process, and its pre-service and in-service components are inseparable.
- This is true because teaching is a complex profession that requires ongoing learning and development. Pre-service teacher education provides teachers with the foundation they need to be successful in the classroom, but it is not enough. In-service teacher education provides teachers with the opportunity to continue learning and to grow professionally.
Statement II: In-service teacher education should take due care of future needs of the teacher's growth.
- This is also true because the needs of teachers change over time. In-service teacher education should be designed to meet the needs of teachers at all stages of their careers.
Here are some of the benefits of continuous teacher education:
- Improved instruction: Continuous teacher education can help teachers to improve their instructional practices. This can lead to better learning for students.
- Increased student achievement: When teachers are able to improve their instructional practices, students are more likely to achieve at high levels.
- Improved teacher satisfaction: Teachers who are able to continue learning and to grow professionally are more likely to be satisfied with their jobs.
There are a variety of ways to provide continuous teacher education. Some common methods include:
- Professional development workshops: Professional development workshops can provide teachers with the opportunity to learn about new teaching methods and to network with other teachers.
- Online courses: Online courses can provide teachers with the flexibility to learn at their own pace.
- Coaching: Coaching can provide teachers with individualized support as they implement new teaching practices.
The best method for continuous teacher education will depend on the needs of the teachers and the resources available.
The correct answer is 1) Statement I and II are true.
Q10: Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Using feedback mechanism on teachers' performance is essential for their improvement.
Reason (R): Students are the best source for feedback on teachers' performance in the classroom.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct.
(d) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct.
Ans: A
Sol: Assertion (A): Using feedback mechanism on teachers' performance is essential for their improvement.
- This is correct because feedback can help teachers to identify areas where they can improve their teaching.
- For example, feedback from students can help teachers to identify areas where they are not explaining concepts clearly, or where they are not engaging students in the learning process.
Reason (R): Students are the best source for feedback on teachers' performance in the classroom.
- This is also correct because students are the ones who are actually experiencing the teachers' teaching. They are the ones who can best say what is working and what is not working in the classroom.
Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct of (A). This is because (R) explains how (A) is true. By getting feedback from students, teachers can identify areas where they can improve their teaching and ultimately become better teachers.
Other Related Points Here are some of the benefits of using feedback mechanisms on teachers' performance:
- Improved teaching: Feedback can help teachers to identify areas where they can improve their teaching. This can lead to better instruction for students.
- Increased student learning: When teachers are able to improve their teaching, students are more likely to learn. This is because students are more likely to be engaged in the learning process when they are taught in a way that is clear, engaging, and relevant to them.
- Increased teacher satisfaction: Teachers who are able to get feedback on their performance are more likely to be satisfied with their jobs. This is because they are able to see how their teaching is impacting students and they are able to make changes to improve their teaching.
There are a variety of ways to get feedback on teachers' performance. Some common methods include:
- Student surveys: Student surveys can be used to get feedback on a variety of topics, such as the clarity of instruction, the level of engagement, and the overall effectiveness of the teacher.
- Classroom observations: Classroom observations can be used to get feedback on the teacher's instructional practices. This can include things like the teacher's use of questioning, the teacher's ability to manage the classroom, and the teacher's ability to create a positive learning environment.
- Peer feedback: Peer feedback can be used to get feedback from other teachers on a teacher's performance. This can be a valuable source of feedback because it can provide teachers with insights from other professionals who are familiar with the challenges and rewards of teaching.
It is important to note that feedback should be used in a constructive way. The goal of feedback is to help teachers improve their teaching, not to criticize them. Feedback should be specific and actionable. It should provide teachers with information that they can use to make changes to their teaching.
Q11: Arrange the following types of learning given by Gagne in
A. Multiple discrimination
B. Chain learning
C. Learning of Principles
D. Learning of concepts
E. Verbal Associate learning
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, A, D, E
(b) C, D, B, A, E
(c) B, E, A, D, C
(d) D, C, A, B, E
Ans: C
Sol: Here is the correct for the sequence of types of learning given by Gagne: B, E, A, D, C
B. Chain learning: This type involves acquiring discrete steps or behaviours and performing them in a specific order. It emphasizes sequential learning, where each step serves as a cue or trigger for the next.
E. Verbal Associate learning: This type of learning involves establishing associations or connections between verbal or symbolic stimuli. It includes associating words, phrases, or symbols with specific meanings or concepts.
A. Multiple discrimination: This type of learning involves distinguishing and responding to various stimuli or cues based on their unique characteristics. It focuses on recognizing and discriminating between different elements or stimuli.
D. Learning concepts involves acquiring and understanding abstract ideas or concepts. It includes identifying and classifying objects or events based on shared characteristics or attributes.
C. Learning of Principles involves understanding and applying general principles or rules to specific situations. It focuses on grasping the underlying concepts or guidelines that govern a particular domain.
Therefore, the correct sequence of types of learning given by Gagne is B, E, A, D, and C.
Q12: Sequence the first five levels of objectives as divided by Anita Harrow for Psychomotor objectives-
A. Reflex movements
B. Physical abilities
C. Perceptual abilities
D. Skilled movements
E. Fundamental movements
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, B, E, D
(b) A, E, C, B, D
(c) A, C, B, D, E
(d) B, C, A, D, E
Ans: B
Sol: The correct for the sequence of the first five levels of objectives is divided by Anita Harrow for Psychomotor objectives: A, E, C, B, D.
- A. Reflex movements: This is the first level of psychomotor objectives, according to Anita Harrow. It involves automatic and involuntary responses or movements.
- E. Fundamental movements: This is the second level of psychomotor objectives. It involves mastering fundamental movements and skills that are the foundation for more advanced movements and activities.
- C. Perceptual abilities: This is the third level of psychomotor objectives. It involves developing sensory awareness and perceptual abilities to recognize and interpret stimuli.
- B. Physical abilities: This is the fourth level of psychomotor objectives. It involves developing basic physical abilities such as coordination, balance, strength, and endurance.
- D. Skilled movements: This is the fifth level of psychomotor objectives. It involves developing more complex and refined movements that require coordination and control.
Therefore, the correct sequence for the first five levels of objectives, as divided by Anita Harrow for Psychomotor objectives, is A, E, C, B, and D.
Q13: Arrange the steps of the model of Instructional designing developed by Heinrich and Molenda in the correct sequence:
A. State
B. Evaluate
C. Require
D. Analyse
E. Utilize
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, A, E, C, B
(b) B, D, C, A, E
(c) E, B, C, A, D
(d) C, A, D, E, B
Ans: A
Sol: The model of Instructional Designing developed by Heinrich and Molenda consists of five steps, which are explained below in detail:
- Analyse (D): The first step in the instructional design process is to analyze the needs and goals of the instructional program. This involves identifying the target audience, their existing knowledge and skills, and their learning needs. The instructional designer assesses the gap between the desired learning outcomes and the learners' capabilities. This analysis helps in understanding the specific requirements and constraints of the instructional design project.
- State (A): In this step, the instructional goals and objectives are defined clearly. The desired learning outcomes are stated, specifying what the learners should be able to do or know after completing the instructional program. The instructional designer identifies the content to be covered and determines the scope and sequence of the instruction. The statement of instructional goals and objectives provides a roadmap for the instructional design process.
- Utilize (E): The third step involves selecting appropriate instructional strategies, resources, and technologies to facilitate learning. The instructional designer chooses instructional methods, materials, and media that align with the stated goals and objectives. This includes selecting instructional materials, designing learning activities, and integrating multimedia or technology-based resources as needed. The utilization step focuses on creating an effective and engaging learning environment for the learners.
- Require (C): In this step, the instructional designer determines the necessary prerequisites for learners to engage in the instructional program. This may include specifying the required entry-level knowledge or skills and any prerequisites for accessing the instructional materials or technologies. The requirements are established to ensure that learners have the foundation to benefit from the instruction and facilitate their progress through the learning process.
- Evaluate (B): Evaluation is the final step in the instructional design process. The instructional designer assesses the effectiveness of the instructional program in achieving the stated goals and objectives. This involves evaluating learner performance and measuring how the desired learning outcomes have been achieved. Various evaluation methods, such as tests, assessments, and feedback mechanisms, are used to gather data on learner progress and the overall effectiveness of the instructional design. Based on the evaluation results, revisions and improvements can be made to enhance the instructional program.
By following these five steps systematically, instructional designers can develop effective and efficient instructional programs that meet the needs of learners and facilitate their learning process. The model emphasizes the importance of analysis, goal-setting, appropriate utilization of instructional strategies and resources, establishing prerequisites, and evaluating the effectiveness of the instruction.
Hence the correct sequence is D, A, E, C, B.
Q14: The first five among seven kinds of conditional judgement (sapta bhanginaya) are:
A. Some how S is P (Syat asti)
B. Some how S is not P (Syat nasti)
C. Some how S is P and is also not P (Syat asti cha, nasti cha)
D. Some how S is P and is also indescribable (Syat asti cha, avaktavyan cha)
E. Some how S is describable (Syat avaktavyam)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, E, C, D
(b) A, B, C, E, D
(c) A, E, B, C, D
(d) A, B, D, C, E
Ans: B
Sol: The "sapta bhanginaya," also known as the sevenfold predication or seven types of conditional judgment, is a concept from Indian philosophy, particularly from the Nyaya school of logic. It is a categorization of different kinds of conditional statements or judgments. These seven types of conditional judgments are:
- Syād-asti (Somehow it is): This type of conditional judgment suggests that something is true or exists. It indicates a positive or affirmative statement with an element of uncertainty or possibility.
- Syād-nāsti (Somehow it is not): This type of conditional judgment suggests that something is false or does not exist in some manner. It indicates a negative statement with an element of uncertainty or possibility.
- Syād-asti-nāsti (Somehow it is and it is not): This type of conditional judgment introduces the idea of contradictory possibilities. It suggests that something can both exist and not exist simultaneously or in different aspects or perspectives.
- Syād-avaktavyaṁ (Somehow it is indescribable): This type of conditional judgment suggests that something is beyond description or verbal expression. It acknowledges the limitation of language or the inability to capture the full essence or nature of the subject.
- Syād-asti-avaktavyaṁ (Somehow it is and it is indescribable): This type of conditional judgment combines the ideas of existence and indescribability. It suggests that something can exist while also being beyond verbal expression or description.
Therefore, the correct sequence for the first five kinds of conditional judgement (sapta bhanginaya) is A, B, C, E, and D.
Other Related Points The remaining two types of conditional judgment in the sapta bhanginaya are:
- Syād-nāsti-avaktavyaṁ (Somehow, it is not, and it is indescribable): This type of conditional judgment combines the ideas of non-existence and indescribability. It suggests that something can not exist and be beyond verbal expression or description.
- Syād-asti-nāsti-avaktavyaṁ (Somehow, it is and is not indescribable): This type of conditional judgment combines all three elements: existence, non-existence, and indescribability. It suggests something can have contradictory possibilities of existence and non-existence beyond verbal expression or description.
The sapta bhanginaya provides a framework for understanding and analyzing the various aspects and possibilities within conditional statements or judgments. It highlights the complexity and nuances of logical and philosophical reasoning.
Q15: Arrange the following in ascending order according to their years
A. RPWD Act
B. Comprehensive action plan on Inclusive Education for children and youth with disabilities
C. NT Act
D. National policy for persons with disabilities
E. RCl Act
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) E, C, B, D, A
(b) A, C, B, D, E
(c) E, B, C, D, A
(d) B, C, D, E, A
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 1) E, C, B, D, A.
Here is a table of the laws and their corresponding years:
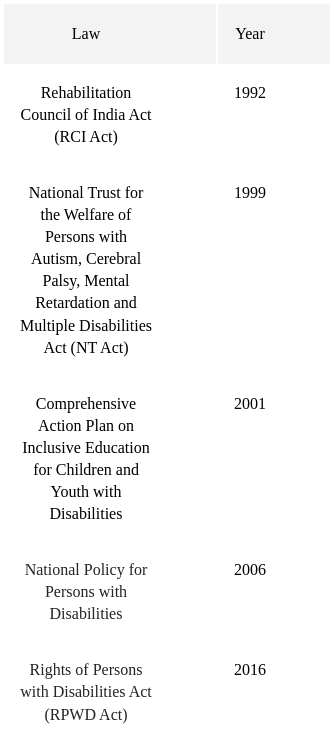
Q16: Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Threats exist outside of the organisation and are beyond its control.
Reason (R): Correcting weaknesses of the organisation can reduce the impact of threat on it.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct.
(d) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct.
Ans: B
Sol: Assertion (A): Threats exist outside of the organisation and are beyond its control.
- This is correct because threats can come from a variety of sources, including natural disasters, economic downturns, and political instability. These threats are often beyond the control of any individual organization.
- There are many different types of threats that can impact an organization, including:
- Natural disasters: These can include events such as earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes.
- Economic downturns: These can lead to decreased demand for products and services, which can impact an organization's bottom line.
- Political instability: This can lead to violence, unrest, and other disruptions that can impact an organization's operations.
- These threats are often beyond the control of any individual organization. For example, an organization cannot control the weather or the global economy. However, organizations can take steps to mitigate the impact of these threats by identifying and correcting weaknesses.
Reason (R): Correcting weaknesses of the organisation can reduce the impact of threat on it.
- Reason (R) suggests that correcting weaknesses within the organization can reduce the impact of threats on it.
- This statement is also generally true because addressing internal weaknesses such as operational inefficiencies, financial vulnerabilities, or strategic shortcomings can indeed enhance the organization's ability to withstand or mitigate the impact of external threats.rol.
- This can help them to protect their assets, their employees, and their customers.
Hence, Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct of (A).
Q17: According to Flanders Interaction Category System, arrange the following verbal behaviors in a sequence for its encoding
A. Lectures
B. Ask Questions
C. Gives directions
D. Accept or uses ideas of pupils
E. Praises or discourages
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, E, A, D, C
(b) D, E, B, A, C
(c) A, C, B, E, D
(d) E, D, B, A, C
Ans: D
Sol: The correct sequence for encoding the verbal behaviours according to Flander's Interaction Category System:
- E. Praises or discourages: This behaviour involves the teacher praising or discouraging students based on their performance or contributions. Praises can be given to acknowledge students' achievements or efforts, while discouragement may be provided to correct behaviour or redirect students' actions.
- D. Accept or uses ideas of pupils: This behaviour involves the teacher accepting and incorporating the ideas and contributions of students during the instructional process. It signifies a collaborative approach where the teacher values and respects the thoughts and opinions of the students, using them to enrich the learning experience.
- B. Ask Questions: This behaviour involves the teacher asking questions to engage students, promote critical thinking, and assess their understanding. Questions can stimulate students' thinking, encourage participation, and deepen their understanding of the subject matter.
- A. Lectures: This behaviour refers to the teacher delivering instructional content through lectures and presenting information to students. The teacher provides s, demonstrations, and presentations to convey knowledge or concepts to the students.
- C. Gives directions: This behaviour involves the teacher giving instructions or directions to guide students' actions or behaviours. Directions can include providing step-by-step guidance, explaining procedures, or specifying expectations regarding a task or activity.
In Flander's Interaction Category System, the sequence represents how these verbal behaviours are typically observed or encoded during classroom interactions. It is important to note that effective teaching involves a combination of these behaviours, and the sequence may vary based on the specific context and instructional goals.
As per Flander's Interaction Category System, the correct sequence for encoding verbal behaviours is E, D, B, A, C.
Q18: Which of the following Indian School of Philosophy does NOT reject Vedic Authority?
(a) Cãrvaka Philosophy
(b) Bauddha Philosophy
(c) Sankhya Philosophy
(d) Jaina Philosophy
Ans: C
Sol: The Indian school of philosophy that does NOT reject Vedic authority is Sankhya
Sankhya:
- The Sankhya school of philosophy is a dualistic school of thought that believes that the world is made up of two substances, matter and spirit. They accept the existence of God, the soul, and the Vedas.
- The Sankhyas believe that the world is made up of two eternal substances, purusha (spirit) and prakriti (matter). They believe that purusha is the conscious principle that animates the universe, and that prakriti is the unconscious principle that provides the material for the universe.
- The Sankhyas believe that the soul is a purusha that is trapped in the cycle of birth and death. They believe that the goal of life is to achieve moksha, or liberation, from the cycle of birth and death.
- The Sankhyas believe that the Vedas are a reliable source of knowledge because they are based on reason and experience.
The other three schools of philosophy, Cãrvaka, Bauddha, and Jaina, all reject Vedic authority.
Cãrvaka:
- The Cãrvaka school of philosophy is a materialistic school of thought that believes that the only thing that exists is matter. They reject the existence of God, soul, and the Vedas.
- The Cãrvakas believe that the world is made up of atoms that are constantly moving and colliding with each other. They believe that the laws of physics and chemistry can explain everything that happens.
- The Cãrvakas do not believe in the existence of God because they believe that there is no evidence to support the existence of a supernatural being. They also believe that the Vedas are not a reliable source of knowledge because they are not based on evidence.
Bauddha:
- The Bauddha School of Philosophy is a non-theistic school of thought that believes the world is an illusion. They reject the existence of God, the soul, and the Vedas.
- The Buddhas believe that the world is made up of individual sensations and perceptions that are constantly changing. They believe that there is no permanent self or soul and that the world is simply a collection of fleeting experiences.
- The Buddhas do not believe in God's existence because they believe there is no need for a creator or sustainer of the universe. They also believe that the Vedas are not a reliable source of knowledge because they are not based on evidence.
