UGC NET Paper 2: Management 9th Jan 2025 Shift 2 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Which of the following are functions of Management Information System (MIS)?
A. To support tactical and operational decision making
B. To process data into meaningful information
C. To predict future data trends
D. To develop artificial intelligence algorithm
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C and D only
(c) A and B only
(d) A and C only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A and B only
Key Points
To support tactical and operational decision making
- Management Information Systems (MIS) provide relevant data to managers at various levels to assist in making tactical and operational decisions.
- The objective is to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of decision-making processes.
To process data into meaningful information
- MIS transforms raw data into useful information through processing, which helps organizations in planning, controlling, and operations.
- This processed information is critical for managers to understand trends and make informed decisions.
Additional Information
Predict future data trends
- While MIS can provide historical data that may help in predicting future trends, the primary function is not to predict future data trends directly.
- Predictive analytics and data mining are more specialized fields focused on forecasting future trends.
Develop artificial intelligence algorithm
- MIS is not specifically designed to develop AI algorithms; its focus is more on providing timely and relevant information for management purposes.
- AI development is a specialized field within computer science and engineering.
Q2: Strategic analysis is concerned with evaluating the organization in terms of which of the following.
(a) Mission, corporate appraisal
(b) Market segmentation, product selection
(c) Selection of competitors, choice of distribution channel
(d) Manpower planning, manpower inventory
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Mission, corporate appraisal
Key Points
Strategic analysis
- Involves evaluating the organization's mission to ensure alignment with long-term objectives.
- Includes conducting a corporate appraisal to understand the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis).
- Ensures that the organization's strategies are aligned with its core values and business goals.
Additional Information
SWOT Analysis
- A framework used to evaluate an organization's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
- Helps in identifying internal and external factors that can impact the organization's success.
Mission Statement
- A concise explanation of the organization's purpose and the unique value it provides to its customers.
- Guides the organization in making strategic decisions and aligns efforts towards achieving its vision.
Corporate Appraisal
- Involves analyzing the organization's current performance, resources, and capabilities.
- Used to identify areas for improvement and potential growth opportunities.
Q3: In Job Analysis, broadening of job design directly results in what, among the following?
(a) Employee motivation and job satisfaction
(b) Autonomy of employees
(c) 360° feed back
(d) Better pay
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Employee motivation and job satisfaction
Key Points
Employee motivation and job satisfaction
- Broadening job design typically involves adding variety and responsibility to a job.
- This can lead to increased employee engagement and a sense of ownership over their work.
- It can result in higher levels of motivation because employees feel their work is more meaningful and impactful.
- Improved job satisfaction can occur as employees find their jobs more fulfilling and challenging.
Additional Information
Job Design
- Job design refers to the process of organizing tasks, duties, and responsibilities into a productive unit of work.
- Effective job design can lead to higher levels of productivity and employee morale.
Autonomy of Employees
- While autonomy can also enhance job satisfaction, it primarily focuses on giving employees the freedom to make decisions about their work.
- It is often a component of broader job design but is not the direct result of broadening job design.
360° Feedback
- This is a performance appraisal method that includes feedback from supervisors, peers, and subordinates.
- It is not directly related to job design but rather to performance evaluation and management.
Better Pay
- Better pay can contribute to job satisfaction but is often a result of compensation policies rather than job design itself.
- Broadening job design may sometimes lead to better pay if additional responsibilities warrant it, but this is not a guaranteed outcome.
Q4: Arrange the following Accounting standard (Ind-AS) according to their number in ascending order.
A. Cash flow statement
B. Income Tax
C. Revenue
D. Property Plant and Equipment
E. Borrowing Cost
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, A, C, D, E
(b) E, A, B, C, D
(c) A, B, D, C, E
(d) A, B, D, E, C
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A, B, D, C, E
Key Points
Cash Flow Statement (Ind-AS 7)
- Ind-AS 7 deals with the presentation of the cash flow statement.
- It provides information about the cash and cash equivalents and the changes in the cash flows of an entity.
Income Taxes (Ind-AS 12)
- Ind-AS 12 prescribes the accounting treatment for income taxes.
- It covers both the current tax and deferred tax.
Property, Plant and Equipment (Ind-AS 16)
- Ind-AS 16 outlines the accounting requirements for property, plant, and equipment (PPE).
- It includes the recognition, measurement, and depreciation of assets.
Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Ind-AS 115)
- Ind-AS 115 specifies the accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers.
- It establishes a comprehensive framework for recognizing revenue.
Borrowing Costs (Ind-AS 23)
- Ind-AS 23 prescribes the accounting treatment for borrowing costs.
- It requires the capitalization of borrowing costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition, construction, or production of a qualifying asset.
Additional Information
Ind-AS Series
- The Ind-AS (Indian Accounting Standards) are converged standards with IFRS.
- They are issued by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- Ind-AS are applicable to companies in India and are designed to bring accounting practices in line with global standards.
