UGC NET Paper 2: Management 12th Mar 2023 Shift 2 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Arrange the following milk product brands developed by the state co-operatives in ascending order of revenue generator.
A. Vita (Haryana)
B. Amul (Gujarat)
C. Nandini (Karnataka)
D. Verka (Punjab)
E. Milma (Kerala)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) E, D, A, B, C
(b) A, D, E, C, B
(c) C, E, A, D, B
(d) D, C, A, E, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, D, E, C, B
Here are some details about the milk product brands developed by the state co-operatives in India, arranged in ascending order of revenue generator:
- A. Vita (Haryana) - ₹1,980 crores
- D. Verka (Punjab) - ₹4,300 crores
- E. Milma (Kerala) - ₹5,240 crores
- C. Nandini (Karnataka) - ₹24,500 crores
- B. Amul (Gujarat) - ₹72,000 crores
Q2: Match List I with List II
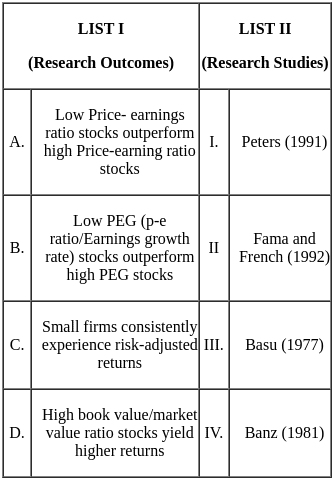
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is: (b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Explanation of the Matching:
| Research Outcome | Research Study | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| A. Low Price-earnings ratio stocks outperform high Price-earning ratio stocks | III. Basu (1977) | Basu’s study demonstrated that low P/E stocks tend to outperform high P/E stocks, contradicting the efficient market hypothesis. |
| B. Low PEG (P/E ratio / Earnings growth rate) stocks outperform high PEG stocks | I. Peters (1991) | Peters discussed PEG ratio-based investing and found that low PEG stocks often outperform. |
| C. Small firms consistently experience risk-adjusted returns | IV. Banz (1981) | Banz found a size effect, where small-cap stocks earned higher risk-adjusted returns. |
| D. High book value/market value ratio stocks yield higher returns | II. Fama and French (1992) | Fama and French introduced the value factor in their 3-factor model showing high B/M stocks outperform. |
Q3: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The status of the person being perceived will greatly influence others’ perception of the person.
Statement II: The visible traits of the person perceived will not influence others’ perception of the person.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
The correct answer is Statement I is true, but Statement II is false.
- Statement I: The status of a person (e.g., job title, social standing) significantly influences how others perceive them, as it shapes assumptions about competence, trustworthiness, etc. This is true.
- Statement II: Visible traits, such as physical appearance, clothing, and body language, do influence others’ perceptions (e.g., attractive individuals are often seen as more likable). Thus, the statement that visible traits do not influence perception is false.
- The solution’s explanation about visible traits influencing perception is correct, but it should explicitly align with Statement II being false.
Other Related Points
Here are some additional points to consider:
- The status of the person being perceived can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as their job title, their level of education, their income, and their social class.
- The visible traits of the person being perceived can include their physical appearance, their clothing, their hairstyle, and their body language.
- The perception of a person is not always accurate. People often make snap judgments about others based on their status and visible traits, and these judgments can be biased.
- It is important to be aware of the factors that influence our perception of others so that we can make more informed judgments.
Q4: Arrange the following steps of marketing process in the sequential order.
A. Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity.
B. Understand the market place and customer needs and wants.
C. Build profitable relationships and create customer delight.
D. Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value.
E. Design a customer-driven marketing strategy.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, E, A, C
(b) B, E, D, C, A
(c) E, B, C, D, A
(d) D, A, B, C, E
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is B, E, D, C, A.
The correct answer is:
- Understand the market place and customer needs and wants (B). This is the first step in the marketing process, as it is important to understand the needs and wants of your target market before you can develop a marketing strategy that will resonate with them.
- Design a customer-driven marketing strategy (E). Once you understand your target market, you can develop a marketing strategy that is tailored to their needs and wants. This strategy should include a clear understanding of your target market, your product or service offering, and your competitive landscape.
- Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value (D). Your marketing strategy should be implemented through an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value to your customers. This program should include a mix of marketing channels, such as advertising, public relations, social media, and direct marketing.
- Build profitable relationships and create customer delight (C). The goal of marketing is not just to sell products or services, but to build profitable relationships with customers and create customer delight. This can be achieved by providing excellent customer service, offering loyalty programs, and listening to customer feedback.
- Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity (A). The final step in the marketing process is to capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity. This can be achieved by charging a fair price for your products or services, upselling and cross-selling, and offering discounts and promotions.
Q5: Which concept states that profit are normally recognized when the title to the goods passes to the customer, not necessarily when money changes hands?
(a) Matching Concept
(b) Realisation Concept
(c) Prudence Concept
(d) Materiality Concept
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Realisation Concept.
- The concept that states that profit are normally recognized when the title to the goods passes to the customer, not necessarily when money changes hands is called the realization concept.
- The realization concept is a fundamental principle of accounting that is closely related to the revenue recognition principle. The realization concept states that revenue should only be recognized when it is realized, which means that it has been earned and there is a reasonable certainty that the economic benefits associated with the transaction will flow to the company.
- In the case of a sale of goods, the realization concept would mean that revenue would be recognized when the goods are delivered to the customer, even though the company may not receive payment until a later date. This is because the company has earned the revenue when it has transferred the title to the goods to the customer.
- The realization concept is important for ensuring that financial statements are accurate and reliable. It helps to prevent companies from recognizing revenue prematurely, which can mislead investors and creditors about the financial health of the company.
Other Related Points
- Matching concept is an accounting principle that states that expenses should be matched with the revenues they generate. This means that expenses should be recognized in the same accounting period as the revenues they generate, even if the expenses are paid in a different accounting period. The matching concept helps to ensure that the financial statements accurately reflect the company's profitability.
- Prudence concept is an accounting principle that states that assets and income should not be overstated, and liabilities and expenses should not be understated. This means that accountants should err on the side of caution when making accounting entries. The prudence concept helps to ensure that the financial statements are not misleading.
- Materiality concept is an accounting principle that states that only material information should be included in the financial statements. Material information is information that is important to the users of the financial statements. The materiality concept helps to ensure that the financial statements are not cluttered with unnecessary information.
Q6: Which of the following enterprises is NOT eligible for Udyog Aadhar registration with Ministry of Micro. Small and Medium Enterprises, Government of India?
(a) Micro enterprise in manufacturing sector with an investment in plant and machinery of Rs 20 lacs
(b) Small enterprise in manufacturing sector with an investment in plant and machinery of Rs 3.5 crores
(c) Small enterprise in services sector with an investment in equipment of Rs 1.50 crores
(d) Medium enterprise in manufacturing sector with an investment in plant and machinery of Rs 15 crores
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Medium enterprise in manufacturing sector with an investment in plant and machinery of Rs 15 crores
A medium enterprise in the manufacturing sector with an investment of Rs 15 crores in plant and machinery is NOT eligible for Udyog Aadhar registration with the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME), Government of India.
Here's why:
- Udyog Aadhar (now Udyam registration) is specifically for Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs), not Medium Enterprises (MEs). The current investment limits for each category are:
- Micro: Investment in plant and machinery or equipment does not exceed Rs 1 crore.
- Small: Investment in plant and machinery or equipment is more than Rs 1 crore but does not exceed Rs 10 crore.
- Medium: Investment in plant and machinery or equipment is more than Rs 10 crore.
Therefore, a medium enterprise with an investment of Rs 15 crores falls outside the eligibility criteria for Udyam registration.
While this enterprise might be considered an MSME by the Indian government for other purposes, it wouldn't qualify for the benefits and support specifically offered through Udyam registration.
So, you were right in identifying the medium enterprise with an investment of Rs 15 crores as ineligible for Udyog Aadhar registration.
Q7: Match List I with List II
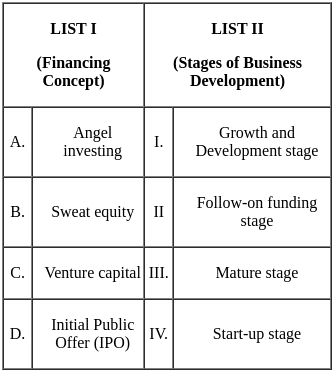
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(c) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III.
- Angel investing is a type of financing that is provided by wealthy individuals or groups of individuals to start-up businesses. Angel investors typically invest in businesses that are in the start-up stage, and they often provide more than just financial capital. They may also offer advice and mentorship to the entrepreneurs.
- Sweat equity is a form of compensation that is given to employees in lieu of cash. Employees who receive sweat equity are essentially given shares in the company, and they are rewarded for their hard work and dedication with an ownership stake in the business. Sweat equity is typically used in the mature stage of a business, when the company is still too small to afford to pay its employees a competitive salary.
- Venture capital is a type of financing that is provided by professional investors to start-up and early-stage businesses. Venture capitalists typically invest in businesses that have the potential for high growth, and they are willing to take on a high degree of risk in exchange for the potential for high returns. Venture capital is often used in the follow-on funding stage of a business, when the company has already raised some initial capital from angel investors or other sources, but it needs more money to grow and scale.
- Initial public offering (IPO) is a process by which a company offers its shares to the public for the first time. IPOs are typically conducted by mature businesses that are seeking to raise additional capital to fund their growth. IPOs are typically seen as a sign that a company has reached the growth and development stage of its development.
Q8: Following are the statements on the Mintzberg's organisational type. Choose the correct statements:
A. Entrepreneurial organisations primarily focus on skills standardization
B. Professional organisations primarily focus on output standardisation
C. Innovative organisations primarily focus on mutual adjustment
D. Missionary organisations primarily focus on norms standardisation
E. Innovative organisations do not focus on mutual adjustment
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D and E only
(b) A, B, C and E only
(c) C and D only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is C and D only.
C. Innovative organizations primarily focus on mutual adjustment:
Innovative organizations are characterized by their emphasis on creativity, flexibility, and adaptability. They often operate in dynamic and rapidly changing environments where traditional methods and structures may not be effective. Mutual adjustment refers to the informal communication and coordination that occurs among employees to solve problems and make decisions on the spot. In innovative organizations, employees collaborate, exchange ideas, and adjust their actions based on the evolving needs of the situation.
D. Missionary organizations primarily focus on norms standardization:
Missionary organizations are typically nonprofit or socially oriented entities that aim to promote a particular set of values, beliefs, or norms within society. These organizations often have a strong ideological or mission-driven focus. Norms standardization refers to the establishment of clear and consistent rules, procedures, and norms that guide the behavior of employees.
The correct answer is (c) C and D only.
- C: Innovative organizations primarily focus on mutual adjustment, as they rely on informal coordination and collaboration to adapt to dynamic environments. This is true.
- D: Missionary organizations primarily focus on norms standardization, emphasizing shared values and ideologies to guide behavior. This is true.
- A: Entrepreneurial organizations rely on direct supervision by a leader, not skills standardization, so A is false.
- B: Professional organizations focus on skills standardization (e.g., professional qualifications), not output standardization, so B is false.
- E: Innovative organizations do focus on mutual adjustment, so E is false.
Q9: Which of the following should not be included in the balance of payments account?
(a) Bonus shares to equity shareholders
(b) Imports of automobile parts
(c) Dividend payment to home-country investors from a foreign subsidiary
(d) Interest payment on loan to the IMF
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Bonus shares to equity shareholders.
Major Points
- Bonus shares to equity shareholders are not included in the balance of payments account. The balance of payments (BoP) is a record of all economic transactions between residents of a country and the rest of the world over a specific period. It is divided into three main components: the current account, the capital account, and the financial account.
- Bonus shares are essentially additional shares given to existing shareholders without any cash payment.
- When bonus shares are issued, the company's capital structure changes, but there is no direct inflow or outflow of foreign exchange or funds between the country and the rest of the world.
- Since bonus shares do not involve any foreign exchange transactions or movement of funds across borders, they are not recorded in the balance of payments.
Other Related Points
The balance of payments focuses on transactions that involve the exchange of goods, services, and financial assets between residents of different countries. While bonus shares may have implications for a company's financial position and its shareholders, they do not impact the international balance of payments since they do not involve cross-border transactions.
Q10: The sequence of steps involved in testing a hypotheses are:
A. Select a suitable test statistic
B. Establish critical or rejection region
C. State the null and alternative hypothesis
D. State the level of significance (α)
E. Formulate a decision rule to evaluate the null hypothesis
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) E, C, D, A, B
(b) C, D, B, A, E
(c) A, B, E, C, D
(d) B, C, A, E, D
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is C, D, B, A, E.
C. State the null and alternative hypothesis:
Hypothesis testing begins with stating a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (H1 or Ha). The null hypothesis typically represents the status quo or no effect, while the alternative hypothesis represents the claim or effect that is being tested.
D. State the level of significance (α):
The level of significance (α) is the probability of making a Type I error, which is rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true. Commonly used values for α are 0.05 (5%) or 0.01 (1%). It helps determine the critical region for decision-making.
B. Establish critical or rejection region:
The critical or rejection region is a range of values that corresponds to the extreme outcomes that would lead to rejecting the null hypothesis. It is determined based on the chosen level of significance (α) and the distribution of the test statistic. The critical region is usually located in the tails of the distribution.
A. Select a suitable test statistic:
The choice of a test statistic depends on the nature of the data and the hypothesis being tested. Different types of data and hypotheses require different test statistics, such as t-test, z-test, chi-squared test, etc. The test statistic is calculated from the sample data and is used to assess whether the observed results are consistent with the null hypothesis.
E. Formulate a decision rule to evaluate the null hypothesis:
The decision rule specifies under what conditions the null hypothesis will be rejected. It is based on comparing the calculated test statistic to the critical values from the distribution. If the calculated test statistic falls within the critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If the test statistic does not fall within the critical region, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Q11: Which of the following are NOT motivational factors according to Herzberg?
A. Interpersonal relations
B. Work itself
C. Advancement
D. Achievement
E. Salary
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and E only
(b) A and B only
(c) B and D only
(d) C and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is and A and E only.
According to Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory, also known as the Motivation-Hygiene Theory, the factors that lead to job satisfaction and motivation are referred to as "motivators" or "satisfiers," while the factors that can lead to job dissatisfaction if not adequately addressed are referred to as "hygiene factors" or "dissatisfiers."
The correct answer is:
A. Interpersonal relations
E. Salary
A. Interpersonal relations: Interpersonal relations refer to the relationships and interactions an employee has with colleagues, supervisors, and peers within the workplace. Herzberg categorized interpersonal relations as a hygiene factor, not a motivator. Good relationships with coworkers can prevent dissatisfaction, but they are not considered direct sources of motivation. If interpersonal relations are poor, they can lead to dissatisfaction, but improving these relationships does not necessarily result in increased motivation.
E. Salary: Salary is also considered a hygiene factor in Herzberg's theory. While adequate compensation is essential to prevent job dissatisfaction, it is not a direct source of motivation. Employees expect to be fairly compensated for their work, and a lack of adequate salary can lead to dissatisfaction. However, increasing salary alone does not necessarily lead to increased motivation and job satisfaction in the long term.
Other Related Points The factors that Herzberg identified as true motivational factors (satisfiers) include:
B. Work itself
C. Advancement
D. Achievement
These factors are related to the nature of the work, opportunities for personal growth and development, and the sense of accomplishment an individual derives from their tasks. They are more intrinsic and directly contribute to a person's sense of motivation and job satisfaction.
In summary, Herzberg's theory suggests that true motivation and job satisfaction come from intrinsic factors related to the work itself and personal growth, while hygiene factors such as interpersonal relations and salary are important to prevent dissatisfaction but do not directly lead to increased motivation.
Q12: Deviation from market portfolio, a point on the Capital Market Line (CML) that differentiates investors’ investing and financing decisions (based on their risk appetite) is describe by :
(a) Convergence theorem
(b) Separation theorem
(c) Efficient market theorem
(d) Arbitrage pricing theorem
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Separation theorem.
- The Separation Theorem, particularly in the context of modern portfolio theory, is about the relationship between the decisions of investors and the construction of efficient portfolios. It states that an investor's portfolio choice can be separated into two independent tasks:
- Determining the optimal risky portfolio (usually the market portfolio), which is a function of the investor's risk tolerance and attitude towards risk.
- Combining the optimal risky portfolio with a risk-free asset to achieve the desired level of risk and return.
- The Capital Market Line (CML) is a graphical representation of the Separation Theorem. It shows the combinations of the risk-free asset and the risky portfolio that result in efficient portfolios for different levels of risk.
Q13: Entrepreneurs in general are _________ obsessed and _________ balanced?
(a) Opportunity, Leadership
(b) Innovation, Risk
(c) Creativity, Innovations
(d) Profit, Creativity
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Opportunity leadership.
Entrepreneurs in general are opportunity obsessed and Leadership balanced.
- Opportunity obsessed: Entrepreneurs are constantly looking for new opportunities. They always think about ways to improve their businesses or start new ones. They are often willing to take risks in order to pursue their dreams.
- Balanced in leadership responsibilities: Entrepreneurs often have to work long hours and make sacrifices in their personal lives in order to make their businesses successful. They may have to miss important events with their families and friends. They may also have to put their health and well-being on the back burner.
It is important to note that not all entrepreneurs are the same. Some entrepreneurs are able to achieve a better balance between their work and personal lives. However, it is generally true that entrepreneurs are more likely to be opportunity obsessed and leadership imbalanced than people who are not entrepreneurs.
Q14: Which of the following outcomes will promote sustainable capitalism?
A. Job creation. wealth generation and equitable income distribution
B. Do good and make profit (Shubh Laabh)
C. Digital transformation and increased corporate profiteering
D. Ethical wealth creation and resource allocation
E. Emergence of monolithic and oligopolistic corporate entities
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A, B and D only
(d) B, C and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and D only.