Jaina:
- The Jaina School of Philosophy is a non-theistic school of thought that believes in the existence of many souls. They reject the existence of God, but they do accept the Vedas as a source of knowledge.
- The Jainas believe that the world is made up of matter and souls. They believe that matter is eternal and that souls are reborn into new bodies after death.
- The Jainas believe in the principle of ahimsa, or non-violence. They believe all living things are sacred and should be treated respectfully.
Q19: Which of the following does NOT belong to the concept of social movement?
(a) Relative Deprivation Theory
(b) Resource mobilization theory
(c) Political process theory
(d) Normative theory
Ans: D
Sol: The normative theory is the only theory that does not belong to the concept of social movement.
- Social movements are collective challenges by people with common purposes and solidarity in sustained interactions with elites, opponents, and authorities. Social movements are often motivated by a sense of injustice or inequality, and they can use a variety of tactics to achieve their goals, including protests, demonstrations, boycotts, and strikes.
Normative theory:
- The normative theory is a theory of social change that argues that social movements can be used to promote positive social change. The normative theory does not explain how social movements emerge or develop. Instead, it focuses on the goals of social movements and how they can be used to achieve those goals.
- For example, the civil rights movement in the United States was motivated by a sense of relative deprivation and a belief in the importance of equality and justice. The movement successfully achieved its goals, such as the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which helped create a more just and equal society.
Other Related Points Relative deprivation theory:
- Relative deprivation theory argues that social movements are more likely to emerge when people feel that they are being deprived of something that they believe they deserve. Several factors, such as economic inequality, social discrimination, or political oppression, can cause this sense of deprivation.
- For example, the civil rights movement in the United States was motivated by a sense of relative deprivation among African Americans. African Americans felt they were being deprived of their civil rights, such as the right to vote and equal access to education and employment. This sense of deprivation led to the emergence of the civil rights movement, which eventually led to the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
Resource mobilization theory
- Resource mobilization theory argues that social movements require resources, such as money, time, and people, to be successful. These resources can be used to organize the movement, communicate with members, and carry out protests and other activities.
- For example, the environmental movement has been successful because it has mobilised resources from various sources, such as foundations, individuals, and businesses. These resources have been used to fund environmental organizations, to conduct research, and to lobby for environmental legislation.
Political process theory
- Political process theory argues that social movements are more likely to emerge with opportunities for political change. These opportunities can be created by changes in the political system, such as the election of a new government, or by changes in the public's opinion, such as a growing awareness of an issue.
- For example, the women's suffrage movement in the United States was successful because it took advantage of opportunities for political change. The movement gained the support of key political figures, such as President Woodrow Wilson, and it mobilised public opinion in favour of women's suffrage. This led to the passage of the 19th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, which granted women the right to vote.
Q20: Select the correct 4th, 8th & 12th link in the twelve links of suffering according to Bauddha Philosophy.
(a) Ignorance, six sense organs, craving
(b) Mind-body organism, craving, suffering
(c) Six sense organs, sense experience, suffering
(d) Consciousness, craving, suffering
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Mind-body organism, craving, suffering.
The twelve links of suffering are Buddhist concepts that describe the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth. The links are:
- Ignorance
- Samskaras (karmic formations)
- Consciousness
- Name and form
- Six sense organs
- Contact
- Feeling
- Craving
- Upadana (grasping)
- Bhava (becoming)
- Jati (birth)
- Jaramarana (ageing and death)
- The twelve links are often depicted as a wheel, with ignorance at the centre and suffering at the outer rim.The wheel is meant to represent the cyclical nature of existence.
- The fourth link, Mind-body organism, refers to the physical body and the mind. The mind-body organism is the result of the combination of ignorance and samskaras.
- The eighth link, Craving, refers to the desire for impermanent, unsatisfying things, not the self. Craving is the result of contact and feeling.
- The twelfth link, Suffering, refers to the pain and dissatisfaction caused by craving. Suffering is the result of upadana, bhava, jati, and jaramarana.
- The twelve suffering links are a complex concept, and there is no definitive interpretation. However, they can be seen as a map of the human experience. By understanding the twelve links, we can understand the causes of suffering and how to end it.
Q21: Spinoza is identified with the idealist tradition because-
(a) he insisted upon famous Cartesian inference, 'I think, therefore I am'.
(b) he insisted that there is an unchanging and abiding existence undergirding all things, one of the chief attributes of which is thought
(c) he insisted upon the primacy of self
(d) he insisted upon the concepts of Monads
Ans: B
Sol: Spinoza:
- Spinoza is not typically identified with the idealist tradition but is known as a philosopher within the rationalist and pantheist traditions. The idealist tradition, often associated with philosophers like Kant or Hegel, emphasizes the primacy of ideas or consciousness in shaping reality.
- However, Spinoza's philosophy, as expressed in his major work "Ethics," is more closely aligned with a pantheistic worldview, which posits that God and the universe are one and the same.
- In Spinoza's philosophy, he argues for the existence of an infinite, necessary, and eternal substance, which he identifies as God or Nature.
- This substance encompasses everything in the universe, including both material and mental aspects. While Spinoza acknowledges the existence of thought as one of the chief attributes of this substance, it is not the same as asserting the primacy of self or placing sole emphasis on consciousness as the foundation of reality.
- Option 2 is the correct answer as it reflects Spinoza's recognition of an unchanging and abiding existence underlying all things, with the thought being one of its attributes.
The correct answer is 2) he insisted that there is an unchanging and abiding existence undergirding all things, one of the chief attributes of which is thought.
Q22: To understand politics, Rational Choice Theory is basically explaining social phenomenon as an outcome of individual action that can, in some way be construed as rational. In this context, which of the following is not the key element in all rational choice s.
(a) Individual preferences
(b) Beliefs of the society
(c) Individual constraints
(d) Individual beliefs
Ans: B
Sol: Rational Choice Theory:
- Rational choice theory is a social science theory that assumes individuals act in their self-interest to maximize their utility. This means that individuals will make choices that they believe will benefit them the most, even if those choices are not always in the best interests of society as a whole.
The key elements of rational choice theory are:
- Individual preferences: Individuals have their preferences about what they want to achieve. These preferences can be based on their values, goals, and desires.
- Individual constraints: Individuals face constraints on their ability to achieve their preferences. These constraints can be physical, such as a lack of resources, or social, such as the expectations of others.
- Rational decision-making: Individuals use rational decision-making to choose the course of action they believe will best achieve their preferences, given their constraints.
Beliefs of society are not a key element of rational choice theory because they are not directly related to individual preferences, constraints, or rational decision-making. However, society's beliefs can indirectly influence individual behaviour by shaping preferences and constraints. For example, suppose a society believes that education is important. In that case, individuals may be more likely to make choices allowing them to get an education, even if those choices are not in their immediate self-interest.
Here are some examples of how rational choice theory can be used to explain political phenomena:
- Voting: Rational choice theory can be used to explain why people vote. Individuals vote because they believe it will help them achieve their preferences, such as electing a candidate who shares their values or policies.
- Lobbying: Rational choice theory can be used to explain why people lobby. Individuals lobby because they believe it will help them achieve their preferences, such as passing a law that benefits their industry or group.
- Donating to political campaigns: Rational choice theory can be used to explain why people donate to political campaigns. Individuals donate because they believe it will help them achieve their preferences, such as electing a candidate who shares their values or policies.
Rational choice theory is a powerful tool for understanding political phenomena. However, it is important to remember that it is just a theory. It does not always accurately predict human behaviour, and measuring individual preferences, constraints, and rational decision-making can be difficult.
Therefore it can be concluded that the Beliefs of society are not a key element of rational choice theory.
Q23: Before starting a school for slum dwellers, the government is required to conduct:
(a) Cost effective analysis
(b) Cost benefit analysis
(c) Zero cost analysis
(d) Budget analysis
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Cost effective analysis.
Cost effective analysis
- Cost effective analysis (CEA) is a method used to determine the most efficient way to achieve a specific objective or outcome. It compares the relative costs and outcomes (effects) of different courses of action.
Other Related Points
Cost benefit analysis
- Cost benefit analysis (CBA) evaluates the total expected costs versus the total expected benefits of one or more actions in order to choose the best or most profitable option.
Zero cost analysis
- Zero cost analysis is not a standard term in economic or project evaluation.
Budget analysis
- Budget analysis involves reviewing the financial plan, allocations, and expenditures to ensure that funds are used effectively and are aligned with the objectives.
Q24: Which among the following is NOT a source of the direct monetary cost for acquiring education?
(a) Tuition Fee
(b) Book Purchased
(c) Forgone Opportunities
(d) Transport Cost
Ans: C
Sol: Direct monetary costs:
The direct monetary costs of acquiring an education are the costs incurred directly due to attending school. These costs include tuition fees, books, supplies, and transportation.
Direct costs
- Tuition fees
- Books
- Supplies
- Transportation
Indirect costs
- Forgone opportunities
- Cost of living
- The opportunity cost of time
Forgone opportunities:
- Forgone opportunities are not a direct monetary cost of acquiring an education. Forgone opportunities are the potential earnings lost by not working while attending school. For example, if students take a year off from work to attend college, they will lose out on a year of earnings. The amount of forgone earnings will depend on the student's salary and when they are out of work.
Cost of living
- The cost of living is the money required to live in a particular area. The cost of living includes housing, food, transportation, and utilities. The cost of living can vary depending on the school's location and the student's lifestyle.
The opportunity cost of time
- The opportunity cost of time is the value of the next best alternative use of time. For example, if a student spends 10 hours per week studying, they are giving up the opportunity to spend those 10 hours working, socializing, or engaging in other activities. The opportunity cost of time will depend on the value of the student's time and the alternative uses of their time.
- The total cost of education can be significant, and students need to be aware of all the costs involved before deciding whether or not to attend school.
So the answer is 3. Forgone Opportunities.
Q25: Which one of the following code describes the 'Directions, Commands or Orders to which a pupil is expected to comply' as per Flander's Interaction Category system?
(a) Category 5
(b) Category 7
(c) Category 3
(d) Category 6
Ans: D
Sol: Flanders' Interaction Analysis System (FIAS):
- Flanders' Interaction Analysis System (FIAS), also known as Flanders' Interaction Category System (FIACS), is a system for coding and analyzing classroom interaction. Ned Flanders developed it in the 1960s, and it is still used today by researchers and educators. The system divides classroom interaction into 10 categories; each assigned a code.
The 10 categories are:
- Accepts feeling: This category includes statements that accept or acknowledge the student's feelings, such as "I understand how you feel" or "That's a good point."
- Positive reinforcement: This category includes statements that praise or reward the student's behaviour, such as "Good job" or "I like the way you're working."
- Accept Student Ideas: The teacher passes on the students' ideas and accepts their views and suggestions.
- Questions: This category includes statements that ask the student a question, such as "What do you think?" or "Can you tell me more about that?"
- Lecture: This category includes statements made by the teacher without any student participation, such as "The Civil War began in 1861."
- Giving directions: This category includes statements that give the student instructions, such as "Please turn to page 20" or "Raise your hand if you know the answer."Criticism: This category includes statements criticising the student's behaviour, such as "That's not right" or "You're not paying attention."
- Reprimand: This category includes statements that reprimand the student's behaviour, such as "Stop talking" or "Go to the principal's office."
- Student talk-response: This category includes statements made by the student in response to a question or direction from the teacher, such as "Yes, I understand" or "I think the answer is 12."
- Student talk-initiation: This category includes statements made by the student without any prompting from the teacher, such as "I have a question" or "I think we should discuss this."
- Silence: This category includes periods when there is no talking in the classroom.
FIAS can measure various aspects of classroom interaction, such as the amount of teacher talk, the amount of student talk, and the type of student talk. FIAS can also be used to identify classroom interaction patterns, such as whether the teacher is more likely to talk to high-achieving or low-achieving students.
FIAS is a valuable tool for researchers and educators interested in understanding classroom interaction. FIAS can be used to identify areas where teachers can improve their teaching, and it can also be used to track student progress over time.
Hence Category 6 is the correct answer.
Q26: If a teacher gives scores to correct responses in a class-test and enlists total marks of each learner, he/she has done:
(a) Assessment
(b) Measurement
(c) Evaluation
(d) Value Judgement
Ans: B
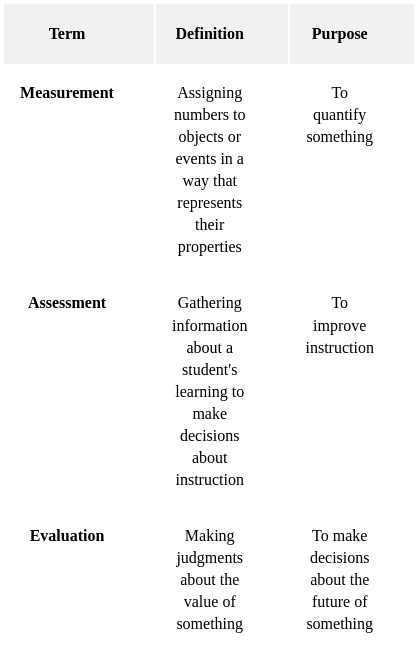
Sol: Measurement:
- Measurement is the process of assigning numbers to objects or events in a way that represents their properties. In the case of a class test, the teacher measures the students' knowledge of the material by assigning scores to their responses.
Assessment:
- Assessment is the process of gathering information about a student's learning in order to make decisions about instruction. In the case of a class test, the teacher uses the scores to assess the students' learning and make decisions about how to proceed with instruction.
Evaluation:
- Evaluation is the process of making judgments about the value of something. In the case of a class test, the teacher may use the scores to evaluate the effectiveness of the instruction or to make judgments about the students' progress.
Value judgment:
- Value judgment is a personal opinion about the worth of something. In the case of a class test, the teacher may make a value judgment about the students' performance, but this is not part of the measurement process.
Here is a table that summarizes the differences between measurement, assessment, and evaluation:
Therefore, If a teacher gives scores to correct responses in a class test and enlists the total marks of each learner, he/she has done Measurement.
Q27: Which among the following is a purpose of a display portfolio?
(a) To diagnose the difficulty areas of learners
(b) To demonstrate highest level of achievement attained by learners
(c) To document students's learning of specific learning outcomes
(d) To demonstrate mastery of learners in any curricular area.
Ans: B
Sol: Display Portfolio:
- A display portfolio is a collection of student work that showcases their best efforts and accomplishments. It is a type of portfolio that is used to demonstrate the highest level of achievement attained by learners. Display portfolios can be used to assess student learning, to track progress over time, and to provide evidence of mastery of specific learning outcomes.
Here are some of the key features of display portfolios:
- Selection: Students select their best work to include in their display portfolios.
- Reflection: Students write about their learning and their process of creating the work in their display portfolios.
- Organization: Display portfolios are typically organized by theme or topic.
- Presentation: Display portfolios are designed to be visually appealing and easy to navigate.
Display portfolios can be used in a variety of settings, including schools, businesses, and community organizations. They can be used to assess student learning, to track progress over time, to provide evidence of mastery of specific learning outcomes, to showcase student work, and to motivate students to achieve their goals.
Here are some of the benefits of using display portfolios:
- Helps students to reflect on their learning: Display portfolios can help students to reflect on their learning and to identify their strengths and weaknesses. This can help them to set goals for future learning and to improve their performance.
- Provides evidence of student learning: Display portfolios can provide evidence of student learning to parents, teachers, and other stakeholders. This can help to demonstrate the value of the learning that is taking place.
- Motivates students to work hard and to achieve their goals: Display portfolios can motivate students to work hard and to achieve their goals. When students see their best work displayed, they are more likely to be motivated to continue working hard and to achieve even greater things.
If you are interested in creating a display portfolio for your students, here are some tips:
- Start by brainstorming a list of the skills and knowledge that you want your students to demonstrate.
- Collect samples of student work that demonstrate these skills and knowledge.
- Encourage students to reflect on their work and to write about their learning.
- Design a portfolio that is visually appealing and easy to navigate.
- Share the portfolio with parents, teachers, and other stakeholders.
Hence, purpose of a display portfolio is to demonstrate highest level of achievement attained by learners.
Q28: Which among the following is a school management tool being used by Kendriya Vidyalayas?
(a) Shaala Siddhi
(b) Shaala Darpan
(c) NISHTHA
(d) Vyas
Ans: B
Sol: Shaala Darpan:
- Shaala Darpan is a school management portal developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC) and is being utilized by Kendriya Vidyalayas (KVs) and other schools under the administrative control of the Department of School Education and Literacy, Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- Shaala Darpan serves as an integrated platform for various school-related activities and functions. It provides digital solutions for administrative tasks, student enrollment, attendance management, academic planning, assessments, result processing, and communication between teachers, students, parents, and school administrators.
- The portal offers features such as student data management, attendance tracking, timetable generation, fee management, examination management, report card generation, and access to various educational resources. It helps in streamlining school operations, facilitating data management, and promoting effective communication and collaboration within the school community.
- Kendriya Vidyalayas and other schools using Shaala Darpan have benefited from the automation and digitization of routine administrative processes, leading to improved efficiency and transparency in school management.
It is important to note that the other options mentioned, Shaala Siddhi, NISHTHA, and Vyas, are also educational initiatives or programs in India, but they are not specifically school management tools being used by Kendriya Vidyalayas.
Therefore, Shaala Darpan is a school management tool being used by Kendriya Vidyalayas.
Q29: Which among the following is not an example of asynchronous learning environment?
(a) You Tube Videos
(b) Pod casts
(c) Video conferencing
(d) Discussion forum
Ans: C
Sol: Key Points Asynchronous learning:
- Asynchronous learning refers to a mode of learning where learners do not need to be present at the same time. It allows learners to access and engage with educational materials, resources, and activities at their own pace and convenience.