Objective of Ind-AS
- The objective is to ensure that the financial statements provide reliable and comparable information.
- They help in enhancing the transparency and credibility of financial reporting.
Implementation
- Ind-AS are implemented in a phased manner, with certain standards applicable to specific classes of companies.
- Companies are required to comply with these standards for the preparation of their financial statements.
Q5: What is the sequence of consumer readiness to try new products?
A. Early majority
B. Early Adopters
C. Innovators
D. Laggards
E. Late Majority
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, D, A, E
(b) C, B, A, E, D
(c) C, B, A, D, E
(d) C, B, E, A, D
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - C, B, A, E, D
Key Points
Innovators (C)
- These are the first individuals to adopt an innovation.
- They are willing to take risks and are often seen as the most adventurous in trying new products.
Early Adopters (B)
- These individuals adopt new products shortly after the innovators.
- They are often opinion leaders and provide feedback to the masses.
Early Majority (A)
- These consumers adopt new products just before the average person.
- They are deliberate and tend to adopt new ideas just before the average person.
Late Majority (E)
- These individuals adopt an innovation after the average person has tried it.
- They are skeptical and adopt new ideas only after the majority of society has accepted them.
Laggards (D)
- These are the last individuals to adopt an innovation.
- They are bound by tradition and very conservative, adopting new products only when it becomes absolutely necessary.
Additional Information
Diffusion of Innovations Theory
- Developed by E.M. Rogers, this theory explains how, why, and at what rate new ideas and technology spread through cultures.
- It categorizes adopters of innovations into five groups: Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, and Laggards.
Characteristics of Innovators
- Risk-takers and highly social.
- Have financial liquidity and are well-educated.
Characteristics of Early Adopters
- Opinion leaders and influencers in their communities.
- They help trigger the critical mass and are seen as respectable.
Adoption Process
- The process includes stages such as awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, and adoption.
- Understanding this process helps in effective marketing strategies to target each group.
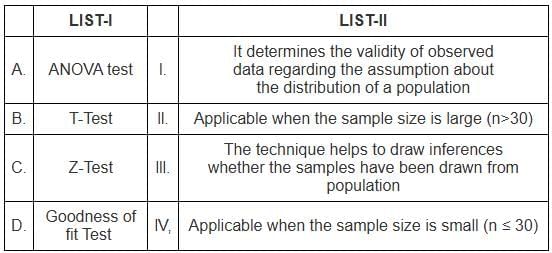
Q6: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(b) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Key Points
ANOVA test
- This technique helps to draw inferences whether the samples have been drawn from the same population.
T-Test
- It is applicable when the sample size is small (n ≤ 30).
Z-Test
- It is applicable when the sample size is large (n > 30).
Goodness of fit Test
- It determines the validity of observed data regarding the assumption about the distribution of a population.
Additional Information
ANOVA Test
- ANOVA stands for Analysis of Variance.
- It is used to compare means among three or more groups to understand if at least one group mean is statistically different from the others.
T-Test
- The T-Test is a statistical hypothesis test used to determine if there is a significant difference between the means of two groups.
- It is commonly used in small sample sizes.
Z-Test
- The Z-Test is used when the sample size is large, and the population variance is known.
- It is applied to test hypotheses about the mean of the population.
Goodness of Fit Test
- This test is used to determine how well sample data fit a distribution from a population with a normal distribution.
- It is used in hypothesis testing to see if a sample matches the population.
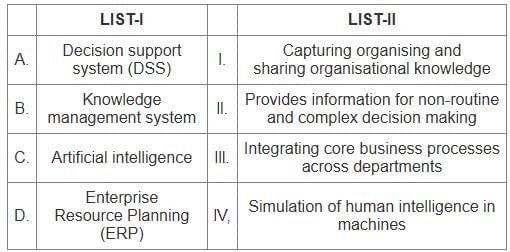
Q7: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(b) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Key Points
Decision Support System (DSS)
- Provides information for non-routine and complex decision-making.
- Supports managers in making informed decisions with the help of data analysis and modeling tools.
Knowledge Management System
- Involves capturing, organizing, and sharing organizational knowledge.
- Aims to improve efficiency and decision-making by ensuring that knowledge is accessible and reusable.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines.
- Enables machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning and problem-solving.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Involves integrating core business processes across departments.
- Aims to streamline and automate processes to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business operations.
Additional Information
Decision Support Systems (DSS)
- Comprise various tools and technologies designed to assist with complex decision-making processes.
- Examples include executive information systems, data warehouses, and business intelligence applications.
Knowledge Management Systems (KMS)
- Utilize databases, document management systems, and other tools to store and retrieve knowledge.
- Support collaboration and knowledge sharing within an organization.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Encompasses a broad range of technologies, including machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics.
- AI systems can be classified into weak AI (designed for specific tasks) and strong AI (with generalized cognitive abilities).
