UGC NET Paper 2: Education 3rd Jan 2025 Shift 1 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: An inclusive curriculum means :
(a) Separate curriculum for children with disabilities
(b) One curriculum for all students
(c) Separate curriculum for children without disabilities
(d) A flexible curriculum
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - One curriculum for all students
Key Points
One curriculum for all students
- An inclusive curriculum ensures that all students, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, learn from the same curriculum.
- This approach promotes equity and accessibility in education.
- It aims to address the diverse learning needs of all students through differentiated instruction and universal design for learning (UDL).
Additional Information
Differentiated Instruction
- Teachers modify their teaching methods and materials to meet the varied needs of their students.
- This can include providing additional support, varying the difficulty level of tasks, or using different modes of instruction.
Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
- An educational framework that guides the development of flexible learning environments.
- Aims to accommodate individual learning differences by providing multiple means of representation, expression, and engagement.
Benefits of an Inclusive Curriculum
- Promotes a sense of belonging and community among all students.
- Prepares students for a diverse society by fostering understanding and respect for differences.
- Encourages higher expectations and academic outcomes for all students.
Q2: Arrange the following steps of Inference as propounded by the Nyaya School of Indian Philosophy.
(A) Conclusion
(B) Reason
(C) Proposition
(D) Example
(E) Application
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (E), (D), (B), (C), (A)
(b) (C), (B), (E), (D), (A)
(c) (C), (B), (D), (E), (A)
(d) (E), (C), (D), (B), (A)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - (C), (B), (D), (E), (A)
Key Points
Nyaya School of Indian Philosophy
- The Nyaya School is one of the six orthodox schools of Hindu philosophy.
- It emphasizes the process of logical reasoning and inference.
Steps of Inference
- According to the Nyaya philosophy, inference follows a structured process.
- The correct sequence of steps in inference is: Proposition (C), Reason (B), Example (D), Application (E), and Conclusion (A).
- This sequence ensures logical coherence and validity in reasoning.
Additional Information
Proposition (Pratijna)
- This is the statement or hypothesis that is intended to be proved.
- It sets the stage for the reasoning process.
Reason (Hetu)
- The reason provides the logical basis for the proposition.
- It connects the proposition with the evidence.
Example (Udaharana)
- An example is provided to illustrate the reason.
- This helps in understanding the applicability of the reason in a similar context.
Application (Upanaya)
- Application involves applying the reason and the example to the proposition.
- This step bridges the logical connection between the hypothesis and the evidence.
Conclusion (Nigamana)
- The final conclusion is drawn based on the application.
- It confirms the validity of the proposition through logical inference.
Q3: Prominent feature of Dick and Carey Model that distinguishes it from ADDIE Model is :
(a) Emphasis on evaluation
(b) Clear learner analysis
(c) Inclusion of formative evaluation at each step
(d) Sequential and Linear Design Process
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Inclusion of formative evaluation at each step
Key Points
Inclusion of formative evaluation at each step
- The Dick and Carey Model emphasizes the inclusion of formative evaluation at each step of the instructional design process.
- This ensures that feedback is continuously incorporated, allowing for ongoing improvements.
- This contrasts with the ADDIE Model, which may not explicitly include formative evaluation at each step in the same detailed manner.
Additional Information
Dick and Carey Model
- Developed by Walter Dick and Lou Carey, this model breaks down the instructional design process into nine detailed steps.
- The steps include identifying instructional goals, conducting instructional analysis, and designing and conducting formative evaluation.
ADDIE Model
- Stands for Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation.
- It is a more general framework compared to the Dick and Carey Model.
- While evaluation is part of the ADDIE Model, it does not emphasize formative evaluation at each individual step as prominently as the Dick and Carey Model does.
Q4: According to Jainism, following are required to attain Moksa :
(A) Samyak Darshan
(B) Samyak Drishti
(C) Samyak Jnan
(D) Samyak Charitra
(E) Samyak Sankalp
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(b) (B) and (E) Only
(c) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(d) (C), (D) and (E) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (C) and (D) Only
Key Points
(A) Samyak Darshan
- It refers to the right faith or correct vision towards the teachings of Jainism.
- It involves understanding and believing in the true nature of reality.
(C) Samyak Jnan
- This means right knowledge.
- It involves having an accurate and precise understanding of the reality as described by the Jain teachings.
(D) Samyak Charitra
- This signifies right conduct.
- It involves living a life of morality and ethics according to Jain principles, including non-violence and truthfulness.
Additional Information
Path to Moksha
- In Jainism, the path to Moksha (liberation) is called the Three Jewels (Ratnatraya).
- These include Samyak Darshan (right faith), Samyak Jnan (right knowledge), and Samyak Charitra (right conduct).
- These three are considered essential and interdependent for achieving liberation.
Non-Included Terms
- (B) Samyak Drishti and (E) Samyak Sankalp are not standard terms within the context of the Jain path to Moksha.
- While Sankalp (resolve) might be important in other contexts, it is not one of the Three Jewels.
Q5: The main curricular areas as per NCFTE-2009 are :
(A) Curriculum and Pedagogy
(B) Educational technology
(C) Foundation of Education
(D) School internship
(E) Learner assessment
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(b) (B), (C) and (E) Only
(c) (C), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (A), (C), (D) and (E) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (C) and (D) Only
Key Points
Main Curricular Areas in NCFTE-2009
Curriculum and Pedagogy
- This area focuses on the principles and methods of teaching, emphasizing effective curriculum development and instructional strategies.
Foundation of Education
- This area addresses the philosophical, psychological, and sociological underpinnings of education.
School Internship
- This component involves practical training in a real school environment, providing hands-on experience in teaching.
Additional Information
National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education (NCFTE-2009)
- The NCFTE-2009 was developed by the National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) to guide teacher education in India.
- It emphasizes the integration of theory and practice in teacher education programs.
- The framework highlights the importance of understanding the learner's context and the need for reflective teaching practices.
Additional Curricular Areas in NCFTE-2009
- Educational Technology
- This area explores the use of technology in enhancing teaching and learning processes.
Learner Assessment
- This component focuses on strategies for evaluating student learning and providing feedback.
Q6: Unruch and Unruch outlined five steps of curriculum development. Arrange these in proper sequence.
(A) Content
(B) Evaluation
(C) Goals and Objectives
(D) Implementation
(E) Needs Assessment
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (C), (E), (A), (D), (B)
(b) (C), (A), (E), (D), (B)
(c) (E), (C), (D), (A), (B)
(d) (E), (D), (C), (A), (B)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - (C), (E), (A), (D), (B)
Key Points
Unruch and Unruch outlined five steps of curriculum development
- Goals and Objectives (C): The first step is identifying the goals and objectives, which define the purpose of the curriculum.
- Needs Assessment (E): After goals are defined, assessing the needs ensures that the curriculum addresses relevant issues and gaps.
- Content (A): Based on the needs and goals, appropriate content is selected and organized.
- Implementation (D): The curriculum is put into practice to deliver the planned learning experiences.
- Evaluation (B): Finally, the curriculum is evaluated to measure its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Additional Information
Detailed Explanation of the Five Steps
Goals and Objectives:
- These are the foundation of curriculum planning, defining what learners should achieve.
- Examples include cognitive, affective, and psychomotor objectives.
Needs Assessment:
- This step involves identifying gaps in learner knowledge, skills, or attitudes.
- Methods include surveys, interviews, and analyzing existing data.
Content:
- Selection and organization of topics, units, and materials align with goals and objectives.
- Content must be relevant, engaging, and appropriate to the learners’ level.
Implementation:
- Execution of the curriculum plan, including teaching strategies and delivery methods.
- Requires effective teacher training and resource allocation.
Evaluation:
- Assessing the success of the curriculum in achieving its objectives.
- Includes formative and summative evaluation methods.
Q7: Which amongst the following theory affirms that inequality is socially constructed and can be eradicated ?
(a) Rational Choice Theory
(b) Theory of Systems Analysis
(c) Marxism
(d) Conservatism
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Marxism
Key Points
Marxism
- Marxism is a theory developed by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels which argues that inequality is a result of social structures and economic conditions.
- It posits that the capitalist system inherently creates class divisions and exploitation.
- According to Marxism, these inequalities can be eradicated through a revolutionary change that abolishes capitalism and establishes a classless society.
- Marxists believe in the collective ownership of the means of production, which would eliminate the class system and the social inequalities that arise from it.
Additional Information
Rational Choice Theory
- Rational Choice Theory assumes individuals make decisions based on the rational calculation of maximizing benefits and minimizing costs.
- It does not focus on social inequalities and does not propose strategies for eradicating them.
Theory of Systems Analysis
- Theory of Systems Analysis is a methodological approach used to understand complex systems and their interactions.
- It is not specifically concerned with social inequalities or their eradication.
Conservatism
- Conservatism is a political philosophy that emphasizes tradition, social stability, and the preservation of established institutions.
- It generally accepts social hierarchies and does not advocate for the eradication of social inequalities.
Q8: Which of the following web 2.0 tool is most effective for collaborative learning in e-learning platform ?
(a) Wiki
(b) Blog
(c) Podcast
(d) Video Conferencing
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Wiki
Key Points
Wiki
- A Wiki allows multiple users to collaboratively create and edit content, making it highly effective for collaborative learning.
- It provides a platform where learners can share knowledge, discuss topics, and work together on projects.
- Wikis are often used in educational settings to promote teamwork and peer learning.
- They offer version control and track changes features, which are essential for monitoring progress and contributions.
Additional Information
Blog
- Blogs are useful for individual reflections and sharing insights but are less effective for real-time collaborative learning.
- They encourage independent learning and personal expression.
Podcast
- Podcasts are great for audio-based learning and can be used to supplement other learning materials.
- They are not inherently collaborative but can be used to share expert knowledge.
Video Conferencing
- Video conferencing is useful for real-time communication and virtual classrooms.
- It supports discussion and interaction but is less effective for document collaboration.
Q9: Etymologically, the term ‘Curriculum’ is derived from the Latin word :
(a) Curricular
(b) Caricature
(c) Curious
(d) Currere
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Currere
Key Points
Currere
- The term curriculum is derived from the Latin word currere, which means "to run" or "to proceed."
- In the context of education, a curriculum represents a course of study or a series of educational experiences that students undergo.
- The concept of curriculum involves the structured, organized plan of the educational content and the learning experiences provided to students.
Additional Information
Historical Context
- The word curriculum has been used in educational contexts since the early 17th century.
- Originally, it referred to the subjects taught in schools or universities.
Modern Usage
- In contemporary education, the curriculum encompasses not just the subjects, but also the methods of instruction, the learning experiences, and the assessment methods.
- It is designed to achieve specific educational goals and outcomes.
Types of Curriculum
- Formal Curriculum: The official, written plan of instruction provided by educational institutions.
- Informal Curriculum: The unplanned, spontaneous learning experiences that occur outside the formal curriculum.
- Hidden Curriculum: The implicit lessons and values taught through the educational environment and culture.
Q10: Put the steps of construction of summated rating attitude scale in a correct order.
(A) Selection of final items
(B) Calculation of item wise critical ratio
(C) Item writing
(D) Administration for final try out
(E) Pre try out
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (E), (C), (D), (B), (A)
(b) (C), (E), (B), (D), (A)
(c) (A), (D), (E), (C), (B)
(d) (C), (E), (D), (B), (A)
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - (C), (E), (D), (B), (A)
Key Points
Item writing
- The first step involves creating or writing items that reflect the construct being measured.
Pre try out
- Preliminary testing of the items is conducted to identify any issues and make necessary revisions.
Administration for final try out
- The refined items are administered to a larger sample to gather data for analysis.
Calculation of item wise critical ratio
- Item analysis is performed to calculate the critical ratio and determine the items' effectiveness.
Selection of final items
- The final selection of items is based on the analysis to ensure reliability and validity.
Additional Information
Summated Rating Scale
- Also known as the Likert scale, it is widely used for measuring attitudes by summing the responses to multiple items.
- Each item typically has a set of ordered response options indicating varying levels of agreement or disagreement.
Critical Ratio
- It is a statistical measure used in item analysis to determine the discriminative power of an item.
- Items with higher critical ratios are considered more effective in differentiating between high and low scorers.
Reliability and Validity
- Reliability refers to the consistency of the scale, while validity refers to how well the scale measures the intended construct.
- Both are crucial for ensuring the accuracy and usefulness of the scale in research and practice.
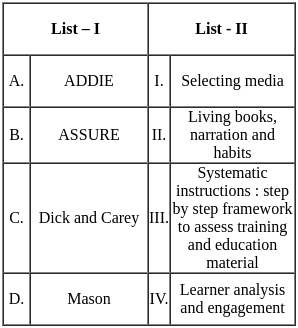
Q11: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(b) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
(d) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Option 4: A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Key Points
ADDIE
- ADDIE stands for Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation.
- This model provides a systematic instruction framework for assessing training and educational materials.
ASSURE
- The ASSURE model is used for designing and delivering instruction.
- It involves steps like Analyzing learners and Selecting media.
Dick and Carey
- This model focuses on learner analysis and engagement through systematic instruction.
- It is a step-by-step framework to assess training and educational materials.
Mason
- Charlotte Mason's educational philosophy emphasizes living books, narration, and habits.
- Her approach is holistic and focuses on the development of the whole person.
Additional Information
ADDIE Model
- The ADDIE model is widely used in instructional design and provides a structured approach to creating effective educational programs.
- Each phase of ADDIE involves specific tasks aimed at improving the overall learning experience.
ASSURE Model
- The ASSURE model is particularly useful in integrating technology into teaching.
- It ensures that instructional materials are selected based on the needs and characteristics of the learners.
Dick and Carey Model
- This model is known for its detailed and systematic approach to instructional design.
- It includes a series of steps that help educators identify learning goals and create effective instructional strategies.
Charlotte Mason's Philosophy
- Mason's educational methods focus on the development of good habits and the use of high-quality literature.
- Her approach is child-centered and aims to cultivate a love for learning.
Q12: The four fold valuation of Indian Culture when arranged in hierarchical order can be represented by following chronology :
(a) Dharma - Arth - Kama - Moksha
(b) Moksha - Dharma - Arth - Kama
(c) Kama - Arth - Dharma - Moksha
(d) Arth- Kama - Dharma - Moksha
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Arth - Kama - Dharma - Moksha
Key Points
Arth
- The term refers to wealth or material prosperity.
- It is considered essential for fulfilling life’s basic needs and securing a stable foundation.
Kama
- It signifies desire or pleasure, encompassing both physical and emotional satisfaction.
- It is important for a balanced and pleasurable life.
Dharma
- Dharma stands for righteousness or moral duty.
- It involves ethical conduct and fulfilling one's responsibilities.
Moksha
- Moksha represents liberation or spiritual freedom.
- It is the ultimate goal, signifying liberation from the cycle of birth and death.
Additional Information
Significance in Indian Culture
- These four principles represent the foundational goals of a well-rounded and meaningful life in Indian philosophy.
- They guide individuals on how to live a balanced life, addressing material, emotional, ethical, and spiritual aspects.
Interconnectedness
- While each goal is distinct, they are interconnected and collectively contribute to an individual's overall well-being.
- Emphasis on one goal should not be at the expense of the others; balance is essential.
Historical Context
- These concepts are rooted in ancient Indian scriptures such as the Vedas, Upanishads, and epics like the Mahabharata and Ramayana.
- They continue to influence contemporary Indian society and values.
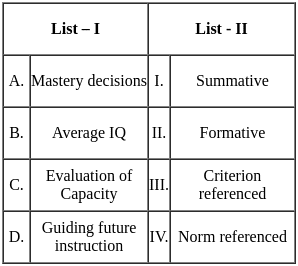
Q13: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(d) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Key Points
A - Mastery decisions - Criterion referenced (III)
- Mastery decisions involve evaluating whether a learner has achieved a predetermined level of understanding or skill. This is best assessed using criterion-referenced tests, which compare the learner's performance against a specific standard.
B - Average IQ - Norm referenced (IV)
- Average IQ is typically assessed using norm-referenced tests, which compare an individual's score to a normative sample to determine relative standing.
C - Evaluation of Capacity - Summative (I)
- Evaluating capacity often involves summative assessments, which measure what a learner has achieved at the end of an instructional period.
D - Guiding future instruction - Formative (II)
- Guiding future instruction is best supported by formative assessments, which provide ongoing feedback to improve learning and instruction.
Additional Information
Criterion-referenced tests
- These tests measure a learner's performance against a fixed set of standards or criteria, not against the performance of other students.
- They are used to determine whether each student has achieved specific skills or concepts.
Norm-referenced tests
- These tests compare a student's performance to that of a norm group, which is a representative sample of peers.
- They are used to rank students and to identify relative performance levels.
Summative assessments
- These assessments evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period, typically for the purpose of assigning grades.
- Examples include final exams, end-of-term projects, and standardized tests.
Formative assessments
- These assessments are conducted during the learning process to monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback.
- They help teachers identify areas where students are struggling and need additional support.
Q14: The four basic leadership styles identified by Bill Reddin were :
(a) Telling, Selling, Participating and Delegating
(b) M1, M2, M3 and M4
(c) DMAIC, DMADV, CTQ, POSDCORB
(d) Related, Integrated, Dedicated, Separated
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Related, Integrated, Dedicated, Separated
Key Points
Related, Integrated, Dedicated, Separated
- Bill Reddin identified four basic leadership styles as Related, Integrated, Dedicated, and Separated.
- Each style represents different approaches to leadership based on the level of task orientation and relationship orientation.
- This classification helps in understanding the flexibility and adaptability of a leader in various organizational contexts.
Additional Information
Related Leadership Style
- Combines a high concern for people with a moderate concern for production.
- Effective in environments where maintaining team morale and collaboration is crucial.
Integrated Leadership Style
- Balances both high task orientation and high relationship orientation.
- Leaders using this style are often seen as dynamic and adaptable.