Let's examine the options to understand that are examples of asynchronous learning environments:
- YouTube videos: YouTube videos are pre-recorded and can be accessed by learners at any time. Learners can watch the videos, pause, rewind, and review the content as needed. This flexibility makes YouTube videos an example of asynchronous learning.
- Podcasts: Podcasts are audio or video recordings that can be downloaded or streamed. Similar to YouTube videos, podcasts allow learners to listen or watch the content at their own convenience. Learners can access podcasts whenever they want, making them an example of asynchronous learning.
- Discussion forum: Discussion forums are online platforms where learners can engage in discussions, ask questions, and share ideas. Discussion forums operate asynchronously, as learners can participate and contribute to the discussions at any time that suits them. They can read and respond to posts, collaborate with peers, and continue the conversation over an extended period.
Let's examine the options to understand that is not example of asynchronous learning environments
- Video conferencing involves real-time communication and interaction between participants. It requires learners to be present at the same time for a live video session, where they can see and hear each other in real-time.
- Video conferencing is an example of synchronous learning, where learners engage with each other and the instructor in real-time.
Hence, option 3) Video conferencing is not an example of an asynchronous learning environment, as it involves synchronous interaction,
Q30: The Computer Assisted Learning (CAL) packages are based on which psychological learning theory?
(a) Cognitivist
(b) Constructivist
(c) Behaviourist
(d) Connectivist
Ans: C
Sol:
- Computer-assisted learning (CAL) packages are based on the behaviourist learning theory.
- Behaviourism is a theory of learning that emphasizes the role of reinforcement and punishment in shaping behaviour.
- CAL packages typically use various techniques to reinforce desired behaviour, such as providing feedback, rewards, and punishments.
Here are some of the ways in which CAL packages are based on behaviourism:
- They often use a step-by-step approach to learning, reinforcing each step before the learner moves on to the next step.
- They often provide immediate feedback so learners know if they are correct or incorrect.
- They often use rewards, such as points or badges, to encourage learners to continue learning.
- They sometimes use punishments, such as time-outs or loss of privileges, to discourage learners from engaging in unwanted behaviour.
Behaviourism has been criticized for being too simplistic and ignoring cognition and motivation's role in learning. However, behaviourism has also been praised for its effectiveness in teaching simple skills.
CAL packages can be a valuable tool for learning various skills, but it is important to remember that they are not a substitute for a good teacher.
Hence, Computer Assisted Learning (CAL) packages are based on Behaviourist learning theory.
Q31: Which of the following implies the 'refreeze' step of Lewin's change management model?
(a) Communicate a change
(b) Execute a change
(c) Plan a change
(d) Reinforce a change
Ans: D
Sol: Lewin's change management model
- Kurt Lewin's change management model is a three-step process that helps organizations to successfully implement change. The three steps are:
- Unfreeze: This step involves creating a sense of urgency for change and helping people to let go of the old way of doing things.
- Change: This step involves implementing the new change and helping people to learn the new way of doing things.
- Refreeze: This step involves solidifying the change and helping people to make the new way of doing things the norm.
The refreeze step is important because it helps to ensure that the change is not reversed. This can be done by providing training, support, and resources to help people to adopt the new way of doing things. It is also important to celebrate successes and to provide positive reinforcement for those who are making the change.
Here are some of the things that can be done to reinforce a change:
- Provide training and support to help people learn the new way of doing things.
- Celebrate successes and provide positive reinforcement for those who are making the change.
- Remove any obstacles that may be preventing people from making the change.
- Monitor the change and make adjustments as needed.
By following these steps, organizations can increase the chances of successfully implementing change.
Hence, Option 4) Reinforce a change implies the 'refreeze' step of Lewin's change management model.
Q32: Which among the following believes in networked learning?
(a) Behaviourism
(b) Cognitivism
(c) Constructivism
(d) Connectivism
Ans: D
Sol: Connectivism is the learning theory that believes in networked learning.
- Connectivism is a learning theory developed by George Siemens and Stephen Downes that emerged in the digital age. It recognizes the transformative impact of digital technologies and networks on how people acquire and share knowledge. Connectivism posits that learning is not solely an individual cognitive process but is distributed across networks of people, resources, and technologies.
Key principles of connectivism include:
- Learning as networked: Connectivism emphasizes that learning occurs through connections and interactions with others, as well as with digital tools and resources. It recognizes the importance of networks and the ability to access, navigate, and contribute to knowledge networks in the digital age.
- Importance of digital technologies: Connectivism acknowledges the role of technology in facilitating learning and knowledge creation. Digital tools and platforms enable learners to access vast amounts of information, engage in collaborative activities, and participate in networked learning environments.
- Focus on connections and patterns: Connectivism highlights the significance of making connections between concepts, ideas, and sources of information. It emphasizes the ability to recognize patterns, filter and evaluate information, and make informed decisions based on the networked resources available.
- Learning as a process of adaptation: Connectivism views learning as an ongoing process of staying current and adapting to changing knowledge landscapes. Learners must be able to engage with new information, critically evaluate it, and apply it to new contexts as needed.
Therefore, Option 4) Connectivism is the learning theory that believes in networked learning.
Q33: Which of the following statements are true?
A. Study of problem of freedom comes under metaphysics.
B. Study of empiricism comes under Epistemology.
C. Induction method falls under the purview of logic.
D. A priori knowledge falls under Axiology.
E. Concept of God falls under Epistemology.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) A, D and E only
Ans: A
Sol: A. Study of the problem of freedom comes under metaphysics. This statement is true.
- Metaphysics deals with fundamental questions about reality, including topics such as existence, causality, determinism, free will, and the nature of being.
B. Study of empiricism comes under epistemology. This statement is true.
- Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that examines the nature of knowledge, belief, and justification. Empiricism is a philosophical position that emphasizes the role of experience and sensory perception in acquiring knowledge.
C. Induction method falls under the purview of logic. This statement is true.
- Induction is a reasoning method that involves drawing general conclusions based on specific observations or evidence. Logic is the study of reasoning and argumentation, including different methods of inference such as deduction and induction.
D. A priori knowledge falls under axiology. This statement is false.
- A priori knowledge refers to knowledge that is independent of experience and is known prior to or independently of empirical evidence. Axiology, on the other hand, is the branch of philosophy that deals with the study of value and ethics.
E. Concept of God falls under epistemology. This statement is false.
- The concept of God typically falls under the domain of philosophy of religion, which is a subfield of philosophy that explores questions related to the existence, nature, and attributes of God, religious experience, and religious language.
Therefore, the correct answer is 1) A, B and C only.
Q34: Which of the following statements are true?
A. Sankhya means the Philosophy of right knowledge (Samyak khyati)
B. Sankhya is a pluralistic spiritualism and an uncompromising dualism
C. Right knowledge is the knowledge of the association of the Purusha with the Prakriti
D. Shankaracharya regards Sankhya as a main 'main opponent' of Vedanta
E. The view of Sankhya yoga is called Prikiti-arambhavada
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) A, C and E only
Ans: C
Sol: A. Sankhya means the Philosophy of right knowledge (Samyak khyati). This statement is true.
- Sankhya is derived from the Sanskrit words "Samyak" meaning right or correct and "Khyati" meaning knowledge or understanding. Sankhya philosophy is concerned with attaining right knowledge and understanding of the nature of reality.
B. Sankhya is a pluralistic spiritualism and an uncompromising dualism. This statement is true.
- Sankhya philosophy is known for its dualistic approach, positing the existence of two fundamental entities: Purusha (consciousness or spirit) and Prakriti (matter or nature). It also recognizes multiple categories and principles in the manifestation of reality.
D. Shankaracharya regards Sankhya as a main 'main opponent' of Vedanta. This statement is true.
- Adi Shankaracharya, a prominent philosopher and exponent of Advaita Vedanta, considered Sankhya philosophy as one of the main opponents of Vedanta. He engaged in debates and discussions with Sankhya philosophers to establish the supremacy of Advaita Vedanta.
Therefore, the correct answer is 3) A, B and D only.
Q35: Which of the following characterise a qualitative research?
A. Researcher dependent
B. Tools dependent
C. Context specific generalization
D. Minimal citation of literature
E. Context-free generalization
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and E only
(b) D, E and B only
(c) E, D and A only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: D
Sol: Qualitative Research:
- Qualitative research is a type of research that focuses on understanding the meaning of human experience. It is often used to explore complex issues that cannot be easily quantified.
- Qualitative research is typically researcher-dependent, meaning that the researcher's own experiences and biases can influence the research findings. Qualitative research is also context-specific, meaning that the findings are only applicable to the specific context in which the research was conducted.
- Finally, qualitative research typically involves minimal citation of literature, as the focus is on understanding the meaning of human experience rather than on building a body of knowledge.
Here is a more detailed of each of the three characteristics of qualitative research:
- Researcher dependent: Qualitative research is often described as being researcher-dependent, meaning that the researcher's own experiences and biases can influence the research findings. This is because qualitative research typically involves the researcher collecting data through interviews, focus groups, or observation. The researcher then interprets this data and draws conclusions based on their own understanding of the data. As a result, the researcher's own experiences and biases can influence the way they interpret the data and the conclusions they draw.
- Context specific: Qualitative research is also context-specific, meaning that the findings are only applicable to the specific context in which the research was conducted. This is because qualitative research typically focuses on understanding the meaning of human experience in a particular context. As a result, the findings of qualitative research cannot be generalized to other contexts.
- Minimal citation of literature: Qualitative research typically involves minimal citation of literature, as the focus is on understanding the meaning of human experience rather than on building a body of knowledge. This is because qualitative research is often exploratory in nature, and the researcher is not necessarily trying to test a specific hypothesis or theory. As a result, there is less of a need to cite previous research in qualitative research.
Overall, qualitative research is a type of research that focuses on understanding the meaning of human experience. It is often used to explore complex issues that cannot be easily quantified. Qualitative research is typically researcher-dependent, context-specific, and involves minimal citation of literature.
The correct answer is 4) A, C and D only.
Q36: Distinguished features of the action research are as follows:
A. Only teachers conduct action research.
B. A small accessible population is used for the study.
C. Sample drawn from a population is used for the study.
D. Researcher is the consumer of the findings.
E. Obtained findings are generalized to the population
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) C and E only
(c) B and D only
(d) D and E only
Ans: C
Sol: Action Research:
- Action research is a research approach that involves systematically studying and evaluating one's own practice or a specific context in order to bring about positive change or improvement. It is typically conducted by practitioners or individuals directly involved in the situation being studied.
- In action research, the researcher actively engages in a cyclical process of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. The research process involves identifying a problem or area for improvement, designing interventions or changes, implementing them, and then reflecting on the outcomes and learning from the experience.
The distinguished features of action research are as follows:
A. Only teachers conduct action research:
- This statement is not correct. While teachers are often involved in conducting action research, it is not limited to teachers only. Action research can be conducted by other professionals, researchers, or individuals involved in a particular context or field.
B. A small accessible population is used for the study:
- This statement is a distinguished feature of action research. Action research typically focuses on a small and accessible population within a specific context or setting. This allows for close engagement, collaboration, and in-depth understanding of the research problem.
C. Sample drawn from a population is used for the study:
- This statement is not a characteristic feature of action research. Action research often involves studying a specific group or context rather than drawing samples from a larger population for generalization purposes.
D. Researcher is the consumer of the findings:
- This statement is a distinguished feature of action research. In action research, the researcher is typically the primary consumer of the findings. The research is often conducted with the intention of informing and improving the researcher's own practice or the practices within a specific context.
E. Obtained findings are generalized to the population:
- This statement is not a characteristic feature of action research. Action research primarily focuses on addressing specific local problems and improving practice within a particular context. The emphasis is on contextual understanding and application rather than generalizing findings to larger populations.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 3) B and D only.
Q37: According to Mager (1997), which among the following are important Characteristics of an instructional objective?
A. Language
B. Performance
C. Behaviour modification
D. Criterion
E. Condition
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) B, D and E only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) B, C and E only
Ans: B
Sol: Robert F. Mager:
- Robert F. Mager was an American educator and author best known for his work on instructional design and performance-based learning. His book, Preparing Instructional Objectives, is a classic in instructional design and is still used today by many trainers and educators.
- In Preparing Instructional Objectives, Mager defines an instructional objective as a statement describing what the learner can do after instruction. He argues that instructional objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Mager's work has had a significant impact on the field of instructional design. His work has been used to develop training programs in various fields, including business, education, and government. Mager's work has also been influential in the development of performance-based learning, which focuses on the learner's ability to perform a specific task.
According to Mager (1997), an instructional objective should have three important characteristics:
- Performance: The objective should describe what the learner can do after instruction.
- Condition: The objective should describe the conditions under which the learner will be able to perform the task.
- Criterion: The objective should describe the criteria for acceptable performance.
Here is an example of an instructional objective that meets all three of Mager's criteria:
- Performance: The learner will be able to write a three-paragraph essay on the topic of their choice.
- Condition: The learner will be given 30 minutes to complete the essay.
- Criterion: The essay must be well-organized, have a clear thesis statement, and be free of errors in grammar and spelling.
Option A is incorrect because language is not an important characteristic of an instructional objective.
Option C is incorrect because behaviour modification is not an important characteristic of an instructional objective.
Therefore the correct answer is B, D and E only.
Q38: Which among the following are not the cognitive processes dimension of Anderson and Krethwohl's taxonomy of instructional objectives:
A. Understand
B. Comprehension
C. Apply
D. Synthesis
E. Evaluate
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B and C only
(c) B and D only
(d) C and E only
Ans: C
Sol: Anderson and Krathwohl's taxonomy of instructional objectives:
- Anderson and Krathwohl's taxonomy of instructional objectives, also known as the Revised Bloom's Taxonomy, is a framework that categorizes learning objectives based on cognitive processes and knowledge dimensions. It provides a structure for educators to design and assess learning experiences effectively.
The taxonomy consists of two main dimensions:
Cognitive Processes:
- This dimension describes different levels of thinking or cognitive processes involved in learning. It categorizes cognitive processes into six levels, listed in ascending order of complexity:
- Remember: Recalling or retrieving information from memory.
- Understand: Grasping the meaning of information or ideas.
- Apply: Using knowledge or skills in different situations or contexts.
- Analyze: Breaking down complex concepts or information into parts and examining their relationships.
- Evaluate: Making judgments or assessments based on criteria or standards.
- Create: Generating new ideas, products, or solutions by combining existing knowledge or skills.
Knowledge Dimensions:
- This dimension describes different types of knowledge that learners can acquire. It categorizes knowledge into four dimensions:
- Factual Knowledge: Knowledge of basic facts, terms, or concepts.
- Conceptual Knowledge: Understanding the interrelationships and organizing principles of a subject.
- Procedural Knowledge: Knowledge of how to do or perform something, including skills and techniques.
- Metacognitive Knowledge: Knowledge of one's own thinking processes and strategies for learning and problem-solving.
- By combining these two dimensions, educators can specify learning objectives that address both the cognitive processes and knowledge dimensions. This taxonomy helps in designing appropriate instructional strategies, selecting suitable assessment methods, and evaluating the depth of understanding and application of knowledge by learners.
- The Revised Bloom's Taxonomy provides a more nuanced and comprehensive framework compared to the original Bloom's Taxonomy, incorporating a greater emphasis on higher-order thinking skills such as analyzing, evaluating, and creating. It serves as a valuable tool for instructional design, curriculum development, and assessment in educational settings.
The options that are not part of the cognitive processes dimension of Anderson and Krathwohl's taxonomy of instructional objectives
B. Comprehension: This refers to the ability to understand or grasp the meaning of information. It involves interpreting, summarizing, and explaining ideas or concepts.
D. Synthesis: This refers to the ability to integrate or combine different elements to create something new. It involves the organization and combination of ideas, concepts, or information to form a coherent whole.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 3) B and D only.
Q39: Which of the following are the symbols of creative common licences?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 
E. 
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) A, B and D only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: A
Sol: Creative Commons:
Creative Commons licenses use symbols to indicate the permissions and restrictions associated with the licensed content. The symbols used by Creative Commons are as follows:
- Attribution (BY): This symbol represents the requirement of giving appropriate credit to the original creator or licensor of the work.
- ShareAlike (SA): This symbol indicates that if you adapt or remix the licensed work, you must distribute it under the same or a compatible license.
- NonCommercial (NC): This symbol signifies that the licensed work cannot be used for commercial purposes without permission from the copyright holder.
- NoDerivatives (ND): This symbol indicates that the licensed work cannot be modified, transformed, or used to create derivative works.
- Public Domain (CC0): This symbol represents the dedication of a work to the public domain, allowing unrestricted use, modification, and distribution without attribution or restrictions.

These symbols are often displayed alongside the Creative Commons license text to visually represent the permissions and restrictions associated with the licensed content. They help users easily understand the conditions under which they can use, share, and modify the work while respecting the original creator's rights.
Therefore A, B and D only is the correct answer.
Q40: The SSA document must incorporate the educational experience of
A. Older PWD's
B. The teacher fraternity
C. Voluntary organisations
D. Educationists
E. Leaders
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D and E only
(b) A, B, C and D only
(c) A, B, D and E only
(d) B, C, D and E only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 2. The SSA document must incorporate the educational experience of older PWDs, the teacher fraternity, voluntary organizations, and educationists.
- Older PWDs have a wealth of experience and knowledge that can be used to improve the educational system. They can provide insights into the challenges that PWDs face in education and can help to develop solutions that address these challenges.