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Integrates various functions such as accounting, human resources, procurement, and supply chain management into a unified system.
- Prominent ERP software includes SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics.
Q8: Arrange the steps in ethical decision making :
A. Decision making and implementation
B. Identification of all stakeholders
C. Getting All the Facts
D. Applying an ethical framework
E. Finding the Subject
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) C, E, B, D, A
(c) C, E, B, A, D
(d) C, E, A, B, D
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - C, E, B, D, A
Key Points
Getting All the Facts
- This is the first step, crucial for understanding the situation completely before making any decisions.
- Ensures that all relevant information is considered to avoid biased or uninformed decisions.
Finding the Subject
- Identify the core issue that requires an ethical decision.
- Helps to narrow down the focus on what needs to be addressed specifically.
Identification of all stakeholders
- Recognizing everyone who will be affected by the decision.
- Ensures that the decision considers the impact on all relevant parties.
Applying an ethical framework
- Use ethical principles or theories to evaluate the options.
- Provides a structured approach to determine the most ethical course of action.
Decision making and implementation
- Make the final decision based on the analysis and implement it.
- Involves putting the decision into action and monitoring its outcomes.
Additional Information
Ethical Frameworks
- Common frameworks include Utilitarianism, Deontology, Virtue Ethics, and Care Ethics.
- Each framework offers a different approach to evaluating ethical dilemmas.
Stakeholder Analysis
- Identifying stakeholders involves considering both direct and indirect effects of the decision.
- Helps to ensure fairness and prevent harm to overlooked groups.
Implementation
- Effective implementation requires clear communication and monitoring of outcomes.
- Feedback mechanisms should be in place to adjust the decision if necessary.
Q9: Which of the following are correct formulas of Financial leverage (FL)?
A. 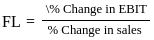
B. 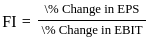
C. 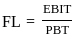
D. 
E. 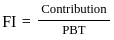
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) A and E only
(d) B and C only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct formulas for Financial Leverage are:
Financial Leverage measures how earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) impact earnings per share (EPS).
Valid formulas include:
- EBIT / EBT (Earnings Before Interest and Tax divided by Earnings Before Tax)
- Percentage change in EPS divided by percentage change in EBIT
Based on this, only the formulas shown in options B and C are correct.
Therefore, the answer is option D (B and C only).
Q10: Which of the following techniques is used for project management in operations research?
(a) PERT
(b) EOQ
(c) VAM
(d) LCM
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - PERT
Key Points
PERT
- PERT stands for Program Evaluation and Review Technique.
- It is a project management tool used to plan, schedule, and control large and complex projects.
- PERT helps in identifying the critical path and the minimum time required to complete a project.
- It involves the use of a network diagram that represents the project activities and their dependencies.
Additional Information
EOQ
- EOQ stands for Economic Order Quantity.
- It is an inventory management technique used to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs.
- This model considers factors such as ordering costs and holding costs.
VAM
- VAM stands for Vogel's Approximation Method.
- It is a heuristic method used to find an initial feasible solution for transportation problems.
- This method helps in minimizing the total transportation cost.
LCM
- LCM stands for Least Common Multiple.
- It is a mathematical concept used to find the smallest multiple that is exactly divisible by two or more numbers.
- LCM is widely used in problems involving fractions and synchronization of cycles.
Q11: Arrange the process of selection in proper sequence.
A. Reference Check
B. Interview
C. Medical Examination
D. Application Review
E. Hiring Decision
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D, C, E
(b) D, B, C, A, E
(c) D, A, B, E, C
(d) A, D, B, C, E
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - D, B, C, A, E
Key Points
D, B, C, A, E
- The selection process typically begins with the Application Review, where candidate resumes and applications are initially screened.
- Next, candidates who pass the initial screening are invited for an Interview to assess their qualifications and suitability for the role.
- Following the interview, a Medical Examination may be conducted to ensure the candidate is fit for the job.
- A Reference Check is performed to verify the candidate's previous employment and background.
- Finally, the Hiring Decision is made based on the accumulated information from the previous steps.
Additional Information
Application Review
- This is the first step in the hiring process where resumes and applications are screened to shortlist candidates.
- It involves checking for basic qualifications, experience, and skills relevant to the job.
Interview
- Interviews can be conducted in various formats such as one-on-one, panel, or group interviews.
- The purpose is to evaluate the candidate's suitability, skills, and cultural fit for the organization.
Medical Examination
- This step ensures that the candidate meets the physical requirements of the job.
- It may involve a general health check-up and specific tests related to the job's demands.
Reference Check
- References are usually previous employers or colleagues who can provide insights into the candidate's work ethic and performance.
- This step helps verify the accuracy of the candidate's resume and interview responses.
Hiring Decision
- The final decision is made after considering all the information gathered from the previous steps.
- The decision-makers evaluate the best fit for the role and extend an offer to the selected candidate.