Dedicated Leadership Style
- Focuses primarily on task completion with a high concern for production.
- Suitable for situations requiring strong direction and control to achieve specific outcomes.
Separated Leadership Style
- Low concern for both tasks and relationships.
- Often considered ineffective in dynamic or complex environments but might be appropriate in highly structured or routine settings.
Q15: Which of the following statement is NOT correct about Vygotsky’s Socio-cultural theory of child development ?
(a) Child’s cultural development appears twice: First on social level and later on individual level.
(b) Human activities take place in cultural settings.
(c) Intra Psychological function comes first then Inter Psychological.
(d) Development is transformation of socially shared activities into internalized process.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Intra Psychological function comes first then Inter Psychological.
Key Points
Intra Psychological function comes first then Inter Psychological.
- According to Vygotsky, Inter Psychological functions, which are social interactions, come first.
- These functions are then internalized to become Intra Psychological functions.
- This process emphasizes the importance of social interactions in the development of higher mental functions.
Additional Information
Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)
- Refers to the difference between what a child can do independently and what they can do with help.
- Vygotsky emphasized the role of social interaction and instruction in learning within the ZPD.
Scaffolding
- A technique used to support learning by providing appropriate assistance.
- As the learner becomes more proficient, the support is gradually removed.
Social Constructivism
- Vygotsky’s theory is a foundation for social constructivism, which emphasizes learning as a socially mediated activity.
- Knowledge is co-constructed through interaction with others.
Q16: Which of the following statements are correct about 'Taylorism' ?
(A) It is also known as 'scientific management'.
(B) Initial name for this approach was 'shop management'
(C) The theory was developed initially within manufacturing industries
(D) It was given by Samuel Taylor.
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (D) and (B) Only
(d) (A), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (B), and (C) Only
Key Points
Taylorism
- Also known as scientific management, Taylorism is a management theory aimed at improving productivity and efficiency through systematic study and analysis of workflow processes.
Shop Management
- The initial name for Taylorism was shop management, as it originated from the study of manufacturing processes within workshops.
Manufacturing Industry
- The theory was first developed in the manufacturing industry, where Frederick Winslow Taylor analyzed tasks to establish standards and improve performance.
Incorrect Statement
- Statement (D) is incorrect because Taylorism was developed by Frederick Winslow Taylor, not Samuel Taylor.
Additional Information
Principles of Taylorism
Key principles of Taylorism include:
- Scientific study of tasks to determine the most efficient way to perform them.
- Selection and training of workers to match their strengths to specific tasks.
- Close cooperation between management and workers to ensure adherence to scientifically devised methods.
- Division of labor between managers (planning) and workers (execution).
Criticism of Taylorism
- Taylorism has been criticized for treating workers as machines, reducing job satisfaction, and ignoring human needs and creativity.
Modern Applications
- Although Taylorism is considered outdated in its original form, its principles of task analysis and efficiency continue to influence modern management practices such as Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma.
Q17: Write the following steps of sampling procedure in a correct order.
(A) Preparing sampling frame
(B) Applying the sampling technique
(C) Administer the tool
(D) Define the universe to be studied
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (D), (B), (C)
(b) (D), (A), (B), (C)
(c) (A), (D), (C), (B)
(d) (D), (A), (C), (B)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - (D), (A), (B), (C)
Key Points
Define the universe to be studied
- The first step is to clearly identify and define the population or universe that is the focus of the study.
- It involves specifying the characteristics of the group being studied.
Preparing sampling frame
- A sampling frame is a list of elements from which the sample will be drawn.
- This step ensures that every element of the population has a chance of being included in the sample.
Applying the sampling technique
- In this step, the researcher selects a sample from the sampling frame using a specific sampling technique.
- Common techniques include random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
Administer the tool
- Finally, the researcher uses the selected sample to administer the data collection tool, such as surveys or interviews.
- This step involves gathering the necessary data from the chosen sample.
Additional Information
Importance of Sampling
- Sampling allows researchers to draw conclusions about a population without having to survey everyone.
- It is cost-effective and less time-consuming than studying the entire population.
Types of Sampling Techniques
Probability Sampling
- Each member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected.
- Examples include simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
Non-Probability Sampling
- Members are selected based on non-random criteria, and not all members have a chance of being included.
- Examples include convenience sampling, judgmental sampling, and quota sampling.
Sampling Frame Errors
- Occurs when the sampling frame does not perfectly match the population.
- This can result in some elements of the population being excluded or overrepresented.
Q18: Which of the following is NOT true ?
(a) Segregation is integral to special education.
(b) Integrated education provides partial opportunities for participation.
(c) Inclusive education recognises rights but not realises all of them.
(d) Inclusive education is least restrictive.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Inclusive education recognises rights but not realises all of them.
Key Points
Inclusive education
- Inclusive education aims to provide equal opportunities for all students, regardless of their abilities.
- It is designed to be the least restrictive environment, allowing students with disabilities to participate fully in general education classrooms.
- Inclusive education not only recognises the rights of all students but actively works towards realising these rights by providing necessary support and accommodations.
Additional Information
Segregation in Special Education
- Segregation involves placing students with disabilities in separate classes or schools, which is considered integral to traditional special education models.
- This approach often limits the interaction between students with and without disabilities.
Integrated Education
- Integrated education places students with disabilities in general education settings but often only allows partial participation.
- Additional support services may be provided, but full inclusion and participation are not always achieved.
Least Restrictive Environment (LRE)
- The concept of LRE is central to inclusive education, ensuring that students with disabilities are educated with their non-disabled peers to the greatest extent appropriate.
- This principle is rooted in the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and emphasizes inclusion as the preferred educational setting.
Q19: Which statement(s) out of the following is/are true :
(A) A valid test will also be reliable as well
(B) A reliable test will also be valid always
(C) A valid test may be or may not be reliable
(D) A reliable test may be or may not be valid
(E) There is no relation between reliability and validity of a test
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (A) and (D) Only
(d) (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - (A) and (D) Only
Key Points
A valid test will also be reliable as well
- A test that is valid effectively measures what it is supposed to measure.
- If a test is valid, it will consistently measure the intended construct, making it also reliable.
A reliable test may be or may not be valid
- A test that is reliable provides consistent results.
- However, a reliable test does not guarantee that it measures what it is supposed to measure, hence it might not be valid.
Additional Information
Reliability
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a test or measurement.
- It is measured through various methods such as test-retest, inter-rater, and internal consistency.
Validity
- Validity refers to how well a test measures what it is intended to measure.
- Types of validity include content validity, criterion-related validity, and construct validity.
The Relationship Between Reliability and Validity
- While a valid test is usually reliable, a reliable test might not always be valid.
- Understanding both concepts is crucial for developing effective assessments and measurements.
Q20: The University of Calcutta, Bombay and Madras were established in 1857 on the recommendations of Wood's despatch in 1854. Who was the viceroy of India, when these were founded ?
(a) Lord Canning
(b) Lord Dalhousie
(c) Lord Wellesley
(d) Lord Bentick
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Lord Canning
Key Points
Lord Canning
- He was the Viceroy of India from 1856 to 1862.
- During his tenure, the University of Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras were established in 1857.
- The establishment of these universities was based on the recommendations of Wood's Despatch of 1854.
Additional Information
Wood's Despatch
- Also known as the Magna Carta of English Education in India.
- It was a comprehensive plan to promote Western education in India.
- Recommended the creation of universities in Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras.
Lord Canning's Contributions
- He was the first Viceroy of India after the Revolt of 1857.
- Also known for introducing the Indian Penal Code and the Indian High Courts Act.
- He played a crucial role in the reorganization of the Indian administration post-1857.
Q21: Which of the following statements are true about hypothesis?
(A) A good hypothesis is based on sound reasoning that is consistent with theory or previous research.
(B) A deductive hypothesis is a generalization based on specific observations.
(C) Tenth grade biology students who are instructed using interactive multimedia achieve at higher level than those who receive regular instruction only' is an example of non-directional hypothesis.
(D) Qualitative researchers may develop guiding hypothesis for the proposed research.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A) and (D) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Option 4
Key Points
(A) A good hypothesis is based on sound reasoning that is consistent with theory or previous research.
- This emphasizes the importance of forming hypotheses that are grounded in established knowledge and logical reasoning.
- Ensures the hypothesis is credible and testable within the framework of existing theory.
(D) Qualitative researchers may develop guiding hypothesis for the proposed research.
- In qualitative research, hypotheses often guide the study and provide direction, though they may be more flexible and evolving compared to quantitative research.
- Helps in setting a preliminary focus while allowing for exploration and discovery during the research process.
Additional Information
(B) A deductive hypothesis is a generalization based on specific observations.
- This statement is incorrect. A deductive hypothesis works the other way around: it starts with a general theory and tests hypotheses derived from it.
(C) Tenth grade biology students who are instructed using interactive multimedia achieve at higher level than those who receive regular instruction only is an example of non-directional hypothesis.
- This statement is incorrect. This is an example of a directional hypothesis because it predicts a specific outcome (higher achievement with interactive multimedia).
Q22: Which of the following statement is NOT related to Freudian Psychoanalytic Approach ?
(a) Id refers to the raw, unorganised, inherited part of personality
(b) Super ego has two sub parts Conscience and the Ego-ideal
(c) Ego defence mechanisms have adaptive value
(d) Super ego helps to control ego impulses
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Ego defence mechanisms have adaptive value
Key Points
Ego defence mechanisms have adaptive value
- While Freud did propose various defense mechanisms used by the ego, the idea that they have adaptive value is not inherently a part of the Freudian Psychoanalytic Approach.
- Freudian theory primarily focuses on defense mechanisms as ways to reduce anxiety and manage conflict between the id and the superego, rather than emphasizing their adaptive value.
Additional Information
Id
- The id is the raw, unorganized, inherited part of personality that contains the basic drives and instincts.
- It operates on the pleasure principle, seeking immediate gratification of its desires.
Superego
- The superego consists of two sub-parts: the conscience, which punishes the ego for wrongdoing through guilt, and the ego-ideal, which rewards the ego with pride for good behavior.
- It helps to control the impulses of the id and strives for perfection, according to societal standards.
Ego
- The ego is the rational part of the personality that mediates between the desires of the id and the moral demands of the superego.
- It operates on the reality principle, trying to satisfy the id’s desires in realistic and socially appropriate ways.
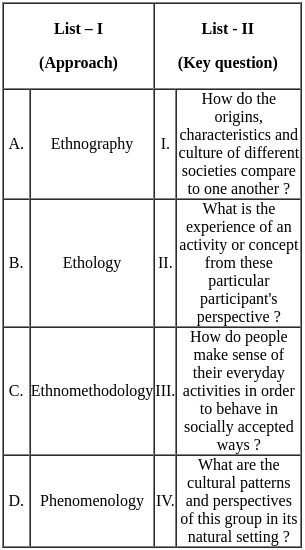
Q23: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
Key Points
Ethnography
- The key question is: What are the cultural patterns and perspectives of this group in its natural setting?
- This approach involves the in-depth study of people and cultures in their natural environment.
Ethology
- The key question is: How do the origins, characteristics and culture of different societies compare to one another?
- This approach studies animal behavior, including human behavior, in a comparative context.
Ethnomethodology
- The key question is: How do people make sense of their everyday activities in order to behave in socially accepted ways?
- This approach examines the methods people use to understand and produce the social order in which they live.
Phenomenology
- The key question is: What is the experience of an activity or concept from these particular participant's perspective?
- This approach focuses on the subjective experiences and interpretations of individuals.
Additional Information
Ethnography
- Researchers immerse themselves in the community to observe and participate in day-to-day activities.
- Data collection methods include participant observation, interviews, and field notes.
Ethology
- This field originated with the study of animal behavior in natural settings.
- Key figures include Konrad Lorenz and Nikolaas Tinbergen.
Ethnomethodology
- Founded by Harold Garfinkel, this approach emphasizes the ways individuals produce and maintain social norms.
- It includes the study of conversational analysis and everyday practices.
Phenomenology
- Developed by Edmund Husserl, this approach seeks to understand the essence of experiences.
- It involves bracketing preconceived notions to explore participants' lived experiences.
Q24: Which of the following statements are correct regarding 'Poka-Yoke' ?
(A) The term poka-yoke originated with the Japanese Baka-yoke.
(B) The contact method of poka-yoke identifies defects through physical attributes.
(C) The fixed value method of poka-yoke is used in a process with non-recurring activity.
(D) The motion-step method of poka-yoke determines whether prescribed steps are completed in order.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (C), (D) and (A) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (D) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (B) and (D) Only
Key Points
Poka-Yoke Origin
- The term poka-yoke originated with the Japanese term Baka-yoke, which means "fool-proofing" or "mistake-proofing."
Contact Method
- The contact method of poka-yoke identifies defects through physical attributes such as shape, size, or color.
Motion-Step Method
- The motion-step method of poka-yoke determines whether prescribed steps are completed in the correct order.
Additional Information
Fixed Value Method
The fixed value method of poka-yoke is used in processes where certain values must be maintained consistently.
- This method is not typically used for non-recurring activities but rather for repetitive tasks to ensure consistency.
Examples of Poka-Yoke
- Examples include mechanisms that prevent incorrect parts from being used in assembly or systems that alert operators if a step is missed.
Importance in Manufacturing
- Poka-yoke techniques are crucial for reducing errors, improving quality, and ensuring safety in manufacturing processes.
Q25: As per NEP-2020, School teachers are expected to spent how much time for continuous professional development ?
(a) 40 hours
(b) 60 hours
(c) 50 hours
(d) 45 hours
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - 50 hours
Key Points
Continuous Professional Development
- As per the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, school teachers are expected to spend 50 hours annually on continuous professional development.
- This professional development is aimed at improving teachers' skills, knowledge, and practices to enhance the quality of education.
- Continuous professional development is crucial for adapting to new teaching methodologies and integrating technology into the classroom.
Additional Information
NEP 2020 Objectives
- The NEP 2020 emphasizes the holistic development of students through a multidisciplinary approach to education.
- Teacher training and development are key components, ensuring that educators are well-equipped to deliver high-quality education.
Implementation Strategies
- Workshops, seminars, and online courses are some of the methods used for continuous professional development.
- Collaboration with educational institutions and experts is encouraged to provide diverse learning opportunities for teachers.
Impact on Education Quality
- Regular professional development helps teachers stay updated with the latest educational trends and practices.
- This ultimately leads to improved student outcomes and a higher standard of education.
Q26: The term ‘Triadic Reciprocal Causation’ is associated with ______
(a) Freud Theory
(b) Piaget Theory
(c) Bandura Theory
(d) Erikson Theory
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Bandura Theory
Key Points
Bandura Theory
- The term Triadic Reciprocal Causation is a key concept in Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory.
- It refers to the dynamic interaction between personal factors, behavior, and the environment.
- This model suggests that these three components influence each other bidirectionally.
- Albert Bandura introduced this concept to explain human functioning and learning processes.
Additional Information
Albert Bandura
- He is a renowned psychologist known for his work in Social Learning Theory, which later evolved into Social Cognitive Theory.
- Bandura's famous experiment, the Bobo doll experiment, demonstrated the role of observational learning in behavior acquisition.
Social Cognitive Theory
- This theory emphasizes the importance of observational learning, imitation, and modeling in human behavior.
- It also introduces the concept of self-efficacy, which is the belief in one's capabilities to execute behaviors necessary to produce specific performance attainments.
Other Related Theories
- Freud's Theory focuses on psychoanalysis and the unconscious mind.
- Piaget's Theory centers around cognitive development in children.
- Erikson's Theory involves psychosocial development across the lifespan.
Q27: Which of the following DOES NOT align with the concept of inclusive education ?
(a) Aiming for Mainstreaming
(b) Catering to diverse learning needs
(c) Catering to Plural society
(d) Considering Individual differences
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Aiming for Mainstreaming
Key Points
Aiming for Mainstreaming
- Inclusive education focuses on including all students in a general education setting, regardless of their abilities or disabilities.
- Mainstreaming often involves placing students with special needs into some general education classes, but it does not fully integrate them into the classroom environment.
- In contrast, inclusive education emphasizes full participation and access to the same learning opportunities for all students.
Additional Information
Catering to diverse learning needs
- Inclusive education ensures that teaching methods, materials, and assessments are designed to accommodate the various learning styles and needs of students.
- This includes differentiated instruction, which tailors teaching to meet individual needs.
Catering to Plural society
- Inclusive education promotes understanding and respect for diverse cultures, languages, and backgrounds.
- It aims to create a learning environment that reflects and values the diversity of the student body.
Considering Individual differences
- Recognizing and valuing individual differences is key to inclusive education.It involves creating an environment where each student's unique abilities and needs are acknowledged and supported.
Q28: The Jurisprudential Inquiry model requires a fair amount of teacher directed activity and directed instruction. Component activities of the model include:
(A) Facts about social problems
(B) Framework for analysing social issues
(C) Competence in social dialogue
(D) Comfort in expressing opinion
(E) Analysing personal values and behaviour
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(b) (B), (C), (D) and (E) Only
(c) (C), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (C) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (B) and (C) Only
Key Points
Facts about social problems
- Understanding the facts about social problems is crucial for students to engage in meaningful discussions and analyses.
- This component helps in framing the context and background necessary for further inquiry.
Framework for analysing social issues
- The model provides a framework that guides students in systematically analysing and understanding various social issues.
- This structured approach ensures that students can critically evaluate different perspectives.
Competence in social dialogue
- Developing competence in social dialogue is essential for students to effectively participate in discussions and debates on social issues.
- This competence includes the ability to listen, articulate thoughts, and engage constructively with others.
Additional Information
Comfort in expressing opinion
- While comfort in expressing opinions is valuable, it is not a core component of the Jurisprudential Inquiry model.
- This skill can be developed through practice and exposure to discussions, but it is not specifically emphasized in the model.
