UGC NET Paper 2: Education 22nd August 2024 Shift 2 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: The congruence-contingency model of curriculum evaluation was given by:
(a) Tyler
(b) Stake
(c) Scriven
(d) Kirkpatrick
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Stake.
Stake’s Responsive Model/Congruence-Contingency Model
Stake’s model of curriculum evaluation is more than just an evaluation process.
- The responsive model is based explicitly on the assumption that the concerns of the stakeholders, those for whom the evaluation is done, should be paramount in determining the evaluation issues.
- There are six key terms, broken down into two groups of three, that we need to know in order to understand Stake’s model and they are as follows.
Development Stage
- Potential prerequisites: The prerequisite is another way of saying “before” or the state of the context before the intervention of teaching. This includes student’s attitude, motivation, prior academic performance, teacher characteristics, and more
- Potential Curriculum: Potential curriculum is the “dream” curriculum that is developed. It includes everything that the teachers want to do.
- Potential results: Potential results are what the teachers hope to see as a result of the use of the curriculum.
Evaluation Stage
- Prerequisites applied in context: In the evaluation stage, the evaluators determine what prerequisites actually impact the curriculum.
- Evaluation of operational curriculum: The Operational curriculum is what was actually used.
- Actual results: Actual results are the real performance of the students.
Q2: Correct sequence of five quality indicators used in Education given by Ogawa and Collum:
A. Description
B. Monitoring
C. Policy Relevance
D. Evaluation
E. Value Judgement
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, B, E, C
(b) A, B, E, C, D
(c) A, C, B, D, E
(d) A, E, D, B, C
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, D, B, E, C'
Ogawa and Collum's Quality Indicators in Education:
- Description: The initial step involves a clear and comprehensive description of the educational context, processes, and outcomes. This sets the stage for further analysis and understanding.
- Evaluation: The next step is to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of the educational processes. This involves determining the value and quality of the educational interventions.
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring is essential to track the progress and implementation of educational strategies. This helps in identifying any deviations and making necessary adjustments.
- Value Judgement: This step involves making informed judgments about the worth and impact of the educational processes based on collected data and evidence.
- Policy Relevance: Finally, the findings and judgments are used to inform and influence educational policies, ensuring they are relevant and effective in achieving educational goals.
Q3: Schooling reproduces norms and values. Norms and values are usually the phenomenological expressions of the ruling class. This idea can be linked to the following:
(a) Realism
(b) Pragmatism
(c) Marxism
(d) Post Modernism
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Marxism'
Schooling reproduces norms and values:
- According to Marxist theory, the education system serves as a tool for the ruling class to reproduce its ideology and maintain its dominant position in society.
- Schools transmit the norms and values of the ruling class, ensuring the continuation of its control over the working class.
- This process helps in socializing individuals into accepting the existing social order and their roles within it.
Other Related Points
Realism:
- Realism in education focuses on the idea that education should be based on the real world and practical knowledge. It emphasizes empirical evidence and the importance of preparing students for real-life challenges.
- This perspective does not specifically address the reproduction of social norms and values as dictated by a ruling class.
Pragmatism:
- Pragmatism is an educational philosophy that values practical outcomes and experiential learning. It emphasizes the importance of problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
- While pragmatism focuses on the practical application of knowledge, it does not inherently involve the reproduction of ruling class ideology.
Postmodernism:
- Postmodernism in education challenges traditional narratives and structures, promoting multiple perspectives and the deconstruction of established norms.
- It does not align with the idea that schooling reproduces a single, dominant set of norms and values, as it advocates for diverse and often conflicting viewpoints.
Q4: According to Guthrie, which is not an important characteristic of matrix leadership?
(a) Vision
(b) Motivation
(c) Symbolic
(d) Matrix orientation
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Symbolic'.
Overview of Matrix Leadership:
- Matrix leadership is a management system in which people have multiple reporting relationships. It is a common organizational structure where employees report to more than one manager, typically both a functional manager and a product or project manager.
- This structure is designed to improve flexibility, communication, and collaboration across different departments and projects within an organization.
Vision:
- Vision is crucial in matrix leadership as it provides a clear direction and long-term goals for the team, ensuring that all members are aligned with the overall objectives of the organization.
- A strong vision helps in motivating and guiding employees through complex projects and organizational changes.
Motivation:
- Motivation is an essential characteristic as it encourages team members to perform at their best and stay engaged with their work despite the complexities of reporting to multiple managers.
- Leaders in a matrix organization need to inspire and incentivize their teams to achieve high performance and meet project goals.
Matrix Orientation:
- Matrix orientation refers to the ability to effectively navigate and manage the complexities of a matrix organization. It includes skills such as balancing competing priorities and managing multiple reporting lines.
- This characteristic is vital for ensuring smooth operations and collaboration across different functional and project-based teams.
Other Related Points
Symbolic:
- Symbolic leadership, which involves using symbols, rituals, and metaphors to inspire and unite people, is not considered a core characteristic of matrix leadership according to Guthrie.
- While symbolic actions can enhance leadership, they are not fundamental to the operational and structural needs of a matrix organization.
Q5: Match the List-I with List-II
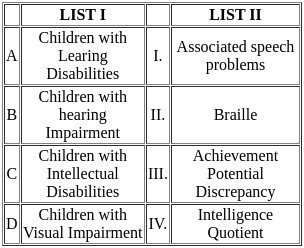
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(c) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II'.
Children with Learning Disabilities (A-III):
- Learning disabilities refer to a variety of disorders that affect the acquisition, retention, understanding, or use of information.
- They are characterized by an achievement potential discrepancy, meaning there is a significant gap between the child’s intellectual capabilities and academic performance.
Children with Hearing Impairment (B-I):
- Hearing impairment refers to partial or complete inability to hear.
- Children with hearing impairment often face associated speech problems due to the difficulty in hearing sounds required to develop speech and language skills.
Children with Intellectual Disabilities (C-IV):
- Intellectual disabilities involve limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior.
- These children are often assessed using measures like the Intelligence Quotient (IQ) to determine the level of intellectual functioning.
Children with Visual Impairment (D-II):
- Visual impairment includes conditions where vision is significantly impaired or entirely absent.
- Braille is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired to read and write.
Q6: Match the List-I with List-II
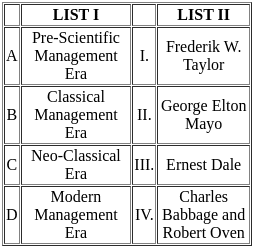
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
(c) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III'
Pre-Scientific Management Era:
- Charles Babbage and Robert Owen were prominent figures during the Pre-Scientific Management Era.
- Babbage is known for his work on the concept of division of labor and Owen for his efforts in improving working conditions.
Classical Management Era:
- Frederick W. Taylor is a key figure in the Classical Management Era.
- Taylor is known as the father of scientific management and introduced principles aimed at improving labor productivity.
Neo-Classical Era:
- George Elton Mayo is associated with the Neo-Classical Era.
- Mayo's Hawthorne Studies highlighted the importance of social relations and employee well-being in the workplace.
Modern Management Era:
- Ernest Dale is a notable figure in the Modern Management Era.
- Dale contributed to the development of modern management theories and practices.
Q7: This theory affirms that education is a sequence of selection between binary options of available long-term utility and short-term risk of failure.
(a) Rational Choice Theory
(b) Systems Analysis Theory
(c) Signalling Theory
(d) Human Capital Theory
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'Rational Choice Theory'
Rational Choice Theory:
- This theory posits that individuals make decisions by comparing the costs and benefits of various options.
- It emphasizes that people weigh the available long-term utility against the short-term risk of failure when making educational choices.
- The decision-making process is seen as a sequence of selections between binary options, where the aim is to maximize overall benefits while minimizing risks.
Other Related Points
Systems Analysis Theory:
- Focuses on understanding and analyzing the components and interactions within a system.
- It is more concerned with the overall structure and functioning of systems rather than individual decision-making processes.
Signalling Theory:
- Explains how individuals send signals to convey information to others, particularly in contexts like job markets.
- This theory does not focus on the binary decision-making process in education but rather on how educational qualifications signal certain traits to potential employers.
Human Capital Theory:
- Emphasizes the value of investing in education and training to improve individual productivity and economic outcomes.
- While it considers the benefits of education, it does not specifically address the binary decision-making process highlighted in Rational Choice Theory.
Q8: Which of the following is true regarding 'grounded theory' research?
A. Axial coding is the process of relating sub-categories to a category.
B. It includes continuous comparative analysis of cases.
C. Selective coding continues the axial coding at a higher level of abstraction.
D. The size of sample is determined by the theoretical saturation of categories.
E. It is a substitute of experimental research.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, B, C and D only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, C, and D only'
Grounded Theory Research:
- Grounded theory is a qualitative research methodology that aims to develop theories grounded in real-world observations.
- It involves the collection and analysis of data to construct theories that are grounded in the data themselves.
- This method is iterative, meaning data collection and analysis occur simultaneously and continue until no new information is emerging.
Axial Coding:
- Axial coding is the process of relating sub-categories to a category and is used to refine and differentiate categories.
- This helps in understanding the relationships among categories and sub-categories.
Continuous Comparative Analysis:
- Grounded theory includes the continuous comparative analysis of cases, where each piece of data is compared with others to identify similarities and differences.
- This process helps in refining categories and developing more robust theories.
Selective Coding:
- Selective coding continues the axial coding process at a higher level of abstraction, focusing on core categories and their relationships.
- This step is crucial for integrating categories to form a comprehensive theory.
Theoretical Saturation:
- The size of the sample in grounded theory research is determined by the theoretical saturation of categories, meaning data collection continues until no new information or insights are being discovered.
Other Related Points
Experimental Research:
- Grounded theory is not a substitute for experimental research. While grounded theory focuses on qualitative data to develop theories, experimental research involves the manipulation of variables to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Both methodologies serve different purposes and are used based on the research question and objectives.
Q9: A class teacher administered Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) to a group of students to assess their:
(a) Achievement
(b) Awareness
(c) Attitude
(d) Personality
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Personality'
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT):
- The TAT is a projective psychological test used to evaluate a person’s patterns of thought, attitudes, observational capacity, and emotional responses to ambiguous test materials.
- Developed by Henry A. Murray and Christiana D. Morgan in the 1930s, the test involves showing individuals a series of ambiguous images and asking them to tell a story about each one.
- The content of these stories is analyzed to uncover underlying motives, concerns, and the way the person sees the social world.
Other Related Points
Achievement:
- Achievement tests are designed to measure a person's level of skill, accomplishment, or knowledge in a specific area.
- Examples include standardized tests like SATs or exams in specific subjects like mathematics or history.
- The TAT is not designed to measure achievement but rather to explore deeper psychological aspects.
Awareness:
- Awareness typically refers to the state of being conscious of something, such as self-awareness or situational awareness.
- Tests measuring awareness often focus on cognitive functions and understanding of one's surroundings.
- The TAT does not specifically measure awareness; it focuses on personality and emotional responses.
Attitude:
- Attitude tests measure people's feelings and predispositions towards specific subjects, objects, or concepts.
- These tests often involve questionnaires or surveys designed to gauge opinions and biases.
- The TAT is not a direct measure of attitude; it looks at the broader aspects of personality.
Q10: Which of the following statements are incorrect?
A. Thorndike's theory is an atomistic theory of intelligence.
B. Assessment is an elementary mental process which means organizing what has been recognized.
C. A group of specific abilities, known as the 's' factor, is a universal innate ability.
D. The structural model of intelligence was given by Spearman.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Only A, B and C
(b) Only B and C
(c) Only B, C and D
(d) Only A, C and D
Ans: c
Sol: "Note:- In the official paper of UGC, option 2 was Only B, C and E, and answer given by UGC is option 2, which is wrong, no E statement is present in official paper so we have changed the option 2."
The correct answer is 'Only B, C, and D'
Thorndike's theory:
- Thorndike's theory is indeed an atomistic theory of intelligence, focusing on individual elements of intelligence and their associations rather than a holistic view.
- Thus, statement A is correct.
Assessment:
- Assessment is not merely an elementary mental process involving organizing what has been recognized. It involves a broader range of activities including evaluating, measuring, and documenting the academic readiness, learning progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students.
- Therefore, statement B is incorrect.
's' factor:
- The 's' factor refers to specific abilities in Spearman's two-factor theory of intelligence, but it is not considered a universal innate ability. Instead, it is specific to particular tasks.
- Thus, statement C is incorrect.
Structural model of intelligence:
- The structural model of intelligence was actually given by Guilford, not Spearman. Spearman is known for his two-factor theory of intelligence, involving the 'g' factor (general intelligence) and 's' factor (specific abilities).
- Hence, statement D is incorrect.
Other Related Points
Thorndike's contribution to educational psychology:
- Thorndike is known for his work in the field of educational psychology, particularly for his laws of learning which include the law of effect, the law of readiness, and the law of exercise.
- His theories have contributed to the development of instructional design and educational assessment.
Spearman's two-factor theory:
- Spearman's two-factor theory of intelligence posits that a person's performance on any cognitive task is influenced by a general intelligence factor ('g') and specific skill factors ('s').
- This theory laid the groundwork for later theories of intelligence and has influenced both psychological assessment and educational practices.
Guilford's structure of intellect model:
- Guilford proposed a three-dimensional model of intelligence, which includes operations, content, and products. This model is known as the Structure of Intellect (SI) model.
- His work expanded the understanding of human intelligence by identifying multiple dimensions and categories of intellectual abilities.
Q11: The correct hierarchy of needs given by Maslow is:
A. Safety Needs
B. Prestige Needs
C. Physiological Needs
D. Self Actualization Needs
E. Needs for Belongingness
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, E, D, B
(b) C, A, E, B, D
(c) A, C, B, E, D
(d) A, B, C, D, E
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is C, A, E, B, D.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs:
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological theory proposed by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation".
- It is often depicted as a pyramid with five levels of needs, with the most basic needs at the bottom and the higher needs at the top.
- The theory suggests that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to higher-level needs.
Other Related Points
Correct Order of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs:
- Physiological Needs (C): Basic survival needs like food, water, and shelter.
- Safety Needs (A): Protection from elements, security, order, law, stability, etc.
- Needs for Belongingness (E): Social needs like friendship, intimacy, trust, and acceptance.
- Prestige Needs (B): Esteem needs like self-esteem, recognition, and respect from others.
- Self-Actualization Needs (D): The desire to become the most one can be; achieving one's full potential.
Q12: Which of the following have direct relevance for inclusive education?
A. UNCRPD
B. Project on Integrated Education for the Disabled (PIED)
C. NEP 2020
D. NPE, 1986
E. Universal Design for Learning
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) A, D and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C, and E only'
UNCRPD (United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities):
- The UNCRPD is an international human rights treaty designed to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities.
- It emphasizes inclusive education by ensuring that persons with disabilities have access to an inclusive, quality, and free education on an equal basis with others.
NEP 2020 (National Education Policy 2020):
- The NEP 2020 aims to transform the Indian education system by making it more inclusive, equitable, and accessible.
- It highlights the need for inclusive education and special education zones to ensure that children with disabilities receive quality education.
Universal Design for Learning (UDL):
- UDL is an educational framework based on research in the learning sciences, including cognitive neuroscience, that guides the development of flexible learning environments.
- It helps in providing all students, including those with disabilities, with equal opportunities to learn.
Other Related Points
Project on Integrated Education for the Disabled (PIED):
- PIED was an initiative in India aimed at integrating children with disabilities into mainstream schools.
- While it was a significant step towards inclusive education, it is not as comprehensive or current as the other frameworks and policies mentioned.
NPE, 1986 (National Policy on Education, 1986):
- The NPE, 1986 focused on achieving universal access to education and provided some attention to the education of children with disabilities.
- However, its approach to inclusive education is not as robust or updated as the NEP 2020 or the international frameworks like UNCRPD and UDL.
Q13: Negative reinforcement is:
(a) same as punishment.
(b) generally disliked by living beings.
(c) related to a decrease in the probability of a behavior occurring.
(d) resulting in directly opposite behavior.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'generally disliked by living beings.'
- Negative reinforcement involves removing an aversive stimulus to increase the probability of a behavior occurring. For example, buckling a seatbelt to stop a car’s alarm increases seatbelt use. The aversive stimulus (e.g., the alarm) is generally disliked, making option (b) correct.
Explanation of Incorrect Options:
- (a) Same as punishment: Incorrect, as punishment decreases behavior, while negative reinforcement increases it.
- (c) Related to a decrease in the probability of a behavior occurring: Incorrect, as negative reinforcement increases behavior probability.
- (d) Resulting in directly opposite behavior: Incorrect, as negative reinforcement reinforces the desired behavior, not an opposite one.
Q14: Which of the following is NOT a part of curriculum development?
(a) Choosing appropriate transaction strategy
(b) Exploring relevant learning experiences
(c) Identifying effective teachers
(d) Progressive testing of the achievement of objectives
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Identifying effective teachers'
Choosing appropriate transaction strategy:
- This involves selecting the methods and techniques for delivering the curriculum content effectively.
- It ensures that the teaching strategies align with the learning objectives and the needs of the students.
Exploring relevant learning experiences:
- This involves identifying and integrating learning activities that are pertinent to the curriculum goals.
- It helps in making the curriculum more engaging and applicable to real-life situations.