Q12: If risk free rate is 7 percent, beta of equity is 1.2, and market risk premium is 8 percent. What is cost of equity?
(a) 16.6 percent
(b) 16.4 percent
(c) 9.6 percent
(d) 18 percent
Ans: a
Sol: To find the cost of equity using the CAPM formula:
- The formula is: Cost of Equity = Risk-Free Rate + (Beta × Market Risk Premium)
- Here, the risk-free rate is 7%, beta is 1.2, and the market risk premium is 8%.
Plug the values into the formula:
- Cost of Equity = 7% + (1.2 × 8%)
- Cost of Equity = 7% + 9.6% = 16.6%
So, the cost of equity is 16.6 percent.
Q13: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
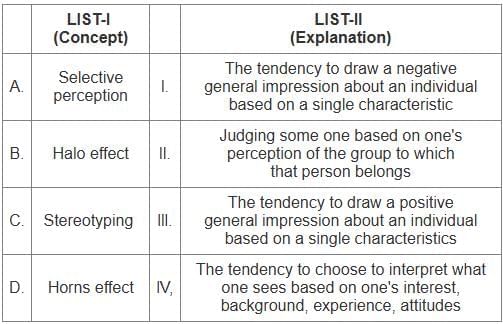
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(b) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - I, B -I I, C - III, D - IV
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Key Points
Selective perception
- Refers to the tendency to interpret what one sees based on one’s interests, background, experience, and attitudes.
Halo effect
- Involves the tendency to draw a positive general impression about an individual based on a single characteristic.
Stereotyping
- Judging someone based on one's perception of the group to which that person belongs.
Horns effect
- The tendency to draw a negative general impression about an individual based on a single characteristic.
Additional Information
Perception
- Perception is a process by which individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions to give meaning to their environment.
Attribution Theory
- Describes how individuals attempt to explain the causes of behavior and events, often categorizing them as either internal (personal control) or external (situational factors).
Self-fulfilling prophecy
- A prediction that causes itself to become true due to the behavior of the believer.
Q14: Which of the following C's should online marketers focus on to create an effective website design?
A. Commerce
B. Connection
C. Contour
D. Content
E. Context
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Only A, B, C, D and E
(b) Only B, D and C
(c) Only B, C, D and E
(d) Only A, B, D and E
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Only A, B, D, and E
Key Points
Commerce
- Commerce refers to the ability to conduct transactions and generate revenue through the website.
- It is a crucial aspect for online marketers focusing on sales and monetization.
Connection
- Connection involves creating a strong relationship with the audience.
- This can be achieved through interactive features and social media integrations.
Content
- High-quality content is essential to attract and retain visitors.
- It includes blog posts, videos, and other media that provide value to the audience.
Context
- Context refers to the relevance and personalization of the content.
- It ensures that the content is aligned with the users' needs and preferences.
Additional Information
Contour
- Contour is not typically a focus area for effective website design in the context of online marketing.
- It generally refers to the shape or outline of a design, which is less critical than the other elements listed.
Online Marketing Strategies
- Successful online marketing incorporates various strategies including SEO, content marketing, and social media engagement.
- Each strategy should align with the broader goals of commerce, connection, content, and context.
Q15: Which of the following labour laws are meant for providing social security?
A. The Employees' State Insurance Act 1948
B. The Industrial Disputes Act 1947
C. The Payment of Gratuity Act 1972
D. The Workmen’s Compensation Act 1923
E. The Companies Act, 2013
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) B, D and E only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) C, D and B only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A, C and D only
Key Points
The Employees' State Insurance Act 1948
- Provides social security and medical care to employees.
- Includes benefits such as sickness, maternity, and employment injury benefits.
The Payment of Gratuity Act 1972
- Ensures payment of gratuity to employees upon termination of employment.
- Gratuity is a lump sum paid to an employee as a mark of recognition for their service.
The Workmen's Compensation Act 1923
- Provides compensation to employees for injuries sustained at work.
- Covers situations like permanent/partial disablement or death due to employment-related accidents.
Additional Information
The Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Primarily deals with the settlement of industrial disputes between employers and employees.
- Provides mechanisms for the investigation and settlement of industrial disputes.
The Companies Act, 2013
- Regulates the incorporation, responsibilities, and dissolution of companies.
- Focuses on corporate governance, rather than labor rights or social security.
Q16: In services marketing the service quality highly depends on:
(a) Internal marketing
(b) Interactive marketing
(c) Service marketing
(d) External marketing
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Interactive marketing
Key Points
Interactive marketing
- Refers to the real-time interaction between service providers and customers.
- It involves direct engagement and communication, ensuring that the service meets the customer's needs and expectations.
- This interaction is crucial in shaping the customer's perception of service quality.
- Examples include customer service interactions, consultations, and face-to-face service delivery.
Additional Information
Internal marketing
- Focuses on training and motivating employees to provide high-quality service.