- Analysing personal values and behaviour
- The focus of the Jurisprudential Inquiry model is more on understanding and analysing social issues rather than personal values and behaviour.
- While personal reflection can enhance understanding, it is not a primary component of this model.
Q29: Needs of curriculum development include:
(A) Sports and games
(B) Acquisition of knowledge
(C) Cultural activities
(D) Proper use of time
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (C) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (B) and (D) Only
(d) (A) and (B) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - (B) and (D) Only
Key Points
Acquisition of knowledge
- The primary goal of curriculum development is to ensure students acquire essential knowledge and skills.
- This includes learning in various subjects such as mathematics, science, and literature.
- Helps in the overall intellectual development of students.
Proper use of time
- Curriculum development aims to structure educational activities to make the best use of time.
- Ensures that students engage in meaningful and productive learning activities.
- Helps in developing time management skills among students.
Additional Information
Sports and games
- While important for physical development, they are not the primary focus of curriculum development.
- Typically included in the overall educational experience but secondary to academic goals.
Cultural activities
- Enhance social and cultural understanding, but like sports, are secondary to academic objectives in curriculum development.
- Help in developing well-rounded individuals, but the focus remains on knowledge and proper use of time.
Q30: The competency based model of curriculum focuses on :
(a) Time spent on acquiring skills
(b) Mastering specific skills
(c) General knowledge skills
(d) General life skills
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Mastering specific skills
Key Points
Mastering specific skills
- The competency-based model of curriculum emphasizes students acquiring and demonstrating specific skills.
- This approach ensures that learners have achieved proficiency in particular skills before progressing.
- It focuses on measurable outcomes and clear standards of performance.
- The goal is to ensure that students can apply what they have learned in real-world scenarios.
Additional Information
Time spent on acquiring skills
- In the competency-based model, the time spent on acquiring skills is flexible; the focus is on mastery rather than time.
General knowledge skills
- While general knowledge is important, the competency-based model prioritizes specific and applicable skills.
General life skills
- General life skills may be included, but the primary focus is on specific competencies that can be measured and demonstrated.
Q31: ‘QUAN → QUAL’ represents a mixed method research design which is :
(a) Concurrent Explanatory
(b) Concurrent Exploratory
(c) Sequential Explanatory
(d) Sequential Exploratory
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Sequential Explanatory
Key Points
Sequential Explanatory
- A mixed methods research design where quantitative data is collected and analyzed first, followed by qualitative data.
- This approach is used to explain or build upon initial quantitative results with in-depth qualitative data.
- Commonly used to explore unexpected results or to develop better understanding of quantitative findings.
- Involves two distinct phases: the quantitative phase (QUAN) followed by the qualitative phase (QUAL).
Additional Information
Concurrent Explanatory
- Involves simultaneous collection and analysis of both quantitative and qualitative data.
- Purpose is to compare and corroborate findings from both data types.
- Does not follow the sequential order as in Sequential Explanatory.
Concurrent Exploratory
- Simultaneously collects and analyzes both data types with an exploratory purpose.
- Aims to explore a phenomenon and develop theories or instruments.
Sequential Exploratory
- Begins with qualitative data collection and analysis followed by quantitative data collection and analysis.
- Useful for exploring phenomena and then testing or generalizing findings.
- Opposite sequence to Sequential Explanatory.
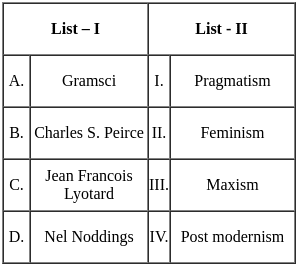
Q32: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Key Points
Gramsci - Marxism
- Antonio Gramsci was an Italian Marxist philosopher and communist politician.
- He is best known for his theory of cultural hegemony, which describes how the state and ruling capitalist class use cultural institutions to maintain power in capitalist societies.
Charles S. Peirce - Pragmatism
- Charles Sanders Peirce was an American philosopher, logician, and mathematician.
- He is known as the father of pragmatism, a philosophical tradition that considers the practical consequences of an idea to be its essential component.
Jean Francois Lyotard - Postmodernism
- Jean-François Lyotard was a French philosopher and sociologist.
- He is best known for his work "The Postmodern Condition," which is a foundational text in postmodern theory.
Nel Noddings - Feminism
- Nel Noddings is an American feminist, educationalist, and philosopher.
- She is best known for her work in the philosophy of education and care ethics.
Additional Information
Marxism
- A socio-economic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict.
- Developed by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels in the mid-to-late 19th century.
Pragmatism
- A philosophical tradition that began in the United States around 1870.
- Pragmatists consider thought as an instrument or tool for prediction, problem-solving, and action.
Postmodernism
- A broad movement that developed in the mid-to-late 20th century across philosophy, the arts, architecture, and criticism.
- It is characterized by broad skepticism, subjectivism, or relativism; a general suspicion of reason; and an acute sensitivity to the role of ideology in asserting and maintaining political and economic power.
Feminism
- A range of social movements, political movements, and ideologies that aim to define and establish the political, economic, personal, and social equality of the sexes.
- Feminism incorporates the position that societies prioritize the male point of view, and that women are treated unjustly within those societies.
Q33: Philosophical Model of Teaching comprising Insight (Plato), Impression (Locke), and Rule (Kant) was propounded by :
(a) RS. Peters
(b) Paul Hirst
(c) D.W. Hamlyn
(d) Israel Scheffler
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Israel Scheffler
Key Points
Israel Scheffler
- The Philosophical Model of Teaching comprising Insight (Plato), Impression (Locke), and Rule (Kant) was propounded by Israel Scheffler.
- Insight refers to the Platonic idea of understanding through forms and ideas.
- Impression pertains to John Locke's theory of knowledge acquisition through sensory experiences.
- Rule is linked to Immanuel Kant's emphasis on the role of principles and rules in the process of learning.
Additional Information
Philosophical Foundations of Education
Plato
- Plato emphasized the role of insight in education, advocating for the discovery of truths through intellectual and philosophical inquiry.
John Locke
- Locke believed in the empirical basis of knowledge, arguing that the mind is a tabula rasa (blank slate) and knowledge is acquired through sensory experiences.
Immanuel Kant
- Kant proposed that learning is governed by rules and principles, highlighting the importance of rationality and moral imperatives in education.
Israel Scheffler's Contributions
- Scheffler's work integrates the ideas of Plato, Locke, and Kant into a comprehensive philosophical model of teaching.
- He emphasized the importance of combining insight, impression, and rule to form a holistic approach to education.
Q34: As per the intent of NEP-2020, All stand-alone Teacher Education Institutions (TEIs) will be required to convert to multidisciplinary institutions by the year _______
(a) 2035
(b) 2030
(c) 2047
(d) 2040
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - 2030
Key Points
NEP-2020
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 aims to overhaul the education system in India.
- One of its key objectives is to transform Teacher Education Institutions (TEIs).
Multidisciplinary Institutions
- Standalone TEIs are required to convert into multidisciplinary institutions.
- This transformation is intended to enhance the quality of teacher education by integrating diverse fields of study.
Target Year
- The deadline for this transformation is 2030.
- By 2030, all standalone TEIs must become part of or convert into multidisciplinary institutions.
Additional Information
Holistic Education
- NEP-2020 emphasizes a holistic, multidisciplinary approach to education.
- It aims to break the silos in higher education and promote a more integrated learning experience.
Flexibility and Choice
- The policy provides students with flexibility in choosing their subjects, allowing for a more tailored education.
- Students can select courses from different disciplines, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of various fields.
Teacher Training
- The NEP-2020 aims to improve the quality of teacher training by incorporating modern pedagogical practices.
- It emphasizes continuous professional development for teachers to keep up with the evolving educational landscape.
Q35: Arrange chronologically the programmes/schemes for Education.
(A) Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
(B) Operation Blackboard (OB)
(C) District Primary Education Programme (DPEP)
(D) Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA)
(E) Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (A), (C), (B), (D), (E)
(b) (C), (B), (A), (E), (D)
(c) (B), (C), (A), (D), (E)
(d) (D), (B), (C), (A), (E)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Option 3: (B), (C), (A), (D), (E)
Key Points
Operation Blackboard (OB)
- Launched in 1987, it aimed to improve the quality of primary education in India.
- Provided essential facilities like blackboards, furniture, and teaching aids in primary schools.
District Primary Education Programme (DPEP)
- Initiated in 1994, it focused on reducing disparities in primary education across districts.
- Supported by the World Bank, it aimed to enhance access, retention, and quality of primary education.
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
- Launched in 2001, it was a flagship program for universalizing elementary education.
- Aimed to bridge social, regional, and gender gaps with active community participation.
Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA)
- Started in 2009, it focused on enhancing access to secondary education and improving its quality.
- Targeted to make secondary education available to all children aged 14-18 by 2017.
Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan
- Launched in 2018, it is an integrated scheme for school education extending from pre-school to class 12.
- Aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education at all levels.
Additional Information
Education Policy Reforms
- The National Policy on Education (NPE) has been a key driver in the formulation of these schemes.
- Periodic revisions of the NPE have aligned educational objectives with socio-economic needs.
Right to Education Act
- Implemented in 2009, it mandates free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14 years.
- SSA was a significant program to achieve the goals set by this Act.
International Support
- Programs like DPEP and SSA received funding and technical support from international bodies like the World Bank and UNICEF.
- Such collaborations aimed at global standards in education quality and access.
Q36: Which of the following are TRUE about inclusive education?
(A) It is a part of a wider strategy to develop an inclusive society.
(B) It acknowledges that not all children can learn in a general class.
(C) It involves restructuring school-cultures.
(D) Diversity is a rich resource to support the learning for all.
(E) Schools should not be expected to change according to learning needs of all children.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C) and (E) Only
(b) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (B), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (A), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (C) and (D) Only
Key Points
Inclusive Education
- Inclusive education is part of a broader strategy to develop an inclusive society (Statement A).
- It involves restructuring school cultures to be more accommodating to diverse learning needs (Statement C).
- Recognizes that diversity is a rich resource to support the learning of all students (Statement D).
Additional Information
Inclusive Education
- It aims to provide quality education for all students by effectively meeting their diverse needs in a way that is responsive and respectful.
- Schools are expected to adapt and change to accommodate the learning needs of all children, rather than expecting children to adapt to the school's existing structure.
- Inclusive education is not just about placing children with disabilities in mainstream classrooms; it involves a fundamental shift in how schools are organized and how they operate to support all students.
Misconceptions
- Inclusive education does not imply that all children can learn in a general class without support. Adequate support systems must be in place.
- It is incorrect to state that schools should not change according to learning needs (Statement E) as inclusive education requires schools to be flexible and adaptive.
Q37: Which of the following statement is NOT correct about PERT ?
(a) PERT was developed primarily to simplify the planning and scheduling of large and complex projects.
(b) In a PERT chart, ‘Nodes’ represent the activities or tasks and ‘Arrows’ represent events or milestones in the project.
(c) PERT may utilize three ‘time estimates’.
(d) PERT was developed between 1950-60.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Option 2
Key Points
Option 2 is incorrect because in a PERT chart, ‘Nodes’ represent events or milestones, and ‘Arrows’ represent the activities or tasks.
- Nodes (also called events) signify the start or end points of tasks.
- Arrows (also called activities) depict the actual tasks or operations that move the project from one event to another.
Additional Information
PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique)
- Developed primarily for planning and scheduling large and complex projects.
- Introduced by the United States Navy in the late 1950s.
- It helps in identifying the critical path and potential delays in the project timeline.
Time Estimates in PERT
- PERT utilizes three-time estimates to account for uncertainty:
- Optimistic Time (O): The minimum possible time required to accomplish a task.
- Most Likely Time (M): The best estimate of the time required to accomplish a task, assuming everything proceeds as normal.
- Pessimistic Time (P): The maximum possible time required to accomplish a task, assuming everything goes wrong.
- These estimates help in calculating the expected time for each activity.
History of PERT
- PERT was developed during the period between 1950-1960.
- It was used in the Polaris missile project by the United States Navy.
- PERT has since been adopted in various industries for project management.
Q38: Selection and placement decisions typically involve prediction about future learning based on present characteristics of the individual. A test that is used for the said purpose is :
(a) Criterion reference test
(b) Attitude test
(c) Aptitude test
(d) Formative test
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Aptitude test
Key Points
Aptitude test
- Designed to measure an individual’s potential to succeed in a particular activity or learning environment.
- Helps predict future performance based on current abilities and skills.
- Commonly used in educational and employment contexts to identify suitable candidates for specific roles or programs.
- Examples include the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) and the Graduate Record Examination (GRE).
Additional Information
Criterion reference test
- Measures an individual’s performance against a fixed set of standards or criteria.
- Used to determine whether a student has learned a specific body of knowledge.
- Examples include end-of-unit tests in classrooms and driving license exams.
Attitude test
- Assesses an individual’s feelings, perceptions, and reactions towards specific situations, objects, or people.
- Often used in organizational settings to gauge employee satisfaction and customer feedback.
- Examples include surveys measuring employee engagement and customer satisfaction.
Frame test
- Not a standard term commonly used in educational or psychological testing.
- Could be a typo or misinterpretation of another type of test.
Q39: The principles of designing in-service teacher education programmes, as per NCFTE-2009 include:
(A) Content and Pedagogic approach
(B) Educational attainment approach
(C) Structural space approach
(D) Addressing teachers as learners
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(b) (A) and (D) Only
(c) (A), (B), (C) and (D)
(d) (A), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - (A) Content and Pedagogic approach and (D) Addressing teachers as learners
Key Points
Content and Pedagogic approach
- This approach ensures that the content taught to teachers is relevant and effectively delivered.
- It emphasizes integrating pedagogical skills with subject knowledge.
Addressing teachers as learners
- This principle acknowledges that teachers are continuous learners.
- Programs are designed to support teachers' ongoing professional development and learning needs.
Additional Information
Educational attainment approach
- This approach focuses on the educational qualifications and achievements of teachers.
- It is not explicitly mentioned as a principle in NCFTE-2009 for in-service teacher education programs.
Structural space approach
- This principle deals with the organizational and infrastructural aspects of educational programs.
- While important, it is not explicitly highlighted in NCFTE-2009 for in-service teacher education.
Q40: Teachers and counsellors are often interested in using tests to determine their students’ strengths and weaknesses, the areas where they are doing well and those where they are doing poorly. Which of the following test can be used for the purpose?
(a) Formative Evaluation
(b) Achievement Evaluation
(c) Summative Evaluation
(d) Criterion-Referenced Evaluation
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Formative Evaluation
Key Points
Formative Evaluation
- It is used to monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback.
- Helps teachers identify student strengths and weaknesses, and target areas that need work.
- It is typically conducted during the instructional process, rather than at the end of a unit or course.
- Aims to improve the teaching and learning process while it's happening.
Additional Information
Achievement Evaluation
- Measures how much students have learned or achieved at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark.
- Often used in standardized testing and final exams.
Summative Evaluation
- Conducted at the end of a course or program to assess student learning, skill acquisition, and academic achievement.
- Used to make final judgments about student performance.
Criterion-Referenced Evaluation
- Measures student performance against a fixed set of criteria or learning standards.
- Focuses on whether students have learned specific skills or concepts.
Q41: In monitoring of policy, ensuring policy programmes are completed on schedule and within budget. In process of policy monitoring, arrange the following steps:
(A) Establish expectations against which the implementer or policy maker monitors the policy delivery process.
(B) Analysis of cause of deviation from planned policy delivery process.
(C) Observing performance indicators on all parameters.
(D) Taking corrective action in case of deviation from policy delivery process.
(E) Application of resources to the policy delivery process.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (E), (C), (B), (D)
(b) (B), (C), (D), (E), (A)
(c) (C), (D), (E), (A), (B)
(d) (D), (E), (C), (A), (B)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Option 1: (A), (E), (C), (B), (D)
Key Points
Establishing expectations
- This step involves setting clear expectations and benchmarks for the policy delivery process.
- It is crucial for creating a framework against which the policy implementation can be monitored.
Application of resources
- Resources need to be allocated effectively to ensure the policy can be implemented as planned.
- This step ensures that the necessary tools, personnel, and finances are in place.
Observing performance indicators
- Tracking key performance indicators helps in monitoring the progress and effectiveness of the policy.
- It involves continuous observation and data collection on various implementation parameters.
Analysis of deviations
- Any deviations from the planned process are analyzed to understand the causes.
- This helps in identifying gaps and areas needing improvement.
Taking corrective actions
- Based on the analysis, corrective actions are taken to align the process with the planned objectives.
- This step ensures that the policy implementation stays on track.
Additional Information
Policy Monitoring Process
- Policy monitoring involves regular and systematic collection of data to track the performance of the policy implementation.
- It helps in ensuring that the policy objectives are met efficiently and effectively.
Importance of Setting Clear Expectations
- Clear expectations provide a benchmark for evaluating the success of the policy.
- They help in aligning the efforts of all stakeholders towards common goals.
Resource Allocation
- Effective resource allocation is critical for the success of policy implementation.
- It ensures that the necessary inputs are available when needed.
Continuous Monitoring
- Continuous monitoring helps in identifying issues early and allows for timely interventions.
- It involves regular data collection and analysis to track progress.
Q42: Arrange the following in chronological order.
(A) Sargent plan
(B) Royal Rescript on Education
(C) Hartog Committee Report
(D) Hunter Commission
(E) Stanley's Despatch
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (C), (A), (D), (E)
(b) (A), (C), (D), (E), (B)
(c) (B), (E), (D), (C), (A)
(d) (A), (D), (E), (C), (B)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (c) - (B), (E), (D), (C), (A).
Key Points:
- Royal Rescript on Education (B): Likely refers to early British education policies, such as the Charter Act of 1813, which allocated funds for education in India.
- Stanley’s Despatch (E): Issued in 1854 (Wood’s Despatch), foundational for modern education in India.
