UGC NET Paper 2: Management 13th Dec 2023 Shift 1 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Match List - I with List - II.
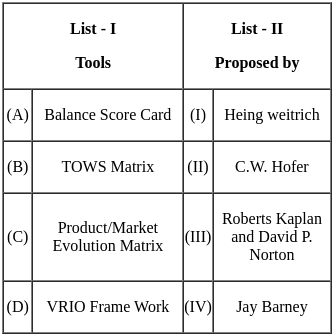
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
(b) (A) - (III), (B) - (I), (C) - (II), (D) - (IV)
(c) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (IV), (D) - (I)
(d) (A) - (IV), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (I)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A) - (III), (B) - (I), (C) - (II), (D) - (IV).
Key Points
- (A) Balance Score Card - (III) Roberts Kaplan and David P. Norton: The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management framework introduced by Kaplan and Norton. It provides a comprehensive set of performance indicators beyond traditional financial measures.
- (B) TOWS Matrix - (I) Heing Weitrich: The TOWS Matrix is a strategic planning tool used for analyzing the external threats, opportunities, internal weaknesses, and strengths of an organization. Although the exact origin of TOWS is not consistently attributed, it has been widely used in strategic management. If Heing Weitrich is associated with it, it might be a specific reference in certain contexts.
- (C) Product/Market Evolution Matrix - (II) C.W. Hofer: C.W. Hofer is associated with the Product/Market Evolution Matrix. This matrix is used to analyze the strategic options for a business in terms of its products and markets.
- (D) VRIO Framework - (IV) Jay Barney: The VRIO Framework, which stands for Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization, is a strategic management tool developed by Jay Barney. It is used to evaluate the competitive advantage of an organization's resources and capabilities.
Q2: Which of the following consists of broad model of HRM/HRD ?
(A) Hard variant of HRM (Matching Model of HRM)
(B) Soft variant of HRM (Harvard Model HRM)
(C) 5P Model of HRM (Model of strategic HRM)
(D) Business Strategic Model of HRM (Business School Model)
(a) (A) and (B) only
(b) (B) and (C) only
(c) (A), (B) and (C) only
(d) (B), (C) and (D) only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (C) only.
- A) Hard variant of HRM (Matching Model of HRM): This model aligns individual skills and abilities with job requirements. It focuses on objective factors like qualifications and experience, making it a "hard" variant. This aligns with the concept of a broad model encompassing various aspects of HRM.
- B) Soft variant of HRM (Harvard Model HRM): This model emphasizes the strategic role of HR in aligning HR practices with business goals. It considers employee motivation, commitment, and development, making it a "soft" variant. Again, it contributes to a broad model by addressing human-centric aspects of HRM.
- C) 5P Model of HRM (Model of strategic HRM): This model focuses on five key drivers of an organization: Purpose, Process, People, Performance, and Philosophy. It considers both hard and soft elements, making it a comprehensive framework for guiding HRM practices. This also fits the notion of a broad model.
- D) Business Strategic Model of HRM (Business School Model): While this model links HR practices to overall business strategy, it might be less encompassing than the previous options. Its focus on the business perspective alone might not fully capture the diverse elements of a broad HRM/HRD model.
Therefore the combination of (A) Hard variant of HRM, (B) Soft variant of HRM, and (C) 5P Model of HRM best represents a broad model of HRM/HRD, as they consider both hard and soft aspects, strategic alignment, and diverse HRM/HRD functions.
Q3: For making a single-channel, single-phase queuing models, which of the following assumption are involved -
(A) Every arrival waits to be served regardless of the length of the time.
(B) Arrival are independent of preceding arrivals, but the average number of arrivals does not change over time.
(C) Arrival come from a finite or very small population on LIFO basis
(D) Service times follow the negative exponential distribution or are constant.
(E) The average service rate is greater than the average arrival rate.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (A), (B), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (B), (C), (D) and (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B).(D) and (E) only.
- (A) Every arrival waits to be served regardless of the length of the time. - This is a common assumption in queuing theory where arrivals wait in line until they can be served. This assumption is generally true.
- (B) Arrivals are independent of preceding arrivals, but the average number of arrivals does not change over time. - This is a typical assumption for many queuing models. It implies a stationary arrival process with independence between arrivals.
- (C) Arrivals come from a finite or very small population on a Last In, First Out (LIFO) basis. - This assumption is not commonly associated with single-channel, single-phase queuing models. Queuing models typically assume a First In, First Out (FIFO) order.
- (D) Service times follow the negative exponential distribution or are constant. - This is a common assumption in queuing theory. The negative exponential distribution is often used to model service times.
- (E) The average service rate is greater than the average arrival rate. - This assumption is known as the stability condition, where the system is assumed to be stable if the service rate is greater than the arrival rate.
So, the correct answer is: (A), (B).(D) and (E) only.
Q4: As per Ries and Trout, which one of the following is NOT a standerd criteria for successful positioning?
(a) Competitiveness
(b) Consistency
(c) Credibility
(d) Commitment
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is commitment.
As per Ries and Trout, the standard criteria for successful positioning, often referred to as the "Four Cs of Positioning," are:
- Competitiveness: The product or brand must be positioned to be competitive within the market. It should offer something that differentiates it from competitors.
- Consistency: The positioning must be consistent across various elements of the marketing mix (product, price, promotion, place) and over time. Consistency helps in building a clear and stable image in the minds of consumers.
- Credibility: The positioning must be believable and align with the actual characteristics of the product or brand. Consumers are more likely to accept and remember a position that they find credible.
- Clarity (or clarity of communication): This is another C often associated with the Four Cs. The positioning should be clear and easily understandable. Complex or confusing positioning messages may not effectively resonate with consumers.
The term "Commitment" is not traditionally included in the Four Cs of Positioning as outlined by Ries and Trout. However, commitment to the chosen positioning strategy is implied in the sense that once a position is established, consistent and long-term efforts are needed to reinforce and maintain that position in the market.
Q5: Performance appraisal too often degenerates into a dishonest annual rituals," who stated this?
(a) Armstrong and Murlis
(b) Newton and Findlay
(c) Barlow
(d) Grint
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Armstrong and Murlis.
The quote "Performance appraisal too often degenerates into a dishonest annual ritual" reflects a critical perspective on the traditional practice of performance appraisal. Michael Armstrong and Angela Murlis, in their book "Performance Management: Key Strategies and Practical Guidelines," address the challenges and shortcomings of performance appraisal systems.
In the context of the quote, Armstrong and Murlis likely emphasize that performance appraisal processes are sometimes perceived as mere formalities conducted annually without genuine feedback or meaningful evaluation. The term "dishonest" may suggest that appraisals are not always conducted objectively, and the ritualistic nature of the process may undermine its effectiveness in driving employee development and organizational performance.
Their book, "Performance Management," is known for providing practical insights into designing and implementing effective performance management systems that go beyond routine appraisals, aiming to enhance employee engagement, development, and overall organizational success.
Q6: If Current Ratio =2.5, Liquid Ratio = 1.5, Working Capital = Rs. 90,000. What is the value of Inventory?
(a) Rs. 60,000
(b) Rs. 90,000
(c) Rs. 1,50,000
(d) Rs. 2,10,000
Ans: a
Sol: To find the value of the inventory, we need to use the given financial ratios and the value of the working capital. Here's how you can calculate it: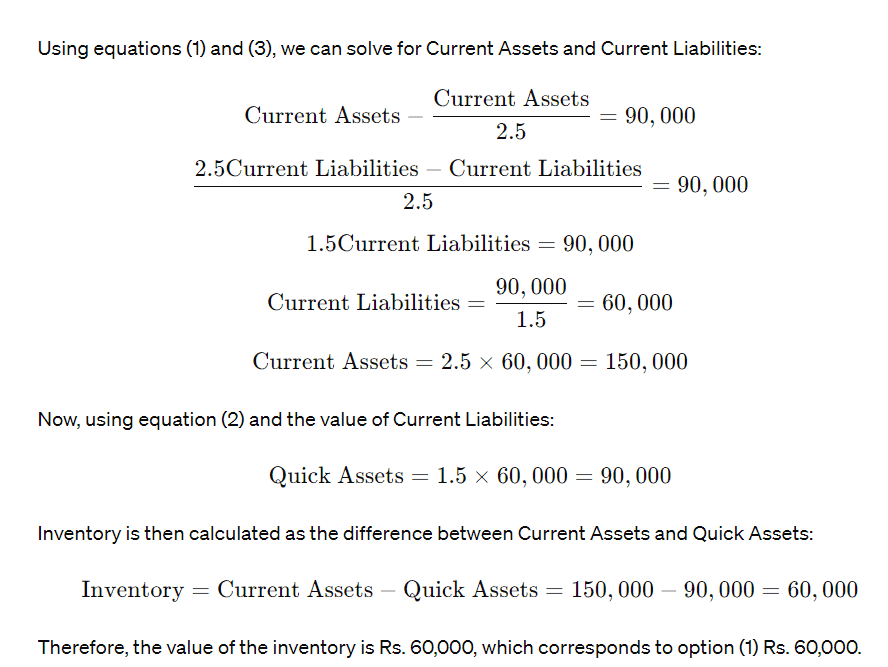
Q7: Arrange the Project Life Cycle Phases in proper order :
(A) Concept Phase
(B) Planning and Organising Phase
(C) Definition Phase
(D) Implementation Phase
(E) Project Clean-up Phase
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C), (B), (D), (E) Only
(b) (A), (B), (C), (D), (E) Only
(c) (C), (A), (B), (D), (E) Only
(d) (A), (D), (C), (B), (E) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The proper order of the Project Life Cycle Phases is typically as follows:
- Concept Phase (A): In this phase, the initial idea for the project is developed and assessed for its feasibility.
- Definition Phase (C): Detailed planning and analysis are done in this phase to define the project scope, objectives, deliverables, and requirements.
- Planning and Organising Phase (B): In this phase, the project plan is developed, and resources are organized to execute the project successfully.
- Implementation Phase (D): This is the phase where the actual work of the project is carried out.
- Project Clean-up Phase (E): Also known as the Closing Phase, this is where the project is finalized, and any remaining activities are completed. Lessons learned are documented, and the project is officially closed.
So, the correct order is: A - C - B - D - E
Q8: Arrange the following steps of the Budgeting process in the proper sequence:
(A) Obtaining estimates
(B) Communicating Budget
(C) Reporting Interim Progress towards budget objectives
(D) Implementing the budget plan
(E) Co-ordinating estimate
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (A), (E), (D), (C) Only
(b) (A), (E), (C), (B), (D) Only
(c) (A), (E), (B), (C), (D) Only
(d) (A), (E), (B), (D), (C) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, E, B, D, C only
Budgeting is a process to track income and expenses in detailed manner in order to make operational decisions. This process ensures consistency and accuracy across departments and ensures the organization is on track to meet its objectives.
The steps in budgeting are:
- Obtaining estimates - It is the process of estimating how much funds company will need to fulfil its objectives over a specific period of time. Estimate of sales, production costs, etc. from each department is obtained.
- Co-ordinating estimates - The various estimates obtained are then evaluated as a whole. The budget committee decides the fair allocation of resources among various units.
- Communicating the budget - The next step is communication of the budget to stakeholders involved that is to the concerned and responsible managers and departments.
- Implementing the budget plan - The budget is implemented that is it is adopted for that particular period.
- Reporting interim progress towards the budget objectives - Performance reports are prepared to inform management and managers about the performance of the budget figures. Interim progress is crucial to track the organization's progress towards its budget objectives.
Hence, the correct answer is A, E, B, D, C only
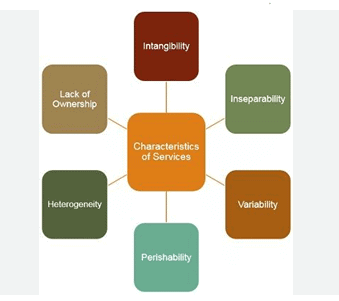
Q9: Which of the following are unique features of services?
(A) Services are perishable.
(B) Services have inseparability of production and consumption.
(C) Services have the quality of perfect standardization.
(D) Services have the characteristic of Variability.
(E) Services are highly tangible so can be touched.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (D) Only
(b) (A) and (C) Only
(c) (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A) and (E) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A and D only.
- Services provided by business refers to activities that benefit the customer but does not help in the delivery of a tangible commodity.
- Examples of services include consulting firms, law firms, banking, etc.
- Tangibility - Services cannot be touched or seen. Hence, they are intangible.
- Perishable - Services are short-lived and cannot be stored for future use.
- Inseparability of production and consumption - Services have to be consumed when produced.
- Non-transferability - Services are non-transferable in nature. Once a customer pays for a service, he does not become the owner. He just pay the service provider for the service rendered.
- Heterogeneous - Services are not standardized. They are heterogeneous.
Q10: The Parenting Fit Matrix related to Strategy Formulation was proposed by-
(a) T.L Wheelan, T D Hunger & K Ranganjan
(b) Marcus Alexander, Andrew Campbell, Michael Goold
(c) G.D. Harrell, R.O Kieper & A Cambell
(d) G Hammel, L. Segel & A C Inkpen
Ans: b
Sol: The Parenting Fit Matrix, also known as the Parenting Advantage Matrix, was proposed by Michael Goold, Andrew Campbell, and Marcus Alexander.
This matrix is a strategic management tool used to analyze and make decisions regarding the allocation of resources and strategic direction among a corporation and its business units.
Other Related Points
The Parenting Fit Matrix composes of two dimensions : Positive contributions and negative effects of corporation (parent). Five positions are created :
i) Heartland
ii) Edge of Heartland
iii) Ballast
iv) Alien territory
v) Value Trap
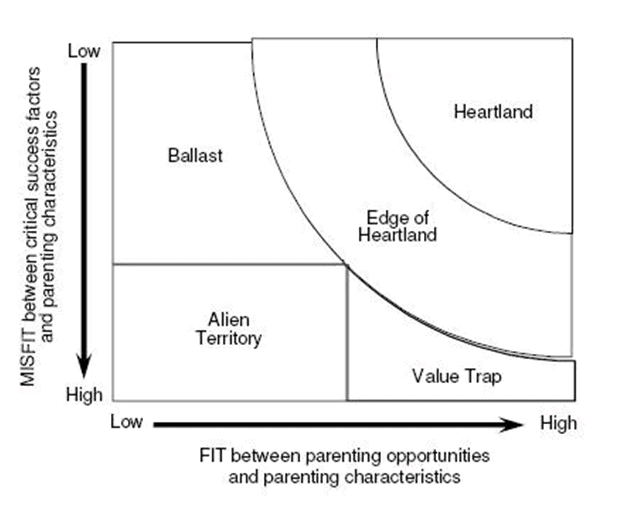
Thus, the correct answer is M. Alexander, A Campbell & M Goold
Q11: Given below are two statements :
Statement (I): Organisation Development Interventions are sets structured activities in which selected organisational units engage in a sequence of tasks that will lead to organisational improvement.
Statement (II): The range of Organisation Development interventions is quite extensive. Interventions have been developed to solve most problems related to the human side of organisations.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
- Organizational Development Interventions are programs and processes designed to improve organization's functioning.
- These structured activities aim to bring about a change in leadership styles, behavioural patterns, and organizational structure.
- Hence, statement I is correct as Organisation Development Interventions are sets structured activities in which selected organisational units engage in a sequence of tasks that will lead to organisational improvement.
- Organizational Development Interventions include human process initiatives.\
- They aim to create positive work environment, opportunities to employees for growth, so that employees feel valued.
Hence, statement II is correct because the range of Organisation Development interventions is quite extensive. Interventions have been developed to solve most problems related to the human side of organisations.
- Organizational Development Initiatives involve specific tasks and target selected organizational units for focused impact.
- Over time, numerous interventions have been developed to address various challenges related to the human side of organizations, encompassing areas like communication, teamwork, leadership, motivation, and organizational culture.
Hence, both the given statements are correct.
Q12: The techniques for appraising performance include:
(A) Graphic Rating Scale Method
(B) Potential Rating
(C) Alternation Ranking Method
(D) Diversity Counts
(E) Paired Comparison Method
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (D) only
(b) (B), (C) and (D) only
(c) (C), (D) and (E) only
(d) (A), (C) and (E) only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, C, and E only
Performance appraisal is a systematic process whereby the performance of an employee on the job is evaluated and documented periodically. The appraisals are based on the goals set by the manager and the progress made by him. It is overall evaluation of the employee's performance and his contribution to the organization.
- Graphic Rating Scale Method - It compares the performance of team members to the ideal traits required for their respective roles in a company. This method uses a scale, often visual, to rate employees on different performance dimensions.
- Alternation Ranking Method - The alternation ranking method is a method used to appraise and rank employees from worst to best.
- Paired Comparison Method - In this method, each employee is compared with every other employee, one at a time. The number of times the employee is compared as better with others determines his or her final ranking.
Behaviourally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS), Critical Incident Technique, Management by Objectives (MBO), Assessment Centres, 360 degree feedback, Essay Appraisal, Checklist Method.
Q13: The location focus for service firms should be determining customer and Revenue volume.
The major determinants of the volume of Customers and Revenue are:
(A) Service and image compatibility with demographics of the customer drawing area.
(B) Proximity to raw materials and suppliers.
(C) Quality of the competition.
(D) Uniqueness of the firm's and competitor's location.
(E) Operating Policies of the competitor
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C) and (E) Only
(b) (C), (D) and (E) Only
(c) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (B), (D) and (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C), and (D) Only.
The major determinants of the volume of customers and revenue are:
Service and image compatibility with demographics of the customer drawing area: The firm's service and its compatibility with the customer help determine the flow of customers in the service store and the volume of revenue generation.
Quality of the competition: If the quality of the nearby competition is low, then the volume of customers and revenue in the service store will be high and vice versa. So, the quality of competition is also an important determinant of customers and revenue.
Uniqueness of the firm's and competitor's location: The choice of the unique location of the service store also affects the customers. Customers choose the location of the service store based on their convenience.
Service Location Strategy:
The main focus for setting the industrial location is on minimising cost and the main focus for setting a good service location is maximizing the revenue. The manufacturing firms find variations in cost upon changing locations and the service firms find that the firm's location impacts the revenue. Therefore, the service firms must focus on determining the impact on revenue and customers if the location changes.
There are eight major determinants of volume and revenue of a service firm:
- Purchasing power of customer- The purchasing power of customers is an important determinant of customers and revenue. If customers do not have good purchasing power, they will not visit any retail store.
- Quality of management- The quality of service staff like the sales team and customer service executive affects the volume of customers in a store.
- Operational policies of the service firm- Having good operating policies helps in the timely delivery of services. This will increase the volume of customers in a store.
- Local competitors- Having high competition in the market will also affect the volume of customers. Customers will have the choice to move to other stores.
- The uniqueness of the firm's products and services- If the firm's products and services are unique, customers will choose to visit that store only.
- Physical facilities of competitors' businesses- The physical facilities of the competitor will also affect the volume of customers because having good customer facilities will attract more demand for customers.
- Service and image compatibility with the demographics of the customer- The firm's service and its compatibility with the customer help determine the flow of customers in the service store and the volume of revenue generation.
- Quality of competition- If the quality of the nearby competition is low, then the volume of customers and revenue in the service store will be high and vice versa. So, the quality of competition is also an important determinant of customers and revenue.
Other Related Points The following points will not come under the volume of customers and revenue:
- Proximity to raw materials and suppliers: Having proximity to raw materials and other suppliers is necessary in a manufacturing firm and not in service service. The customers visit service stores where they can get final products.
Operating Policies of the competitor: The operating policies of the competitor will not affect the volume of customers and revenue in the service firm because it does not affect the demand for products and services.
Q14: Match List - I with List - II.