- Job creation, wealth generation and equitable income distribution are all important components of sustainable capitalism. When businesses create jobs, they provide income for workers, which helps to boost the economy and reduce poverty. Wealth generation allows businesses to invest in new technologies and products, which can lead to further economic growth and innovation. Equitable income distribution ensures that everyone benefits from economic growth, not just the wealthy.
- Do good and make profit (Shubh Laabh) is also a good goal, but it is not as essential as the other three. Businesses can still be profitable while being good stewards of the environment and society. However, it is important for businesses to have a clear commitment to sustainability and social responsibility.
- Digital transformation and increased corporate profiteering can be a double-edged sword. On the one hand, digital transformation can lead to increased efficiency and productivity, which can benefit businesses and consumers alike. On the other hand, it can also lead to increased energy consumption and pollution. Increased corporate profiteering can also lead to income inequality and a concentration of wealth in the hands of a few.
- Emergence of monolithic and oligopolistic corporate entities can also be a problem. These large corporations can have a lot of power and influence, which can be used to stifle competition and innovation. They can also be more likely to engage in unethical practices.
In conclusion, the outcomes that are most likely to promote sustainable capitalism are job creation, wealth generation, equitable income distribution, and a commitment to sustainability and social responsibility.
Hence, The correct answer is A, B and D only.
Q15: Employees’ belief in the degree to which they affect their work environment, their competence. the meaningfulness of their job and perceived autonomy in their work is known as:
(a) Job involvement
(b) Job satisfaction
(c) Psychological empowerment
(d) Organizational commitment
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Psychological empowerment.
Employees’ belief in the degree to which they affect their work environment, their competence, the meaningfulness of their job and perceived autonomy in their work is known as psychological empowerment.
Psychological empowerment is a concept in organizational behavior that describes the degree to which employees feel they have control over their work and their ability to make a difference. It is a multidimensional construct that includes four dimensions:
- Internal locus of control: The belief that one's actions can influence the outcome of events.
- Self-efficacy: The belief in one's own ability to perform a task successfully.
- Meaningfulness of work: The belief that one's work is important and worthwhile.
- Autonomy: The freedom to make decisions about one's work.
- Employees with high levels of psychological empowerment are more likely to be engaged in their work, have a positive attitude, and be productive. They are also less likely to experience burnout and turnover.
Other Related Points
There are a number of things that organizations can do to promote psychological empowerment among their employees, such as:
- Giving employees a voice: Employees should be given the opportunity to participate in decision-making and to have their ideas heard.
- Setting clear goals and expectations: Employees should know what is expected of them and how their work contributes to the overall goals of the organization.
- Providing training and development opportunities: Employees should have the opportunity to learn new skills and to grow in their careers.
- Recognizing and rewarding employee accomplishments: Employees should be recognized for their contributions and their hard work.
- Creating a supportive work environment: Employees should feel safe and respected in their work environment.
Q16: "Udyam Assist Platform" developed by the SIDBI cater to which of the following enterprises?
(a) Small Enterprises
(b) Medium Enterprises
(c) Export Oriented Enterprises
(d) Informal Micro Enterprises
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Informal Micro Enterprises.
- The Udyam Assist Platform (UAP) developed by SIDBI caters to informal micro enterprises (IMEs). IMEs are small businesses that do not have a formal registration with the government. They are often unregistered and operate in the informal sector.
- The UAP aims to help IMEs to formalize their businesses and to avail the benefits of priority sector lending. It provides a single window platform for IMEs to register their businesses, to get loans and other financial assistance, and to access government schemes and services.
- The UAP is a step towards the government's goal of formalizing the MSME sector. It will help to create a more level playing field for IMEs and to boost their growth and productivity.
Other Related Points
Here are some of the benefits that IMEs can avail through the UAP:
- They can register their businesses online and get a digital Udyam registration certificate.
- They can apply for loans and other financial assistance from banks and financial institutions.
- They can access government schemes and services, such as training and capacity building programs, marketing assistance, and technology support.
- They can connect with other IMEs and businesses, and to mentors and experts.
- They can get information on government policies and regulations, and on market trends.
- The UAP is a valuable resource for IMEs. It can help them to grow their businesses and to become more competitive.
Hence, the correct answer is Informal Micro Enterprises
Q17: Internal reliability of a test instrument is defined as
(a) The increase and decrease in scores measured over time produce a variance of less than 50%
(b) The consistency of results across items within a single test administration
(c) The identical observation of single individual's scores
(d) The property of a distribution to achieve mean of 0 and variance of 1
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is The consistency of results across items within a single test administration.
- Internal reliability of a test instrument is defined as the consistency of results across items within a single test administration, often measured by Cronbach’s alpha. It reflects how well the items measure the same underlying construct. The provided definition (consistency over two points in time) describes test-retest reliability, not internal reliability.
- There are a number of different methods for assessing internal reliability, but the most common is Cronbach's alpha.
- Cronbach's alpha is a statistic that calculates the average correlation between all the items on the test. A high Cronbach's alpha (greater than 0.7) indicates that the items on the test are internally consistent and are measuring the same underlying construct.
- A low Cronbach's alpha (less than 0.7) indicates that the items on the test are not internally consistent and may not be measuring the same underlying construct.
Important Points
- Internal reliability is important for a number of reasons. First, it ensures that the test is measuring what it is supposed to measure. Second, it helps to ensure that the test is reliable, meaning that it will produce consistent results when it is administered to the same people on different occasions. Third, it helps to ensure that the test is valid, meaning that it is measuring what it is supposed to measure and not anything else.
- If the internal reliability of a test is low, it may be necessary to revise the test or to develop new items for the test. It is also important to consider the purpose of the test when interpreting the results of the internal reliability analysis. For example, a test with a low Cronbach's alpha may be acceptable for screening purposes, but it may not be acceptable for making important decisions about individuals.
Other Related Points
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about internal reliability:
- Internal reliability is not the same as validity. Validity is a broader concept that refers to the extent to which a test measures what it is supposed to measure. Internal reliability is a more specific concept that refers to the consistency of the items on a test in measuring the same underlying construct.
- Internal reliability can be affected by a number of factors, such as the length of the test, the difficulty of the items, and the heterogeneity of the sample.
- It is important to consider the purpose of the test when interpreting the results of the internal reliability analysis. For example, a test with a low Cronbach's alpha may be acceptable for screening purposes, but it may not be acceptable for making important decisions about individuals.
Q18: Arrange the following causes of work stoppages in India in the ascending order:
A. Retrenchment of personnel
B. Bonus
C. Leave and hours of work
D. Wages and allowances
E. Indiscipline and violence
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) C, B, E, A, D
(b) E, C, A, B, D
(c) D, B, C, E, A
(d) C, A, E, B, D
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is C, B, E, A, D.
Here is a brief explanation of the causes of work stoppages in India in ascending order:
1. Leave and hours of work: Workers may go on strike if they are not satisfied with their leave or hours of work. This is especially common in industries where workers are required to work long hours or where they are not given enough leave. For example, in 2021, employees of Maruti Suzuki India went on strike demanding an increase in the number of leaves.
2. Bonus: Workers may go on strike if they are not satisfied with their bonus. This is especially common in industries where bonuses are a significant part of a worker's pay. For example, in 2022, employees of Infosys went on strike demanding a higher bonus.
3. Indiscipline and violence: Indiscipline and violence are less common causes of work stoppages, but they can still be very disruptive. Workers may go on strike if they are dissatisfied with the management of the company, or if they feel that they are not being treated fairly. For example, in 2022, employees of Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited went on strike demanding the removal of the managing director.
4. Wages and allowances: Workers may go on strike if they are not satisfied with their wages or allowances. This is especially common in industries where wages are low or where there is a lot of competition for jobs. For example, in 2021, employees of the Indian Railways went on strike demanding an increase in their wages.
5. Retrenchment of personnel: Retrenchment of personnel is the most common cause of work stoppages in India. This is when an employer lays off workers. This can be a very disruptive event for workers, and it can lead to feelings of insecurity and anxiety. Workers may go on strike to protest retrenchment, and they may also demand higher wages and better working conditions in order to compensate for the loss of their jobs. For example, in 2020, employees of the Maruti Suzuki India went on strike protesting the retrenchment of 5000 employees.
It is important to note that these are just some of the most common causes of work stoppages in India. There are many other factors that can contribute to work stoppages, such as political instability, natural disasters, and economic recessions
Q19: Characteristics of industrial relations include:
A. An outcome of employment relationships in an organisation
B. Develop the skills and methods of adjusting to and cooperating with each other
C. Create rules and regulations to maintain harmonious relations
D. Government is not involved in shaping industrial relations
E. Parties to industrial relations are employees. their organisations and employers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, E only
(b) A, B, C only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) A, B, C, E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C, E only.
The correct answer is A, B, C, and E.
- Industrial relations are the interactions between employers and employees, or labour/trade unions, employer groups, and the state. They are the outcome of employment relationships in an organization. Industrial relations develop the skills and methods of adjusting to and cooperating with each other.
- They create rules and regulations to maintain harmonious relations. And, the parties to industrial relations are employees, their organizations, and employers.
- The government is often involved in shaping industrial relations through legislation, regulation, and other interventions.
- However, the government is not always directly involved in the day-to-day interactions between employers and employees.
Other Related Points Here are some additional characteristics of industrial relations:
- They are complex and dynamic.
- They are influenced by a variety of factors, including the economic climate, the political climate, and the social climate.
- They can be both cooperative and conflictual.
- They are essential for the smooth functioning of the economy.
- They play a role in ensuring that workers are treated fairly and that they have a voice in the workplace.
- Industrial relations are an important part of the fabric of society. They help to ensure that employers and employees can work together to achieve common goals.
Q20: Which of the following models identifies the strategy development process, the value creation process. multi-channel integration process. performance assessment process and the information management process as its core processes?
(a) The IDIC Model
(b) The CRM value chain
(c) Payne & Frow's Model of CRM
(d) The SCHEMA Model
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Payne & Frow's Model of CRM.
The model identifies strategy development, value creation, multi-channel integration, performance assessment, and information management as core processes.
Payne and Frow's model is a customer relationship management (CRM) framework that emphasizes a cross-functional approach to customer management. The model identifies five core processes that are essential for effective CRM:
- Strategy development: This process involves developing a customer-centric strategy that aligns with the overall business strategy.
- Value creation: This process involves creating and delivering value to customers through products, services, and experiences.
- Multi-channel integration: This process involves integrating different channels of customer interaction so that customers can have a seamless experience across all channels.
- Performance assessment: This process involves measuring and evaluating the effectiveness of CRM initiatives.
- Information management: This process involves collecting, storing, and analyzing customer data to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences.
The Payne and Frow's Five Forces CRM model is a comprehensive framework that can be used to guide the development and implementation of a successful CRM strategy. The model is applicable to all types of businesses, regardless of size or industry.
Q21: Earnings per share of a company is Rs 4, Return on Investment is 20 percent and the return required by shareholder is 16 percent. Assuming Walter valuation model. if the payout ratio is 40 percent. what will be the price per share?
(a) Rs 16.75
(b) Rs 20.65
(c) Rs 28.75
(d) Rs 30.15
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Rs 28.75
Step 1: Calculate the Retained Earnings
- Earnings per Share (EPS) = Rs 4
- Payout Ratio = 40%, so Retention Ratio = 60%
- Retained Earnings per Share = EPS * Retention Ratio
- Retained Earnings per Share = 4 * 0.60 = Rs 2.40
Step 2: Determine the Return on Retained Earnings
- Return on Investment (ROI) = 20%
- Return on Retained Earnings = Retained Earnings * ROI
- Return on Retained Earnings = 2.40 * 0.20 = Rs 0.48
Step 3: Calculate New Earnings per Share
- New Earnings per Share = Retained Earnings per Share + Return on Retained Earnings
- New Earnings per Share = 2.40 + 0.48 = Rs 2.88
Step 4: Calculate the Price per Share Using Walter's Model
- Price per Share = (Dividend per Share + Return on Investment * Retained Earnings) / Required Rate of Return
- Dividend per Share = EPS * Payout Ratio = 4 * 0.40 = Rs 1.60
- Price per Share = (1.60 + (0.20 * 2.40)) / 0.16
- Price per Share = (1.60 + 0.48) / 0.16 = 2.08 / 0.16 = Rs 13
Verification
- Note that the above steps show how to derive part of the formula application. To fully apply Walter's model correctly:
- Price = D + (R - k) * E * (1 - b) / k
- With D = Dividend, R = Return on Retained Earnings, E = EPS, b = Retention Ratio, k = Required Rate
- Price = (1.60 + (0.20 - 0.16) * 4 * 0.60) / 0.16
- Price = (1.60 + 0.24) / 0.16 = 1.84 / 0.16 = Rs 28.75
Important Points
- Understanding Walter's Model: This model relates the value of a stock to its dividend policy and the internal rate of return of the company.
- Importance of ROI vs. Required Return: Higher ROI than the required return boosts share price when earnings are reinvested.
- Retention vs. Payout Ratio: Balancing between paying dividends and retaining earnings is critical. Improper balancing can affect stock price.
- Formula Application Variance: Misapplication of the formula can lead to incorrect stock prices. Double-check calculations.
- Influencing Variables: Market conditions and company performance can alter the outcome of the Walter's model.
Q22: Cash flows are grouped in the of Cash Flow statement as per IND AS - 3 into which of the following major categories?
(a) Cash receipts, cash disbursements and non-cash activities
(b) Direct cash flows and indirect cash flows
(c) Operating activities, investing activities and collection activities
(d) Operating activities, investing activities and financing activities
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Operating activities, investing activities and financing activities.
Cash flows are grouped in the Cash Flow Statement as per IND AS - 3 into the following major categories:
- Operating activities: These are the cash flows from the principal revenue-producing activities of the entity and from other activities that are not investing or financing activities.
- Investing activities: These are the cash flows from the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents.
- Financing activities: These are the cash flows from the raising and repayment of capital and from other activities that result in changes in the entity's liabilities and equity, other than those arising from operating activities.
Q23: Match List I with List II
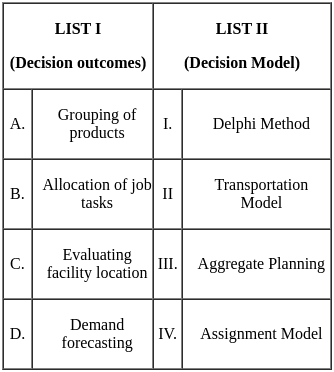
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(b) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(d) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I.
Key Points
Here is the explanation of each of the matches:
- A. Grouping of products: Aggregate planning is a decision-making process that helps organizations to determine the best way to allocate resources over a specified period of time. It is often used to group products together based on their demand patterns.
- B. Allocation of job tasks: The assignment model is a mathematical model that can be used to allocate tasks to resources in order to minimize costs or maximize profits. It is often used to allocate job tasks to employees or machines.
- C. Evaluating facility location: The transportation model is a mathematical model that can be used to determine the best way to transport goods from one location to another. It is often used to evaluate the location of new facilities.
- D. Demand forecasting: The Delphi method is a forecasting technique that uses a panel of experts to provide input on the likely future demand for a product or service. It is often used to forecast demand for new products or services.
Q24: A consumer wants to purchase a laptop. S/he makes a list of selected brands and then evaluates selected brands in terms of each relevant attribute and computes a weighted score for each brand. Then. s/he selects the highest scoring brand. Which consumer decision making rule has s/he employed?
(a) Compensatory
(b) Conjunctive
(c) Affect Referral
(d) Lexicographic
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is (a) Compensatory.
The consumer employs the compensatory decision-making rule, where they evaluate selected brands by assigning weights to relevant attributes (e.g., price, processor speed, brand reputation) and compute a weighted score for each brand, selecting the one with the highest score. In this model, a high score on one attribute can compensate for a low score on another. Unlike non-compensatory rules (e.g., conjunctive, where brands must meet minimum attribute thresholds, or lexicographic, where attributes are prioritized sequentially), the compensatory rule allows trade-offs between attributes.
Other Related Points:
- The conjunctive rule (b) requires brands to meet minimum thresholds on all attributes.
- The affect referral rule (c) relies on emotional or heuristic judgments rather than systematic evaluation.
- The lexicographic rule (d) prioritizes attributes in order of importance, selecting the brand that performs best on the top attribute.
Q25: Arrange the following types of intelligence which a computer can simulate in the ascending order:
A. Visual-spatial
B. Logical mathematical
C. Linguistic
D. Interpersonal
E. Bodily kinesthetic
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) C, D, A, E, B
(b) C, A, D, E, B
(c) A, C, E, B, D
(d) A, C, B, E, D
Ans: a
Sol: The correct ascending order of the types of intelligence which a computer can simulate is:
- C. Linguistic: This intelligence involves the ability to understand and use language effectively. Computers can simulate linguistic intelligence through natural language processing, speech recognition, and language generation algorithms.
- D. Interpersonal: Interpersonal intelligence relates to understanding and interacting effectively with other people. Simulating interpersonal intelligence in computers involves developing algorithms for social interaction, empathy recognition, and understanding human emotions.
- A. Visual-Spatial: Visual-spatial intelligence involves the ability to perceive and manipulate visual information in space. Computers can simulate this intelligence through computer vision, image recognition, and spatial reasoning algorithms.
- E. Bodily Kinesthetic: This intelligence is associated with physical movement and coordination. While computers lack a physical body, they can simulate aspects of bodily kinesthetic intelligence through robotics, motion tracking, and simulations of physical activities.
- B. Logical-Mathematical: Logical-mathematical intelligence involves the ability to analyze problems logically and perform mathematical operations. Computers excel in simulating logical-mathematical intelligence through algorithms, calculations, and problem-solving processes.