- Hunter Commission (D): Appointed in 1882 to review education progress.
- Hartog Committee Report (C): Published in 1929 to assess educational challenges.
- Sargent Plan (A): Formulated in 1944 for educational reconstruction.
Q43: Online Repository for accessing full academic articles and research papers completely free of charge is :
(a) Researchgate
(b) JSTOR
(c) PubMed
(d) Google Books
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Researchgate
Key Points
Researchgate
- ResearchGate is a professional network for scientists and researchers.
- It allows users to access and share academic publications for free.
- Users can upload their own research papers and access those uploaded by others, facilitating knowledge sharing.
- It is a widely-used platform in the academic community for collaboration and access to research.
Additional Information
JSTOR
- JSTOR provides access to thousands of academic journals, books, and primary sources.
- However, it is not completely free; access usually requires a subscription or is provided through educational institutions.
PubMed
- PubMed is a free resource developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
- It provides access to a vast database of biomedical and life sciences literature.
- While the abstracts are free, full-text articles may not always be freely accessible.
Google Books
- Google Books is a service from Google that searches the full text of books and magazines.
- It provides access to a vast collection of digitized books, but not all content is freely available.
- Full access to some books might require purchase or be restricted to previews.
Q44: Match List - I with List - II.
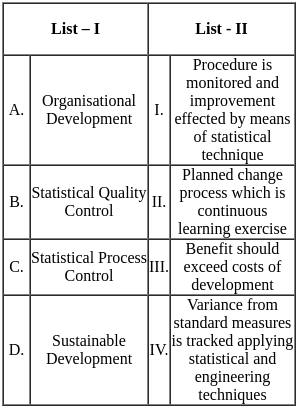
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Key Points
Organisational Development
- It is a planned change process that is a continuous learning exercise.
- Aims to improve the overall health and effectiveness of the organization.
- Involves interventions in the organization's processes and structures.
Statistical Quality Control
- Focuses on monitoring procedures and effecting improvement by means of statistical techniques.
- Ensures that the manufacturing process adheres to specific standards.
- Helps in identifying areas of deviation and implementing corrective measures.
Statistical Process Control
- Tracks variance from standard measures by applying statistical and engineering techniques.
- Used to control and monitor processes to ensure consistent quality.
- Helps in identifying process variations and maintaining process stability.
Sustainable Development
- Ensures that the benefits exceed the costs of development.
- Focuses on meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
- Incorporates economic, social, and environmental considerations.
Additional Information
Organisational Development Techniques
- Team building activities.
- Leadership development programs.
- Organizational assessments and feedback mechanisms.
Statistical Quality Control Tools
- Control charts.
- Histograms.
- Cause-and-effect diagrams.
Statistical Process Control Methods
- Use of control charts to monitor process behavior.
- Capability analysis to assess the ability of a process to meet specifications.
Sustainable Development Goals
- Eradicate poverty and hunger.
- Promote good health and well-being.
- Ensure quality education and gender equality.
- Promote sustainable economic growth and decent work for all.
Q45: Match List - I with List - II.
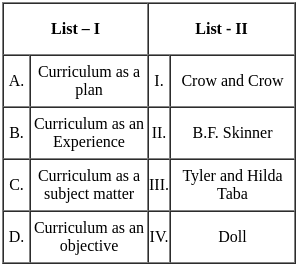
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(b) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Key Points
Curriculum as a plan
- Associated with Tyler and Hilda Taba, who emphasized systematic planning and organizing educational experiences.
Curriculum as an Experience
- Linked to Crow and Crow, who viewed curriculum as a set of learning experiences and activities.
Curriculum as a subject matter
- Identified with Doll, focusing on the content and subjects to be taught.
Curriculum as an objective
- Related to B.F. Skinner, emphasizing clear, measurable objectives in the curriculum.
Additional Information
Tyler and Hilda Taba
- Both educators are known for their influential work in developing the concept of curriculum planning and design.
- Tyler’s rationale and Taba’s grassroots model are key frameworks in curriculum development.
Crow and Crow
- Famous for their contributions to educational psychology and the understanding of learning experiences.
- They emphasized the importance of student experiences in the learning process.
Doll
- Known for emphasizing the importance of subject matter in the curriculum.
- Focuses on the core content that students need to learn.
B.F. Skinner
- A pioneer in behaviorism, Skinner emphasized the use of clear objectives and measurable outcomes in education.
- His work influenced the development of programmed instruction and behavior modification techniques in teaching.
Q46: Tfhe concept of ‘randomness’ is based on which of the following assumption ?
(a) While individual events cannot be predicted with accuracy, aggregate events can.
(b) While aggregate events cannot be predicted with accuracy, individual events can.
(c) While individual events cannot be studied with accuracy, aggregate events can.
(d) Sampling errors are not predictable with randomization.
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - While individual events cannot be predicted with accuracy, aggregate events can.
Key Points
Randomness
- The concept of randomness suggests that individual events cannot be predicted with accuracy.
- However, when considering a large number of events, known as aggregate events, patterns can be observed, and predictions become more accurate.
- This is because random variations tend to cancel each other out when a large number of events are considered, leading to a more predictable outcome.
Additional Information
Law of Large Numbers
- The Law of Large Numbers states that as the number of trials or observations increases, the average of the results obtained from these trials will get closer to the expected value.
- This law is fundamental in probability and statistics, providing the foundation for many statistical principles.
Central Limit Theorem
- The Central Limit Theorem states that the distribution of the sum (or average) of a large number of independent, identically distributed random variables tends to be normally distributed, regardless of the original distribution of the variables.
- This theorem explains why aggregate events tend to follow a predictable pattern even if the individual events are random.
Predictability in Statistics
- In statistical analysis, the predictability of aggregate events allows researchers to make accurate predictions about populations based on sample data.
- This is key for fields like economics, medicine, and social sciences, where individual behavior may be unpredictable, but aggregate behavior is measurable and predictable.
Q47: Match List - I with List - II.
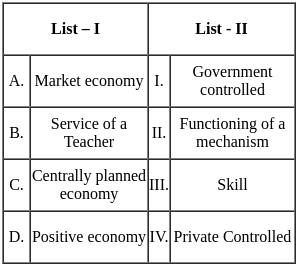
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(b) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Key Points
Market economy
- A market economy is characterized by private control over the production and distribution of goods and services.
- Prices and production are driven by competition among private businesses.
Service of a Teacher
- The service of a teacher involves a high level of skill and expertise in imparting knowledge and facilitating learning.
- Teachers require specialized education and training to effectively perform their roles.
Centrally planned economy
- A centrally planned economy is one where the government controls all major aspects of economic production and distribution.
- Decisions about what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce are made by the government.
Positive economy
- Positive economics focuses on describing and explaining economic phenomena as they are, often using the functioning of a mechanism approach.
- It is based on factual statements and avoids value judgments.
Additional Information
Market economy
- Examples include the United States and most Western countries where businesses operate with minimal government interference.
- Market economies are often associated with high levels of innovation and efficiency due to competitive pressures.
Service of a Teacher
- The role of a teacher extends beyond just delivering content; it includes mentoring, evaluating, and supporting students' overall development.
- Professional development and continuous learning are crucial for teachers to stay updated with the latest educational methodologies.
Centrally planned economy
- Examples include the former Soviet Union and North Korea, where the government has significant control over economic activities.
- Centrally planned economies often face challenges such as inefficiencies and lack of innovation due to the absence of competition.
Positive economy
- Positive economics is concerned with "what is" rather than "what ought to be," making it distinct from normative economics.
- It uses scientific methods to analyze economic behavior and outcomes, often utilizing data and empirical evidence.
Q48: The measurement of human abilities/personality/interest encounters problems in:
(A) Selecting attributes of variables
(B) Developing Educational devices/Test
(C) Quantifying the attributes
(D) Determining operations to isolate the attributes
(E) Preparing standard scores
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), (D) and (E) Only
(b) (B), (C), (D) and (E) Only
(c) (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (C), (D) and (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
Key Points
Selecting attributes of variables
- The process of identifying which human abilities, personality traits, or interests to measure can be complex and subjective.
Developing Educational devices/Test
- Creating reliable and valid tests to measure these attributes requires careful planning and expertise.
Quantifying the attributes
- Assigning numerical values to abstract qualities such as personality or interest involves sophisticated psychometric techniques.
Determining operations to isolate the attributes
- It is challenging to develop procedures that can accurately isolate and measure individual attributes without interference from other factors.
Additional Information
Preparing standard scores
- While preparing standard scores is important, it is generally a step that follows the initial measurement and analysis of attributes.
- Standard scores are used to interpret and compare individual scores within a normative framework.
Psychometrics
- This field focuses on the theory and technique of psychological measurement, which includes the development of tests and the quantification of attributes.
- Key areas include test reliability, validity, and standardization.
Validity and Reliability
- Validity: Refers to the degree to which a test measures what it claims to measure.
- Reliability: Refers to the consistency of a test in measuring an attribute over time.
Q49: T-Score of a particular score in a data set is 50. If each score of the data set is multiplied by 10, what will be the new T-score of that particular score ?
(a) 500
(b) 5
(c) 50
(d) 0
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - 50
Key Points
T-Score Calculation
- The T-score is a standard score that indicates how many standard deviations a data point is from the mean.
- It is calculated using the formula: T = 50 + 10 * z, where z is the z-score of the data point.
Effect of Multiplying Scores
- Multiplying each score by a constant scales both the mean and the standard deviation by the same factor.
- However, the z-score (which is the number of standard deviations away from the mean) remains unchanged.
Impact on T-Score
- Since the z-score remains the same, the T-score, which is derived from the z-score, also remains unchanged.
- Hence, if the original T-score is 50, the new T-score will still be 50.
Additional Information
Standard Scores
- Standard scores, such as z-scores and T-scores, are used to compare data points from different distributions.
- These scores help in understanding the position of a data point relative to the mean of the distribution.
Z-Score
- The z-score is calculated using the formula: z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the data point, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation.
- A z-score indicates how many standard deviations a data point is from the mean.
Implications in Data Analysis
- Understanding transformations such as multiplication is crucial for data normalization and standardization.
- These concepts are widely used in statistical analysis, machine learning, and other data science applications.
Q50: Arrange the sequence of indirect teacher talk category in Flanders' Interaction Analysis:
(A) Accepts feeling
(B) Praises or encourages
(C) Asks questions
(D) Using pupils idea
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Note:- This question is dropped by NTA in UGC NET Exam, so we have made some changes in question and options too.
(a) (A), (B), (D), (C)
(b) (A), (B), (C), (D)
(c) (C), (A), (B), (D)
(d) (D), (A), (C), (B)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - (B), (A), (D), (C)
Key Points
Indirect Teacher Talk Categories
- Accepts feeling (A)
- This involves acknowledging and accepting students' emotions or feelings.
- Praises or encourages (B)
- This includes positive reinforcement given by the teacher to the students.
- Using pupils' ideas (D)
- This category includes integrating and utilizing students' ideas into the teaching process.
- Asks questions (C)
- Teachers use this category to inquire and stimulate student thinking and responses.
Additional Information
Flanders' Interaction Analysis
- Developed by Ned Flanders, this system is used to analyze classroom interaction.
- It categorizes teacher and student behaviors into different types to evaluate the teaching process.
- Helps in understanding the dynamics of classroom communication and improving teaching strategies.
Benefits of Using Flanders' Interaction Analysis
- Provides a systematic method to observe and improve teaching effectiveness.
- Encourages reflective teaching practices.
- Helps in identifying areas that need improvement in classroom interaction.
Q51: On the recommendation of which of the following committee on transformative reforms in accreditations, the executive committee of NAAC had proposed launching of reforms in two phases-Binary Accreditation and Maturity Based Graded Level ?
(a) Dr. D. P. Singh Committee
(b) Dr. Ganesh Kannabiran Committee
(c) Dr. Radhakrishnan Committee
(d) Dr. Subhas Roy Committee
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Dr. Radhakrishnan Committee
Key Points
Dr. Radhakrishnan Committee
- This committee was formed to propose transformative reforms in the accreditation processes of higher education institutions in India.
- The committee recommended introducing a two-phase accreditation system:
- Binary Accreditation: A simplified process to assess whether an institution meets the basic standards of quality.
- Maturity-Based Graded Level: A more detailed evaluation based on the institution's level of maturity and quality improvement over time.
- The recommendations were aimed at making the accreditation process more transparent and efficient, ensuring wider participation of institutions.
Additional Information
National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC)
- NAAC is an autonomous institution under the University Grants Commission (UGC), responsible for assessing and accrediting higher education institutions in India.
- Its primary objective is to ensure the quality of education by evaluating institutions on criteria such as teaching-learning processes, infrastructure, and research output.
Binary Accreditation
- This phase determines whether an institution meets the minimum quality benchmarks set by NAAC.
- Institutions are given a simple "Yes" or "No" accreditation status based on their compliance with basic criteria.
Maturity-Based Graded Level
- This phase evaluates an institution on a graded scale, taking into account its growth, sustainability, and continuous quality improvements.
- Institutions are awarded grades such as A++, A+, A, etc., based on their performance in various parameters.
Transformative Reforms
- The reforms aim to simplify and strengthen the accreditation framework, enabling institutions to focus on quality enhancement rather than just compliance.
- This initiative aligns with the goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasizes improving the quality of higher education in India.
Q52: Match List - I with List - II.
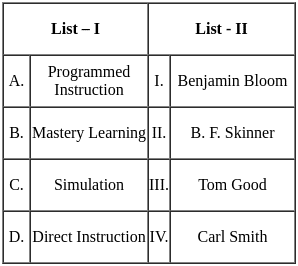
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Key Points
Programmed Instruction
- Associated with B. F. Skinner, who developed the concept of instructional programs that allow students to work at their own pace and receive immediate feedback.
Mastery Learning
- Proposed by Benjamin Bloom, emphasizing that students must achieve a level of mastery in prerequisite knowledge before moving forward to learn subsequent information.
Simulation
- Linked with Carl Smith, who utilized simulations for teaching complex systems and processes.
Direct Instruction
- Associated with Tom Good, focusing on structured, explicit teaching methods.
Additional Information
Programmed Instruction
- Uses teaching machines or computer-assisted instruction to provide personalized learning experiences.
- Based on the principles of operant conditioning.
Mastery Learning
- Involves formative assessments to identify learning gaps.
- Ensures all students achieve a high level of understanding before progressing.
Simulation
- Enables experiential learning through role-playing and scenario-based activities.
- Helps in understanding complex systems and decision-making processes.
Direct Instruction
- Characterized by teacher-led demonstrations and practices.
- Focuses on clear, specific teaching objectives and structured lessons.
Q53: As per the gazette notification of 2021, w.r.t. ITEP, which of the following degree will be the outcome of the four-year Integrated Teacher Education Programme :
(a) B.A. B.Ed / B.Sc. B.Ed / B.Com. B.Ed
(b) ITEP
(c) B.Ed
(d) BA.Ed/BSc.Ed/BCom.Ed
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - B.A. B.Ed / B.Sc. B.Ed / B.Com. B.Ed
Key Points
Four-Year Integrated Teacher Education Programme (ITEP)
- The ITEP is designed to integrate general and teacher education programs.
- Graduates will receive dual degrees, such as B.A. B.Ed, B.Sc. B.Ed, or B.Com. B.Ed, upon successful completion.
- This integrated approach ensures that future teachers are well-prepared with both subject matter expertise and pedagogical skills.
Gazette Notification of 2021
- The 2021 notification formally introduced and outlined the structure of the ITEP.
- It specified the degrees conferred upon completion, which are B.A. B.Ed, B.Sc. B.Ed, and B.Com. B.Ed.
Additional Information
Benefits of the ITEP
- Prepares teachers with a deep understanding of both their subject and teaching methodologies.
- Streamlines the process of becoming a qualified teacher by combining undergraduate and teacher education.
Other Details
- The program aims to produce highly skilled and qualified teachers to meet the demands of modern education systems.
- ITEP includes practical teaching experience and internships to ensure hands-on learning.
Q54: Match List - I with List - II.
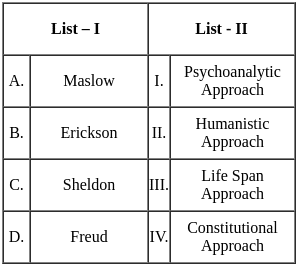
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(b) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Key Points
Maslow - Humanistic Approach
- Maslow is known for his Hierarchy of Needs, which is a key concept in the Humanistic Approach to psychology.
Erickson - Life Span Approach
- Erik Erikson developed the Eight Stages of Psychosocial Development, which is integral to the Life Span Approach.
Sheldon - Constitutional Approach
- William Sheldon is known for his theory of Somatotypes (body types), which is a part of the Constitutional Approach.
Freud - Psychoanalytic Approach
- Sigmund Freud is the father of the Psychoanalytic Approach, focusing on the unconscious mind and early childhood experiences.
Additional Information
Humanistic Approach
- Focuses on individual potential and personal growth.
- Emphasizes concepts such as self-actualization and free will.
Life Span Approach
- Examines the development of individuals from birth to death.
- Addresses various stages and challenges encountered throughout life.
Constitutional Approach
- Explores the relationship between body types and personality traits.
- Sheldon categorized individuals into endomorphs, mesomorphs, and ectomorphs.
Psychoanalytic Approach
- Founded by Freud, it explores the influence of the unconscious mind.
- Involves concepts such as the id, ego, and superego.
Q55: Put the five stages of the 'Design for Six Sigma' in a correct order:
(A) Design the process at a high level before moving onto a more detailed version.
(B) Verify that the final iteration of the product or process is approved by all customers and clients.
(C) Define realistic goals that suit customer requirements.
(D) Analyse multiple options and alternatives for the customer along with the estimated total life cycle of the project.