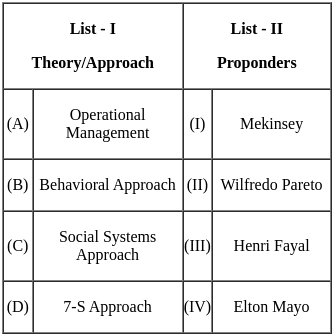
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) (A) - (III), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (I)
(b) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
(c) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (II), (D) - (I)
(d) (A) - (I), (B) - (IV), (C) - (III), (D) - (II)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct options are (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (II), (D) - (I).
The operational approach was given by Henry Fayol. The behavioral approach was given by Elton Mayo. The social systems approach was given by Vilfredo Pareto and the 7-S framework was developed by McKinsey.
Important Points
- Henry Fayol developed the theory of general management and administration. He developed 14 principles of management. It gave a broader understanding of the principles of management. His operational approach to management was in the area of increasing productivity by developing a good organizational structure and human behavior.
- The behavioral approach was given by Elton Mayo. This approach of management was based upon studying an individual's beliefs and values to their productivity and efficiency in the organization.
- Social systems approach was given by Vilfredo Pareto. As per this approach, the organization is a cultural system of people who work in cooperation. This corporation among people is necessary to achieve the organizational objectives.
- 7-S framework was developed by McKinsey. The goal of this tool or approach was to identify the effectiveness of the organization through the interaction of these seven elements. These elements were Structure, strategy, systems, style, staff, shared values, and skills.
Hence, the correct answers are (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (II), (D) - (I).
Q15: Which of the following is summarised under the three Cs for human resource development?
(A) Competence
(B) Communication
(C) Commitment
(D) Culture
(a) (A), (B) and (C) only
(b) (A), (C) and (D) only
(c) (B), (C) and (D) only
(d) (A), (B) and (D) only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C), and (D) only.
Competence, commitment, and culture come under the 3 C's of human resource development. Human resource development focuses on developing the competence, commitment, and work culture of the employee in the organization. This enhances organizational productivity. Having a competent workforce will result in good productivity. A good working culture will encourage employees to perform better and increase their commitment to the organization.
Important Points
Human Resource Development (HRD) refers to the organization's plan to help its employees in developing skills, abilities, and competencies. This will help in improving organizational efficiency and productivity. The organization does this through career planning, training, and development.
The three C's of Human resource development are competence, commitment, and culture.
- Competency refers to the capacity of an individual that help in performing the job role. An increase in competence level will lead to career growth.
- Commitment refers to the willingness of the employee to give their time and energy towards the organizational goal. Through training and development, the commitment of the employee.
- Culture refers to the environment in which an employee works. HRD focuses on developing a learning culture for their employees. It tries to bring out the hidden talent and competencies of the employees.
Other Related Points
The development of communication skills does not come under the human resource department. An employee will have to develop their communication skills to perform better. Communication does not come under the 3 C's of Human resources development.
Hence, the correct answer is (A), (C), and (D) only.
Q16: Conditions under which companies may find more advantages to locate production in foreign countries than export to them are :
(A) When production abroad is costlier than at home?
(B) When transportation costs are too high for moving goods or services internationally?
(C) When companies lack domestic capacity ?
(D) When government inhibit the import of foreign products?
(E) When products and services need not be altered substantially to gain sufficient consumer demand abroad ?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(b) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (C), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (E), (A) and (B) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct options are (B), (C) and (D) Only
The companies may find it easier to move their production abroad when they find that their transportation costs are high, they do not have enough resources domestically, and when the government restricts companies from importing foreign products. The companies can now get skilled workforces, reduce their transportation costs, and will not have to export or import foreign products.
Important Points
International Business refers to the business activities which are carried out in international locations. It takes place between two or more countries. It may occur in different modes like exporting, licensing, contract, manufacturing, assembly, production, and joint ventures.
Advantages of International Business:
- Countries can Import goods that cannot be produced domestically.
- It results in maximum utilization of resources without any wastage.
- Consumers can buy and consume international products.
- It reduces trade fluctuations which makes the prices more stable.
- Companies can export their surplus produce.
Other Related Points
When the production cost is higher abroad, then the companies will not move their manufacturing unit there, as this will increase their cost of production. Also, if the products and services cannot be altered abroad, then moving the production facility abroad will not be a good decision.
Hence, the correct options are (B), (C), and, (D) Only.
Q17: Which one of the following is correct about NPV and IRR of project (A) and project (B)?
(a) NPV (A) + NPV (B) = NPV of (A + B)
(b) NPV (A) = NPV (B) ≠ NPV of (A + B)
(c) IRR (A) + IRR (B) = IRR of (A + B)
(d) IRR (A) × IRR (B) ≠ IRR of (A - B)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is NPV (A) + NPV (B) = NPV of (A + B).
In the case of NPV, the sum of their NPVs should equal the NPV of the combined cash flows of both projects (A + B) when evaluated together. This is because, in the case of NPV, the discounted rate is known, while in the case of IRR, the discounted rate of return is not known. So, in IRR, the combined value of individual IRRs will not necessarily be the total of individual IRRs.
Important Points
Net Present Value: Net Present Value or NPV is the difference between present values of cash inflows and present values of cash outflows in a particular period. This method is used in evaluating long-term investment opportunities. For calculating NPV, an estimation of timing and future cash flows is needed. The discount rate is also used in calculating NPV to reflect the cost of capital. If the rate of return is above the discount rate, it means a positive NPV.
Net Present Value Formula:
NPV = Cash flows/(1 + i)t - Initial investment
Where,
i= Discount rate or required return
t= Time period
Important Point:
- If NPV > 0, the project is acceptable.
- If NPV = 0, the Project can be accepted or rejected.
- If NPV < 0, the Project has to be rejected.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR):
IRR refers to the discount rate that equates the total outlay with the net present value of annual cash flows. It is also known as the "discounted rate of returns" or "time-adjusted rate of return". IRR is ideal for capital budgeting decisions for evaluating the rate of return over a period of time.
Other Related Points
- NPV (A) = NPV (B) ≠ NPV of (A + B) is not a correct option because if the NPV of projects A and B is equal, then the combined value of NPV of two projects will not be equal to their individual project values.
- IRR (A) + IRR (B) = IRR of (A + B) is incorrect because in the case of IRR the discounted value of cash flows is not available.
- IRR (A) × IRR (B) ≠ IRR of (A - B) is also an incorrect option because in this case, the combined value of the IRR of two projects will be more than the individual values of IRR of two projects.
Hence, the correct answer is NPV (A) + NPV (B) = NPV of (A + B).
Q18: Co-operative credit system in India mainly consists of :
(A) the short-term agricultural credit institutions.
(B) the long term agricultural credit institutions.
(C) the non-agricultural credit co-operatives.
(D) the short term industrial credit institutions.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) Only
(b) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(c) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct options are (A), (B), and (C) Only.
Cooperative credit institutions in India consist of short-term agricultural credit institutions, long-term agricultural credit institutions, and non-agricultural credit cooperatives. These institutions provide long-term and short-term credits to small traders and businessmen.
Important Points
Co-operative Credit Institutions are the institutions that provide help to small businesses and individuals in rural areas. They provide loans and mortgages at low-interest rates to farmers and other small traders. These institutions operate both at the state and central levels.
Structure of Co-operative Credit Institutions in India:
- State co-operative Institutions: These institutions act as a link between the state-level cooperative banks and joint stock banks. These institutions are primarily engaged in attracting deposits from the rich urban classes.
- Central cooperative institutions: These institutions are also known as "banking associations". These institutions are a federation of primary societies in a particular area.
- Primary Agricultural Credit Institutions: These institutions are the association of borrowers and non-borrowers residing in a particular locality. The membership of these institutions is open to all the inhabitants of a locality. These institutions provide short-term and medium-term loans to farmers for agricultural purposes.
Other Related Points
The short-term industrial credit institutions are not part of cooperative societies in India because these institutions do not provide industrial credit and are only engaged in providing short-term and long-term credits to small traders and farmers.
Hence, the correct options are (A), (B), and (C) Only.
Q19: Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): The failure of the international market to connect firms as collaborators will entice a company to enter with wholly owned operations or wholly owned FDI.
Reason (R): The company perceives having operating advantages to overcome its liability of foreignness.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
(d) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
When a firm finds out that the international market is not under its control and the firm is not able to connect with the market, then it might choose to invest in international firms or start its operations internationally. Through this decision, the company will get operational advantages.
Additional Information
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
Foreign direct investment refers to the investment by one nation in another nation in their manufacturing or business. Usually, it is done through investment in securities and shares. It occurs when an investor based in one country buys or acquires assets of another country.
Other types of Foreign investment:
- Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI): FPI is an investment made by foreign nations on Indian securities like shares, bonds, and other financial instruments.
- Foreign Institutional Investments (FII): FII refers to the investment in securities, real estate, and other assets by foreign nations.
Types of FDI:
- Horizontal FDI: In this case, a company establishes the same kind of business operations in another country, as they have developed in their own country.
- Vertical FDI: In this case, a company or a business acquires complementary business in another country. Complementary business means a business that is related to the core business of another country.
- Conglomerate FDI: In this case, a company or firm will invest in different businesses in another country.
Hence, the correct answer is both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Q20: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
In this modern digitalized world, business are required to be mindful both in terms of what they are doing and how they are doing it. The company's brand is not just dependent on the quality of products they are offering to people but on the overall impact of the company's operations on the society, environment and the economy.
Their sense of social responsibility provides them with a competitive edge over their competitors in a crowded marketplace. CSR is a holistic and integrated management concept whereby companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It works on a Triple Bottom Line Approach i.e. Company focuses on 3P's; People, Planet and Profit while addressing all the expectations of its stakeholders. The majority of policy initiatives in the country are driven by the objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, focus on fundamental rights, etc. thereby leading to strong human development.
The choices that we make today will be going to affect and influence our future generations. Despite all this, inequality and disparity still exists. This year, the Indian Government implemented new CSR guidelines. These guidelines require Indian companies to spend 2 percent of their net profit on CSR. India is the first country in the world to make CSR mandatory. Including the CSR mandate in Companies Act, 2013, is a great step of engaging the corporate sector in the equitable development of the country. Earlier companies were required to spend 2 percent of the profits towards CSR and in case of failure to do so; they were required to give reasons. But as per the present amendment, companies are required to spent 2 percent of profit towards CSR in the given time limit or are required to turn over this amount of profits in the funds which are run by the government.
The new amendment will require all the companies which qualify the provisions under CSR guidelines to spend the specified part of their profits towards Corporate Social Responsibility without failing.
What is the consequence for companies that fail to most the CSR spending requirement as per the new amendments?
(a) Companies may file a suitable explanation.
(b) Companies may seek grace from the Government.
(c) Companies may get it done from the Sister Companies.
(d) Companies are required to turn over the profits to government - run funds.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Companies are required to turn over the profits to government-run funds.
This passage states that companies nowadays focus on providing quality products and services along with their social and environmental impact. Companies are not only producing good products but they are also concerned about the environment. These concerns for society are also creating a competitive advantage for the companies in the market. Consumers are also preferring products which does not harm the environment. Companies are meeting both their social and business objectives. Most of the companies are focusing on achieving social objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, etc. thereby leading to strong human development For this reason, the government of India in the Companies Act 2013 has made it mandatory to invest 2% of their profits for CSR. India is the first country to develop a CSR policy for the company.
As per the latest amendment in the Companies Act 2013, companies are required to spend 2 percent of profit towards CSR within the given time limit or are required to turn over this amount of profits to the funds that are run by the government.
Important Points
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Corporate social responsibility refers to the activities that corporations exercise to perform their moral duties towards society. It is the responsibility of the corporates towards the society. The companies should focus on the nation's development by working on the living standards and quality of life of their employees and their families. The major drivers of CSR for corporates are increased competition, creating goodwill in the market, demand for disclosure, and government policies.
CSR in Indian Law and Compliance:
- Under section 135 of the Company Act, 2013, any company with a net worth of Rs. 500 cr or more, or turnover of Rs. 1000 cr or more, or a net profit of Rs. 5 cr or more will have to spend at least 2% of last 3years of average net profits on CSR activities.
- The provisions of CSR are not only applicable to Indian companies but also to the offices of foreign companies in India.
- India is the first country to bring laws on CSR.
- There is no specific penal provision for noncompliance of the law. If a company does not spend any funds on CSR, it will have to disclose the reason for not spending. Nondisclosure of reason will lead to a penalty of Rs.50,000 to Rs. 25 lac or even imprisonment for up to 3 years.
- The company should attach its CSR report along with financial statements.
- Some CSR activities include slum area development, rural development projects, training to promote rural sports, eradicating hunger and poverty, promoting healthcare facilities, and protecting national heritage.
Hence, the correct answer is Companies are required to turn over the profits to government-run funds.
Q21: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
In this modern digitalized world, business are required to be mindful both in terms of what they are doing and how they are doing it. The company's brand is not just dependent on the quality of products they are offering to people but on the overall impact of the company's operations on the society, environment and the economy.
Their sense of social responsibility provides them with a competitive edge over their competitors in a crowded marketplace. CSR is a holistic and integrated management concept whereby companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It works on a Triple Bottom Line Approach i.e. Company focuses on 3P's; People, Planet and Profit while addressing all the expectations of its stakeholders. The majority of policy initiatives in the country are driven by the objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, focus on fundamental rights, etc. thereby leading to strong human development.
The choices that we make today will be going to affect and influence our future generations. Despite all this, inequality and disparity still exists. This year, the Indian Government implemented new CSR guidelines. These guidelines require Indian companies to spend 2 percent of their net profit on CSR. India is the first country in the world to make CSR mandatory. Including the CSR mandate in Companies Act, 2013, is a great step of engaging the corporate sector in the equitable development of the country. Earlier companies were required to spend 2 percent of the profits towards CSR and in case of failure to do so; they were required to give reasons. But as per the present amendment, companies are required to spent 2 percent of profit towards CSR in the given time limit or are required to turn over this amount of profits in the funds which are run by the government.
The new amendment will require all the companies which qualify the provisions under CSR guidelines to spend the specified part of their profits towards Corporate Social Responsibility without failing.
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Companies are required to spend 2\% of profits towards CSR in the given time limit.
Reason (R): The Government of India has made stringent provisions for CSR in the Companies Act, 2013.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
(d) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
This passage states that companies nowadays focus on providing quality products and services along with their social and environmental impact. Companies are not only producing good products but they are also concerned about the environment. These concerns for society are also creating a competitive advantage for the companies in the market. Consumers are also preferring products which does not harm the environment. Companies are meeting both their social and business objectives. Most of the companies are focusing on achieving social objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, etc. thereby leading to strong human development For this reason, the government of India in the Companies Act 2013 has made it mandatory to invest 2% of their profits for CSR. India is the first country to develop a CSR policy for the company.
The government of India has made stringent provisions for CSR in the Companies Act, of 2013. These provisions will make it compulsory for companies to follow CSR policies. The company will have to invest 2 & of their profits in CSR funds. Important Points
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Corporate social responsibility refers to the activities that corporations exercise to perform their moral duties towards society. It is the responsibility of the corporates towards the society. The companies should focus on the nation's development by working on the living standards and quality of life of their employees and their families. The major drivers of CSR for corporates are increased competition, creating goodwill in the market, demand for disclosure, and government policies.
Causes for Growing Concern for Social Responsibility:
- Social responsibility helps the organization in public relations.
- Companies can build their image in society by putting their efforts towards societal development.
- Companies can create more employment opportunities for the people in the society.
- Companies can contribute towards the economic development of the backward region of the society.
- Companies can make the best use of natural resources to improve the living standards of the people.
CSR in Indian Law and Compliance:
- Under section 135 of the Company Act, 2013, any company with a net worth of Rs. 500 cr or more, or turnover of Rs. 1000 cr or more, or a net profit of Rs. 5 cr or more will have to spend at least 2% of last 3years of average net profits on CSR activities.
- The provisions of CSR are not only applicable to Indian companies but also to the offices of foreign companies in India.
- India is the first country to bring laws on CSR.
- There is no specific penal provision for non-compliance with the law. If a company does not spend any funds on CSR, it will have to disclose the reason for not spending. Nondisclosure of reason will lead to a penalty of Rs.50,000 to Rs. 25 lac or even imprisonment for up to 3 years.
- The company should attach its CSR report along with financial statements.
- Some CSR activities include slum area development, rural development projects, training to promote rural sports, eradicating hunger and poverty, promoting healthcare facilities, and protecting national heritage.
Hence, the correct answer is Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Q22: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
In this modern digitalized world, business are required to be mindful both in terms of what they are doing and how they are doing it. The company's brand is not just dependent on the quality of products they are offering to people but on the overall impact of the company's operations on the society, environment and the economy.
Their sense of social responsibility provides them with a competitive edge over their competitors in a crowded marketplace. CSR is a holistic and integrated management concept whereby companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It works on a Triple Bottom Line Approach i.e. Company focuses on 3P's; People, Planet and Profit while addressing all the expectations of its stakeholders. The majority of policy initiatives in the country are driven by the objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, focus on fundamental rights, etc. thereby leading to strong human development.
The choices that we make today will be going to affect and influence our future generations. Despite all this, inequality and disparity still exists. This year, the Indian Government implemented new CSR guidelines. These guidelines require Indian companies to spend 2 percent of their net profit on CSR. India is the first country in the world to make CSR mandatory. Including the CSR mandate in Companies Act, 2013, is a great step of engaging the corporate sector in the equitable development of the country. Earlier companies were required to spend 2 percent of the profits towards CSR and in case of failure to do so; they were required to give reasons. But as per the present amendment, companies are required to spent 2 percent of profit towards CSR in the given time limit or are required to turn over this amount of profits in the funds which are run by the government.
The new amendment will require all the companies which qualify the provisions under CSR guidelines to spend the specified part of their profits towards Corporate Social Responsibility without failing.
According to the passage, what is the significance of a company's Social responsibility in the modern digitalized world?
(a) It has no impact on the company's brand.
(b) It depends solely on the quality of products.
(c) It provides a competitive edge in the crowded market place.
(d) It leads to higher profits.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is It provides a competitive edge in the crowded marketplace.
This passage states that companies nowadays focus on providing quality products and services along with their social and environmental impact. Companies are not only producing good products but they are also concerned about the environment. These concerns for society are also creating a competitive advantage for the companies in the market. Consumers are also preferring products which does not harm the environment. Companies are meeting both their social and business objectives. Most of the companies are focusing on achieving social objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, etc. thereby leading to strong human development For this reason, the government of India in the Companies Act 2013 has made it mandatory to invest 2% of their profits for CSR. India is the first country to develop a CSR policy for the company.
In the modern digitalized world, if the company is putting its efforts into achieving social and environmental objectives, then the company will have a competitive edge in the market because it will be able to satisfy the needs of both direct and indirect stakeholders of the company. The direct stakeholders include the customers and dealers while the indirect stakeholders include the community in which the company is operating. Having concern about society will help in building image and customers will buy more company's products and services.
Important Points
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Corporate social responsibility refers to the activities that corporations exercise to perform their moral duties towards society. It is the responsibility of the corporates towards the society. The companies should focus on the nation's development by working on the living standards and quality of life of their employees and their families. The major drivers of CSR for corporates are increased competition, creating goodwill in the market, demand for disclosure, and government policies. Companies like Starbucks achieve their social objective by putting investments in employees' stock grants and providing additional, family and medical benefits. In terms of the environment, this company also has a goal of 50% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Importance of CSR:
- Survival: CSR is important for corporations because these organizations only focus on earning profits. It cannot flourish in a society where there is social injustice and inequality. So, meeting social objectives is important in the long run.
- Balance: CSR helps the organization in balancing between the direct and indirect stakeholders. Direct stakeholders include customers, suppliers, and government dealers. Indirect stakeholders include the community in which the organization is operating.