- It ensures that employees understand their roles and are committed to the organization's goals.
Service marketing
- Involves promoting and selling services, rather than products.
- It includes the strategies and techniques used to attract and retain customers.
External marketing
- Refers to traditional marketing efforts directed at potential and current customers.
- It includes advertising, public relations, and promotions.
Q17: With reference to the consumer decision-making process, which of the following sets consists of brands that consumers are indifferent to because they are viewed as having no significant advantage?
(a) Sample Set
(b) Incentivized set
(c) Inert set
(d) Inappropriate set
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Inert set
Key Points
Inert set
- The inert set consists of brands that consumers are indifferent to.
- These brands are neither seen as particularly good or bad, leading to no significant advantage in the minds of consumers.
- Consumers do not include these brands in their consideration set due to lack of perceived value.
Additional Information
Consumer Decision-Making Process
- Includes stages such as problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior.
- Understanding these stages helps marketers influence consumer decisions at each point.
Consideration Set
- This is the subset of brands that a consumer considers acceptable for future purchase.
- Brands in the consideration set have a significant advantage over those in the inert set.
Evoked Set
- Refers to brands that come to mind when a consumer thinks about a product category.
- These are brands the consumer is aware of and may consider purchasing.
Q18: Arrange the following in the order in which the following appear in the cost sheet.
A. Prime cost
B. Factory cost
C. Material Consumed
D. Cost of production
E. Cost of sales
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B , C, D, E
(b) C, A, D, B, E
(c) A, C, B, D, E
(d) C, A, B, D, E
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - C, A, B, D, E
Key Points
Material Consumed
- The cost of materials consumed is the first item to be recorded in the cost sheet.
- This includes the cost of raw materials used in production.
Prime Cost
- Prime cost is calculated next and includes the direct costs of production, i.e., direct materials, direct labor, and direct expenses.
- It is a sum of material consumed and other direct costs.
Factory Cost
- The total cost incurred to manufacture goods, including prime cost and factory overheads.
- Factory overheads include indirect materials, indirect labor, and other indirect manufacturing costs.
Cost of Production
- This includes the total factory cost plus administrative expenses related to production.
- It gives a complete picture of the cost to produce the goods.
Cost of Sales
- The final figure includes the cost of production plus selling and distribution expenses.
- This represents the total cost incurred to sell the goods produced.
Additional Information
Cost Sheet
- A cost sheet is a statement showing the various components of total cost of a product.
- It helps in determining the selling price of a product and controlling the cost of production.
Direct Costs
- Direct costs are those that can be directly attributed to the production of a specific product.
- Examples include direct materials and direct labor.
Indirect Costs
- Indirect costs are those that cannot be directly linked to a specific product.
- They include overheads like indirect labor and indirect materials.
Overheads
- Overheads are the ongoing expenses of operating a business that are not directly attributable to a specific product or service.
- They are divided into categories like factory overheads, administrative overheads, and selling and distribution overheads.
Q19: Which of the following theories corresponds to the statement 'A type of conditioning in which desired voluntary behaviour leads to a reward or prevents a punishment'.
(a) Social learning theory
(b) Classical conditioning theory
(c) Behaviorism theory
(d) Operant conditioning theory
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Operant conditioning theory
Key Points
Operant conditioning theory
- Developed by B.F. Skinner, operant conditioning involves learning through the consequences of voluntary behavior.
- A reward or a punishment is used to reinforce or discourage behavior.
- Behaviors followed by positive outcomes are more likely to be repeated, while those followed by negative outcomes are less likely to be repeated.
Additional Information
Social learning theory
- Proposed by Albert Bandura, this theory emphasizes learning through observation and modeling of others' behavior.
- It incorporates both cognitive and environmental factors in the learning process.
Classical conditioning theory
- Developed by Ivan Pavlov, this theory involves learning through the association of a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response.
- It is primarily concerned with involuntary, reflexive behaviors.
Behaviorism theory
- A broader theory that focuses on the study of observable and measurable behavior, often associated with John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner.
- Emphasizes the role of environmental stimuli in shaping behavior.
Q20: Innovation in text and voice messaging is an example of what type of innovation. Choose one option from the following:
(a) Radical Innovation
(b) Breakthrough Innovation
(c) Technological Innovation
(d) Ordinary Innovation
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Technological Innovation
Key Points
Technological Innovation
- Innovation in text and voice messaging represents the application of new technologies to improve or create communication methods.
- This type of innovation focuses on the development and implementation of new technological tools and systems.
- Technological innovation can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, functionality, and user experience.
Additional Information
Types of Innovation
Radical Innovation
- Involves creating entirely new industries or markets.
- Examples include the invention of the airplane or the internet.
Breakthrough Innovation
- Represents substantial technological advancements that significantly alter existing products or services.
- Examples include the development of the smartphone.