(E) Measure and identify the customer's critical to quality requirements and translate these into project goals.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (C), (E), (D), (A), (B)
(b) (E), (C), (A), (D), (B)
(c) (C), (E), (A), (D), (B)
(d) (A), (B), (E), (C), (D)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - (C), (E), (D), (A), (B)
Key Points
Define
- First, you need to define realistic goals that align with customer requirements. This step is crucial to ensure that the project is aligned with what the customer expects.
Measure
- Next, you need to measure and identify the customer's critical to quality (CTQ) requirements and translate these into project goals. This ensures that the project objectives are quantifiable and aligned with customer needs.
Analyse
- After defining and measuring, you should analyse multiple options and alternatives for the customer, including the estimated total life cycle of the project. This step helps in identifying the best possible solutions.
Design
- Once the analysis is complete, you can then design the process at a high level before moving on to more detailed versions. This step ensures that the design is robust and meets the project requirements.
Verify
- Finally, you need to verify that the final iteration of the product or process is approved by all customers and clients. This step ensures that the product meets all customer requirements and is ready for implementation.
Additional Information
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)
- DFSS is a systematic approach to designing products and processes that meet customer expectations and can be produced at Six Sigma quality levels.
- It involves using Six Sigma tools and methodologies during the design phase to prevent defects and ensure quality.
Critical to Quality (CTQ)
- CTQ represents the key measurable characteristics of a product or process that must be met to satisfy the customer.
- Identifying CTQ requirements is essential for ensuring that the design and final product align with customer needs.
Total Life Cycle
- Considering the total life cycle of a project involves evaluating all phases from conception to disposal, ensuring that the design is sustainable and cost-effective over time.
Q56: Which of the following statements are True?
(A) Alfred Adler disagreed with Freud's idea that the cause of human emotionality was 'unconscious conflicts'.
(B) Aaron Beck developed Cognitive Psychotherapy in 1960's.
(C) Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) came into usage around early 1950's.
(D) In ABC Model, 'C' represents the resultant emotion or behaviour.
(E) In ABC model, 'A' represents assimilation.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (D), (B) Only
(b) (A), (C), (D) Only
(c) (E), (D), (B) Only
(d) (A), (B), (E) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Option 1
Key Points
Alfred Adler disagreed with Freud's idea that the cause of human emotionality was 'unconscious conflicts'.
- Adler believed that human behavior was motivated by social influences and a striving for superiority, rather than Freud's emphasis on unconscious conflicts.
Aaron Beck developed Cognitive Psychotherapy in the 1960's.
- Beck's cognitive therapy focuses on changing unhelpful cognitive distortions and behaviors, improving emotional regulation, and developing personal coping strategies.
In the ABC Model, 'C' represents the resultant emotion or behavior.
- The ABC Model stands for Antecedent (A), Belief (B), and Consequence (C).
- 'C' refers to the emotional or behavioral outcome resulting from the belief about the activating event.
Additional Information
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)
- CBT was developed in the 1960s and 1970s, not the early 1950s.
- It combines cognitive and behavioral techniques to address maladaptive thinking patterns and behaviors.
In the ABC Model, 'A' represents the activating event, not assimilation.
- 'A' stands for the antecedent or activating event that triggers a belief (B) which then leads to a consequence (C).
Freud's Theories
- Freud's psychoanalytic theory emphasizes the role of unconscious conflicts, mainly arising from childhood experiences, in shaping personality and behavior.
Q57: According to the leader-member exchange theory, the sub-group of Low-quality exchanges is viewed as:
(a) Out-group
(b) In-group
(c) Advisors
(d) Followers
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Out-group
Key Points
Out-group
- According to the leader-member exchange theory, relationships between leaders and members are categorized into high-quality and low-quality exchanges.
- Members who experience low-quality exchanges are considered to be part of the Out-group.
- These members typically have limited interaction with the leader and receive fewer opportunities and support.
Additional Information
Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory
- LMX theory emphasizes the dyadic relationship between leaders and each of their followers.
- The theory suggests that leaders develop unique relationships with each member, which can impact job satisfaction and performance.
High-Quality Exchanges
- Members in the In-group have high-quality exchanges, characterized by trust, respect, and mutual obligation.
- These members often receive more support, resources, and recognition from their leader.
Implications of Low-Quality Exchanges
- Members in the Out-group might experience lower morale and job dissatisfaction.
- This can affect their overall work performance and motivation.
Q58: Which statements define educational finance at the micro and macro levels?
(A) Macro finance is framed for the needs used of an individual, small industries and small business units.
(B) Macro finance includes drafting policy, subsidies, multiyear expansion plans.
(C) The main aim of micro finance is to help economy grow and to generate employment.
(D) Macro finance has direct effect on whole economy and indirect effect on the whole population.
(E) Micro finance is an endless activity.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (E) Only
(b) (B) and (D) Only
(c) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - (B), (C) and (D) Only
Key Points
Macro finance
- Involves drafting policy, providing subsidies, and planning multiyear expansion plans which affect the broader economy. (Statement B)
- Has a direct effect on the whole economy and an indirect effect on the general population. (Statement D)
Micro finance
- Aims to help the economy grow and to generate employment. (Statement C)
Additional Information
Macro finance
- Includes nationwide financial strategies and policy implementations that impact the country's overall economic framework.
- Examples: Federal budget, fiscal policies, and large-scale infrastructure projects.
Micro finance
- Targets individuals, small businesses, and local economies by providing access to financial services like loans, savings, and insurance.
- Helps in poverty alleviation and economic development at the grassroots level.
Q59: Which of the following is TRUE about Learning Theories?
(A) Kurt Lewin was one of the founding fathers of Gestalt Psychology.
(B) Albert Bandura described Human Behaviour and learning on the basis of three key concepts Life spaces, Vector, insight
(C) Kohler's book related to experiments on chimpanzees was 'Mentality of Apes'
(D) Skinner opposed the "no stimulus, no response" mechanism in the evolution of behaviour.
(E) A positive reinforcer is any stimulus the removal or withdrawl of which decreases the likelihood of a particular behaviour.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C), (D) Only
(b) (B), (D), (E) Only
(c) (A), (C), (E) Only
(d) (A), (B), (E) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (C), (D) Only
Key Points
Kurt Lewin
- Kurt Lewin is recognized as one of the founding fathers of Gestalt Psychology.
- Gestalt Psychology emphasizes understanding the human mind and behavior as a whole rather than in parts.
Kohler's book
- Kohler’s book titled ‘Mentality of Apes’ focuses on his experiments with chimpanzees.
- The book is a significant contribution to the field of Gestalt Psychology and problem-solving.
Skinner's opposition
- Skinner opposed the "no stimulus, no response" mechanism, emphasizing that behavior can be shaped through reinforcement.
- He is well-known for his work on Operant Conditioning.
Additional Information
Albert Bandura
- Albert Bandura is known for his Social Learning Theory, which emphasizes learning through observation, imitation, and modeling.
- Key concepts of Bandura's theory include attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation.
Positive Reinforcer
- A positive reinforcer is any stimulus that, when presented after a behavior, increases the likelihood of that behavior occurring again.
- It is the opposite of a negative reinforcer, which increases behavior by removing an unpleasant stimulus.
Q60: Which of the following is NOT correct ?
(a) Qualitative research often avoid stating hypotheses before data are collected.
(b) A positivist believes that qualities of natural phenomenon must be verified by evidence after considering them as knowledge.
(c) The quantitative framework in educational research involves the application of the scientific method to try to answer questions about education.
(d) Quantitative research usually tests a specific hypotheses, qualitative research often does not.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A positivist believes that qualities of natural phenomenon must be verified by evidence after considering them as knowledge.
Key Points
Positivist Approach
- A positivist believes that knowledge should be derived from scientific evidence and empirical data.
- They emphasize observation, measurement, and experimentation.
- The statement that "qualities of natural phenomenon must be verified by evidence after considering them as knowledge" is incorrect because positivists do not consider phenomena as knowledge until verified.
Additional Information
Qualitative Research
- Qualitative research often avoids stating hypotheses before data collection to remain open to new findings.
- Researchers use methods such as interviews, focus groups, and observations.
Quantitative Research
- Quantitative research involves the application of the scientific method to answer specific questions.
- It typically involves the formulation of hypotheses, data collection, and statistical analysis.
- Quantitative research usually tests a specific hypothesis, while qualitative research often does not.
Scientific Method
- The scientific method is a systematic way of learning about the world through observation and experimentation.
- It is fundamental to quantitative research and involves forming hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing data to draw conclusions.
Q61: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
Key Points
Perceptual Reasoning (A - III)
- Includes tasks that assess the ability to interpret and organize visually presented material.
- Examples of such tasks are Block Design, Matrix Reasoning, and Visual Puzzles.
Working Memory (B - II)
- Involves the ability to hold and manipulate information in the mind over short periods.
- Examples include Digit Span and Arithmetic.
Processing Speed (C - IV)
- Measures the speed of mental and eye/hand coordination tasks.
- Examples include Symbol Search and Coding.
Verbal Comprehension (D - I)
- Assesses the understanding of language-based tasks and information.
- Examples include Similarities, Vocabulary, and Information.
Additional Information
Perceptual Reasoning
- In cognitive assessments, it is crucial for problem-solving involving visual-motor and spatial skills.
- Tasks often require the participant to conceptualize and reason with visual information.
Working Memory
- This cognitive function is critical for tasks involving the temporary storage and manipulation of information.
- It is a core component of executive function and is highly correlated with overall intellectual ability.
- Processing Speed
- Important for tasks that require quick and efficient mental operations.
- Higher processing speed is associated with better performance on complex cognitive tasks.
Verbal Comprehension
- Key in understanding and processing language, important for academic success and everyday communication.
- Includes tasks that measure knowledge of words, the ability to reason using language, and general knowledge.
Q62: As per NEP-2020, National Educational Technology Forum will have the following functions:
(A) Envision strategic thrust areas in educational technology
(B) Articulate new directions for research and innovation
(C) Establish a state of art "Technology Centre' in Gujarat
(D) Provide independent evidence based advice to Centre and state government on technology based intervention
(E) Allocate research projects in field of educational technology from 2026.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C), (D), (E) Only
(b) (A), (B), (D) Only
(c) (B), (D), (E) Only
(d) (A), (D), (E) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (B), (D) Only
Key Points
Envision strategic thrust areas in educational technology
- The National Educational Technology Forum (NETF) is tasked with identifying key strategic areas for the integration and advancement of educational technology.
- This includes the development and implementation of technological solutions that can enhance the educational landscape in India.
Articulate new directions for research and innovation
- One of the core functions of the NETF is to promote and guide research and innovation in the field of educational technology.This involves identifying emerging trends and facilitating research that can lead to innovative educational tools and practices.
Provide independent evidence-based advice to Centre and state governments on technology-based interventions
- The NETF is responsible for providing unbiased, evidence-based recommendations to both central and state governments.
- These recommendations are aimed at ensuring that technology-based educational interventions are effective and aligned with national educational goals.
Additional Information
National Educational Technology Forum (NETF)
- The NETF is a part of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which aims to transform the educational landscape in India through technology.
- It serves as a platform for free exchange of ideas on the use of technology to enhance learning, assessment, planning, administration, and so on.
Functions Not Included
- Establishing a state-of-the-art Technology Centre in Gujarat: This is not one of the stated functions of the NETF as per NEP-2020.
- Allocating research projects in the field of educational technology from 2026: There is no specific mention of NETF allocating research projects starting from a particular year like 2026.
Q63: A Teacher uses Socratic method to help students in developing critical thinking skills during a lesson on global warming. This method best aligns with which theorist’s principle?
(a) Skinner
(b) Piaget
(c) Vygotsky
(d) Bruner
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Bruner
Key Points
Bruner
- Jerome Bruner's theories emphasize the importance of discovery learning and inquiry-based learning.
- The Socratic method aligns with Bruner's principles as it encourages students to explore, question, and construct their own understanding.
- Using this method, the teacher guides students to develop critical thinking skills by asking probing questions.
Additional Information
Socratic Method
- An approach where the teacher asks a series of thought-provoking questions to stimulate students' critical thinking and illuminate ideas.
- Encourages students to engage in dialogue rather than passively receiving information.
Other Theorists
- Skinner: Known for Behaviorism, focusing on reinforcement and punishment as key to learning, not inquiry-based learning.
- Piaget: Emphasized cognitive development stages and how children construct knowledge over time, but not specifically the Socratic method.
- Vygotsky: Focused on social interaction and the Zone of Proximal Development as crucial to learning, but not directly tied to the Socratic method.
Q64: Kolb's experiential learning model follows the cycle:
(A) Formation of abstract concepts and generalisation
(B) Students make their own observations
(C) Concrete experience
(D) Testing implications of the concepts in new situations (E) Reflections
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (A), (C), (D), (E)
(b) (C), (B), (E), (A), (D)
(c) (C), (A), (E), (B), (D)
(d) (B), (C), (A), (E), (D)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Option 2: (C), (B), (E), (A), (D)
Key Points
Kolb’s Experiential Learning Model
- This model describes the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience.
- It is a cyclical model consisting of four stages:
- Concrete Experience (C): The learner actively experiences an activity.
- Reflective Observation (B): The learner consciously reflects back on that experience.
- Abstract Conceptualization (A): The learner attempts to conceptualize a theory or model of what is observed.
- Active Experimentation (D): The learner tries to plan how to test a model or theory or plan for a forthcoming experience.
Additional Information
Detailed Stages of Kolb’s Model
- Concrete Experience (CE)
- This is the first stage where the learner encounters a new experience or reinterprets an existing experience.
- Reflective Observation (RO)
- In this stage, the learner reflects on the experience on a personal basis.
- Abstract Conceptualization (AC)
- Reflection gives rise to a new idea, or a modification of an existing abstract concept.
- Active Experimentation (AE)
- The learner applies the new ideas to the world around them to see what happens.
Application of Kolb’s Model
- It is widely used in various fields like education, training, and personal development.
- Helps in designing effective learning experiences and activities.
Q65: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Key Points
Q Methodology
- Developed by William Stephenson in 1953.
- This method is used to study people's "subjectivity"—that is, their viewpoint.
'Guess Who'
- Associated with Hartshorne and May (1929).
- It is a sociometric technique used to study children's social relationships and attitudes.
Student's distribution
- Created by William Sealy Gosset, who published under the pseudonym "Student".
- Used in small sample size statistics to estimate the mean of a normally distributed population.
Bootstrap Method
- Introduced by Bradley Efron in 1979.
- It is a resampling method that involves repeatedly drawing samples from a dataset to estimate the distribution of a statistic.
Additional Information
Q Methodology
- Combines both qualitative and quantitative research techniques.
- Participants sort statements according to their level of agreement, providing a basis for understanding their perspectives.
'Guess Who'
- Used to measure social traits such as leadership, popularity, and aggression among children.
- Helps in identifying peer relationships and social structures within groups.
Student's t-distribution
- Critical in small-sample hypothesis testing.
- Provides a basis for t-tests, which are used to determine if there are significant differences between groups.
Bootstrap Method
- Useful in estimating the sampling distribution of almost any statistic.
- Does not rely on the assumption of normality, making it versatile for various types of data.
Q66: Swami Vivekanand in his famous speech in Chicago, 1893 conceptualised ‘Universal Acceptance’.
Which of the following statement encapsulates his philosophy about religion and human nature
(a) The ultimate goal of all humanity is to see the divinity in oneself and in others.
(b) All religions are merely path to the same truth, one must transcend religious dogma to realize the awareness of all.
(c) The true spirituality is renunciation from all worldly affairs.
(d) Every human is an embodiment and manifestation of the divine and thus all forms of worship are equally valid.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - All religions are merely paths to the same truth, one must transcend religious dogma to realize the awareness of all.
Key Points
Swami Vivekananda's Philosophy
- Swami Vivekananda emphasized the idea that all religions lead to the same ultimate truth.
- He advocated for transcending religious dogma and realizing the awareness of the divine in all.
- This perspective promotes the idea of Universal Acceptance among different faiths.
Additional Information
Universal Acceptance
- In his 1893 Chicago speech, Swami Vivekananda spoke about tolerance and acceptance of all religions.
- He believed that every religion has a unique way to reach the divine but ultimately aims for the same truth.
Impact on Interfaith Harmony
- Swami Vivekanand's ideas have been influential in promoting interfaith dialogue and understanding.
- His teachings encourage people to see beyond the differences and focus on the commonalities among various religions.
Philosophical Context
- His philosophy aligns with the Vedantic idea that the divine is present in all beings.
- This idea also resonates with the concept of spiritual unity and the belief in the inherent divinity of all individuals.
Q67: Keeping in consideration wide range of special education and related services, most schools provide a continuum of services. Arrange the following in order of increasing severity of disabilities.
(A) Full-time separate classroom
(B) Regular classroom with supplementary instruction and services
(C) Regular classroom
(D) Special school
(E) Regular classroom and Resource room
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (C), (E), (B), (D), (A)
(b) (C), (B), (E), (A), (D)
(c) (C), (A), (B), (E), (D)
(d) (C), (D), (E), (B), (A)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - (C), (B), (E), (A), (D)
Key Points
Regular classroom (C)
- Students with disabilities spend the majority of their time in general education classrooms.
- They receive the same education as their non-disabled peers.
Regular classroom with supplementary instruction and services (B)
- Students are in general education classrooms but receive additional support such as tutoring or therapy.
- This helps them keep up with the curriculum.
Regular classroom and Resource room (E)
- Students split time between general education classrooms and specialized resource rooms.
- Resource rooms provide targeted instruction to address specific needs.
Full-time separate classroom (A)
- Students spend most or all of their school day in a specialized classroom.
- These classrooms are designed for students with significant disabilities requiring specialized instruction.
Special school (D)
- Students attend a school specifically designed for individuals with significant disabilities.
- These schools offer highly specialized programs and services.
Additional Information
Least Restrictive Environment (LRE)
- IDEA mandates that students with disabilities should be educated in the least restrictive environment appropriate for their needs.