- Sustainable Growth: CSR helps in attaining sustainable goals which will help the organization in the longer run.
- Environment Protection: Environmental issues like pollution, global warming, and ozone depletion need attention. Hence, the corporations should focus on environmental protection.
Hence, the correct answer is It provides a competitive edge in the crowded marketplace.
Q23: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
In this modern digitalized world, business are required to be mindful both in terms of what they are doing and how they are doing it. The company's brand is not just dependent on the quality of products they are offering to people but on the overall impact of the company's operations on the society, environment and the economy.
Their sense of social responsibility provides them with a competitive edge over their competitors in a crowded marketplace. CSR is a holistic and integrated management concept whereby companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It works on a Triple Bottom Line Approach i.e. Company focuses on 3P's; People, Planet and Profit while addressing all the expectations of its stakeholders. The majority of policy initiatives in the country are driven by the objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, focus on fundamental rights, etc. thereby leading to strong human development.
The choices that we make today will be going to affect and influence our future generations. Despite all this, inequality and disparity still exists. This year, the Indian Government implemented new CSR guidelines. These guidelines require Indian companies to spend 2 percent of their net profit on CSR. India is the first country in the world to make CSR mandatory. Including the CSR mandate in Companies Act, 2013, is a great step of engaging the corporate sector in the equitable development of the country. Earlier companies were required to spend 2 percent of the profits towards CSR and in case of failure to do so; they were required to give reasons. But as per the present amendment, companies are required to spent 2 percent of profit towards CSR in the given time limit or are required to turn over this amount of profits in the funds which are run by the government.
The new amendment will require all the companies which qualify the provisions under CSR guidelines to spend the specified part of their profits towards Corporate Social Responsibility without failing.
What is the 'Triple Bottom Line Approach' in CSR as mentioned in the passage?
(a) Focus on customer satisfaction, revenue and profit.
(b) Focus on people, Planet and profit.
(c) Focus on shareholder's interest, environmental sustainability and innovation.
(d) Focus on reducing costs, increasing production and market share.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is to Focus on people, planet, and profit.
This passage states that companies nowadays focus on providing quality products and services along with their social and environmental impact. Companies are not only producing good products but they are also concerned about the environment. These concerns for society are also creating a competitive advantage for the companies in the market. Consumers are also preferring products which does not harm the environment. Companies are meeting both their social and business objectives. Most of the companies are focusing on achieving social objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, etc. thereby leading to strong human development For this reason, the government of India in the Companies Act 2013 has made it mandatory to invest 2% of their profits for CSR. India is the first country to develop a CSR policy for the company
The triple bottom approach has been mentioned in the passage about the 3P of Corporate social responsibility i.e. People, planet, and profit. This approach focuses on achieving the social, environmental, and business objectives of the company.
Important Points Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Corporate social responsibility refers to the activities that corporations exercise to perform their moral duties towards society. It is the responsibility of the corporates towards the society. The companies should focus on the nation's development by working on the living standards and quality of life of their employees and their families. The major drivers of CSR for corporates are increased competition, creating goodwill in the market, demand for disclosure, and government policies.
Importance of CSR:
- Survival: CSR is important for corporations because these organizations only focus on earning profits. It cannot flourish in a society where there is social injustice and inequality. So, meeting social objectives is important in the long run.
- Balance: CSR helps the organization in balancing between the direct and indirect stakeholders. Direct stakeholders include customers, suppliers, and government dealers. Indirect stakeholders include the community in which the organization is operating.
- Sustainable Growth: CSR helps in attaining sustainable goals which will help the organization in the longer run.
- Environment Protection: Environmental issues like pollution, global warming, and ozone depletion need attention. Hence, the corporations should focus on environmental protection.
Hence, the correct answer is to Focus on people, the planet, and profit.
Q24: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
In this modern digitalized world, business are required to be mindful both in terms of what they are doing and how they are doing it. The company's brand is not just dependent on the quality of products they are offering to people but on the overall impact of the company's operations on the society, environment and the economy.
Their sense of social responsibility provides them with a competitive edge over their competitors in a crowded marketplace. CSR is a holistic and integrated management concept whereby companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives. It works on a Triple Bottom Line Approach i.e. Company focuses on 3P's; People, Planet and Profit while addressing all the expectations of its stakeholders. The majority of policy initiatives in the country are driven by the objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, focus on fundamental rights, etc. thereby leading to strong human development.
The choices that we make today will be going to affect and influence our future generations. Despite all this, inequality and disparity still exists. This year, the Indian Government implemented new CSR guidelines. These guidelines require Indian companies to spend 2 percent of their net profit on CSR. India is the first country in the world to make CSR mandatory. Including the CSR mandate in Companies Act, 2013, is a great step of engaging the corporate sector in the equitable development of the country. Earlier companies were required to spend 2 percent of the profits towards CSR and in case of failure to do so; they were required to give reasons. But as per the present amendment, companies are required to spent 2 percent of profit towards CSR in the given time limit or are required to turn over this amount of profits in the funds which are run by the government.
The new amendment will require all the companies which qualify the provisions under CSR guidelines to spend the specified part of their profits towards Corporate Social Responsibility without failing.
Given below are two statements :
Statement (I): CSR is a holistic and integrated management concept whereby companies integrate their social and environmental objectives with their business objectives.
Statement (II): In this modern digitalized world, business are required to be mindful both in terms of what they are doing and how they are doing.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
This passage states that companies nowadays focus on providing quality products and services along with their social and environmental impact. Companies are not only producing good products but they are also concerned about the environment. These concerns for society are also creating a competitive advantage for the companies in the market. Consumers are also preferring products which does not harm the environment. Companies are meeting both their social and business objectives. Most of the companies are focusing on achieving social objectives of equal opportunities, minimizing poverty and human deprivation, etc. thereby leading to strong human development For this reason, the government of India in the Companies Act 2013 has made it mandatory to invest 2% of their profits for CSR. India is the first country to develop a CSR policy for the company.
CSR is holistic and integrated which helps in combining both business and social objectives of the organization. In this modern world, companies should indeed focus on what they are doing and how they are doing it because it should not affect the environment while making any product.
Important Points
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Corporate social responsibility refers to the activities that corporations exercise to perform their moral duties towards society. It is the responsibility of the corporates towards the society. The companies should focus on the nation's development by working on the living standards and quality of life of their employees and their families. The major drivers of CSR for corporates are increased competition, creating goodwill in the market, demand for disclosure, and government policies. Companies like Starbucks achieve their social objective by putting investments in employees' stock grants and providing additional, family and medical benefits. In terms of the environment, this company also has a goal of 50% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Importance of CSR:
- Survival: CSR is important for corporations because these organizations only focus on earning profits. It cannot flourish in a society where there is social injustice and inequality. So, meeting social objectives is important in the long run.
- Balance: CSR helps the organization in balancing between the direct and indirect stakeholders. Direct stakeholders include customers, suppliers, and government dealers. Indirect stakeholders include the community in which the organization is operating.
- Sustainable Growth: CSR helps in attaining sustainable goals which will help the organization in the longer run.
- Environment Protection: Environmental issues like pollution, global warming, and ozone depletion need attention. Hence, the corporations should focus on environmental protection.
Hence, the correct answer is Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Q25: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
Introduction of Corporate Governance in a company brings order and methods in decision making process and fixes who should own the responsibility. The company will focus on its mission, vision and not any personal likes dislikes of a few top officers. The benefits of corporate governance are difficult to quantify in short range.
Accounting jugglery and showing profits give a company's short term gains but they are not long term policies for financial credibility. True financial performance of a company, openness and governance policies give investor's confidence.
The unethical policies or mismanagement by CEO or director of a company will be exposed by adhering to corporate governance principles. Corporate governance will throw light on excessive remunerations given to directors or CEOs. It improves investors confidence and relations.
The occurrence of frauds and mismanagement can be detected early for remedial actions. It is also agreed that no system can remove fraudulent practices fully. Corporate governance is an open democratic system. They may appear long winded or time consuming or individual decision making is hindered.
How does corporate governance help in exposing unethical policies or mismanagement in a company?
(a) By promoting company's flag ship brand.
(b) By enhancing employees productivity.
(c) By fixing responsibilities and promoting openness.
(d) By encouraging accounting Jugglery.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is By fixing responsibilities and promoting openness.
This passage is about Corporate Governance. The passage states that corporate governance brings order and method to decision-making. Through corporate governance, companies will only focus on the mission and vision of the company. The corporate governance policies help in gaining investors' confidence by showing the true financial performance of the company. Corporate governance will also help in showing light into the unethical practices taking place in the organization. All the unethical practices in the organization can be detected and removed through corporate governance.
Through corporate governance policies, the companies can fix responsibilities and promote openness in the organization. The unethical policies or mismanagement in the organization will get exposed when the companies are not operating as per these governance policies. The company can take action against the same.
Important Points
Corporate Governance:
Corporate governance is the set of processes, customs, and policies that affect how the organization is directed, administrated, and controlled. It also includes relationships among the stakeholders and governance of the goals of the organization. Principle stakeholders are management, shareholders, and other boards of directors. Other stakeholders include labor, employees, customers, and creditors. It helps the management to perform the tasks within the structure and system of corporate governance.
Factors Influencing Corporate Governance:
- Ownership Structure: Ownership structure determines how the corporation is managed and controlled. This pattern varies across the globe. The ownership structure is characterized by the co-existence of private, state, and multinational enterprises.
- Board Structure: The board structure of the company also influences corporate governance. The board is responsible for establishing the objectives and policies of the organization.
- Management: The corporate governance is also based upon the management ethics and how management operates.
- Communication and Reporting: Effective communication and reporting systems will lead to better compliance with ethical standards.
- Institutional Environment: The quality of corporate governance is also determined by the legal, regulatory, and political environment operating within the company.
Hence, the correct answer is By fixing responsibilities and promoting openness.
Q26: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
Introduction of Corporate Governance in a company brings order and methods in decision making process and fixes who should own the responsibility. The company will focus on its mission, vision and not any personal likes dislikes of a few top officers. The benefits of corporate governance are difficult to quantify in short range.
Accounting jugglery and showing profits give a company's short term gains but they are not long term policies for financial credibility. True financial performance of a company, openness and governance policies give investor's confidence.
The unethical policies or mismanagement by CEO or director of a company will be exposed by adhering to corporate governance principles. Corporate governance will throw light on excessive remunerations given to directors or CEOs. It improves investors confidence and relations.
The occurrence of frauds and mismanagement can be detected early for remedial actions. It is also agreed that no system can remove fraudulent practices fully. Corporate governance is an open democratic system. They may appear long winded or time consuming or individual decision making is hindered.
Which one of the following is one of the advantages of corporate governance mentioned in the passage?
(a) Hiding excessive remuneration of directors and CEOs.
(b) Discouraging individual decision making.
(c) Improving investors confidence and relations.
(d) Avoiding competition.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Improving investor's confidence and relations.
This passage is about Corporate Governance. The passage states that corporate governance brings order and method to decision-making. Through corporate governance, companies will only focus on the mission and vision of the company. The corporate governance policies help in gaining investors' confidence by showing the true financial performance of the company. Corporate governance will also help in showing light into the unethical practices taking place in the organization. All the unethical practices in the organization can be detected and removed through corporate governance.
Corporate governance helps in improving the investor's confidence because there is transparency among the stakeholders. The company does not hide any information from its stakeholders if they are investing in the company.
Important Points Corporate Governance:
Corporate governance is the set of processes, customs, and policies that affect how the organization is directed, administrated, and controlled. It also includes relationships among the stakeholders and governance of the goals of the organization. Principle stakeholders are management, shareholders, and other boards of directors. Other stakeholders include labor, employees, customers, and creditors. It helps the management to perform the tasks within the structure and system of corporate governance.
- It helps in building trust among investors, customers, and other stakeholders.
- It helps the companies in gaining long-term financial stability and growth.
- Chances of financial loss, risk, and fraudulent practices are reduced through corporate governance.
- It brings transparency to the organization and aligns the interests of various stakeholders of the organization towards one goal.
- Raising capital means that people have trust in companies that are transparent in dealing with stakeholders.
Other Related Points
- Hiding excessive remuneration from the top management is not a part of corporate governance policy. These policies allow transparency in the organization.
- Corporate governance policies do not discourage individual decision-making because the policies are developed as per the interests of the stakeholders.
- Governance policies create a healthy working environment which creates healthy competition among the employees.
- Hence, the correct answer is Improving investor's confidence and relations.
Q27: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
Introduction of Corporate Governance in a company brings order and methods in decision making process and fixes who should own the responsibility. The company will focus on its mission, vision and not any personal likes dislikes of a few top officers. The benefits of corporate governance are difficult to quantify in short range.
Accounting jugglery and showing profits give a company's short term gains but they are not long term policies for financial credibility. True financial performance of a company, openness and governance policies give investor's confidence.
The unethical policies or mismanagement by CEO or director of a company will be exposed by adhering to corporate governance principles. Corporate governance will throw light on excessive remunerations given to directors or CEOs. It improves investors confidence and relations.
The occurrence of frauds and mismanagement can be detected early for remedial actions. It is also agreed that no system can remove fraudulent practices fully. Corporate governance is an open democratic system. They may appear long winded or time consuming or individual decision making is hindered.
What is one of the primary goals of including corporate governance in a company?
(a) Maximizing short-term profits.
(b) Discouraging personal likes and dislikes of top management.
(c) Bringing order and method to decision making.
(d) Enhancing competition in the market.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is bringing order and method to decision-making.
This passage is about Corporate Governance. The passage states that corporate governance brings order and method to decision-making. Through corporate governance, companies will only focus on the mission and vision of the company. The corporate governance policies help in gaining investors' confidence by showing the true financial performance of the company. Corporate governance will also help in showing light into the unethical practices taking place in the organization. All the unethical practices in the organization can be detected and removed through corporate governance.
The primary goal of corporate governance is to bring order to the organization. Through corporate governance policies, the companies will work in a system.
Corporate governance is the set of processes, customs, and policies that affect how the organization is directed, administrated, and controlled. It also includes relationships among the stakeholders and governance of the goals of the organization. Principle stakeholders are management, shareholders, and other boards of directors. Other stakeholders include labor, employees, customers, and creditors. It helps the management to perform the tasks within the structure and system of corporate governance.
Goals of Corporate Governance:
- To improve the company's competitive position in the industry.
- To encourage professional and working relationships among the employees, staff, and other communities.
- To encourage professionalism, independence, and objectivity in the company's policy.
- To avoid any kind of unethical practices in the organization.
Hence, the correct answer is bringing order and method to decision-making.
Q28: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
Introduction of Corporate Governance in a company brings order and methods in decision making process and fixes who should own the responsibility. The company will focus on its mission, vision and not any personal likes dislikes of a few top officers. The benefits of corporate governance are difficult to quantify in short range.
Accounting jugglery and showing profits give a company's short term gains but they are not long term policies for financial credibility. True financial performance of a company, openness and governance policies give investor's confidence.
The unethical policies or mismanagement by CEO or director of a company will be exposed by adhering to corporate governance principles. Corporate governance will throw light on excessive remunerations given to directors or CEOs. It improves investors confidence and relations.
The occurrence of frauds and mismanagement can be detected early for remedial actions. It is also agreed that no system can remove fraudulent practices fully. Corporate governance is an open democratic system. They may appear long winded or time consuming or individual decision making is hindered.
According to the passage, what is the benefit of adhering to corporate governance for investors?
(a) Short term gains
(b) Confidence in true financial performance
(c) Higher rates of dividend
(d) Possibilities of rights issues
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Confidence in true financial performance.
This passage is about Corporate Governance. The passage states that corporate governance brings order and method to decision-making. Through corporate governance, companies will only focus on the mission and vision of the company. The corporate governance policies help in gaining investors' confidence by showing the true financial performance of the company. Corporate governance will also help in showing light into the unethical practices taking place in the organization. All the unethical practices in the organization can be detected and removed through corporate governance.
Corporate governance helps the investors in gaining access to the true financial statements of the company. Corporate governance policies help bring transparency to the organization. This helps the investors in getting access to the true financial statements of the company.
Important Points Corporate Governance:
Corporate governance is the set of processes, customs, and policies that affect how the organization is directed, administrated, and controlled. It also includes relationships among the stakeholders and governance of the goals of the organization. Principle stakeholders are management, shareholders, and other boards of directors. Other stakeholders include labor, employees, customers, and creditors. It helps the management to perform the tasks within the structure and system of corporate governance.
- It helps in building trust among investors, customers, and other stakeholders.
- It helps the companies in gaining long-term financial stability and growth.
- Chances of financial loss, risk, and fraudulent practices are reduced through corporate governance.
- It brings transparency to the organization and aligns the interests of various stakeholders of the organization towards one goal.
- Raising capital means that people have trust in companies that are transparent in dealing with stakeholders.
Hence, the correct answer is Confidence in true financial performance.
Q29: Read the following passage carefully, and answer question.
Introduction of Corporate Governance in a company brings order and methods in decision making process and fixes who should own the responsibility. The company will focus on its mission, vision and not any personal likes dislikes of a few top officers. The benefits of corporate governance are difficult to quantify in short range.
Accounting jugglery and showing profits give a company's short term gains but they are not long term policies for financial credibility. True financial performance of a company, openness and governance policies give investor's confidence.
The unethical policies or mismanagement by CEO or director of a company will be exposed by adhering to corporate governance principles. Corporate governance will throw light on excessive remunerations given to directors or CEOs. It improves investors confidence and relations.
The occurrence of frauds and mismanagement can be detected early for remedial actions. It is also agreed that no system can remove fraudulent practices fully. Corporate governance is an open democratic system. They may appear long winded or time consuming or individual decision making is hindered.
How does the passage describe corporate governance as as system?
(a) Time-consuming but effective.
(b) Hinding the risk of fraud.
(c) An open democratic system with some drawbacks.
(d) A system capable of removing fraudulent activities 100%.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is An open democratic system with some drawbacks.
This passage is about Corporate Governance. The passage states that corporate governance brings order and method to decision-making. Through corporate governance, companies will only focus on the mission and vision of the company. The corporate governance policies help in gaining investors' confidence by showing the true financial performance of the company. Corporate governance will also help in showing light into the unethical practices taking place in the organization. All the unethical practices in the organization can be detected and removed through corporate governance.
Corporate governance is a system of principles and practices that governs an organization. This system is an open system which allows the management to make changes as per the requirement. All the principles are developed to make the organization work in order and there are very less chances of any mistake in the system. Important Points
Corporate Governance:
Corporate governance is the set of processes, customs, and policies that affect how the organization is directed, administrated, and controlled. It also includes relationships among the stakeholders and governance of the goals of the organization. Principle stakeholders are management, shareholders, and other boards of directors. Other stakeholders include labor, employees, customers, and creditors. It helps the management to perform the tasks within the structure and system of corporate governance.
- It helps in building trust among investors, customers, and other stakeholders.
- It helps the companies in gaining long-term financial stability and growth.
- Chances of financial loss, risk, and fraudulent practices are reduced through corporate governance.
- It brings transparency to the organization and aligns the interests of various stakeholders of the organization towards one goal.
- Raising capital means that people have trust in companies that are transparent in dealing with stakeholders.
Hence, the correct answer is An open democratic system with some drawbacks.
Q30: What shall be the transportation cost if a researcher uses North-West Corner Rule to get the basic feasible solution to the following:
(a) 112
(b) 102
(c) 105
(d) 116
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 112.
Transportation Cost Using North-West Corner Rule
Following the North-West Corner Rule step-by-step:
- Start at the top-left corner (S1-D1): Assign minimum of Supply and Demand, which is 2. Update Supply (S1: 2-2 = 0) and cross out D1 column.
- Move right (S1-D2): Assign minimum of remaining Supply and Demand, which is 3. Update Supply (S1: 0-3 = -3) and cross out D2 column.