Progressive testing of the achievement of objectives:
- This involves continuous assessment to monitor students' progress toward the learning objectives.
- It helps in identifying areas where students may need additional support or enrichment.
Other Related Points
Identifying effective teachers:
- While identifying effective teachers is crucial for the successful implementation of a curriculum, it is not a direct component of curriculum development.
- Curriculum development focuses on the design and organization of educational content and experiences, whereas identifying effective teachers pertains to human resource management and teacher evaluation processes.
Q15: Those who are soft and round, such personalities are categorized by Sheldon as:
(a) Ectomorphic
(b) Mesomorphic
(c) Aesthetic
(d) Endomorphic
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Endomorphic'
Endomorphic:
- According to William H. Sheldon, people with an endomorphic body type are characterized by a round and soft physique.
- Endomorphs tend to have a higher percentage of body fat, wide hips, and a softer, rounder appearance.
- This body type is often associated with a sociable, relaxed, and comfortable personality.
Other Related Points
Ectomorphic:
- Ectomorphs are characterized by a slim, linear, and delicate build with little body fat and muscle.
- This body type is often associated with a personality that is introverted, thoughtful, and reserved.
Mesomorphic:
- Mesomorphs have a muscular, well-built physique with a high metabolism and responsive muscle cells.
- They are often associated with being active, assertive, and bold in their personality traits.
Aesthetic:
- The term 'aesthetic' typically refers to an appreciation of beauty or good taste, rather than a specific body type or personality.
- This option is not related to Sheldon's classification of body types.
Q16: Which of the following statements are true about "hypothesis"?
A. The minor premise of the older deductive method was gradually replaced by hypothesis.
B. Snow (1973) described six levels of theory, with the first level being hypothesis formation.
C. For the hypothesis to be testable, the variables must be operationally defined.
D. The most common use of hypothesis is to test whether an existing theory can be used to solve a problem.
E. The hypothesis focuses the investigation on indefinite targets.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C and D only
(b) B, C, D and E only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) C and D only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is B, C, and D only.
Hypothesis:
- A hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction that can be tested by scientific research.
- It is an essential component of the scientific method, allowing researchers to make predictions that can be tested through experiments and observations.
Correct Statements:
Snow (1973) described six levels of theory, with the first level being hypothesis formation (B):
- This statement is true as Snow's theory includes hypothesis formation as the initial level of scientific inquiry.
For the hypothesis to be testable, the variables must be operationally defined (C):
- Operational definitions specify the exact procedures used to measure or manipulate variables, making it possible to test the hypothesis.
The most common use of hypothesis is to test whether an existing theory can be used to solve a problem (D):
- Hypotheses often derive from existing theories and are used to test the validity and applicability of these theories in specific situations.
Other Related Points
Incorrect Statements:
The minor premise of the older deductive method was gradually replaced by hypothesis (A):
- This statement is incorrect because the minor premise in deductive reasoning is not necessarily replaced by a hypothesis. Deductive reasoning and hypothesis formation are different aspects of scientific methodology.
The hypothesis focuses the investigation on indefinite targets (E):
- This statement is incorrect because a hypothesis actually aims to focus the investigation on specific, testable predictions, not indefinite targets.
Q17: Match the List-I with List-II
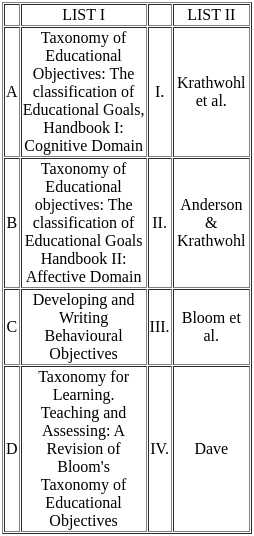
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(b) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II'
Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The classification of Educational Goals, Handbook I: Cognitive Domain - Bloom et al.
- This work, published in 1956, is a foundational text in educational psychology. It introduced the widely used Bloom's Taxonomy, which classifies educational goals and objectives into cognitive levels such as Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.
Taxonomy of Educational objectives: The classification of Educational Goals Handbook II: Affective Domain - Krathwohl et al.
- Published in 1964, this book expands on Bloom's original taxonomy by addressing the affective domain, which includes emotions, attitudes, and values. The affective domain categorizes objectives into levels like Receiving, Responding, Valuing, Organization, and Characterization.
Developing and Writing Behavioural Objectives - Dave
- This work focuses on the practical aspects of creating clear, measurable educational objectives. Dave's approach often emphasizes the psychomotor domain, which involves physical skills and actions.
Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives - Anderson & Krathwohl
- Published in 2001, this book revises Bloom's original taxonomy, adding new dimensions like "Remembering," "Understanding," and "Creating." It also redefines the hierarchy to be more dynamic and applicable to modern educational practices.
Q18: Match the List-I with List-II
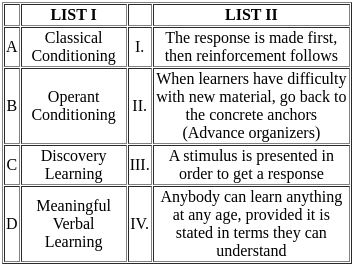
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(b) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II'
Classical Conditioning:
- Classical conditioning is a learning process where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus, eliciting a conditioned response.
- Example: Pavlov's dogs learned to associate the sound of a bell (neutral stimulus) with food (meaningful stimulus), eventually salivating (conditioned response) at the sound of the bell alone.
Operant Conditioning:
- Operant conditioning is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior.
- In this type of conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence for that behavior.
- Example: A rat presses a lever (response) and receives food (reinforcement).
Discovery Learning:
- Discovery learning is a constructivist approach where learners build their own understanding and knowledge through experiences and exploring.
- This method encourages active engagement and enhances problem-solving skills.
- Example: Students in a science lab experiment to discover principles of physics on their own rather than being directly taught.
Meaningful Verbal Learning:
- Meaningful verbal learning involves understanding and relating new information to existing cognitive structures (prior knowledge).
- It is facilitated by using advance organizers, which are tools that help anchor new information to known concepts.
- Example: Introducing a new topic by first discussing related concepts that students are already familiar with.
Q19: What is the primary focus of Poka-Yoke model in educational leadership?
(a) Eliminating financial inefficiencies
(b) Preventing errors in educational process
(c) Enhancing student-teacher communication
(d) Developing innovative teaching materials
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Preventing errors in educational process'
Preventing errors in educational process:
- Poka-Yoke is a Japanese term that translates to "mistake-proofing" or "error prevention." It is a concept originally used in manufacturing to avoid mistakes by designing processes in a way that errors are impossible or immediately detectable.
- In educational leadership, the Poka-Yoke model focuses on designing educational processes and systems that prevent errors in teaching and learning, ensuring a more effective and efficient educational experience.
- This can include techniques like standardized testing protocols, automated grading systems, and clearly defined instructional guidelines to minimize the chance of human error.
- The goal is to create a fail-safe environment where mistakes are either impossible or caught early, thereby improving overall educational outcomes.
Other Related Points
Eliminating financial inefficiencies:
- While eliminating financial inefficiencies is important, it is not the primary focus of the Poka-Yoke model. Financial management is more related to budgeting, resource allocation, and financial planning rather than error prevention in educational processes.
Enhancing student-teacher communication:
- Improving communication between students and teachers is crucial for effective learning but is not the central aim of the Poka-Yoke model. This focus area is more aligned with pedagogical strategies and communication tools.
Developing innovative teaching materials:
- Creating innovative teaching materials is essential for engaging and effective education; however, it does not directly align with the error-prevention focus of the Poka-Yoke model. This area is more about curriculum development and instructional design.
Q20: Pick the INCORRECT match:
A. Education and Schooling are ideological state apparatuses - Althusser
B. Education is for Cultural and Social Reproduction - Bourdieu
C. School is a miniature society - Parsons
D. Education helps the individual to grow and achieve her potentials - Marx
E. Education for democracy is thus education freed from the authoritarian relationships - Dewey
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A only
(b) D only
(c) B and C only
(d) C and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'D only'.
Education and Schooling are ideological state apparatuses - Althusser:
- Louis Althusser, a Marxist philosopher, introduced the concept of Ideological State Apparatuses (ISAs), which include education systems. According to Althusser, these institutions serve to perpetuate the ideology of the ruling class.
Education is for Cultural and Social Reproduction - Bourdieu:
- Pierre Bourdieu argued that education systems contribute to cultural and social reproduction, meaning they perpetuate existing social structures and inequalities.
School is a miniature society - Parsons:
Talcott Parsons described school as a miniature society where children learn social norms and values, preparing them for their roles in adult society.
Education helps the individual to grow and achieve her potentials - Marx:
- Incorrect. Karl Marx did not focus on education as a means for individual growth and potential. Instead, he critiqued educational systems for perpetuating class structures and serving the interests of the ruling class.
Education for democracy is thus education freed from the authoritarian relationships - Dewey:
- John Dewey emphasized the importance of education in a democratic society, advocating for an educational system free from authoritarian relationships to foster critical thinking and participatory democracy.
Other Related Points
Althusser's Ideological State Apparatuses:
- ISAs include institutions like schools, churches, and media, which function to maintain and perpetuate the ideology of the ruling class indirectly through cultural means.
Bourdieu's Theory of Cultural Capital:
- Bourdieu's concept of cultural capital explains how education systems can reproduce social inequalities by valuing the cultural knowledge and skills of the dominant class.
Parsons' Functionalist Perspective:
- Parsons saw education as a vital institution for socializing children and maintaining social order, emphasizing its role in teaching shared norms and values.
Dewey's Philosophy of Education:
- Dewey believed in experiential learning and the role of education in promoting democratic values and social reform.
Q21: It is a learning platform that brings together an integrated environment, a range of resources that enable the learners and teachers to interact online and includes content delivery and tracking.
(a) SPSS
(b) META AI
(c) SWAYAM
(d) R
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'SWAYAM'
SWAYAM:
- SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds) is a digital learning platform initiated by the Government of India.
- It integrates various resources to facilitate online learning, enabling interaction between learners and teachers.
- The platform offers courses from school-level to post-graduate level, covering a wide range of subjects.
- It includes features like content delivery, assessment, and tracking of learner progress, making it a comprehensive educational tool.
Other Related Points
SPSS:
- SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) is a software used for statistical analysis.
- It is not designed for content delivery or online interaction between learners and teachers.
META AI:
- META AI is a research and development lab focusing on artificial intelligence advancements.
- It does not serve as a learning platform for integrated online education.
R:
- R is a programming language and software environment used for statistical computing and graphics.
- It is not a platform designed for educational content delivery and tracking.
Q22: The tenth category of Flanders Interaction analysis is related to:
(a) Teacher Talk
(b) Pupil Talk
(c) Accepting the ideas of pupil
(d) Silence or Pause or Confusion
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Silence or Pause or Confusion'
V Interaction Analysis:
- Flanders Interaction Analysis is a system used to observe and categorize the types of interactions that occur in a classroom setting.
- It divides interactions into different categories to better understand the dynamics between teachers and students.
- The system includes categories for teacher talk, pupil talk, and other types of interactions.
Tenth Category - Silence or Pause or Confusion:
- This category specifically deals with periods of silence, pauses, or confusion during classroom interactions.
- It is important to note these moments as they can indicate the need for clarification or a break in the flow of the lesson.
- These moments are crucial for understanding the effectiveness of communication and teaching strategies.
Other Related Points
Teacher Talk:
- This category includes all verbal communication initiated by the teacher, such as giving instructions, asking questions, and providing feedback.
- It is further divided into subcategories like lecturing, giving directions, and criticizing or justifying authority.
Pupil Talk:
- This category encompasses all verbal responses from students, including answering questions, asking questions, and expressing ideas.
- It can be further divided into subcategories such as pupil-initiated talk and pupil response.
Accepting the Ideas of Pupils:
- This category involves the teacher acknowledging and building upon the ideas and suggestions made by students.
- It encourages a more interactive and student-centered learning environment.
Q23: Match the List-I with List-II
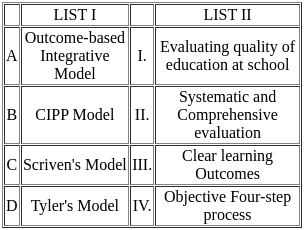
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
(d) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV.'
Outcome-based Integrative Model:
- This model emphasizes clear learning outcomes. It focuses on what students are expected to achieve at the end of an educational process.
- It helps in aligning teaching, learning, and assessment practices to achieve these outcomes.
CIPP Model:
- The CIPP (Context, Input, Process, Product) Model is used for evaluating the quality of education at schools.
- It provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating different aspects of educational programs and their effectiveness.
Scriven's Model:
- Scriven's Model is known for its systematic and comprehensive approach to evaluation.
- It includes both formative and summative evaluations to provide a holistic understanding of the educational program's effectiveness.
Tyler's Model:
- Tyler's Model involves an objective four-step process to evaluate educational programs.
- The steps include defining objectives, selecting learning experiences, organizing experiences, and evaluating the outcomes.
Q24: Identify the impact of C.K. Prahalad's theory on curriculum design in teacher education:
A. Enhancing value through innovative curriculum elements.
B. Aligning curriculum with the long-term goals of Educational Institution.
C. Focusing on high-income student populations to maximize returns.
D. Integrating core competencies into curriculum development.
E. Addressing the needs of underserved student groups within the curriculum.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D and E only
(b) A, C, D and E only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) A, B, C and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, D, and E only
Overview of C.K. Prahlad's Theory:
- C.K. Prahlad's theory, particularly his concept of "Core Competencies," emphasizes the importance of identifying and leveraging unique strengths to create value.
- His ideas have been influential across various fields, including education, where they inform curriculum design and development.
Impact on Curriculum Design in Teacher Education:
- Enhancing value through innovative curriculum elements (Option A): Incorporating innovative practices and strategies to ensure that the curriculum remains relevant and effective.
- Aligning curriculum with the long-term goals of Educational Institutions (Option B): Ensuring that the curriculum supports the strategic objectives and vision of the educational institution.
- Integrating core competencies into curriculum development (Option D): Embedding essential skills and knowledge areas that are critical for future educators to master, aligning with Prahlad's idea of leveraging unique strengths.
- Addressing the needs of underserved student groups within the curriculum (Option E): Focusing on inclusivity and ensuring that the curriculum caters to diverse student populations, particularly those who are often marginalized.
Q25: Which of the following CC licenses of OER allows others to distribute, change, remix and build upon your work, even commercially, as long as they credit you for the original work:
(a) CC BY-NC-SA
(b) CC BY-NC
(c) CC BY
(d) CC BY-SA
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'CC BY'
CC BY (Creative Commons Attribution License):
- Allows others to distribute, change, remix, and build upon your work, even for commercial purposes, as long as they credit you for the original creation.
- This is the most accommodating of licenses offered, in terms of what others can do with the works licensed under it.
- Provides the maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials.
Other Related Points
CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike):
- Allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon your work non-commercially, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms.
- Others can download and redistribute the works, but cannot use them for commercial purposes.
CC BY-NC (Attribution-NonCommercial):
- Allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon your work non-commercially, and although their new works must also acknowledge you and be non-commercial, they don’t have to license their derivative works on the same terms.
- Prohibits commercial use of the licensed material.
CC BY-SA (Attribution-ShareAlike):
- Allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon your work even for commercial purposes, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms.
- All new works based on yours will carry the same license, so any derivatives will also allow commercial use.
Q26: The Paideia Proposal by Mortimer Adler involves:
A. Providing all children with the same quality of schooling.
B. A school curriculum that is primarily liberal and humanistic.
C. Having different objectives for different students.
D. The curriculum consisting of only one kind of learning.
E. Remedial and compensatory interventions for individual differences.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and E only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, and E only'
The Paideia Proposal by Mortimer Adler:
- The Paideia Proposal is an educational manifesto by Mortimer J. Adler that advocates for a single-track, liberal arts education for all students, regardless of their future career plans.
- It emphasizes the importance of providing all children with the same quality of schooling (Option A).
- The curriculum proposed is primarily liberal and humanistic, focusing on intellectual and moral development (Option B).
- It also includes remedial and compensatory interventions to cater to individual differences among students (Option E).
Other Related Points
Incorrect Options:
- Option C: The Paideia Proposal does not support having different objectives for different students. It advocates for a unified curriculum and educational objectives for all students.
- Option D: The curriculum does not consist of only one kind of learning. Instead, it includes three types of learning: didactic instruction, coaching, and Socratic questioning.
Q27: Which of the following is NOT true about critical thinking/critical pedagogy?
(a) The focus is to understand the oppressions of the individual, group and society which might be self-imposed.
(b) The focus is to understand the oppressions of the individual, group and society which might be created via external forces.
(c) According to Freire dialogue is capable of generating critical thinking.
(d) According to Freire dialogue does not need any pre-requirement in the classroom.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'According to Freire dialogue does not need any pre-requirement in the classroom.'
Understanding Oppressions:
- The focus of critical thinking and critical pedagogy is to understand the oppressions of the individual, group, and society which might be self-imposed. This involves recognizing internalized beliefs and behaviors that contribute to one's own oppression.
- Additionally, it aims to understand oppressions created via external forces. This includes examining how societal structures, systems, and institutions perpetuate inequality and injustice.