- The teacher fraternity is responsible for delivering education to students. They have a deep understanding of the educational system and can provide valuable insights into how it can be improved.
- Voluntary organizations are often involved in providing education to marginalized groups. They have a wealth of experience and knowledge that can be used to improve the educational system.
- Educationists are experts in the field of education. They can provide valuable insights into how the educational system can be improved.
Leaders can also provide valuable insights into how the educational system can be improved. However, they are not directly involved in the delivery of education and may not have the same level of understanding of the educational system as the other groups mentioned above.
Q41: Students with dyscalculia face difficulty in the following:
A. Problems related to number graphs
B. Numbers dealing
C. Numbers placing
D. Problems related to spatial concept
E. Problems related to reading numbers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, D and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: B
Sol: Dyscalculia:
- Dyscalculia is a specific learning disorder that affects an individual's ability to understand and work with numbers and mathematical concepts. It is often referred to as "math dyslexia" or "number dyslexia." People with dyscalculia have difficulties in various areas of mathematics, despite having average or above-average intelligence in other areas.
Students with dyscalculia commonly face difficulties in the following areas:
B. Numbers dealing: Dyscalculic students may struggle with basic number concepts, such as counting, recognizing numerical symbols, and understanding mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
C. Numbers placing: Dyscalculia can affect a student's ability to understand and correctly place numbers in their appropriate positions within mathematical equations or number sequences.
D. Problems related to spatial concepts: Dyscalculic students often have difficulties with spatial concepts, which can include understanding and visualizing spatial relationships, directions, and orientations. This can make it challenging for them to comprehend spatial aspects of mathematics, such as geometry and measurement.
Therefore, the correct answer is B, C, and D only.
Q42: Match List I with List II
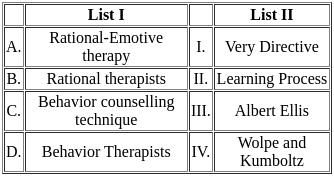
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(d) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Ans: D
Sol:  Hence the correct matching is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Hence the correct matching is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Q43: Match List I with List II
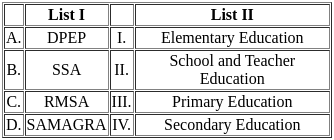
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
Ans: C
Sol: 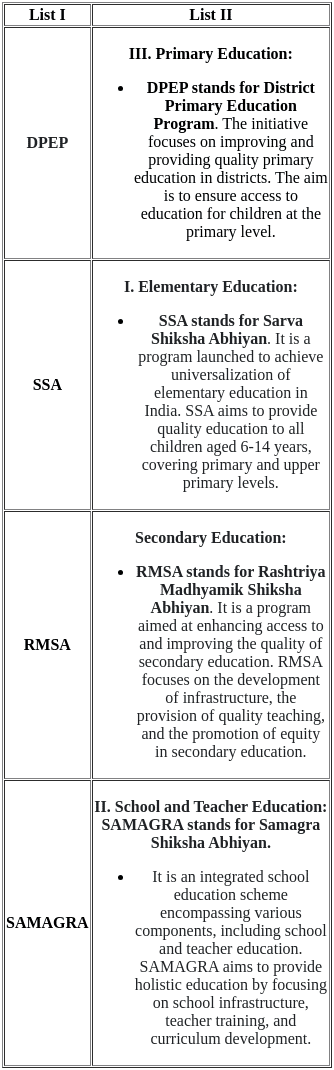 Therefore, the correct match is A - III, B - I, C - IV, and D - II.
Therefore, the correct match is A - III, B - I, C - IV, and D - II.
Q44: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: B
Sol:
- Placement Assessment determines a student's starting point in a particular subject or skill. This information can be used to group students appropriately and to plan instruction.
- Formative Assessment is used to provide feedback to students on their progress throughout a unit of instruction. This feedback can help students learn more effectively and identify areas where they need additional help.
- Diagnostic Assessment is used to identify specific areas where a student is struggling. This information can be used to plan targeted instruction to help students improve their skills.
- Summative Assessment measures student learning at the end of a unit of instruction. This information can be used to evaluate instructional effectiveness and decide future instruction.
Q45: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(c) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
Ans: A
Sol: 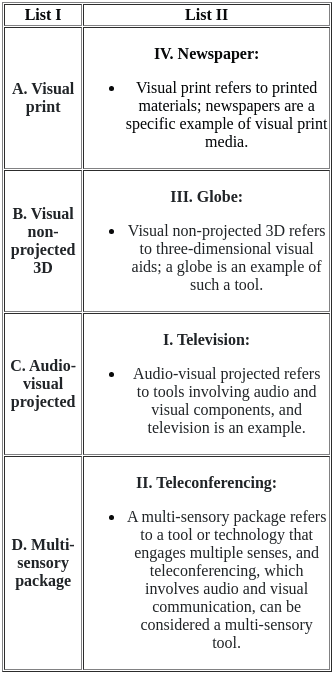 Therefore, the correct match is A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II.
Therefore, the correct match is A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II.
Q46: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it
Mahatma Gandhi said: Education is "the basic tool for development of consciousness and reconstruction of society". The Universal Declaration of Human rights, 1948 (UDHR) states: "Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory.
"This was said prior to the labeling of the current 21st century as the century of knowledge; and before the level of education in the community was recognised as an index of human development. The Constitution of India, recognizing this aspect enacted initially the Directive Principles of State Policy in Article 45 to achieve the goal of free and compulsory education upto the age of fourteen within ten years, but the task remaining unfulfilled for over half a century, the fundamental right in Article 21A has been inserted as amendment to reinforce its importance along with corresponding amendments in Article 45 and 51 A.
Teacher is the medium to achieve this goal. Hence, the quality of teacher education to provide quality teachers is an important component for the success of this programme. The report of the Education Commission states:" The destiny of India is now being shaped in her classrooms. This, we believe is no more a rhetoric." The key player in the process is the teacher. Mahatma Gandhi said, "I have always felt that the true text book for the pupil is the teacher". A true teacher is a role model who triggers the thought process of his students to realize their true potential. He teaches by 'practice' and not merely by "precept".
While making education as a fundamental right, which among the following articles of the Constitution of India was not amended/inserted?
(a) Article 15
(b) Article 21 A
(c) Article 45
(d) Article 51 A
Ans: A
Sol:
- The passage mentions the insertion of Article 21A, along with corresponding amendments in Article 45 and Article 51A, to reinforce the importance of free and compulsory education.
- However, it does not mention any amendments or insertions related to Article 15
Q47: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it
Mahatma Gandhi said: Education is "the basic tool for development of consciousness and reconstruction of society". The Universal Declaration of Human rights, 1948 (UDHR) states: "Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory.
"This was said prior to the labeling of the current 21st century as the century of knowledge; and before the level of education in the community was recognised as an index of human development. The Constitution of India, recognizing this aspect enacted initially the Directive Principles of State Policy in Article 45 to achieve the goal of free and compulsory education upto the age of fourteen within ten years, but the task remaining unfulfilled for over half a century, the fundamental right in Article 21A has been inserted as amendment to reinforce its importance along with corresponding amendments in Article 45 and 51 A.
Teacher is the medium to achieve this goal. Hence, the quality of teacher education to provide quality teachers is an important component for the success of this programme. The report of the Education Commission states:" The destiny of India is now being shaped in her classrooms. This, we believe is no more a rhetoric." The key player in the process is the teacher. Mahatma Gandhi said, "I have always felt that the true text book for the pupil is the teacher". A true teacher is a role model who triggers the thought process of his students to realize their true potential. He teaches by 'practice' and not merely by "precept".
The passage is focusing on establishing the importance of:
(a) Schooling
(b) University education
(c) Teacher
(d) Curriculum
Ans: C
Sol:
- The passage emphasizes the role of teachers in education and society. It highlights the significance of teacher education and the quality of teachers in achieving the goal of providing free and compulsory education.
- The passage quotes Mahatma Gandhi, who states that the teacher is the true textbook for the pupil and that a true teacher serves as a role model, guiding students to realize their true potential.
Q48: Early childhood experiences are critical especially for emotional/social/cognitive development, is influenced by the thoughts of ______.
(a) Carl Rogers
(b) Edwin Gordon
(c) Sigmund Freud
(d) Max Wertheimer
Ans: C
Sol: Sigmund Freud:
- Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist and psychiatrist who founded the school of thought known as psychoanalysis. He believed early childhood experiences are critical for emotional, social, and cognitive development. He also believed that our personality is formed in early childhood and that our adult behaviour often reflects our childhood experiences.
- Freud's theory of psychosexual development is one of the most influential early childhood development theories. He believed children go through a series of stages; each focused on a different erogenous zone. If a child does not successfully resolve the conflict of a particular stage, they may become fixated on that stage and develop unhealthy personality traits.
- Freud's theory has been criticized for being too deterministic and focusing too much on the negative aspects of childhood. However, his theory has also been praised for its insights into the importance of early childhood experiences.
Here are some of the key points of Freud's theory of psychosexual development:
- Children go through a series of stages; each focused on a different erogenous zone.
- The successful resolution of each stage is essential for healthy development.
- If a child does not successfully resolve the conflict of a particular stage, they may become fixated on that stage and develop unhealthy personality traits.
Freud's theory of psychosexual development has had a profound impact on our understanding of early childhood development. It has helped us understand the importance of early childhood experiences and the role parents play in shaping their children's personalities.
The correct answer is 3) Sigmund Freud.
Q49: For Mastery Goal Orientation, which one of the following is considered as a standard used under avoidance focus?
(a) Perfectionists do not make mistakes
(b) Self improvement
(c) Winning the competition
(d) Be the slowest
Ans: A
Sol: Mastery Goal Orientation:
- Mastery goal orientation is a type of motivation focused on learning and improvement. People with mastery goal orientation are motivated to do their best and to improve their skills and knowledge. They are not concerned with comparing themselves to others or winning or losing.
- Avoidance focus is a type of motivation focused on avoiding failure or negative consequences. People with an avoidance focus are motivated to avoid making mistakes or looking bad. They are often perfectionists, and they are afraid of failure.
- The statement "Perfectionists do not make mistakes" exemplifies an avoidance focus standard. This standard is used to avoid failure or negative consequences. People who use this standard are motivated to avoid making mistakes at all costs. This can lead to anxiety, stress, and perfectionism.
Here are some other examples of avoidance focus standards:
- I must always get good grades.
- I must never make a mistake.
- I must always be the best.
- I must never look bad.
Avoidance focus standards can be harmful to motivation and learning. They can lead to anxiety, stress, and perfectionism. It is important to focus on mastery goal orientation instead of avoidance focus. Mastery goal orientation is more likely to lead to positive outcomes such as learning, improvement, and confidence.
The correct answer is 1) Perfectionists do not make mistakes.
Q50: As per the National Education Policy-2020, which of the following is correct about continuous professional development of school teachers?
(a) Every school teacher requires minimum 40 hours of continuous professional development every year
(b) Every school teacher requires minimum 50 hours of continuous professional development per year
(c) Every school teacher requires minimum 40 hours of continuous professional development in his/her career
(d) Continuous professional development is not essential for school teachers
Ans: B
Sol:
- The National Education Policy 2020 (NEP 2020) emphasizes the need for continuous professional development (CPD) for school teachers.
- The policy states that every school teacher should participate in at least 50 hours of CPD every year.
- CPD can be in workshops, conferences, online courses, or other forms of professional development. CPD aims to help teachers stay up-to-date on the latest teaching methods and educational research. It also helps teachers to improve their skills and knowledge and to become more effective in the classroom.
Here are some of the benefits of CPD for teachers:
- It helps teachers stay current on the latest teaching methods and educational research.
- It helps teachers to improve their skills and knowledge.
- It helps teachers to become more effective in the classroom.
- It helps teachers to be more motivated and engaged in their work.
- It helps teachers to be more satisfied with their jobs.
- It helps teachers to be more productive.
- It helps teachers to be more effective in supporting student learning.
CPD is an essential part of the professional development of school teachers. It helps teachers to stay up-to-date on the latest teaching methods and educational research, and it helps them to improve their skills and knowledge. CPD also helps teachers to become more effective in the classroom, and it helps them to be more motivated and engaged in their work.
Hence option 2 is the correct answer.
Q51: Which of the following is not an example of 'reflective teaching'?
(a) Writing journal
(b) Reading textbook
(c) Gathering feedback from students
(d) Recording a class
Ans: B
Sol: Reflective teaching:
- Reflective teaching refers to a process in which educators self-reflect and critically analyse their teaching practices, experiences, and outcomes to improve their effectiveness in the classroom. It involves thoughtful consideration of instructional methods, student learning, and personal and professional development.
Let's examine the options that are examples of reflective teaching:
- Writing journal: Keeping a journal allows teachers to reflect on their daily experiences, challenges, and successes in the classroom. They can analyze their teaching strategies, student engagement, and areas for improvement. Journal writing helps teachers gain insights, set goals, and make adjustments to enhance their teaching practices.
- Gathering feedback from students: Seeking feedback is an important aspect of reflective teaching. By asking students for their perspectives and opinions on the learning process, teachers can gain valuable insights into their teaching effectiveness, student engagement, and areas of improvement. This feedback helps teachers reflect on their instructional strategies and adjust to meet students' needs.
- Recording a class: Recording a class allows teachers to review their teaching in detail. Teachers can observe their teaching style, student interactions, and classroom dynamics by watching the recorded class session. This provides an opportunity for self-reflection, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and improving teaching strategies and delivery.
On the other hand, reading a textbook does not involve actively reflecting and analysing one's teaching practices. While reading a textbook can provide valuable information and knowledge, it does not directly contribute to the process of self-reflection and improvement in teaching.
Therefore, option 2) Reading the textbook is not an example of 'reflective teaching'.
Q52: Who is the writer of famous book "Foundations of Education (1926)"?
(a) William Kilpatrick
(b) John Dewey
(c) Ralph W. Tyler
(d) Hollies Caswell
Ans: A
Sol: William Heard Kilpatrick:
- William Heard Kilpatrick was an American educator and philosopher best known for his work on progressive education.
- Kilpatrick's book "Foundations of Education" was published in 1926 and is considered one of the most influential works on education in the 20th century.
- In his book, Kilpatrick argues that education should be based on the principles of democracy and social cooperation. He also emphasizes the importance of experiential learning and problem-solving. Kilpatrick's ideas had a major impact on the development of progressive education, and they continue to be influential today.
Here are some of the key ideas that Kilpatrick discusses in his book:
- Education should be based on the principles of democracy and social cooperation.
- Education should be active and experiential.
- Education should focus on problem-solving.
- Education should be relevant to the student's life.
- Education should be lifelong.
Kilpatrick's book "Foundations of Education" is a classic work of educational thought. It is a valuable resource for anyone interested in the history of education or the principles of progressive education.
Hence, the writer of the famous book "Foundations of Education (1926)" is William Kilpatrick.
Q53: Which of the following is not a basic principle suggested by Tyler?
(a) Determine the teacher's purposes
(b) Identify educational experiences related to those purposes
(c) Ascertain how the experiences are organized
(d) Evaluate the purposes
Ans: A
Sol:
Ralph W. Tyler's basic principles for curriculum development are:
- State the objectives. What do you want students to learn?
- Select learning experiences. What activities will help students achieve the objectives?
- Organize learning experiences. How will the activities be sequenced and paced?
- Evaluate the learning. How will you know if students have achieved the objectives?
- Tyler's model is a linear, step-by-step approach to curriculum development. It is based on the belief that the curriculum should be designed to achieve specific objectives. Tyler's model has been widely used in schools around the world. However, it has also been criticized for being too rigid and for not considering students' individual needs.
- The teacher's purposes are not a basic principle of curriculum development because they are not always clear or consistent. Teachers may have different student goals, which may change over time. Teachers need to be aware of their purposes, but they should also be flexible and willing to adapt their goals to the needs of their students.
Hence, Determine the teacher's purposes is not a basic principle suggested by Tyler.
Q54: In a given score distribution of 12, 14, 16, 18 and 20 , the sum of square deviation is:
(a) 12
(b) 24
(c) 40
(d) Zero
Ans: C
Sol: The sum of square deviation is calculated by taking the square of the difference between each score and the mean and then adding all of the squares together. The mean of the scores 12, 14, 16, 18, and 20 is 16.
The square of the difference between each score and the mean is:
- (12 - 16)^2 = 16
- (14 - 16)^2 = 4
- (16 - 16)^2 = 0
- (18 - 16)^2 = 4
- (20 - 16)^2 = 16
The sum of these squares is 40.
Therefore, the sum of the square deviation for the given score distribution is 40.
Here is the solution in mathematical form:
Where:
- x is a score
- μ is the mean
- Σ is the sum
In this case, the sum of the square deviation is:
Q55: Six Sigma focusses on the enhancement of the following through DMAIC as a data-driven quality methodology:
(a) Process
(b) Product
(c) Purchase
(d) Power
Ans: A
Sol: Six Sigma focuses on the enhancement of processes through DMAIC as a data-driven quality methodology.
DMAIC is a five-step process that stands for:
- Define: Define the problem or opportunity that you want to improve.
- Measure: Measure the current state of the process.
- Analyze: Analyze the data to identify the root causes of the problem.
- Improve: Implement changes to the process to address the root causes of the problem.
- Control: Implement controls to ensure that the improvements are sustained.
Six Sigma is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the quality of products and services, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. It has been used successfully by many organizations, including General Electric, Motorola, and Toyota.
Here are some of the benefits of using Six Sigma:
- Improved quality: Six Sigma can help to improve the quality of products and services by reducing defects and errors.