- Move down (S2-D2): Assign minimum of remaining Supply and Demand, which is 0. Update Supply (S2: 1-0 = 1) and cross out D2 column.
- Move right (S2-D3): Assign minimum of remaining Supply and Demand, which is 1. Update Supply (S2: 1-1 = 0) and cross out D3 column.
- Move down (S3-D3): Assign minimum of remaining Supply and Demand, which is 5. Update Supply (S3: 5-5 = 0) and Demand (D3: 3-5 = -2).
- Move right (S3-D4): Assign remaining Demand of D4 (2). Update Supply (S3: 0-2 = -2) and Demand (D4: 2-2 = 0).
Transportation Cost:
Cost = Unit Cost * Allocated Units
Calculate the cost for each cell with non-zero allocation:
- S1-D1: 2 (unit cost) * 2 (allocated) = 4
- S1-D2: 3 (unit cost) * 3 (allocated) = 9
- S2-D3: 6 (unit cost) * 1 (allocated) = 6
- S3-D3: 15 (unit cost) * 5 (allocated) = 77
- S3-D4: 9 (unit cost) * 2 (allocated) = 20
Total Transportation Cost: 4 + 9 + 6 + 77 + 20 = 116
Therefore, the transportation cost using the North-West Corner Rule for this problem is 116.
Q31: Which of the following related to Combined Leverage (CL)
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 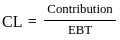
(D) 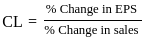
(E) CL = Operating leverage × Financial leverage
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (A), (B) and (E) only
(b) (B), (C) and (E) only
(c) (A), (D) and (E) only
(d) (A), (B) and (C) only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (E) only.
Let's go into more detail about the statements related to Combined Leverage (CL):
Combined Leverage (CL) is a measure that combines both operating leverage and financial leverage to assess the overall impact on the company's earnings and risk.
The correct statements are:
- (A) CL = Contribution/EBIT
- This equation expresses Combined Leverage as the ratio of Contribution to Profit Before Tax (PBT). Contribution typically refers to the excess of sales over variable costs and is a key component in assessing operating leverage.
- (B) CL = PBT/EBIT
- This equation expresses Combined Leverage as the ratio of Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) to Profit Before Tax (PBT). EBIT is a measure of operating profit and is also used in the analysis of operating leverage.
- (E)CL = Operating leverage×Financial leverage
This equation highlights that Combined Leverage is the product of Operating Leverage and Financial Leverage. Operating Leverage is associated with fixed operating costs, while Financial Leverage is associated with fixed financial costs such as interest on debt. The combination of these two types of leverage results in Combined Leverage.
In summary, Combined Leverage (CL) is influenced by both the operational structure (Operating Leverage) and the financial structure (Financial Leverage) of a company. The provided equations (A), (B), and (E) capture different aspects of how Combined Leverage is calculated or expressed
Q32: Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): A brand is an important corporate resource.
Reason (R): A brand embodies all of the characteristics of a company's product in the mind of the consumer.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
(d) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Assertion (A): This statement is true. A brand is indeed considered an important corporate resource. Brands represent the identity of a company, and a strong brand can have a significant impact on consumer perception, loyalty, and overall business success.
Reason (R): This statement is also true. A brand is not just a logo or a name; it encompasses the entire set of associations, perceptions, and feelings that consumers have about a product or company. A strong brand creates a certain image and expectation in the mind of the consumer.
Conclusion:
Both the assertion and the reason are correct, and the reason explains why the assertion is true. Therefore, the correct answer is that both the assertion and the reason are correct and related.
Important PointsAssertion (A): A brand is an important corporate resource.
Brands are considered crucial corporate resources for several reasons:
- Identification and Differentiation: A brand serves as a unique identifier for a company's products or services. It helps differentiate them from competitors in the market.
- Consumer Trust and Loyalty: A strong brand builds trust and loyalty among consumers. It represents a promise of quality and consistency.
- Value Perception: Brands contribute to the perceived value of a product. Consumers may be willing to pay more for a product associated with a strong brand.
- Market Positioning: Brands help companies position themselves in the market. They can be positioned as luxury, affordable, innovative, etc.
- Market Expansion: A recognized brand can facilitate market expansion and entry into new markets.
Reason (R): A brand embodies all of the characteristics of a company's product in the mind of the consumer.
This reason is aligned with the concept of how a brand is perceived by consumers. A brand is not just a name or logo; it encapsulates the overall image and characteristics associated with a company's products or services:
- Brand Image: A brand includes the perceptions, emotions, and associations that consumers have with a particular product or company.
- Brand Personality: Brands often have distinct personalities that resonate with consumers. For example, a brand may be seen as friendly, innovative, or reliable.
- Brand Promise: Brands convey a promise or commitment to consumers. This promise is based on the consistent delivery of certain attributes or qualities associated with the brand.
- Brand Recognition: Consumers may identify and recall a brand based on its distinctive features, whether visual, auditory, or symbolic.
In conclusion, the assertion is supported by the reason. Brands are indeed vital corporate resources because they embody the characteristics of a company's products in the minds of consumers, influencing their perceptions and choices.
Q33: Which one of the following is correct Accounting Equation?
(a) Assets = Liabilities - Capital
(b) Capital = Assets + Liabilities
(c) Liabilities = Capital + Assets
(d) Liabilities = Assets - Capital
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Liabilities = Assets - Capital.
The accounting equation is a fundamental principle in accounting that represents the relationship between a company's assets, liabilities, and equity. The equation is expressed as:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This equation must always balance, reflecting the accounting concept of the dual aspect or double-entry system. Here's a breakdown of each component:
- Assets: These are the economic resources owned or controlled by a business that provide future benefits. Assets include items such as cash, accounts receivable, inventory, property, and equipment.
- Liabilities: These represent the obligations or debts that a business owes to external parties. Liabilities include items such as loans, accounts payable, and other debts.
- Equity: Also known as owner's equity or shareholders' equity, this represents the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting liabilities. Equity includes the owner's investment in the business and any retained earnings.
Q34: In which institutions of women entrepreneurship Jyoti Jeevan Naik was associated?
(a) Shri Mahila Griha Udyog Lijjat Papad
(b) Sahkari Mahila Gram Samittee
(c) Jivika
(d) Self-employed Women's Association
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Shri Mahila Griha Udyog Lijjat Papad.
Shri Mahila Griha Udyog Lijjat Papad, popularly known as Lijjat, is indeed one of the institutions of women entrepreneurship with which Jyoti Jeevan Naik was associated.
- Jyoti Jeevan Naik held significant roles within Lijjat for over 25 years, contributing immensely to its success and empowering women through entrepreneurship. Here's a brief overview of her involvement:
- Joining Lijjat: Naik joined Lijjat in 1972 as a young woman seeking livelihood opportunities.
- Rising through the ranks: Through her dedication and hard work, she climbed the ranks, eventually becoming a supervisor and then a manager.
- Leadership and training: Naik played a key role in training and mentoring new members, teaching them Lijjat's papad-making process and fostering a collaborative spirit.
- Community outreach: She actively participated in community outreach programs, representing Lijjat at various events and promoting its message of women's empowerment.
- Innovation and expansion: Naik contributed to the development of new papad flavors and products, helping Lijjat diversify its offerings and cater to changing market demands.
- Jyoti Jeevan Naik's story is a testament to the transformative power of Lijjat and its commitment to empowering women through economic independence. Her dedication and achievements within the organization continue to inspire generations of aspiring women entrepreneurs.
Q35: Who has authored the book "the Third Wave"?
(a) Hammel and Prahlad
(b) Toffler
(c) Aldrich
(d) Nilkant and Ram Narayan
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Toffler.
"The Third Wave" is a book authored by Alvin Toffler. The book, published in 1980, is a futurist work that explores the impact of technological advancements on society and predicts the emergence of a third wave of societal development, characterized by the Information Age and the widespread use of technology. Alvin Toffler was a prominent American writer, futurist, and social critic, and "The Third Wave" is one of his well-known work.
Important Points Key Themes:
- Waves of Societal Change: Toffler introduces the concept of societal change occurring in waves. The "first wave" represents the agricultural revolution, the "second wave" corresponds to the industrial revolution, and the "third wave" refers to the information and technology-driven revolution.
- Information Age: Toffler predicts the rise of the Information Age as the dominant force in shaping the future. He discusses the impact of information technology on various aspects of society, including communication, economy, and culture.
- Shift in Power Structures: The book explores the transformation of power structures and social institutions in the third wave. Toffler discusses how knowledge and information would become key sources of power.
- Adaptation to Change: Toffler emphasizes the need for individuals and societies to adapt to the accelerating pace of change brought about by technological advancements. He discusses the challenges and opportunities presented by this shift.
- The De-Massification of Society: Toffler discusses the trend toward more customized and personalized experiences in the third wave, contrasting with the mass production and standardization of the industrial era.
- Impacts on Work and Economy: The book delves into how the third wave would affect work, employment, and the economy, with a focus on the role of knowledge and information workers.
Q36: Which of the following statements are correct about International Trade Theories?
(A) According to mercantilism, countries should import more than they export.
(B) A country that practices neo-mercantilism attempts to run, export surplus to achieve a social or political objective.
(C) Theory of absolute advantage reasoned that restricted trade would lead country to specialize in those products that gave it a competitive advantage.
(D) According to theory of comparative advantage gains from trade will occur even in a country that has absolute advantage in all products because the country must give up less efficient output to produce more efficient output.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (C) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (C) and (D) Only
(d) (B) and (D) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is (B) and (D) only.
The correct statements about International Trade Theories are:
(B) A country that practices neo-mercantilism attempts to run an export surplus to achieve a social or political objective.
(D) According to the theory of comparative advantage, gains from trade will occur even in a country that has an absolute advantage in all products because the country must give up less efficient output to produce more efficient output.
Explanation:
- Statement (A): This statement is incorrect. According to mercantilism, countries should aim for an export surplus, not import more than they export.
- Statement (B): This statement is correct. Neo-mercantilism involves attempting to achieve an export surplus to fulfill social or political objectives.
- Statement (C): This statement is incorrect. The theory of absolute advantage, associated with Adam Smith, reasoned that unrestricted trade would lead countries to specialize in products where they had a competitive advantage.
- Statement (D): This statement is correct. According to the theory of comparative advantage, even a country with an absolute advantage in all products can benefit from trade by specializing in the production of goods for which it has a comparative advantage.
Q37: "Innovation is the specific instruments of entrepreneurship-the act that endows resources with a new capacity to create wealth" who said this?
(a) Peter Drucker
(b) J. A. Shumpeter
(c) Frank H. Knight
(d) Frank W. Young
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Peter Drucker
The quote — "Innovation is the specific instrument of entrepreneurship—the act that endows resources with a new capacity to create wealth." — is attributed to Peter F. Drucker, a renowned management consultant, educator, and author.
Drucker emphasized that entrepreneurship is not just about starting businesses but about using innovation as a tool to transform resources into new wealth-creating capacities. He is well known for integrating innovation and entrepreneurship into management theory and practice.
Other options:
J.A. Schumpeter also linked innovation with entrepreneurship but framed it as "creative destruction."
Frank H. Knight is known for distinguishing between risk and uncertainty in entrepreneurship.
Frank W. Young is known for his sociological theory of entrepreneurship.
Thus, the quote is best aligned with Peter Drucker's philosophy.
Hence, the correct answer is Peter Drucker.
Q38: What should be the maximum size of numbers of representatives in the Joint Management Council?
(a) Six only
(b) Twelve only
(c) Sixteen only
(d) Twenty only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is twelve only.
Joint Management Councils (JMC) were introduced in 1958. Following were the responsibilities of JMCs:
- Responsibility of safety and welfare of workers, vocational training, etc.
- Prepare holiday schedules.
- Improve work efficiency and enhance productivity.
- Joint Management Councils are consultative bodies.
- They consist of equal number of representatives of employees and employers.
- These representatives should not exceed twelve in number.
Other Related Points The difference between Joint Management Council and Works Committee is :
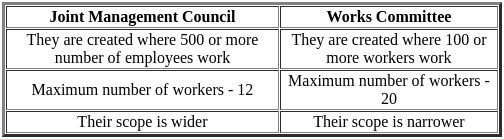
Q39: Match List - I with List - II.
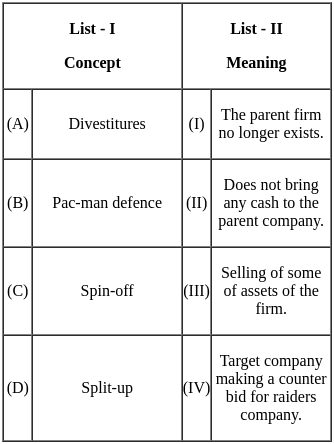
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (IV), (B) - (III), (C) - (II), (D) - (I)
(b) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (II), (D) - (I)
(c) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
(d) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
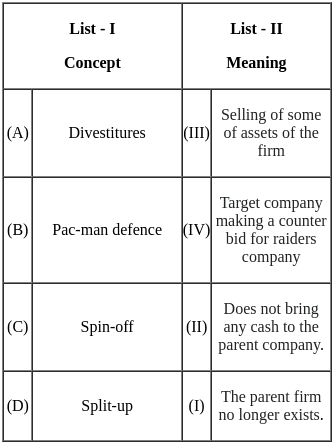
Important Points
- Divestitures - Divestitures is the process of selling of some assets of the firm such as property, product line, or a division. For example, a mining company selling off a particular division to pay off their loans.
- Pac-man defence is a defensive strategy used by targeted company in case of hostile takeover whereby, the targeted company tries to acquire the company that has made an attempt to takeover the targeted company. For example, Company XYZ tries to takeover company PQR in a hostile attempt to gain control over company PQR. So, company PQR uses pac-man defence and purchases large number of shares of company XYZ thereby gaining control over the latter.
- Spin-off - It is where a parent company converts one of its division or subsidiaries into separate independent structures or companies. For example, spin-off of PayPal from its parent company EBay.
- Spit-up - In split-up, parent company is split in two or more entities and the parent company ceases to exist. For example, Hewlett Packard Company split-up and formed Hewlett Packard Enterprises and HP Inc. in 2015.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (II), (D) - (I)
Q40: Which of the following strategies are types of combination strategies?
(A) No change strategies
(B) Pause/Proceed with caution strategies
(C) Turn around strategies
(D) Profit strategies
(E) Concentration strategies
(a) (B) and (C) Only
(b) (E) and (D) Only
(c) (A) and (B) Only
(d) None of the above
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is none of the above
- Combination strategy is a combination of other strategies - stability, expansion, and retrenchment. Combination strategy uses these other strategies simultaneously.
- It is used for complex businesses in competitive environments.
- The combination strategies are : Simultaneous strategy, Sequential strategy, and a combination of both.
Other Related PointsExample of combination strategy : A glue company launching different products like adhesives and sealants, acquiring other international companies, and divesting its construction division is an example of combination strategy.
Important Points The other options are incorrect because :
- No change strategies: These involve maintaining the current state of affairs and don't actively combine other strategies.
- Pause/Proceed with caution strategies: These are temporary measures within a single strategy, not a combination of different approaches.
- Turn around strategies: These involve reversing a previous decision and returning to an earlier state, not combining multiple strategies.
- Profit strategies: These are goals or objectives, not specific strategies, and can be pursued through various combinations of other strategies.
- Concentration strategies: These involve focusing on a particular market or product line, which can be part of a larger expansion or stability strategy but isn't itself a combination strategy.
Thus, the correct answer is none of the above.
Q41: Who is known as the 'Father of brainstorming?
(a) Alex F. Osborn
(b) Frank Gilbreeth
(c) Elton Mayo
(d) Peter Drucker
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Alex F. Osborn
- Brainstorming is a creative technique to solve a problem in a group. It is a method of solving problems by spontaneous contribution of ideas and solutions.
- Each participant is think and share as many ideas as possible based on one's diverse knowledge and experience.
- It generates many radical ideas.
Hence, the correct answer is Alex F. Osborn.
Q42: As per Henry Mintsberg, which of the following is NOT a part of his conception of types of strategies?
(a) Intended Strategy
(b) Unrealised Strategy
(c) Contingency Strategy
(d) Emergent Strategy
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Contingency Strategy.
Contingency strategy is not part of Mitzberg 5P's strategy. Contingency strategies are planning strategies that can occur by evaluating current and future events.
Henry Mitzberg 5P's Strategy:
Henry Mitberg has developed the 5 P's strategy which defines the five alternative methods of formulating a strategy. Strategies help deal with the competitors with the help of organizational values and principles. Each of the five P's has a distinct strategic approach.
The Five P's are as follows:
- Plan: For developing a good strategy, it is necessary that proper planning is done. Better planning helps in the achievement of goals with less risk.
- Ploy: Ploy is referred to as distracting and disrupting the competitors to gain an advantage against them.
- Pattern: Patterns of organizational behavior should be analyzed before developing any business strategy. Patterns are the unspoken element in developing a business strategy.
- Position: It focuses on how the company wants to position its products and services in the market to create customer value. This analysis helps in creating a competitive advantage.
- Perspective: The business strategy should be developed by considering audiences, investors, employees, and management. The strategy of the organization should be beneficial for all.
Other Related Points
Emergent strategies are unplanned strategies, these strategies have to be developed as per the current situation without much analysis. Umbrella strategies guide developing other programs and hybrid strategies are a combination of two or more strategies.
Hence, the correct answer is Contingency Strategy.
Q43: Consumers who are open to new ideas and are among the first to try new products, services or practices are called as-
(a) Dogmatic
(b) Laggards
(c) Innovators
(d) Early Majority
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Innovators.
Innovators are those consumers who adopt new technology or ideas and are ready to take risks. They often try new products and services.
Rogers Adoption Curve:
Rogers' adoption curve describes how the innovation is accepted by consumers. This theory was developed by Joe M. Bohlen, George M. Beal, and Everett M. Rogers in 1957. The adoption curve highlights the acceptance of new ideas or technology by society in five stages. these stages are:
- Innovators: Innovators are the first to adopt new ideas. They are ready to take risks. They are younger and are highly social.
- Early Adopters: These individuals adopt new ideas after a certain time. They have a slower adoption process and have average social status.
- Early Majority: These individuals also take time to adopt new ideas. They are slower than early adopters and also have average social status.
- Late Majority: These individuals will adopt an innovation after a large number of people. They are highly skeptical and have little financial lucidity.
- Laggards: These individuals are the last to adapt to any innovation. They have no opinion and follow old traditions. They have low social status and are older in age.
Other Related Points
Laggards are the last type of individuals who adapt to any innovation. Early Majority are individuals adapting to new ideas after a certain time.
Hence, the correct answer is Innovators.
Q44: Which of the following are the main issues to be tackled by the conceptual component of Customer Relationship Management Programme?
(A) Processing all customer requests coming in through multiple channels.
(B) Setting out the CRM objectives in clear terms.
(C) Creating a good product and mass marketing it.
(D) Putting customers first.
(E) Segmenting the market on the basis of occupations.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B) and (D) Only
(b) (A) and (E) Only
(c) (C) and (D) Only
(d) (D) and (E) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct options are (B) and (D) Only.
CRM or customer relationship management helps in resolving issues related to customers. It helps in developing clear objectives about maintaining good relationships with the customers and developing policies for better customer satisfaction at the earliest. These policies help in prioritising customers problems and solving them at the earliest.
Customer Relationship Management:
Customer relationship management refers to the principles and practices that an organization follows to satisfy its customers. These practices are also used while interacting with customers. There are various CRM technologies used by companies to analyze customer needs and satisfy them. These practices are mostly used in technology companies which require daily interaction with the customers.
Benefits of CRM:
Some of the benefits of CRM include:
- It helps in organizing information about the customers in databases for easier access.
- It helps in optimizing sales and marketing and results in better customer retention.