Dialogue and Critical Thinking:
- According to Paulo Freire, dialogue is capable of generating critical thinking. Freire emphasized the importance of dialogue in education as a means of fostering critical consciousness and empowering individuals to challenge and transform oppressive conditions.
Pre-requirements for Dialogue:
- The incorrect statement is that "According to Freire dialogue does not need any pre-requirement in the classroom." Freire actually argued that meaningful dialogue requires certain preconditions, such as mutual respect, openness, and a willingness to engage in the process of learning and unlearning together.
Other Related Points
Critical Pedagogy:
- Critical pedagogy is a philosophy of education that seeks to help students question and challenge domination, and the beliefs and practices that dominate.
- It is a teaching approach inspired by critical theory and other radical philosophies, which focuses on the development of critical consciousness.
Freire's Approach:
- Paulo Freire, a Brazilian educator and philosopher, is one of the most influential figures in the field of critical pedagogy. His book "Pedagogy of the Oppressed" is considered one of the foundational texts in the field.
- Freire's approach involves a participatory and collaborative form of education where teachers and students learn from each other and work together to understand and address issues of oppression and injustice.
Q28: Match the List-I with List-II
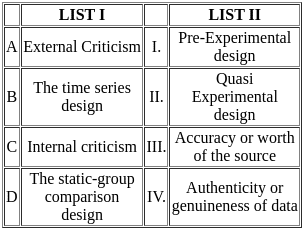
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(b) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I'
External Criticism (A-IV):
- External criticism refers to the evaluation of the authenticity or genuineness of data sources.
- This involves verifying whether the document or data is genuine and not a forgery.
- It ensures that the source is what it claims to be and is not tampered with.
The Time Series Design (B-II):
- This is a type of Quasi-Experimental design.
- It involves repeated observations of variables over time to detect patterns or trends.
- This design is used to understand the effect of an intervention over a period of time.
Internal Criticism (C-III):
- Internal criticism assesses the accuracy or worth of the source.
- It focuses on the content of the document to determine its reliability and validity.
- This involves checking the consistency and coherence of the information provided.
The Static-Group Comparison Design (D-I):
- This design falls under Pre-Experimental design.
- It involves comparing two groups, one that has received the treatment and one that has not, without random assignment.
- This design helps in assessing the impact of an intervention but lacks strong internal validity.
Q29: Which of the following statements are TRUE?
A. Medical Model of disabilities find its base in psychology.
B. Human Rights Model of disabilities talks about equity.
C. Charity Model of disabilities treats people with disabilities as incapable.
D. Economic model of disabilities considers disabilities as burden.
E. Religious model of disabilities relates disabilities with God's Wrath.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'B, C, and E only'
Human Rights Model of disabilities talks about equity:
- This model emphasizes equal rights and opportunities for people with disabilities, focusing on removing barriers to participation and ensuring that all individuals have equitable access to resources and opportunities.
- The Human Rights Model supports the idea that people with disabilities should be treated with dignity and respect, and that their rights should be protected and promoted.
Charity Model of disabilities treats people with disabilities as incapable:
- This model views people with disabilities as objects of charity and pity, often portraying them as dependent and in need of help.
- It tends to undermine the capabilities of individuals with disabilities and can perpetuate stereotypes and discrimination.
Religious Model of disabilities relates disabilities with God's Wrath:
- This model is based on the belief that disabilities are a form of punishment or a test from a higher power.
- It can contribute to stigma and discrimination against people with disabilities, as it often implies that they are to blame for their condition.
Other Related Points
Medical Model of disabilities:
- The Medical Model views disabilities primarily as a medical issue that needs to be treated or cured. It is more closely related to the fields of medicine and healthcare rather than psychology.
- This model can often overlook the social and environmental factors that contribute to disability and can lead to a focus on what individuals cannot do rather than what they can.
Economic Model of disabilities:
- This model considers disabilities in terms of their economic impact, often viewing people with disabilities as a financial burden on society.
- While it recognizes the economic challenges and costs associated with disabilities, it can also perpetuate negative perceptions and undervalue the contributions that individuals with disabilities can make to society.
Q30: Arrange the following theorists chronologically.
A. Functionalist - Durkheim
B. Open System Theory - Bertalanffy
C. Symbolic Interactionist - Mead
D. Conflict Theorist - Weber
E. Conflict Theorist - Marx
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) E, B, C, A, D
(b) A, B, C, D, E
(c) A, D, B, C, E
(d) E, A, C, D, B
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'E, A, C, D, B'
Key Points:
- Karl Marx (1818–1883): Conflict theory.
- Émile Durkheim (1858–1917): Functionalism.
- George Herbert Mead (1863–1931): Symbolic interactionism.
- Max Weber (1864–1920): Conflict theory.
- Ludwig von Bertalanffy (1901–1972): Open System Theory.
Q31: Match the List-I with List-II
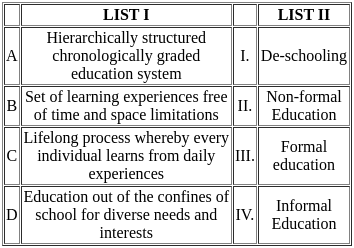
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(c) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I.
A - Hierarchically structured chronologically graded education system (III. Formal education):
- Formal education refers to a structured education system that is organized chronologically and graded by levels, typically including primary, secondary, and higher education.
- This type of education is typically provided by schools and universities and follows a set curriculum.
B - Set of learning experiences free of time and space limitations (II. Non-formal Education):
- Non-formal education encompasses educational activities that are structured and systematic but do not take place within the formal education system.
- These activities can occur outside traditional school settings and are flexible in terms of time and place.
C - Lifelong process whereby every individual learns from daily experiences (IV. Informal Education):
- Informal education is the lifelong learning process where individuals gain knowledge, skills, and values from daily experiences and environmental interactions.
- This form of education is not structured or institution-based and happens naturally in everyday life.
D - Education out of the confines of school for diverse needs and interests (I. De-schooling):
- De-schooling refers to the idea of learning outside the traditional school environment, often emphasizing more individualized and interest-based education.
- This concept advocates for alternative methods of education that cater to the diverse needs and interests of individuals.
Q32: Following are significant milestones in the field of inclusive education. Arrange them chronologically.
A. National Education Policy
B. Salamanca Statement
C. United Nations Convention on Rights of the Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD)
D. Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan
E. National Policy on Disabilities
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, A, E, D
(b) B, E, C, A, D
(c) B, D, E, C, A
(d) B, C, A, D, E
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'B, D, E, C, A'
Salamanca Statement (1994):
- The Salamanca Statement was a major international policy document that called for inclusive education for all children, particularly those with disabilities.
- Adopted in 1994 by representatives of 92 governments and 25 international organizations at the World Conference on Special Needs Education in Salamanca, Spain.
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (2001):
- India's flagship program aimed at the universalization of elementary education.
- Launched in 2001, it aims to provide quality elementary education to all children aged 6-14 years.
- Focuses on inclusive education by integrating children with special needs into regular schools.
National Policy on Disabilities (2006):
- India's comprehensive policy to address the needs of persons with disabilities.
- Adopted in 2006, it emphasizes the importance of inclusive education for children with disabilities.
United Nations Convention on Rights of the Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD) (2006):
- An international treaty that aims to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities.
- Adopted in 2006, it emphasizes the right to inclusive education for persons with disabilities.
National Education Policy (2020):
- India's latest education policy, adopted in 2020.
- Emphasizes inclusive education and aims to ensure that no child is left behind, including children with disabilities.
Q33: The correct sequence of the steps for developing an Instructional Design is:
A. Assessment
B. Delivery of Instructions
C. Deciding Instructional Goals
D. Need Analysis
E. Task Analysis
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D, B, E
(b) C, A, D, E, B
(c) D, C, E, B, A
(d) A, B, D, C, E
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'D, C, E, B, A'
Need Analysis (D):
- This is the first step where the instructional designer identifies the specific needs and gaps in knowledge or skills that the instruction aims to address.
- It involves gathering data to understand the learners' requirements and the context in which learning will occur.
Deciding Instructional Goals (C):
- Based on the needs analysis, clear and measurable instructional goals and objectives are set.
- These goals guide the design and development of instructional materials and activities.
Task Analysis (E):
- This step involves breaking down the instructional goals into specific tasks and sub-tasks that the learners need to accomplish.
- It helps in identifying the skills, knowledge, and attitudes required to perform each task.
Delivery of Instructions (B):
- At this stage, the instructional materials and methods are implemented and delivered to the learners.
- This can include various formats such as lectures, online modules, workshops, etc.
Assessment (A):
- The final step involves evaluating the effectiveness of the instruction through assessments and feedback.
- This helps in determining whether the instructional goals were met and identifying areas for improvement.
Q34: Match the List-I with List-II
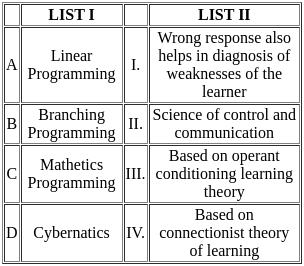
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II'
Linear Programming (A-III):
- Linear programming is a method used to achieve the best outcome in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear relationships.
- It is based on operant conditioning learning theory, which emphasizes the reinforcement of desired behaviors.
Branching Programming (B-I):
- Branching programming is an instructional method that provides different paths or branches based on the learner's responses.
- Wrong responses help in diagnosing the weaknesses of the learner, allowing for a tailored and corrective learning experience.
Mathetics Programming (C-IV):
- Mathetics programming is based on the connectionist theory of learning, which focuses on the idea that learning is the result of forming connections or associations between stimuli and responses.
Cybernetics (D-II):
- Cybernetics is the science of control and communication in animals, humans, and machines.
- It deals with systems, feedback, and control processes.
Q35: Which of the following statement is correct about null hypothesis?
(a) The null hypothesis relates to a statistical method of interpreting conclusions about sample characteristics that are inferred from the variable relationships observed in samples.
(b) The null hypothesis relates to a statistical method of interpreting conclusions about population characteristics that are inferred from the variable relationships observed in samples.
(c) The null hypothesis relates to a statistical method of interpreting conclusions about population characteristics that are inferred from the variable relationships observed in populations.
(d) The null hypothesis relates to a statistical method of interpreting conclusions about sample characteristics that are inferred from the variable relationships observed in population.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'The null hypothesis relates to a statistical method of interpreting conclusions about population characteristics that are inferred from the variable relationships observed in samples.'
Null Hypothesis:
- The null hypothesis (H0) is a foundational concept in inferential statistics.
- It represents a general statement or default position that there is no relationship between two measured phenomena or no association among groups.
- The purpose of hypothesis testing is to determine whether there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of an alternative hypothesis (HA).
- In the context of statistical methods, the null hypothesis is used to make inferences about population characteristics based on sample data.
Other Related Points
Understanding the Null Hypothesis:
- The null hypothesis is essential for statistical testing, providing a basis for comparison with the alternative hypothesis.
- It helps in determining the statistical significance of observed data patterns, guiding researchers in making informed conclusions about broader populations.
Q36: In his work during nineteenth century, Charles Darwin,
(a) used the inductive method of Bacon.
(b) used the deductive method of Aristotle.
(c) integrated the deductive method of Aristotle and the inductive method of Bacon.
(d) discarded the deductive method and the inductive method completely.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'integrated the deductive method of Aristotle and the inductive method of Bacon.'
Charles Darwin's Methodology:
- Charles Darwin, in his groundbreaking work on evolution, utilized both inductive and deductive reasoning.
- Inductive reasoning, as championed by Bacon, involves making generalizations based on specific observations. Darwin observed various species and their adaptations.
- Deductive reasoning, as advocated by Aristotle, involves deriving specific predictions from general principles. Darwin formulated hypotheses about natural selection and tested them against empirical data.
- By integrating both methods, Darwin was able to develop a robust theory of evolution that was both evidence-based and theoretically sound.
Other Related Points
Used the inductive method of Bacon:
- While Darwin did use inductive reasoning to gather data and form generalizations, this alone does not capture the full extent of his methodological approach.
Used the deductive method of Aristotle:
- Darwin also employed deductive reasoning, but focusing solely on this aspect overlooks the importance of his empirical observations and inductive reasoning.
Discarded the deductive method and the inductive method completely:
- This is incorrect as Darwin's work is a hallmark of combining both inductive and deductive methods.
Q37: Which of the following statements are incorrect?
A. Asynchronous Interaction takes place in real time.
B. A blog offers interaction with reflective comments and also the ability to interlink related ideas.
C. Synchronous Interaction gives freedom to the learner to learn at his/her own pace and as per the availability of time at his/her disposal.
D. Question Mark Perception is a software which provides scope for submission of answers to multiple choice questions.
E. Calibrand Marker is an Intranet based workflow application through which assessment can be carried out for formative tests.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and D only
(b) A, C and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) A, B and C only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C and D only'
Asynchronous Interaction:
- Asynchronous interaction does not take place in real time. It allows participants to engage in communication at different times. Examples include emails, discussion forums, and recorded lectures.
Synchronous Interaction:
- Synchronous interaction occurs in real-time, allowing immediate feedback and interaction. Examples include live chats, video conferences, and real-time classroom interactions.
- Synchronous interaction does not give freedom to the learner to learn at their own pace since it requires participants to be present at the same time.
Question Mark Perception:
- This is a software tool that provides scope for the submission of answers to multiple-choice questions, along with other assessment types.
Other Related Points
Blog Interaction:
- A blog allows for asynchronous interaction, where users can leave reflective comments and interlink related ideas. This promotes thoughtful discussion and sharing of resources.
Calibrand Marker:
- This is an Intranet-based workflow application designed for formative assessments, enabling structured and efficient evaluation processes.
Q38: Match the List-I with List-II
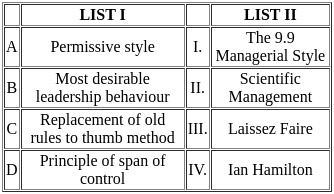
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(b) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(d) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV.'
Permissive Style (Laissez Faire):
- The permissive style of management, also known as the Laissez Faire style, refers to a hands-off approach where employees are given a high degree of autonomy and responsibility for their own work.
- Managers provide minimal direction and allow employees to make their own decisions.
Most Desirable Leadership Behaviour (The 9.9 Managerial Style):
- The 9.9 managerial style, often referred to in the Blake Mouton Managerial Grid, represents a high concern for both people and production.
- This style is considered the most desirable as it aims for high employee satisfaction and high productivity simultaneously.
Replacement of Old Rules to Thumb Method (Scientific Management):
- Scientific Management, introduced by Frederick Taylor, emphasizes replacing old, informal methods of work with systematic, scientific procedures.
- This approach seeks to improve efficiency and productivity through time studies, standardization of tools, and systematic training.
Principle of Span of Control (Ian Hamilton):
- The principle of span of control refers to the number of subordinates that a manager or supervisor can effectively oversee.
- Ian Hamilton is associated with this principle, which suggests a balance between too many direct reports (leading to managerial overload) and too few (leading to underutilization of managerial capacity).
Q39: According to Hackney and Cormier (2005), the correct sequence of steps of counselling process is:
A. Goal Setting
B. Problem Assessment
C. Evaluation, Termination or Referral
D. Relationship Building
E. Counselling Intervention
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, B, A, E, C
(b) B, A, D, C, E
(c) A, B, D, C, E
(d) A, D, B, E, C
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'D, B, A, E, C'
Relationship Building (D):
- This initial phase involves establishing trust and rapport between the counselor and the client.
- It sets the foundation for effective communication and a strong therapeutic alliance.
Problem Assessment (B):
- In this phase, the counselor gathers detailed information about the client's issues, concerns, and overall situation.
- This involves understanding the problem from the client's perspective and identifying the underlying factors contributing to it.
Goal Setting (A):
- Once the problems are assessed, specific and achievable goals are set collaboratively between the counselor and the client.
- These goals guide the direction of the counseling process and provide measurable outcomes to work towards.
Counselling Intervention (E):
- This phase involves implementing strategies and techniques to address the client's issues and work towards the established goals.
- Interventions are tailored to the client's needs and may include cognitive-behavioral techniques, psychoeducation, and other therapeutic approaches.
Evaluation, Termination, or Referral (C):
- In this final phase, the counselor evaluates the progress made towards the goals and determines whether the counseling process should be concluded or if further sessions are needed.
- If the client's needs are beyond the counselor's expertise, a referral to another professional may be made.
Q40: Match the List-I with List-II
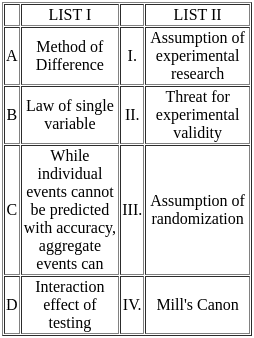
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(b) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
(d) A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II'
Method of Difference:
- Associated with Mill's Canon (IV).
- It is a method used in scientific research to identify causal relationships.
- This method involves comparing two cases that are identical except for one variable.
Law of Single Variable:
- It is an Assumption of Experimental Research (I).
- This law states that in an experiment, only one variable is changed at a time to isolate its effects.
- This helps in maintaining the integrity of the experiment and obtaining clear results.
While individual events cannot be predicted with accuracy, aggregate events can:
- This is the Assumption of Randomization (III).
- Randomization helps in reducing bias and making the groups comparable in experiments.