- General education classrooms are considered the least restrictive, followed by supplementary services, resource rooms, separate classrooms, and special schools.
Individualized Education Program (IEP)
- Each student with a disability has an IEP outlining specific educational goals and the services required to achieve them.
- The IEP team determines the appropriate setting and services based on the student's unique needs.
Continuum of Services
- This refers to the range of placement options available to meet the diverse needs of students with disabilities.
- It ensures that students receive the appropriate level of support while being included in general education settings to the maximum extent possible.
Q68: Which of the following is NOT a basic principle of curriculum development ?
(a) Principle of Totality
(b) Principle of Leisure
(c) Principle of Maturity
(d) Principle of Flexibility
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Principle of Leisure
Key Points
Principle of Leisure
- The Principle of Leisure is not commonly recognized as a foundational element in curriculum development.
- Curriculum development focuses on comprehensive educational goals, and leisure is not a primary consideration.
- Key principles of curriculum development include elements that support structured learning and educational growth.
Additional Information
Principle of Totality
- This principle ensures that the curriculum addresses the holistic development of the learner, integrating various aspects of education.
- It considers the learner's physical, emotional, social, and intellectual needs.
Principle of Maturity
- This principle acknowledges the developmental stages of learners, ensuring that the curriculum is appropriate for their age and maturity level.
- It helps in creating content that is relevant and engaging for different age groups.
Principle of Flexibility
- This principle emphasizes the need for the curriculum to be adaptable to changes in society, technology, and the needs of the learners.
- It allows for modifications and updates to the curriculum to keep it relevant and effective.
Q69: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(b) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Key Points
Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act - 2009
- This act came into force on 1 April 2010.
- It ensures free and compulsory education for all children aged 6 to 14 years.
Commission for Protection of Child Rights Act - 2005
- This act was enacted to ensure the protection of child rights and the establishment of a National Commission for Protection of Child Rights.
- The commission is responsible for monitoring and examining the safeguards provided for the protection of child rights.
National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) Act - 1993
- The NCTE Act was established to formally oversee standards, procedures, and processes in the Indian education system.
- The council ensures that teacher education programs are conducted within the prescribed norms and standards.
University Grant Commission (UGC) Act - 1956
- This act led to the establishment of the UGC, which coordinates, determines, and maintains the standards of university education in India.
- The UGC provides recognition to universities in India and disburses funds to such recognized universities and colleges.
Additional Information
Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act
- The act mandates that every child has the right to full-time elementary education of satisfactory and equitable quality in a formal school.
- It also includes provisions for the establishment of a child-friendly and inclusive school environment.
Commission for Protection of Child Rights Act
- The act provides for the constitution of a National Commission and State Commissions for the protection of child rights.
- It aims to review the existing policies and make recommendations for the effective implementation of child rights.
National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) Act
- The act empowers the NCTE to regulate the standards and norms for teacher education institutions.
- It ensures that teachers are well-prepared to cater to the diverse needs of students in various educational settings.
University Grant Commission (UGC) Act
- The UGC ensures that universities meet the required standards of higher education.
- It also provides grants to universities and colleges for their development and to improve their infrastructure.
Q70: Which of the following statements are INCORRECT ?
(A) Rehabilitation Council of India Act was passed in 1992.
(B) Persons with Disabilities Act was modified in 2010.
(C) UNCRPD talks about compulsory inclusive education.
(D) National Policy on Disabilities originated from RTE Act 2009.
(E) National Curriculum Framework was prepared in 2005.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (C) Only
(b) (B) and (D) Only
(c) (B) and (E) Only
(d) (A) and (B) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - (B) and (D) Only
Key Points
(B) Persons with Disabilities Act was modified in 2010
- This statement is incorrect because the Persons with Disabilities (Equal Opportunities, Protection of Rights and Full Participation) Act was enacted in 1995 and not modified in 2010.
- In 2016, it was replaced by the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, which broadened the definition and scope of disabilities.
(D) National Policy on Disabilities originated from RTE Act 2009
- This statement is incorrect because the National Policy for Persons with Disabilities was formulated in 2006, well before the Right to Education (RTE) Act of 2009.
- These two are separate policies addressing different aspects of social welfare and rights.
Additional Information
Rehabilitation Council of India Act, 1992
- This act was passed to regulate and monitor the training of rehabilitation professionals and personnel, and to promote research in the rehabilitation field.
UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD)
- Adopted in 2006, it emphasizes the importance of inclusive education for persons with disabilities.
- It promotes accessible and inclusive educational environments at all levels of education.
National Curriculum Framework, 2005
- This framework aimed to make education more flexible and relevant to the needs of children.
- It was developed by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) in India.
Q71: Match List - I with List - II.
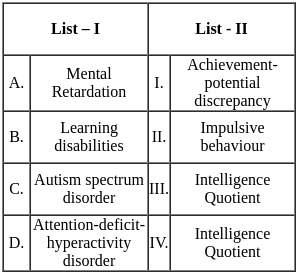
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Key Points
A. Mental Retardation - III. Intelligence Quotient
- Mental retardation is characterized by significantly below-average intellectual functioning which is often measured by an Intelligence Quotient (IQ) test.
B. Learning disabilities - I. Achievement-potential discrepancy
- Learning disabilities are often identified by a significant discrepancy between a student's achievement and their potential, as measured by intelligence tests.
C. Autism spectrum disorder - IV. Intelligence Quotient
- Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disorder that affects communication and behavior. It can also be associated with varying levels of intelligence which can be measured by an Intelligence Quotient (IQ) test.
D. Attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder - II. Impulsive behaviour
- Attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is characterized by patterns of impulsivity, inattention, and hyperactivity.
Additional Information
Mental Retardation
- Refers to intellectual disability involving significant limitations in both intellectual functioning and in adaptive behavior.
- IQ tests are commonly used to assess the level of cognitive functioning.
Learning Disabilities
- Conditions that affect the brain's ability to receive, process, store, and respond to information.
- Includes dyslexia, dyscalculia, and dysgraphia.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- A range of neurodevelopmental conditions characterized by challenges with social skills, repetitive behaviors, and communication.
- Individuals with ASD may have a wide range of intellectual abilities.
Attention-Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- A mental health disorder that includes a combination of persistent problems, such as difficulty sustaining attention, hyperactivity, and impulsive behavior.
- Often diagnosed in childhood but can continue into adulthood.
Q72: The first written examination to test spelling achievement of students was used by :
(a) Joseph M. Rice
(b) R. M. Thorndike
(c) Binet-Simon
(d) DuBois
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Joseph M. Rice
Key Points
Joseph M. Rice
- Joseph M. Rice was an American educator and a pioneer in the field of educational testing.
- He is credited with conducting the first large-scale written examinations to assess spelling achievement among students.
- His work in the early 20th century laid the foundation for modern standardized testing practices.
Additional Information
Standardized Testing
- Standardized testing refers to a testing method that administers the same test in the same manner to all test takers.
- It is designed to ensure consistency and comparability of scores, making it possible to evaluate student performance objectively.
- Common examples include SAT, ACT, and GRE exams.
History of Educational Testing
- Early educational testing was influenced by the need to measure educational outcomes systematically.
- Key figures include Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon, who developed the first intelligence tests, and E. L. Thorndike, who contributed to the development of multiple-choice testing formats.
- These developments have significantly shaped modern educational assessment practices.
Q73: A job application ‘Portfolio’ is a :
(a) Finished Portfolio
(b) Documentation Portfolio
(c) Progress Portfolio
(d) Working Portfolio
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Finished Portfolio
Key Points
Finished Portfolio
- A Finished Portfolio is a comprehensive collection of an applicant's best work and achievements.
- It is typically presented during the final stages of a job application process to demonstrate proficiency and readiness.
- This type of portfolio is well-organized and includes completed projects that highlight the applicant's skills and accomplishments.
- Employers use Finished Portfolios to assess an applicant's capabilities and suitability for the role.
Additional Information
Types of Portfolios
Documentation Portfolio
- Contains records and evidence of an applicant's skills, experiences, and learning over time.
- Used primarily for educational purposes and to track an individual's progress and development.
Progress Portfolio
- Focuses on an individual's growth and improvement in specific areas.
- Includes drafts, revisions, and self-assessments to show the learning process.
Working Portfolio
- Used for ongoing projects and is a collection of current work and tasks.
- Helps in tracking progress and planning future work.
Q74: Which of the following value is enshrined in the preamble of the Constitution ?
(a) Individualism
(b) Progressivism
(c) Cosmopolitianism
(d) Secularism
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Secularism
Key Points
Secularism
- The Preamble of the Indian Constitution declares India to be a secular state.
- It implies that the state has no official religion and treats all religions equally.
- This principle ensures that citizens have the freedom to practice, profess, and propagate any religion of their choice.
- Secularism is a fundamental aspect of India's democratic framework, promoting religious harmony and tolerance.
Additional Information
Preamble of the Constitution
- The Preamble outlines the objectives of the Constitution, which include Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity.
- It serves as an introduction to the Constitution and reflects the aspirations and values of the people.
Other Values in the Preamble
- Sovereign
- India is free from external control and has the authority to make its own laws.
- Socialist
- It emphasizes social and economic equality, aiming to reduce income disparities.
- Democratic
- The government is elected by the people, ensuring representation and participation in governance.
- Republic
- The head of the state is elected, not a hereditary monarch.
Q75: Which of the following are features of MOOCs?
(A) Open access to learning content
(B) Optional certificate
(C) Limited enrolment
(D) Low completion rate
(E) Lack of interactivity
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (D), (E) Only
(b) (A), (D), (C) Only
(c) (A), (B), (D) Only
(d) (B), (A), (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (B), (D) Only
Key Points
Open access to learning content
- MOOCs provide unrestricted access to learning materials online, making education accessible to a wide audience.
- This feature promotes inclusive learning by removing barriers related to location, cost, and prerequisites.
Optional certificate
- MOOCs often offer the option to earn a certificate upon completion, providing formal recognition of the learner’s achievement.
- These certificates can be used to enhance resumes or professional portfolios.
Low completion rate
- Despite high enrollment rates, MOOCs typically experience low completion rates.
- Factors contributing to low completion rates include lack of motivation, time constraints, and insufficient support systems.
Additional Information
Limited enrolment
- Unlike traditional courses, MOOCs are designed to handle a large number of participants, often with unlimited enrollment.
- This scalability is one of the key features that distinguish MOOCs from conventional classroom settings.
Lack of interactivity
- Some MOOCs might face challenges related to interactivity due to the high number of participants and the format of online delivery.
- However, many MOOCs are incorporating interactive elements such as forums, peer assessments, and live sessions to enhance engagement.
Q76: According to human capital theory, the main benefit of investing in education is:
(A) Higher wages
(B) Individual Growth
(C) World Ranking of Country
(D) Empowerment of People
(E) Productivity
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(b) (A) and (C) Only
(c) (B) and (D) Only
(d) (A) and (E) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Higher wages and Productivity
Key Points
Higher wages
- According to the human capital theory, investing in education enhances an individual's skills and knowledge.
- This increased skillset makes individuals more valuable to employers, leading to higher wages.
Productivity
- Education and training improve an individual's ability to perform tasks more efficiently and effectively.
- Higher levels of education are associated with increased productivity in the workplace.
Additional Information
Human Capital Theory
- Developed by economists like Gary Becker, the theory posits that investments in education and training are similar to investments in physical capital.
- These investments enhance an individual's economic productivity and potential earnings.
Benefits of Education
- Besides higher wages and productivity, education contributes to personal development and empowerment.
- However, the primary economic rationale for education investment, according to human capital theory, remains the enhancement of wages and productivity.
Q77: The National Commission on Teachers (1983) provided criteria for selection of trainees for becoming teachers. This commission was headed by :
(a) R. N. Chattopadhyaya
(b) D. S. Kothari
(c) V. KR. V. Rao
(d) D. P. Chattopadhyaya
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - D. P. Chattopadhyaya
Key Points
D. P. Chattopadhyaya
- D. P. Chattopadhyaya was the head of the National Commission on Teachers in 1983.
- The commission provided important criteria for the selection of trainees for becoming teachers.
- The commission aimed to improve the quality and standards of teaching and teacher education in India.
Additional Information
National Commission on Teachers (1983)
- Established to address various issues related to teacher education and to provide recommendations for improvement.
- Focused on enhancing the professional development and training of teachers.
Other Key Figures in Educational Commissions
D. S. Kothari
- Chaired the Kothari Commission (1964-66), which aimed to examine all aspects of the educational sector in India.
R. N. Chattopadhyaya
- Also known for contributions in the field of education, but not associated with the 1983 National Commission on Teachers.
V. KR. V. Rao
- Not directly related to the National Commission on Teachers (1983) but known for his significant contributions to Indian education and economic planning.
Q78: Arrange the following in reverse chronological order.
(A) National Commission on Teachers
(B) Kothari Commission
(C) Justice J. S. Verma Committee
(D) National Knowledge Commission
(E) Radhakrishnan Commission
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (D), (B), (A), (C), (E)
(b) (A), (B), (C), (E), (D)
(c) (B), (A), (C), (D), (E)
(d) (C), (D), (A), (B), (E)
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - (C), (D), (A), (B), (E)
Key Points
Justice J. S. Verma Committee (C)
- Established in 2012 to review teacher education and make recommendations for improvement.
National Knowledge Commission (D)
- Formed in 2005 to provide recommendations for reforming the education sector in India.
National Commission on Teachers (A)
- Formed in 1983 to address issues related to teacher education and training.
Kothari Commission (B)
- Established in 1964-66 to formulate general principles and guidelines for the development of education in India.
Radhakrishnan Commission (E)
- Set up in 1948-49 to report on university education and suggest improvements.
Additional Information
Justice J. S. Verma Committee
- Focused on enhancing the quality of teacher education in India.
- Recommended the establishment of state-level teacher education institutions.
National Knowledge Commission
- Advised the Prime Minister on policy related to education, research, and innovation.
- Emphasized the importance of knowledge as a key driver of economic growth.
National Commission on Teachers
- Investigated issues affecting teachers' status, training, and service conditions.
- Recommended measures for improving the quality of teacher training institutions.
Kothari Commission
- Also known as the Education Commission of 1964-66.
- Played a pivotal role in shaping India's educational policy post-independence.
Radhakrishnan Commission
- Officially known as the University Education Commission.
- Laid the foundation for modern higher education in India.
Q79: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
(b) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
Key Points
Arthapatti
- Arthapatti is a method of postulation or presumption in Indian philosophy.
- It is used to explain something that is not directly observed but is inferred from the known facts.
- Example: "He does not eat in day time; he is fat. He eats in night."
Abhava
- Abhava refers to the concept of non-existence or absence in Indian philosophy.
- It is used to denote the absence of something in a particular place at a particular time.
- Example: "A chair is not a table."
Upamana
- Upamana is the process of comparison or analogy in Indian philosophy.
- It is used to gain knowledge about something unknown by comparing it with something known.
- Example: "This cow is different from domestic cow must be a nilgai."
Sabda
- Sabda refers to verbal testimony or the knowledge gained from reliable sources in Indian philosophy.
- It is considered a valid means of knowledge if the source is trustworthy.
- Example: "Conchshell is not a bone according to vedas."
Additional Information
Pramanas
- In Indian philosophy, Pramanas are the means of obtaining knowledge.
- There are six commonly accepted Pramanas: Pratyaksha (perception), Anumana (inference), Upamana (comparison), Arthapatti (postulation), Anupalabdhi (non-cognition), and Sabda (verbal testimony).
Epistemology in Indian Philosophy
- Epistemology is the study of knowledge and justified belief.
- Different Indian philosophical systems have varying interpretations and classifications of Pramanas.
- The Nyaya school, for example, recognizes four Pramanas, while the Mimamsa school recognizes six.
Q80: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - IV, B - II, C - I, D - III
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(c) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
Key Points
The Salamanca Statement
- Adopted in 1994 at the World Conference on Special Needs Education.
- Focuses on inclusive education and the rights of children with disabilities to receive education.
The Rehabilitation Council of India Act
- Enacted in 1992 to regulate and standardize training policies and programs for rehabilitation professionals.
- Aims to ensure the quality of services provided to persons with disabilities.
The Persons with Disabilities Act
- Enacted in 1995 and focuses on the rights and opportunities for persons with disabilities.
- Provides for education, employment, and social security for persons with disabilities.
National Policy for Persons with Disabilities
- Introduced in 2006 to address the needs and rights of persons with disabilities.
- Emphasizes on prevention, early detection, education, employment, and rehabilitation.
Additional Information
Inclusive Education
- Inclusive education ensures that all children, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, learn together in the same age-appropriate classroom.
- It is a fundamental principle of the Salamanca Statement.
Legislation for Disabilities
- Several laws have been enacted globally to protect the rights of persons with disabilities, ensuring equal opportunities and preventing discrimination.
- Examples include the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UN CRPD).
Rehabilitation Services
- Rehabilitation services are critical in helping persons with disabilities achieve and maintain optimal physical, sensory, intellectual, psychological, and social functional levels.
- These services include medical care, therapy, counseling, and vocational training.
Q81: Main features of the grass root approach of curriculum change are:
(A) Small scale experiments
(B) Bottom-up approach
(C) Democratic process
(D) Goal-setting by the practitioners
(E) Face to face problem solving
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (B), (D) and (E) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - (B), (C) and (D) Only
Key Points
Bottom-up approach
- This approach involves initiatives from the grassroots level, ensuring that changes are relevant and practical for those directly involved in the educational process.
Democratic process
- Involves participation from all stakeholders, including teachers, students, and community members, ensuring the curriculum is developed through a collective and inclusive effort.
Goal-setting by the practitioners
- Allows those who are directly involved in the teaching and learning process to set relevant and achievable goals, making the curriculum more practical and effective.
Additional Information
Small scale experiments
- These are initial testing phases often used in curriculum development to assess feasibility and impact before wider implementation.