- Reduced costs: Six Sigma can help to reduce costs by eliminating waste and improving efficiency.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Six Sigma can help to improve customer satisfaction by delivering products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Q56: In which of the following educational policy/act of India, Indian sign language for teaching and monitoring is involved?
(a) NPE-1986
(b) RPwD-2016
(c) NEP-2020
(d) PwD-1995
Ans: C
Sol: National Education Policy (NEP) 2020:
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 is a new education policy for India that was released in 2020. The NEP 2020 has a number of provisions for the education of people with disabilities, including the use of Indian Sign Language (ISL) for teaching and monitoring.
- The NEP 2020 states that "Indian Sign Language will be standardised across the country, and national and state curriculum materials will be developed, for use by students with hearing impairment. Local sign languages will be respected and taught, where possible and relevant."
- The NEP 2020 also states that "All educational institutions will be required to provide appropriate infrastructure and support to students with disabilities, including sign language interpreters and other assistive technologies."
- The use of ISL for teaching and monitoring is a significant step forward in the inclusion of people with disabilities in the education system in India. It will allow students with hearing impairment to access the same quality of education as their peers and to reach their full potential.
Here are some of the benefits of using ISL for teaching and monitoring:
- Improved access to education: ISL can help students with hearing impairment to access the same quality of education as their peers.
- Improved communication: ISL can help students with hearing impairment to communicate more effectively with their teachers and peers.
- Improved participation: ISL can help students with hearing impairment to participate more fully in class discussions and activities.
- Improved self-esteem: ISL can help students with hearing impairment to feel more confident and included in the classroom.
Hence, in NEP-2020 of India, Indian sign language for teaching and monitoring is involved.
Q57: What are the four basic questions raised by Ralph Tyler for curriculum planning?
A. What educational goals are to be attained?
B. What instructional materials are needed for attaining the goals?
C. How the methods and strategies are to be organised?
D. How will attainment of goals to be evaluated?
E. What learning experiences are to be provided for attaining the goals?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C and D only
(b) A, C, D and E only
(c) C, D, E and B only
(d) A, B, D and E only
Ans: B
Sol: Ralph Tyler:
- Ralph Winfred Tyler (April 22, 1902 – February 18, 1994) was an American educator and curriculum theorist. He is best known for his development of the Tyler rationale, a four-step process for curriculum development.
- Tyler was born in Chicago, Illinois, in 1902. He received his bachelor's degree from Doane College in Nebraska in 1921 and his master's degree and doctorate from the University of Chicago in 1923 and 1927, respectively.
- After completing his doctorate, Tyler taught at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Ohio State University. In 1938, he returned to the University of Chicago, where he served as chairman of the Department of Education and dean of the Division of Social Sciences.
- In 1953, Tyler left the University of Chicago to become the founding director of the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences in Stanford, California. He remained at the Center until his retirement in 1967.
- Tyler's work has had a significant impact on education in the United States. His Tyler rationale is still widely used as a framework for curriculum development. He also played a key role in the development of the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), a national assessment of student achievement.
- Tyler was a prolific writer and author of several books, including Basic Principles of Curriculum and Instruction (1949) and The Curriculum Maker: A Guide for Developing Aims and Objectives (1950). He was also a frequent speaker and consultant to educators around the world.
- Tyler was a respected and influential educator who made significant contributions to the field of curriculum development. His work continues to be relevant today, and it continues to help educators to improve the quality of education for all students.
He developed a four-step process for curriculum development, known as the Tyler rationale. The four steps are:
- Identifying educational goals. What do we want students to learn?
- Selecting learning experiences. What activities will help students achieve the goals?
- Organizing learning experiences. How will the activities be sequenced and presented?
- Evaluating learning outcomes. How will we know if students have achieved the goals?
The four questions that are listed in question all related to the second step of the Tyler rationale, which is selecting learning experiences. The questions are:
- What learning experiences are to be provided for attaining the goals?
- How will attainment of goals to be evaluated?
The other two questions, about educational goals and methods and strategies, are related to the first and third steps of the Tyler rationale, respectively.
Therefore the correct answer is A, C, D and E only.
Q58: Find the correct pairs-
A. Rationalist- Teacher as source of ideas, facts and information
B. Empiricist- Teacher as demonstrator of process
C. Existentialist- Teacher as facilitator of choice
D. Pragmatist- Teacher as controller
E. Idealist- Teacher as friend
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) D, E and A only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is option 1) A, B, and C only.
The pairs that match the correct philosophical perspectives are as follows:
A. Rationalist-
- Teacher as source of ideas, facts, and information: Rationalists believe that knowledge is derived from reason and logical thinking. In this perspective, the teacher is seen as the primary source of knowledge and imparts information, ideas, and facts to the students.
B. Empiricist-
- Teacher as demonstrator of process: Empiricists emphasize the importance of observation and experience in acquiring knowledge. In this perspective, the teacher plays the role of a demonstrator who provides opportunities for students to engage in hands-on experiences and discover knowledge through direct observation and experimentation.
C. Existentialist-
- Teacher as facilitator of choice: Existentialists focus on individual freedom, choice, and personal responsibility. In this perspective, the teacher acts as a facilitator who helps students explore their own values, make choices, and take responsibility for their own learning and development.
The pairs that does not match the correct philosophical perspectives are as follows:
D. Pragmatist-
- Teacher as controller: This pair does not align correctly. Pragmatists believe in practical, problem-solving approaches to learning. They emphasize the application of knowledge in real-life situations. The teacher in pragmatism is more of a guide or facilitator, rather than a controller.
E. Idealist-
- Teacher as friend: This pair does not align correctly. Idealists emphasize the importance of values, ethics, and the pursuit of higher truths. While the teacher-student relationship is important in idealism, the teacher is typically seen as a mentor or guide rather than a friend.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 1) A, B, and C only.
Q59: Which of the following are within the quality indicator framework of NAAC for assessing Higher Education Institutions (HEls)?
A. Curricular and co-curricular aspects
B. Teaching-learning and Evaluation
C. Instructional and Learning Resources
D. Student support and progression
E. Institutional values and Best practices
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, D and E only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 2. The NAAC quality indicator framework for assessing Higher Education Institutions (HEls) includes the following:
- Teaching-learning and Evaluation: This criterion assesses the institution's teaching and learning quality. It includes factors such as the quality of the curriculum, the teaching methods used, and the assessment of student learning.
- Student support and progression: This criterion assesses the support provided to students to help them succeed in their studies. It includes factors such as academic and personal counselling availability, financial aid provision, and career guidance.
- Institutional values and Best practices: This criterion assesses the values the institution promotes and the best practices in place. It includes factors such as the institution's commitment to equity and diversity, promoting academic integrity, and providing a safe and healthy student environment.
Curricular Aspects (A) and Infrastructure and Learning Resources (C) as part of NAAC’s framework. Suggest revising options to include all five.
The other options are not included in the NAAC quality indicator framework.
Q60: National development as a core value within the Accreditation Framework of NAAC for universities includes which of the following:
A. Ensuring equity
B. Institutionalizing peace
C. Increasing access
D. Serving the cause of social justice
E. Consolidating truth
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D and E only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: C
Sol: National development as a core value within the Accreditation Framework of NAAC for universities includes ensuring equity, increasing access, and serving the cause of social justice.
- Ensuring equity means that all students can access and benefit from higher education regardless of their background. This can be done by providing financial assistance to students from low-income families, offering flexible learning options for students with disabilities, and creating a welcoming and inclusive environment for all students.
- Increasing access means making higher education more affordable and accessible to more people. This can be done by expanding the number of colleges and universities, offering online and distance learning options, and reducing the cost of tuition.
- Serving the cause of social justice means using higher education to address social problems and inequalities. This can be done by training students to work in social service fields, researching social issues, and advocating for policies that promote social justice.
Institutionalizing peace and consolidating truth are important goals but are not directly related to national development. Peace and truth are important values that all institutions should promote but are not specific to higher education.
Hence the correct answer is A, C and D only.
Q61: Match List I with List II
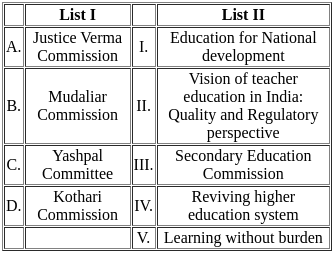
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - V, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - III, C - V, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(d) A - I, B -IV, C - V, D - II
Ans: B
Sol: 
Therefore, the correct match between List I and List II is A - II, B - III, C - V, D - I.
Q62: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
Living with a disability, or a different ability is undeniably challenging. Not only are individuals with different abilities challenged to overcome the physical trials associated with their medical conditions, but they must also persevere through the lifelong process of reconciling their personal views of themselves with the negative perceptions and prejudices of society. In addition to combating social stigma, the differently abled community is confronted with numerous physical barriers, political restrictions, and a history plagued with inferior status. Fortunately, the world has progressed in its acceptance and is continuing to improve its treatment of individuals with different abilities. Nevertheless, there is still great progress to be made in the movement toward equality and full inclusion. Differently abled women, for example, are continuously faced with the trial of intersectionality, the results of being both female and differently abled, which primarily includes sexual oppression. Thus, individuals with different abilities are encouraged to be more engaged in practice of self advocacy. Families, Friends and allies must also maintain their support of individuals with different abilities, an element that is critical to community's success. Helping professionals, who serve the differently-abled community, are urged to educate themselves on the adversity experienced by the community, to acknowledge how other cultural identities intersect with the differently abled culture, and to employ strengths based theoretical paradigm that will produce the most empowering results for their clients. Helping professionals with different abilities, furthermore, are called upon to lead the identity and civil rights movement of the differently-abled community.
Why does the author suggest people with different abilities to remain encouraged to engage in the practice of self-advocacy?
(a) As they are to combat social stigma.
(b) As they have to deal with their disabilities throughout their lives.
(c) As they need to take initiative to articulate their voices for their rights.
(d) As there is little progress made towards inclusion and equality.
Ans: C
Sol: Key Points
- The author suggests people with different abilities remain encouraged to engage in self-advocacy to take the initiative to articulate their voices for their rights.
- People with disabilities have the right to be treated with respect and dignity. Self-advocacy can help them to articulate their voices and to demand the rights they deserve.
Q63: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
Living with a disability, or a different ability is undeniably challenging. Not only are individuals with different abilities challenged to overcome the physical trials associated with their medical conditions, but they must also persevere through the lifelong process of reconciling their personal views of themselves with the negative perceptions and prejudices of society. In addition to combating social stigma, the differently abled community is confronted with numerous physical barriers, political restrictions, and a history plagued with inferior status. Fortunately, the world has progressed in its acceptance and is continuing to improve its treatment of individuals with different abilities. Nevertheless, there is still great progress to be made in the movement toward equality and full inclusion. Differently abled women, for example, are continuously faced with the trial of intersectionality, the results of being both female and differently abled, which primarily includes sexual oppression. Thus, individuals with different abilities are encouraged to be more engaged in practice of self advocacy. Families, Friends and allies must also maintain their support of individuals with different abilities, an element that is critical to community's success. Helping professionals, who serve the differently-abled community, are urged to educate themselves on the adversity experienced by the community, to acknowledge how other cultural identities intersect with the differently abled culture, and to employ strengths based theoretical paradigm that will produce the most empowering results for their clients. Helping professionals with different abilities, furthermore, are called upon to lead the identity and civil rights movement of the differently-abled community.
Which of the following is not suggested by the author to the professionals dealing with people with different abilities to educate themselves?
(a) leading civil rights movement of the differently abled community.
(b) Empower the persons with different abilities
(c) Community Services
(d) Understanding the intersection of differently-abled culture with other cultural identities
Ans: C
Sol: The author suggests the following to the professionals dealing with people with different abilities to educate themselves.
- Helping professionals, who serve the differently-abled community, are urged to educate themselves on the adversity experienced by the community, to acknowledge how other cultural identities intersect with the differently-abled culture,
- and to employ a strengths-based theoretical paradigm to produce the most empowering results for their clients.
- Helping professionals with different abilities are called upon to lead the differently-abled community's identity and civil rights movement.
Hence Community Services are not suggested by the author to the professionals dealing with people with different abilities to educate themselves.
Q64: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
Living with a disability, or a different ability is undeniably challenging. Not only are individuals with different abilities challenged to overcome the physical trials associated with their medical conditions, but they must also persevere through the lifelong process of reconciling their personal views of themselves with the negative perceptions and prejudices of society. In addition to combating social stigma, the differently abled community is confronted with numerous physical barriers, political restrictions, and a history plagued with inferior status. Fortunately, the world has progressed in its acceptance and is continuing to improve its treatment of individuals with different abilities. Nevertheless, there is still great progress to be made in the movement toward equality and full inclusion. Differently abled women, for example, are continuously faced with the trial of intersectionality, the results of being both female and differently abled, which primarily includes sexual oppression. Thus, individuals with different abilities are encouraged to be more engaged in practice of self advocacy. Families, Friends and allies must also maintain their support of individuals with different abilities, an element that is critical to community's success. Helping professionals, who serve the differently-abled community, are urged to educate themselves on the adversity experienced by the community, to acknowledge how other cultural identities intersect with the differently abled culture, and to employ strengths based theoretical paradigm that will produce the most empowering results for their clients. Helping professionals with different abilities, furthermore, are called upon to lead the identity and civil rights movement of the differently-abled community.
The author is mentioning about the psychological consequences of which of the following tasks?
(a) Task of dealing with challenges related to one's medical conditions
(b) Task of living with disability throughout one's life
(c) Task of remaining motivated through life long process of dealing with disabilities
(d) Task of reconciling the personal views and social perceptions
Ans: D
Sol:
- Living with a disability or a different ability is undeniably challenging. Not only are individuals with different abilities challenged to overcome the physical trials associated with their medical conditions, but they must also persevere through the lifelong process of reconciling their personal views of themselves with society's negative perceptions and prejudices.
Hence option 4 is the correct answer.
Q65: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
Living with a disability, or a different ability is undeniably challenging. Not only are individuals with different abilities challenged to overcome the physical trials associated with their medical conditions, but they must also persevere through the lifelong process of reconciling their personal views of themselves with the negative perceptions and prejudices of society. In addition to combating social stigma, the differently abled community is confronted with numerous physical barriers, political restrictions, and a history plagued with inferior status. Fortunately, the world has progressed in its acceptance and is continuing to improve its treatment of individuals with different abilities. Nevertheless, there is still great progress to be made in the movement toward equality and full inclusion. Differently abled women, for example, are continuously faced with the trial of intersectionality, the results of being both female and differently abled, which primarily includes sexual oppression. Thus, individuals with different abilities are encouraged to be more engaged in practice of self advocacy. Families, Friends and allies must also maintain their support of individuals with different abilities, an element that is critical to community's success. Helping professionals, who serve the differently-abled community, are urged to educate themselves on the adversity experienced by the community, to acknowledge how other cultural identities intersect with the differently abled culture, and to employ strengths based theoretical paradigm that will produce the most empowering results for their clients. Helping professionals with different abilities, furthermore, are called upon to lead the identity and civil rights movement of the differently-abled community.
Which of the following do NOT convey the true meaning of the word 'undeniable'?
(a) Certain
(b) Evident
(c) Obvious
(d) Refutable
Ans: D
Sol:
- The word "refutable" does not convey the true meaning of the word "undeniable." Something that is undeniable cannot be disputed or denied. Something that is refutable, on the other hand, can be challenged or disproven.
- The other three words, "certain," "evident," and "obvious," all convey the true meaning of the word "undeniable." Something that is certain is known to be true. Something that is evident is clearly visible or apparent. Something that is obvious is easy to understand or perceive.
Q66: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
Living with a disability, or a different ability is undeniably challenging. Not only are individuals with different abilities challenged to overcome the physical trials associated with their medical conditions, but they must also persevere through the lifelong process of reconciling their personal views of themselves with the negative perceptions and prejudices of society. In addition to combating social stigma, the differently abled community is confronted with numerous physical barriers, political restrictions, and a history plagued with inferior status. Fortunately, the world has progressed in its acceptance and is continuing to improve its treatment of individuals with different abilities. Nevertheless, there is still great progress to be made in the movement toward equality and full inclusion. Differently abled women, for example, are continuously faced with the trial of intersectionality, the results of being both female and differently abled, which primarily includes sexual oppression. Thus, individuals with different abilities are encouraged to be more engaged in practice of self advocacy. Families, Friends and allies must also maintain their support of individuals with different abilities, an element that is critical to community's success. Helping professionals, who serve the differently-abled community, are urged to educate themselves on the adversity experienced by the community, to acknowledge how other cultural identities intersect with the differently abled culture, and to employ strengths based theoretical paradigm that will produce the most empowering results for their clients. Helping professionals with different abilities, furthermore, are called upon to lead the identity and civil rights movement of the differently-abled community.
What does being 'persevere' mean in the above passage?
(a) Remaining motivated during difficult situations in life.
(b) Making continuous efforts to achieve something which is difficult
(c) Avoiding the situations that are destructive
(d) Remaining indeterminant during difficult situations in life.
Ans: B
Sol:
- Making continuous efforts to achieve something which is difficult is the correct answer. It is called perseverance. Perseverance is the ability to keep trying even when things are tough. It's a key quality for anyone who wants to achieve their goals.
Q67: 'Empirical' means
(a) Based on Research questions
(b) Based on data
(c) Based on hypothesis
(d) Based on controlling variables
Ans: B
Sol: Empirical:
- Empirical means based on observation or experience rather than theory. It is derived from the Greek word "empirikos", which means "experienced".