- It underlines the principle that while individual outcomes can be uncertain, overall trends and averages can be predicted with some accuracy.
Interaction Effect of Testing:
- It is a Threat for Experimental Validity (II).
- Occurs when the testing itself influences the participants' behaviour, thereby affecting the outcomes of the experiment.
- This threat needs to be controlled to ensure the validity of the experimental results.
Q41: According to which commission, a majority of stand-alone Teacher Education Institutions - over 10,000 in number - are not even attempting serious teacher education but are essentially selling degrees for a price?
(a) Radhakrishnan Commission
(b) Mudaliar Commission
(c) Kothari Commission
(d) J.S. Verma Commission
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'J.S. Verma Commission.'
J.S. Verma Commission:
- The J.S. Verma Commission was established to review the existing teacher education system in India.
- The commission found that a majority of stand-alone Teacher Education Institutions (TEIs) were not engaged in serious teacher education.
- Instead, these institutions were primarily selling degrees for a price, compromising the quality of teacher education.
- This finding highlighted the need for stringent regulations and reforms in the teacher education sector to ensure quality and integrity.
Other Related Points
Radhakrishnan Commission:
- Also known as the University Education Commission (1948-1949), it was established to report on Indian university education and suggest improvements.
- It did not specifically focus on teacher education institutions.
Mudaliar Commission:
- Formally known as the Secondary Education Commission (1952-1953), it focused on secondary education reforms.
- Its primary focus was not on the commercialization of teacher education.
Kothari Commission:
- Also known as the National Education Commission (1964-1966), it aimed at formulating a general education policy for India.
- While it covered teacher education, it did not specifically address the issue of institutions selling degrees.
Q42: The Dynamic Model of Learner Autonomy is:
A. a tool for self-assessment
B. a tool for choosing appropriate pedagogy by the teacher in classroom
C. given by Tassinari
D. to be followed in fixed ascending order.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) A and C only
(c) B and C only
(d) B and D only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A and C only'
Dynamic Model of Learner Autonomy:
- The Dynamic Model of Learner Autonomy is a conceptual framework aimed at understanding and enhancing learner autonomy in educational settings.
- This model helps learners assess their own autonomy and provides tools for self-assessment, enabling them to reflect on their learning processes and take more control over their educational journey.
- This model was given by Tassinari, making it a significant contribution to the field of educational theory and practice.
Other Related Points
Other Options Explained:
- Option B (Incorrect): While the Dynamic Model of Learner Autonomy can inform pedagogical choices, its primary function is not to serve as a tool for teachers to choose appropriate pedagogy. It focuses more on the learner's perspective.
- Option D (Incorrect): The model is dynamic and not meant to be followed in a fixed ascending order. It emphasizes flexibility and adaptability in developing learner autonomy.
Q43: When for a particular degree of freedom, a null hypothesis could not be rejected at the .05 level of significance then -
(a) It will definitely be rejected at the .01 level of significance.
(b) It may or may not be rejected at the .01 level of significance
(c) It will definitely not be rejected at the .01 level of significance
(d) The given information is insufficient to decide upon.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'It will definitely not be rejected at the .01 level of significance.'
Null Hypothesis Significance Testing:
- Null hypothesis significance testing (NHST) is a statistical method used to determine if there is enough evidence to reject a null hypothesis.
- The level of significance (alpha) is a threshold set by the researcher below which the null hypothesis will be rejected. Common alpha levels are 0.05 and 0.01.
- If a null hypothesis is not rejected at a 0.05 level of significance, it indicates that the p-value is greater than 0.05.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
- If a null hypothesis cannot be rejected at the 0.05 level, it means the p-value is greater than 0.05.
- Since the 0.01 level of significance is more stringent than the 0.05 level, a p-value greater than 0.05 will also be greater than 0.01.
- Therefore, the null hypothesis will definitely not be rejected at the 0.01 level of significance if it was not rejected at the 0.05 level.
Q44: Match the List-I with List-II
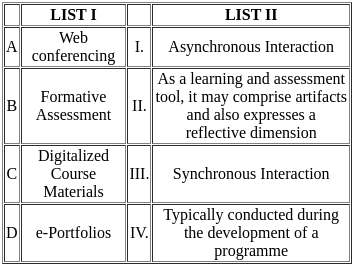
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II'
Web conferencing (A-III):
- Web conferencing refers to online meetings or presentations conducted via the internet in real-time.
- This type of interaction is synchronous, meaning participants interact simultaneously.
Formative Assessment (B-IV):
- Formative assessment is typically carried out during the development of a program or course.
- Its main purpose is to monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback that can be used to improve the teaching and learning process.
Digitalized Course Materials (C-I):
- These materials include digital versions of textbooks, lecture notes, videos, and other resources used in the learning process.
- They are often used for asynchronous interaction, where learners can access and engage with the content at their own pace.
e-Portfolios (D-II):
- An e-portfolio is a digital collection of artifacts that demonstrate a learner's achievements and learning progress.
- It also includes a reflective dimension, where learners can reflect on their learning experiences and growth.
Q45: Select the correct statement in the following:
(a) The state spends six percent of GDP on education.
(b) Education is a subject matter of the state government.
(c) The State of Karnataka has established its own State Education Policy Commission to review NEP and give alternative policy for the state.
(d) Education Cess levied goes to the accounts of the State Government.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'The State of Karnataka has established its own State Education Policy Commission to review NEP and give alternative policy for the state.'
The State of Karnataka has established its own State Education Policy Commission to review NEP and give alternative policy for the state:
- Karnataka, as a state, has taken the initiative to critically review the National Education Policy (NEP) and formulate its own recommendations tailored to the state's needs.
- This move signifies the state's proactive approach in customizing national guidelines to better fit local educational contexts and requirements.
- The establishment of a State Education Policy Commission demonstrates Karnataka's commitment to enhancing the quality and relevance of education within the state.
Other Related Points
The state spends six percent of GDP on education:
- This statement is incorrect as the actual expenditure on education varies by state and is not uniformly six percent of GDP across all states.
- Spending on education is a significant indicator of a state's commitment to improving educational infrastructure and services, but the percentage can differ based on budgetary allocations and priorities.
Education is a subject matter of the state government:
- This statement is partially incorrect. Education is actually a subject on the Concurrent List of the Indian Constitution, meaning both the central and state governments can legislate on it.
- However, the central government plays a significant role in formulating policies and providing funding, while state governments are primarily responsible for implementation.
Education Cess levied goes to the accounts of the State Government:
- This statement is incorrect. The education cess collected by the central government is primarily utilized for funding central schemes in education, such as the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan and Mid-Day Meal Scheme.
- The funds from education cess do not directly go into the state government's accounts but are allocated to educational initiatives as per national priorities.
Q46: Choose the correct order of events for a true experimental design:
A. Random selection of total sample units
B. Exposure to the treatment
C. Identification of population
D. Random assignment of treatment to one group
E. Random division of sampled units into two (one for experimental and one for control) groups
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, A, E, D, B
(b) C, E, A, B, D
(c) C, E, A, D, B
(d) B, C, E, A, D
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, A, E, D, B'
Steps in a True Experimental Design:
- Identification of population (C): The first step is to clearly define the population from which you will draw your sample units. This ensures that your study results can be generalized to this population.
- Random selection of total sample units (A): After identifying the population, you randomly select a sample from this population to avoid selection bias.
- Random division of sampled units into two groups (E): The sample units are then randomly divided into two groups – one for the experimental treatment and one for the control.
- Random assignment of treatment to one group (D): Within these groups, the treatment is randomly assigned to one group to ensure that any differences observed are due to the treatment itself and not other factors.
- Exposure to the treatment (B): Finally, the experimental group is exposed to the treatment, while the control group is not, allowing for comparison and analysis of the treatment's effect.
Q47: Which of the following is NOT correct about ANOVA?
(a) The F-ratio is computed in ANOVA.
(b) It is a ratio between 'between-groups variance' and 'within-group variance'
(c) The 'between-groups variance' represents the sampling error in the distributions.
(d) F-ratio is named after Sir Ronald Fisher.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'The 'between-groups variance' represents the sampling error in the distributions.'
ANOVA (Analysis of Variance):
- ANOVA is a statistical method used to compare means of three or more samples to understand if at least one sample mean is significantly different from the others.
- The F-ratio is computed in ANOVA to determine the significance of the differences between groups.
- It is a ratio between 'between-groups variance' and 'within-group variance'.
Between-Groups Variance:
- This represents the variation due to the interaction between the different groups (or treatments).
- It is not the sampling error but rather the systematic differences between the groups being compared.
- The F-ratio helps in assessing if these differences are significant.
Within-Group Variance:
- This represents the variation within each group or sample and is due to random sampling error.
- It measures the degree of variability that occurs within each group.
F-Ratio:
- The F-ratio is named after Sir Ronald Fisher, a pioneer in the field of statistics.
- The F-ratio is calculated as the ratio of the between-groups variance to the within-group variance.
- If the F-ratio is significantly larger than 1, it suggests that the between-groups variance is much greater than the within-group variance, indicating a significant difference between the groups.
Other Related Points
ANOVA Assumptions:
- Independence of observations: The samples must be independent of each other.
- Normality: The data should follow a normal distribution.
- Homogeneity of variances: The variances among the groups should be approximately equal.
Types of ANOVA:
- One-way ANOVA: Used when comparing means of three or more independent groups based on one factor.
- Two-way ANOVA: Used when comparing means based on two factors, which allows for the assessment of interaction effects between the factors.
Q48: Who was the Chairperson of National Commission on Teachers (1983)?
(a) Prof. Yashpal
(b) Dr. Ram Murti
(c) Sam Pitroda
(d) Prof. D. P. Chattopadhyay
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Prof. D. P. Chattopadhyay
Prof. D. P. Chattopadhyay:
- Prof. D. P. Chattopadhyay was the Chairperson of the National Commission on Teachers in 1983.
- The National Commission on Teachers was constituted to examine various issues related to teacher education, recruitment, and service conditions in India.
- The commission aimed to improve the quality of education by addressing the challenges faced by teachers and proposing measures for their professional development.
Other Related Points
Prof. Yashpal:
- Prof. Yashpal was a renowned Indian scientist and educator, but he was not the Chairperson of the National Commission on Teachers in 1983.
- He is best known for his contributions to science education and his role in the Yashpal Committee, which focused on school education reforms in the 1990s.
Dr. Ram Murti:
- Dr. Ram Murti was involved in various educational reforms, but he did not serve as the Chairperson of the National Commission on Teachers in 1983.
- He chaired the Ram Murti Committee in 1990, which focused on reforms in higher education in India.
Sam Pitroda:
- Sam Pitroda is a well-known telecom engineer and policymaker, particularly recognized for his work in telecommunications and technology in India.
- He did not have a direct role in the National Commission on Teachers in 1983.
Q49: Which of the following statements are TRUE for Signalling Theory of Economics of Education?
A. Michael Spence is one of the theorist.
B. Individuals have different levels of innate productivity.
C. Education helps to enhance the innate levels of productivity.
D. Education helps to identify different levels of productivity
E. More years of schooling lead to more productivity.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) C and E only
(c) B, C, D and E only
(d) A, B, C and D only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B and D only'
Signalling Theory of Economics of Education:
- This theory, proposed by Michael Spence, suggests that education serves as a signal to employers about the inherent productivity levels of potential employees.
- The theory assumes that individuals have different levels of innate productivity, which are not directly observable by employers.
- Education acts as a mechanism to reveal or signal these productivity differences to employers.
Michael Spence:
- Michael Spence is one of the key theorists behind the Signalling Theory.
- His work emphasizes how education serves as a signal rather than directly enhancing productivity.
Individuals' Innate Productivity:
- The theory recognizes that individuals have different levels of innate productivity that are not easily observable.
Role of Education in Identifying Productivity:
- Education helps to identify different levels of productivity, acting as a signal to employers about an individual's potential productivity.
Other Related Points
Incorrect Statements:
- Education Enhances Productivity: The Signalling Theory does not focus on education enhancing innate productivity (Option C), but rather on education serving as a signal of existing productivity levels.
- More Schooling Leads to More Productivity: While more years of schooling may signal higher productivity, the theory does not assert that education directly increases productivity levels (Option E).
Human Capital Theory:
- This theory contrasts with Signalling Theory by proposing that education directly enhances an individual's productivity and skills.
- While Signalling Theory focuses on the informational role of education, Human Capital Theory emphasizes the developmental role.
Q50: Arrange the following chronologically:
A. Hunter Commission
B. The Education Dispatch
C. Grant's Plan
D. Establishment of Universities at Calcutta, Bombay and Madras
E. Charter allocating one lakh rupees
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, B, E, D, A
(b) A, C, D, E, B
(c) A, E, C, B, D
(d) C, E, B, D, A
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, E, B, D, A'
C – Grant's Plan (1792–1797)
E – Charter Act ₹1 lakh (1813)
B – Wood’s Dispatch (1854)
D – Univ. of Calcutta, Bombay, Madras (1857)
A – Hunter Commission (1882)
Significance of Educational Reforms:
- These educational reforms laid the foundation for modern education in India and have had a lasting impact on the country’s educational landscape.
- The establishment of universities and the emphasis on Western education helped in the creation of a new class of educated Indians who played a crucial role in India’s independence movement.
Q51: Which of the following does not come under the updated D & M IS Success Model (2003)?
(a) Information Quality
(b) System Quality
(c) Net Benefits
(d) Organisational Impact
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Organisational Impact.'
Updated D&M IS Success Model (2003):
- The DeLone and McLean Information Systems (D&M IS) Success Model, initially proposed in 1992 and updated in 2003, is a framework for measuring the success of information systems.
- The updated model includes six dimensions: Information Quality, System Quality, Service Quality, Use, User Satisfaction, and Net Benefits.
- The model helps organizations understand and assess the effectiveness of their information systems.
Information Quality:
- Refers to the quality of the information produced by the system, including accuracy, completeness, relevance, and timeliness.
- High information quality ensures that users can make better decisions and perform tasks more efficiently.
System Quality:
- Measures the performance of the information system itself, including its reliability, flexibility, and ease of use.
- A higher system quality leads to greater user satisfaction and higher usage rates.
Net Benefits:
- Represents the overall impact of the information system on the organization, including improved decision-making, increased productivity, and competitive advantage.
- Net benefits are often considered the ultimate measure of information system success.
Other Related Points
Organisational Impact:
- The term 'Organisational Impact' is not explicitly included in the updated D&M IS Success Model (2003).
- While the model does assess the impact of information systems on organizations, this is covered under 'Net Benefits,' which includes organizational improvements as one of its components.
- Focusing on 'Net Benefits' provides a more comprehensive view, encompassing various positive outcomes of the information system, not just organizational impact.
Q52: Which of the following are NOT steps of Instructional Technology?
A. Selection of Instructional material
B. Suggestions for improvements
C. Selection of Appropriate Alternative
D. Reinforced Practice
E. Description of Restrictions
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, D and E only'
Steps of Instructional Technology:
- Selection of Instructional Material (A): This step involves choosing the appropriate materials to support the instructional goals and objectives.
- Suggestions for Improvements (B): This step involves providing feedback and recommendations to enhance the effectiveness of instructional strategies and materials.
Non-Inclusive Steps:
- Selection of Appropriate Alternative (C): This step is not a standard part of instructional technology as it pertains more to decision-making processes outside the educational scope.
- Reinforced Practice (D): While practice is important in learning, reinforced practice specifically is not typically listed as a distinct step in instructional technology.
- Description of Restrictions (E): This step is not relevant to instructional technology, as it refers to outlining constraints rather than focusing on the instructional design and delivery process.
Other Related Points
Instructional Technology Overview:
- Instructional technology refers to the systematic application of technology and pedagogical principles to enhance learning and teaching.
- It involves the design, implementation, and evaluation of instructional materials and activities to improve learning outcomes.
Importance of Feedback:
- Suggestions for improvements are crucial as they provide constructive feedback to refine and optimize instructional strategies.
- Continuous improvement ensures that instructional materials remain effective and relevant.
Q53: Among the following which is NOT an advantage of SWOT:
(a) It is easy to understand
(b) It is easy to communicate
(c) Data collection, evaluation and decision-making are easily confused
(d) Applicable to many levels in an organization
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Data collection, evaluation and decision-making are easily confused'
SWOT Analysis:
- SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a business or project.
- It helps organizations understand internal and external factors that could impact their objectives.
- The goal of SWOT analysis is to create a clear picture of the current situation and develop strategies to address potential challenges and leverage opportunities.
Easy to Understand:
- SWOT analysis is straightforward and simple, making it easy for stakeholders at all levels to comprehend.
- Its intuitive nature allows quick grasping of the concept without requiring extensive training or specialized knowledge.
Easy to Communicate:
- The structure of SWOT analysis makes it easy to communicate findings and strategies to others within the organization.
- It provides a clear and organized framework that facilitates discussion and decision-making.
Applicable to Many Levels in an Organization:
- SWOT analysis can be used at various organizational levels, from individual projects to company-wide strategic planning.
- It is versatile and can be tailored to suit different contexts and objectives.
Other Related Points
Data Collection, Evaluation and Decision-Making are Easily Confused:
- This statement highlights a common pitfall in SWOT analysis where the process of gathering data, evaluating it, and making decisions can become conflated, leading to confusion.