Ordinary Innovation
- Involves incremental improvements or updates to existing products or services.
- Examples include annual updates to software applications.
Q21: Match List I with List II:
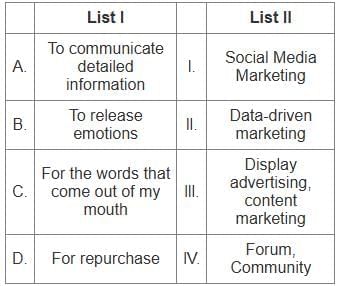
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Key Points
To communicate detailed information
- Matched with Display advertising, content marketing because these methods are often used to provide in-depth information about products or services.
To release emotions
- Matched with Social Media Marketing as social media platforms are commonly used for expressing emotions and engaging with audiences.
For the words that come out of my mouth
- Matched with Forum, Community as these platforms facilitate discussions and the exchange of verbal communication.
For repurchase
- Matched with Data-driven marketing because this approach uses customer data to encourage repeat purchases and loyalty.
Additional Information
Display advertising
- Involves visual ads placed on websites, social media, and other digital platforms to engage viewers and communicate detailed product information.
Content marketing
- Focuses on creating valuable and relevant content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience.
Social Media Marketing
- Utilizes social platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to connect with the audience, share content, and build brand loyalty.
Forum, Community
- Online spaces where users can post discussions, ask questions, and share knowledge. Examples include Reddit, Quora, and specialized forums.
Data-driven marketing
- Uses data analytics to understand customer behavior and preferences, enabling personalized marketing strategies that enhance customer experience and encourage repeat purchases.
Q22: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(b) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
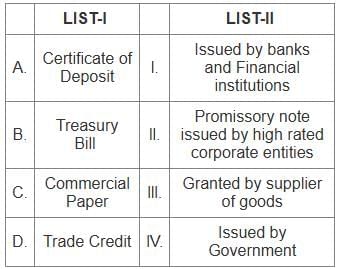
Key Points
Certificate of Deposit
- Issued by banks and financial institutions.
Treasury Bill
- Issued by the government.
Commercial Paper
- Promissory note issued by high-rated corporate entities.
Trade Credit
- Granted by supplier of goods.
Additional Information
Certificate of Deposit (CD)
- A time deposit with a bank.
- Usually negotiable and can be traded in the secondary market.
Treasury Bills (T-Bills)
- Short-term government securities with maturities ranging from a few days to 52 weeks.
- Highly liquid and considered risk-free.
Commercial Paper (CP)
- Unsecured, short-term debt instrument.
- Used by corporations to finance payroll, accounts payable, and inventories.
Trade Credit
- Credit extended by suppliers to their customers.
- Facilitates the financing of inventory and operational expenses.
Q23: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - IV, B - II, C - I, D - III
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
Key Points
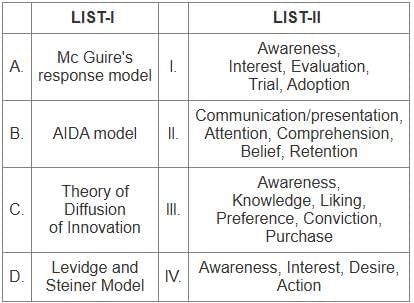
McGuire's response model
- Aligns with Awareness, Interest, Desire, and Action in the AIDA model.
- This model emphasizes the sequence of stages through which a consumer progresses in response to marketing communications.
AIDA model
- Stands for Awareness, Interest, Desire, and Action.
- Describes the steps a consumer goes through before making a purchase.
Theory of Diffusion of Innovation
- Includes stages like Awareness, Interest, Evaluation, Trial, and Adoption.
- Explains how, why, and at what rate new ideas and technology spread through cultures.
Levidge and Steiner Model
- Includes stages such as Awareness, Knowledge, Liking, Preference, Conviction, and Purchase.
- Describes the process consumers go through when making purchasing decisions.
Additional Information
Hierarchy of Effects Model
- Similar to the Levidge and Steiner Model, it includes stages: Awareness, Knowledge, Liking, Preference, Conviction, and Purchase.
- Focuses on the sequence of steps leading to a consumer's purchase decision.
DAGMAR Model
- Stands for Defining Advertising Goals for Measured Advertising Results.
- Includes the stages of Awareness, Comprehension, Conviction, and Action.
- Focuses on setting specific advertising goals and measuring the effectiveness of advertising campaigns.
Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM)
- Focuses on how people process persuasive communication and the likelihood of them elaborating on the information.
- Includes two routes to persuasion: the central route and the peripheral route.
Q24: A data warehouse is primarily:
(a) A system used for transaction processing
(b) A tool for generating real time analysis
(c) A database for unstructured data storage
(d) A central repository for integrated data
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A central repository for integrated data
Key Points
A central repository for integrated data
- A data warehouse serves as a consolidated database where data from multiple sources is stored.