Face to face problem solving
- This involves direct interaction among stakeholders to address and resolve specific issues in the curriculum, promoting a collaborative and immediate approach to problem-solving.
Q82: Arrange the following as per the competency based curriculum model:
(A) Identification of general competencies
(B) Assessing competencies
(C) Organizing competencies into specific themes
(D) Creating learning experiences
(E) Evaluating the effectiveness of curriculum
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), (C), (D), (E)
(b) (A), (E), (B), (C), (D)
(c) (A), (C), (D), (B), (E)
(d) (A), (C), (D), (E), (B)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - (A), (C), (D), (B), (E)
Key Points
Identification of general competencies
- This is the initial step where general competencies required for the curriculum are identified.
Organizing competencies into specific themes
- Once general competencies are identified, they are organized into specific themes or categories to give structure to the curriculum.
Creating learning experiences
- Based on the organized competencies, relevant learning experiences are designed to help students acquire the identified competencies.
Assessing competencies
- After the learning experiences, assessments are designed to evaluate whether students have acquired the competencies.
Evaluating the effectiveness of curriculum
- The final step involves evaluating the overall effectiveness of the curriculum in achieving its goals and making necessary adjustments.
Additional Information
Competency-Based Curriculum
- This model focuses on the outcomes of learning, where the primary goal is for students to develop specific competencies.
- Competencies are defined as a combination of skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for effective performance.
Steps in Competency-Based Curriculum
- Identification of Competencies: Determine what students need to know and be able to do.
- Organization into Themes: Group the competencies into coherent themes for better structure.
- Learning Experiences: Develop activities and experiences that help students acquire these competencies.
- Assessment: Measure the extent to which students have acquired the competencies.
- Evaluation: Review and refine the curriculum based on feedback and assessment results.
Q83: In 1848, Savitribai Phule along with her husband Jyotiba Phule and Fatima Sheikh opened the first girls’ school. The School’s name was :
(a) Zubeida School
(b) Phule Shikshan Mandir
(c) Bal Gandharva Vidyalaya
(d) Pune Vidyapeeth
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Phule Shikshan Mandir
Key Points
Phule Shikshan Mandir
- It was the first girls’ school in India, established in 1848.
- Founded by Savitribai Phule and her husband Jyotiba Phule along with Fatima Sheikh.
- Aimed to provide education to girls, which was a revolutionary step towards women's empowerment in that era.
- Located in Pune, Maharashtra.
Additional Information
Savitribai Phule
- Considered the first female teacher of India.
- Played a significant role in social reform and women's rights.
- Worked towards abolishing discrimination and promoting education for all.
Jyotiba Phule
- A prominent social reformer and advocate for the education of women and lower castes.
- Founded the Satyashodhak Samaj to promote equality and fight against social evils.
Fatima Sheikh
- One of the first Muslim women educators in India.
- Supported the Phules in their mission to provide education to girls and lower castes.
Educational Reform in 19th Century India
- The establishment of the first girls' school marked a significant step in the movement for women's education.
- It challenged the prevailing gender norms and laid the foundation for future educational reforms.
Q84: Arrange the following according to their licensing and usages flexibility.
(A) Creative Commons Share Alike (CC BY-SA)
(B) Public Domain (PD)
(C) Creative Commons Non directive (CC BY-ND)
(D) Creative Commons by (CC BY)
(E) Creative Commons Non-Commercial (CC BY-NC)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C), (E), (B), (D)
(b) (B), (D), (A), (E), (C)
(c) (D), (E), (A), (C), (B)
(d) (E), (D), (A), (C), (B)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - (B), (D), (A), (E), (C)
Key Points
Public Domain (PD)
- Works in the public domain can be used by anyone for any purpose without restrictions.
- This is the most flexible licensing option.
Creative Common by (CC BY)
- Allows others to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the work, even commercially, as long as they credit the original creation.
- Highly flexible in terms of usage.
Creative Common Share Alike (CC BY-SA)
- Allows others to remix, adapt, and build upon the work even for commercial purposes, as long as they credit the original creation and license their new creations under identical terms.
- Ensures derivatives are also open and free.
Creative Common Non-Commercial (CC BY-NC)
- Allows others to remix, adapt, and build upon the work non-commercially, and although their new works must also acknowledge the original creation, they don’t have to license their derivative works on the same terms.
- Restricts commercial usage.
Creative Common Non-Directive (CC BY-ND)
- Allows for redistribution, commercial and non-commercial, as long as it is passed along unchanged and in whole, with credit to the original creation.
- Does not allow for derivatives.
Additional Information
Public Domain (PD)
- Typically includes works for which copyright has expired, works released by the creator into the public domain, or works that were never eligible for copyright protection.
Creative Commons (CC)
- A licensing system that allows creators to communicate which rights they reserve and which they waive for the benefit of recipients or other creators.
- There are several types of Creative Commons licenses, each with different levels of flexibility.
Q85: Nalanda University was first established during Gupta dynasty. It was a known _____ centre of learning.
(a) Jain
(b) Vedic
(c) Buddhist
(d) Samkhya
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Buddhist
Key Points
Buddhist
- Nalanda University was an ancient center of higher learning in India.
- It was established during the Gupta dynasty in the 5th century CE.
- The university was a renowned Buddhist educational institution.
- It attracted scholars from various parts of the world, including China, Korea, Japan, Tibet, Mongolia, Turkey, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia.
- Renowned for its vast library, Nalanda offered education in various fields but was primarily known for its Buddhist teachings and philosophy.
Additional Information
Gupta Dynasty
- The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire that existed approximately from 320 to 550 CE.
- It is known as a period of significant achievements in arts, science, and political administration.
- During this period, many renowned educational institutions like Nalanda University flourished.
Structure and Curriculum
- The curriculum at Nalanda included not only religious teachings but also a wide array of subjects such as logic, grammar, medicine, meta-physics, and arts.
- The university had eight separate compounds, ten temples, meditation halls, classrooms, lakes, and parks.
Decline and Rediscovery
- Nalanda University declined in the 12th century due to the invasions and destruction by Bakhtiyar Khilji, a Turkish Muslim invader.
- In the 19th century, the ruins of Nalanda were rediscovered and excavated by the Archaeological Survey of India.
Q86: Which of the following is NOT a test of Creativity ?
(a) Remote Associate Test
(b) Sharma’s Divergent Production Ability Test
(c) Minnesota Test of Creative Thinking
(d) Guilford Test of Product Improvement
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Guilford Test of Product Improvement
Key Points
- Remote Associate Test (a): Measures convergent thinking, a component of creativity.
- Sharma’s Divergent Production Ability Test (b): Directly assesses divergent thinking, a core creativity metric.
- Minnesota Test of Creative Thinking (c): Measures fluency, originality, and flexibility in creative thinking.
- Guilford Test of Product Improvement (d): Part of Guilford’s Structure of Intellect, focuses on improving products, which is less directly tied to creativity’s core aspects like ideation and originality.
Additional Information
Creativity Tests
- These tests are designed to assess different dimensions of creative thinking, such as:
- Fluency: The ability to generate a large number of ideas.
- Originality: The ability to produce unique or novel ideas.
- Flexibility: The capacity to produce a variety of ideas or solutions.
- Examples include:
- Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT)
- Wallach-Kogan Creativity Tests
Practical Problem-Solving Tests
- These tests evaluate a person's ability to improve or optimize existing solutions or products, focusing more on practical application rather than pure creative ideation.
- Examples include:
- Guilford's Structure of Intellect (SOI) Model
Q87: Pick the correct statements.
(A) Education is a subject matter of the Central list.
(B) The state of Karnataka has established its own state education policy commission to review NEP 2020 and to give alternative policy for the state.
(C) The government of India spends 6% of GDP on education.
(D) With multiple entry-multiple exit of NEP 2020 one can drop after two years of MBBS with a diploma in nursing.
(E) NEP 2020 promotes private participation in education through the philanthropy.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), (D) and (E) Only
(b) (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (B) and (E) Only
(d) (A), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - (B) and (E) Only
Key Points
(B) The state of Karnataka has established its own state education policy commission to review NEP 2020 and to give alternative policy for the state.
- This indicates the state-level autonomy in educational policy-making.
- It reflects the state's initiative to tailor education policies according to its specific needs and context.
(E) NEP 2020 promotes private participation in education through the philanthropy.
- NEP 2020 encourages the involvement of private entities in the education sector.
- This participation is aimed at enhancing the quality and reach of education through philanthropic efforts.
Additional Information
Education and the Central List
- Education is actually a subject in the Concurrent List, allowing both the central and state governments to legislate on it.
- This means that statement (A) is incorrect as it is not solely a subject matter of the Central list.
Government Spending on Education
- The government of India aims to increase its spending on education to 6% of GDP as per various policy documents, but this target has not been consistently met.
- Statement (C) is therefore misleading as it does not reflect the current expenditure accurately.
NEP 2020 and Medical Education
- The NEP 2020 does propose flexibility in higher education, including multiple entry and exit points.
- However, the specific provision mentioned in statement (D) about dropping out of MBBS with a diploma in nursing is not accurate under NEP 2020.
Q88: In 1987, NCERT launched the ‘Project on Integrated Education for Disabled (PIED)’ in conjunction with :
(a) UNESCO
(b) WHO
(c) Asian Development Bank (ADB)
(d) UNICEF
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - UNICEF
Key Points
Project on Integrated Education for Disabled (PIED)
- The project was launched in 1987 by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
- It aimed to promote inclusive education for children with disabilities.
- In conjunction with UNICEF, the project sought to integrate disabled children into mainstream education systems.
Additional Information
UNICEF
- UNICEF stands for the United Nations Children's Fund.
- It works globally to promote the rights and well-being of every child.
- UNICEF's educational programs focus on improving access to quality education and inclusive education for children with disabilities.
NCERT
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an organization set up by the Government of India.
- Its primary aim is to assist and advise the central and state governments on academic matters related to school education.
- NCERT conducts various programs and initiatives to improve the quality of education in India.
Q89: From the given events of instruction of Gagne, Arrange these in a sequence.
(A) Provide Reinforcement
(B) Stimulate Recall of Prior learning
(C) Describe goal and inform the learner of the objectives
(D) Provide guidance for learning
(E) Gain attention
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (D), (C), (A), (B), (E)
(b) (E), (B), (C), (D), (A)
(c) (D), (E), (C), (A), (B)
(d) (E), (C), (B), (D), (A)
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - (E), (C), (B), (D), (A)
Key Points
Gain attention
- This is the first step in Gagne's Nine Events of Instruction.
- It involves capturing the learner's interest and curiosity.
Describe goal and inform the learner of the objectives
- The second step involves explaining what the learners will achieve by the end of the instruction.
- Clear objectives guide learners in understanding what is expected of them.
Stimulate Recall of Prior learning
- In the third step, instructors help learners connect new information with previously learned knowledge.
- This helps in building a foundation for new learning.
Provide guidance for learning
- The fourth step involves giving learners tips and strategies to help them understand and remember the content.
- Guidance can include examples, analogies, and other instructional aids.
Provide Reinforcement
- The final step in this sequence, reinforcement involves providing feedback to ensure learners have correctly understood the material.
- Reinforcement helps in consolidating learning and encourages further learning efforts.
Additional Information
Gagne's Nine Events of Instruction
- Robert Gagne proposed a systematic approach to instructional design that includes nine steps.
- These steps are designed to provide a structured approach to teaching and ensure effective learning.
Steps in Gagne's Nine Events
- 1. Gain attention
- 2. Inform learners of objectives
- 3. Stimulate recall of prior learning
- 4. Present the content
- 5. Provide learning guidance
- 6. Elicit performance (practice)
- 7. Provide feedback
- 8. Assess performance
- 9. Enhance retention and transfer
Application
- Gagne's model is widely used in instructional design for creating effective teaching and training programs.
- It is applicable in both classroom settings and online learning environments.
Q90: A National Curricular and Pedagogical Framework for Early Childhood Care and Education (NCPFECCE) for children up to the age of 8 will be developed by :
(a) D. P. E. P
(b) N.C. T.E
(c) N. C. E. R. T
(d) S. C. E. R. T
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - N.C.E.R.T
Key Points
National Curricular and Pedagogical Framework for Early Childhood Care and Education (NCPFECCE)
- It is aimed at developing a comprehensive and standardized framework for the education of children up to the age of 8.
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (N.C.E.R.T) is responsible for its development.
- NCERT's involvement ensures that the framework aligns with national educational policies and standards.
Additional Information
NCERT
- Established in 1961, NCERT is an autonomous organization of the Government of India.
- It assists and advises the central and state governments on academic matters related to school education.
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE)
- ECCE refers to the holistic development of children in their early years, encompassing physical, cognitive, emotional, and social growth.
- A well-structured ECCE program can significantly impact a child's lifelong learning and development.
Importance of NCPFECCE
- It aims to provide a strong foundation for children's learning and development.
- The framework will help standardize early childhood education across different regions and institutions in India.
- It addresses the needs of diverse learners and ensures inclusive and equitable education.
Q91: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
When many cultures co-exist in a given geographical area, without one dominating the other, it is known as “cultural pluralism”. There is a common national culture in India, but at the same time the various communities have the freedom to maintain and develop their own cultural and religious traditions, so long as they are not detrimental to the unity and general welfare of the nation. This is cultural pluralism in the Indian context. Nehru (1946) described the “unity in diversity” within India when he said, “it is fascinating to find how the Bengalis, the Marathas, the Gujaratis, the Tamils, the Andhras, the Oriyas, the Assamese, the Kannadigas, the Malayalis, the Sindhis, the Punjabis, the Pathans, the Kashmiris, the Rajputs and the great Central block of the Hindusthani speaking people, have retained their peculiar characteristics for hundreds of years.... have remained distinctively Indian. “Indian Culture is grand and unique and has fostered other cultures. We can call Gandhi the embodiment of Indian cultural Heritage. He was the one who highlighted India’s culture and spoke of its characteristics of magnanimity, flexibility and above all of its synthesis. The history of the country’s culture goes back to the ancient past or we can certainly line it up at least with the Dravidian era. Later on, many other cultures came in contact with the Indian Culture and easily merged themselves into it according to the circumstances and conditions that prevailed in India. In the same context, Gandhi ji regarded the homogeneity of the Indian environment as the basis of this synthesis.
The embodiment of Indian Cultural heritage is perceived in:
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) Jawahar Lal Nehru
(c) Subhash Chandra Bose
(d) Rabindra Nath Tagore
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Mahatma Gandhi
Key Points
Mahatma Gandhi
- Gandhi is widely recognized as the embodiment of Indian cultural heritage due to his principles of non-violence, truth, and civil disobedience.
- He played a crucial role in India's independence movement, promoting the values of self-reliance and satyagraha.
- His lifestyle and practices reflected traditional Indian values and beliefs, making him a symbol of Indian cultural identity.
Additional Information
Jawahar Lal Nehru
- Nehru was the first Prime Minister of India and a central figure in Indian politics both before and after independence.
- He is known for his vision of a modern, secular, and industrialized India.
Subhash Chandra Bose
- Bose was a prominent freedom fighter who advocated for complete and immediate independence from British rule.
- He founded the Indian National Army (INA) to fight against British forces during World War II.
Rabindra Nath Tagore
- Tagore was a renowned poet, writer, and philosopher who won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913.
- He contributed significantly to Indian cultural and artistic heritage through his literary works and educational reforms.
Q92: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
When many cultures co-exist in a given geographical area, without one dominating the other, it is known as “cultural pluralism”. There is a common national culture in India, but at the same time the various communities have the freedom to maintain and develop their own cultural and religious traditions, so long as they are not detrimental to the unity and general welfare of the nation. This is cultural pluralism in the Indian context. Nehru (1946) described the “unity in diversity” within India when he said, “it is fascinating to find how the Bengalis, the Marathas, the Gujaratis, the Tamils, the Andhras, the Oriyas, the Assamese, the Kannadigas, the Malayalis, the Sindhis, the Punjabis, the Pathans, the Kashmiris, the Rajputs and the great Central block of the Hindusthani speaking people, have retained their peculiar characteristics for hundreds of years.... have remained distinctively Indian. “Indian Culture is grand and unique and has fostered other cultures. We can call Gandhi the embodiment of Indian cultural Heritage. He was the one who highlighted India’s culture and spoke of its characteristics of magnanimity, flexibility and above all of its synthesis. The history of the country’s culture goes back to the ancient past or we can certainly line it up at least with the Dravidian era. Later on, many other cultures came in contact with the Indian Culture and easily merged themselves into it according to the circumstances and conditions that prevailed in India. In the same context, Gandhi ji regarded the homogeneity of the Indian environment as the basis of this synthesis.
India is land of :
(a) A pervasive dominant culture
(b) Multiple cultures
(c) Individualistic identities
(d) Earliest civilizations
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Multiple cultures
Key Points
Multiple cultures
- India is known for its cultural diversity, reflecting a wide range of traditions, languages, and religions.
- The coexistence of various communities contributes to the rich cultural tapestry of the nation.
- Examples include festivals like Diwali, Eid, Christmas, and Navratri, which showcase the pluralistic nature of Indian society.
- This diversity is a result of India's long history of migration and colonization, influencing its cultural landscape.
Additional Information
Regional Diversity
- India is divided into multiple regions, each with its own distinct cultural practices and languages.
- The northern states such as Punjab and Uttar Pradesh have different cultural practices compared to southern states like Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
Linguistic Diversity
- India is home to several hundred languages, with 22 officially recognized by the Constitution of India.
- Hindi and English are the primary languages used for official purposes, but regional languages play a significant role in day-to-day communication.
Religious Diversity
- India is the birthplace of major religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism.
- It also has significant populations of Muslims, Christians, and other religious communities, contributing to its multi-religious fabric.