- It emphasizes the need for clear separation of these steps to ensure accurate and effective analysis and strategic planning.
- Proper training and structured approach can mitigate this issue and enhance the effectiveness of the SWOT analysis.
Q54: A teacher conducts an assessment in her class and then adjusts the next lesson to meet the students' needs. She is doing:
(a) Assessment of learning
(b) Assessment for learning
(c) Assessment as learning
(d) Assessment through learning
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Assessment for learning'
Assessment for learning:
- Refers to the practice of using assessments to provide feedback and guide the teaching and learning process.
- Helps teachers to understand students' current knowledge, skills, and abilities, and adjust their teaching strategies accordingly.
- Aims at improving students' learning outcomes by identifying their needs and addressing them promptly.
- Involves continuous and formative assessments rather than summative assessments.
Other Related Points
Assessment of learning:
- Summative in nature and usually conducted at the end of a learning period to measure what students have learned.
- Often used for grading or ranking students rather than to inform teaching practices.
Assessment as learning:
- Focuses on the role of the student in the assessment process, encouraging self-assessment and reflection.
- Helps students develop metacognitive skills and take responsibility for their own learning.
Assessment through learning:
- Not a commonly recognized term in educational assessment frameworks.
- May imply that learning itself is a form of assessment, but lacks the structured feedback mechanism inherent in 'assessment for learning.'
Q55: Which of the following statements are TRUE?
A. Bismillah - a ritual was performed at the age of 4 years 4 month and 4 days in Muslim Education.
B. Pabbaja - a ritual performed at the age of 8 years in Buddhist education
C. Upasampada - a ritual post-education for permanent membership of a Sangh in Buddhist education
D. Upanayana- a ritual to begin education at the ages of 8, 11, 12 and 15 years of age for brahmins, kshatriyas, Vaisyas and Shudras
E. Ballabhi and Jagdalla - Centres of Vedic education
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, B, D and E only
(c) D and E only
(d) B, C, D and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, and C only
Bismillah - a ritual was performed at the age of 4 years 4 months and 4 days in Muslim Education:
- This ritual marks the beginning of a child's formal education in Islamic tradition.
- The child starts learning to read the Quran.
Pabbaja - a ritual performed at the age of 8 years in Buddhist education:
- This is an initial ordination ceremony for young boys entering monastic life.
- It marks the start of their formal religious education and training.
Upasampada - a ritual post-education for permanent membership of a Sangh in Buddhist education:
- This is the higher ordination that allows a novice monk to become a fully ordained monk.
- It signifies full membership in the Buddhist monastic community (Sangha).
Other Related Points
Upanayana - a ritual to begin education at the age of 8, 11, 12 and 15 years of age for brahmins, kshatriyas, Vaisyas and Shudras:
- This statement is partially incorrect. Upanayana is indeed a ritual to begin education, but traditionally, it was performed only for Brahmins, Kshatriyas, and Vaishyas, not Shudras.
- The ages mentioned (8, 11, and 12) are accurate for Brahmins, Kshatriyas, and Vaishyas respectively.
Ballabhi and Jagdalla - Centres of Vedic education:
- This statement is incorrect. Ballabhi and Jagdalla were not centers of Vedic education; rather, they were prominent centers of Buddhist learning.
- Notable centers of Vedic education included places like Takshashila and Nalanda.
Q56: Which of the following statements are TRUE as per Functionalist Perspective on Sociology of Education?
A. The major function of education is the transmission of society's norms and values.
B. School serves a function that cannot be provided either by family or peers.
C. School is a focal socializing agency.
D. Educational system is a part of superstructure and reproduces ruling ideology.
E. Mass education began in industrial society and is an established requirement of an industrial society.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, D and E only
(b) A, C and D only
(c) B, C, D and E only
(d) A, B, C and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, C and E only'
Functionalist Perspective on Sociology of Education:
- A. Transmission of society's norms and values: The major function of education is to transmit society's norms and values to the younger generations, ensuring cultural continuity.
- B. Unique function of schools: Schools serve a function that cannot be provided either by family or peers, such as formal education, standardized testing, and preparation for future societal roles.
- C. Focal socializing agency: Schools act as a focal socializing agency, where children learn to interact with others, follow rules, and develop social skills that are crucial for societal integration.
- E. Mass education in industrial society: Mass education began in industrial society and is an established requirement of an industrial society, providing a trained and skilled workforce.
Q57: Identify those which best represent the benefits of implementing six-sigma in teacher education?
A. Improved teacher effectiveness.
B. Enhanced student-learning outcomes.
C. Increased Administrative work load.
D. More efficient use of Resources.
E. Greater standardization of teaching practices.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, B and E only
(b) A, B and E only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) A, C, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B, and D only'
Improved teacher effectiveness:
- Six-Sigma methodologies focus on reducing variability and improving processes, which can lead to more effective teaching strategies and methods.
Enhanced student-learning outcomes:
- By improving teaching effectiveness and optimizing educational processes, Six-Sigma can directly contribute to better student performance and learning outcomes.
More efficient use of resources:
- Six-Sigma aims to eliminate waste and optimize resources, leading to more efficient use of time, materials, and financial resources in educational settings.
Other Related Points
Greater standardization of teaching practices:
- While standardization can be a benefit, it may not always be desirable in teaching, as it can limit creativity and adaptability in the classroom. Therefore, it is not highlighted as a primary benefit of Six-Sigma in teacher education.
Increased Administrative workload:
- Six-Sigma implementation can initially increase administrative tasks due to data collection and process analysis. However, this is generally seen as a temporary phase rather than a long-term benefit.
Q58: Choose the correct order for the steps involved in the process of construction of a standardized test:
A. Writing the items
B. Pre-try out
C. Dress-rehearsal
D. Planning of the test
E. Final try out
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, B, C, E
(b) A, D, C, B, E
(c) D, A, B, E, C
(d) D, A, C, B, E
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'D, A, B, E, C'
Planning of the test (D):
- This is the initial step, where the objectives of the test, the content to be covered, and the format of the test are decided.
- This phase includes defining the purpose of the test, target audience, and the skills or knowledge to be assessed.
Writing the items (A):
- Once the planning is complete, individual test items or questions are written.
- Items should align with the objectives and content outlined in the planning phase.
Pre-try out (B):
- In this step, the initial set of test items is administered to a small group to identify any issues.
- Feedback is collected to revise and improve the items.
Final try out (E):
- This step involves administering the revised test to a larger sample that is representative of the target population.
- The purpose is to gather data on the test's reliability and validity.
Dress-rehearsal (C):
- The final step involves a full-scale administration of the test to ensure everything works smoothly.
- This is essentially a pilot test to fine-tune logistics and administration procedures before the actual deployment.
Q59: Which model of leadership relies on reward and punishments to motivate followers?
(a) Transformational
(b) Democratic
(c) Transactional
(d) Servant
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Transactional Leadership'
Transactional Leadership:
- Transactional leadership is a style that relies on rewards and punishments to motivate followers.
- This approach focuses on predefined goals and objectives, with leaders providing clear instructions and expectations.
- Leaders using this style often monitor followers' performance and provide feedback based on outcomes.
- Positive performance is rewarded (e.g., bonuses, promotions), while negative performance is punished (e.g., reprimands, demotions).
Other Related Points
Transformational Leadership:
- Transformational leadership focuses on inspiring and motivating followers to achieve their highest potential and to drive change.
- Leaders using this style often emphasize vision, innovation, and fostering a strong sense of purpose among their followers.
Democratic Leadership:
- Democratic leadership, also known as participative leadership, involves leaders making decisions based on the input and consensus of the group.
- This style values collaboration and open communication, allowing team members to have a say in the decision-making process.
Servant Leadership:
- Servant leadership prioritizes the needs of followers, with leaders acting as stewards who support and empower their team members.
- Leaders using this approach often focus on personal growth, well-being, and the development of others.
Q60: Organise sequentially the components of an effective curriculum development process:
A. Defining course goals.
B. Developing assessment items to measure student progress.
C. Identifying key issues and trends in the content area.
D. Determining the success of the program.
E. Identifying resource materials.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, B, A, E, D
(b) B, A, E, D, C
(c) A, B, C, D, E
(d) C, A, E, B, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, A, E, B, D'
Identifying key issues and trends in the content area (C):
- This initial step involves researching and understanding the latest developments and trends in the subject matter. This foundational knowledge helps in creating a relevant and up-to-date curriculum.
Defining course goals (A):
- After understanding the key issues and trends, the next step is to establish clear and achievable goals for the course. These goals guide the direction and outcomes of the curriculum.
Identifying resource materials (E):
- Once the goals are set, the necessary resources and materials that will support the curriculum must be identified. This includes textbooks, online resources, and other instructional materials.
Developing assessment items to measure student progress (B):
- Assessments are then created to evaluate whether students are meeting the course goals. These can include tests, quizzes, projects, and other evaluative tools.
Determining the success of the program (D):
- The final step is to assess the effectiveness of the curriculum. This involves reviewing student performance data, feedback, and other metrics to determine if the course goals were achieved.
Q61: Islamic philosophers divide natural/universal expressions in five types:
A. Common Accident
B. Species
C. Property
D. Difference
E. Genus
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) E, A, C, B. D
(b) E, B, D, C, A
(c) A, B, D, E, C
(d) E, D, C, B, A
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'E, B, D, C, A'
Islamic Philosophers' Division of Universal Expressions:
- Islamic philosophers, including notable figures such as Al-Farabi, Avicenna, and Averroes, contributed significantly to metaphysical and logical discussions. They classified universal or natural expressions into five distinct types.
- These classifications help in understanding the essence and existence of entities and their various attributes.
Correct Sequence - E, B, D, C, A:
- Genus (E): The broadest category, representing a general class under which species fall. For example, 'Animal' can be considered a genus.
- Species (B): A more specific category under a genus. For instance, 'Human' is a species under the genus 'Animal'.
- Difference (D): Attributes that distinguish one species from another within the same genus. For example, 'Rationality' differentiates humans from other animals.
- Property (C): Characteristics that necessarily accompany a species but do not define it. An example is 'Laughter' for humans.
- Common Accident (A): Attributes that can exist in any entity without being essential to its essence. For example, 'Being seated' or 'Having a color'.
Q62: Who is known as the Father of Management Process?
(a) Elton Mayo
(b) Abraham H. Maslow
(c) Henry Fayol
(d) Edgar Henry Schein
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Henry Fayol'
Henry Fayol:
- Henry Fayol, a French mining engineer and management theorist, is widely regarded as the 'Father of Management Process'.
- He developed a general theory of business administration that is often called Fayolism.
- Fayol identified five primary functions of management: planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, and controlling.
- His work laid the foundational principles of modern management practices and emphasized the importance of managerial education.
Other Related Points
Elton Mayo:
- Elton Mayo was an Australian psychologist, industrial researcher, and organizational theorist.
- He is best known for his role in the Hawthorne Studies, which laid the groundwork for the human relations movement in management.
- Mayo's work emphasized the importance of social relations and employee well-being in the workplace.
Abraham H. Maslow:
- Abraham H. Maslow was an American psychologist best known for creating Maslow's hierarchy of needs, a theory of psychological health based on fulfilling innate human needs.
- His work is highly influential in the fields of psychology and human resource management but does not directly relate to the management process.
Edgar Henry Schein:
- Edgar Henry Schein is a prominent organizational psychologist known for his work on organizational culture and leadership.
- He introduced the concept of "corporate culture" and developed frameworks for understanding and changing organizational culture.
- While his contributions are significant, they are more focused on organizational development rather than the fundamental management process.
Q63: Arrange following categories of children in order of increasing IQ -
A. Slow learners
B. Moderate Mental Retardation
C. Mild Mental Retardation
D. Profound Mental Retardation
E. Severe Mental Retardation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D. E, B, C, A
(b) E, D, C, B, A
(c) D, B, C, E, A
(d) E, C, A, D, B
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'D, E, B, C, A'
Understanding the IQ levels of different categories of children:
- Profound Mental Retardation: This category includes individuals with an IQ below 20-25. They require intensive support and have severe limitations in their ability to perform daily living activities.
- Severe Mental Retardation: Individuals in this category have an IQ between 20-34. They need close supervision and help with many aspects of daily life, including personal care and communication.
- Moderate Mental Retardation: This category involves individuals with an IQ between 35-49. They can perform simple tasks under supervision but have limited academic abilities and social skills.
- Mild Mental Retardation: Individuals in this category have an IQ between 50-69. They can achieve a fair degree of independence in self-care and practical skills but may struggle with academic work beyond a basic level.
- Slow Learners: This category includes children with an IQ between 70-89. They generally fall behind their peers academically but can function relatively independently in daily life.
Q64: The function of search engine to scour the internet for content, looking over the code/content for each URL they find, is called:
(a) Indexing
(b) Crawling
(c) Ranking
(d) URL
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Crawling'
Crawling:
- Crawling is the process by which search engines scour the internet for content, examining the code/content of each URL they find.
- Search engines use bots, often called spiders or crawlers, to discover new and updated pages to be added to the index.
- This process is fundamental for search engines to gather data about the vast number of web pages available on the internet.
Other Related Points
Indexing:
- Indexing refers to the process of storing and organizing the content found during crawling so that it can be quickly retrieved when needed.
- It involves creating an index, which is a massive database of all the content discovered by the crawlers.
- This is crucial for providing relevant search results in response to user queries.
Ranking:
- Ranking is the process of ordering search results based on their relevance to the user's query.
- Search engines use various algorithms to rank pages, taking into account factors like keyword usage, site structure, and user engagement.
- Although ranking determines the order of search results, it is different from crawling, which is about discovering content.
URL:
- URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator and is the address used to access web pages.
- While URLs are essential for identifying web pages, they are not related to the process of crawling.
- Crawlers discover URLs to visit, but the act of crawling itself involves exploring the content behind those URLs.
Q65: Which component is NOT a part of RMSA initiative?
(a) Construction of new classrooms
(b) Provision of scholarships
(c) Establishment of laboratories
(d) Appointment of additional teaching faculties
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Provision of scholarships'
Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA):
- RMSA is a flagship program by the Government of India aimed at enhancing the quality of secondary education and increasing the enrollment rate in secondary schools across the country.
- The initiative focuses on improving infrastructure, providing better learning environments, and ensuring access to quality education for all students.
Construction of new classrooms:
- One of the primary components of RMSA is the construction of new classrooms to accommodate the increasing number of students and to reduce dropout rates.
- This helps in improving the student-teacher ratio and provides a conducive learning environment.
Establishment of laboratories:
- The establishment of well-equipped laboratories in schools is a crucial part of RMSA to enhance the quality of education in subjects like science and mathematics.
- It ensures that students have hands-on experience and practical knowledge, which is essential for their overall development.
Appointment of additional teaching faculties:
- RMSA also focuses on the appointment of additional teaching faculties to improve the student-teacher ratio and to ensure that students receive personalized attention and quality education.
- This includes hiring qualified and trained teachers, especially in rural and remote areas.
Other Related Points
Provision of scholarships:
- While the provision of scholarships is an important aspect of supporting students' education, it is not a core component of the RMSA initiative.
- Scholarships are generally provided under different schemes and programs aimed at financial assistance for students but are not specifically part of RMSA’s framework.
Other Education Initiatives:
- There are various other educational initiatives by the government such as the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) which focuses on elementary education and scholarship programs like the National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship Scheme (NMMSS).
- These initiatives complement the RMSA by addressing different levels and aspects of the educational system in India.
Q66: 'Core Design' is an example of:
(a) Learner-centered curriculum
(b) Problem-centred curriculum
(c) Subject-centred curriculum
(d) Core-curriculum
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Problem-centred curriculum'.
Problem-centred curriculum:
- Focuses on addressing real-world problems and practical issues.
- Encourages students to develop problem-solving skills and critical thinking.
- Often involves interdisciplinary approaches, integrating knowledge from various subjects to solve complex problems.
- Promotes active learning and student engagement by making learning relevant to students' lives and future careers.
Other Related Points
Learner-centered curriculum:
- Focuses on the needs, interests, and learning styles of students.
- Encourages student autonomy and active participation in the learning process.
- Teachers act as facilitators rather than direct instructors.
Subject-centered curriculum:
- Organizes content around specific subjects or disciplines.
- Emphasizes mastery of subject matter and academic achievement.
- Traditional approach often involving lectures, textbooks, and exams.
Core-curriculum:
- Centers around a set of common knowledge and skills that all students should learn.
- Often includes essential subjects like math, science, and language arts.
- Aims to provide a well-rounded education and ensure a shared foundation of knowledge.
Q67: 3 x 3 factorial design of experiment represents -
(a) Three independent variables with three dependent variables
(b) Two independent variables with three conditions of each
(c) Three independent variables with three conditions of each.
(d) Three independent variables with two conditions of each.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Two independent variables with three conditions of each'
3 x 3 factorial design of experiment:
- In a factorial design, researchers examine the effects of two or more independent variables simultaneously.
- A 3 x 3 design specifically involves two independent variables, each with three levels or conditions.
- This setup results in a total of 9 experimental conditions (3 levels for the first variable multiplied by 3 levels for the second variable).
- It allows researchers to study not only the main effects of each independent variable but also the interaction effect between them.
Other Related Points
Three independent variables with three dependent variables:
- The focus is on the independent variables and their conditions rather than the number of dependent variables.