- Empirical evidence is data that is collected through observation or experiment. It is used to support or refute hypotheses.
- Empirical evidence is considered to be the most reliable type of evidence because it is based on real-world data.
Here are some examples of empirical evidence:
- The results of a scientific experiment
- The data collected from a survey
- The observations made by a scientist
Empirical evidence is essential for scientific research. It is used to test hypotheses and to develop theories. Without empirical evidence, science would be based on speculation and conjecture.
The following are some of the key features of empirical evidence:
- It is based on observation or experiment.
- It is collected from the real world.
- It is objective and unbiased.
- It can be used to support or refute hypotheses.
Empirical evidence is a valuable tool for scientific research. It is used to test hypotheses, to develop theories, and to make predictions about the world.
Hence 'Empircal' means Based on data.
Q68: Who gave the theory of psychosocial development?
(a) Benjamin Spoch
(b) Erik Erikson
(c) Jean Erikson
(d) Benjamin Bloom
Ans: B
Sol: Erik Erikson:
- Erik Erikson was a German-American developmental psychologist and psychoanalyst well-known for his psychosocial development theory.
- He expanded upon Sigmund Freud's theory of psychosexual development and emphasized the importance of social and cultural factors in human development.
- According to Erikson's theory, individuals go through eight stages of psychosocial development across their lifespan, each characterized by a unique developmental task or crisis. These stages encompass the entire lifespan, from infancy to old age. The stages are as follows:
- Trust vs. Mistrust (Infancy): The first stage occurs in infancy, and the main developmental task is developing a sense of trust in the world and others.
- Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt (Early Childhood): This stage occurs during early childhood, and the central focus is developing a sense of independence and autonomy while exploring the environment.
- Initiative vs Guilt (Preschool Age): The third stage occurs during the preschool years, and the key task is developing a sense of purpose and taking the initiative in one's activities.
- Industry vs Inferiority (School Age): This stage occurs during the school years, and the primary task is to develop a sense of competence and accomplishment in academic, social, and extracurricular activities.
- Identity vs Role Confusion (Adolescence): The fifth stage occurs during adolescence, and the central focus is forming a coherent sense of self-identity and establishing personal values and beliefs.
- Intimacy vs Isolation (Early Adulthood): This stage occurs in early adulthood, and the main developmental task is establishing intimate and meaningful relationships with others.
- Generativity vs Stagnation (Middle Adulthood): The seventh stage occurs in middle adulthood, and the primary task is to contribute to society and the next generation through work, parenting, mentoring, or other forms of productivity.
- Integrity vs Despair (Late Adulthood): The final stage takes place in late adulthood, and the central focus is on reflecting on one's life and accepting the inevitability of death with a sense of integrity and fulfilment.
Erikson's theory highlights individuals' psychosocial conflicts at each stage and suggests that successfully resolving these conflicts leads to healthy development and the acquisition of specific psychological strengths. Conversely, unresolved conflicts can result in maladaptive behaviours or psychological difficulties.
It is worth noting that Erikson's theory incorporates both individual psychological processes and the influence of social interactions and cultural contexts. He believed that social relationships, cultural norms, and historical factors are crucial in shaping human development.
The theory of psychosocial development was proposed by Erik Erikson, making option 2) Erik Erikson the correct answer.
Q69: The establishment of DIETs was the result of recommendation by
(a) University Education Commission, 1948
(b) Education Commission (1964-66)
(c) The National Policy on Education, 1968
(d) National Policy on Education, 1986
Ans: D
Sol:
- The National Policy on Education, 1986 (NPE 86) was a major document outlining India's government's vision for education. The policy emphasized the need to improve the quality of elementary education and called for the establishment of DIETs to provide in-service training to elementary school teachers.
- DIETs are now an integral part of the teacher education system in India. They offer a variety of in-service training programs for elementary school teachers, covering topics such as pedagogy, curriculum development, and assessment. DIETs also conduct research and develop innovative practices in elementary education.
- The establishment of DIETs has significantly impacted the quality of elementary education in India. DIETs have helped to improve the knowledge and skills of elementary school teachers, and they have also helped to develop more effective teaching and learning practices. As a result, DIETs have played a key role in the government's efforts to achieve universal elementary education in India.
Here are some of the specific benefits of DIETs:
- They provide in-service training to elementary school teachers, which helps to improve their knowledge and skills.
- They conduct research and develop innovative practices in elementary education, which helps improve teaching and learning quality.
- They provide academic and resource support to elementary schools, which helps improve the quality of education provided to children in India.
The establishment of DIETs has been a major success story in the government's efforts to improve the quality of elementary education in India. DIETs have played a key role in achieving universal elementary education, and they continue to play an important role in improving the quality of education provided to children in India.
Hence, the establishment of DIETs resulted from a recommendation by the National Policy on Education in 1986.
Q70: In educational management as a system:
(a) processes are unpredictable.
(b) processes are mechanical.
(c) outputs are uniform in nature.
(d) inputs are not same.
Ans: A
Sol:
- In educational management as a system, the processes are unpredictable.
- This is because the inputs into the system are not always the same. The students, teachers, and resources are different, which can lead to different outcomes. The outputs of the system are also not always uniform. Some students will learn more than others, and some teachers will be more effective.
- The unpredictability of the processes in educational management makes it a challenging field. However, it also makes it an exciting field. There is always room for improvement and the potential to make a difference in students' lives.
Here are some of the factors that can make the processes in educational management unpredictable:
- The students: Students come from different backgrounds and have different learning styles.
- The teachers: Teachers have different teaching styles and different levels of experience.
- The resources: Schools have different levels of funding and different access to resources.
- The environment: The school environment can significantly impact student learning.
Hence, In educational management as a system, the processes are unpredictable.
Q71: Inclusive education:
(a) Encourages strict admission procedures
(b) Celebrate diversity in classroom
(c) Includes indoctrination of facts
(d) Includes teachers from marginalized groups
Ans: B
Sol: Inclusive education:
- Inclusive education is a philosophy of education that values and celebrates the diversity of all learners. It is based on the belief that all students, regardless of their background or abilities, can learn and succeed. Inclusive education seeks to create a learning environment where all students feel welcome, respected, and supported.
Here are some of the key features of inclusive education:
- Celebration of diversity: Inclusive education values and celebrates the diversity of all learners. This includes diversity of race, ethnicity, gender, socioeconomic status, ability, and learning style.
- High expectations: Inclusive education holds all students to high expectations. This means that all students are expected to learn and succeed, regardless of their background or abilities.
- Support: Inclusive education provides support to all students who need it. This support can be in the form of specialized instruction, accommodations, or modifications.
- Collaboration: Inclusive education requires collaboration between teachers, administrators, parents, and other stakeholders. This collaboration is essential to creating a learning environment where all students can succeed.
Here are some of the benefits of inclusive education:
- Increased student achievement: Inclusive education has been shown to increase student achievement for all students, including students with disabilities.
- Improved social-emotional development: Inclusive education has been shown to improve social-emotional development for all students. This includes increased self-esteem, empathy, and understanding of others.
- Reduced prejudice and discrimination: Inclusive education can help to reduce prejudice and discrimination against students with disabilities. This is because inclusive education exposes students to diversity and teaches them to value and respect all people.
- Increased community involvement: Inclusive education can increase community involvement in education. This is because inclusive education requires collaboration between the school and the community.
Hence, Inclusive education is a philosophy of education that values and celebrates the diversity of all learners
Q72: Which of the following statements is not correct with reference to Assistive Technologies (AT) in general:
(a) Leads to greater autonomy in all spheres of life.
(b) Aids in sustaining self-motivation.
(c) Promote inclusion at home and community.
(d) Helps in attaining increased dependence.
Ans: D
Sol: Assistive Technologies (AT):
- AT are designed to assist individuals with disabilities or special needs in overcoming limitations and achieving greater independence. These technologies encompass a wide range of devices, equipment, software, and systems that are specifically developed to support individuals in various aspects of their lives.
- 1- Leads to greater autonomy in all spheres of life (Correct): Assistive technologies enable individuals to perform tasks and activities that they may have difficulty with due to their disabilities or limitations. For example, individuals with mobility impairments can use mobility aids such as wheelchairs, walkers, or prosthetic limbs to move around independently. Similarly, individuals with visual impairments can use screen readers or magnification software to access information and engage in educational or professional pursuits. By providing these tools and resources, assistive technologies empower individuals to have greater control over their lives and participate actively in society.
2. Aids in sustaining self-motivation (Correct):
- Assistive technologies not only address physical limitations but also provide support for emotional and cognitive well-being. For instance, individuals with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) can utilize task management apps or reminders to improve their organizational skills and maintain focus. Similarly, individuals with learning disabilities can benefit from assistive technologies such as text-to-speech software or graphic organizers to enhance their learning experience. By facilitating effective learning strategies and promoting self-motivation, assistive technologies contribute to personal growth and success.
3. Promote inclusion at home and community (Correct):
- Assistive technologies play a crucial role in promoting inclusion by breaking down barriers and enabling individuals to actively participate in various environments. For example, communication devices and augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) tools help individuals with speech impairments to express themselves and engage in conversations. Moreover, assistive technologies facilitate accessibility in public spaces, transportation, and digital platforms, ensuring equal participation and inclusion for all individuals. By creating inclusive environments, assistive technologies foster social integration and empower individuals to live fulfilling lives.
4. Helps in attaining increased dependence (incorrect):
- It is important to note that the primary objective of assistive technologies is not to foster dependence but rather to enhance independence and self-reliance. These technologies are developed to provide individuals with the necessary support and tools to overcome limitations and actively engage in activities that they would otherwise find challenging. By promoting independence, assistive technologies empower individuals to lead more fulfilling and meaningful lives while reducing barriers and promoting equal opportunities.
Hence Statement 4 is not correct with reference to Assistive Technologies (AT) in general.
Q73: If a researcher computes ten (10) t-tests for comparing five means at the 0.05 significance level, then:
A. The overall Type II Error rate for the experiment will increase.
B. The probability is 0.50 to reject at least one null hypothesis, when it is true.
C. There will be an unacceptable high error rate for the total experiment.
D. The overall Type I Error rate for the experiment will increase.
E. The rate of Type I and II errors for the experiment will remain equal.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, D and E only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: C
Sol: When a researcher computes multiple t-tests for comparing multiple means, the following statements hold true:
B. The probability is 0.50 to reject at least one null hypothesis when it is true:
- This statement is known as the concept of familywise error rate. As the number of statistical tests increases, the likelihood of rejecting at least one null hypothesis (Type I Error) when it is true also increases. Therefore, there is a higher probability of making a Type I Error in this scenario.
C. There will be an unacceptable high error rate for the total experiment:
- As mentioned in statement B, conducting multiple tests increases the likelihood of making Type I Errors. This can lead to an overall high error rate for the entire experiment. However, the acceptability of this high error rate depends on the specific context and significance level chosen.
- D. The overall Type I Error rate for the experiment will increase: This statement is consistent with the concept mentioned in statement B. Conducting multiple tests increases the chances of making Type I Errors, which refers to rejecting a null hypothesis when it is actually true.
When a researcher computes multiple t-tests for comparing multiple means, the following statements hold false.
A. The overall Type II Error rate for the experiment will increase:
- This statement is not necessarily true. Conducting multiple tests does not directly impact the Type II Error rate, which refers to failing to reject a null hypothesis when it is actually false.
E. The rate of Type I and II errors for the experiment will remain equal:
- This statement is not correct. Conducting multiple tests primarily affects the Type I Error rate and does not directly impact the Type II Error rate.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 3) B, C, and D only.
Q74: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Ans: B
Sol: 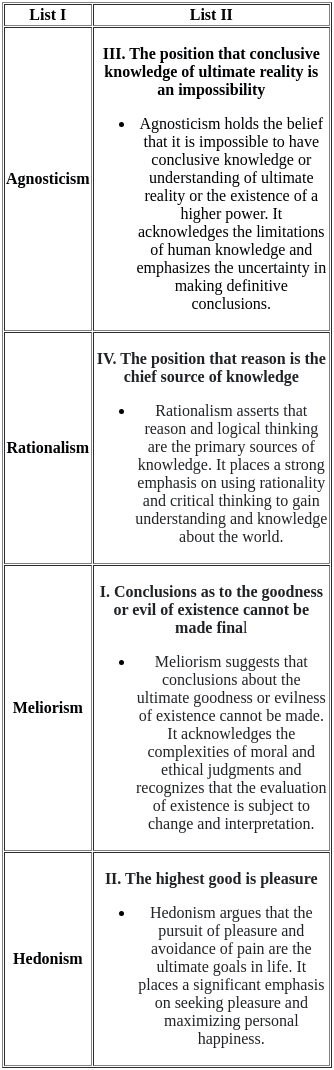
Therefore, the correct match between List I and List II is:
A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV.
Q75: Match List I with List II
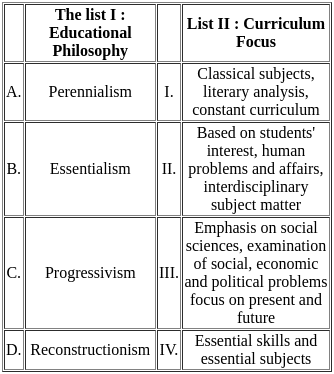
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D- II
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(d) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
Ans: C
Sol: An of the match between List I and List II:
- Perennialism is an educational philosophy that emphasizes teaching traditional subjects like math, science, and literature. Perennialists believe that these subjects are essential for developing a well-rounded education.
- Essentialism is an educational philosophy emphasising the importance of teaching essential skills and knowledge. Essentialists believe that students need to learn these skills and knowledge to succeed in life.
- Progressivism is an educational philosophy emphasising the importance of teaching students based on their interests and needs. Progressives believe that students learn best when actively engaged in the learning process.
- Reconstructionism is an educational philosophy emphasising the importance of using education to solve social problems. Reconstructionists believe that education can create a more just and equitable society.
It is important to note that these are just four educational philosophies. There is no one "right" educational philosophy, and the best approach for a particular student or group of students may vary depending on their individual needs and interests.
Hence the correct matching is A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III.
Q76: The Teacher Education Institutes are Accredited by:
(a) QCl
(b) NCTE
(c) NCERT
(d) NAAC
Ans: D
Sol: National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC):
- The National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) is an autonomous body that was established in 1994 by the University Grants Commission (UGC) and the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) to assess and accredit institutions of higher education in India. NAAC's accreditation process is based on criteria that assess the quality of teaching, learning, research, and other aspects of an institution's functioning.
- NAAC accredits Teacher Education Institutes (TEIs) to ensure they meet the required quality standards. The accreditation process for this is similar to the process for other higher education institutions. NAAC sends a team of experts to assess the TEI and the TEI is then awarded a grade based on the team's findings.
- The accreditation of TEIs is important because it helps ensure that the teachers trained in these institutes are of high quality. This is important because teachers play a vital role in children's education. High-quality teachers can help ensure that children receive a quality education, leading to better outcomes for them in their personal and professional lives.
Here are some of the benefits of NAAC accreditation for TEIs:
- It helps to ensure that the TEI meets the required standards of quality.
- It provides the TEI with feedback on its strengths and weaknesses.
- It helps the TEI to improve its performance.
- It enhances the reputation of TEI.
- It makes the TEI more attractive to students and employers.
NAAC accreditation is a valuable tool for TEIs. It helps to ensure that the TEI is providing quality education to its students and helps the TEI improve its performance. NAAC accreditation is also a valuable asset for students and employers. It gives students confidence that they are receiving a quality education, and it gives employers confidence that the graduates of the TEI are qualified for the jobs they seek.
Hence, the Teacher Education Institutes are accreditated by NAAC.
Q77: Technical-Scientific curriculum developers focused upon ______ aspect.
(a) Subjective
(b) Personal
(c) Universal
(d) Aesthetic
Ans: C
Sol: Technical-scientific curriculum:
- Technical-scientific curriculum developers focused on universal aspects. They believe that there is a body of knowledge that is essential for all students to learn, regardless of their interests or backgrounds. This body of knowledge includes the basic skills and concepts in mathematics, science, and language arts. Technical-scientific curriculum developers also believe students should be taught to think critically and solve problems. They believe these skills are essential for students to succeed in the workforce and in life.
- Technical-scientific curriculum developers typically use a top-down approach to curriculum design. They begin by identifying the knowledge and skills that students need to learn. They then develop a curriculum to help students acquire this knowledge and skills. Technical-scientific curriculum developers often use textbooks and other materials designed to help students learn the content in a linear, step-by-step manner.
- Technical-scientific curriculum developers believe that their approach to curriculum design is the most effective way to ensure that students learn the necessary knowledge and skills. They argue that their approach is objective, unbiased, and based on the latest education research. However, critics of technical-scientific curriculum development argue that it is too rigid and does not allow for enough creativity or innovation. They also argue that it does not consider students' individual needs.
Here are some of the key features of technical-scientific curriculum development:
- Emphasis on content: Technical-scientific curriculum developers focus on the content students need to learn.
- Top-down approach: Technical-scientific curriculum developers develop a curriculum from the top down, starting with the knowledge and skills students need to learn.
- Use of textbooks and other materials: Technical-scientific curriculum developers often use textbooks and other materials designed to help students learn the content in a linear, step-by-step manner.
- Focus on objectivity and unbiasedness: Technical-scientific curriculum developers believe their approach is objective and unbiased.
- Based on research: Technical-scientific curriculum developers believe their approach is based on the latest education research.