- Through this, companies can track the performances of various projects and campaigns and analyze them through visual dashboards.
Types of CRM:
- Sales CRM - It is used to increase sales and increase the customer base.
- Marketing CRM- This is used to segment the target and develop marketing campaigns.
- Service CRM- This includes dedicated customer service support for the purpose of sales and marketing.
- Collaborative CRM- It includes sharing customer service data across various departments to improve the efficiency of the organization.
- Small Business CRM- This system has been developed to support small businesses in providing the best possible experience.
Other Related Points
CRM does not help in segmenting the market and mass marketing. It is mainly used for the purpose of developing good relationships with customers and retain them for the future.
Hence, the correct options are (B) and (D) Only.
Q45: Fixing the zero date is important step in establishing a project-
(a) Priliminary steps
(b) Secondary steps
(c) Definition steps
(d) Last steps
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Preliminary steps.
- Zero Date of a Project means a date is fixed from which implementation of the project begins.
- It is a starting point of incurring cost. The project completion period is counted from the zero date.
- Pre-project activities should be completed before zero date. Pre-project activities are identification of project/product, determination of plant capacity, selection of site, manpower planning, and finance scheduling.
Other Related Points
- In project management, initiating the project involves defining its scope, objectives, stakeholders, and other essential elements.
- Part of this initiation process is setting a start date for the project, which serves as a reference point for scheduling and planning activities.
- The last step of a project usually involves closing it out. This includes completing final deliverables, obtaining customer or stakeholder acceptance, conducting project reviews, documenting lessons learned, and officially closing the project.
- Fixing the zero date is one of the preliminary steps in establishing a project.
Therefore, the correct answer is Preliminary steps.
Q46: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (I), (B) - (III), (C) - (II), (D) - (IV)
(b) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (I), (D) - (IV)
(c) (A) - (IV), (B) - (III), (C) - (II), (D) - (I)
(d) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (IV), (D) - (I)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
- An attitude "is a summary evaluation of an object of thought. An attitude object can be anything a person discriminates or holds in mind.
- Attitudes include beliefs, emotional responses and behavioural tendencies.
- Different employers may have different attitudes towards their employees.
- My boat attitude - It means the employer has more of a dominant attitude. He is of the view to get work done from his employees without collaborating with them.
- Shared Boat Attitude - Employers work jointly with employees to complete the task.
- Our Boat Attitude - Employers have a shared interest in the organisational objectives.
- Your Boat Attitude - Employers let employees contribute to the cause of the enterprise.
Q47: What is the major assumption we make when computing a mean form Grouped data:
(a) All values are discrete.
(b) Every value in a class is equal to the midpoint.
(c) Each class contains exactly the same number of values.
(d) No value occurs more than once.
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is every value in a class is equal to the midpoint.
- A mean in maths is the average of a data set, found by adding all numbers together and then dividing the sum of the numbers by the number of numbers.
- It is the mathematical average of two or more numbers.
- In calculating the mean of grouped data, the frequencies are centred at the class marks of the classes.
- So, while computing mean of grouped data, we assume that the frequencies are centred at the class marks of the classes.
Therefore, the correct answer is every value in a class is equal to the midpoint.
Q48: Which is the value of P/V Ratio?
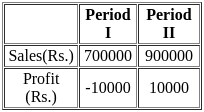
(a) 10%
(b) 20%
(c) 30%
(d) 25%
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 10%.

P/V Ratio = Change in Sales / Change in Profit × 100
Change in Profit = Profit in Period II − Profit in Period I = 10000 −(−10000) = 20000
Change in Sales = Sales in Period II − Sales in Period I = 900000 − 700000 = 200000
P/V Ratio = 20000 / 200000 × 100 = 10%.
Hence, the correct answer is 10%.
Q49: Match List - I with List - II.
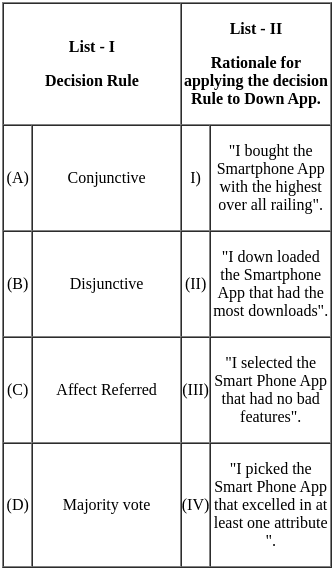
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (IV), (B) - (III), (C) - (II), (D) - (I)
(b) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (IV), (D) - (I)
(c) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
(d) (A) - (I), (B) - (IV), (C) - (II), (D) - (III)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
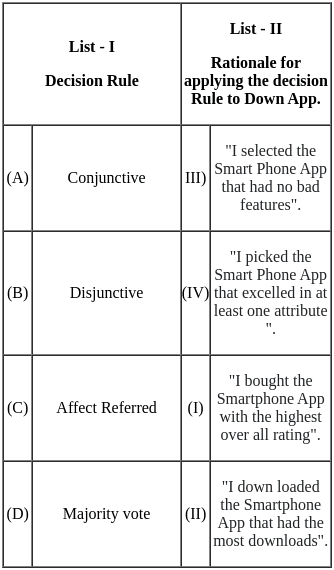
Other Related Points
- Decision rules play an important role in the theory of statistics and economics, and are closely related to the concept of a strategy in game theory.
- A decision rule is a set of conditions that classify records. The rule predicts an outcome in the target field. Viewing the decision rules helps you determine which conditions are likely to result in a specific outcome.
There are various choice models :
Conjunctive rule - A minimally acceptable cut off point is established for each attribute. The brands are evaluated, and the brand that falls below the minimally acceptable limit on any of the attributes is eliminated/rejected.
Disjunctive rule - A minimally acceptable cut off point is established for each attribute. The brands are evaluated, and the brand that falls above the cut-off point on any of the attributes is selected.
Affect-referred rule - A type of consumer decision rule in which a consumer makes a product choice on the basis of his previously established experience and rating of the product/brand rather than on specific attributes.
Majority vote - Majority decision-making involves making decisions based on the support of the majority of the users.
Therefore, the correct answer is (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
Q50: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (IV), (B) - (I), (C) - (II), (D) - (III)
(b) (A) - (IV), (B) - (I), (C) - (III), (D) - (II)
(c) (A) - (I), (B) - (IV), (C) - (II), (D) - (III)
(d) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (I), (D) - (IV)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is (A) - (IV), (B) - (I), (C) - (II), (D) - (III).
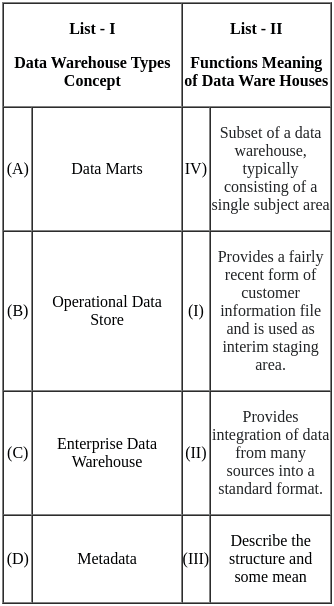
Other Related Points
- Data Mart - A data mart is a data storage system that contains information specific to an organization's business unit. It contains a small and selected part of the data that the company stores in a larger storage system.
- Operational Data Store - An operational data store (ODS) is a central database that provides a snapshot of the latest data from multiple transactional systems for operational reporting. It enables organizations to combine data in its original format from various sources into a single destination to make it available for business reporting.
- Enterprise Data Warehouse - An enterprise data warehouse (EDW) is a database, or collection of databases, that centralizes a business's information from multiple sources and applications, and makes it available for analytics and use across the organization. EDWs can be housed in an on-premise server or in the cloud.
Metadata - Metadata is defined as the data providing information about one or more aspects of the data; it is used to summarize basic information about data that can make tracking and working with specific data easier.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) - (IV), (B) - (I), (C) - (II), (D) - (III).
Q51: Who argued that 'Attitude follow behavior'?
(a) Leon Festinger
(b) Elton Mayo
(c) Mary P. Follet
(d) F. Herzberg
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Leon Festinger.
- Festinger's theory proposes that inconsistency among beliefs or behaviours causes an uncomfortable psychological tension (i.e., cognitive dissonance), leading people to change one of the inconsistent elements to reduce the dissonance or to add consonant elements to restore consonance.
- Cognitive dissonance theory postulates that an underlying psychological tension is created when an individual's behaviour is inconsistent with his or her thoughts and beliefs. This underlying tension then motivates an individual to make an attitude change that would produce consistency between thoughts and behaviours.
The principle that "Attitude follows behaviour" is associated with the theory of cognitive dissonance.
Other Related Points
- There are four theoretic paradigms of cognitive dissonance, the mental stress people experienced when exposed to information that is inconsistent with their beliefs, ideals or values: Belief Disconfirmation, Induced Compliance, Free Choice, and Effort Justification.
Cognitive dissonance is typically experienced as psychological stress when persons participate in an action that goes against one or more of those things.
Therefore, the correct answer is Leon Festinger.
Q52: In case of financial enterprises, cash flow arisen from flow dividend received and paid is shown in cash statement under-which one of the following activities?
(a) Operating Activities.
(b) Financing Activities.
(c) Investing Activities.
(d) Dividend received is investing activities and dividend paid is financing activities.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Dividend received is investing activities and dividend paid is financing activities.
- Cash flow is the movement of money in and out of a company. Cash received signifies inflows, and cash spent is outflows. The cash flow statement is a financial statement that reports a company's sources and use of cash over time.
- A cash flow statement summarizes the amount of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving a company.
- The CFS highlights a company's cash management, including how well it generates cash. This financial statement complements the balance sheet and the income statement.
The main components of the CFS are cash from three areas: Operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
Operating Activities - The operating activities on the CFS include any sources and uses of cash from business activities.
Investing Activities - Investing activities include any sources and uses of cash from a company’s investments.
Financing Activities - Cash from financing activities includes the sources of cash from investors and banks, as well as the way cash is paid to shareholders.
Other Related Points
- The cash flow statement paints a picture as to how a company’s operations are running, where its money comes from, and how money is being spent.
- Also known as the statement of cash flows, the CFS helps its creditors determine how much cash is available (referred to as liquidity) for the company to fund its operating expenses and pay down its debts.
The CFS is equally important to investors because it tells them whether a company is on solid financial ground.
Thus, the correct answer is Dividend received is investing activities and dividend paid is financing activities.
Q53: Arrange the following components of Value-Delivery Process in proper sequence from 1st to 6th step.
(A) Communicating the Value
(B) Enhancing the Value (including sustaining the value)
(C) Capturing the value back from the market (through pricing)
(D) Delivering the value
(E) Selecting the value (including exploring the value)
(F) Creating the Value
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (E), (F), (A), (D), (C), (B) Only
(b) (F), (B), (D), (E), (A), (C) Only
(c) (E), (F), (C), (D), (A), (B) Only
(d) (A), (E), (F), (B), (C), (D) Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is (E), (F), (A), (D), (C), (B) Only.
Key Points
The correct sequence of value delivery process is as follows:
- Selecting the value
- Creating the value
- Communicating the value
- Delivering the value
- Capturing the value
- Enhancing the value
Value delivery: Value delivery refers to providing solutions to the customer that are beyond the anticipating. It refers to providing additional value to the customers than they have demanded. This provides a higher level of satisfaction to the customers along with a higher return on the investment. E.g. While buying phones, consumers get additional benefits like warranty and free application downloads.
Value delivery process:
The value delivery process steps are as follows:
- Selecting the value: For providing value, companies will have to select the values that the consumers demand. It may include any service, product benefit, or monetary benefit.
- Creating value: After selecting a value, the company will have developed the value for customers like price offers, discounts, warranty, after-sale service, etc.
- Communicating the value: The next step is to communicate the value to the consumers. This is done through promotion and advertisement.
- Delivering the value: The company will have to provide those values to the consumers during the sale or after the sale. For this company will have to select the target consumers.
- Capturing the value: Capturing value refers to changes made in delivering the value. This makes the value more useful for the consumers. It can be done though direct marketing and product alliances.
- Enhancing the value: Once the value has been accepted by the consumer, the next step is to enhance the value by providing more benefits and quality to the consumers.
Hence, the correct answer is (E), (F), (A), (D), (C), (B) Only.
Q54: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (III), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (I)
(b) (A) - (III), (B) - (II), (C) - (I), (D) - (IV)
(c) (A) - (II), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (III)
(d) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (I), (D) - (IV)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (A) - (II), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (III).
Source Inspection is a type of inspection that involves quality inspection at the point of production or purchase. Attribute Inspection inspects the specific attributes of a product or service. Poka Yoke inspection is done to prevent any kind of human error that may hamper the whole production process. Variable Inspection takes control over the whole manufacturing. In this type of manufacturing process, the quality inspection for the variable characteristics of the items like length and weight.
Quality Inspection:
- Quality inspection is the process of inspecting the quality of production before it reaches the end user. It involves comparing the results of the measures with the standard specification. If the inspection finds any defects in the production process, then those errors can be rectified as soon as possible.
Importance of Quality inspection:
- It helps in reducing the inspection cost by inspecting the quality of products and services at each stage of production.
- It ensures the correct quantity of products is maintained throughout the process.
- It tries to prevent any damage to the product by finding errors during the inspection process.
- Maintaining quality production results in better customer satisfaction.
- It also reduces any unnecessary communication between the suppliers and dealers.
Inspection types:
- Source Inspection: Source inspection is the process of inspecting the materials and equipment that are being supplied to the facilities.
- Attribute Inspection: Attribute inspection deals with inspecting the attributes or characteristics of materials used in the production. They should meet the specific standards.
- Poka Yoke: This is a type of inspection that is done to find human error in the production process and take action.
- Variable Inspection: Variable inspection is done to inspect the variable characteristics in the production. These characteristics might vary during production. Corrective actions are taken before it reaches the rejection level.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) - (II), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (III).
Q55: 'Making the brand a meaningful part of consumers’ conversations and likes. by fostering direct and continuous customer involvement in shaping brand conversations, experiences and community'.
The above description pertains to which of the following concepts?
(a) Customer Generated Marketing
(b) Societal Marketing Concept
(c) Customer Relationship Management
(d) Customer Engagement Marketing
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Customer Engagement Marketing.
Customer-engagement marketing goes beyond traditional one-way marketing messages. Instead, it aims to:
- Foster direct and continuous customer involvement: This involves creating opportunities for customers to directly interact with the brand, share their thoughts and feedback, and participate in shaping the brand's messaging, experiences, and community.
- Make the brand a meaningful part of consumers' conversations and likes: This means going beyond simply selling products or services and focusing on building a deeper emotional connection with customers. You want them to genuinely identify with your brand values, advocate for it, and incorporate it into their own conversations and online interactions.
Other Related Points
Here are some specific examples of how brands can achieve customer-engagement marketing:
Social media interaction: Responding to comments and messages, hosting contests and giveaways, and encouraging user-generated content.
Loyalty programs: Rewarding customers for their engagement and providing exclusive benefits.
Community building: Creating online or offline communities where customers can connect with each other and the brand.
Personalized experiences: Tailoring content, offers, and recommendations to individual customers based on their preferences and needs.
Co-creation initiatives: Involving customers in product development, marketing campaigns, or other creative projects.
Q56: Likert had proposed only six dimensions of organisational climate. Who proposed seven steps of organisational climate?
(a) Litwin and Stringer
(b) Schein
(c) Kluckhohn and strodtbeck
(d) Hofstede
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Litwin and Stringer.
Litwin and Stringer are most likely credited with proposing seven steps of organizational climate. Their model, developed in 1968, outlines seven stages of increasing employee motivation and organizational effectiveness:
- Survival: Basic needs are met, and employees focus on securing their jobs.
- Security: Job security and benefits become important, leading to higher loyalty.
- Affiliation: Strong social bonds and relationships develop within the organization.
- Status: Recognition and achievement become motivating factors.
- Autonomy: Employees desire independence and control over their work.
- Achievement: Personal accomplishment and contribution to organizational goals become central.
- Competence: Mastery and self-actualization through challenges and growth opportunities.
Other Related Points
- Hofstede: Defined five dimensions of national culture that can influence organizational climate across cultures.
- Schein: Developed a model of organizational culture based on shared assumptions, values, and artifacts.
- Kluckhohn and Strodtbeck: Identified five value orientations that shape cultural differences, applicable to organizational settings as well.
Q57: 'A furnishing retailer company opens a new generation of furniture galleries that are part store, part interior design studio and part restaurant'.
This is an example of which of the following?
(a) Franchise Retailing
(b) Experiential Retailing
(c) Departmental Store Retailing
(d) Mega Retailing
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Experiential Retailing.
Experiential Retailing involves creating a unique and immersive shopping experience for customers. It goes beyond traditional retail by offering a combination of products and services that engage customers on a sensory and emotional level. In the case you mentioned:
- Part Store: This refers to the traditional retail aspect where customers can browse and purchase furniture.
- Part Interior Design Studio: This suggests that customers can receive personalized design assistance or advice, enhancing the shopping experience.
- Part Restaurant: The inclusion of a restaurant adds a social and experiential element, allowing customers to relax, socialize, and spend more time in the retail space.
By combining these elements, the retailer aims to create an environment where customers not only shop for furniture but also engage in a broader experience that involves design inspiration and social interaction. This approach is designed to attract and retain customers through a more holistic and enjoyable retail experience.
Q58: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
(b) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
(c) (A) - (IV), (B) - (III), (C) - (II), (D) - (I)
(d) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (I), (D) - (IV)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 'A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III'.
Theory of Opportunities and Innovation (A) is associated with Peter F. Drucker (II).
- Explanation: Peter F. Drucker is widely acknowledged for his contributions to management theory, and his work on innovation and entrepreneurship is highly influential. He proposed that opportunities for innovation exist in various forms, such as changes in market structures, new knowledge, demographic shifts, and more.
- Drucker’s approach emphasizes the proactive identification and exploitation of opportunities to drive growth and success in both existing and new markets.
- For example, the advent of digital technology has created numerous innovations in communication, healthcare, and retail sectors.
- Key Point: Drucker’s theory highlights that innovation can be systematic and methodical rather than just a stroke of genius, making it accessible to organizations willing to engage in strategic planning and research.
Theory of Change (B) is attributed to Frank W. Young (I).
- Explanation: Frank W. Young’s Theory of Change focuses on the social and cultural factors that drive change within societies. He posited that societal change is often the result of external influences, conflicts, or innovations that disrupt the existing social order.
- Young’s theory underscores the dynamic interactions between various social groups and institutions and how these interactions can lead to significant transformations over time.
- For instance, globalization and technological advancements are key factors driving modern societal changes.
- Key Point: Understanding the underlying mechanisms of societal change can help policymakers and leaders to better navigate and manage the transition processes within their communities.
Theory of Religious Beliefs (C) is linked to Max Weber (IV).
- Explanation: Max Weber’s work on the sociology of religion examines how religious beliefs and practices influence various aspects of society, including economics, politics, and culture. His most famous work, "The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism," explores the connection between Protestant ethics and the development of capitalist economies.
- Weber’s theory suggests that religious beliefs can shape attitudes towards work, savings, and investments, thus impacting economic behavior and societal development.
- For example, the Protestant ethic emphasized hard work, discipline, and frugality, which Weber argued were conducive to the growth of capitalism.
- Key Point: Weber’s insights help explain the role of religion in shaping economic and social structures, highlighting the significant impact of cultural values on societal progress.
Theory of Entrepreneurship Supply (D) is associated with John H. Kunkel (III).
- Explanation: John H. Kunkel's theory addresses the factors influencing the supply of entrepreneurs in a given society. He argued that the presence of entrepreneurial talent and its application is vital for economic development.
- Kunkel’s theory emphasizes the importance of socio-economic and psychological factors, including education, family background, social networks, and cultural attitudes towards risk and innovation.