Your ordering emphasizes the progression from linguistic and interpersonal aspects to visual-spatial, bodily kinesthetic, and logical-mathematical aspects. It's important to note that different intelligence frameworks may yield different orders, and the development of computer simulations for each type of intelligence depends on the specific characteristics and challenges associated with that intelligence.
Therefore, the ascending order of difficulty for computers to simulate these types of intelligence C, D, A, E, B.
Q26: Which of the following are concerns and challenges of industrial revolution 4.0?
A. Invasion of privacy
B. Reduced capital expenditure on infrastructure
C. Low cost and affordable service
D. Blurring differences between the men and machines
E. Environmental concerns
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) B and D only
(d) A and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A and E only.
The concerns and challenges of Industrial Revolution 4.0 that are mentioned in the options A. Invasion of privacy and E. Environmental concerns are the most appropriate answers.
The use of advanced technologies in Industrial Revolution 4.0 could lead to the following:
- Invasion of privacy: As more and more data is collected and stored by machines, there is a risk that this data could be used to track our movements, monitor our activities, and even predict our behavior. This could have a negative impact on our privacy and security.
- Environmental concerns: The use of advanced technologies could have a negative impact on the environment. For example, the production of batteries for electric vehicles requires a significant amount of energy and resources.
Other Related Points
Other concerns and challenges of Industrial Revolution 4.0 include:
- Job displacement: As machines become more sophisticated, they are capable of performing tasks that were once done by humans. This could lead to job displacement in some industries.
- Skills gap: The rapid pace of technological change means that workers need to constantly upskill and reskill in order to keep up. This could create a skills gap, as there may not be enough skilled workers to meet the demand for jobs.
- Unequal distribution of wealth: The benefits of Industrial Revolution 4.0 could be unevenly distributed, leading to increased inequality.
- It is important to be aware of these concerns and challenges so that we can mitigate them and ensure that Industrial Revolution 4.0 is a force for good
Q27: Which of the following is NOT a base of product related segmentation?
(a) Consumption of the product
(b) Loyalty for the product
(c) Decision criteria for product evaluation
(d) Product use situations
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Loyalty for the product
Loyalty for a product is indeed not typically considered a base for product-related segmentation. Here's why:
Product-related segmentation focuses on grouping customers based on their interactions and preferences with the product itself. This means considering factors like:
- Usage: How often do they use the product? What features do they use most?
- Needs and preferences: What are their desired features or benefits? What are their pain points related to the product?
- Purchase behavior: How often do they buy the product? What factors influence their purchase decisions?
While loyalty can be influenced by the product and its features, it goes beyond the product itself. It's a broader concept that reflects a customer's overall relationship with the brand or company. Loyalty can be driven by various factors, including:
- Customer satisfaction: Positive experiences with the product and service.
- Emotional connection: Feeling valued and identified with the brand.
- Trust and reliability: Consistent performance and positive brand image.
Therefore, loyalty is not a direct indicator of a customer's specific preferences or interactions with the product itself. It's a more holistic measure of their relationship with the brand, which could be relevant for broader marketing strategies but not necessarily for product-specific segmentation.
Q28: Match List I with List II
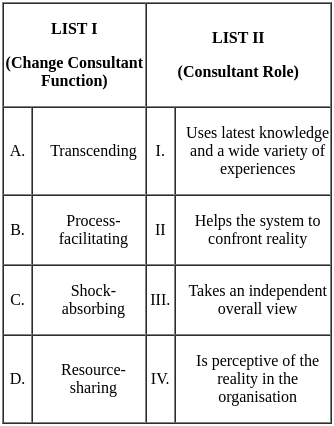
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(d) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Here is the explanation of each of the matches:
- Transcending: This is a consultant role that involves taking an independent overall view of the situation. The consultant helps the organization to see the bigger picture and to think outside the box. This matches with III. because the consultant takes a step back from the situation and looks at it from a different perspective.
- Process-facilitating: This is a consultant role that involves helping the organization to manage the change process. The consultant helps the organization to set goals, to develop plans, and to implement change. This matches with IV. because the consultant helps the organization to confront reality and to make changes.
- Shock-absorbing: This is a consultant role that involves helping the organization to cope with the stress of change. The consultant provides support and guidance to help the organization to manage the difficult emotions that can accompany change. This matches with II. because the consultant helps the organization to see the reality of the situation and to deal with it.
- Resource-sharing: This is a consultant role that involves sharing knowledge and expertise with the organization. The consultant brings their own knowledge and experience to the table and helps the organization to learn and grow. This matches with I. because the consultant shares their knowledge and experience with the organization
Q29: A flexible organisation design which can form and re-form varied patterns of connection. is known as :
(a) Virtual Organisation
(b) Fishnet Organisation
(c) Learning Organisation
(d) Spaghetti Organisation
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Fishnet Organisation.
A fishnet organization is a type of network organization. It is a flexible organizational design that can form and re-form varied patterns of connection. The term "fishnet" is used because the organization resembles a fishnet, with a central core and a series of interconnected nodes.
The central core of the fishnet organization is responsible for providing strategic direction and coordination. The nodes are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day operations of the organization. The nodes are connected to each other by a variety of relationships, such as shared goals, resources, or expertise.
The fishnet organization is a relatively new organizational design, and it is still evolving. However, it has the potential to be a more flexible and adaptable way of organizing than traditional hierarchical organizations.
Important Points
Here are some of the key characteristics of a fishnet organization:
- Flexibility: The fishnet organization is able to adapt and respond to change more quickly than traditional hierarchical organizations.
- Decentralization: Decision-making is decentralized in the fishnet organization, which gives the nodes more autonomy.
- Interdependence: The nodes in the fishnet organization are interdependent, which means that they need to collaborate and cooperate in order to achieve their goals.
- Networked: The fishnet organization is a network of independent units, which means that there is no clear hierarchy.
- Adaptive: The fishnet organization is adaptive, which means that it can change its structure and processes in order to meet the needs of the environment.
The fishnet organization is a promising new organizational design that has the potential to be more flexible and adaptable than traditional hierarchical organizations. However, it is still a relatively new design, and it is important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages before deciding if it is the right fit for your organization.
Q30: Which of the following economic identities states that One (1) extra percent unemployment costs two (2) percent of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
(a) Sacrifice ratio
(b) Phillips curve
(c) Misery index
(d) Okun's law
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Okun's law,
Okun's law is the economic identity that states that one extra percent of unemployment costs two percent of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Okun's law is named after Arthur Melvin Okun, an American economist who developed the law in the 1960s. Okun's law is based on the observation that there is a negative relationship between unemployment and GDP. In other words, when unemployment is high, GDP is low, and vice versa.
- The exact relationship between unemployment and GDP is not constant, but Okun's law typically assumes that a 1% increase in unemployment will lead to a 2% decrease in GDP. This means that if the unemployment rate is 5%, then the GDP is about 10% lower than it would be if the unemployment rate was 4%.
- Okun's law is not without its critics. Some economists argue that the relationship between unemployment and GDP is not as strong as Okun's law suggests. Others argue that Okun's law is not applicable to all countries or all economic conditions.
- Despite these criticisms, Okun's law remains an important tool for economists and policymakers. It is used to assess the impact of economic policies on unemployment and GDP. It is also used to forecast future economic growth.
Other Related Points
Here are some of the limitations of Okun's law:
- It is based on historical data, and the relationship between unemployment and GDP may change over time.
- It does not take into account other factors that can affect GDP, such as inflation and interest rates.
- It is only a rough estimate, and the actual impact of unemployment on GDP can vary depending on the specific circumstances.
- Overall, Okun's law is a useful tool for economists and policymakers, but it should be used with caution.
Q31: Population variance differ from sample variance in which of the following manner:
A. μ ± 3σ is replaced by x̅ + 9σ2
B. μ is replaced by x̅
C. μ2 is replaced by 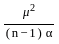
D. N is replaced by n - 1
E. N is replaced by n - 1 - α
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B and D only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A and E only
(d) D and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is B and D only.
Here is an explanation of the differences between population variance and sample variance in detail:
Population variance: The population variance is the variance of the entire population. It is calculated using the following formula:
σ2 = Σ(x - μ)2 / N
where:
σ2 is the population variance
Σ is the sum of
x is a value in the population
μ is the population mean
N is the population size
The population variance is used to measure the amount of variation in a population. It is a measure of how spread out the data is from the population mean.
Other Related Points Sample variance: The sample variance is the variance of a sample from the population. It is calculated using the following formula:
s2 = Σ(x - x̅)2 / n - 1
where:
- s^2 is the sample variance
- Σ is the sum of
- x is a value in the sample
- x̅ is the sample mean
- n is the sample size
The sample variance is used to estimate the population variance. It is calculated by using the sample mean instead of the population mean, and by using the sample size minus 1 in the denominator.
Important Points
- The reason why the sample size minus 1 is used in the denominator of the sample variance is because it is a correction factor that helps to reduce the bias of the estimate.
- The bias of an estimate is the difference between the expected value of the estimate and the true value of the population parameter.
- The bias of the sample variance is negative, which means that the sample variance is typically underestimates the population variance. The sample size minus 1 correction factor helps to reduce the bias of the sample variance.
- In conclusion, the only differences between population variance and sample variance are that in the sample variance, the population mean is replaced by the sample mean, and the population size is replaced by the sample size minus 1.
Q32: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: b
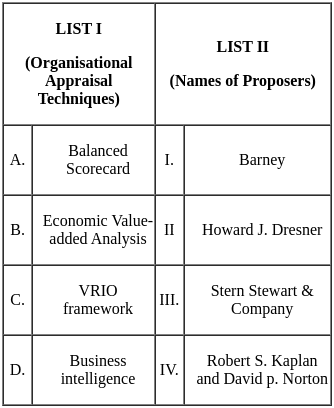
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II.
Here is an explanation of each of the terms:
Balanced Scorecard: This is a performance measurement framework that helps organizations to set goals, measure their performance, and track their progress towards their goals. It was developed by Robert S. Kaplan and David p. Norton in the early 1990s.
Economic Value-added Analysis: This is a financial performance measure that measures the amount of value created by a company for its shareholders. It was developed by Stern Stewart & Company in the 1980s.
VRIO framework: This is a business analysis framework that helps organizations to identify their resources and capabilities and assess their value, rarity, imitability, and organization. It was developed by Jay Barney in the 1990s.
Business intelligence: This is a broad term that refers to the collection, analysis, and presentation of data to help organizations make better decisions. It can be used to track performance, identify trends, and make predictions.
Q33: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(d) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
Ans: b
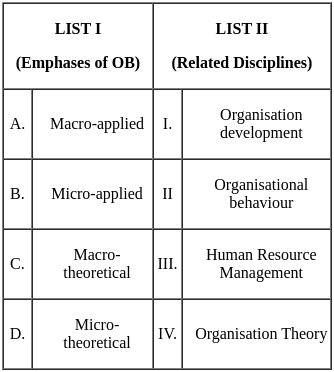
Sol: The correct answer is A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II.
Here is the explanation of each of the matches:
- Macro-applied: OD is a field that focuses on improving the overall performance of organizations. It does this by helping organizations to change and adapt to their environment. OD is a macro-applied discipline because it focuses on the overall organization, rather than on individuals or groups within the organization.
- Micro-applied: HRM is a field that focuses on the management of people in organizations. It does this by developing and implementing HR policies and practices that are designed to attract, motivate, and retain employees. HRM is a micro-applied discipline because it focuses on individuals and groups within the organization, rather than on the overall organization.
- Macro-theoretical: OT is a field that focuses on understanding the nature of organizations. It does this by developing theories that explain how organizations work and how they change. OT is a macro-theoretical discipline because it focuses on the overall organization, rather than on individuals or groups within the organization.
- Micro-theoretical: OB is a field that focuses on understanding the behavior of individuals and groups in organizations. It does this by developing theories that explain how individuals and groups behave in organizations. OB is a micro-theoretical discipline because it focuses on individuals and groups within the organization, rather than on the overall organization.
Q34: Arrange the following steps of job evaluation in the proper sequence
A. Review job descriptions and job specifications
B. Select compensable factors
C. Choose benchmark jobs
D. Define each factor's degree
E. Assign weights to compensable factors
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) A, E, B, D, C
(b) C, B, E, D, A
(c) A, C, B, E, D
(d) C, B, E, A, D
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (c) A, C, B, E, D. The steps of job evaluation are:
- A. Review job descriptions and job specifications: Understand the roles and requirements of jobs to ensure accurate evaluation.
- C. Choose benchmark jobs: Select representative jobs to set standards for comparison.
- B. Select compensable factors: Identify factors (e.g., skill, effort, responsibility) to evaluate job value.
- E. Assign weights to compensable factors: Determine the relative importance of each factor.
- D. Define each factor’s degree: Specify levels or grades for each factor to assess jobs.
Rationale: Reviewing job descriptions is the foundational step to gather data, followed by selecting benchmarks and defining evaluation criteria.
Q35: Which one of the following statements is true for Type II error?
(a) Rejecting an incorrect hypothesis
(b) Accepting an incorrect hypothesis
(c) Accepting a correct hypothesis
(d) Rejecting a correct hypothesis
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Accepting an incorrect hypothesis.
- Type II error is accepting an incorrect hypothesis.
- In statistics, a type II error is the error of failing to reject a false null hypothesis. This means that the researcher concludes that there is no difference between the groups being studied, when in reality there is a difference.
- Type II errors are often called false negatives. They can occur when the sample size is too small, the power of the test is too low, or when the effect size is small.
Other Related Points Here is an example of a type II error:
A researcher is testing a new drug to see if it is effective in reducing blood pressure. The researcher conducts a study and finds that there is no statistically significant difference between the blood pressure of the group that took the drug and the group that took a placebo. However, the researcher fails to realize that the sample size was too small to detect a difference. As a result, the researcher makes a type II error and concludes that the drug is not effective, when in reality it is.
Type II errors can have serious consequences. In the example above, the researcher may decide not to use the drug, even though it could be effective in reducing blood pressure.
There are a number of things that researchers can do to reduce the risk of type II errors. These include:
- Increasing the sample size
- Increasing the power of the test
- Using a more sensitive test
- Accounting for known sources of variability
- By taking these steps, researchers can reduce the risk of making type II errors and ensure that their conclusions are accurate.
Q36: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow
Accepted wisdom holds that the less competition a business faces, the more it thrives. The concept is at the core of the Blue Ocean Strategy (Kim and Mauborgne, 2005) which advocates launching in the uncontested markets, in order to avoid pain of going head-to-head with rivals. Research shows that exposure to competition in early stages of a firm's life increases its long-term survival prospects.
Companies established in crowded markets had a higher likelihood of failing in the first year than those started in less crowded markets. Early exposure to competition may immunize a company. How does a competition help firms in their youth thrive? A challenging environment causes startups to be tightly focused on satisfying customer needs along with lowering and containing costs. Many companies develop internal competition. Venture investors can help to create a similar dynamics by being careful not to overfund a new company, as having too much cash-on- hand can make it harder to establish a low-cost culture. Of course, early competition has a downside: some new businesses fail before they have time to build up immunity. Still managers of young businesses will bear in mind the advantages of exposure to safe levels of external competition or to a competitive environment that's been generated inside the organization. Such exposure can have long-lasting positive effects on efficiency and survival.
A strategy referred to in the passage that enables firms to create a new market space for themselves is:
(a) Red Ocean strategy
(b) Blue Ocean strategy
(c) Budding in the Ocean strategy
(d) Occasional strategy
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Blue Ocean strategy.
he correct answer is (b) Blue Ocean strategy. The Blue Ocean strategy, as outlined by Kim and Mauborgne (2005), advocates creating uncontested market spaces (blue oceans) to avoid competition in saturated markets (red oceans). It involves:
- Reconstructing market boundaries: Redefining the industry to create new demand.
- Focusing on buyer utility: Offering unique value to customers.
- Raising and creating new factors: Enhancing key elements and introducing novel features.
- Eliminating and reducing non-essential factors: Removing or minimizing less valuable aspects to lower costs.
- This strategy contrasts with competing in crowded markets, promoting innovation and value creation.
Q37: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow
Accepted wisdom holds that the less competition a business faces, the more it thrives. The concept is at the core of the Blue Ocean Strategy (Kim and Mauborgne, 2005) which advocates launching in the uncontested markets, in order to avoid pain of going head-to-head with rivals. Research shows that exposure to competition in early stages of a firm's life increases its long-term survival prospects.
Companies established in crowded markets had a higher likelihood of failing in the first year than those started in less crowded markets. Early exposure to competition may immunize a company. How does a competition help firms in their youth thrive? A challenging environment causes startups to be tightly focused on satisfying customer needs along with lowering and containing costs. Many companies develop internal competition. Venture investors can help to create a similar dynamics by being careful not to overfund a new company, as having too much cash-on- hand can make it harder to establish a low-cost culture. Of course, early competition has a downside: some new businesses fail before they have time to build up immunity. Still managers of young businesses will bear in mind the advantages of exposure to safe levels of external competition or to a competitive environment that's been generated inside the organization. Such exposure can have long-lasting positive effects on efficiency and survival.
More competition in the early years of the business results in:
(a) Reducing the chances of its survival in the long-run
(b) Increasing the chances of its survival in the long-run
(c) Neutralising the life of the business
(d) Making difficult for the new firm to raise funds from the market
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Increasing the chances of its survival in the long-run.
The correct answer is (b) Increasing the chances of its survival in the long-run. According to the passage, early exposure to competition enhances a firm’s long-term survival by fostering a focus on customer needs and cost containment, creating a disciplined and efficient organization. This “immunization” effect helps startups adapt to challenging environments, improving their resilience over time.
Surviving in the long run in business requires a combination of strategic planning, adaptability, and a focus on sustainability. Here are some key strategies to increase the chances of a business's survival over the long term:
Strategic Planning:
- Develop a clear and realistic business plan that outlines your goals, target market, and strategies for growth.
- Regularly revisit and update your business plan to adapt to changing market conditions and emerging opportunities.