Technical-scientific curriculum development is a widely used approach to curriculum design. It is used in many schools around the world. However, it is not without its critics. Critics argue that it is too rigid and does not allow for enough creativity or innovation. They also argue that it does not consider students' individual needs.
Therefore, Technical-Scientific curriculum developers focused upon the Universal aspect.
Q78: Yashpal Committee Report (2009) advocated for:
A. Proliferation of deemed universities
B. Promoting privatisation of Higher Education
C. Curriculum Reforms
D. Full-fledged University status to IIT and IIM
E. Establishing National Commission for Higher Education
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) D, E and A only
Ans: C
Sol: The Yashpal Committee Report (2009) advocated for the following:
C. Curriculum Reforms: The report emphasized the need for comprehensive curriculum reforms in higher education. It highlighted the importance of updating and aligning the curriculum with changing societal needs, incorporating interdisciplinary approaches, and promoting critical thinking and creativity among students.
D. Full-fledged University status to IIT and IIM: The report recommended granting full-fledged university status to premier institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT) and the Indian Institutes of Management (IIM). This was aimed at providing them with more autonomy and flexibility in academic and administrative matters.
E. Establishing National Commission for Higher Education: The Yashpal Committee recommended the establishment of a National Commission for Higher Education to oversee and regulate the higher education sector in India. The proposed commission would replace the existing regulatory bodies like the University Grants Commission (UGC) and All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), and would be responsible for maintaining quality standards and promoting excellence in higher education.
Option A, Proliferation of deemed universities, and Option B, Promoting privatisation of Higher Education, are not mentioned in the Yashpal Committee Report (2009).
Therefore, the correct answer is 3) C, D and E only.
Q79: Select the steps used in curriculum designs-
A. Selection of learning experiences
B. Detailing the budget
C. Formulation of objectives
D. Diagnosis of needs
E. Selection of appropriate human resources
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) A, B and C only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: C
Sol: The steps used in curriculum design are:
- Diagnosis of needs: This step involves identifying the needs of the learners and society. The needs of the learners can be identified by conducting surveys, interviews, and focus groups. The needs of society can be identified by analyzing economic, political, and social trends.
- Formulation of objectives: This step involves defining the goals of the curriculum. The objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Selection of learning experiences: This step involves selecting the content and activities that will be used to achieve the objectives. The content should be relevant to the needs of the learners and the society. The activities should be engaging and effective in helping the learners achieve the objectives.
- Organization of learning experiences: This step involves logically sequencing the content and activities.
- Evaluation of the curriculum: This step involves assessing the effectiveness of the curriculum in meeting the needs of the learners and society.
The steps that are not used in curriculum design are:
- Detailing the budget: This is not a step in curriculum design because the school or district usually determines the budget.
- Selection of appropriate human resources: This is not a step in curriculum design because the school or district usually selects human resources.
A, C and D only is the correct answer.
Q80: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it
Mahatma Gandhi said: Education is "the basic tool for development of consciousness and reconstruction of society". The Universal Declaration of Human rights, 1948 (UDHR) states: "Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory.
"This was said prior to the labeling of the current 21st century as the century of knowledge; and before the level of education in the community was recognised as an index of human development. The Constitution of India, recognizing this aspect enacted initially the Directive Principles of State Policy in Article 45 to achieve the goal of free and compulsory education upto the age of fourteen within ten years, but the task remaining unfulfilled for over half a century, the fundamental right in Article 21A has been inserted as amendment to reinforce its importance along with corresponding amendments in Article 45 and 51 A.
Teacher is the medium to achieve this goal. Hence, the quality of teacher education to provide quality teachers is an important component for the success of this programme. The report of the Education Commission states:" The destiny of India is now being shaped in her classrooms. This, we believe is no more a rhetoric." The key player in the process is the teacher. Mahatma Gandhi said, "I have always felt that the true text book for the pupil is the teacher". A true teacher is a role model who triggers the thought process of his students to realize their true potential. He teaches by 'practice' and not merely by "precept".
In which of the following, the demand for free and compulsory education was made at the first?
(a) The Right to Education Act
(b) Report of the Education Commission
(c) The Directive Principles of the State Policy
(d) The Universal Declaration of Human Rights
Ans: D
Sol:
- According to the passage, the demand for free and compulsory education was made in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR).
- The passage mentions that the UDHR, adopted in 1948, states that "Everyone has the right to education" and emphasizes that education should be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Therefore, the demand for free and compulsory education was indeed made in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Q81: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it
Mahatma Gandhi said: Education is "the basic tool for development of consciousness and reconstruction of society". The Universal Declaration of Human rights, 1948 (UDHR) states: "Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory.
"This was said prior to the labeling of the current 21st century as the century of knowledge; and before the level of education in the community was recognised as an index of human development. The Constitution of India, recognizing this aspect enacted initially the Directive Principles of State Policy in Article 45 to achieve the goal of free and compulsory education upto the age of fourteen within ten years, but the task remaining unfulfilled for over half a century, the fundamental right in Article 21A has been inserted as amendment to reinforce its importance along with corresponding amendments in Article 45 and 51 A.
Teacher is the medium to achieve this goal. Hence, the quality of teacher education to provide quality teachers is an important component for the success of this programme. The report of the Education Commission states:" The destiny of India is now being shaped in her classrooms. This, we believe is no more a rhetoric." The key player in the process is the teacher. Mahatma Gandhi said, "I have always felt that the true text book for the pupil is the teacher". A true teacher is a role model who triggers the thought process of his students to realize their true potential. He teaches by 'practice' and not merely by "precept".
Which among the following statement is not true about the teacher, according to the passage?
(a) Teacher educator is at the centre stage of teaching-learning process.
(b) Teacher is the best source of knowledge for students
(c) Teacher triggers the thought process of students
(d) Practice of teaching is more important than directions.
Ans: A
Sol:
- The statement "Teacher educator is at the centre stage of the teaching-learning process" is true according to the passage.
- The passage emphasizes the role of the teacher rather than the teacher educator. It highlights the importance of the teacher as a role model, the teacher's role in triggering the thought process of students, and the significance of teaching by practice over mere precept.
Q82: Read the passage and answer the questions based on it
Mahatma Gandhi said: Education is "the basic tool for development of consciousness and reconstruction of society". The Universal Declaration of Human rights, 1948 (UDHR) states: "Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory.
"This was said prior to the labeling of the current 21st century as the century of knowledge; and before the level of education in the community was recognised as an index of human development. The Constitution of India, recognizing this aspect enacted initially the Directive Principles of State Policy in Article 45 to achieve the goal of free and compulsory education upto the age of fourteen within ten years, but the task remaining unfulfilled for over half a century, the fundamental right in Article 21A has been inserted as amendment to reinforce its importance along with corresponding amendments in Article 45 and 51 A.
Teacher is the medium to achieve this goal. Hence, the quality of teacher education to provide quality teachers is an important component for the success of this programme. The report of the Education Commission states:" The destiny of India is now being shaped in her classrooms. This, we believe is no more a rhetoric." The key player in the process is the teacher. Mahatma Gandhi said, "I have always felt that the true text book for the pupil is the teacher". A true teacher is a role model who triggers the thought process of his students to realize their true potential. He teaches by 'practice' and not merely by "precept".
The commission referred as "Education Commission" was chaired by:
(a) Sam Pitroda
(b) D. S. Kothari
(c) Lakshman Swami Mudaliar
(d) Dr. Sarvpalli Radha Krishnan
Ans: B
Sol: Key Points
- The Kothari Commission, officially known as the Education Commission (1964-66), was chaired by D. S. Kothari.
- The commission was established in India to assess and recommend improvements in the education system.
Q83: Which among the following responsibilities of a teacher is related to behaviour management of children with disabilities?
(a) Establishing weekly time-table
(b) Evaluate student's progress, either individually or as a group
(c) Plan positive shaping Interventions and supports for whole class and for individual students
(d) Reviews the IEP regularly with the support staff
Ans: C
Sol: The responsibility of planning positive shaping interventions and supports for the whole class and for individual students is related to behavior management of children with disabilities.
- Children with disabilities may exhibit challenging behaviors that require special attention and intervention. As a teacher, it is essential to create a positive and supportive learning environment that addresses the specific needs of these children. This responsibility involves:
- Developing strategies and interventions: The teacher should plan and implement effective strategies to manage and shape positive behaviors in the classroom. This may include implementing behavior management techniques, using visual supports, providing clear expectations, and establishing routines that support the learning and behavioral needs of children with disabilities.
- Individualized support: Each child with a disability may have unique behavioral challenges. The teacher should collaborate with special education professionals, parents, and support staff to develop individualized behavior support plans. These plans outline specific strategies, accommodations, and interventions tailored to address the behavioral needs of individual students.
- Whole-class strategies: In addition to individualized support, the teacher should plan and implement strategies that promote positive behavior for the entire class. This may involve teaching social skills, implementing proactive behavior management techniques, and fostering a supportive and inclusive classroom environment that encourages positive interactions and cooperation among all students.
- By actively planning positive shaping interventions and supports, teachers can create an inclusive and conducive learning environment for children with disabilities, helping them to effectively manage their behaviors and actively participate in the learning process.
Hence option 3 is the correct answer.
Q84: Which of the following are related to the scientific management approach?
A. E. Mayo
B. F. W. Taylor
C. D. E. Griffiths
D. L. D. Brandeis
E. C. L. Bernard
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) D and E only
(c) B and C only
(d) B and D only
Ans: D
Sol: Frederick Winslow Taylor and Louis Dembitz Brandeis are both associated with the scientific management approach.
- Frederick Winslow Taylor (F. W. Taylor) is considered the father of scientific management. He was an American mechanical engineer who sought to improve industrial efficiency by applying scientific methods to the study of work. Taylor's principles of scientific management included time and motion studies, standardization of tools and equipment, and the use of piece rates to reward workers for increased productivity.
- Louis Dembitz Brandeis (L. D. Brandeis) was an American lawyer and associate justice of the United States Supreme Court from 1916 to 1939. He pioneered the Brandeis Brief, which emphasized the importance of facts and economic data in legal arguments. Brandeis was also a proponent of scientific management, arguing that it could improve public and private efficiency.
Therefore the correct answer is B and D only.
Other Related Points
- Elton Mayo, Daniel Edward Griffiths, and Chester Irving Barnard are all associated with the human relations approach to management.
- This approach emphasizes the importance of human factors in the workplace, such as motivation, morale, and group dynamics.
Q85: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - IV, B - II, C - I, D - III
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
Ans: C
Sol: 
Therefore, the correct match is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Q86: Which of the following is NOT a source for curriculum design?
(a) Science as a source
(b) Economy as a source
(c) Society as a source
(d) Knowledge as a source
Ans: B
Sol: Curriculum design: Curriculum design is developing a plan for what students will learn. It is a complex process that involves many different factors, including the needs of the students, the demands of society, the latest scientific knowledge, and the most important aspects of human knowledge.
Curriculum designers typically follow a process that includes the following steps:
- Identify the needs of the students. What do students need to know and be able to do to succeed in school, the workforce, and life?
- Identify the demands of society. What knowledge and skills are essential for students to participate in and contribute to society?
- Identify the latest scientific knowledge. What do we know about how students learn, and what are the most effective ways to teach them?
- Identify the most important aspects of human knowledge. What knowledge and skills are essential for students to have a broad and deep understanding of the world?
- Create a curriculum that meets the needs of the students, the demands of society, the latest scientific knowledge, and the most important aspects of human knowledge.
Sources of Curriculum Design:
- Science provides a foundation for curriculum design by providing knowledge about the natural world. This knowledge can be used to teach students about the physical world, the biological world, and the human body.
- Society provides a foundation for curriculum design by providing knowledge about the social world. This knowledge can be used to teach students about history, government, economics, and culture.
- Knowledge is a source for curriculum design because students need a broad and deep understanding of the world. This knowledge can be used to teach students about various subjects, including science, math, history, language arts, and the arts.
Curriculum designers typically draw on all of these sources when designing a curriculum. They consider the students' needs, society's demands, the latest scientific knowledge, and the most important aspects of human knowledge. They then use this information to create a curriculum to help students learn and grow.
Hence, the Economy is not a source for curriculum design.
Q87: When 'between-groups variance' is substantially greater than the 'within-groups variance', the difference between the means may be ascribed only to:
(a) Sampling error
(b) Measurement error
(c) Constant error
(d) Chance error
Ans: A
Sol: Sampling error:
- Sampling error is the variation in measurements because the sample does not represent the population perfectly. It is also known as chance error or random error. Sampling error is unavoidable and can be reduced by increasing the sample size.
- When the between-groups variance is substantially greater than the within-groups variance, it suggests that the difference between the means is due to sampling error.
- This means that the difference is not real and that it is because the sample is not a perfect representation of the population.
- For example, if you compare the heights of men and women, you might find that the between-groups variance is substantially greater than the within-groups variance. This suggests that the difference in height between men and women is due to sampling error. This means that the difference is not real and that it is because the sample is not a perfect representation of the population.
- It is important to note that sampling error can never be eliminated. However, it can be reduced by increasing the sample size. The larger the sample size, the less likely it is that sampling error will have a significant impact on the results.
When between-groups variance is substantially greater than within-groups variance, the difference between means is likely due to the treatment effect, not sampling error (a), measurement error (b), constant error (c), or chance error (d).
Q88: A teacher is attempting to help students question and challenge domination, the beliefs and practices that dominates them. In this way, teacher is trying to connect knowledge to power and the ability to take constructive action. What is this educational approach called?
(a) Pedagogical analysis
(b) Dialogue method
(c) Critical pedagogy
(d) Pedagogy
Ans: C
Sol: Critical pedagogy:
- Critical pedagogy is a philosophy of education that encourages students to be critical towards their reality – its power structures, contradictions and flaws. It is a way of teaching that helps students to understand the world around them and to challenge the status quo.
- Critical pedagogy is based on the belief that education is a political act. It is an attempt to help students to understand the power structures that shape their lives and to develop the skills to challenge these structures.
- Critical pedagogy is often used in schools to help students to understand issues of race, class, gender, and sexuality. It can also help students understand the impact of globalization and the media on their lives.
- Critical pedagogy is a controversial approach to education. Some people believe it is too political and does not focus enough on academic learning. Others believe it is an essential approach to education that can help students become more critical thinkers and make a positive difference in the world.
Here are some of the key features of critical pedagogy:
- Focus on social justice: Critical pedagogy is based on the belief that education should be used to promote social justice. This means that it should help students to understand the power structures that shape their lives and to develop the skills to challenge these structures.
- Dialogue: Critical pedagogy is based on dialogue. This means teachers and students should be engaged in critical reflection and discussion.
- Action: Critical pedagogy is not just about understanding the world. It is also about taking action to change the world. This means that teachers and students should be engaged in collective action to challenge the status quo.
Critical pedagogy is a powerful approach to education that can help students to become more critical thinkers and to make a positive difference in the world.
A teacher attempts to help students question and challenge domination, the beliefs and practices that dominate them. In this way, the teacher tries to connect knowledge to power and the ability to take constructive action. This educational approach is called Critical pedagogy.
Q89: As per the National Education Policy-2020, Professional Standard Setting Bodies will be the members of the following:
(a) National Accreditation Council
(b) Higher Education Grants Council
(c) National Higher Education Regulatory Council
(d) General Education Council
Ans: D
Sol: General Education Council (GEC):
- The General Education Council (GEC) is a new body that has been created under the National Education Policy 2020.
- The GEC will be responsible for setting professional standards for teachers and other education professionals.
- The GEC will be composed of representatives from the National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE), the University Grants Commission (UGC), the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), and other relevant bodies.
- The GEC will be responsible for developing a set of national professional standards for teachers and other education professionals. These standards will be based on the following principles:
- Competency: The standards will be based on the competencies that are required for effective teaching and learning.
- Relevance: The standards will be relevant to the needs of the 21st century economy and society.
- Aspirational: The standards will be aspirational and will challenge teachers and other education professionals to continuously improve their practice.
- The GEC will also be responsible for monitoring and evaluating the implementation of the national professional standards. The GEC will also be responsible for providing support to teachers and other education professionals in meeting the standards.
- The establishment of the GEC is a significant step in the reform of the education system in India. The GEC will play a vital role in ensuring that teachers and other education professionals are equipped with the skills and knowledge that they need to educate the next generation of Indians.
Here are some of the benefits of having a Professional Standard Setting Body (PSSB):
- Improved quality of education: PSSBs can help to improve the quality of education by ensuring that teachers and other education professionals meet high standards of professional competence.
- Increased accountability: PSSBs can help to increase accountability by ensuring that teachers and other education professionals are held accountable for meeting the standards.
- Enhanced professional development: PSSBs can help to enhance professional development by providing teachers and other education professionals with opportunities to learn and grow.
- Improved career prospects: PSSBs can help to improve career prospects by providing teachers and other education professionals with opportunities to advance their careers.
Hence, as per the National Education Policy-2020, Professional Standard Setting Bodies will be the members General Education Council.
Q90: Which of the following purposes have been served by family as a social institution?
A. It socializes children.
B. It provides practical and emotional support for its members.
C. It establishes a goal of social equality.
D. It regulates sexual reproduction.
E. It provides its members with a social identity.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D and E only
(b) A, B, D and E only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: B
Sol: Family:
- The family is a social institution that serves a number of purposes. These purposes are essential to the functioning of society and the well-being of individuals. These purposes include:
- Socialization: The family is the primary agent of socialization for children. This means that the family is responsible for teaching children the norms, values, and beliefs of their society. This is done through both direct instruction and modeling. For example, parents may teach their children about the importance of honesty and respect, and they may also model these values in their own behavior.