- For example, societies that value independence and innovation are more likely to produce a higher number of entrepreneurs.
- Key Point: Kunkel’s theory provides a framework for understanding how different factors can encourage or hinder entrepreneurial activities, which can be crucial for policy formulation aimed at stimulating economic growth.
Q59: In the case of an Executive Chairman, what is the minimum percentage of Independent Directors required on the Board?
(a) At least one-third
(b) At least half
(c) At least one-fourth
(d) At least two-thirds
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Atleast half.
- Companies Act, 2013 mandates one-third of the Board (excluding the Chairperson) to be Independent Directors, regardless of the type of Chairperson.
- For listed companies, at least half of the Independent Directors should not have any prior relationship with the promoter or management to further ensure their independence.
- The Act defines an "Independent Director" as a Director who meets certain criteria to ensure their independence from the company, its promoters, and its management.
- The Act also specifies that listed companies must have a Nomination and Remuneration Committee, which is responsible for recommending the appointment of Independent Directors.
- The Act empowers shareholders to remove Independent Directors at a general meeting, which further strengthens their accountability and independence.
Q60: Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (I), (B) - (III), (C) - (II), (D) - (IV)
(b) (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
(c) (A) - (III), (B) - (I), (C) - (II), (D) - (IV)
(d) (A) - (IV), (B) - (II), (C) - (I), (D) - (III)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
Key Points
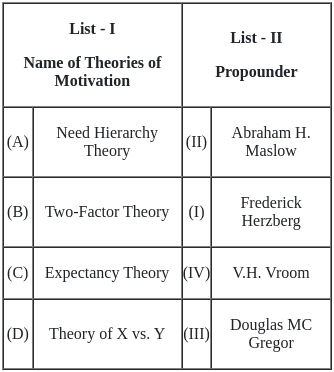
- Need Hierarchy Theory - Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a model for understanding the motivations for human behaviour. These include physiological needs, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. The psychologist Abraham Maslow created this model.
- Two-Factor Theory - The two-factor theory states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction, all of which act independently of each other. It was developed by psychologist Frederick Herzberg.
- Expectancy Theory - Expectancy theory proposes that an individual will behave or act in a certain way because they are motivated to select a specific behaviour over others due to what they expect the result of that selected behaviour will be. The expectancy theory was proposed by Victor Vroom of Yale School of Management in 1964.
Theory X and Theory Y - Theory X is based on the assumptions that employees don't really want to work, lack ambition, only work to collect a pay check, and need constant supervision. Theory Y is based on the assumptions that employees want to work, want to take responsibility, and do not need much supervision. They were created by Douglas McGregor while he was working at the MIT Sloan School of Management in the 1950.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
Q61: There exists certain requirements for effective control. Arrange the requirements from later to initial as proposed by Koontz and Weihrich.
(A) Tailoring controls to individual managers.
(B) Fitting the control system to the organisational culture.
(C) Making sure that control point up exceptions at critical point.
(D) Seeking objectivity of controls.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (A), (C), (D)
(b) (B), (C), (D), (A)
(c) (B), (A), (D), (C)
(d) (B), (D), (C), (A)
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is B, D, C, A
The key requirements in effective control are:
- Fitting the control system to the organisational culture - It helps to establish the foundation for other controls. The control system should be such that it positions itself with the company's values, norms, culture that is already in place.
- Seeking objectivity of controls - Control should be based on something that can be measured and tested, rather than on an ambiguous rule. This will help to ensure that organization's goals are met. It will also help to more accurate evaluation.
- Making sure that control point up exceptions at critical point - Control requires attention at critical points. Deviations from desired performance should be identified and corrective action should be taken.
- Tailoring controls to individual managers - Managers will be able to carry out their tasks and functions more effectively when controls are tailored to individual managers. This is because every individual manager has a different way of working with different strengths and weaknesses.
- Control ensures that there is effective utilization of resources of the organization so as to fulfil organizational goals.
- According to KOONTZ & WEIHRICH, “Management is the process of designing and maintaining of an environment in which individuals working together in groups efficiently accomplish selected goals.”
Thus, the correct answer is B, D, C, A
Q62: Which of the following are the important principles of Re-engineering according to Michael Hammer?
(A) Develop value added jobs to balance out job elimination.
(B) Take specific actions to make the program operational.
(C) Subsume information processing work into the real work that produces the information.
(D) Develop action plan of activities needed to achieve the objectives.
(E) Treat geographically dispersed resources as though they were centralised.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (C) Only
(b) (B) and (D) Only
(c) (C) and (E) Only
(d) (B) and (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct options are (C) and (E) Only.
The important principles of reengineering model developed by Michael Hammer are processing the data for using them at work and centralizing all the geographically based data. All the data that has been collected for various purposes should be centralized in the organization database.
Important Points
Business Process Reengineering: Business Process Reengineering is a management strategy through which companies evaluate their business process and find out the areas for improvement. These strategies are helpful in both small and large organizations. This helps in improvement in areas of cost, customer service, and overall efficiency.
Michael Hammer's Seven Principles of Business Reengineering: Michael Hammer and James Champy have defined seven principles of business reengineering in their book "Reengineering the Corporation: A Manifesto for Business Revolution". These principles illustrate how business process reengineering can help develop business operations.
The 7 principles of Business Reengineering are as follows:
- Focus on results instead of tasks: The companies should focus on the outcome of the tasks instead of its process.
- Allow all individuals to be part of the process: This principle states that all individuals should be part of the process and become active contributors.
- Combining Data collection with data processing: This principle states that the person involved in data collection should also do the processing work to reduce human error.
- Sharing resources between departments: This principle states that the information that has been collected should be shared between various departments which will centralize the operation.
- Joining parallel processes: This principle states that all the processes should take place in coordination. This will help in ensuring that there are no delays in the overall process.
- Integrating decision-making throughout the process: This principle states that decision-making should be involved in each stage of the process to accelerate the processing time.
- Data collection from accurate source: This principle states that the data should be collected once and from a good and reliable source.
Other Related Points
Developing value-added jobs, developing an action plan for activities, and taking actions for making the program operations are not part of business reengineering principles.
Hence, the correct options are (C) and (E) Only.
Q63: Which of the following Industry 4.0 technologies shall detect temperature, humidity and vibration changes, enabling avoidance of system malfunction and human protection in Oil and Gas Industry?
(a) Artificial Intelligence (AI)
(b) Internet of Things (IOT)
(c) Big Data
(d) Machine Learning (ML)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Internet of Things (IoT).
Internet of Things technology is used in developing sensors in devices through which temperatures, humidity, and vibration changes can be detected. It helps in detecting temperatures, humidity, and vibration changes and helps in avoiding any system malfunction.
Important Points
Internet of Things (IoT):
Internet of Things or IoT refers to the network of related devices that connects and exchange information or data through IoT devices and the cloud. These devices have sensors and can include mechanical and digital devices. IoT devices help people to live smarter. Some IoT devices are incorporated in cars, smartphones, and thermostats.
Benefits of IoT to organizations:
- It saves time and energy
- Helps in improving customer service
- Helps in the generation of revenue
- Enhances organizational productivity
- Manages overall business processes
- Helps in better decision-making
Other Related Points
- Artificial Intelligence is a technology through which human intelligence is incorporated into machines and digital devices.
- Big Data refers to large diverse sets of data.
- Machine Learning focuses on using data and algorithms to imitate how humans learn.
Hence, the correct answer is Internet of Things (IoT).
Q64: Company's current price of share is Rs. 60 and dividend per share is Rs. 4 . If its capitalisation rate is 12 percents. What is dividend growth rate?
(a) 10%
(b) 20%
(c) 3.2%
(d) 5%
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 5%.
Key Points
- Dividend growth calculates the annualized average rate of increase in the dividends paid by a company.
- Calculating the dividend growth rate is necessary for using a dividend discount model for valuing stocks.
- A history of strong dividend growth could mean future dividend growth is likely, which can signal long-term profitability.
- Formula of Gordon Growth Model :
Now it is given that P = 60, D1 = 4, r = 0.12, g = ?
60 = 4 / (0.12 - g)
0.12 - g = 4 / 60
0.12 - g = 0.6667
0.12 - 0.667 = g
So g = 0.547 or 5 % (approximately)
Hence, the correct answer is 5%.
Q65: Which of the following are four stages of Psychosexual Development for personality development according to Freud?
(A) Oral
(B) Anal
(C) Phallic
(D) Meticulous
(E) Genital
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), (C), (D) Only
(b) (A), (B), (C), (E) Only
(c) (B), (C), (D), (E) Only
(d) (A), (C), (D), (E) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C, and E only.
- According to the famous psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud, children go through a series of psychosexual stages that lead to the development of the adult personality.
- Freud's stages of human development, which consisted of five psychosexual stages of development, described how personality developed over the course of childhood.
- The stages are oral, anal, phallic, latent, and genital.
- These different stages are associated with the driving force in child development or libido, expressed in different ways and parts of the body.
- Oral stage - This stage occurs between birth and the first year of life. The oral stage is about the experience of pleasure perceived through the mouth.
- Anal stage - The anal stage occurs until the third year of life after the child has passed through the oral stage. It is a phase in which children learn the rules of society.
- Phallic stage - The phallic stage occurs between the third and sixth years of life, during which the superego develops.
- Genital stage - It is directed toward the formation of adult relationships.
Hence, the correct answer is A, B, C, and E only.
Q66: 'A channel structure in which producers, wholesalers, and retailers act as a unified system. One channel member owns the others, has contracts with them or has so much power that they all cooperate.' ?
The above description pertains to which of the following concepts?
(a) Conventional Distribution Channel
(b) Vertical Marketing System
(c) Franchise System
(d) Horizontal Marketing System
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Vertical Marketing System.
- A vertical marketing system is a form of collaboration between the different parts of a supply chain.
- It involves a manufacturer, distributor, and retailer joining forces to provide goods to their customers.
- Such an arrangement seeks to increase efficiency and create cost savings through economies of scale.
- It allows one company to have control over the entire process of producing and selling a product.
- The three types of Vertical Marketing System are: Corporate, Contractual, and Administered.
Other Related Points
- Benefits of VMS : 1. VMS enables companies to control and coordinate different stages of product production and distribution. This can result in more efficient use of resources, decreased expenses, and improved product quality. 2. It also leads to increased market share and customer loyalty by creating partnerships between different companies.
- Example : Zara - The brand has complete control over all activities of the supply chain.
Hence, the correct answer is Vertical Marketing System.
Q67: Arrange the steps of process of learning in proper order :
(A) Acquiring Knowledge
(B) Internalization of new knowledge
(C) Using learning on all situation
(D) Assimilation or retention
(E) Application of new learning
(F) Self-monitored learning
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (D), (B), (E), (C), (F)
(b) (A), (B), (C), (D), (E), (F)
(c) (A), (C), (B), (D), (E), (F)
(d) (B), (D), (F), (C), (A), (E)
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (D), (B), (E), (C), (F).
- Acquiring knowledge (A): This is the starting point, where individuals encounter new information through various means like reading, listening, or observing.
- Assimilation or retention (D): The acquired knowledge needs to be integrated into existing knowledge structures and stored in memory for future use.
- Internalization of new knowledge (B): Through reflection and connection with personal experiences, the new knowledge becomes deeper and more meaningful.
- Application of new learning (E): Individuals test and implement the acquired knowledge in various situations, solidifying their understanding and gaining practical skills.
- Using learning on all situation (C): With successful application, the learned knowledge becomes readily available and can be adapted to new contexts and challenges.
- Self-monitored learning (F): Throughout the process, individuals should actively monitor their progress, identify areas for improvement, and adjust their learning strategies as needed.
Therefore, the correct answer is (A), (D), (B), (E), (C), (F).
Q68: Put in sequence the four steps to convert the raw real-world data into minable data sets :
(A) Data Cleaning
(B) Data Reduction
(C) Data Transformation
(D) Data Consolidation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) (B), (A), (C), (D) Only
(b) (D), (A), (C), (B) Only
(c) (A), (D), (C), (B) Only
(d) (B), (C), (A), (D) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (D), (A), (C), (B) Only.
The correct sequence of steps for converting raw real-world data into minable data is as follows:
- Data consolidation
- Data cleaning
- Data Transformation
- Data reduction
Important Points
Data Processing:
Data processing is an important step in the data mining process. It includes cleaning, transformation, and integrating data so that it is ready for further analysis. It helps improve the quality of data and makes it suitable for data mining tasks.
Steps in Data processing:
- Data consolidation: It is the process of combining and storing varied data into a single space. This helps provide proper insight into the data, leading to faster decision-making.
- Data Cleaning: This includes finding errors in data and correcting them. Techniques like imputation, removal, and transformation are used for this purpose.
- Data Transformation: This involves converting data into suitable formats. This is done through normalization, standardization, and discretization. Normalization helps in scaling the data. Standardization helps in making the data ready for further analysis through mean and variance. Discretization helps in converting data into discrete categories.
- Data reduction: This involves reducing the size of the data. This is done through feature selection and feature extraction. Feature selection involves selecting certain features from the subset. Feature extraction means transforming data into lower dimensional space.
Hence, the correct answer is (D), (A), (C), (B) Only.
Q69: After 10 years of deadlock, European Union (EU) is ready to negotiate with India in WTO on which issue related to food security?
(a) Public Stockholding Norms
(b) Climate Change
(c) Non-tariff barriers to trade
(d) Sanitary & Phytosanitary measures
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Public Stockholding Norms.
Recently, WTO has given a positive response to the issue of public stakeholding for food security purposes. These norms need to be developed to present illegitimate exports from excessive food stocks. European Union has expressed its willingness to negotiate on global terms regarding the purchase, stockpiling, and distribution of stocks.
Public stockholding norms are policy instruments used by the government to meet the food security of the country. These programs are carried out by countries to meet the food scarcity. Current rules suggest that around 10% of food procurement should be used to feed the poor.
World Trade Organization (WTO):
WTO is an international organization that oversees the rules and regulations of global trade of various nations. It was superseded by GATT(General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs). WTO developed various trade agreements which are signed by member nations. It includes agreements related to services, intellectual property rights, and foreign investments. Currently, there are 164 members in this organization.
Principles of WTO:
- Most favored nation: All the member nations should treat other countries equally without any discrimination.
- National Treatment: Imported goods that have entered the domestic market should be treated equally as locally produced goods.
- Free trade: This principle states that trade agreements should reduce the trade barriers between nations and encourage the free flow of trade.
- Fair Competition: There should be free and fair competition among all the member nations.
- Predictability: This principle states that member nations should not raise any kind of trade barriers between nations.
European Union:
European Union is an alliance of 27 European member countries. It helps promote democratic values among the member nations, It was formed in 1933. It was formed after the signing of the Maastricht Treaty by 28 countries.
Objectives of the European Union:
- To improve political cooperation among the member nations.
- To provide common citizenship rights to its member countries.
- To enhance cooperation in the area of judiciary and immigration.
- To enhance economic integration among nations.
Hence, the correct answer is Public Stockholding Norms.
Q70: Arrange the following stages of international development in sequential ascending order.
(A) Primarily domestic company with international division
(B) Domestic company
(C) Multinational corporation with global emphasis
(D) Multinational corporation with multidomestic emphasis
(E) Domestic company with export division
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (E), (B), (C), (A), (D) Only
(b) (B), (E), (A), (D), (C) Only
(c) (B), (E), (A), (C), (D) Only
(d) (B), (A), (E), (D), (C) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A) - (II), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (III).
The five stages of international development are as follows:
- Domestic company
- Domestic company with Export division
- Primary domestic company with an international division
- Multinational Corporation with Multidomestic Emphasis
- Multinational Corporation with a Global Emphasis
International Development:
International development aims at improving the government policies of the developing nations. It refers to strengthening the regional institutions necessary to support long-term, political, social, and economic development. It includes improving the lives of people in society in various areas of interest like health and education. This is done through collaborating with internal multinational corporations.
The five stages of international development are as follows:
- Domestic company: In this stage, the domestic company exports some of its products to the foreign nation through local dealers.
- Domestic company with export division: After the success of stage 1, the company now establishes an export division in a foreign country.
- Primary domestic company with an international division: The company in this stage establishes an international division to conduct most of its business functions.
- Multinational Corporation with Multidomestic Emphasis: After the establishment of an international division, the product lines are developed and local manufacturing is established. The company will now acquire the local business.
- Multinational Corporation with a Global Emphasis: In the fifth stage, the companies establish personnel, R&D, and financing strategies.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) - (II), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (III).
Q71: Which types of employees are included in the definition of IHRM by P. Morgan?
(A) Host-Country Nationals
(B) Parent Country Nationals
(C) Third Country Nationals
(D) Domestic Country Nationals
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) Only
(b) (A), (B), (C) Only
(c) (B), (C), (D) Only
(d) (A), (B), (C), (D) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B), (C) only
P. Morgan's definition of International Human Resource Management (IHRM) includes the management of employees from various categories, and these categories are often classified based on their nationality and the location of their employment. Here's an explanation of the terms mentioned:
Host-Country Nationals (HCNs):
- These are individuals who are citizens of the country where the foreign subsidiary or branch is located.
- For example, if a U.S. company has a subsidiary in France, French employees working in that subsidiary would be considered Host-Country Nationals.
Parent-Country Nationals (PCNs):
- These are employees who are citizens of the country where the multinational company is headquartered.
- Using the same example, if a U.S. company has a subsidiary in France, U.S. employees sent to work in the French subsidiary would be Parent-Country Nationals.
Third-Country Nationals (TCNs):
- These are individuals who are citizens of a country other than the home country of the multinational company or the host country of the subsidiary.
- For instance, if a U.S. company has a subsidiary in France and hires employees from Germany to work in the French subsidiary, those German employees would be considered Third-Country Nationals.
Domestic Country Nationals:
- This term is not commonly used in the context of international staffing. Instead, the focus is often on the home country (PCNs), host country (HCNs), and third countries (TCNs).
In summary, the inclusion of Host-Country Nationals, Parent-Country Nationals, and Third-Country Nationals in P. Morgan's definition of IHRM emphasizes the diverse workforce composition that multinational companies may have across different locations. Managing this diversity is a key aspect of International Human Resource Management.
Q72: Arrange the following process of working capital cycle of manufacturing concern in a proper sequence :
(A) Raw material
(B) Cash
(C) Debtors
(D) Finish goods
(E) Work in progress
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (A), (E), (D), (C) Only
(b) (A), (E), (B), (C), (D) Only
(c) (A), (E), (D), (B), (C) Only
(d) (A), (E), (D), (C), (B) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is
- (A) Raw material
- (E) Work in progress
- (D) Finished goods
- (C) Debtors
- (B) Cash
- Raw Material (A): This is the starting point where the manufacturing process begins. Raw materials are the basic inputs used in the production of goods. It represents the inventory of materials that a company holds to support its production process.
- Work in Progress (E): This stage involves materials that are in the process of being transformed into finished goods. Work in progress represents the partially completed goods on the production floor.
- Finished Goods (D): Finished goods are the completed products that are ready for sale. At this stage, the goods are ready to be sent to customers or distributors.
- Debtors (C): Debtors, also known as accounts receivable, represent the amount of money owed to the company by its customers for the goods sold on credit. This is the stage where the company waits to receive payments from its customers.
- Cash (B): Cash is the final stage where the company receives payment for the goods sold. This cash can then be used to purchase new raw materials and restart the working capital cycle.
In summary, the working capital cycle starts with acquiring of raw materials, moves through the production stages (work in progress and finished goods), involves selling goods on credit (debtors), and ultimately concludes with the receipt of cash. The cycle then repeats as the company uses the received cash to purchase new raw materials and continue its operations.
So, the correct sequence is: (A), (E), (D), (C), (B).