Three independent variables with three conditions of each:
- A 3 x 3 x 3 design involves three independent variables each having three levels, resulting in 27 conditions (3 x 3 x 3).
Three independent variables with two conditions of each:
- A 2 x 2 x 2 design involves three independent variables each with two levels, resulting in 8 conditions (2 x 2 x 2).
Q68: Mass education, or the idea that anybody and everybody can learn owes its genesis to:
(a) Colonialism
(b) Modernism
(c) Postmodernism
(d) Reformism
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Modernism
Modernism:
- Modernism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, characterized by a shift towards new ways of thinking, including the belief in progress, science, and the capacity for human improvement.
- This period saw the rise of mass education, driven by the idea that education was a tool for societal progress and individual betterment.
- The advent of public schooling systems and the focus on universal education were rooted in modernist ideals.
- Modernism advocated for the democratization of education, making it accessible to all segments of society, regardless of class or background.
Other Related Points
Colonialism:
- While colonial powers did establish educational institutions in their colonies, the primary aim was often to create a class of intermediaries who could assist in administration rather than to provide mass education.
- Colonial education systems were typically limited and exclusive, aimed at serving the needs of the colonial rulers rather than promoting widespread literacy and education.
Postmodernism:
- Postmodernism, arising in the mid to late 20th century, often critiques the grand narratives and ideologies of modernism, including the universalizing tendencies of mass education.
- It emphasizes relativism, diversity, and the deconstruction of established norms, which contrasts with the modernist push for standardized, universal education.
Reformism:
- Reformism refers to efforts to improve existing systems and institutions through gradual change rather than radical transformation.
- While education reforms have played a significant role in expanding access and improving quality, the foundational idea of mass education is more closely aligned with the principles of modernism.
Q69: Curriculum was defined by _______as "a plan for action, or a written document, which includes strategies for achieving desired goals or ends".
(a) Galen Saylor (1970)
(b) Tanner & Tanner (1980)
(c) Tyler and Hilda Taba (1962)
(d) Oliva (1982)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Tyler and Hilda Taba (1962)
Definition by Tyler and Hilda Taba:
Ralph Tyler, in his 1949 work Basic Principles of Curriculum and Instruction, defined curriculum as 'a plan for action, or a written document, which includes strategies for achieving desired goals or ends.' Hilda Taba, in her 1962 work Curriculum Development: Theory and Practice, expanded on Tyler’s framework, emphasizing systematic curriculum planning.
Other Related Points
Galen Saylor (1970):
- Galen Saylor, along with William Alexander, defined curriculum in 1974 as a plan for providing sets of learning opportunities for persons to be educated.
- Their focus was on the opportunities provided rather than the detailed strategies and goals.
Tanner & Tanner (1980):
- Tanner & Tanner defined curriculum as the planned and guided learning experiences and intended outcomes, formulated through systematic reconstruction of knowledge and experiences.
- While similar, this definition places more emphasis on the experiences and outcomes rather than a specific action plan.
Oliva (1982):
- Oliva defined curriculum as a plan or program for all the experiences that the learner encounters under the direction of the school.
- This definition is broader and includes all aspects of the learner's experiences within the educational environment.
Q70: Which amongst the following is NOT a Marxist theorist of Sociology of Education?
(a) Emile Durkheim
(b) Althusser
(c) Gramsci
(d) Bowles and Gintis
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Emile Durkheim
Marxist Theorists in Sociology of Education:
- Marxist theorists focus on how education systems perpetuate class inequalities and serve capitalist interests.
- They argue that education reproduces the ideology of the ruling class and maintains the status quo.
Emile Durkheim:
- Emile Durkheim was a prominent sociologist, but his theories are not rooted in Marxism.
- He viewed education as a means to promote social cohesion and stability, emphasizing the role of education in moral development and integration of individuals into society.
Other Related Points
Althusser:
- Louis Althusser was a Marxist philosopher who argued that educational institutions are part of the Ideological State Apparatus (ISA).
- According to Althusser, schools serve to reproduce class structure by promoting the ideology of the ruling class.
Gramsci:
- Antonio Gramsci, another Marxist theorist, introduced the concept of cultural hegemony.
- Gramsci believed that education is a tool for the dominant class to maintain control by shaping cultural norms and values.
Bowles and Gintis:
- Samuel Bowles and Herbert Gintis are known for their work "Schooling in Capitalist America," which argues that education reproduces social class inequality.
- They introduced the "correspondence principle," suggesting that the structure of schooling mirrors the hierarchical structure of the capitalist workforce.
Q71: Which of the following is NOT a principle of guidance?
(a) Holistic development of an individual
(b) Recognition of individual needs and differences
(c) Non-cognizance of individual differences
(d) Acceptance of individual needs
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Non-cognizance of individual differences'
Holistic development of an individual:
- This principle emphasizes the all-round development of an individual, including physical, emotional, social, and intellectual growth.
- Guidance should address all aspects of a person's life to help them become well-rounded individuals.
Recognition of individual needs and differences:
- This principle highlights the importance of acknowledging that every individual has unique needs and differences.
- Effective guidance takes these differences into account to provide personalized support.
Acceptance of individual needs:
- Accepting individual needs involves understanding and validating the specific requirements and aspirations of each person.
- This principle ensures that guidance is empathetic and supportive of individual goals.
Other Related Points
Non-cognizance of individual differences:
- This is not a principle of guidance. Ignoring individual differences would lead to a one-size-fits-all approach, which is ineffective in addressing the unique needs of each person.
- Guidance should be tailored to the individual, recognizing their specific context and requirements.
Q72: Problem-based Learning (PBL) approach is used for curriculum development as it results in:
(a) Reducing the gap between curriculum and syllabus
(b) Enhancing the employability of learners
(c) filling the gap between academics and practioners
(d) economic growth of the country
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'filling the gap between academics and practitioners'
Problem-based Learning (PBL) Approach:
- PBL is a student-centered pedagogy in which students learn about a subject through the experience of solving an open-ended problem.
- This method is often used in medical education but has also been applied in other disciplines.
- It emphasizes self-directed learning and the application of knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Filling the gap between academics and practitioners:
- PBL integrates theoretical knowledge with practical application, thereby bridging the gap between academic learning and real-world practice.
- Students engage with real-life problems that professionals encounter, making the transition from academic settings to professional environments smoother.
- Through this approach, students develop skills that are directly relevant to their future careers, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and teamwork.
Other Related Points
Reducing the gap between curriculum and syllabus:
- While PBL can enhance the curriculum by making it more relevant and integrated, it does not necessarily address the gap between curriculum (overall educational plan) and syllabus (specific content to be taught).
Enhancing the employability of learners:
- PBL can enhance employability by developing relevant skills, but this is an indirect benefit rather than the primary focus of PBL.
- Employability is influenced by many factors, including market conditions, personal networks, and additional skills beyond those developed through PBL.
Economic growth of the country:
- While a well-educated workforce can contribute to economic growth, PBL's direct impact is primarily on education quality and student preparedness, rather than immediate economic outcomes.
- Economic growth is influenced by a wide range of factors including policy, infrastructure, and global economic conditions.
Q73: Identify the challenges involved in in service teacher education programme:
A. Resistance to change
B. High motivation among teachers
C. Insufficient time allocation
D. Strong institutional support
E. Lack of Resources
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and E only
(b) A, B and E only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) A, B and D only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C and E only'
Resistance to change (A):
- Teachers may be resistant to adopting new methods or updating their skills, often due to comfort with existing practices or skepticism about new approaches.
Insufficient time allocation (C):
- Teachers often have packed schedules, making it challenging to allocate sufficient time for professional development and in-service education programs.
Lack of resources (E):
- Many in-service programs suffer from insufficient funding, lack of access to up-to-date materials, and inadequate infrastructure, hampering their effectiveness.
Other Related Points
High motivation among teachers (B):
- While high motivation is beneficial, it is not a challenge. Instead, it facilitates the success of in-service education programs.
Strong institutional support (D):
- Strong institutional support is also not a challenge. It is a positive factor that can significantly enhance the effectiveness of in-service teacher education programs.
Q74:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(b) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
Functions of school and universities should be different (A-II):
- This view was emphasized by the University Education Commission, which was chaired by Dr. S. Radhakrishnan in 1948-49.
- The commission highlighted the need for a clear differentiation in the roles and functions of schools and universities to cater to different stages of education.
Schools should play a crucial role in developing democratic citizenship (B-IV):
- This principle was underlined by the Secondary Education Commission (1952-53), chaired by Dr. A. Lakshmanswami Mudaliar.
- The commission emphasized the role of secondary education in fostering democratic values and citizenship among students.
Education plays a crucial role in national development (C-I):
- The Kothari Commission (1964-66), officially known as the Indian Education Commission, stressed this point.
- The commission's report suggested that education is vital for national development and modernization.
Learning must not be a burden on the learner (D-III):
- The Yashpal Committee Report (1993), also known as "Learning without Burden," focused on reducing the academic burden on students.
- The report recommended reforms to simplify the curriculum and make learning more enjoyable and meaningful.
Q75: Which of the following are the assumptions of Knowles' theory of Andragogy?
A. Readiness to learn
B. Internally motivated (Motivation to learn)
C. Self-concept
D. Mandatory guidance
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) A and B only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, B and C only'
Knowles' Theory of Andragogy:
- Andragogy refers to the method and practice of teaching adult learners, as opposed to pedagogy, which is focused on teaching children.
- Malcolm Knowles is widely known for his work on adult learning theory, which emphasizes the unique characteristics and needs of adult learners.
Assumptions of Knowles' Theory of Andragogy:
- Readiness to learn: Adults are ready to learn when they experience a need to cope with real-life tasks or problems.
- Internally motivated (Motivation to learn): Adults are mostly driven by internal factors such as self-esteem, curiosity, desire to achieve, and satisfaction of accomplishment.
- Self-concept: As a person matures, their self-concept moves from one of being a dependent personality toward one of being a self-directed human being.
Other Related Points
Mandatory guidance:
- This is not one of the assumptions of Knowles' theory of Andragogy. Adult learning theory emphasizes self-directed learning rather than mandatory guidance.
Q76: Match the List-I with List-II
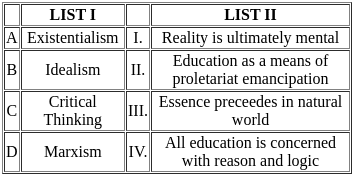
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(b) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
(c) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(d) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II'
Existentialism:
- Existentialism posits that existence precedes essence, meaning individuals create their own meaning and essence through their choices and actions in the natural world.
- It emphasizes individual freedom, choice, and subjective experience.
- Key philosophers include Jean-Paul Sartre and Søren Kierkegaard.
Idealism:
- Idealism is the philosophical theory that reality is fundamentally mental or spiritual rather than physical.
- In education, idealism emphasizes the development of the mind and the pursuit of truth, beauty, and goodness.
- Prominent idealists include Plato and George Berkeley.
Critical Thinking:
- Critical thinking involves the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue to form a judgment.In education, it is concerned with reason and logic, encouraging students to think independently and question assumptions.
- It is essential for problem-solving and decision-making processes.
Marxism:
- Marxism is a socio-political and economic theory originated by Karl Marx, focusing on class struggle and the need for proletariat (working class) emancipation.
- It views education as a means to achieve social change and empower the working class.
- Marxist education aims to develop a critical consciousness in students about societal inequalities.
Q77: Match the List-I with List-II
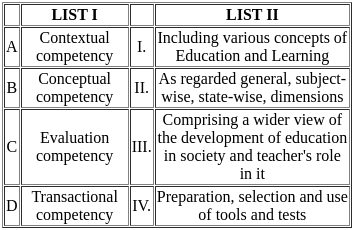
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(b) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II'
Contextual competency (A-III):
- Comprising a wider view of the development of education in society and the teacher's role in it.
- Involves understanding the broader context in which education operates, including socio-cultural, historical, and political dimensions.
Conceptual competency (B-I):
- Including various concepts of Education and Learning.
- Encompasses understanding fundamental theories, principles, and models related to education and pedagogy.
Evaluation competency (C-IV):
- Preparation, selection, and use of tools and tests.
- Involves skills related to assessing and measuring educational outcomes, using various evaluation tools and techniques.
Transactional competency (D-II):
- As regarded general, subject-wise, state-wise, dimensions.
- Refers to the ability to effectively manage and facilitate learning experiences across different subjects and educational settings.
Q78: Which of these accurately reflect the limitations of cost benefit analysis in education?
A. Difficulty in quantifying non-monetary benefits.
B. Short-term focus on costs.
C. Overemphasis on quantitative data.
D. Inclusion in intangible cost.
E. Lack of consideration for long-term outcomes.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) A, D and E only
(c) A, C and E only
(d) A, B and D only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'A, C, and E only.'
Limitations of Cost-Benefit Analysis in Education:
- Difficulty in quantifying non-monetary benefits (Option A): Non-monetary benefits such as improved quality of life, increased civic participation, and enhanced social cohesion are challenging to measure and incorporate into cost-benefit analysis.
- Overemphasis on quantitative data (Option C): Cost-benefit analysis often relies heavily on quantitative data, potentially neglecting qualitative aspects that are crucial in educational contexts, such as student well-being and teacher satisfaction.
- Lack of consideration for long-term outcomes (Option E): Cost-benefit analysis may focus more on immediate costs and benefits, overlooking the long-term impacts of educational investments, which can be significant but harder to measure.
Other Related Points
Short-term focus on costs (Option B):
- This option is incorrect as the primary issue is not the short-term focus on costs but rather the broader challenges in capturing the full scope of benefits and costs in education.
Inclusion of intangible costs (Option D):
- This option is incorrect because including intangible costs would actually enhance the analysis rather than being a limitation. The real issue is the difficulty in accurately measuring these intangible factors.
Q79: Which of the following statements are correct?
A. Gagne has classified learning into Six (06) types in a hierarchical order.
B. The study of instrumental conditioning started from the puzzle box experiments on cats by Skinner.
C. The law of disuse states that other things being equal, when a modifiable connection between stimulus - response (S-R) is not made over a period of time, the strength of that connection is weakened.
D. Hull's theory of learning is called 'Drive-Reduction Theory'.
E. Shaping is the most important mechanism used in classical conditioning.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) B and D only
(c) A and E only
(d) C and D only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'C and D only'
The law of disuse:
- States that other things being equal, when a modifiable connection between stimulus and response (S-R) is not made over a period of time, the strength of that connection is weakened.
- This principle was formulated by Edward Thorndike as part of his theory of learning.
Hull's Drive-Reduction Theory:
- Clark Hull proposed that learning is a function of drive reduction. Drives are internal states of arousal or tension which must be reduced.
- According to Hull, behaviors are learned because they lead to the reduction of drives, which in turn reinforces the behavior.
Other Related Points
Gagne's Classification of Learning:
- Gagne classified learning into eight types, not six, in a hierarchical order. These include signal learning, stimulus-response learning, chaining, verbal association, discrimination learning, concept learning, rule learning, and problem-solving.
Instrumental Conditioning and Puzzle Box Experiments:
- The study of instrumental conditioning began with Edward Thorndike, not Skinner. Thorndike used puzzle box experiments with cats to formulate the Law of Effect.
- B.F. Skinner later expanded on these ideas with his operant conditioning theory using the Skinner box, focusing on reinforcement and punishment.
Shaping in Classical Conditioning:
- Shaping is a technique used in operant conditioning, not classical conditioning. It involves reinforcing successive approximations of a desired behavior.
- In classical conditioning, the focus is on associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response.
Q80: The correct sequence of functions of management is:
A. Directing
B. Organising
C. Planning
D. Controlling
E. Staffing
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, B, A, E, D
(b) C, B, E, A, D
(c) A, C, B, E, D
(d) A, D, B, E, C
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, B, E, A, D'
Correct Sequence of Functions of Management:
- Planning (C): The first step in the management process involves setting objectives and determining the best course of action to achieve them. This stage is crucial for outlining the direction and strategy of the organization.
- Organising (B): Once plans are made, resources must be organized to implement the plan. This involves structuring the organization, allocating resources, and assigning tasks to achieve the planned objectives.
- Staffing (E): This function involves recruiting, selecting, training, and placing the right people in the right positions within the organization to ensure that it can achieve its goals.
- Directing (A): This step involves leading, guiding, and motivating employees to perform their tasks efficiently and effectively. It includes communicating with employees, resolving conflicts, and providing leadership.
- Controlling (D): The final step involves monitoring and evaluating the progress towards the organizational goals. It includes setting performance standards, measuring actual performance, and taking corrective actions if necessary.
Q81: The main difference between Galloway's system of interaction analysis and Flanders interaction analysis is :
(a) Augmentation and integration of non-verbal communication aspects by Galloway.
(b) Removal of verbal communication aspects by Galloway.
(c) Removal of non-verbal communication aspects by Galloway.
(d) Augmentation and integration of non-verbal communication aspects by Flander.
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'Augmentation and integration of non-verbal communication aspects by Galloway.'
Augmentation and integration of non-verbal communication aspects by Galloway:
- Galloway’s system of interaction analysis incorporates non-verbal communication, recognizing its importance in understanding the full scope of classroom interactions.
- This inclusion allows for a more comprehensive analysis of the dynamics between teachers and students, considering gestures, facial expressions, and other non-verbal cues.