Financial Management:
- Maintain a strong financial foundation by managing cash flow effectively, controlling expenses, and ensuring profitability.
- Diversify revenue streams to reduce dependence on a single source of income.
Customer Focus:
- Understand your customers' needs and preferences, and consistently deliver value to them.
- Build strong customer relationships through excellent customer service, engagement, and feedback mechanisms.
Innovation and Adaptability:
- Embrace innovation and stay ahead of industry trends. Be open to adopting new technologies and processes.
- Adapt quickly to changes in the business environment, and be willing to pivot your strategies when necessary.
Talent Management:
- Attract and retain skilled and motivated employees. Invest in training and development to keep your team's skills current.
- Foster a positive and collaborative work culture to enhance employee satisfaction and productivity.
Q38: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow
Accepted wisdom holds that the less competition a business faces, the more it thrives. The concept is at the core of the Blue Ocean Strategy (Kim and Mauborgne, 2005) which advocates launching in the uncontested markets, in order to avoid pain of going head-to-head with rivals. Research shows that exposure to competition in early stages of a firm's life increases its long-term survival prospects.
Companies established in crowded markets had a higher likelihood of failing in the first year than those started in less crowded markets. Early exposure to competition may immunize a company. How does a competition help firms in their youth thrive? A challenging environment causes startups to be tightly focused on satisfying customer needs along with lowering and containing costs. Many companies develop internal competition. Venture investors can help to create a similar dynamics by being careful not to overfund a new company, as having too much cash-on- hand can make it harder to establish a low-cost culture. Of course, early competition has a downside: some new businesses fail before they have time to build up immunity. Still managers of young businesses will bear in mind the advantages of exposure to safe levels of external competition or to a competitive environment that's been generated inside the organization. Such exposure can have long-lasting positive effects on efficiency and survival.
The best way for a firm to survive in a highly-competitive environment is:
(a) Hiring highly competitive human resources
(b) Focusing on customer needs along with lowering the cost
(c) Improving the quality of the product without caring for the costs involved
(d) Making huge investment in state-of-the art technology
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Focusing on customer needs along with lowering the cost.
- In today's economy, customers have more choices than ever before. They can easily compare prices and find the best product or service for their needs. This means that businesses need to focus on providing excellent customer service and value for money in order to stay competitive.
- One way to focus on customer needs is to conduct market research to understand what customers are looking for. This research can be done by surveying customers, conducting focus groups, or analyzing social media data. Once businesses understand what customers want, they can develop products and services that meet those needs.
- Another way to focus on customer needs is to personalize the customer experience. This can be done by collecting customer data and using it to provide personalized recommendations, offers, and support. By personalizing the customer experience, businesses can make customers feel valued and appreciated.
- In addition to focusing on customer needs, businesses also need to lower their costs in order to be competitive. This can be done by streamlining operations, negotiating better prices with suppliers, and reducing waste. By lowering their costs, businesses can offer lower prices to customers and improve their bottom line.
- By focusing on customer needs and lowering costs, businesses can create a competitive advantage that will help them survive and thrive in a highly-competitive environment.
The passage states that a competitive environment encourages startups to tightly focus on satisfying customer needs while containing costs, creating a low-cost culture that enhances efficiency and competitiveness. This approach helps firms thrive in highly competitive markets by delivering value and maintaining profitability.
Q39: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow
Accepted wisdom holds that the less competition a business faces, the more it thrives. The concept is at the core of the Blue Ocean Strategy (Kim and Mauborgne, 2005) which advocates launching in the uncontested markets, in order to avoid pain of going head-to-head with rivals. Research shows that exposure to competition in early stages of a firm's life increases its long-term survival prospects.
Companies established in crowded markets had a higher likelihood of failing in the first year than those started in less crowded markets. Early exposure to competition may immunize a company. How does a competition help firms in their youth thrive? A challenging environment causes startups to be tightly focused on satisfying customer needs along with lowering and containing costs. Many companies develop internal competition. Venture investors can help to create a similar dynamics by being careful not to overfund a new company, as having too much cash-on- hand can make it harder to establish a low-cost culture. Of course, early competition has a downside: some new businesses fail before they have time to build up immunity. Still managers of young businesses will bear in mind the advantages of exposure to safe levels of external competition or to a competitive environment that's been generated inside the organization. Such exposure can have long-lasting positive effects on efficiency and survival.
According to the passage, venture capitalists should:
(a) build a low-cost structure
(b) be aggressive in financing
(c) take steps to acquire poor performing companies that they have funded
(d) not overfund a new business
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is not overfund a new business.
The passage highlights that venture capitalists should avoid overfunding to maintain a low-cost culture, as excess cash can lead to waste, inefficiency, diluted ownership, and reduced incentives for cost discipline.
- A: Incorrect, as building a low-cost structure is the firm’s responsibility, not venture capitalists’.
- B: Incorrect, as aggressive financing contradicts the passage’s advice against overfunding.
- C: Incorrect, as acquiring poor-performing companies is not mentioned in the passage.
Q40: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow
Accepted wisdom holds that the less competition a business faces, the more it thrives. The concept is at the core of the Blue Ocean Strategy (Kim and Mauborgne, 2005) which advocates launching in the uncontested markets, in order to avoid pain of going head-to-head with rivals. Research shows that exposure to competition in early stages of a firm's life increases its long-term survival prospects.
Companies established in crowded markets had a higher likelihood of failing in the first year than those started in less crowded markets. Early exposure to competition may immunize a company. How does a competition help firms in their youth thrive? A challenging environment causes startups to be tightly focused on satisfying customer needs along with lowering and containing costs. Many companies develop internal competition. Venture investors can help to create a similar dynamics by being careful not to overfund a new company, as having too much cash-on- hand can make it harder to establish a low-cost culture. Of course, early competition has a downside: some new businesses fail before they have time to build up immunity. Still managers of young businesses will bear in mind the advantages of exposure to safe levels of external competition or to a competitive environment that's been generated inside the organization. Such exposure can have long-lasting positive effects on efficiency and survival.
Which of the following is a type of competitive strategy?
(a) Product differentiation
(b) Minimum currency cost
(c) Maximum cost structure
(d) Profit maximisation
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Product differentiation.
Product differentiation is a competitive strategy where firms distinguish their products through unique features, premium positioning, or targeting specific market niches, enabling them to stand out in competitive markets. The passage’s emphasis on satisfying customer needs aligns with differentiation by offering tailored value.
- B: Incorrect, as “minimum currency cost” is not a recognized strategy.
- C: Incorrect, as “maximum cost structure” is not a strategy and contradicts cost containment.
- D: Incorrect, as profit maximization is an outcome, not a competitive strategy.
Q41: Which of the following narratives explain the Leontief paradox in international business:
(a) USA's exports were capital intensive and imports were labour intensive
(b) USA's exports and imports both were capital intensive
(c) USA's exports were labour-intensive and imports were capital intensive
(d) USA's exports and imports both were labour-intensive
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (c) USA's exports were labour-intensive and imports were capital-intensive. The Leontief Paradox contradicts the Heckscher-Ohlin theory, which predicts that capital-abundant countries like the USA should export capital-intensive goods and import labor-intensive goods. Instead, Leontief found that the USA exported labor-intensive goods and imported capital-intensive goods. Possible explanations include:
- The USA’s comparative advantage in high-tech, labour-intensive goods.
- High productivity in labour-intensive industries due to skilled labor.
- A large domestic market enabling economies of scale.
Note: Replace "effects" with "affects" in any discussion of change (e.g., "change in one element affects other elements").
Other Related Points
Here are some other possible explanations for the Leontief paradox:
The United States has a high level of productivity in labor-intensive industries.
The United States has a high level of investment in human capital, which makes its labor force more productive.
The United States has a strong domestic market, which allows it to produce goods at a lower cost than other countries.
The United States has a favorable trade policy, which makes it easier for its exports to compete in foreign markets.
The Leontief paradox is a complex issue, and there is no single definitive explanation for it. However, it is an important paradox that has challenged our understanding of international trade.
Q42: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(c) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I.
- A. Strangers - III. Low profitability, low loyalty: Customers unfamiliar with the organization, unlikely to generate significant revenue or remain loyal.
- B. Barnacles - IV. Low profitability, high loyalty: Loyal but unprofitable customers who consume resources.
- C. True Friends - II. High profitability, high loyalty: Valuable, loyal customers who promote the organization.
- D. Butterflies - I. High profitability, low loyalty: Profitable but opportunistic customers likely to switch to competitors.
Note: Organizations should focus on True Friends and Butterflies for revenue, convert Strangers to loyal customers, and minimize Barnacles.
Q43: Arrange the steps of novel product design thinking process in a sequential order.
A. Define
B. Test
C. Prototype
D. Empathise
E. Ideate
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) E, D, A, B, C
(b) A, C, D, E, B
(c) D, A, E, C, B
(d) B, C, D, E, A
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is D, A, E, C, B.
The correct order of the steps of the novel product design thinking process is:
Empathize (D): Understand the user and their needs.
Define (A): Define the problem that you are trying to solve.
Ideate (E): Generate ideas for solutions to the problem.
Prototype (C): Build a prototype of your solution.
Test (B): Test your prototype with users and get feedback.
Other Related Points
Here is a more detailed explanation of each step:
- Empathize: The first step is to empathize with the user. This means understanding their needs, wants, and pain points. You can do this by conducting user research, such as interviews, surveys, and observations.
- Define: Once you have a good understanding of the user, you can define the problem that you are trying to solve. This is important because it will help you to focus your efforts and to come up with solutions that are actually relevant to the user.
- Ideate: The next step is to ideate. This means generating ideas for solutions to the problem. There are many different ways to ideate, such as brainstorming, sketching, and prototyping.
- Prototype: Once you have some ideas, you can build a prototype of your solution. This will help you to test your ideas and to get feedback from users.
- Test: The final step is to test your prototype with users and get feedback. This is important because it will help you to refine your solution and to make sure that it meets the needs of the user.
Q44: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
An enterprise resource planning is at the center of the institution. In spite of a definite need to integrate functionality in areas like accounting, sales and order management, customer relationship management and SCM, the investments made by companies is not enough. Enterprises need to transform business processes to respond to fast changing customer demands and survive the intense global competition.
Enterprises globally have been seeking information systems with the capacity to automate, communication and integrate information by collecting data in a highly standardized form. The selection of the ERP package is daunting task requiring a variety of infrastructural and managerial considerations. Both present and future business process scenarios need to be considered along with flexibility and cost. One dilemma before the decision makers is the possible intervention of non-proprietary technology standards. ERP implementation is a strategic activity requiring a comprehensive analysis of pre and post implementation scenarios and intensive training of people especially the front-end users. While some managers need to be involved in the design and implementation process, others have to learn the functionalities. The integration process passes through tough phases of accounting for differences in segments, departments and business processes, though with a unified managerial intent. A prototype of the required integration of business process needs to be developed after discussion with the people at different levels. The quality of ERP carries a long-term impact on the process of the organization and it is not easy to switch to another product with concomitant scale of investment and complexities. Fundamentally, everybody in the organization should understand how ERP will be used to bridge between "How it is" and "How it needs to be".
The most important step of ERP implementation is the __________ phase
(a) Installation
(b) Gap analysis
(c) Testing
(d) Training
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Gap analysis.
- Gap analysis is the correct answer. It is the process of identifying the gaps between the current state of an organization and its desired future state. This is done by comparing the organization's current systems and processes to the requirements of the ERP software.
- The gap analysis is a critical step in the ERP implementation process because it helps the organization to identify the changes that need to be made in order to successfully implement the software. By identifying these gaps early on, the organization can avoid costly mistakes and delays.
- The gap analysis is typically conducted by a team of experts from the organization and the ERP vendor. The team will gather data from a variety of sources, including interviews with employees, surveys, and documentation. This data is then analyzed to identify the gaps between the current state and the desired future state.
Q45: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
An enterprise resource planning is at the center of the institution. In spite of a definite need to integrate functionality in areas like accounting, sales and order management, customer relationship management and SCM, the investments made by companies is not enough. Enterprises need to transform business processes to respond to fast changing customer demands and survive the intense global competition.
Enterprises globally have been seeking information systems with the capacity to automate, communication and integrate information by collecting data in a highly standardized form. The selection of the ERP package is daunting task requiring a variety of infrastructural and managerial considerations. Both present and future business process scenarios need to be considered along with flexibility and cost. One dilemma before the decision makers is the possible intervention of non-proprietary technology standards. ERP implementation is a strategic activity requiring a comprehensive analysis of pre and post implementation scenarios and intensive training of people especially the front-end users. While some managers need to be involved in the design and implementation process, others have to learn the functionalities. The integration process passes through tough phases of accounting for differences in segments, departments and business processes, though with a unified managerial intent. A prototype of the required integration of business process needs to be developed after discussion with the people at different levels. The quality of ERP carries a long-term impact on the process of the organization and it is not easy to switch to another product with concomitant scale of investment and complexities. Fundamentally, everybody in the organization should understand how ERP will be used to bridge between "How it is" and "How it needs to be".
Which of the following is a precursor to ERP implementation?
(a) Business modelling
(b) Business process reengineering
(c) Project analysis
(d) Business continuity analysis
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is (b) Business process reengineering. BPR is a precursor to ERP implementation, involving the redesign of business processes to align with the ERP system’s capabilities and improve efficiency. It ensures that the organization’s processes are optimized before integrating the ERP software.
- Business modeling (a): Part of implementation, not a precursor, as it documents existing processes.
- Project analysis (c): Occurs during implementation, not as a precursor.
- Business continuity analysis (d): Focuses on risk management, not process alignment.
Other Related Points
The business modeling process typically involves the following steps:
- Identify the key processes: The organization needs to identify the key processes that are essential to its business. These are the processes that will be affected by the ERP implementation.
- Define the inputs and outputs of each process: The organization needs to define the inputs and outputs of each process. This will help to understand how the process works and what data it needs.
- Map the relationships between the processes: The organization needs to map the relationships between the processes. This will help to understand how the processes interact with each other.
Q46: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
An enterprise resource planning is at the center of the institution. In spite of a definite need to integrate functionality in areas like accounting, sales and order management, customer relationship management and SCM, the investments made by companies is not enough. Enterprises need to transform business processes to respond to fast changing customer demands and survive the intense global competition.
Enterprises globally have been seeking information systems with the capacity to automate, communication and integrate information by collecting data in a highly standardized form. The selection of the ERP package is daunting task requiring a variety of infrastructural and managerial considerations. Both present and future business process scenarios need to be considered along with flexibility and cost. One dilemma before the decision makers is the possible intervention of non-proprietary technology standards. ERP implementation is a strategic activity requiring a comprehensive analysis of pre and post implementation scenarios and intensive training of people especially the front-end users. While some managers need to be involved in the design and implementation process, others have to learn the functionalities. The integration process passes through tough phases of accounting for differences in segments, departments and business processes, though with a unified managerial intent. A prototype of the required integration of business process needs to be developed after discussion with the people at different levels. The quality of ERP carries a long-term impact on the process of the organization and it is not easy to switch to another product with concomitant scale of investment and complexities. Fundamentally, everybody in the organization should understand how ERP will be used to bridge between "How it is" and "How it needs to be".
Organisation wide training is required to take full advantage of an ERP implementation. In this context. which of the following statements are true?
I. Learning of the steering team on system performance is a must for ERP implementation
II. Training of functional managers in process analysis and redesign is required continually
III. IT department needs to be fully aware of system architecture
(a) Both I and II
(b) Both II and III
(c) Both I and III
(d) I, II and III
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Both I and III.
"Both I and III" is the correct answer.
- Statement I: The steering team is responsible for overseeing the ERP implementation project. They need to understand how the system works in order to make informed decisions about the project. Therefore, it is important for them to be trained on system performance.
- Statement II: Functional managers are responsible for the day-to-day operations of the organization. They need to understand how the ERP system will impact their work and how to use it effectively. Therefore, it is important for them to be trained on process analysis and redesign.
- Statement III: The IT department is responsible for the technical aspects of the ERP implementation. They need to understand the system architecture in order to support it and troubleshoot any problems that may arise. Therefore, it is important for them to be fully aware of system architecture.
Q47: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
An enterprise resource planning is at the center of the institution. In spite of a definite need to integrate functionality in areas like accounting, sales and order management, customer relationship management and SCM, the investments made by companies is not enough. Enterprises need to transform business processes to respond to fast changing customer demands and survive the intense global competition.
Enterprises globally have been seeking information systems with the capacity to automate, communication and integrate information by collecting data in a highly standardized form. The selection of the ERP package is daunting task requiring a variety of infrastructural and managerial considerations. Both present and future business process scenarios need to be considered along with flexibility and cost. One dilemma before the decision makers is the possible intervention of non-proprietary technology standards. ERP implementation is a strategic activity requiring a comprehensive analysis of pre and post implementation scenarios and intensive training of people especially the front-end users. While some managers need to be involved in the design and implementation process, others have to learn the functionalities. The integration process passes through tough phases of accounting for differences in segments, departments and business processes, though with a unified managerial intent. A prototype of the required integration of business process needs to be developed after discussion with the people at different levels. The quality of ERP carries a long-term impact on the process of the organization and it is not easy to switch to another product with concomitant scale of investment and complexities. Fundamentally, everybody in the organization should understand how ERP will be used to bridge between "How it is" and "How it needs to be".
In ERP implementation, which is not a constraint in the process of integration of different business entities?
(a) Functional differences
(b) Geographical differences
(c) Managerial differences
(d) Operational differences
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Managerial differences.
Managerial differences is not a constraint in the process of integration of different business entities in ERP implementation.
Here are some of the constraints that can affect the integration of different business entities in ERP implementation:
- Technical differences: The different business entities may use different systems and technologies, which can make it difficult to integrate them.
- Data differences: The different business entities may use different data formats and standards, which can make it difficult to integrate their data.