Q73: To support Indian Artificial Intelligence (AI) Startups, which technological infrastructure is expected to be developed by Government of India?
(a) Creation of EPZ
(b) Creation of GPU Clusters
(c) Creation of SEZ Clusters
(d) Creation of IT Parks
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Creation of GPU Clusters.
The creation of GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) clusters is indeed a crucial technological infrastructure that can support the development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) startups. GPU clusters are powerful computing resources that are particularly well-suited for training deep learning models, which are a fundamental component of many AI applications.
Here's why GPU clusters are relevant for AI startups:
- Parallel Processing Power: GPUs are designed to handle parallel processing tasks, making them highly efficient for the matrix computations involved in training deep neural networks. Clusters of GPUs can provide significant computational power for complex AI algorithms.
- Accelerated Training: Training deep learning models can be computationally intensive, and GPUs significantly accelerate the training process compared to traditional CPUs. GPU clusters allow startups to scale their computational resources to handle larger datasets and more complex models.
- Model Iteration: AI startups often need to iterate quickly on their models to improve performance. GPU clusters enable faster experimentation and iteration, allowing startups to fine-tune their models and algorithms more rapidly.
- Resource Scalability: GPU clusters offer scalability, allowing startups to increase or decrease computing resources based on their needs. This flexibility is crucial for handling varying workloads and adapting to the growth of the startup.
- Cost Efficiency: While GPUs can be more expensive than traditional CPUs, their efficiency in training deep learning models often results in overall cost savings. GPU clusters allow startups to leverage this efficiency for cost-effective AI development.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): GPU clusters are part of the broader landscape of high-performance computing, providing the computational muscle needed for complex simulations, data analytics, and AI workloads
Q74: Given below are two statements :
Statement (I): Planning premises are defined as the anticipated environment in which plans are expected to operate. They include assumptions or forecasts of the future ans known conditions that will affect the operation of plans.
Statement (II): No distinction should be drawn between forecasts that are planning premises and forecasts that are translated into future expectancies, usually in financial terms, from actual plans developed.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
Statement (I):
"Planning premises are defined as the anticipated environment in which plans are expected to operate. They include assumptions or forecasts of the future and known conditions that will affect the operation of plans."
This statement is accurate. Planning premises are the foundational assumptions or forecasts about the future conditions under which plans will be implemented. These premises provide the context for decision-making and planning, helping organizations anticipate and adapt to the expected environment.
Statement (II):
"No distinction should be drawn between forecasts that are planning premises and forecasts that are translated into future expectancies, usually in financial terms, from actual plans developed."
This statement is not entirely clear, and its intent might be open to interpretation. However, if interpreted as suggesting that there should not be a significant distinction between the forecasts used as planning premises and those translated into actual plans, it may be considered incorrect. In practice, there is typically a distinction between the assumptions made during the planning phase (planning premises) and the actual outcomes and projections included in formal plans.
Conclusion:
In summary, Statement (I) accurately describes the nature of planning premises, while Statement (II) appears to suggest a perspective that may not align with common planning practices. Planning premises are the foundational assumptions used for planning, and there is generally a distinction between these assumptions and the actual plans that are developed, especially when considering financial terms and projections.
Q75: Which of the following is one of the five main factors given by E. M. Rogers that influence adoption of an innovation?
(a) Accountability
(b) Trialability
(c) Flexibility
(d) Salability
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Trialability.
E. M. Rogers, a communication scholar, proposed the Diffusion of Innovations theory, which explores how and why people adopt new ideas or technologies. The five main factors influencing the adoption of an innovation, as identified by Rogers, are:
- Relative Advantage: The degree to which an innovation is perceived as better than the existing alternatives.
- Compatibility: The extent to which an innovation is perceived as consistent with existing values, experiences, and needs of potential adopters.
- Complexity: The degree to which an innovation is perceived as difficult to understand or use.
- Trialability: The extent to which an innovation can be experimented with or tested before a commitment to adopt is made.
- Observability: The extent to which the results of an innovation are visible to others, influencing others to adopt.
The correct answer in the context ofthe question is indeed "Triability." It corresponds to the factor of trialability, emphasizing the importance of being able to experiment with or test an innovation before fully committing to its adoption.
Q76: Which of the following are assumption of Net Operating Income Approach of Capital Structure?
(A) There is no Corporate Tax
(B) Cost of debt remain constant at all level
(C) The Business risk remain constant every level of debt and equity mix
(D) The cost of Debt is less than cost of equity
(E) Overall cost of Capital remain constant
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) only
(b) (A) and (B) only
(c) (C), (D) and (E) only
(d) (A), (B), (C) and (E) only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C, and E only.
- The Net Income Approach is a theory of Capital Structure developed by David Durand.
- According to the theory, the market value of a firm is not affected by the capital structure.
- The approach says that value of a firm depends on its earnings/operating income and associated business risk, and is not affected by change in debt and equity components.
- Corporate taxes do not exist.
- The cost of debt is constant.
- The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is constant at all levels of debt and equity.
- Business risk remains constant at all levels of debt and equity mix. The NOI approach assumes that the firm's overall business risk does not change with its capital structure.
Thus, the correct answer is A, B, C, and E only.
Q77: 'Creating a seamless cross-channel buying experience that integrates in-store, online, and mobile shopping.'
The above is the description of which of the following?
(A) In store Marketing
(B) Direct Marketing
(C) Omni Channel Retailing
(D) Online Marketing
(E) Digital Marketing
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (D) Only
(b) (C) Only
(c) (A) and (B) Only
(d) (D) and (E) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is C only
- Omni-channel retailing is where customers are engaged through multiple physical and digital touchpoints.
- It involves a seamless shopping experience across all channels including in-store, mobile, and online.
Other Related Points
Some examples of omni-channel retail brands in India are:
Mamaearth, Pepperfry, Nykaa, Zara, Nike, etc.
Important Points
Other options are incorrect because:
- In-store Marketing: Focuses on marketing efforts within a physical store and doesn't involve online or mobile integration.
- Direct Marketing: Involves personalized communication directly with customers but doesn't necessarily encompass different shopping channels.
- Online Marketing: Focuses on marketing efforts through online channels but doesn't necessarily integrate it with physical stores or mobile shopping.
- Digital Marketing: Encompasses online marketing and other digital channels like social media. While it can touch upon creating a cross-channel experience, it doesn't necessarily address integration across physical and digital channels as specifically as in omni-channel retailing.
Thus, the correct answer is C only.
Q78: What is a misuse of committees?
(A) Authority
(B) Membership
(C) Replacement for a manager
(D) For decisions beyond participants authority
(a) (C) and (D) only
(b) (A) and (B) only
(c) (C) and (A) only
(d) (A) and (D) only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct options are (C) and (D) only.
The misuse of a committee will happen if the committee is formed to replace a manager and when the decisions are made beyond the participants' authority. A committee is formed for a specific purpose and it should not take the roles and responsibilities of a manager as the manager is responsible for controlling this committee. The decisions made in these committees should be through proper discussions.
Committee:
Committees are a group of people who perform certain managerial functions. The organization has various kinds of committees like Wage and tax committees. These committees have a board that controls the committee. The members of the committee are fixed and appointed for a specific period. The manager may accept or reject the recommendation made by these committees on specific functions.
Benefits of the Committee:
- Enhances group knowledge
- Develop plans and policies
- Builds Teamwork
- Encourages shared representation
Misuse of Committee:
- Committee is developed for unimportant reasons: A committee is said to be misused when a works committee is formed for unimportant reasons.
- Committee takes the place of a manager: A committee is said to be misused when it takes the responsibilities of a manager.
- Consolidate dividend authority: A committee is said to be misused when it takes all the dividend-related decisions.
- For research and study: A committee is said to be misused when it has been developed for the sole purpose of research and study only.
- Taking decisions beyond participants: A committee is said to be misused when the members of the committee make decisions beyond taking participants' viewpoints.
Other Related Points
Having good membership in a committee and proper delegation of authority will not lead to misuse of any works committee.
Hence, the correct options are (C) and (D) only.
Q79: Given below are two statements :
Statement (I): Economic exposure refers to the change in the value of firm caused by unexpected changes in the exchange rate.
Statement (II): Transaction exposure refers to long term cash flow exposure.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- The three types of foreign exchange exposure that one may face when making transactions in FX include transaction, translation, and economic exposure.
- Economic exposure, also sometimes called operating exposure, is a measure of the change in the future cash flows of a company as a result of unexpected changes in foreign exchange rates (FX).
- Economic forex exposure arises from the effect that unexpected currency fluctuations have on market value and future cash flows. Economic exposure is usually long-term and for this reason may affect your long-term strategies.
- Transaction exposure is the most basic type of foreign exchange exposure and is associated with business transactions in foreign currency.
The exposure may arise due to the time it takes from an entitlement to receive money from a customer and the actual date of the money’s delivery. It may also arise during the time between placing a purchase order and settling the invoice.
Important Points
- Statement I is correct because economic exposure refers to the change in the value of firm caused by unexpected changes in the exchange rate.
- Statement II is incorrect because transaction exposure refers to short term cash flow exposure, and not long term cash flow exposure.
Therefore, the correct answer is Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
Q80: Which one of the following is characterised in the interest rate parity?
(a) The exchange rate between the currencies of two countries equal the ratio between the price of goods in these countries.
(b) The forward rate must be equal to the expected future spot rate.
(c) Nominal interest rate differential must be equal to the expected inflation rate differential in the two countries.
(d) The relationship between interest rates and exchange rate of two countries.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is the relationship between interest rates and exchange rate of two countries.
- Interest rate parity is the fundamental equation that governs the relationship between interest rates and currency exchange rates.
- According to the theory, the forward exchange rate should be equal to the spot exchange rate times the interest rate of the home country, divided by the interest rate of the foreign country.
- Interest rate parity is also important in understanding exchange rate determination.
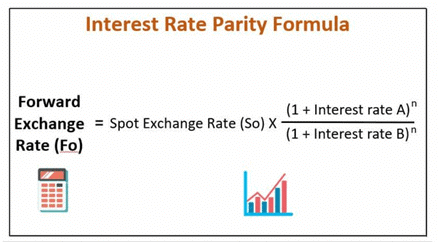
- IRP is the fundamental equation that governs the relationship between interest rates and currency exchange rates.
- The basic premise of IRP is that hedge returns from investing in different currencies should be the same, regardless of their interest rates.
Therefore, the correct answer is the relationship between interest rates and exchange rate of two countries.
Q81: G20 Summit (2023) Proposed which Economic corridor including shipping and rail lines?
(a) IMEE (India Middle East Europe Economic Corridor)
(b) BRI (Bolt and Road Initiative)
(c) CMREC (China Mongolia Russia Economic Corridor)
(d) NELB (New Eurasian Land Bridge (Corridor))
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is IMEE (India Middle East Europe Economic Corridor).
- Joe Biden co-chaired a special event on Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII) and India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), on 9 September 2023 on the sidelines of the G20 Summit in New Delhi.
- This ambitious infrastructure project aims to improve connectivity and trade flows between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- By enhancing connectivity, the corridor could significantly increase trade volume between India, the Middle East, and Europe. Rail and shipping routes offer a more cost-effective way to move goods compared to air freight, potentially leading to lower prices for consumers.
- It aims to link Middle East countries by railway and connect them to India by port, helping the flow of energy and trade from the Gulf to Europe, by cutting shipping times, costs and fuel use.
Other Related Points
- The project will also involve investments in a new railway line in Africa stretching all the way from a port in Angola to the Democratic Republic of Congo and Zambia, all the way to the Indian Ocean on the other side of the continent.
A key component of the corridor includes investments in shipping and rail infrastructure extending from India all over Europe, connected by the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan and Israel.
Therefore, the correct answer is IMEE (India Middle East Europe Economic Corridor).
Q82: "Demonstrating statistically a relationship between scores on a selection procedure and job performance of a sample of workers" is called:
(a) Content Validity
(b) Construct Validity
(c) Criterion Validity
(d) Test Validity
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Criterion Validity.
Criterion validity refers to the extent to which a measure is related to an outcome. It represents whether the measure under study is a valid representation of a particular concept.
Examples of criterion validity - i) Aptitude scores are used in admissions in colleges because they have criterion validity for predicting academic success.
ii) Test to predict how an applicant will perform in a job has criterion validity if it correlates highly with actual job performance.
Additional Information
- Criterion validity - Criterion validity (or criterion-related validity) measures how well one measure predicts an outcome for another measure. It is the extent to which a measure accurately predicts or correlates with the construct it is supposed to be measuring.
- Construct validity - Construct validity concerns how well a set of indicators represent or reflect a concept that is not directly measurable. Construct validity concerns the identification of the causes, effects, settings, and participants that are present in a study.
- Test validity - Test validity is the extent to which a test accurately measures what it is supposed to measure.
Content validity - Content validity is the degree to which a test evaluates all aspects of the topic, construct, or behavior that it is designed to measure.
Other given options are incorrect.
Therefore, the correct answer is Criterion Validity.
Q83: Which of the following are methods of assessment of economic viability of the project?
(A) Pay Back Period (PBP)
(B) Return on Investment (ROI)
(C) Net Present Value (NPV)
(D) Benefit cost Ratio (BCR)
(E) Critical Path Method (CPM)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (B), (C), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (A), (C), (D) and (E) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B), (C), and (D) Only.
Pay Back period method, return on investment, net present value, and benefit-cost ratio are the techniques of capital budgeting that help in evaluating the economic viability of the project.
Capital Budgeting:
Capital budgeting is the process of planning long-term projects, raising funds, and allocating resources to those projects. The capital budgeting decisions are irreversible in nature as they include huge investments in fixed assets. The decisions are made by evaluating the economic viability of the project. These decisions affect the profitability of the project.
Techniques of Capital Budgeting:
Payback Method:
This method helps in finding the time period in which the whole investment will be recovered. It does not take into account depreciation on fixed assets. The investment decision where the payback period is less is selected.
Payback period = 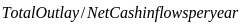
Average Rate of Return (ARR) :
This technique is also known as average return on investment. It is calculated by finding the ratio of net average annual income from the initial outlet of the project. A project with a higher ARR is selected.
ARR% = Average return per year/ Total Average investment * 100
Net present Value (NPV):
Net Present Value or NPV is the difference between present values of cash inflows and present values of cash outflows in a particular period. This method is used in evaluating long-term investment opportunities. For calculating NPV, an estimation of timing and future cash flows is needed. The discount rate is also used in calculating NPV to reflect the cost of capital. If the rate of return is above the discount rate, it means a positive NPV.
Net Present Value Formula:
NPV = Cash flows/(1 + i)t - Initial investment
Where,
i= Discount rate or required return
t= Time period
- If NPV > 0, the project is acceptable.
- If NPV = 0, the Project can be accepted or rejected.
- If NPV < 0, the Project has to be rejected.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR):
IRR refers to the discount rate that equates the total outlay with the net present value of annual cash flows. It is also known as the "discounted rate of returns" or "time-adjusted rate of return". IRR is ideal for capital budgeting decisions for evaluating the rate of return over a period of time.
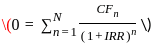
Where,
- N = Total number of time periods
- n = Time period
- CF
n " id="MathJax-Element-3-Frame" role="presentation" style="box-sizing: inherit; margin: 0px; padding: 1px 0px; border: 0px; font-variant: inherit; font-stretch: inherit; line-height: 0; font-optical-sizing: inherit; font-kerning: inherit; font-feature-settings: inherit; font-variation-settings: inherit; vertical-align: baseline; display: inline-block; overflow-wrap: normal; word-spacing: normal; text-wrap: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; position: relative;" tabindex="0">n = Net cash flow at time period
Profitability Index;
It is the ratio of the net present value of cash inflows to the present values of cash outflows. A higher PI index of a project is considered as favourable project.
PI = Present value of cash inflows/ Present value of cash outflows
Benefit-cost Ratio (BCR):
Benefit cost ratio shows the relative cost and benefit of a specific project. The ratio is expressed in monetary or quantitative terms. A project with a BCR greater than 1 is selected.
Hence, the correct answer is (A), (B), (C), and (D) Only.
Q84: Which of the following reasons may be attributed to the individuals time preference for money?
(A) Risk
(B) Value of money would be increased
(C) Future uncertainties
(D) Preference for consumption
(E) Investment opportunities
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), and (C) Only
(b) (B), (C), and (D) Only
(c) (A), (C), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (A), (D), and (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C), (D) and (E) Only.
The correct answer to this question is:
(A), (C), (D), and (E). All four options can be attributed to an individual's time preference for money.
Here's why each option plays a role:
- (A) Risk: People generally prefer present rewards over future ones, even if the future amount is larger, because the future is uncertain and carries risk. Having money now allows them to avoid potential financial risks in the future.
- (C) Future uncertainties: The unknown nature of the future makes future rewards less valuable than present ones. Inflation, unexpected expenses, and changes in financial circumstances can all diminish the value of future income, increasing the preference for present money.
- (D) Preference for consumption: Many people simply prefer immediate gratification and the ability to satisfy current needs or desires, rather than waiting for future benefits. This preference for present consumption contributes to the time preference for money.
- (E) Investment opportunities: Having money now allows you to invest it and potentially receive a return in the future. This potential for growth can make having money now more valuable than receiving the same amount later.
Therefore, all four options contribute to an individual's time preference for money, highlighting how the prospect of immediate benefits, reduced risk, and potential investment opportunities outweigh the promise of future, uncertain rewards
Q85: The variety of approaches to management analysis, the amount of research and the number of different views have resulted in much confusion as to what management is, what management theory and science is and how managerial events should be analysed. Who called this situation 'the management theory jungle'?
(a) Chester Barnard
(b) Elton Mayo
(c) Harold Koontz
(d) Henry L. Gantt
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Harold Koontz.
"The management theory jungle" is a term coined by Harold Koontz. He used this term to describe the confusion and complexity that arises from the variety of approaches to management analysis, the extensive research, and the multitude of different views in the field of management. The term highlights the challenges and diversity in understanding management, management theory, and the analysis of managerial events. Harold Koontz was a management consultant and professor who contributed significantly to the field of management and organizational theory.
Harold Koontz, along with co-author Cyril O'Donnell, wrote the influential management book titled "Principles of Management: An Analysis of Managerial Functions," which was first published in 1955. Koontz was a management consultant, educator, and author, and he made notable contributions to the field of management.
In the book, Koontz and O'Donnell discussed the challenges and complexities within the field of management. They referred to the multitude of theories, approaches, and perspectives as the "management theory jungle." This term reflects the idea that the management field can be likened to a dense and intricate jungle, where various theories and concepts coexist, creating confusion and making it challenging for practitioners and scholars to navigate.
Q86: The Contingency table in statistics is one:
(a) That consists of rows and columns that is used to classify data on two dimensions.
(b) That summarizes the number of measurements which are less than the upper-class boundary of each class.
(c) That summarizes the percentage of items (or measurement) in each of several non-overlapping classes.
(d) That displays points representing each class frequency above their class midpoints.
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is that consists of rows and columns that is used to classify data on two dimensions.
The contingency table consists of rows and columns that are used in classifying two-dimensional data.
Contingency Table:
A contingency table is a table having two rows and columns that are used in presenting categorical data in frequency terms. This table is used in understanding the relationship between two categorical variables.
These tables are used in statistics for measuring the frequency distribution of multiple variables. These tables are used in classifying the outcome of one variable with another variable in rows and columns. These tables can also be created in Microsoft Excel with the help of pivot table tool.
Example of a Contingency Table:
The below contingency table shows sales data for two types of phones among males and females.
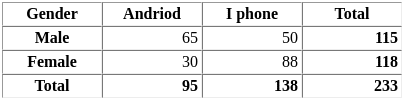
Through this representation of data, one can easily analyze the sales figures of two types of phones among various groups at a glance.
Hence, the correct answer is that consists of rows and columns that is used to classify data on two dimensions.