- By integrating non-verbal communication, Galloway's system provides a richer and more nuanced understanding of classroom behavior and interaction.
Other Related Points
Removal of verbal communication aspects by Galloway:
- This option is incorrect because Galloway did not remove verbal communication aspects but rather augmented the analysis framework to include non-verbal elements.
Removal of non-verbal communication aspects by Galloway:
- This is incorrect as Galloway actually integrated non-verbal communication aspects, not removed them.
Augmentation and integration of non-verbal communication aspects by Flander:
- This is incorrect as Flander's interaction analysis primarily focuses on verbal communication and does not emphasize non-verbal aspects as Galloway’s system does.
Q82: Which of the following is NOT a quadrant of MOOCs?
(a) e-Tutorial
(b) e-Content
(c) Web resources
(d) Assessment by the Tutor
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Assessment by the Tutor'
MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses):
- MOOCs are online courses aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the web.
- They provide a flexible way to learn new skills and deliver quality educational experiences to a broad audience.
Quadrants of MOOCs:
- e-Tutorial: This includes video lectures or tutorials to help students understand the course material.
- e-Content: This involves reading materials, reference content, and other multimedia resources that supplement the learning process.
- Web Resources: This quadrant provides additional links and resources from the web, including articles, blogs, and videos relevant to the course content.
- Assessment by the Tutor: This is NOT a standard quadrant of MOOCs. Typically, assessments in MOOCs are automated and include quizzes, peer-reviewed assignments, and other forms of self-assessment.
Other Related Points
Evaluation in MOOCs:
- Evaluation methods in MOOCs typically include automated quizzes, peer-reviewed assignments, and self-assessment tools.
- These methods are designed to handle large numbers of students efficiently and provide timely feedback.
Benefits of MOOCs:
- MOOCs offer flexibility in learning, allowing students to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule.
- They provide access to high-quality education from reputable institutions, often for free or at a low cost.
Challenges of MOOCs:
- High dropout rates are a common challenge, as students may lack the motivation or support to complete the course.
- Ensuring the quality and credibility of assessments can be difficult with the large scale of participants.
Q83: These are dominant traits of one's personality which may dominate personality to such an extent that the person may become known for those traits only.
(a) Secondary Traits
(b) Learning Traits
(c) Cardinal Traits
(d) Central Traits
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Cardinal Traits'
Cardinal Traits:
- Cardinal traits are the dominant traits that shape a person's behavior and personality to such an extent that the person becomes known for these traits.
- These traits are rare and tend to develop later in life.
- Examples include traits like altruism, narcissism, or Machiavellianism.
Other Related Points
Secondary Traits:
- These are traits that are not as dominant as central or cardinal traits but still influence behavior.
- They are more situational and less consistent across different contexts.
Learning Traits:
- This term is not typically used in personality psychology.
- It may refer to traits acquired through learning and experience, but it is not a recognized category in trait theory.
Central Traits:
- Central traits are general characteristics that form the basic foundation of personality.
- These traits are not as overwhelming as cardinal traits but are more noticeable than secondary traits.
- Examples include honesty, sociability, and shyness.
Q84: Which of the following is related to Web 2.0?
(a) Read only pages
(b) Semantic Integration and Data Interoperability
(c) Social Networking and User Generated Content
(d) Advance Virtual Reality
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Social Networking and User Generated Content'
Social Networking and User Generated Content:
- Web 2.0 is characterized by the shift from static, read-only web pages to dynamic and interactive platforms where users can create, share, and collaborate on content.
- Examples include social networking sites like Facebook, Twitter, and platforms like YouTube and Wikipedia, which rely heavily on user-generated content.
- This era of the web has enabled greater interaction and collaboration among users, leading to the growth of online communities and social networks.
Other Related Points
Read only pages:
- Read-only pages are characteristic of Web 1.0, the early stage of the internet, where content was static and users could only view information without interacting with it.
- Web 1.0 lacked the interactive and social features that define Web 2.0.
Semantic Integration and Data Interoperability:
- These concepts are more closely related to Web 3.0, also known as the Semantic Web, which aims to create a more intelligent and connected web by enabling machines to understand and process data.
- Web 3.0 focuses on data integration and interoperability, making it easier for different systems to work together.
Advance Virtual Reality:
- While virtual reality (VR) is a growing field, it is not specifically related to Web 2.0. VR is more aligned with advancements in technology that span multiple phases of the web.
- VR focuses on creating immersive digital experiences, which is more a part of the broader technological evolution rather than a specific web phase.
Q85: The correct sequence of consequential leadership style of Managerial Grid is:
A. Country Club
B. Team Management
C. Impoverished Management
D. Authority compliance
E. Middle-of-the Road
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, E, C, D
(b) B, C, D, A, E
(c) D, A, B, C, E
(d) C, A, D, E, B
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'C, A, D, E, B'
Managerial Grid:
- The Managerial Grid, developed by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton, is a model used to identify a variety of leadership styles based on a manager's concern for people and concern for production.
- The grid features five major styles: Impoverished Management, Country Club Management, Authority Compliance, Middle-of-the-Road Management, and Team Management.
Sequence Explanation:
- Impoverished Management (C): This style shows low concern for both people and production, leading to minimal effort and often ineffective leadership.
- Country Club Management (A): Here, there is a high concern for people but low concern for production, resulting in a comfortable and friendly environment but potentially poor performance.
- Authority Compliance (D): This style emphasizes high concern for production and low concern for people, focusing on efficiency and results at the expense of team morale.
- Middle-of-the-Road Management (E): This balanced approach shows moderate concern for both people and production, striving for a satisfactory performance without excelling in either area.
- Team Management (B): This ideal style exhibits high concern for both people and production, aiming for high performance through teamwork and mutual respect.
Q86: What leads to curriculum change?
A. National priorities
B. Job placement
C. Socio-cultural context
D. Availability of effective teachers
E. Government ideology
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Only B, C and E
(b) Only B, C and D
(c) Only A, C and E
(d) Only A, B and E
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Only A, C and E'.
National priorities:
- National priorities often drive curriculum change to align education with the country's development goals and to address emerging needs in areas such as technology, economy, and social development.
- For instance, a country focusing on technological advancement may integrate more STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) subjects into the curriculum.
Socio-cultural context:
- Socio-cultural context influences curriculum change to ensure that the education system reflects the values, traditions, and social norms of the society.
- Changes in societal attitudes, such as increased emphasis on gender equality or environmental sustainability, can lead to corresponding changes in the curriculum.
Government ideology:
- Government ideology significantly impacts curriculum change as the ruling party or coalition's policies and beliefs often shape educational priorities and content.
- For example, a government with a focus on nationalism may emphasize history and civic education that promotes national identity and pride.
Other Related Points
Job placement:
- While job placement is an important outcome of education, it is not a direct factor that leads to curriculum change. It might influence changes indirectly through national priorities or socio-economic demands.
Availability of effective teachers:
- The availability of effective teachers is crucial for the implementation of the curriculum but is not a primary driver of curriculum change itself. It can influence the feasibility and success of new curricular initiatives.
Q87: The correct sequence of the five steps of Morrison's teaching model is:
A. Recitation
B. Organisation
C. Assimilation
D. Presentation
E. Exploration
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, C, A, B, E
(b) B, A, C, D, E
(c) E, D, C, B, A
(d) E, D, C, A, B
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'E, D, C, B, A'
Morrison's Teaching Model:
- Morrison's teaching model is a systematic approach to education designed to enhance the learning process and ensure effective knowledge transfer.
- The model consists of five key steps: Exploration, Presentation, Assimilation, Organization, and Recitation.
Correct Sequence:
- Exploration: This is the initial stage where learners are introduced to the new material, stimulating their curiosity and interest.
- Presentation: In this stage, the teacher presents the new content systematically and clearly.
- Assimilation: Students process and internalize the information presented to them.
- Organization: Learners organize the assimilated information to make sense of it and relate it to previous knowledge.
- Recitation: This final stage involves students recalling and applying the new knowledge through activities and assessments.
Q88: The Dave Committee report is especially focused on:
(a) Minimum Levels of Learning (M.L.L.) at Secondary Level
(b) Minimum Levels of Learning (M.L.L.) at Primary Level
(c) Art and Craft Education at Primary Level
(d) Early Childhood Education
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Minimum Levels of Learning (M.L.L.) at Primary Level'
Minimum Levels of Learning (M.L.L.) at Primary Level:
- The Dave Committee report was primarily focused on establishing Minimum Levels of Learning (M.L.L.) at the primary school level in India.
- M.L.L. refers to the essential learning outcomes that all students should achieve by the end of a particular grade or educational stage.
- The aim is to ensure that all children acquire basic literacy, numeracy, and other foundational skills, which are critical for their future educational success.
- The committee emphasized standardizing learning outcomes to address disparities in educational quality across different regions and schools.
Other Related Points
Minimum Levels of Learning (M.L.L.) at Secondary Level:
- Dave Committee's primary focus was on the primary level, not the secondary level.
- While secondary education is important, the foundational skills targeted by M.L.L. are most crucial at the primary level.
Art and Craft Education at Primary Level:
- Dave Committee report was not focused specifically on art and craft education.
- While art and craft are important for holistic development, the committee's concern was more about basic literacy and numeracy skills.
Early Childhood Education:
- Early childhood education focuses on the developmental needs of children before they enter formal schooling, whereas the Dave Committee's focus was on primary education levels.
Q89: Match the List-I with List-II
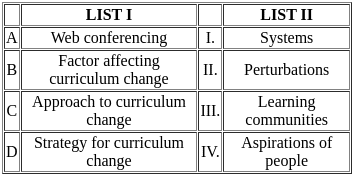
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(b) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(d) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
A-II: Web conferencing - Perturbations
- Web conferencing creates a dynamic environment that can lead to perturbations, such as disruptions or challenges in collaborative systems.
- These perturbations are often technological or logistical in nature and require adaptive strategies to overcome.
B-IV: Factor affecting curriculum change - Aspirations of people
- One of the major factors affecting curriculum change is the aspirations of people, including societal and cultural expectations.
- Curriculum reform often aligns with the evolving needs and goals of the community or nation.
C-I: Approach to curriculum change - Systems
- Curriculum change often requires a systematic approach, where various systems are integrated to streamline the transition process.
- This includes institutional systems, teaching methodologies, and resource allocation frameworks.
D-III: Strategy for curriculum change - Learning communities
- Building learning communities is a key strategy for effective curriculum change as it fosters collaboration among educators, students, and stakeholders.
- Such communities help in sharing ideas, resources, and best practices to implement the change effectively.
Other Related Points
Web conferencing
- Web conferencing platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet play a vital role in modern education and collaborative environments.
- They enable real-time interactions and discussions, which are crucial in remote learning and professional settings.
Aspirations of people
- Curriculum changes often reflect societal aspirations such as technological advancement, career readiness, and global competitiveness.
- Governments and educational institutions frequently conduct surveys to understand public expectations for education reforms.
Systems approach
- A systems approach ensures that all components of an educational framework—such as teaching methods, assessments, and resources—work harmoniously.
- This approach is critical for effective curriculum implementation and sustainable change.
Learning communities
- Learning communities provide a platform for continuous professional development and active learning among educators and students.
- These communities often leverage technology for resource sharing and collective problem-solving
Q90: The term 'Andragogy' was coined by:
(a) Malcolm Shepherd Knowles
(b) Edward C. Linderman
(c) Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi
(d) Alexander Kapp
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Alexander Kapp'
Alexander Kapp:
- Alexander Kapp, a German educator, coined the term 'Andragogy' in 1833.
- The term was initially used to describe the educational theory and practice specifically focused on adult learning.
- Although the term fell out of use, it was revived in the 20th century, most notably by Malcolm Knowles.
Other Related Points
Malcolm Shepherd Knowles:
- Although Knowles did not coin the term 'Andragogy,' he was pivotal in popularizing it in the United States during the 20th century.
- He developed a theory of adult learning that contrasted with traditional pedagogy, highlighting the unique needs and characteristics of adult learners.
Edward C. Linderman:
- Edward C. Linderman was an American educator and sociologist known for his work in adult education and community development.
- While influential in the field, he did not coin the term 'Andragogy.'
Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi:
- Pestalozzi was a Swiss educator known for his educational reforms and child-centered pedagogy.
- He did not coin the term 'Andragogy,' but his work influenced broader educational theories.
Q91: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Freedom does not exist without order. The two go together. If you cannot have order, you cannot have freedom. The two are inseparable. If you say: "I will do what I like. I will turn up for my meals when I like; I will come to the class when I like" - you create disorder. You have to take into consideration what other people want. To run things smoothly, you have to come on time. If I had come ten minutes late this morning, I would have kept you waiting. So I have to have consideration. I have to think of others. I have to be polite, considerate, be concerned about other people. Out of that consideration, out of that thoughtfulness, out of that watchfulness, both outward and inward, comes order and with that order there comes freedom. You know, soldiers all over the world are drilled every day, they are told what to do, to walk in line. They obey orders implicitly without thinking. Do you know what that does to man? When you are told what to do, what to think, to obey, to follow, do you know what it does to you? Your mind becomes dull, it loses its initiative, its quickness. This external, outward imposition of discipline makes the mind stupid, it makes you conform, it makes you imitate. But if you discipline yourself by watching, listening, being considerate, being very thoughtful - out of that watchfulness, that listening, that consideration for others, comes order. Where there is order, there is always freedom. If you are shouting, talking, you cannot hear what others have to say. You can only hear clearly when you sit quietly, when you give your attention.
Being on time, punctuality brings:
(a) Discipline
(b) Inward Imposition
(c) Order
(d) Conformity
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Order'
Order:
- Order is essential for the smooth functioning of any system, including a classroom or workplace.
- Being on time and punctual is a fundamental aspect of maintaining order.
- When everyone adheres to a schedule, it ensures that activities proceed without unnecessary interruptions or delays.
- This leads to a harmonious environment where all participants can function effectively.
Other Related Points
Discipline:
- Discipline refers to the practice of training people to obey rules or a code of behavior.
- While being on time can be a result of discipline, it is not the only factor that contributes to order.
Inward Imposition:
- Inward imposition implies self-regulation and personal adherence to certain standards.
- Though it can lead to punctuality, it does not directly equate to the creation of order.
Conformity:
- Conformity involves aligning one's behavior to match the expectations of others or societal norms.
- While conformity can contribute to order, it is more about adhering to external expectations rather than being punctual.
Q92: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Freedom does not exist without order. The two go together. If you cannot have order, you cannot have freedom. The two are inseparable. If you say: "I will do what I like. I will turn up for my meals when I like; I will come to the class when I like" - you create disorder. You have to take into consideration what other people want. To run things smoothly, you have to come on time. If I had come ten minutes late this morning, I would have kept you waiting. So I have to have consideration. I have to think of others. I have to be polite, considerate, be concerned about other people. Out of that consideration, out of that thoughtfulness, out of that watchfulness, both outward and inward, comes order and with that order there comes freedom. You know, soldiers all over the world are drilled every day, they are told what to do, to walk in line. They obey orders implicitly without thinking. Do you know what that does to man? When you are told what to do, what to think, to obey, to follow, do you know what it does to you? Your mind becomes dull, it loses its initiative, its quickness. This external, outward imposition of discipline makes the mind stupid, it makes you conform, it makes you imitate. But if you discipline yourself by watching, listening, being considerate, being very thoughtful - out of that watchfulness, that listening, that consideration for others, comes order. Where there is order, there is always freedom. If you are shouting, talking, you cannot hear what others have to say. You can only hear clearly when you sit quietly, when you give your attention.
A teacher shouts, 'Pindrop Silence in the Class.' She is:
(a) Making her students considerate of orders
(b) Making the students thoughtful and watchful
(c) Making outward imposition of discipline
(d) Making order in the class to make her students free
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is ‘Making outward imposition of discipline’.
Making her students considerate of orders:
- When a teacher shouts "Pindrop Silence in the Class," she is imposing discipline externally, aligning with the passage’s description of external discipline that leads to conformity and imitation.
- This is distinct from fostering consideration for orders (a), thoughtfulness (b), or freedom through order (d).
Other Related Points
Making the students thoughtful and watchful:
- This option suggests that the teacher's command is aimed at making students more reflective and cautious.
- However, the primary goal of shouting for silence is more about immediate compliance rather than fostering thoughtfulness.
Making outward imposition of discipline:
- While the teacher is indeed imposing discipline, this option misses the nuance of teaching students to be considerate of orders.
- It focuses more on the authoritarian aspect rather than the educational intent behind it.
Making order in the class to make her students free:
- This option is somewhat contradictory as it suggests that imposing silence is aimed at giving freedom.
- The primary intent is to maintain immediate order, not necessarily to create freedom.
Q93: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Freedom does not exist without order. The two go together. If you cannot have order, you cannot have freedom. The two are inseparable. If you say: "I will do what I like. I will turn up for my meals when I like; I will come to the class when I like" - you create disorder. You have to take into consideration what other people want. To run things smoothly, you have to come on time. If I had come ten minutes late this morning, I would have kept you waiting. So I have to have consideration. I have to think of others. I have to be polite, considerate, be concerned about other people. Out of that consideration, out of that thoughtfulness, out of that watchfulness, both outward and inward, comes order and with that order there comes freedom. You know, soldiers all over the world are drilled every day, they are told what to do, to walk in line. They obey orders implicitly without thinking. Do you know what that does to man? When you are told what to do, what to think, to obey, to follow, do you know what it does to you? Your mind becomes dull, it loses its initiative, its quickness. This external, outward imposition of discipline makes the mind stupid, it makes you conform, it makes you imitate. But if you discipline yourself by watching, listening, being considerate, being very thoughtful - out of that watchfulness, that listening, that consideration for others, comes order. Where there is order, there is always freedom. If you are shouting, talking, you cannot hear what others have to say. You can only hear clearly when you sit quietly, when you give your attention.