- Support: The family provides practical and emotional support for its members. This support can take many forms, such as financial assistance, childcare, and emotional support. For example, parents may provide their children with financial support for their education, and they may also provide childcare when their children are young. Additionally, parents may provide emotional support to their children by listening to them and offering advice.
- Regulation of sexual reproduction: The family regulates sexual reproduction by providing a socially acceptable context for sexual activity and procreation. This means that the family provides a setting in which sexual activity is considered to be acceptable and in which children are born and raised. For example, in many societies, sexual activity outside of marriage is not considered to be acceptable. Additionally, in many societies, children are expected to be raised by their parents.
- Social identity: The family provides its members with a social identity. This identity is based on the family's position in society and the individual's role within the family. For example, a child may be identified as a member of a particular family, and they may also be identified as a son or daughter, brother or sister, etc.
Hence A, B, D and E only is the correct answer.
Q91: Why is the professional development of teachers required?
A. To expand the knowledge domain of subjects
B. To get entry in teaching profession
C. Enactment of policies and schemes
D. Due to changing pedagogy
E. To meet personal financial requirement
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, D and E only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: D
Sol: Professional development of teachers:
- Professional development of teachers refers to the ongoing process of improving and enhancing the knowledge, skills, attitudes, and competencies of educators.
- It is a systematic approach to support teachers in their continuous growth and development throughout their careers. Professional development aims to improve teaching practices, enhance student learning outcomes, and keep educators updated with current research, innovative methodologies, and changes in education policies.
Let's go through each option:
A. To expand the knowledge domain of subjects: This is one of the reasons for the professional development of teachers. Ongoing professional development helps teachers expand their knowledge and understanding of the subjects they teach. It enables them to stay updated with the latest research, developments, and advancements in their respective fields.
B. To get entry into the teaching profession: This is not the primary reason for professional development. Professional development is typically undertaken after entering the teaching profession to enhance teaching skills and improve instructional practices.
C. Enactment of policies and schemes: Professional development of teachers is required to enable them to effectively implement and incorporate policies and schemes introduced by educational authorities and institutions. It helps teachers understand the objectives, guidelines, and requirements of these policies and schemes, ensuring their effective enactment.
D. Due to changing pedagogy: Professional development is necessary because of the changing nature of pedagogy. Educational approaches and instructional methods continually evolve with research and best practices. Teachers need to update their knowledge and skills to adapt to changing pedagogical strategies, incorporate innovative teaching methods, and cater to the diverse learning needs of students.
E. To meet personal financial requirements: This is not a direct reason for professional development. While professional development may contribute to career growth and potential salary increments, its primary purpose is to enhance teaching effectiveness and student learning outcomes.
Based on the options given, the correct answer is 4) A, C, and D only as professional development of teachers is required to expand subject knowledge, effectively implement policies and schemes, and adapt to changing pedagogy.
Q92: Which of the following are not considered as a content for Instructional Technology?
A. Criterion tests
B. Task analysis
C. Modification of behaviour
D. Controlling of teaching
E. Planning of teaching
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: B
Sol: Instructional Technology:
- Instructional Technology refers to the systematic application of technology and related techniques to facilitate and enhance teaching, learning, and the overall educational process. It involves the design, development, implementation, and evaluation of instructional materials, tools, and strategies to support effective and efficient learning experiences.
- Instructional Technology integrates various educational theories, instructional design principles, and technological advancements to create engaging and interactive learning environments. It aims to improve learning outcomes, increase learner engagement, and promote active participation and collaboration among learners.
Among the given options, the items that are considered as content for Instructional Technology are:
A. Criterion tests:
- Criterion tests, which assess learners' knowledge or skills against specific criteria, can be considered as content for Instructional Technology. They can be used in conjunction with Instructional Technology to evaluate learning outcomes and inform instructional decisions.
B. Task analysis:
- Task analysis, which involves breaking down complex tasks into smaller components, is also considered as content for Instructional Technology. It helps in designing effective instructional materials and activities by understanding the cognitive processes and steps required to accomplish a particular task.
Among the given options, the items that are not considered as content for Instructional Technology are:
C. Modification of behavior:
- While modification of behavior is an important aspect of instructional design and educational psychology, it is not specifically considered as content for Instructional Technology. It is more related to the psychological and behavioral aspects of learning and teaching.
D. Controlling of teaching:
- Controlling of teaching refers to the process of managing and regulating instructional activities. While it is an important aspect of instructional practice, it is not considered as content for Instructional Technology. Instructional Technology primarily focuses on the integration and use of technological tools, resources, and methods to enhance teaching and learning.
E. Planning of teaching:
- Planning of teaching is an essential component of instructional design, but it is not specifically considered as content for Instructional Technology. Instructional Technology encompasses the selection, development, and use of various technologies and media to support teaching and learning.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 2) C, D, and E only.
Q93: Which among the following are not open educational resource repositories?
A. NROER
B. e-gyankosh
C. National Digital Library
D. OASIS
E. Gyandarshan
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and D only
(b) B, C and E only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: B
Sol: Open Educational Resource (OER):
- Open Educational Resource (OER) repositories are platforms or websites that host a wide range of educational materials that are freely available for use, reuse, adaptation, and sharing. These repositories provide educators, students, and self-learners with access to a wealth of educational resources that can support teaching, learning, and research activities. Some popular OER repositories include:
- A. NROER (National Repository of Open Educational Resources): NROER is an initiative by the Indian government to create a digital repository of open educational resources. It aims to provide access to a wide range of educational materials, including textbooks, lesson plans, multimedia content, audio resources, and more. NROER focuses on providing resources specifically designed for the Indian context, catering to various educational levels and subjects.
D. OASIS (Openly Available Sources Integrated Search):
- OASIS is a search engine for discovering open educational resources. It indexes a vast collection of openly licensed educational materials from various sources, including OER repositories, universities, colleges, and digital libraries. OASIS provides a centralized platform for finding and accessing freely available resources, including textbooks, course materials, videos, and more.
Therefore, both NROER and OASIS are open educational resource repositories, and they do not belong to the category of options that are not open educational resource repositories.
Among the options provided, the repositories that are not open educational resource (OER) repositories are:
B. e-gyankosh:
- e-gyankosh is not an open educational resource repository. It is a digital repository maintained by the Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU) in India that primarily stores course materials and resources for IGNOU students. However, these materials are not openly accessible to the public as OERs are.
C. National Digital Library:
- The National Digital Library (NDL) is not an open educational resource repository. It is a digital platform that provides access to a vast collection of educational resources, including textbooks, journals, articles, videos, and more, covering various subjects and disciplines.
E. Gyandarshan:
- Gyandarshan is not an open educational resource repository. It is a television channel in India that broadcasts educational programs. While it provides educational content, it is not a digital repository where resources can be freely accessed and shared as OERs.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 2) B, C, and E only
Q94: The Kothari commission recommended:
A. Part-time and correspondence courses should be discouraged at university stage
B. Science education and research should receive high priority
C. Establishment of school complexes
D. Secondary education should be largely vocationalised
E. In non Hindi speaking states, use of Hindi should be discouraged.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and Conly
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and A only
(d) A, D and E only
Ans: B
Sol: Kothari Commission:
- The Kothari Commission was a commission set up by the Government of India in 1964 to review the state of education in India and to make recommendations for its improvement. The commission was chaired by Dr. Daulat Singh Kothari, who was then the chairman of the University Grants Commission. The commission submitted its report in 1966.
The Kothari Commission recommended the following:
- B. Science education and research should receive high priority: The commission emphasized the importance of prioritizing science education and research to foster scientific and technological advancement in the country.
- C. Establishment of school complexes: The commission recommended the establishment of school complexes to promote resource sharing, effective utilization of facilities, and collaboration among schools.
- D. Secondary education should be largely vocationalized: The commission suggested integrating vocational education into secondary education to provide students with practical skills and enhance their employability.
Option A, Part-time and correspondence courses should be discouraged at the university stage, and Option E, In non-Hindi speaking states, use of Hindi should be discouraged, are not mentioned in the recommendations of the Kothari Commission.
Therefore, the correct answer is 2) B, C and D only.
Q95: What is NOT Counselling?
A. Giving information
B. Giving suggestions
C. Influencing client's values, attitudes, beliefs
D. Bringing voluntary change
E. Giving warmth to client
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) A, B and C only
(c) B, D and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: B
Sol: Counselling:
- Counselling is a process of helping people to understand and resolve their problems. It is a collaborative process in which the counsellor and the client work together to identify and address the client's concerns. The goal of counselling is to help clients make positive life changes.
- Counselling is not about giving information or suggestions or influencing the client's values, attitudes, or beliefs. It is about helping clients explore their thoughts and feelings and find solutions to their problems.
- Counselling can be a very effective way to help people to deal with a wide range of problems, including stress, anxiety, depression, relationship problems, and addiction. Counselling may be a good option if you are struggling with a problem.
Here are some of the things that counselling is not:
- Giving Information: Counseling is not about telling the client what to do. The counsellor's role is to help clients explore their thoughts and feelings and find solutions to their problems.
- Giving suggestions: Counseling is not about telling the client what they should do. The counsellor's role is to help clients explore their thoughts and feelings and find solutions to their problems.
- Influencing the client's values, attitudes, or beliefs: Counseling is not about changing the client's values, attitudes, or beliefs. The counsellor's role is to help the client to explore their thoughts and feelings and to find their own solutions to their problems.
If you are considering counselling, it is important to find a counsellor who is a good fit for you. You should feel comfortable with the counsellor, and you should feel like you can trust them. The counsellor should be someone you feel comfortable talking to about your problems.
Therefore A, B and C only is the correct answer.
Q96: The National Policy on Education (NPE-1986) recommended the launch of centrally sponsored schemes of teacher education. Which of the following institutes are the outcome of this scheme?
A. DIETs
B. RIEs
C. CTEs
D. IASES
E. TLCs
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) A, C and D only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: B
Sol: The National Policy on Education (NPE-1986) recommended the launch of centrally sponsored schemes of teacher education, which resulted in the establishment of various institutes. The correct outcome of this scheme is as follows:
A. DIETs (District Institutes of Education and Training):
- DIETs were established as a result of the centrally sponsored scheme of teacher education. They serve as district-level institutions responsible for providing pre-service and in-service training to elementary school teachers. DIETs focus on improving the quality of education at the primary and upper primary levels.
C. CTEs (Colleges of Teacher Education):
- CTEs are the correct outcome of the centrally sponsored scheme of teacher education. They were established to provide pre-service and in-service training to secondary school teachers. CTEs focus on enhancing the pedagogical skills and subject knowledge of teachers at the secondary level.
D. IASEs (Institutes of Advanced Studies in Education):
- IASEs are also the correct outcome of the centrally sponsored scheme of teacher education. They were established to provide advanced training and research opportunities in education. IASEs offer specialized programs for teacher educators, curriculum development, educational administration, and research in education.
Other Related Points B. RIEs (Regional Institutes of Education):
- RIEs are not directly linked to the centrally sponsored scheme of teacher education mentioned in the NPE-1986. However, RIEs are autonomous institutions established by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) to cater to the educational needs of different regions in India. They offer teacher education programs, research facilities, and curriculum development initiatives.
E. TLCs (Technology Learning Centers):
- TLCs are not directly linked to the centrally sponsored scheme of teacher education mentioned in the NPE-1986. They might refer to technology centers or initiatives focused on integrating technology into education, but they are not specifically mentioned in relation to this particular scheme.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 2) A, C, and D only.
Q97: The vision of National Knowledge Commission (NKC) was to-
(a) examine the existing system of secondary education in the country.
(b) develop a common school system.
(c) develop a sense of self reliance and dignity of the individual.
(d) enable the development of a vibrant knowledge based society.
Ans: D
Sol: The vision of the National Knowledge Commission (NKC) was to enable the development of a vibrant knowledge-based society. This vision was based on the belief that knowledge is the key to economic growth, social development, and national security.
National Knowledge Commission:
- NKC was established in 2005 by the Government of India to advise the Prime Minister on how to transform India into a knowledge society.
- The NKC submitted its final report in 2009, which contained several recommendations for improving India's education system, research and development, and information and communication technology infrastructure.
The NKC's vision for a knowledge-based society is based on the following principles:
- Education for all: The NKC believes that all Indians should have access to quality education, regardless of their social or economic background.
- Research and development: The NKC believes that India needs to invest more in research and development to become a global leader in innovation.
- Information and communication technology: The NKC believes that information and communication technology (ICT) can be used to improve education, healthcare, and other services in India.
The NKC's vision for a knowledge-based society is ambitious but achievable. With the right policies and investments, India can become a knowledge superpower in the 21st century.
Following are some of the other key elements of the NKC's vision for a knowledge-based society:
- Empowerment of women and minorities: The NKC believes empowering women and minorities is essential for building a knowledge-based society.
- Sustainable development: The NKC believes India's knowledge economy must be sustainable to benefit future generations.
- Global engagement: The NKC believes India must engage with the global knowledge community to stay competitive.
Q98: Creative pupils are at higher risk of-
A. Exploitation
B. Disengagement
C. Ignorance
D. School dropout
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B and C only
(c) B and D only
(d) C and D only
Ans: C
Sol: Creative pupils:
- Creative pupils refer to students who demonstrate high levels of creativity in their thinking, problem-solving, and expression. These students often possess unique perspectives, original ideas, and a willingness to take risks in their learning process.
- They may exhibit characteristics such as curiosity, imagination, open-mindedness, and the ability to think outside the box. Creative pupils can be found across various age groups and educational settings, from early childhood through higher education.
- They may excel in areas such as arts, sciences, literature, music, or any field that allows for creative thinking and expression. It is important for educators and institutions to recognize and nurture the creativity of these students to support their development and foster their unique talents and abilities.
Creative pupils are at higher risk of-
A. Exploitation: This may be a risk for creative pupils, but it is not directly stated or implied in the question.
B. Disengagement: Creative pupils may be at a higher risk of disengagement. Due to their unique perspectives and needs, they may struggle with traditional educational approaches that do not provide enough opportunities for creativity and self-expression. This can lead to disengagement from the learning process.
C. Ignorance: While creative pupils may face challenges in being understood or recognized, the term "ignorance" is not directly associated with the risks they may face.
D. School dropout: Creative pupils may be at a higher risk of school dropout. If their creative abilities and needs are not recognized or nurtured in the educational system, they may become disengaged, frustrated, or feel undervalued, leading to a higher likelihood of dropping out of school.
Based on the options given, the correct answer is 3) B and D only, as creative pupils are at a higher risk of disengagement and school dropout.
Q99: Which of the following is a principle of experimental research design?
(a) Maximizing treatment variance
(b) Minimizing error variance
(c) Maximizing error and minimizing treatment variance
(d) Maximizing treatment and minimizing error variance
Ans: D
Sol: Experimental Research:
- Experimental research is a scientific approach that involves manipulating variables to observe the effects and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- In experimental research, researchers aim to systematically investigate the impact of an independent variable (treatment) on a dependent variable while controlling for potential sources of error.
- To ensure the validity and reliability of the findings, experimental research design follows certain principles, including maximizing treatment variance and minimizing error variance.
- Maximizing treatment variance: Maximizing treatment variance involves creating distinct and meaningful differences between the treatment groups. By maximizing treatment variance, researchers can effectively examine the effects of different levels or types of treatments on the dependent variable. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of how the independent variable influences the outcome of interest. Maximizing treatment variance helps identify the treatment's specific effects and determine its effectiveness or impact.
- Minimizing error variance: Error variance refers to the variability in the data that is not attributable to the treatment or the independent variable. It includes random errors, measurement errors, or other extraneous factors that may influence the dependent variable. Minimizing error variance is crucial in experimental research to ensure that the observed effects are primarily due to the treatment and not confounded by unrelated factors. By controlling and minimizing error variance, researchers can increase the study's internal validity and enhance the findings' accuracy.
It is important to note that experimental research design is just one approach among many research designs, and its applicability depends on the research question, feasibility, ethical considerations, and other factors.
Therefore, Maximizing treatment and minimizing error variance is a principle of experimental research design.
Q100: The maximum value of reliability coefficient of a certain test is:
(a) with in a range of ±1.00
(b) between 0.00 to 1.00
(c) +1.00
(d) -1.00
Ans: C
Sol: Reliability coefficient:
- The reliability coefficient is a measure of how consistent a test is. It is calculated by dividing the variance of the scores on the test by the total variance of the scores.
- The maximum value of the reliability coefficient is +1.00, which indicates that the test is perfectly reliable. A reliability coefficient of +1.00 means the test measures the same thing every time.
- A reliability coefficient of 0.00 indicates that the test is unreliable. This means that the test does not measure anything consistently.
- A reliability coefficient of 0.50 indicates that the test is moderately reliable. This means the test measures something consistently, but there is some error.
- Reliability coefficients are typically used to assess the quality of tests. A high-reliability coefficient indicates that the test is a good measure of what it is supposed to measure. A low-reliability coefficient indicates that the test is not a good measure of what it is supposed to measure.
Hence, The maximum value of the reliability coefficient of a certain test is +1.00.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Education 14th March 2023 Shift 2 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the significance of the UGC NET exam in the field of education? |  |
| 2. What subjects are covered in Paper 2 of the UGC NET exam related to education? |  |
| 3. How can candidates prepare effectively for the UGC NET Paper 2 in education? |  |
| 4. What is the marking scheme for UGC NET Paper 2? |  |
| 5. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET exam for the education subject? |  |