- Cultural differences: The different business entities may have different cultures and ways of doing things, which can make it difficult to integrate their processes.
- Legal differences: The different business entities may be subject to different laws and regulations, which can make it difficult to integrate their systems.
- Financial constraints: The different business entities may not have the financial resources to invest in ERP implementation.
Q48: Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
An enterprise resource planning is at the center of the institution. In spite of a definite need to integrate functionality in areas like accounting, sales and order management, customer relationship management and SCM, the investments made by companies is not enough. Enterprises need to transform business processes to respond to fast changing customer demands and survive the intense global competition.
Enterprises globally have been seeking information systems with the capacity to automate, communication and integrate information by collecting data in a highly standardized form. The selection of the ERP package is daunting task requiring a variety of infrastructural and managerial considerations. Both present and future business process scenarios need to be considered along with flexibility and cost. One dilemma before the decision makers is the possible intervention of non-proprietary technology standards. ERP implementation is a strategic activity requiring a comprehensive analysis of pre and post implementation scenarios and intensive training of people especially the front-end users. While some managers need to be involved in the design and implementation process, others have to learn the functionalities. The integration process passes through tough phases of accounting for differences in segments, departments and business processes, though with a unified managerial intent. A prototype of the required integration of business process needs to be developed after discussion with the people at different levels. The quality of ERP carries a long-term impact on the process of the organization and it is not easy to switch to another product with concomitant scale of investment and complexities. Fundamentally, everybody in the organization should understand how ERP will be used to bridge between "How it is" and "How it needs to be".
For success of ERP, the issues to be considered do not include :
(a) Adaptability to changes in business processes in the future
(b) ERP package free from the intervention of non-proprietary technology standards
(c) Customisations to support varied business practices
(d) Flexibility and cost-effectiveness of ERP
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is ERP package free from the intervention of non-proprietary technology standards.
The statement "ERP package free from the intervention of non-proprietary technology standards" is not an issue to be considered for the success of ERP.
Here are some of the key issues to be considered for the success of ERP:
- Top management commitment: ERP implementation is a major undertaking that requires the commitment of top management. Top management must be willing to provide the resources needed for the implementation and must be willing to support the changes that will be required.
- Change management: ERP implementation will require changes to the organization's processes, systems, and culture. Change management is the process of managing these changes and ensuring that they are successful.
- User involvement: Users must be involved in the ERP implementation process from the beginning. This will help to ensure that the system meets their needs and that they are willing to use it.
- Training: Users must be trained on how to use the ERP system. This training should be comprehensive and should cover all of the features and functionality of the system.
- Support: The organization must provide ongoing support for the ERP system. This support should include helpdesk services, training, and upgrades.
Q49: Which of the following statements are applicable to Mckinsey's 7S framework?
A. A priori, it is obvious which of the seven factors will be the driving force in changing a particular organisation at a particular point of time.
B. Effective organisational change is the relationship between seven factors of the framework.
C. Change in any one element effects change in other elements for effective organisational change.
D. Framework can be used for facilitating organisational change.
E. Strategy, Structure, Systems and Style are ‘Hard S' of the Model while Staff. Skill and Shared values are the 'Soft S' of the framework.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, B, C and D only
(d) A, B, C and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is B, C and D only.
The correct answers are B, C, and D.
The McKinsey 7S framework is a model that can be used to facilitate organizational change. It identifies seven key factors that need to be aligned in order for change to be successful. These factors are strategy, structure, systems, style, staff, skills, and shared values.
The statements that are applicable to the McKinsey 7S framework are:
- B. Effective organizational change is the alignment of the seven factors of the framework. This means that the seven factors need to be working together in a way that is supportive of the organization's goals.
- C. Change in any one element effects change in other elements for effective organizational change. This is because the seven factors are interconnected. If one factor changes, it will likely have an impact on the other factors.
- D. Framework can be used for facilitating organisational change. The McKinsey 7S framework can be used to help organizations plan and implement change. It can help organizations to identify the key factors that need to be changed and to develop a plan for how to make those changes.
The statement that is not applicable to the McKinsey 7S framework is:
- A. A priori, it is obvious which of the seven factors will be the driving force in changing a particular organisation at a particular point of time. This is not always the case. The driving force for change can vary depending on the organization and the situation
Q50: Which one of the following is NOT an extramural function of Trade Unions?
(a) Provision of education
(b) Job security
(c) Housing facilities
(d) Extension of medical facilities during sickness
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Job security.
Job security is not an extramural function of trade unions.
Extramural functions of trade unions are those that are carried out outside the factory premises. These functions include:
- Social welfare: Trade unions provide social welfare benefits to their members, such as scholarships, insurance, and housing.
- Political activities: Trade unions may engage in political activities, such as lobbying the government on behalf of their members.
- Community service: Trade unions may provide community service, such as running literacy programs or helping to build schools.
- Education: Trade unions may provide education to their members, such as training on labor laws or how to negotiate with employers.
- Intramural functions of trade unions are those that are carried out within the factory premises.
- Other Related Points
These functions include:
- Collective bargaining: Trade unions negotiate with employers on behalf of their members to improve wages, benefits, and working conditions.
- Dispute resolution: Trade unions help to resolve disputes between employers and employees.
- Representation: Trade unions represent their members in disciplinary hearings and other workplace matters.
- Health and safety: Trade unions promote health and safety in the workplace.
- Training: Trade unions provide training to their members on a variety of topics, such as workplace skills and labor laws.
- Job security is an important issue for trade unions, but it is not an extramural function. Job security is achieved through collective bargaining and other intramural functions.
Q51: A workman hired in place of a permanent workman or probationer who is temporarily absent is called:
(a) Temporary workman
(b) Casual workman
(c) Probationer workman
(d) Badli workman
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Badli workman.
- A workman hired in place of a permanent workman or probationer who is temporarily absent is called a badli (Hindi for substitute) worker.
- A badli worker is employed on a temporary basis to fill in for a permanent worker who is absent from work. Badli workers are typically paid a lower wage than permanent workers, and they do not have the same benefits.
- The term "badli" is most commonly used in India, but it is also used in other countries with a large Indian workforce, such as Singapore and Malaysia.
Other Related Points Here are some of the key features of a badli worker:
- They are employed on a temporary basis.
- They are paid a lower wage than permanent workers.
- They do not have the same benefits as permanent workers.
- They are typically hired to fill in for a permanent worker who is absent from work.
Badli workers can play an important role in an organization, as they can help to ensure that the work continues even when a permanent worker is absent. However, it is important to note that badli workers are typically not entitled to the same benefits as permanent workers, and they may be treated differently by the organization.
Q52: Which of the following motives were articulated by J. M. Keynes for holding cash?
A. Precautionary
B. Return generation
C. Speculative
D. Investment
E. Transaction
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, D and E only
(c) A, C and E only
(d) A, C and D only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A, C, and E only.
John Maynard Keynes proposed four motives for holding cash in his book "The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money". These motives are:
- Transaction motive: People hold cash to meet their day-to-day expenses. This is the most common motive for holding cash.
- Precautionary motive: People hold cash to guard against unexpected expenses or emergencies.
- Speculative motive: People hold cash to take advantage of investment opportunities.
- Finance motive: People hold cash to make future payments, such as taxes or loan repayments.
However, the finance motive is not widely accepted by economists today. They argue that people can use other assets, such as bonds, to meet their future payment needs.
Important Points
So, the three motives that are still widely accepted are the transaction motive, the precautionary motive, and the speculative motive.
- The transaction motive is the most important motive for holding cash. It is determined by the level of economic activity. When economic activity is high, people need to hold more cash to meet their day-to-day expenses.
- The precautionary motive is determined by the level of uncertainty in the economy. When people are more uncertain about the future, they are more likely to hold more cash to guard against unexpected expenses.
- The speculative motive is determined by the expected return on alternative investments. When the expected return on alternative investments is low, people are more likely to hold more cash in anticipation of higher returns in the future
Q53: Many consumers seek to be different and exclusive by demanding less of a commodity as more people consume it, is called?
(a) Bandwagon effect
(b) Snob effect
(c) Veblen effect
(d) Substitution effect
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Snob effect.
The snob effect occurs when consumers demand less of a commodity as more people consume it, seeking exclusivity and social distinction. Unlike the Veblen effect (where demand increases with price due to status), the snob effect is about reduced consumption to maintain uniqueness. It is seen in luxury goods or niche markets.
- A (Bandwagon effect): Demand increases as more people consume the product.
- C (Veblen effect): Demand rises with higher prices due to perceived status.
- D (Substitution effect): Consumers switch to alternatives due to price changes.
Q54: Which of the following is NOT a fundamental principle of KAIZEN?
(a) Let it go
(b) Empower people
(c) Know your customer
(d) Go to Gemba
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Let it Go.
The fundamental principles of Kaizen are:
- Continuous improvement: Kaizen is a philosophy of continuous improvement. It is about making small, incremental changes that can lead to big results over time.
- Empowerment: Kaizen believes that everyone in the organization should be empowered to make suggestions for improvement. This is because everyone has insights that can help to improve the way things are done.
- Respect for people: Kaizen respects the dignity and worth of all people. It believes that everyone has the potential to contribute to improvement.
- Teamwork: Kaizen is a team effort. It is about working together to achieve common goals.
- Focus on the customer: Kaizen focuses on the customer. It is about understanding the customer's needs and then continuously improving the product or service to meet those needs.
Important Points
The principle of "let it go" is not a fundamental principle of Kaizen. Kaizen is about continuous improvement, and this means that we should never stop trying to improve. We should always be looking for ways to make things better, even if it is just a small improvement.
The principle of "let it go" can be seen as a way of giving up on improvement. It can be seen as saying that we are satisfied with the way things are and that we do not need to make any changes. This is not the Kaizen way. Kaizen is about always striving for improvement, no matter how small.
Q55: Which of the following is NOT an element of 'Trade-relations mix’ in International Business?
(a) Product variety
(b) Price policy
(c) Mutual service and responsibilities
(d) Distributor's territorial rights
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Product Variety.
The trade-relations mix in international business includes elements like:
- Price policy (b): Pricing strategies tailored to international markets.
- Mutual service and responsibilities (c): Agreements on service levels between partners.
- Distributor’s territorial rights (d): Defining regions for distributors.
- Product variety is a product strategy, not a direct component of the trade-relations mix, which focuses on relational and transactional policies.
Q56: Which of the following is a post-offer takeover defense mechanism in which target company buys back shares at a significant premium?
(a) Poison pills
(b) Golden parachute
(c) Greenmail
(d) Crown jewel defense
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Greenmail.
- The post-offer takeover defense mechanism in which a target company buys back its shares at a significant premium is called Greenmail.
- Greenmail is a type of share repurchase that is used by a target company to buy back its shares from a hostile bidder at a premium price. The goal of greenmail is to make the takeover bid prohibitively expensive for the bidder.
- Greenmail is a controversial practice, and it is often seen as a way for target companies to avoid the scrutiny of a hostile takeover. However, greenmail can also be used by target companies to protect their shareholders from being taken over by a hostile bidder.
Other Related Points Here are some other post-offer takeover defense mechanisms:
- Poison pill: This is a provision in a company's charter that allows the company to issue new shares at a discounted price to existing shareholders if a hostile bidder acquires a certain percentage of the company's shares. This makes it prohibitively expensive for the bidder to acquire the company.
- White knight: This is a friendly acquirer that is brought in by the target company to fend off a hostile bidder. The white knight will typically offer to buy the target company at a price that is higher than the hostile bidder's offer.
- Pac-Man defense: This is a strategy in which the target company makes a hostile bid for the hostile bidder. This is a risky strategy, but it can be effective in deterring a takeover
Q57: Arrange (in descending order) the following present value of a growing perpetuity which makes first payment of Rs. 3,000 in next year.
A. Present value at 8% growth and 10% discount rate.
B. Present value at 3% growth and 9% discount rate.
C. Present value at 6% growth and 11% discount rate.
D. Present value at 5% growth and 6% discount rate.
E. Present value at 1% growth and 4% discount rate.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) A, D, C, B, E
(b) C, B, E, D, A
(c) D, A, E, C, B
(d) B, E, C, A, D
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is D, A, E, C, B.
Formula: PV = 3,000 / (Discount Rate - Growth Rate)
Calculations:
- A: 8% growth, 10% discount → PV = 3,000 / (0.10 - 0.08) = 3,000 / 0.02 = 150,000
- B: 3% growth, 9% discount → PV = 3,000 / (0.09 - 0.03) = 3,000 / 0.06 = 50,000
- C: 6% growth, 11% discount → PV = 3,000 / (0.11 - 0.06) = 3,000 / 0.05 = 60,000
- D: 5% growth, 6% discount → PV = 3,000 / (0.06 - 0.05) = 3,000 / 0.01 = 300,000
- E: 1% growth, 4% discount → PV = 3,000 / (0.04 - 0.01) = 3,000 / 0.03 = 100,000
Descending order: D (300,000), A (150,000), E (100,000), C (60,000), B (50,000)
The present value of a growing perpetuity is calculated as PV = Payment / (Discount Rate - Growth Rate), where the first payment is Rs. 3,000. Higher growth rates and lower discount rates increase PV. Calculated values are:
- D: PV = 3,000 / (0.06 - 0.05) = 300,000
- A: PV = 3,000 / (0.10 - 0.08) = 150,000
- E: PV = 3,000 / (0.04 - 0.01) = 100,000
- C: PV = 3,000 / (0.11 - 0.06) = 60,000
- B: PV = 3,000 / (0.09 - 0.03) = 50,000
Ordered in descending PV: D, A, E, C, B.
Q58: Hofstede's dimensions of culture were based on a study conducted at:
(a) Intel Ltd
(b) IBM
(c) Pepsico
(d) Microsoft
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is IBM.
Hofstede's dimensions of culture were based on a study conducted at IBM.
The study was conducted by Geert Hofstede, a Dutch social psychologist, in the 1960s and 1970s. Hofstede surveyed IBM employees from over 70 countries on their values and beliefs. He found that there were significant differences in the values and beliefs of employees from different countries.
Hofstede identified four dimensions of culture:
- Power Distance Index (PDI): This dimension measures the extent to which people in a society accept that power is distributed unequally.
- Individualism-Collectivism (IC): This dimension measures the extent to which people in a society value individual or collective goals.
- Masculinity-Femininity (MAS): This dimension measures the extent to which a society values traditionally masculine or feminine values.
- Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI): This dimension measures the extent to which people in a society feel threatened by uncertainty and ambiguity.
Hofstede's dimensions of culture have been widely used in cross-cultural research. They have been used to explain differences in business practices, consumer behavior, and political systems.
Other Related Points
In addition to the four dimensions identified by Hofstede, other researchers have proposed additional dimensions of culture. For example, Fons Trompenaars has proposed seven dimensions of culture:
- Universalism versus particularism
- Individualism versus collectivism
- Neutral versus emotional
- Specific versus diffuse
- Achievement versus ascription
- Time orientation
- Human orientation
- Power distance
Q59: In competitive markets, a new firm will enter the market in which of the following situations?
(a) P > ATC
(b) P < ATC
(c) P = MC
(d) P = MR = MC
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is P > ATC.
The inequality P > ATC represents a situation where a firm is making a profit. Let me break down the terms:
- P represents the price at which the firm sells its product or service.
- ATC stands for Average Total Cost, which is the total cost per unit of output.
When P > ATC, it means that the price at which the firm is selling its product is higher than the average cost of producing each unit. In other words, the firm is selling its product at a price that covers not only the variable costs but also contributes to covering the fixed costs. This situation leads to a positive economic profit.
If P = ATC, the firm is breaking even, covering all its costs but not making any economic profit. If P < ATC, the firm is incurring losses because the price is not sufficient to cover all the costs.
This relationship is often used in economic analysis to understand the financial performance of a firm in the short run. It's important to note that in the long run, firms would ideally enter or exit the market based on their ability to cover all costs and make a normal profit.
Q60: In which method of capital budgeting, cash flows are re-invested at the required rate of return?
(a) Net Present Value (NPV)
(b) Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
(c) Profitability Index (PI)
(d) Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Net Present Value.
- Net present value (NPV) is a capital budgeting method that measures the profitability of a project by discounting its future cash flows to the present value. The NPV is calculated by taking the present value of all of a project's future cash flows and subtracting the initial investment.
- A positive NPV means that the project is expected to generate a return that is greater than the required rate of return. A negative NPV means that the project is expected to generate a return that is less than the required rate of return.
- The NPV method is considered to be a more accurate measure of a project's profitability than other capital budgeting methods, such as the payback period and the internal rate of return, because it takes into account the time value of money.
Other Related PointsThe time value of money is the idea that money today is worth more than money in the future because it can be invested and earn a return. The NPV method takes into account the time value of money by discounting the future cash flows to the present value.
The NPV method is a widely used capital budgeting method, but it is not without its limitations. One limitation of the NPV method is that it can be difficult to estimate the future cash flows of a project. Another limitation is that the NPV method does not take into account the risk of a project.
Q61: An organisational vision should include:
A. An organisational charter of core values and principles
B. A strategy or plan and a view from the top
C. The source of priorities, plans and goals
D. A pusher into the future
E. A determination and publication of what makes an organisation unique
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and D only
(b) A, C and D only
(c) A, C and E only
(d) A, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A, C and E only.
The organizational vision should include the following:
- An organizational charter of core values and principles: This is a statement of the organization's core values and principles. These values and principles should guide the organization's actions and decisions.
- The source of priorities, plans and goals: The organizational vision should be the source of the organization's priorities, plans, and goals. These priorities, plans, and goals should be aligned with the organization's vision.
- A determination and publication of what makes an organisation unique: The organizational vision should be a determination and publication of what makes the organization unique. This is what sets the organization apart from its competitors and inspires employees and stakeholders to work towards achieving the organization's goals.