According to the given paragraph, Freedom without order is:
(a) Invaluable
(b) Indiscipline
(c) Invalid
(d) Non-existent
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'Non-existent'
Freedom without order:
- Freedom and order are interdependent concepts; without order, true freedom cannot exist.
- Order provides the necessary structure within which freedom can be exercised responsibly and safely.
- Without order, society would descend into chaos, making it impossible for individuals to exercise their freedoms effectively or safely.
Other Related Points
Invaluable:
- While freedom is indeed invaluable, the term doesn't address the necessity of order for freedom to exist.
- This option does not capture the essence of the relationship between freedom and order.
Indiscipline:
- Indiscipline refers to a lack of control or order, but it doesn't fully convey the concept that freedom cannot exist without order.
- It implies a negative aspect rather than the foundational need for order to sustain freedom.
Invalid:
- Invalid suggests that freedom is void without order, but the term "non-existent" more accurately captures the complete absence of true freedom without order.
Q94: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Freedom does not exist without order. The two go together. If you cannot have order, you cannot have freedom. The two are inseparable. If you say: "I will do what I like. I will turn up for my meals when I like; I will come to the class when I like" - you create disorder. You have to take into consideration what other people want. To run things smoothly, you have to come on time. If I had come ten minutes late this morning, I would have kept you waiting. So I have to have consideration. I have to think of others. I have to be polite, considerate, be concerned about other people. Out of that consideration, out of that thoughtfulness, out of that watchfulness, both outward and inward, comes order and with that order there comes freedom. You know, soldiers all over the world are drilled every day, they are told what to do, to walk in line. They obey orders implicitly without thinking. Do you know what that does to man? When you are told what to do, what to think, to obey, to follow, do you know what it does to you? Your mind becomes dull, it loses its initiative, its quickness. This external, outward imposition of discipline makes the mind stupid, it makes you conform, it makes you imitate. But if you discipline yourself by watching, listening, being considerate, being very thoughtful - out of that watchfulness, that listening, that consideration for others, comes order. Where there is order, there is always freedom. If you are shouting, talking, you cannot hear what others have to say. You can only hear clearly when you sit quietly, when you give your attention.
Conformism and imitation are the learning outcomes of the pedagogy that believes in:
(a) External Discipline
(b) Internal Discipline
(c) Freedom of Learners
(d) Individual Difference
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'External Discipline'
External Discipline:
- The concept of external discipline emphasizes control and order imposed by external authorities such as teachers or educational institutions.
- Conformism and imitation are learning outcomes where learners are expected to follow established norms and behaviors set by these authorities.
- This approach often relies on strict rules and regulations to ensure that students adhere to predefined standards.
- It is believed that discipline imposed from outside helps in maintaining order and achieving educational objectives efficiently.
Other Related Points
Internal Discipline:
- Internal discipline refers to self-regulation and self-control developed by the learners themselves.
- This approach encourages students to take responsibility for their actions and learning processes.
- Unlike external discipline, it focuses on intrinsic motivation rather than adherence to external rules.
Freedom of Learners:
- This pedagogical approach emphasizes providing students with the freedom to explore and learn independently.
- It encourages creativity, critical thinking, and personal growth.
- Freedom of learners is contrary to conformism and imitation, as it values individual expression and unique learning paths.
Individual Difference:
- This concept acknowledges that each learner is unique with different abilities, interests, and learning styles.
- Pedagogy focusing on individual differences aims to tailor educational experiences to meet the diverse needs of students.
- It opposes the idea of uniformity and standardization inherent in conformism and imitation.
Q95: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Freedom does not exist without order. The two go together. If you cannot have order, you cannot have freedom. The two are inseparable. If you say: "I will do what I like. I will turn up for my meals when I like; I will come to the class when I like" - you create disorder. You have to take into consideration what other people want. To run things smoothly, you have to come on time. If I had come ten minutes late this morning, I would have kept you waiting. So I have to have consideration. I have to think of others. I have to be polite, considerate, be concerned about other people. Out of that consideration, out of that thoughtfulness, out of that watchfulness, both outward and inward, comes order and with that order there comes freedom. You know, soldiers all over the world are drilled every day, they are told what to do, to walk in line. They obey orders implicitly without thinking. Do you know what that does to man? When you are told what to do, what to think, to obey, to follow, do you know what it does to you? Your mind becomes dull, it loses its initiative, its quickness. This external, outward imposition of discipline makes the mind stupid, it makes you conform, it makes you imitate. But if you discipline yourself by watching, listening, being considerate, being very thoughtful - out of that watchfulness, that listening, that consideration for others, comes order. Where there is order, there is always freedom. If you are shouting, talking, you cannot hear what others have to say. You can only hear clearly when you sit quietly, when you give your attention.
If a teacher wants her students to obey orders without thinking, she is making her students:
(a) Rationalists
(b) Conformists
(c) Progressives
(d) Authoritarian
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Conformists.'
Conformists:
- Conformists are individuals who comply with rules, standards, or laws without questioning or challenging them.
- They tend to follow orders and adhere to established norms and expectations.
- In an educational context, a teacher who wants students to obey without thinking is encouraging conformity, discouraging independent thought and critical thinking.
Other Related Points
Rationalists:
- Rationalists prioritize reason and critical thinking over acceptance of beliefs or commands without evidence.
- If a teacher encourages rationalism, students are taught to question and understand the rationale behind orders and knowledge.
Progressives:
- Progressives advocate for reform and improvement through progressive education methods.
- They emphasize critical thinking, problem-solving, and the application of knowledge to real-world situations.
Authoritarian:
- Authoritarianism involves strict obedience to authority at the expense of personal freedom.
- While related, an authoritarian approach is more about enforcing strict control, whereas conformism is about the tendency to comply with such control.
Q96: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Inclusive education means that all people - regardless of their gender, religion, cultural and social origin, cognitive, physical and psychological preconditions - are entitled to equal access to higher education, and that existing entry barriers have to be removed. This broad understanding of inclusive education is fixed to the Curriculum Framework as a cross-cutting theme. As a pedagogical approach with the essential principle of appreciation and acknowledgement of diversity, the scientific foundation and acceptance of inclusive education has increased since the 1990s. At school it is about "the appropriate non-hierarchical and democratic response to the existing heterogeneity of students" (see Boban; Hinz, 2003: Index für Inklusion). The implementation of inclusive education is one of the big challenges to our education system and its stakeholders. Institutions of formal and non-formal education and their activities should be designed in a way that the learning environment adjusts to the students and respects the individual personalities with their different preconditions. Such an orientation towards the students requires a high personal commitment but also differentiated material and activating methods of education which support the individual and at the same time cooperation.
Inclusive education:
(a) Negates cultural diversity
(b) Celebrates teacher's authority
(c) Celebrates heterogeneity of students
(d) Negates social needs
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'Celebrates heterogeneity of students'
Inclusive Education:
- Inclusive education ensures that all individuals, regardless of their diverse backgrounds, have equal access to education.
- It emphasizes the removal of barriers to entry and participation in educational environments.
- The core principle of inclusive education is the appreciation and acknowledgment of diversity among students.
Celebrates Heterogeneity of Students:
- Inclusive education aims to respond appropriately to the diverse needs of students in a non-hierarchical and democratic manner.
- It values the differences in students’ cognitive, physical, psychological, cultural, and social backgrounds.
- This approach ensures that educational practices are tailored to meet the individual needs of each student while fostering cooperation among them.
Q97: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Inclusive education means that all people - regardless of their gender, religion, cultural and social origin, cognitive, physical and psychological preconditions - are entitled to equal access to higher education, and that existing entry barriers have to be removed. This broad understanding of inclusive education is fixed to the Curriculum Framework as a cross-cutting theme. As a pedagogical approach with the essential principle of appreciation and acknowledgement of diversity, the scientific foundation and acceptance of inclusive education has increased since the 1990s. At school it is about "the appropriate non-hierarchical and democratic response to the existing heterogeneity of students" (see Boban; Hinz, 2003: Index für Inklusion). The implementation of inclusive education is one of the big challenges to our education system and its stakeholders. Institutions of formal and non-formal education and their activities should be designed in a way that the learning environment adjusts to the students and respects the individual personalities with their different preconditions. Such an orientation towards the students requires a high personal commitment but also differentiated material and activating methods of education which support the individual and at the same time cooperation.
Inclusive education mainly focuses on education of:
(a) Children with disabilities
(b) Children with challenging behaviours
(c) Children with learning difficulties
(d) All children
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'All children'
Inclusive Education:
- Inclusive education is an educational approach that aims to cater to all students, regardless of their physical, intellectual, social, emotional, linguistic, or other conditions.
- It ensures that all children, including those with disabilities, challenging behaviors, and learning difficulties, have equal access to education and opportunities.
- This approach promotes diversity, respect, and acceptance within the educational environment, fostering a sense of belonging for all students.
- Inclusive education is grounded in the belief that every child can learn and has the right to be educated with their peers in a supportive environment.
Other Related Points
Children with disabilities:
- Although inclusive education includes children with disabilities, it is not limited to them alone.
- Focusing solely on children with disabilities would exclude other groups who also benefit from inclusive educational practices.
Children with challenging behaviors:
- Children with challenging behaviors are an important part of inclusive education, but they represent just one segment of the broader student population.
- Effective inclusive education strategies also address the needs of other groups.
Children with learning difficulties:
- Children with learning difficulties are also a focus of inclusive education, but this approach aims to support all students, not just those with specific learning challenges.
- Inclusive education ensures that educational practices are adaptable to meet diverse learning needs.
Q98: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Inclusive education means that all people - regardless of their gender, religion, cultural and social origin, cognitive, physical and psychological preconditions - are entitled to equal access to higher education, and that existing entry barriers have to be removed. This broad understanding of inclusive education is fixed to the Curriculum Framework as a cross-cutting theme. As a pedagogical approach with the essential principle of appreciation and acknowledgement of diversity, the scientific foundation and acceptance of inclusive education has increased since the 1990s. At school it is about "the appropriate non-hierarchical and democratic response to the existing heterogeneity of students" (see Boban; Hinz, 2003: Index für Inklusion). The implementation of inclusive education is one of the big challenges to our education system and its stakeholders. Institutions of formal and non-formal education and their activities should be designed in a way that the learning environment adjusts to the students and respects the individual personalities with their different preconditions. Such an orientation towards the students requires a high personal commitment but also differentiated material and activating methods of education which support the individual and at the same time cooperation.
It is necessary for these institutions to be inclusive :
(a) Institutions of formal education only
(b) Institutions of informal education only
(c) both the institutions of formal and informal education
(d) Institutions of non-formal education only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 'both the institutions of formal and informal education'
The passage specifies that both formal (e.g., schools) and non-formal institutions should adjust to student needs. Although “informal” isn't mentioned explicitly, the spirit of inclusion applies to all learning contexts. Hence, (c) is correct as an encompassing response.
Inclusivity in Education:
- Inclusivity in education ensures that all individuals, regardless of their socio-economic status, physical abilities, or cultural background, have equal access to educational opportunities.
- Both formal and informal educational institutions play crucial roles in the comprehensive development of individuals.
- Formal education includes structured and systematic learning environments such as schools, colleges, and universities.
- Informal education refers to learning that occurs outside of the formal school system, such as community education, vocational training, and life experiences.
- Inclusive practices in both settings promote diversity, equity, and the holistic development of all learners.
Other Related Points
Institutions of Formal Education:
- Examples include primary and secondary schools, higher education institutions, and professional certification programs.
- These institutions follow a set curriculum and offer recognized qualifications.
- While they are crucial for academic learning, focusing solely on formal education excludes the valuable learning experiences provided by informal settings.
Institutions of Informal Education:
- These include community learning centers, museums, libraries, and online courses.
- Informal education is flexible, often self-directed, and addresses practical skills and knowledge.
- Limiting inclusivity to informal education would overlook the importance of structured learning environments.
Institutions of Non-Formal Education:
- Non-formal education includes adult education programs, continuing education, and extracurricular activities.
- It bridges the gap between formal and informal education but still requires inclusivity to be fully effective.
- Focusing solely on non-formal education would miss the comprehensive approach needed for inclusivity across all types of education.
Q99: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Inclusive education means that all people - regardless of their gender, religion, cultural and social origin, cognitive, physical and psychological preconditions - are entitled to equal access to higher education, and that existing entry barriers have to be removed. This broad understanding of inclusive education is fixed to the Curriculum Framework as a cross-cutting theme. As a pedagogical approach with the essential principle of appreciation and acknowledgement of diversity, the scientific foundation and acceptance of inclusive education has increased since the 1990s. At school it is about "the appropriate non-hierarchical and democratic response to the existing heterogeneity of students" (see Boban; Hinz, 2003: Index für Inklusion). The implementation of inclusive education is one of the big challenges to our education system and its stakeholders. Institutions of formal and non-formal education and their activities should be designed in a way that the learning environment adjusts to the students and respects the individual personalities with their different preconditions. Such an orientation towards the students requires a high personal commitment but also differentiated material and activating methods of education which support the individual and at the same time cooperation.
In inclusive education, an orientation towards the students requires:
(a) A high personal commitment only
(b) Non-differentiated materials.
(c) Passive methods of education
(d) High personal commitment along with differential material
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 'High personal commitment along with differential material'
Inclusive Education:
- Inclusive education refers to an education system that works to include all children, regardless of their physical, intellectual, social, emotional, linguistic, or other conditions.
- It aims to provide all students with the most appropriate learning environments and opportunities for them to achieve their full potential.
- Inclusion involves a high degree of personalization in teaching methods and materials to meet the diverse needs of all students.
High Personal Commitment Along with Differential Material:
- Teachers need to be highly committed to the success of every student, which includes being dedicated to continuous learning and adapting their methods to be inclusive.
- Differential material involves using various types of educational resources and strategies to cater to the diverse learning needs and styles of students.
- This approach ensures that all students, including those with special needs, have access to learning opportunities that are tailored to their individual requirements.
Other Related Points
High Personal Commitment Only:
- While personal commitment is essential, it alone is insufficient. Teachers must also use differentiated materials to effectively address the diverse needs of their students.
Non-Differentiated Materials:
- Non-differentiated materials do not cater to the diverse needs of students and can lead to some students being left behind, especially those with special educational needs.
Passive Methods of Education:
- Passive methods, such as rote learning, do not engage students actively in the learning process and are less effective in an inclusive education setting where active participation is crucial.
Q100: Direction: Read the given passage below and answer the question that follows:
Inclusive education means that all people - regardless of their gender, religion, cultural and social origin, cognitive, physical and psychological preconditions - are entitled to equal access to higher education, and that existing entry barriers have to be removed. This broad understanding of inclusive education is fixed to the Curriculum Framework as a cross-cutting theme. As a pedagogical approach with the essential principle of appreciation and acknowledgement of diversity, the scientific foundation and acceptance of inclusive education has increased since the 1990s. At school it is about "the appropriate non-hierarchical and democratic response to the existing heterogeneity of students" (see Boban; Hinz, 2003: Index für Inklusion). The implementation of inclusive education is one of the big challenges to our education system and its stakeholders. Institutions of formal and non-formal education and their activities should be designed in a way that the learning environment adjusts to the students and respects the individual personalities with their different preconditions. Such an orientation towards the students requires a high personal commitment but also differentiated material and activating methods of education which support the individual and at the same time cooperation.
Inclusive education is a pedagogical approach having a principle of :
(a) Acceptance of learning difficulties only
(b) Appreciation of diversity
(c) Acceptance of group dynamics
(d) Appreciation of singularity
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 'Appreciation of diversity.'
Inclusive Education:
- Inclusive education is a pedagogical approach that aims to integrate all students, regardless of their abilities, disabilities, or other differences, into mainstream classrooms.
- It focuses on providing equal opportunities for learning and participation to all students.
- The principle of appreciating diversity underpins inclusive education, ensuring that differences among students are acknowledged and valued.
Other Related Points
Acceptance of learning difficulties only:
- This option is too narrow as it focuses solely on learning difficulties and does not encompass the broader spectrum of diversity that inclusive education addresses.
Acceptance of group dynamics:
- While understanding group dynamics is important in a classroom setting, it is not the core principle of inclusive education, which is more focused on individual differences and diversity.
Appreciation of singularity:
- This option emphasizes uniqueness but does not fully capture the essence of inclusive education, which is about appreciating and integrating a wide range of diversities.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Education 22nd August 2024 Shift 2 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and its significance in the field of education? |  |
| 2. What subjects are covered in UGC NET Paper 2 for Education? |  |
| 3. How can candidates prepare effectively for UGC NET Paper 2 in Education? |  |
| 4. What is the marking scheme for UGC NET Paper 2? |  |
| 5. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in UGC NET Paper 2? |  |
