- It is designed to store structured data for analysis, reporting, and data mining purposes.
- The data is integrated from various operational systems, making it consistent and reliable.
- It supports historical analysis by storing large amounts of historical data, which is crucial for trend analysis and decision-making.
Additional Information
Transaction Processing Systems
- These systems are designed for real-time data processing and handle day-to-day transactional data.
- They are optimized for fast query processing and high transaction throughput.
Real-Time Analysis
- Involves analyzing data as it is created and collected, often using systems designed for real-time processing.
- Data warehouses are typically used for batch processing and historical data analysis, not real-time analysis.
Unstructured Data Storage
- Refers to systems designed to store unstructured data such as text, images, and videos.
- Data warehouses primarily store structured data in a highly organized manner.
Q25: Which components of an MIS involve gathering and storing data?
(a) Hardware
(b) Software
(c) Data processing
(d) Database
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Database
Key Points
Database
- A Database is a structured collection of data that is stored and accessed electronically.
- In the context of a Management Information System (MIS), the Database is used to gather, store, and manage data.
- It ensures data is organized in a manner that allows for efficient retrieval and use for decision-making processes.
- This component is crucial for maintaining the integrity, security, and consistency of the data stored.
Additional Information
Hardware
- Refers to the physical devices and equipment used in an MIS, such as servers, computers, and networking devices.
- Hardware is essential for the operation of software applications and databases but does not directly involve data gathering and storage.
Software
- Includes the programs and applications used to process and analyze data within an MIS.
- While software is crucial for data processing, it relies on the database to store and retrieve the data it manipulates.
Data processing
- Involves the transformation of raw data into meaningful information through various computational techniques.
- This process is dependent on both software and the database but does not constitute the gathering and storing of data itself.
Q26: Alex F. Osborn is known as the father of?
(a) Bounded rationality
(b) Invention
(c) Heuristics
(d) Brainstorming
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Brainstorming
Key Points
Brainstorming
- Alex F. Osborn is renowned for introducing the concept of Brainstorming.
- This technique involves a group of people coming together to generate ideas and solutions in a spontaneous and unstructured manner.
- Osborn's method emphasizes quantity over quality during the initial idea-generation phase, encouraging participants to think freely and creatively.
- Brainstorming is widely used in various fields such as business, education, and creative arts to foster innovative thinking and problem-solving.
Additional Information
Bounded Rationality
- Concept introduced by Herbert A. Simon, describing the limitations of human decision-making processes due to constraints in information and cognitive capacity.
Invention
- Refers to the creation of a new device, method, or process, often attributed to inventors such as Thomas Edison or Nikola Tesla.
Heuristics
- Simple, efficient rules or strategies used by individuals to make decisions and solve problems quickly, often studied in the context of cognitive psychology.
Q27: Which one of the following is related to Cash Flow Statement?
(a) Ind AS-2
(b) Ind AS-3
(c) Ind AS-16
(d) Ind AS-7
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Ind AS-7
Key Points
Ind AS-7
- This standard deals specifically with the preparation and presentation of Cash Flow Statements.
- It requires an entity to provide information about the historical changes in cash and cash equivalents through a cash flow statement.
- The cash flow statement must classify cash flows during the period as arising from operating, investing, and financing activities.
- It helps users of financial statements to evaluate the changes in net assets and the entity's ability to generate cash and cash equivalents.
Additional Information
Ind AS-2
- This standard deals with the valuation of inventories.
- It provides guidance on the determination of cost and its subsequent recognition as an expense, including any write-down to net realizable value.
Ind AS-3
- Note: Ind AS-3 is not currently in use under Indian Accounting Standards. It was previously related to Consolidated Financial Statements under older standards.
Ind AS-16
- This standard deals with Property, Plant, and Equipment.
- It provides guidelines on the recognition, measurement, and depreciation of property, plant, and equipment.
Q28: Choose the correct sequence from the given steps of enterprise registration process:
A. Obtaining a digital signature certificate
B. File for incorporation
C. Deciding your business structure
D. File for name approval
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D, C
(b) C, A, D, B
(c) C, B, D, A
(d) A, D, C, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - C, A, D, B
Key Points
Deciding your business structure
- This is the initial step as it determines the legal and operational framework of your enterprise.
- Options include sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability partnership (LLP), or private limited company.
Obtaining a digital signature certificate
- A digital signature certificate (DSC) is required for filing forms electronically with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- It ensures the security and authenticity of the documents submitted.
File for name approval
- After obtaining the DSC, the next step is to apply for the approval of the company name with the MCA.
- This ensures that the proposed name is unique and not in conflict with existing entities.
File for incorporation
- This is the final step where you file the incorporation documents with the MCA to legally register your company.
- Documents include the Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA).
Additional Information
Business Structure
The choice of business structure affects tax obligations, liability, and the ability to raise capital.
Common structures include:
- Sole Proprietorship: Simplest form, owned and operated by one person.