Important Points
The organizational vision should not include the following:
- A strategy or plan: A strategy or plan is a roadmap for how the organization will achieve its vision. The vision is the destination, and the strategy or plan is the route to get there. The organizational vision should not be confused with a strategy or plan.
- A pusher into the future: A pusher into the future is something that forces the organization to change. The vision should be something that the organization aspires to, but it should not be something that is forced upon it
Q62: An unfavourable overhead volume variance indicates that:
(a) Total fixed overhead has exceeded the standard budgeted amount
(b) Variable overhead per unit has exceeded the standard budgeted amount
(c) Actual production was less than the normal level of output .
(d) Actual production was more than the normal level of output
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Actual Production was less than the normal level of output.
- An unfavorable overhead volume variance indicates that actual production was less than the normal level of output.
- The overhead volume variance is the difference between the budgeted overhead and the actual overhead incurred. The budgeted overhead is based on the normal level of output. The actual overhead is based on the actual level of output.
- An unfavorable overhead volume variance occurs when the actual level of output is less than the normal level of output. This means that the fixed overhead costs were spread over a smaller number of units, which resulted in a higher per unit overhead cost.
- There are a few reasons why actual production might be less than the normal level of output. For example, the company might have had a machine breakdown or a shortage of materials. The company might also have had a slowdown in sales.
- The overhead volume variance can be corrected by adjusting the budgeted overhead to reflect the actual level of output. The company can also try to improve its production efficiency to reduce the amount of fixed overhead per unit
Q63: UNCTAD compiled 'Transnationality Index’ consists of which of the following three ratios?
(a) Foreign assets/Total assets : Foreign sales/Total sales and Foreign employment/Total employment
(b) Foreign assets/Total assets : Foreign sales/Total output and Foreign employment/Total employment
(c) Foreign assets/Total GDP : Foreign sales/Total GDP and Foreign employment/ Total GDP
(d) Foreign assets/Total output : Foreign sales/Total sales and Foreign employment/ Total GDP
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Foreign assets/Total assets : Foreign sales/Total sales and Foreign employment/Total employment.
The UNCTAD Transnationality Index (TNI) is a composite measure of the foreign activities of transnational corporations (TNCs). It is calculated as the average of three ratios:
- Foreign assets to total assets: This ratio measures the extent to which a TNC's assets are located abroad.
- Foreign sales to total sales: This ratio measures the extent to which a TNC's sales are generated from abroad.
- Foreign employment to total employment: This ratio measures the extent to which a TNC's employment is located abroad.
- The higher the TNI, the more transnational the TNC. A TNI of 100 means that all of a TNC's assets, sales, and employment are located abroad. A TNI of 0 means that none of a TNC's assets, sales, and employment are located abroad.
The TNI is a useful tool for measuring the extent of globalization and the impact of TNCs on the global economy. It is also used by governments and businesses to make decisions about trade and investment policies.
Q64: Which of the following goods (commodities) have positive elasticities?
A. Necessities
B. Substitutes
C. Luxury goods
D. Complementary goods
E. Inferior goods
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) B, C and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and C only.
The correct answer is A, B, and C only.
The demand for luxury goods, substitutes, and necessities are all elastic. This means that a small change in the price of these goods will have a large impact on the quantity demanded.
The demand for complementary goods is inelastic. This means that a small change in the price of a complementary good will have a small impact on the quantity demanded of the other good.
The demand for inferior goods is also inelastic. However, the demand for inferior goods can become elastic if the price of the good becomes very high.
Here are some examples of goods with elastic demand:
- Luxury goods: Jewelry, fur coats, vacations
- Substitutes: Coffee and tea, Coke and Pepsi, Android and iPhone
- Necessities: Food, water, housing
- Here are some examples of goods with inelastic demand:
- Complementary goods: Cars and gasoline, computers and software
- Inferior goods: Ramen noodles, used clothing
Q65: Which one of the following is NOT a justification for preferring ethnocentric approach to staffing?
(a) Hiring host country nationals eliminates language barriers
(b) Perceived lack of qualified host country nationals
(c) United corporate culture can be maintained
(d) Good communication. coordination and control links with headquarters
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Hiring host country nationals eliminates language barriers.
Hiring host country nationals eliminates language barriers. The ethnocentric approach involves staffing foreign subsidiaries with home-country nationals, justified by:
- B: Perceived lack of qualified host-country nationals.
- C: Maintaining a unified corporate culture.
- D: Ensuring effective communication and control with headquarters.
- Option (a) relates to the polycentric approach, not ethnocentric, as hiring locals reduces language barriers.
Other Related Points
- Another justification for preferring the ethnocentric approach to staffing is that it can help to reduce the risk of cultural clashes. When employees from the parent company are sent to work in a foreign subsidiary, they may not be familiar with the local culture or customs. This can lead to misunderstandings and conflict. By hiring host country nationals, the company can reduce the risk of these problems.
- However, the statement Hiring host country nationals eliminates language barriers is not a justification for preferring the ethnocentric approach to staffing. This is because language barriers can still exist even when host country nationals are hired. For example, if the host country language is not the same as the language used by the parent company, there may still be communication problems.
- In addition, the ethnocentric approach to staffing can be expensive and time-consuming. It can be difficult to find qualified employees from the parent company who are willing to relocate to a foreign subsidiary. The company may also have to pay relocation expenses and provide language training.
Q66: Why do companies pursue a retrenchment strategy?
A. Better opportunities in the environment are perceived elsewhere.
B. Its main strategic decisions focus on the conscious use of reversal grand strategies.
C. The environment is seen so threatening that internal strengths are insufficient to meet the challenge.
D. Its easier and comfortable to pursue retrenchment strategy.
E. The firm is not doing well or perceives itself as doing poorly.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) B, D and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, C and E only.
The correct answer is A, C, and E only.
The reasons why companies pursue a retrenchment strategy are:
- Declining sales: When a company's sales are declining, it may need to retrench in order to reduce costs and stay afloat.
- Increased competition: When a company is facing increased competition, it may need to retrench in order to become more efficient.
- Changing market conditions: When the market conditions are changing, a company may need to retrench in order to adapt to the new environment.
- The firm is not doing well or perceives itself as doing poorly: If a company is not doing well, it may need to take action quickly to avoid further losses.
Other Related Points The other options are not correct reasons for pursuing a retrenchment strategy.
- Better opportunities in the environment are perceived elsewhere: This is a reason for pursuing a growth strategy, not a retrenchment strategy.
- Its main strategic decisions focus on the conscious use of reversal grand strategies. This is a description of a particular type of retrenchment strategy, not a reason for pursuing a retrenchment strategy.
- Its easier and comfortable to pursue retrenchment strategy. This is not a reason for pursuing any type of strategy. Companies pursue strategies because they believe they will help them achieve their goals
Q67: Which one of the following is NOT a standard categorization of stress?
(a) Acute stress
(b) Imported stress
(c) Chronic stress
(d) Eustress
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Imported stress.
The statement Imported stress is not a standard categorization of stress.
- Imported stress is a term that is sometimes used to describe stress that is caused by factors outside of a person's control. However, this is not a standard categorization of stress.
- The three standard categorizations of stress are acute stress, episodic acute stress, and chronic stress. These categorizations are based on the duration of the stressor and the frequency of exposure to the stressor.
- Imported stress is not a standard categorization because it does not specify the duration of the stressor or the frequency of exposure to the stressor. It is also not clear what factors would be considered to be "imported" stressors.
- For example, a person might experience stress because of a job loss. This would be considered to be chronic stress because it is a long-term stressor. However, the job loss could be caused by factors that are outside of the person's control, such as a recession or a corporate restructuring.
- In this case, the stress could be considered to be "imported" because it is caused by factors that are outside of the person's control. However, it would still be considered to be chronic stress because it is a long-term stressor.
- Overall, the term imported stress is not a standard categorization of stress. It is a term that is sometimes used to describe stress that is caused by factors outside of a person's control, but it is not clear what factors would be considered to be "imported" stressors
Standard stress categorizations include:
- Acute stress (a): Short-term stress from specific events.
- Chronic stress (c): Long-term stress from ongoing issues.
- Eustress (d): Positive stress that motivates performance.
- Imported stress (b) is not a recognized category, as it lacks specificity in duration or impact.
Q68: Arrange the following steps of organization planning in the proper sequence:
A. Develop of the organization a culture that promotes growth and implement a documented promotion policy.
B. We are committed to achieve financial growth of our organization by fostering growth and creativity among our valued employees.
C. To foster growth and creativity.
D. Provide opportunities for growth of employees.
E. To achieve excellence in human resource management and foster growth and creativity.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) B, C, E, D, A
(b) E, B, A, C, D
(c) E, B, D, C, A
(d) B, E, C, D, A
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is B, E, C, D, A.
The correct sequence of the steps of organization planning is B, E, C, D, A.
Here is a brief explanation of each step:
- Set the organization's goals (B): This includes defining what the organization wants to achieve in terms of financial growth, customer satisfaction, and employee development.
- Foster growth and creativity (E): This is a way to achieve the organization's goals by providing opportunities for employees to grow and develop their skills.
- Provide opportunities for growth of employees (C): This is a specific way to implement the goal of fostering growth and creativity.
- We are committed to achieve financial growth of our organization by fostering growth and creativity among our valued employees (D): This reiterates the organization's goal and explains how it will achieve it.
- Develop of the organization a culture that promotes growth and implement a documented promotion policy (A): This is the last step in the process, which is to create a culture that supports growth and creativity and to implement a promotion policy that reflects this culture.
Q69: Artificial Intelligence has simulation potential of the following kinds of intelligence:
A. Visual-spatial
B. Intrapersonal
C. Interpersonal
D. Creative
E. Logical-mathematical
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and E only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) B, C, D and E only
(d) A and B only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, C and E only.
The statements A, C, and E are correct about the simulation potential of AI.
Here is a brief explanation of each statement:
- A. Visual-spatial intelligence: AI systems can be programmed to perform some tasks that require visual-spatial intelligence, such as recognizing objects and navigating environments. However, they cannot truly understand or create images in the same way that humans do.
- C. Interpersonal intelligence: AI systems can be programmed to perform some tasks that require interpersonal intelligence, such as generating text that is similar to human language. However, they cannot truly understand or interact with people in the same way that humans do.
- E. Logical-mathematical intelligence: AI systems have the potential to simulate logical-mathematical intelligence, which is the ability to reason, solve problems, and think abstractly. AI systems can be programmed to perform these tasks by using algorithms and logic. For example, AI systems can be used to solve complex mathematical problems, play games like chess and Go, and make predictions about the future.
Other Related Points The other statements are not always true. For example, AI systems do not have the potential to simulate creative intelligence. Creative intelligence is the ability to generate new ideas and solve problems in novel ways. While AI systems can be programmed to perform some tasks that require creative intelligence, such as generating text that is similar to human language, they cannot truly generate new ideas in the same way that humans do.
AI systems are still under development, and it is possible that they will eventually be able to simulate all of the types of intelligence mentioned in the question. However, for now, AI systems have the most potential to simulate logical-mathematical intelligence, visual-spatial intelligence, and interpersonal intelligence
Q70: Match List I with List II
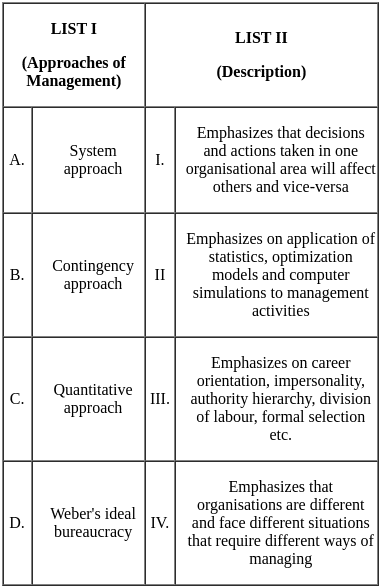
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(b) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III.
Here is the explanation of each of the approaches:
- System approach is a holistic approach that views the organization as a system of interrelated parts. This approach emphasizes that the organization is made up of different components, such as the people, the structure, the processes, and the environment, and that these components are all interconnected. Any change in one component will affect the other components.
- Contingency approach is a situational approach that recognizes that there is no one best way to manage. The best way to manage will vary depending on the specific situation. This approach emphasizes the importance of flexibility and adaptability in management.
- Quantitative approach is an approach that uses quantitative methods, such as statistics, optimization models, and computer simulations, to solve management problems. This approach is often used in areas such as production, finance, and marketing.
- Weber's ideal bureaucracy is a model of organization that emphasizes efficiency, order, and predictability. This model is characterized by a clear hierarchy of authority, a division of labor, and formal rules and procedures.
Q71: Which of the statements are true of innovations?
A. Innovations are a must to survive in business
B. Discontinuous innovations lead to failures
C. Continuous innovations do not disrupt established usage and behaviour patterns
D. Line extensions are discontinuous innovations
E. In discontinuous innovations, there is a change not only in technology but also in behavioural patterns of usage and consumption
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D and E only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) A, C and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, C and E only.
The statements A, C, and E are correct about innovations.
Here is a brief explanation of each statement:
- A. Innovations are a must to survive in business: This is true because innovations can help businesses to create new products and services, improve their existing products and services, and reduce costs. These can help businesses to stay ahead of the competition and survive in the long run.
- C. Continuous innovations do not disrupt established usage and behaviour patterns: This is true because continuous innovations are incremental improvements to existing products and services. They do not change the way that people use or consume the products or services.
- E. In discontinuous innovations, there is a change not only in technology but also in behavioural patterns of usage and consumption: This is true because discontinuous innovations are new technologies that create new markets and disrupt existing markets. They change the way that people use or consume products and services.
The other statements are not always true. For example, discontinuous innovations do not always lead to failures. Some discontinuous innovations can be very successful, such as the iPhone, the personal computer, and the electric car. Line extensions are not discontinuous innovations, but they are still innovations because they are new products that are added to an existing product line.
Q72: Consumer buying behaviour in situations characterized by high involvement but few perceived differences among brands is known as ___________.
(a) Complex buying behaviour
(b) Dissonance reducing buying behaviour
(c) Habitual Buying behaviour
(d) Variety seeking buying behaviour
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Dissonance reducing buying behaviour.
Consumer buying behavior in situations characterized by high involvement but few perceived differences among brands is known as dissonance-reducing buying behavior.
In this type of buying behavior, the consumer is highly involved in the purchase decision because the product is expensive, risky, or important. However, there are few perceived differences between brands, so the consumer is not sure which brand to choose. This can lead to post-purchase dissonance, where the consumer feels uneasy about their decision.
Important Points To reduce dissonance, consumers may engage in a number of activities, such as:
- Seeking out information about the product from other sources, such as reviews or word-of-mouth.
- Comparing prices between brands.
- Reading product specifications.
- Talking to friends or family about their experiences with the product.
- By engaging in these activities, the consumer hopes to confirm their decision and reduce any feelings of uncertainty or doubt.
Q73: The major problems faced by rural entrepreneurs are
A. Rate of interest charged by commercial banks is too high
B. Inability to market their products and services
C. Lack of comprehensive training on required skills
D. Inability to handle cultural issues
E. Difficulty in opening bank accounts due to lack of documents
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) A, D and E only
(c) B and C only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is B and C only.
The correct answer is both B. Inability to market their products and services and C. Lack of comprehensive training on required skills.
The other options are also valid problems faced by rural entrepreneurs, but they are not as common as the two mentioned above.
Here are some additional details about the two problems:
- Inability to market their products and services: Rural entrepreneurs often face challenges in marketing their products and services due to the factors mentioned earlier, such as lack of access to markets, knowledge about marketing, and financial resources.
- Lack of comprehensive training on required skills: Rural entrepreneurs often lack the skills and training necessary to run a successful business. This can include skills in areas such as business management, marketing, and finance.
- These two problems are closely related. If rural entrepreneurs cannot market their products and services effectively, they will not be able to generate enough revenue to sustain their business. And if they do not have the necessary skills, they will not be able to run their business efficiently.
There are many organizations and programs that are working to help rural entrepreneurs overcome these challenges. These organizations provide training, financial assistance, and other resources to help rural entrepreneurs succeed.
Q74: Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of digital media?
(a) Digital media is "pull" media
(b) Mass customization is possible in digital media
(c) Digital media is lean-back media
(d) Digital media is intense media
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Digital media is lean-back media.
- Lean-back media is a term used to describe media that is consumed in a passive and relaxed manner. This type of media typically requires little or no interaction from the user, such as watching television or listening to music.
- Digital media, on the other hand, is a broad term that encompasses any media that is delivered or consumed in a digital format. This includes things like websites, social media, e-books, and streaming videos.
- Digital media can be both lean-back and lean-forward. Lean-forward media is media that requires more interaction from the user, such as playing video games or using social media.
Other Related Points Here are some of the characteristics of digital media:
- Interactive: Digital media can be interactive, meaning that users can interact with it in a variety of ways.
- Personalized: Digital media can be personalized to the individual user's interests and preferences.
- Accessible: Digital media can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Dynamic: Digital media can be updated and changed easily.
- Portable: Digital media can be stored and transported easily.
Q75: Which of the following is a measure of appropriateness of organizational goals and how well these goals are being met?
(a) Organizational transparency
(b) Organizational citizenship
(c) Organizational effectiveness
(d) Organizational efficiency
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Organizational effectiveness.
Organizational effectiveness is a measure of the appropriateness of organizational goals and how well these goals are being met. It is a broad concept that can be measured in a variety of ways, such as:
- Productivity: This is the ratio of outputs to inputs. A more productive organization is one that produces more outputs with the same or fewer inputs.
- Profitability: This is the amount of money an organization makes after expenses are paid. A more profitable organization is one that makes more money.
- Customer satisfaction: This is the degree to which customers are happy with the products or services provided by the organization. A more satisfied customer base is one that is more likely to do business with the organization again.
- Employee satisfaction: This is the degree to which employees are happy with their work environment and their jobs. A more satisfied workforce is one that is more likely to be productive and stay with the organization.