Q87: Gross working capital refers to firms:
(a) Total Current Assets
(b) The difference between current assets and current liabilities.
(c) Total liquid assets
(d) Total investment in the firms
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Total Current Assets.
Key Points
The gross working capital refers to the total current assets of the firm. Net working capital refers to the difference between the current assets and current liabilities.
Working Capital: Working capital is also known as the net working capital. It is the difference between the company's current assets and current liabilities. Working capital measures the company's liquidity and short-term financial status. A negative working shows that the current liabilities of the company are more than the current assets. A positive working capital of a company shows that the company can fund its current liabilities and make investments in future activities.
Gross Working Capital: Gross working capital refers to the company's total assets. It includes all the current assets like accounts receivable, inventory, and marketable securities. It does not provide a full picture of the company's liquidity position. Gross working capital has more value when a company tracks its changes over time. It is the sum of all the current assets of the firm including the following:
- Cash and cash equivalents: This includes all the cash in hand and certain other investments that have low risk and low investment terms.
- Marketable securities: These are financial instruments that can quickly be converted into cash.
- Interest receivable: This refers to the interest to be received during the year for the investments, loans, or overdue invoices.
- Account receivable: This refers to all the claims for cash to be received during the year for the inventory of goods sold.
- Inventory: Inventories are the unsold goods and raw materials.
Hence, the correct answer is total current assets.
Q88: Which of the following assumptions are based on Walter's Model of dividend ?
(A) Internal Financing
(B) 100 percent pay out ratio
(C) The firm has a short term life
(D) Constant EPS and Dividend per Share (DPS)
(E) Increasing return and minimise cost of Capital
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (B), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (D) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B), (D) only.
Assumptions based on Walter's Model:
- A) Internal Financing: Walter's Model assumes the firm relies solely on internal financing (retained earnings) for future investments, not external sources like debt or equity.
- B) 100 percent pay out ratio: While not always the case, Walter's Model suggests that firms with low return on investment (r < k) might opt for a 100% dividend payout ratio, distributing all earnings to shareholders.
- C) The firm has a short term life: No, Walter's Model applies to firms with an infinite lifespan, allowing for long-term analysis of dividend policy's impact on share value.
- D) Constant EPS and Dividend per Share (DPS): This assumption simplifies the model but isn't crucial. Walter's Model can handle dynamic changes in EPS and dividends.
- E) Increasing return and minimise cost of Capital: This isn't an inherent assumption of the model. While growth firms (r > k) might prioritize reinvestment for higher returns, minimizing capital cost isn't a direct assumption.
Therefore, the correct answer (A, B, and D) aligns perfectly with the core principles of Walter's Model.
Q89: Two sets of theories are popular in the organisational behavior literature - The Behavioral and Cognitive. Behavioral theory constitutes of :
(A) Classical conditioning
(B) Operant conditioning
(C) Perceived consequences
(D) Social learning
(E) Prior learning
(a) (A), (B) and (C) only
(b) (A), (B) and (D) only
(c) (B), (C) and (E) only
(d) (B), (C) and (D) only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (D) only.
The correct statements about Behavioral theories in organizational behavior are:
(A) Classical conditioning
(B) Operant conditioning
(D) Social learning
- Classical conditioning (A): This is a behavioral theory associated with the work of Ivan Pavlov. It involves the process of learning through association, where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus to produce a specific response.
- Operant conditioning (B): This is a behavioral theory associated with B.F. Skinner. It involves learning through consequences, where behavior is strengthened or weakened by the consequences that follow it.
- Social learning (D): Social learning theory, developed by Albert Bandura, emphasizes the role of observational learning and modeling in shaping behavior. Individuals learn by observing others and imitating their actions.
So, the correct answer is (A) Classical conditioning, (B) Operant conditioning, and (D) Social learning.
Q90: Six Sigma is:
(A) a strategy that focuses on total customer satisfaction.
(B) a mathematical function that connects quality lost and cost.
(C) a program to reduce defects.
(D) a disciplines that follows DMAIC model.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (D) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (B), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C) and (D) Only.
The correct answer is:
(A), (C) and (D) Only
- (A) a strategy that focuses on total customer satisfaction: Six Sigma indeed places a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction by striving to deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- (B) a mathematical function that connects quality loss and cost: This statement is not accurate. While Six Sigma involves statistical methods and tools, it is not specifically a mathematical function connecting quality loss and cost.
- (C) a program to reduce defects: Reducing defects is a core objective of Six Sigma. The methodology aims to improve processes, reduce variation, and ultimately minimize defects to enhance overall quality.
- (D) a discipline that follows DMAIC model: The DMAIC model (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) is a key framework within the Six Sigma methodology. It provides a structured approach for process improvement.
So, the correct answer is (A), (C) and (D) Only
Q91: What is the minimum prescribed net profit threshold for Companies to be required to undertake Corporate Social Responsibility activities under clause 135 of the Companies Act, 2013?
(a) 1% of net profit
(b) 2% of net profit
(c) 3% of net profit
(d) 5% of net profit
Ans: b
Sol: The correct option is 2% of net profit.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is the responsibility of businesses/organizations towards the welfare of society, beyond its objective of making profit. Companies need to contribute to the well-being of society through social and environmental measures.
The minimum prescribed net profit threshold for Companies to be required to undertake Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) activities under clause 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 is 2% of the net profit.
Other Related Points
The provisions of CSR applies to companies fulfilling the below mentioned conditions in the preceding financial year:
- Net worth of more than Rs.500 crore
- Turnover of more than Rs.1000 crore
- Net profit of more than Rs.5 crore
Hence, the correct answer is 2% of net profit.
Q92: Match List - I with List - II.
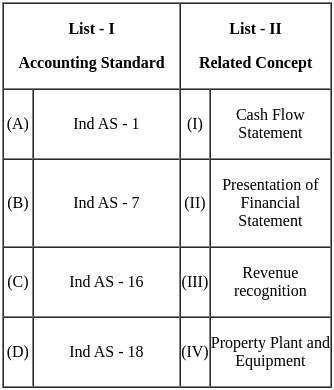
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
(b) (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
(c) (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
(d) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III).
The correct accounting standards are:
- IND AS 1: Financial statements
- IND AS 7- Cash flow statement
- IND AS 16- Property, plant, and equipment
- IND AS 18- Revenue recognition.
Accounting Standards:
Accounting standards are the set of principles and standards that define the basic accounting principles. The Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS) is notified under section 133 of the Companies Act, 2013. It helps in improving the financial reporting in all countries. Accounting standards help in improving the transparency in financial reporting. External entities like banks, investors, and regulatory agencies make use of these standards to ensure that information is relevant and accurate.
The accounting standards in India are issued by the Accounting Standard Board (ASB). This board was established by the Institute of Chartered Accounts in India in the year 1977.
The list of accounting standards is as follows:
Hence, the correct answer is (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III).
Q93: Which of the followings are the national financial institutions?
(A) Industrial Development Bank of India
(B) Industrial Finance Corporation of India
(C) The State Industrial Development Corporation
(D) United Nations Development Programme
(E) State Financial Corporations.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (A), (B), (C) and (E) Only
(d) (A), (C), (D) and (E) Only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C and E only.
- National Financial Institutions work as instruments of public policy.
- They are a group composed of financial regulatory bodies that play a pivotal role in the financial markets.
- The Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDCs), and State Financial Corporations are all national financial institutions in India that provide financial support for industrial development.
They play a crucial role in financing and promoting various industries and projects.
Other Related Points
- IDBI - The IDBI Bank Limited is a development finance institution under the ownership of Life Insurance Corporation of India and Government of India. It was established in 1964 as Industrial Development Bank of India, a development finance institution, which provided financial services to industrial sector.
- IFCI - IFCI Ltd (IFCI) was set up as a Statutory Corporation (“then Industrial Finance Corporation of India”) in 1948 for providing medium and long-term finance to industry.
- SIDCs - The State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDCs) are government enterprises controlled by the state that work to develop and promote medium and big businesses.
- SFC - State Financial Corporations (SFCs) are the financial institutions that were set up by the state governments in India, post-Independence. The objective was to provide credit and other support services to small businesses and farmers.
- Therefore, the correct answer is A, B, C and E only.
Q94: Arrange the Indian Trade Unions/Associations according to their formation/establishment from earlier to later.
(A) Madras Labour Union
(B) Bhartiya Mazdoor Sangh
(C) The Indian National Trade Union Congress
(D) All India Trade Union Congress
(E) The Red Trade Union Congress
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C), (B), (D), (E) Only
(b) (A), (D), (E), (C), (B) Only
(c) (B), (A), (C), (D), (E) Only
(d) (D), (A), (E), (C), (B) Only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (D), (E), (C), (B) Only.
Indian Trade Associations as per their establishment and formation dates:
- Madras Labour Union
- All India Trade Union Congress
- The Red Trade Union Congress
- The Indian National Trade Union Congress
- Bhartiya Mazdoor Sangh
Trade Unions: A trade union is an organization or union of employees formed to secure a diverse range of benefits, rights, and privileges for the workers in an organization. These are voluntary associations of workers. They work collectively through the joint action of members. It is a continuous action body and has permanent or temporary management.
Objectives of trade union:
- To provide steady employment to workers with good pay and normal working conditions.
- To achieve improved terms and conditions of employment for all the members of the union.
- To support the bargaining advantage of the individual against the management.
- To increase the democratic power of the unions.
- To provide legal power to the demand of the workers.
Major Trade Unions of India:
- Madras Labour Union: It was the first labor union formed in 1918 by the textile workers of Madras City. This labor union worked continuously since its formation and did not face any threats from rival organizations.
- All India Trade Union Congress: This was founded in 1920 and its first president was Lala Rajpat Rai. This was the central trade association of India. Currently, this organization has a membership of 3.5 million.
- The Red Trade Union Congress: This organization was formed by S.V Deshpande and B.T.Randive in the year in the year 1931.
- The Indian National Trade Union Congress: It is the largest trade union federation in India. It was formed in the year 1947 in cooperation with Indian National Congress.
- Bhartiya Mazdoor Sangh: This organization was formed on 23rd July 1955 on the birth anniversary of Lok Manya Bal Gangadhar Tilak – a veteran of the Freedom Movement.
Hence, the correct answer is (A), (D), (E), (C), (B) Only.
Q95: Which type of Intrapreneur is known for generating innovative ideas and seeking ways to improve processes?
(a) Employee Intrapreneur
(b) Doers Intrapreneur
(c) Creator Intrapreneur
(d) Implementers Intrapreneur
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Creator Intrapreneur.
Creators intrapreneurs are individuals who are focused on generating new and innovative ideas, often with the goal of improving existing processes or creating entirely new solutions within the organization. They play a key role in driving innovation and contributing to the growth and success of the company.
Other Related Points
reators Intrapreneurs:
- Definition: Creators intrapreneurs are individuals within an organization who excel at generating new and innovative ideas. They are often characterized by their creativity, imagination, and ability to think outside the box.
- Role: In the context of intrapreneurship, creators intrapreneurs are crucial for introducing novel concepts, solutions, and approaches. They contribute to the organization's innovation efforts and are particularly valuable in environments that encourage and reward creative thinking.
- Focus on Process Improvement: Creators intrapreneurs, as mentioned in the original question, are likely to focus on improving processes. They may identify inefficiencies, propose new methods, and seek ways to enhance existing workflows for greater efficiency and effectiveness.
Q96: The objective of Scheduling is to allocate and prioritize demand to available facilities, the Scheduling decisions ranges from years to minutes/hours/days. Arrange the following Scheduling decisions:
(A) Aggregate Planning
(B) Short-term Scheduling
(C) Master Schedule
(D) Capacity Planning
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (A), (C), (D) Only
(b) (D), (A), (C), (B) Only
(c) (A), (D), (C), (B) Only
(d) (B), (C), (A), (D) Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is (B), (C), (A), (D) Only
Scheduling decisions range from long-term capacity planning to short-term job assignments. The sequence should reflect this progression:
- Capacity Planning (D): This is the most strategic and long-term decision. It determines the overall production capacity needed to meet future demand over several years.
- Aggregate Planning (A): This builds upon capacity planning and sets the overall production levels for a specific period (e.g., 3-12 months). It considers factors like demand forecasts, inventory levels, and production costs.
- Master Schedule (C): This further refines the aggregate plan by detailing specific products, quantities, and delivery dates for each period. It translates the general plan into actionable instructions.
- Short-term Scheduling (B): This involves allocating individual jobs to machines or workstations within a given production period (days, hours, or minutes). It considers factors like machine availability, worker skills, and priority of jobs.
Why other options are incorrect:
- (a) (B), (A), (C), (D): This sequence is incorrect because short-term scheduling (B) is placed before the master schedule (C). Short-term scheduling relies on the information provided by the master schedule.
- (c) (A), (D), (C), (B): This sequence is incorrect because aggregate planning (A) should come before the master schedule (C). Aggregate planning determines the overall production quantities, while the master schedule specifies the details of how those quantities will be produced.
- (b) (D), (A), (C), (B): This sequence is incorrect for the same reasons as option (a). Capacity planning (D) is the most long-term decision, followed by aggregate planning (A), master scheduling (C), and then short-term scheduling (B).
Q97: What represents basic convictions that 'a specific mode of conduct or end-state of existence is personally or socially preferable to an opposite or converse mode of conduct or end-state of existence'?
(a) Ethics
(b) Belief
(c) Values
(d) Personality
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Values.
The term that represents "basic convictions that a specific mode of conduct or end-state of existence is personally or socially preferable to an opposite or converse mode of conduct or end-state of existence" is values.
Values are fundamental beliefs that guide our behaviors, decisions, and actions. They represent our core convictions about what is right or wrong, good or bad, and socially acceptable or unacceptable. Values play a crucial role in shaping individual and societal norms, influencing ethical decision-making, and guiding personal and professional conduct.
Other Related Points
Values:
- Definition: Values are the fundamental beliefs or principles that guide and influence our attitudes and behaviors. They are the core convictions about what is important and desirable in life.
- Role: Values serve as a foundation for ethical decision-making. They help individuals determine what is right or wrong, and they influence choices in various aspects of life, including persoal, professional, and social domains.
- Example: Common values include honesty, integrity, fairness, loyalty, and compassion.
Ethics:
- Definition: Ethics refers to the study of what is morally right or wrong and the application of moral principles to guide behavior.
- Role: Ethics provides a framework for evaluating and making decisions based on principles of right and wrong. It often involves considering the consequences of actions and the impact on individuals and society.
- Example: Ethical considerations may include issues such as honesty in business dealings, respect for others' rights, and transparency.
Beliefs:
- Definition: Beliefs are convictions or acceptance that something is true or exists, often without direct proof.
- Role: Beliefs shape an individual's perception of reality and influence attitudes and behaviors. They can be based on personal experiences, cultural upbringing, or societal influences.
- Example: Religious beliefs, political beliefs, and beliefs about personal capabilities are common examples.
Personality:
- Definition: Personality refers to the unique set of individual characteristics, traits, and behaviors that distinguish one person from another.
- Role: Personality influences how individuals approach situations, interact with others, and make decisions. While personality traits can shape behavior, they may not explicitly represent convictions about what is morally preferable.
- Example: Personality traits include extroversion, introversion, openness, conscientiousness, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
Q98: Given below are two statements :
Statement (I): The adaptation of leadership styles to different contingencies has been well characterised by Robert Tannenbaum and Warren H. Schmidt, developers of leadership continuum concept.
Statement (II): They see leadership as involving variety of styles, ranging from one that is highly boss-oriented to one that is highly subordinate centered.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
The two statements describe the concept of the leadership continuum developed by Robert Tannenbaum and Warren H. Schmidt.
- Statement (I) is correct in stating that the adaptation of leadership styles to different contingencies has been well characterized by Tannenbaum and Schmidt.
- Statement (II) is also correct. Tannenbaum and Schmidt's leadership continuum involves a range of leadership styles, from one that is highly boss-oriented (managerial) to one that is highly subordinate-centered (democratic).
So, both statements are accurate and describe the Tannenbaum and Schmidt leadership continuum concept. The most appropriate answer would be that both statements are true.
Statement (I): "The adaptation of leadership styles to different contingencies has been well characterized by Robert Tannenbaum and Warren H. Schmidt, developers of the leadership continuum concept."
Tannenbaum and Schmidt are known for their work on leadership styles and the leadership continuum. Their model suggests that leadership is not a one-size-fits-all concept, and effective leaders adapt their style based on various contingencies or situational factors.
Statement (II): "They see leadership as involving a variety of styles, ranging from one that is highly boss-oriented to one that is highly subordinate-centered."
Tannenbaum and Schmidt's leadership continuum describes a range of leadership styles along a continuum. At one extreme, you have a highly boss-oriented or autocratic style where the leader makes decisions without much input from subordinates. At the other extreme, you have a highly subordinate-centered or democratic style where subordinates are actively involved in decision-making.
In summary, Tannenbaum and Schmidt's leadership continuum recognizes that effective leadership requires adapting to different situations, and the continuum illustrates the spectrum of leadership styles from autocratic to democratic. Leaders must consider factors such as the nature of the task, the maturity of subordinates, and the context to determine the most appropriate leadership style for a given situation.
Q99: Which of the following are cash from financing activities of ?
(A) Cash receipt from issue of share
(B) Cash payment for buy-back of share
(C) Brokerage paid for acquisition of fixed assets
(D) Payment of cash dividend
(E) Cash receipt of interest and dividend on Long-term investment
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) only
(b) (A), (C) and (D) only
(c) (B), (C) and (D) only
(d) (A), (B) and (D) only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is:
(A) Cash receipt from issue of share
(B) Cash payment for buy-back of share
(D) Payment of cash dividend
- (A) Cash receipt from issue of share: This represents cash received by a company when it issues new shares, which is a financing activity.
- (B) Cash payment for buy-back of share: When a company buys back its own shares, it involves a cash outflow, and it is considered a financing activity.
- (C) Brokerage paid for acquisition of fixed assets: This is a cash outflow related to the acquisition of fixed assets and is classified as a cash outflow from investing activities, not financing activities.
- (D) Payment of cash dividend: Payment of cash dividends to shareholders is a cash outflow from financing activities.
- (E) Cash receipt of interest and dividend on Long-term investment: Receipt of interest and dividend on long-term investments is typically considered a cash inflow from investing activities.
So, the correct answer is (A), (B), (D) only.
Q100: The primary difference between CPM and PERT is that:
(a) PERT has one time estimate and CPM has three time estimates.
(b) PERT has two time estimates and CPM has three time estimates.
(c) PERT has three time estimates and CPM requires only one time factor for each activity.
(d) PERT makes the assumption that activities time are known with certainty and CPM employs three time estimates to compute expected values.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is PERT has three time estimates and CPM requires only one time factor for each activity.
The primary difference between Critical Path Method (CPM) and Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is:
- PERT has three time estimates, and CPM requires only one time factor for each activity.
- PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique):
- PERT uses three time estimates for each activity: optimistic time (a), pessimistic time (b), and most likely time (m). These estimates are then used to calculate an expected duration time for each activity, incorporating a probability distribution.
- CPM (Critical Path Method):
- CPM typically uses a single time estimate for each activity. The time estimate used in CPM is the most likely time (m). CPM assumes a deterministic approach, where activity durations are assumed to be known with certainty.
In summary, while PERT introduces variability and uncertainty in activity durations by using three time estimates, CPM takes a deterministic approach with a single time estimate for each activity.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Management 13th Dec 2023 Shift 1 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and what subjects does it cover? |  |
| 2. How is the UGC NET Management paper structured? |  |
| 3. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET Management exam? |  |
| 4. What preparation strategies can be effective for UGC NET Management candidates? |  |
| 5. Are there any specific books or resources recommended for UGC NET Management preparation? |  |





