Q93: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
When many cultures co-exist in a given geographical area, without one dominating the other, it is known as “cultural pluralism”. There is a common national culture in India, but at the same time the various communities have the freedom to maintain and develop their own cultural and religious traditions, so long as they are not detrimental to the unity and general welfare of the nation. This is cultural pluralism in the Indian context. Nehru (1946) described the “unity in diversity” within India when he said, “it is fascinating to find how the Bengalis, the Marathas, the Gujaratis, the Tamils, the Andhras, the Oriyas, the Assamese, the Kannadigas, the Malayalis, the Sindhis, the Punjabis, the Pathans, the Kashmiris, the Rajputs and the great Central block of the Hindusthani speaking people, have retained their peculiar characteristics for hundreds of years.... have remained distinctively Indian. “Indian Culture is grand and unique and has fostered other cultures. We can call Gandhi the embodiment of Indian cultural Heritage. He was the one who highlighted India’s culture and spoke of its characteristics of magnanimity, flexibility and above all of its synthesis. The history of the country’s culture goes back to the ancient past or we can certainly line it up at least with the Dravidian era. Later on, many other cultures came in contact with the Indian Culture and easily merged themselves into it according to the circumstances and conditions that prevailed in India. In the same context, Gandhi ji regarded the homogeneity of the Indian environment as the basis of this synthesis.
Which of the following is NOT true ?
(a) India has a common national culture
(b) India has a pluralistic culture
(c) The pathans have retained their peculiar characteristics over time
(d) Majoritarian culture should dominate minority cultures in India
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Majoritarian culture should dominate minority cultures in India
Key Points
India's Cultural Pluralism
- India is known for its pluralistic culture, which means it is composed of multiple diverse cultural groups.
- This diversity is reflected in the languages, religions, traditions, and customs that coexist within the country.
Equality and Non-dominance
- The Indian Constitution promotes equality and non-dominance of one culture over another.
- Articles such as Article 14 (Right to Equality) and Article 15 (Prohibition of Discrimination) ensure that all cultural groups have equal rights and opportunities.
Incorrect Statement
- The statement that "Majoritarian culture should dominate minority cultures in India" contradicts the principles of equality and cultural pluralism that India stands for.
Additional Information
National Culture
- While India has a common national identity, it is a blend of various cultural elements from across the country.
- This national culture is inclusive and representative of the diverse cultural heritage of India.
Retention of Cultural Characteristics
- Various cultural groups, such as the Pathans, have retained their unique characteristics over time, contributing to the country's cultural mosaic.
Constitutional Safeguards
- The Indian Constitution provides safeguards to protect minority cultures and ensure their rights are upheld.
- Examples include Article 29 and Article 30, which protect the interests of minorities and allow them to conserve their distinct language, script, and culture.
Q94: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
When many cultures co-exist in a given geographical area, without one dominating the other, it is known as “cultural pluralism”. There is a common national culture in India, but at the same time the various communities have the freedom to maintain and develop their own cultural and religious traditions, so long as they are not detrimental to the unity and general welfare of the nation. This is cultural pluralism in the Indian context. Nehru (1946) described the “unity in diversity” within India when he said, “it is fascinating to find how the Bengalis, the Marathas, the Gujaratis, the Tamils, the Andhras, the Oriyas, the Assamese, the Kannadigas, the Malayalis, the Sindhis, the Punjabis, the Pathans, the Kashmiris, the Rajputs and the great Central block of the Hindusthani speaking people, have retained their peculiar characteristics for hundreds of years.... have remained distinctively Indian. “Indian Culture is grand and unique and has fostered other cultures. We can call Gandhi the embodiment of Indian cultural Heritage. He was the one who highlighted India’s culture and spoke of its characteristics of magnanimity, flexibility and above all of its synthesis. The history of the country’s culture goes back to the ancient past or we can certainly line it up at least with the Dravidian era. Later on, many other cultures came in contact with the Indian Culture and easily merged themselves into it according to the circumstances and conditions that prevailed in India. In the same context, Gandhi ji regarded the homogeneity of the Indian environment as the basis of this synthesis.
According to Gandhi ji, which of the following is a characteristic of Indian culture ?
(a) Individuality
(b) Majoritarianism
(c) Magnanimity
(d) Metamorphosis
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Magnanimity
Key Points
Magnanimity
- According to Gandhi ji, one of the fundamental characteristics of Indian culture is its inherent magnanimity.
- Magnanimity refers to the quality of being generous, kind-hearted, and forgiving, which Gandhi ji believed was deeply embedded in the Indian ethos.
- This characteristic is reflected in India's long history of tolerance and acceptance of diverse cultures, religions, and ideas.
- Gandhi ji emphasized that this quality of magnanimity should be upheld to maintain harmony and peace within the society.
Additional Information
Gandhi ji's Views on Indian Culture
- Gandhi ji often spoke about the importance of preserving the core values of Indian culture, including non-violence (Ahimsa) and truth (Satya).
- He believed that Indian culture's strength lies in its ability to assimilate and integrate various influences while maintaining its unique identity.
- Gandhi ji also highlighted the significance of simplicity and self-sufficiency as key aspects of Indian culture.
Other Characteristics of Indian Culture
- Spirituality
- Indian culture places a strong emphasis on spiritual growth and the quest for inner peace and enlightenment.
- Major religions originating in India, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism, emphasize spiritual practices and ethical living.
Communal Harmony
- India's diverse population has coexisted for centuries, fostering a culture of mutual respect and understanding.
- Festivals, traditions, and communal activities often bring people from different backgrounds together, promoting social cohesion.
Q95: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
When many cultures co-exist in a given geographical area, without one dominating the other, it is known as “cultural pluralism”. There is a common national culture in India, but at the same time the various communities have the freedom to maintain and develop their own cultural and religious traditions, so long as they are not detrimental to the unity and general welfare of the nation. This is cultural pluralism in the Indian context. Nehru (1946) described the “unity in diversity” within India when he said, “it is fascinating to find how the Bengalis, the Marathas, the Gujaratis, the Tamils, the Andhras, the Oriyas, the Assamese, the Kannadigas, the Malayalis, the Sindhis, the Punjabis, the Pathans, the Kashmiris, the Rajputs and the great Central block of the Hindusthani speaking people, have retained their peculiar characteristics for hundreds of years.... have remained distinctively Indian. “Indian Culture is grand and unique and has fostered other cultures. We can call Gandhi the embodiment of Indian cultural Heritage. He was the one who highlighted India’s culture and spoke of its characteristics of magnanimity, flexibility and above all of its synthesis. The history of the country’s culture goes back to the ancient past or we can certainly line it up at least with the Dravidian era. Later on, many other cultures came in contact with the Indian Culture and easily merged themselves into it according to the circumstances and conditions that prevailed in India. In the same context, Gandhi ji regarded the homogeneity of the Indian environment as the basis of this synthesis.
When the majority culture dominates in a society of multiple cultures, it is :
(a) Cultural pluralism
(b) Communism
(c) Majoritarianism
(d) Sectarianism
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Majoritarianism
Key Points
Majoritarianism
- It refers to a situation where the majority culture or group in a society imposes its values, practices, and beliefs on the minority cultures.
- This concept often leads to the marginalization or suppression of the cultural practices of minority groups.
- Majoritarianism can result in social and political imbalances, often leading to conflicts and a lack of cultural diversity.
Additional Information
Cultural pluralism
- Contrary to majoritarianism, cultural pluralism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultures within a society.
- It emphasizes mutual respect and the maintenance of distinct cultural identities.
- Cultural pluralism is often associated with inclusive policies that support minority rights and cultural diversity.
Communism
- An ideology and socioeconomic system where property and resources are communally owned, and each person contributes and receives according to their ability and needs.
- It is not directly related to cultural dominance but rather focuses on economic and social equality.
Sectarianism
- Involves conflict or discrimination arising from attachment to a particular sect or group, often within a religion.
- Unlike majoritarianism, which is about the dominance of a cultural majority, sectarianism deals with divisions within a larger community or religion.
Q96: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
Althusser argues that no class can hold power for any length of time simply by the use of force. Ideological control provides a far more effective means of maintaining class rule. If members of the subject class accept their position as normal, natural and inevitable, and fail to realize the true nature of their situation, then they will be unlikely to challenge ruling class dominance. Physical force is an inefficient means of control compared to winning over hearts and minds. The maintenance of class rule largely depends on the reproduction of ruling class ideology. Thus Althusser argues that ‘the reproduction of labour power requires not only a reproduction of its skills, but also, at the same time a reproduction of its submission to the ruling ideology’. This submission is reproduced by a number of ‘Ideological State Apparatuses’ which include the mass media, the law, religion and education. Ideological State Apparatuses transmit ruling class ideology thereby creating false class consciousness which largely maintains the subject class in its subordinate position. In pre-capitalist society, Althusser sees the church as the dominant ideological state apparatus. In capitalist society it has largely been replaced by the educational system.
For the longest possible duration to hold power, the most efficient is :
(a) Media control
(b) Economic control
(c) Religious control
(d) Ideological control
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is (d) Ideological control.
Key Points:
- Ideological control: Althusser argues it is more effective than physical force, as it wins hearts and minds through ISAs like media, religion, and education.
- Religious control: Effective in pre-capitalist societies (via the church), but less dominant in capitalist societies.
- Media and economic control: Secondary to ideological control, as they are tools within ISAs or economic structures.
Q97: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
Althusser argues that no class can hold power for any length of time simply by the use of force. Ideological control provides a far more effective means of maintaining class rule. If members of the subject class accept their position as normal, natural and inevitable, and fail to realize the true nature of their situation, then they will be unlikely to challenge ruling class dominance. Physical force is an inefficient means of control compared to winning over hearts and minds. The maintenance of class rule largely depends on the reproduction of ruling class ideology. Thus Althusser argues that ‘the reproduction of labour power requires not only a reproduction of its skills, but also, at the same time a reproduction of its submission to the ruling ideology’. This submission is reproduced by a number of ‘Ideological State Apparatuses’ which include the mass media, the law, religion and education. Ideological State Apparatuses transmit ruling class ideology thereby creating false class consciousness which largely maintains the subject class in its subordinate position. In pre-capitalist society, Althusser sees the church as the dominant ideological state apparatus. In capitalist society it has largely been replaced by the educational system.
Subject-members take their position as :
(a) ascribe, ideological and submissive
(b) normal, natural and inevitable
(c) prescribed, predetermined and necessary
(d) given, required and adhered
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - normal, natural and inevitable
Key Points
normal, natural and inevitable
- In sociological and psychological contexts, subject-members often perceive their roles and positions as normal, natural, and inevitable due to social conditioning.
- This perception is shaped by societal norms, values, and expectations, making their roles seem unquestionable and inevitable.
- Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing how social structures and institutions maintain their stability and continuity.
- It emphasizes the power of socialization in shaping individuals' perceptions of their roles within a society.
Additional Information
Socialization
- Socialization is the process through which individuals learn and internalize the values, beliefs, and norms of their society.
- This process begins at a young age and continues throughout an individual's life, influencing their perception of what is normal and natural.
- Institutions such as family, education, and media play a significant role in the socialization process.
Social Norms
- Social norms are the unwritten rules and expectations about how individuals should behave in society.
- These norms help maintain social order by providing guidelines for acceptable behavior.
- They can vary significantly across different cultures and societies.
Role Theory
- Role theory examines how individuals fulfill the expectations of their social roles.
- It suggests that people behave in certain ways based on the roles they occupy, such as parent, employee, or student.
- Understanding role theory helps explain why individuals perceive their positions as normal and inevitable.
Q98: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
Althusser argues that no class can hold power for any length of time simply by the use of force. Ideological control provides a far more effective means of maintaining class rule. If members of the subject class accept their position as normal, natural and inevitable, and fail to realize the true nature of their situation, then they will be unlikely to challenge ruling class dominance. Physical force is an inefficient means of control compared to winning over hearts and minds. The maintenance of class rule largely depends on the reproduction of ruling class ideology. Thus Althusser argues that ‘the reproduction of labour power requires not only a reproduction of its skills, but also, at the same time a reproduction of its submission to the ruling ideology’. This submission is reproduced by a number of ‘Ideological State Apparatuses’ which include the mass media, the law, religion and education. Ideological State Apparatuses transmit ruling class ideology thereby creating false class consciousness which largely maintains the subject class in its subordinate position. In pre-capitalist society, Althusser sees the church as the dominant ideological state apparatus. In capitalist society it has largely been replaced by the educational system.
False class consciousness does not make people :
(a) accept their position
(b) accept the working class ideology
(c) accept the insubordination
(d) accept church, media and education
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - accept the insubordination
Key Points
False class consciousness
- It is a term in Marxist theory that refers to the way in which material, ideological, and institutional processes mislead the proletariat about the true nature of their social and economic situation.
- False class consciousness can lead to the working class accepting ideas and beliefs that are contrary to their own best interests.
Accept the insubordination
- This means not recognizing or accepting the authority or leadership that exploits them.
- False class consciousness does not make people accept insubordination because it masks the true power dynamics and inequalities that exist.
Additional Information
Working class ideology
- Refers to the set of beliefs and values that are in line with the interests of the working class.
- False class consciousness often prevents the working class from fully adopting and acting upon this ideology.
Role of institutions
- Institutions like the church, media, and education play a significant role in perpetuating false class consciousness by promoting ideas that maintain the status quo.
- They often disseminate ideologies that justify social inequalities and discourage critical thinking about social structures.
Q99: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
Althusser argues that no class can hold power for any length of time simply by the use of force. Ideological control provides a far more effective means of maintaining class rule. If members of the subject class accept their position as normal, natural and inevitable, and fail to realize the true nature of their situation, then they will be unlikely to challenge ruling class dominance. Physical force is an inefficient means of control compared to winning over hearts and minds. The maintenance of class rule largely depends on the reproduction of ruling class ideology. Thus Althusser argues that ‘the reproduction of labour power requires not only a reproduction of its skills, but also, at the same time a reproduction of its submission to the ruling ideology’. This submission is reproduced by a number of ‘Ideological State Apparatuses’ which include the mass media, the law, religion and education. Ideological State Apparatuses transmit ruling class ideology thereby creating false class consciousness which largely maintains the subject class in its subordinate position. In pre-capitalist society, Althusser sees the church as the dominant ideological state apparatus. In capitalist society it has largely been replaced by the educational system.
Schools :
(a) Reproduce ruling class ideology
(b) Reproduce communities
(c) Reproduce popular culture
(d) Reproduce state control
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Reproduce ruling class ideology
Key Points
Reproduce ruling class ideology
- Schools play a crucial role in transmitting the ideologies and values of the ruling class to the younger generation.
- Educational institutions often embed the dominant culture and societal norms into their curricula, which reflects the interests of those in power.
- This process helps in maintaining the existing social order and legitimizing the authority of the ruling class.
- By reproducing ruling class ideology, schools contribute to the perpetuation of the status quo and the reinforcement of social hierarchies.
Additional Information
Functionalist perspective
- The functionalist perspective views education as a means of socializing individuals and promoting social cohesion.
- It emphasizes the role of schools in transmitting shared values and norms, which are necessary for the functioning of society.
Conflict perspective
- The conflict perspective, often associated with Karl Marx, argues that education serves to reproduce the inequalities and power dynamics of the capitalist system.
- It suggests that schools perpetuate the interests of the ruling class by shaping the consciousness of students in ways that support the existing economic and social structures.
Hidden curriculum
- The hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons and values that are taught in schools, which are not part of the formal curriculum.
- These lessons often reinforce societal norms and the dominant ideology, contributing to the reproduction of social inequality.
Q100: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions based on it:
Althusser argues that no class can hold power for any length of time simply by the use of force. Ideological control provides a far more effective means of maintaining class rule. If members of the subject class accept their position as normal, natural and inevitable, and fail to realize the true nature of their situation, then they will be unlikely to challenge ruling class dominance. Physical force is an inefficient means of control compared to winning over hearts and minds. The maintenance of class rule largely depends on the reproduction of ruling class ideology. Thus Althusser argues that ‘the reproduction of labour power requires not only a reproduction of its skills, but also, at the same time a reproduction of its submission to the ruling ideology’. This submission is reproduced by a number of ‘Ideological State Apparatuses’ which include the mass media, the law, religion and education. Ideological State Apparatuses transmit ruling class ideology thereby creating false class consciousness which largely maintains the subject class in its subordinate position. In pre-capitalist society, Althusser sees the church as the dominant ideological state apparatus. In capitalist society it has largely been replaced by the educational system.
Which of the following is NOT an ideological state apparatus ?
(a) Religion
(b) Media
(c) Education
(d) Class
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Class
Key Points
Class
- Unlike other options, Class is not an Ideological State Apparatus (ISA).
- ISAs are institutions that propagate the ideologies of the ruling class to maintain the status quo.
- Class refers to a social stratification that is an outcome of economic factors, not an institution.
Additional Information
Ideological State Apparatuses (ISAs)
- Concept introduced by the Marxist theorist Louis Althusser.
- ISAs include institutions such as:
- Religion - Churches and religious institutions.
- Media - Newspapers, television, and online platforms.
- Education - Schools and universities.
- These institutions function primarily by ideology and secondarily by repression.
Repressive State Apparatus (RSA)
- Contrasts with ISAs, functioning through violence and coercion.
- Examples include the police, military, and judiciary.
Role of ISAs
- ISAs help maintain the dominance of the ruling class by promoting its ideology.
- They are more effective in controlling the populace as they work subtly through cultural means.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Education 3rd Jan 2025 Shift 1 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and its significance in the field of education? |  |
| 2. What are the key topics covered in UGC NET Paper 2 for education? |  |
| 3. How can candidates effectively prepare for UGC NET Paper 2 in education? |  |
| 4. What is the exam pattern for UGC NET Paper 2 in education? |  |
| 5. What resources are recommended for studying for UGC NET Paper 2 in education? |  |
