- Innovation: This is the ability of the organization to develop new products or services. A more innovative organization is one that is more likely to stay ahead of the competition.
Organizational effectiveness is important because it helps organizations to achieve their goals and objectives. It can also help organizations to identify areas where they can improve.
Q76: Which one of the following 1s not the view of ethics among the following of views ?
(a) Utilitarian view of ethics
(b) Rights view of ethics
(c) Theory of justice view of ethics
(d) Non-integrative social view
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Non-integrative social view.
The correct answer is Non-integrative social view.
The other views of ethics are:
- Individualist view: This view holds that individuals are responsible for their own actions and that ethics is based on individual rights and responsibilities.
- Consequentialist view: This view holds that the rightness or wrongness of an action is determined by its consequences.
- Deontological view: This view holds that the rightness or wrongness of an action is determined by its inherent moral character, regardless of its consequences.
- Virtue ethics: This view holds that the rightness or wrongness of an action is determined by the character of the person who performs the action.
The non-integrative social view is not a view of ethics because it does not take into account the individual or the consequences of an action. It is based on the idea that there is a single set of ethical standards that applies to everyone, regardless of their individual circumstances or the consequences of their actions.
Other Related Points
- This view is often criticized for being unrealistic and for failing to take into account the complexities of human behavior. It is also criticized for being too rigid and for not allowing for individual moral judgment.
- The other views of ethics are more flexible and allow for individual moral judgment. They also take into account the consequences of an action, which is important in making ethical decisions.
Q77: Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R:
Assertion A : A stereotyped and male-centered vision discourages some women from participating in business activities that could have a consequence on people who interact with women at the community level.
Reason R : Attributions of the society and the different socialisation processes relating to men and women may create obstacles for women due to unequal distribution of assets and services.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
The correct answer is Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
- Assertion A states that a stereotyped and male-centered vision discourages some women from participating in business activities that could have a consequence on people who interact with women at the community level.
- This is because women may feel that they are not welcome in business or that they will not be successful because of their gender. They may also feel that they will be discriminated against or that they will not be taken seriously.
- Reason R states that attributions of the society and the different socialization processes relating to men and women may create obstacles for women due to unequal distribution of assets and services.
- This is because women may be socialized to believe that they are not as capable as men in business or that they should not be involved in business. They may also face discrimination in terms of access to resources, such as loans and training.
Other Related Points
- However, Reason R is not the correct explanation of Assertion A. The reason is that Assertion A is talking about the discouragement of women from participating in business activities, while Reason R is talking about the obstacles that women face in business.
- A better explanation of Assertion A could be that the stereotyped and male-centered vision leads to the attribution of society that women are not as capable as men in business, which in turn creates obstacles for women in business, such as unequal distribution of assets and services.
Q78: Which of the following focus of OD interventions are relevant if the nature of intervention is unstructured?
A. Role negotiation
B. Development of internal facilitators
C. Counselling
D. Work review
E. Team development
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C only
(b) B, C, E only
(c) B, C, D only
(d) A, D, E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is B, C, E only.
Let's thoroughly analyze each option:
B. Development of internal facilitators
- Explanation: Internal facilitators are individuals within the organization who are trained to guide and support change initiatives. In unstructured interventions, where the change process is more fluid and less predefined, having skilled internal facilitators is crucial. These facilitators can adapt strategies in real-time and ensure that the organization remains responsive to emerging needs and challenges.
- Relevance: Their development ensures that there is a knowledgeable and adaptable team capable of managing uncertainties and guiding the organization through unstructured processes. This focus directly supports the flexibility and responsiveness required in unstructured interventions.
C. Counselling
- Explanation: Counselling provides psychological and emotional support to individuals within the organization. Unstructured interventions often involve significant changes and uncertainties that can cause stress and anxiety among employees.
- Relevance: Counselling helps employees cope with these challenges, facilitating personal adjustment and emotional well-being. This focus is pertinent because it addresses the human element of change, ensuring that employees can manage the stress of unstructured interventions, thereby maintaining productivity and morale.
E. Team development
- Explanation: Team development activities aim to enhance the ability of groups to work effectively together. This includes improving communication, collaboration, and understanding within the team.
- Relevance: In unstructured interventions, teams need to be highly adaptable and work cohesively to navigate unpredictable changes. Team development ensures that teams are strong, flexible, and able to support each other through the unstructured process. This focus is essential for maintaining effective teamwork and achieving the desired outcomes in a dynamic environment.
Other Related Points
A. Role negotiation
- Explanation: Role negotiation involves defining and clarifying roles and responsibilities within the organization. This process generally requires some structure and clarity to be effective.
- Relevance: While important, role negotiation is typically more relevant in structured interventions where roles can be clearly delineated and agreed upon. In unstructured interventions, the fluid nature of change might make it challenging to undertake effective role negotiation.
D. Work review
- Explanation: Work review involves the regular assessment and evaluation of work processes and outcomes. This process generally relies on pre-defined criteria and structured methods of evaluation.
- Relevance: Work review is more aligned with structured interventions where there are clear benchmarks and goals to measure against. In unstructured interventions, the lack of predefined goals can make traditional work reviews less applicable.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 2: B, C, E only, because the development of internal facilitators, counselling, and team development are integral components that support the adaptive, flexible, and human-centric approach required in unstructured interventions. They collectively address the need for skilled guidance, individual support, and effective teamwork, which are essential for navigating the complexities of unstructured change processes successfully.
Q79: "A company in the sewing machine business diversifies into kitchenware and household appliances and sells these items through a chain of retail stores to family consumers”
This is an example of
(a) Marketing-related concentric diversification
(b) Technology-related concentric diversification
(c) Marketing and technology-related concentric diversification
(d) Unrelated diversification
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is (a)
- Concentric diversification is a marketing strategy that involves expanding into related products or services. This strategy is often used by companies that want to grow their business without sacrificing their core competencies. By expanding into related products or services, companies can leverage their existing resources and capabilities. This can help them to reduce costs and increase profits.
- In the given scenario, the sewing machine company is using a concentric diversification strategy to expand into kitchenware and household appliances. This is a related product market because they are all products that are used in the home. The company is leveraging its existing expertise in manufacturing and marketing to enter the kitchenware and household appliance market. This will allow the company to reach a wider range of customers and grow its business.
- Technology can play a role in concentric diversification, but it is not the primary factor. In the given scenario, the technology that the sewing machine company uses to manufacture and market its products will be the same for both sewing machines and kitchenware and household appliances. However, the marketing strategy will be different for the two product markets.
- For example, the company may use different marketing channels to reach customers for the two product markets. It may also use different pricing strategies. The company will need to carefully consider the needs of the customers in each product market in order to develop a successful marketing strategy.
Overall, the given scenario is more related to marketing than technology. The company is using a concentric diversification strategy to expand into related product markets. This strategy will allow the company to leverage its existing resources and capabilities to grow its business.
Q80: Contrast to individual stocks, stability of Portfolio Risk (β) dramatically increases with
A. High return portfolios (RP > RF)
B. Larger portfolios (np > 50)
C. Longer investment duration (tp > 26 weeks)
D. Increased trading volume (RP > RM)
E. High premium portfolios (RP > RM)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) A, D and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and C only.
The question asks when portfolio beta (β) — a measure of systematic risk — becomes more stable compared to individual stocks. Let’s evaluate the options in this context:
- A. High return portfolios (RP > RF) – Correct
This means the portfolio earns more than the risk-free rate.
Portfolios that outperform the risk-free rate tend to contain well-performing, less volatile assets, offering more predictable beta. - B. Larger portfolios (np > 50) – Correct
Larger number of stocks diversifies away unsystematic risk, making beta more representative and stable of the market/systematic risk.
As the number of stocks increases, the portfolio beta converges to a stable average. - C. Longer investment duration (tp > 26 weeks) – Correct
Over longer durations, temporary volatility and noise are reduced.
Beta calculated over longer horizons is less sensitive to short-term fluctuations, hence more stable. - D. Increased trading volume (RP > RM) – Incorrect
This suggests higher portfolio return than market, not about trading volume.
High trading volume doesn’t necessarily stabilize beta; in fact, it could signal volatility, making beta less stable. - E. High premium portfolios (RP > RM) – Incorrect
This refers to excess return over market, not beta stability.
A high premium portfolio may be more volatile, especially if driven by high-risk assets — beta could fluctuate more, not stabilize.
Final Answer: (a) A, B and C only
These three factors—high returns over risk-free rate, larger portfolio size, and longer investment duration—are directly linked to increased beta stability.
Therefore, the correct answer is (A), (B), and (C)
Q81: Given below are two statements. one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: IFRS and GAAP are two accounting systems competing for international acceptance.
Reason R: Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) are in convergence with both. the IFRS and the GAAP.
In light of the above statements. choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is not correct
(d) A is not correct but R is correct
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A is correct but R is not correct.
Assertion A is correct because IFRS and GAAP are indeed two accounting systems competing for international acceptance.
- IFRS is the abbreviation for International Financial Reporting Standards, and GAAP is the abbreviation for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. IFRS is a set of global accounting standards that are used by over 150 countries. GAAP is a set of accounting standards that are used in the United States.
- There are a number of reasons why IFRS and GAAP are competing for international acceptance. One reason is that the increasing globalization of business makes it more important for companies to have their financial statements prepared in a way that is understandable and comparable to investors and creditors around the world.
- Another reason is that IFRS are seen as being more principles-based than GAAP, which means that they provide more flexibility for companies to apply the standards in different situations. This can be seen as an advantage by some companies, while others prefer the more detailed guidance of GAAP.
Reason R is incorrect because Ind AS convergence with IFRS does not mean that it is not a competitor to GAAP. Ind AS is still converging with GAAP, which means that it is still a competitor to both systems.
- Ind AS is a set of accounting standards that are used in India. They are currently converging with both IFRS and GAAP. This means that Ind AS are becoming more similar to IFRS over time. However, Ind AS are not yet fully converged with IFRS or GAAP. This means that there are still some differences between Ind AS and the other two systems.
- Even if Ind AS fully converges with IFRS, it will still be a competitor to GAAP because it will still be a different set of accounting standards. For example, Ind AS may have different rules for how to account for certain transactions than GAAP. This means that companies that use Ind AS will have different financial statements than companies that use GAAP.
In conclusion, Assertion A is correct because IFRS and GAAP are indeed two accounting systems competing for international acceptance. Reason R is incorrect because Ind AS convergence with IFRS does not mean that it is not a competitor to GAAP.
Hence, the correct answer is the correct answer is A is correct but R is not correct.
Q82: If the Net Present Value (NPV) of an investment proposal is positive, what conclusions can be drawn?
A. The investment generated present value of cashflows exceed cost of investment
B. The discount rate used is less than the investments estimated return
C. The discount rate used equals the minimum return required by the investors
D. The investment generated present value of cashflows equals the cost of investment
E. The investment's Internal Rate of Return (IRR) exceeds the Cost of Capital
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and E only.
A, B, and E are the correct conclusions that can be drawn from a positive NPV.
Option A: The investment generated present value of cashflows exceed cost of investment
- This is the most basic conclusion that can be drawn from a positive NPV. It simply means that the investment is expected to generate a profit.
Option B: The discount rate used is less than the investments estimated return
- This conclusion is also correct. The discount rate is the rate of return that is used to discount the future cash flows of the investment. If the NPV is positive, it means that the present value of the future cash flows exceeds the initial investment cost. This can only happen if the discount rate is less than the investment's estimated return.
Option E: The investment's Internal Rate of Return (IRR) exceeds the Cost of Capital
- The IRR is the discount rate that makes the NPV of an investment equal to zero. If the NPV is positive, then the IRR must be greater than the cost of capital. The cost of capital is the minimum return that a company must earn on its investments in order to satisfy its investors.
Therefore, options A, B, and E are the only correct conclusions that can be drawn from a positive NPV.
Here are some other conclusions that can be drawn from a positive NPV, but they are not as certain as the three conclusions mentioned above:
- The investment is less risky than other investments with similar returns.
- The investment is expected to generate a higher return than other investments with similar risk.
- The investment is a good use of the company's resources.
- Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to invest in an opportunity with a positive NPV will depend on a number of factors, including the company's financial situation, its risk tolerance, and its investment objectives
Q83: Gantt chart is applicable to:
(a) Time study
(b) Production scheduling
(c) Sales Forecasting
(d) Motion Study
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Production scheduling.
Gantt charts are a popular tool for production scheduling. They can be used to visualize the production process, identify potential scheduling conflicts, and track the progress of production.
Here are the steps on how to use a Gantt chart for production scheduling:
- Identify the tasks that need to be completed in order to produce the product.
- Estimate the time required to complete each task.
- Create a Gantt chart that shows the start and end dates of each task.
- Identify any potential scheduling conflicts.
- Monitor the progress of production and make adjustments to the Gantt chart as needed.
- Gantt charts can be a valuable tool for production scheduling, but they are not a perfect solution. They can be difficult to create and maintain, and they can only be as accurate as the information that is entered into them.
Other Related Points
Here are some other tools that can be used for production scheduling:
- Critical path method (CPM): CPM is a more complex tool than Gantt charts, but it can be used to identify the critical path of a project, which is the sequence of tasks that must be completed on time in order to avoid delays.
- Scheduling software: There are a number of scheduling software programs available that can help to automate the scheduling process
Q84: Which of the following statements are true about line balancing?
A. The total amount of work on a line is divided into different tasks
B. Line balancing mainly ensures that each work station gets approximately equal amount of time
C. Cycle time is determined by the minimum time required at any workstation
D. Line balancing is not useful for the process industry
E. Tasks are assigned to workstations that allow the work to be performed in a feasible sequence
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, D and E only
(b) A and E only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A and E only.
Here are the explanations for each of the statements:
- Statement A: The total amount of work on a line is divided into different tasks. This is true because line balancing is a process of assigning tasks to workstations in a way that minimizes idle time and maximizes efficiency.
- Statement E: Tasks are assigned to workstations that allow the work to be performed in a feasible sequence. This is also true because the tasks must be assigned in a way that the work can be completed in a logical and efficient manner.
- Statement B is not true because line balancing does not necessarily ensure that each workstation gets an equal amount of time. The goal of line balancing is to minimize idle time, and this may mean that some workstations have more work than others.
- Statement C: Cycle time is determined by the minimum time required at any workstation. This is also not true because the cycle time is the amount of time it takes to complete one unit of product. The minimum time required at any workstation is the bottleneck of the line, and the cycle time must be greater than or equal to this time.
- Statement D is not true because line balancing can be used in the process industry. The process industry is a type of manufacturing where products are made by a continuous process. Line balancing can be used to optimize the flow of materials and products through the process.
Hence, the correct answer is A and E.
Q85: Dimension reduction methods have the goal of using the correlation structure among the predictor variables to accomplish which of the following:
A. To reduce the number of predictor components
B. To help ensure that these components are dependent
C. To provide a framework for interpretability of the results
D. To help ensure that these components are independent
E. To increase the number of predictor components
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D and E only
(b) A, C and D only
(c) A, B, C and E only
(d) B, C, D and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, C and D only,
- Option A: Dimension reduction methods are used to reduce the number of predictor components. This is done by identifying the underlying patterns in the data and then representing the data in a lower-dimensional space.
- Option C: Dimension reduction methods can provide a framework for interpretability of the results. This is because it can help to simplify the data and make it easier to understand the relationships between the variables.
- Option D: Dimension reduction methods can help to ensure that these components are independent. This is because the goal of dimension reduction is to identify the underlying patterns in the data, and independent components do not share any common patterns.
- Option B is incorrect because dimension reduction methods do not necessarily ensure that the components are dependent. In fact, the goal of dimension reduction is to identify the underlying patterns in the data, and independent components do not share any common patterns.
- Option E is incorrect because dimension reduction methods are used to reduce the number of predictor components, not increase them
Q86: "We don't have a marketing department: we have a customer department.”
Herb Kelleher's statement given above refers to which one of the following concepts?
(a) Social Responsibility Marketing Concept
(b) Internal Marketing Concept
(c) Marketing Concept
(d) Customer Relationship Management Concept
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Marketing Concept.
- Herb Kelleher's statement refers to the outside-in perspective in marketing. The outside-in perspective is a way of thinking about marketing that starts with the customer and then works backwards to develop products and services that meet their needs.
- In contrast, the traditional inside-out perspective starts with the company and then tries to sell its products and services to customers. The outside-in perspective is more customer-centric and is becoming increasingly popular as companies realize that they need to focus on meeting the needs of their customers in order to be successful.
- Kelleher's statement reflects his belief that the customer is the most important part of any business. He understood that by putting the customer first, Southwest Airlines could create a loyal and satisfied customer base that would be more likely to fly with the airline again.
Other Related Points The outside-in perspective is based on the following principles:
- The customer is the focus of all marketing activities.
- The customer's needs and wants are the starting point for developing products and services.
- The customer's experience is the most important measure of success.
- The company must be responsive to the customer's needs and wants.
- The outside-in perspective is a powerful way to think about marketing. It can help companies to create products and services that meet the needs of their customers, build strong relationships with their customers, and achieve their marketing goals.
Q87: Which of the following are included in the work place diversity?
A. Ethnicity
B. Career experience
C. Gender
D. Geographic experiences
E. Sexual orientation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C only
(b) A, C, E only
(c) B, D, E only
(d) A, B, C, D and E
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C, D and E.
The correct answer is A, C and E.
- A. Ethnicity: Workplace diversity includes individuals from different ethnic backgrounds. This involves people of various races, cultures, and nationalities contributing to a rich and varied work environment.
- B. Career Experience: Diversity in career experience involves individuals with different levels of expertise, skills, and backgrounds. This could include individuals who are new to the workforce as well as those with extensive experience in their field.
- C. Gender: Gender diversity refers to the inclusion of people of all genders. This recognizes and values the unique perspectives and contributions that individuals of different genders bring to the workplace.
- D. Geographic Experiences: This aspect of diversity takes into account individuals with different geographic experiences. It could involve people from various regions or countries, each bringing their own cultural perspectives and global insights.
- E. Sexual Orientation: Workplace diversity also encompasses individuals of different sexual orientations. This includes people who identify as heterosexual, homosexual, bisexual, or any other sexual orientation.
In summary, workplace diversity is a comprehensive concept that goes beyond traditional notions of diversity, such as ethnicity and gender, to include a broad range of factors such as career experience, geographic experiences, and sexual orientation. Embracing diversity in all its forms can lead to a more inclusive and innovative work environment.
Q88: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II.
Here's the explanation for each match:
- A. Operating Profit: Operating Profit is calculated by subtracting Total Variable Costs and Fixed Costs from Sales Revenue. Therefore, it matches (Sales × P/V ratio) - Fixed Cost.
- B. Profit-Volume Ratio: Profit-Volume Ratio is calculated by dividing Contribution Margin by Sales Revenue. This can be rewritten as (Unit sale price - Variable costs per unit)/Unit sale price. Therefore, it matches IV. (Unit sale price - Variable costs per unit)/Unit sale price.
- C. Margin of safety: Margin of safety is calculated by subtracting Breakeven Sales Volume from Actual Sales Volume. Therefore, it matches I. Actual sales volume - Breakeven sales volume.
- D. Contribution margin: Contribution Margin is calculated by subtracting Variable Costs from Sales Revenue. Therefore, it matches II. Sales Revenue - Total variable costs.
Q89: According to the HRD score card developed by TVRLS India. HRD Systems Maturity Score includes:
A. HR Information System
B. Potential Appraisal and Development
C. Job-rotation
D. Performance Management Systems
E. Feedback and Coaching Mechanisms
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D, E only
(b) A, D only
(c) B, C, E only
(d) A, B, C, D and E
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C, D and E
The HRD Systems Maturity Score is a comprehensive tool that assesses the maturity level of all aspects of an organization's HR systems. It is not just limited to performance management systems. The other dimensions that are included in the scorecard are:
- HR planning and development
- Training and development
- Compensation and benefits
- Recruitment and selection
- Employee relations
- Health and safety
The HRD Systems Maturity Score is a valuable tool for organizations that want to improve their HR practices and ensure that they are aligned with their business goals. It can help organizations identify areas where their HR systems need to be strengthened and make improvements that will have a positive impact on their bottom line
Q90: Which of the following statements explains the Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC) concept?
A. IMC is the specific blend of promotion tools to communicate customer value and build customer relationships
B. IMC calls for recognising only those touch points where the customer physically encounters the company and its brands
C. IMC's goal is to deliver a consistent and clear massage about the organisation and its products
D. IMC ties together all of the company's messages and images
E. IMC calls for integration and coordination of the company's many communication channels
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) A, B and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) A, B and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is C, D and E only.
Key Points
- Statement C: IMC's goal is to deliver a consistent and clear message about the organization and its products. This means that all of the company's communication channels, such as advertising, public relations, social media, and direct marketing, should be used to deliver the same message. The goal is to create a unified customer experience so that the customer sees and hears the same message no matter how they interact with the company.
- Statement D: IMC ties together all of the company's messages and images. This means that all of the company's communication materials, such as its website, brochures, and advertising, should use the same branding and messaging. The goal is to create a consistent brand identity that will be familiar and memorable to customers.
- Statement E: IMC calls for integration and coordination of the company's many communication channels. This means that the company's communication efforts should be planned and executed in a coordinated way. The goal is to ensure that all of the company's communication channels are working together to achieve the desired outcome.
In addition to statements C, D, and E, there are other key elements of IMC, such as:
- Audience analysis: IMC should be based on a clear understanding of the target audience. This includes understanding their needs, wants, and interests.
- Measurability: IMC should be measurable so that the company can track the results of its marketing efforts.
- Flexibility: IMC should be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the market or the target audience.
IMC is a complex and challenging marketing strategy, but it can be very effective if it is done correctly. By delivering a consistent and clear message through a variety of channels, IMC can help businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers and achieve their marketing goals.
Hence, the correct answer is C, D and E only.
Q91: From the viewpoint of stockholder. which of the following relationships is of the least significance?
(a) The return on assets is consistently of higher than the industry average
(b) The return on equity has increased in each of the past five years
(c) Net income is greater than the amount of working capital
(d) The return on assets is greater than the rate of interest being paid to the lenders
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Net income is greater than the amount of working capital.
The relationship of least significance to a stockholder is net income is greater than the amount of working capital.
Net income is the profit a company makes after all its expenses have been deducted. Working capital is the difference between a company's current assets and its current liabilities. A positive working capital means that a company has enough cash to pay its short-term debts.
From a stockholder's perspective, the most important relationships are those that affect the company's profitability and the value of its stock. These include:
- Return on assets (ROA): This measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate profits.
- Return on equity (ROE): This measures how much profit a company generates for its shareholders.
- Debt-to-equity ratio (D/E ratio): This measures the amount of debt a company has relative to its equity.
- Dividend yield: This measures the amount of dividend a company pays out to its shareholders each year.
The relationship between net income and working capital is less significant to stockholders because it does not directly affect the company's profitability or the value of its stock. However, it can be an indicator of a company's financial health. A company with a negative working capital may be struggling to meet its short-term obligations, which could put its long-term viability at risk.
Therefore, the answer to the question is (c)
Q92: In order to shorten its operating cycle, a manufacturing company focuses on which of the following decisions ?
A. Reducing operating expenses
B. Enhanced coordination of firm activities
C. Manufacturing automation
D. Longer production schedule
E. Tightening credit policy
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) B and D only
(d) B, C and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is B, C and E only.
The following decisions can help a manufacturing company shorten its operating cycle:
- Enhanced coordination of firm activities: This can help to reduce the time it takes to move materials through the production process, get products to customers, and collect payments from customers.
- Manufacturing automation: This can help to improve efficiency, which can shorten the DSO and DPO.
- Tightening credit policy: This can help to shorten the DSO.
- The other options, reducing operating expenses and a longer production schedule, are not as effective in shortening the operating cycle. Reducing operating expenses can help to improve the company's profitability, but it does not directly shorten the operating cycle. A longer production schedule can help to ensure that the company has enough inventory to meet demand, but it will also increase the amount of money tied up in inventory.
Other Related Points
Here are some additional ways to shorten the operating cycle:
- Reduce the amount of inventory: This can be done by improving forecasting accuracy, managing demand, and using just-in-time inventory methods.
- Improve the collection process: This can be done by automating the billing process, sending out reminders, and following up with customers who are late on payments.
Negotiate better payment terms with suppliers: This can help to shorten the DPO.
To shorten the operating cycle (time from inventory purchase to cash collection):
- B: Enhanced coordination reduces delays in production and delivery.
- C: Manufacturing automation speeds up production, reducing Days Sales Outstanding (DSO).
- E: Tightening credit policy accelerates cash collection, shortening DSO.
- A: Reducing operating expenses improves profitability, not cycle time.
- D: Longer production schedules increase cycle time.
Q93: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: If there are differences in consumers’ responses, brand-name. product is essentially a commodity and competition will probably be based on price.
Statement II: Brand equity is reflected in perceptions, performance and behaviour related to all aspects of the marketing of a brand.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
The correct answer is Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
- Statement I is incorrect: If there are differences in consumer responses, it implies that the brand-name product is not simply a commodity. Consumers perceive a difference based on factors beyond just price, which is the essence of brand equity. Therefore, competition might not solely focus on price.
- Statement II is correct: This statement accurately defines brand equity by encompassing the various perceptions, performance aspects, and behavioral responses related to all marketing elements of the brand.
Hence, "Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct" is the most appropriate answer in this context.
Q94: Which one of the following is not an internal force for organizational change?
(a) Managerial Behaviour
(b) Change in leadership
(c) Workforce Diversity
(d) Change in Employee and customer expectations
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Change in Employee and customer expectations.
Change in employee and customer expectations is an internal force for organizational change.
- Employees and customers are constantly changing their expectations of what they want from an organization.
- For example, employees may expect more flexibility and opportunities for development, while customers may expect more personalized and convenient service.
- Organizations that fail to meet the changing expectations of their employees and customers will be at a competitive disadvantage.
Other Related Points
Here are some specific examples of how change in employee and customer expectations can lead to organizational change:
- Employees may expect more flexibility and opportunities for development. This could lead to organizations offering more telecommuting options, flexible work hours, or tuition reimbursement programs.
- Customers may expect more personalized and convenient service. This could lead to organizations investing in customer relationship management (CRM) software, or creating self-service portals for customers.
- Employees may expect more transparency and communication from management. This could lead to organizations creating more open and transparent communication channels, or holding regular town hall meetings.
- Customers may expect more sustainable products and services. This could lead to organizations investing in sustainable practices, or developing new products and services that are more environmentally friendly.
- Organizations that are able to adapt to the changing expectations of their employees and customers will be more successful in the long run. They will be able to attract and retain top talent, and they will be able to build relationships with customers that are based on trust and loyalty.
Q95: Lowering of costs that a firm often experiences when it produces two or more products together than each alone is known as ________.
(a) Economies of scale
(b) Economies of Scope
(c) Economies of Specialisation
(d) Technical Efficiency
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Economies of Scope .
That is known as Economies of Scope.
- Economies of scope occur when a firm can produce two or more products at a lower cost than if it produced each product separately. This can happen when there are shared resources or inputs between the products, or when the production of one product makes it easier to produce another product.
- For example, a car manufacturer might be able to produce cars and trucks at a lower cost than if it produced each product separately. This is because the car manufacturer can share some of the same resources, such as assembly lines and machinery, between the two products.
Economies of scope can be a significant source of competitive advantage for firms. By producing a wider variety of products, firms can lower their costs and become more profitable.
Other Related Points
Here are some examples of economies of scope:
- A restaurant that serves both breakfast and lunch can share some of the same kitchen equipment and staff.
- A clothing manufacturer that produces both men's and women's clothing can share some of the same fabric and sewing machines.
- A software company that develops both operating systems and applications can share some of the same programming code.
- Economies of scope can be contrasted with economies of scale. Economies of scale occur when a firm can produce a larger quantity of a product at a lower cost per unit. This can happen when the firm can spread its fixed costs over a larger number of units.
Economies of scope and economies of scale can sometimes work together to give firms a significant cost advantage. For example, a car manufacturer that produces a large number of different models of cars can benefit from both economies of scope and economies of scale
Q96: The major components of Nicosia Model of consumer decision-making are:
A. The consumer's attitude based on firm's message exposure
B. Perceptual and learning constructs
C. Feedback in the form of purchase experience
D. Extensive problem solving by consumer
E. Consumer's product search and evaluation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) B, D and E only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, C and E only.
The Nicosia Model is a model of consumer decision-making that is based on the following assumptions:
- Consumers are rational decision-makers who make choices that are in their best interests.
- Consumers have limited time and resources, so they will only engage in extensive problem solving for high-involvement purchases.
- Consumers are influenced by the firm's marketing messages, but they also have their own unique set of needs, wants, and preferences.
- The Nicosia Model is a simplified model of consumer decision-making. It does not take into account all of the factors that can influence consumer decision-making, such as the consumer's personality, demographics, social and cultural environment, past experiences, financial resources, and perceived risk of making a purchase.
The Nicosia Model is also a static model, which means that it does not take into account the dynamic nature of consumer decision-making. Consumers may change their minds about a purchase decision over time, or they may be influenced by new information that they receive.
The Nicosia Model is a useful tool for understanding consumer decision-making, but it is important to keep its limitations in mind. The model is not a perfect representation of how consumers make decisions, but it can be a helpful starting point for understanding the factors that influence consumer behavior.
The Nicosia Model includes:
- A: Consumer attitude based on firm’s message exposure (Field 1: Firm’s attributes and consumer attributes).
- C: Feedback from purchase experience (Field 4: Feedback).
- E: Consumer’s product search and evaluation (Field 2: Search and evaluation).
- B: Perceptual and learning constructs are not a distinct component.
- D: Extensive problem solving is not a core part of the model.
Other Related Points
Here are some of the other models of consumer decision-making that are more comprehensive than the Nicosia Model:
- The Howard-Sheth Model
- The Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model
- The Consumer Decision Journey Model
These models take into account a wider range of factors that can influence consumer decision-making, such as the consumer's personality, demographics, social and cultural environment, past experiences, financial resources, and perceived risk of making a purchase.
The Consumer Decision Journey Model is a newer model of consumer decision-making that is based on the idea that consumers go through a series of stages before making a purchase. These stages include:
- Awareness
- Consideration
- Purchase
- Post-purchase
The Consumer Decision Journey Model is a useful tool for understanding how consumers make decisions over time. It can be used by marketers to develop more effective marketing strategies that target consumers at different stages of the decision-making process.
Q97: Which of the following prevent the majority of managers from effective implementation and sustainability?
A. Hollow talk
B. Debilitating fear
C. Complex measurement systems
D. Mindless reliance
E. Constructive internal competition
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C only
(b) A, B, D only
(c) A, B, C, D only
(d) C, D, E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, D only.
The other options, C. Complex measurement systems and E. Constructive internal competition, are not as likely to prevent managers from effective implementation and sustainability.
- Complex measurement systems can be a challenge to implement and manage, but they can be helpful in tracking the progress of an initiative and identifying areas where improvement is needed. Constructive internal competition can be a motivating force, but it can also lead to conflict and resentment if it is not managed effectively.
- Debilitating fear, hollow talk, and mindless reliance are all more likely to prevent managers from effective implementation and sustainability.
- Debilitating fear can paralyze managers and prevent them from taking action.
- Hollow talk can create a sense of false progress and lead to complacency.
- Mindless reliance on the status quo can prevent managers from exploring new ideas and making necessary changes.
- If managers want to be successful in implementing and sustaining new initiatives, they need to be aware of these barriers and take steps to overcome them.
Q98: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: To exist and be successful in a competitive world a business has to be ethical.
Statement II: An ethical organisation can be recognized on the basis of its corporate excellence and not on its relations with the stakeholders.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Statement I: To exist and be successful in a competitive world a business has to be ethical.
Correct
Ethics in business build trust, reputation, and long-term sustainability. Ethical behavior fosters customer loyalty, employee satisfaction, and stakeholder confidence. In today’s transparent and competitive environment, unethical practices can quickly damage a company’s brand and lead to legal or financial troubles.
Statement II: An ethical organisation can be recognized on the basis of its corporate excellence and not on its relations with the stakeholders.
Incorrect
Ethical organizations are recognized both for their corporate excellence and their strong, fair, and transparent relationships with stakeholders—including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and shareholders. Stakeholder relationships are a core component of ethical business practices, and ignoring them contradicts the principles of corporate ethics and social responsibility.
Q99: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(c) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
Here is an explanation of each of the terms:
- Implicit Costs: These are the costs of inputs that are owned and used by the firm, but are not directly paid for. For example, the cost of using the firm's own capital is an implicit cost.
- Marginal Cost: This is the change in the total cost per unit change in output. For example, if the total cost of producing 10 units is $100, and the total cost of producing 11 units is $105, then the marginal cost of producing the 11th unit is $5.
- Incremental Cost: This is the total increase in costs resulting from the implementation of a particular managerial decision. For example, if a firm decides to hire an additional worker, the incremental cost of that decision would be the wage paid to the worker plus any other costs associated with the hiring, such as the cost of training the worker.
- Sunk Cost: These are the costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered. For example, the cost of purchasing a machine is a sunk cost if the machine is no longer used by the firm.
Q100: Arrange the following statements corresponding to different levels of Brand Dynamics
Pyramid in a sequence starting with the base of the pyramid:
a. Belief that the brand delivers acceptable product performance and is on the consumer's short-list
b. Rational and emotional attachments to the brand to the exclusion of most other brands
c. Active familiarity with the brand based on post trial, saliency or knowledge of the brand promise
d. Relevance of brand to consumer's needs in the right price range or in the consideration set
e. Belief that the brand has an emotional or rational advantage over other brands in the category
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) c, d, a, e, b
(b) d, c, a, e, b
(c) d, c, a, b, e
(d) c, d, a, b, e
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is c, d, a, e, b.
The sequence c, d, a, e, b is the accurate order for the Brand Dynamics Pyramid. Here's the revised explanation:
1. c. Active familiarity with the brand based on post trial, saliency or knowledge of the brand promise: This forms the base of the pyramid. Consumers have encountered the brand through experience, advertising, or word-of-mouth, creating an initial level of recognition and awareness.
2. d. Relevance of brand to consumer's needs in the right price range or in the consideration set: Following familiarity, consumers assess the brand's relevance to their needs and budget. It enters their consideration set for potential purchase if it falls within their acceptable price range and addresses their basic requirements.
3. a. Belief that the brand delivers acceptable product performance and is on the consumer's short-list: After considering relevance, consumers evaluate the brand's perceived performance based on reviews, recommendations, or personal experience. Those meeting basic performance expectations move onto the shortlist for further evaluation.
4. e. Belief that the brand has an emotional or rational advantage over other brands in the category: Consumers who shortlisted the brand may perceive it to have a distinct edge over competitors. This advantage could be based on emotional connection, unique features, or superior value proposition.
5. b. Rational and emotional attachments to the brand to the exclusion of most other brands: At the peak of the pyramid, consumers develop strong emotional and rational bonds with the brand. They become loyal advocates, often preferring it over most other options in the category and actively recommending it to others.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Management 12th Mar 2023 Shift 2 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and its significance in the field of management? |  |
| 2. What subjects are covered in Paper 2 of the UGC NET exam for management? |  |
| 3. How can candidates prepare effectively for the management section of the UGC NET exam? |  |
| 4. What is the marking scheme for Paper 2 in the UGC NET exam? |  |
| 5. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET exam for management? |  |