- Partnership: Owned by two or more individuals, sharing profits and liabilities.
- LLP: Combines the benefits of a partnership and limited liability.
- Private Limited Company: Separate legal entity, providing limited liability to its shareholders.
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
- Issued by certifying authorities in India such as eMudhra, Sify, and NSDL.
- It is necessary for e-filing documents under the Information Technology Act, 2000.
There are three types of DSCs:
- Class 1: Basic level, for securing email communications.
- Class 2: For verifying the identity of a person against a trusted pre-verified database.
- Class 3: Highest level, used for e-commerce and online transactions.
Name Approval
- The proposed name should comply with the Companies Act, 2013, and the Company (Incorporation) Rules, 2014.
- It must not be identical or similar to an existing company or trademark.
Incorporation Process
- Involves filing the SPICe+ form (Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company Electronically Plus).
- Includes details like the company's address, director identification numbers (DIN), and share capital.
Q29: The decision making process in MIS can be classified into which levels?
(a) Operational, Tactical, Strategic
(b) Local, National, Global
(c) Financial, Managerial, Operational
(d) Direct, Indirect, Strategic
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Operational, Tactical, Strategic
Key Points
Operational
- Deals with day-to-day operations of the organization.
- Focuses on short-term tasks and activities that support tactical and strategic plans.
- Examples include inventory management, scheduling, and data entry.
Tactical
- Involves mid-level management and focuses on the implementation of strategies.
- Plans are usually short- to medium-term and are designed to achieve specific objectives.
- Examples include marketing campaigns, budget allocations, and workforce management.
Strategic
- Involves top-level management and focuses on long-term goals and overall direction.
- Encompasses the overall vision and mission of the organization.
- Examples include mergers and acquisitions, market expansion, and major investment decisions.
Additional Information
Information Systems in Management
- Management Information Systems (MIS) support managerial functions by providing relevant data and reports.
- These systems help in decision-making processes at all levels - operational, tactical, and strategic.
Decision-Making Process
- Involves problem identification, data collection, solution generation, and implementation.
- Effective decision-making requires accurate and timely information, which MIS provides.
Examples of MIS
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS).
Q30: Identify the accurate sequence of the Marketing Process.
A. Construct an integrated marketing programme that delivers superior value
B. Capture value from customers to create profit and customer equity
C. Build profitable relationship and create customers' delight
D. Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants
E. Design a customer-driven marketing strategy
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) D, E, A, C, B
(c) D, E, A, B, C
(d) D, A, E, C, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - D, E, A, C, B
Key Points
Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants
- This is the starting point of the marketing process where companies must gather data and insights about customer needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Effective market research helps in identifying target markets and understanding customer pain points.
Design a customer-driven marketing strategy
- Based on the insights gathered, companies develop strategies that focus on delivering value to the target customers.
- This involves segmenting the market, targeting specific segments, and positioning the brand effectively.
Construct an integrated marketing programme that delivers superior value
- This step involves the implementation of marketing strategies through various marketing mix elements - product, price, place, and promotion.
- The goal is to create a comprehensive marketing plan that ensures consistent and superior value to customers.
Build profitable relationship and create customers' delight
- Fostering strong, long-term relationships with customers is crucial for sustained success.
- Delivering exceptional customer experiences and maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction are key objectives.
Capture value from customers to create profit and customer equity
- The final step involves capturing the value generated from customers in the form of sales, market share, and customer loyalty.
- Successful value capture leads to increased profitability and customer equity, ensuring the long-term growth of the company.
Additional Information
Market Segmentation
- Involves dividing a broad target market into subsets of consumers who have common needs and priorities.
- Segmentation allows companies to target different segments with tailored marketing strategies.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- CRM systems help companies manage interactions with current and potential customers.
- CRM tools are used to improve business relationships, focusing on customer retention and driving sales growth.
Value Proposition
- The value proposition is a statement that explains how a product solves a problem, delivers benefits, and why it is better than alternatives.
- It is a crucial part of a company's overall marketing strategy.
Q31: A Company is expected to pay dividend of Rs. 60 at the end of year one. The dividend is expected to grow at 10% indefinitely. The cost of equity is 20%. The intrinsic value of the share will be?
(a) Rs. 660
(b) Rs. 600
(c) Rs. 300
(d) Rs. 330
Ans: b
Sol: The intrinsic value of the share can be found using the Gordon Growth Model:
- The formula is: Intrinsic Value = Dividend / (Cost of Equity – Growth Rate)
- Here, the expected dividend is Rs. 60, the growth rate is 10% (0.10), and the cost of equity is 20% (0.20).
- Substitute the values:
Intrinsic Value = 60 / (0.20 – 0.10) = 60 / 0.10 = Rs. 600
So, the intrinsic value of the share is Rs. 600.
Additional Information
Gordon Growth Model
- This model is commonly used for valuing companies with stable dividend growth.
- It assumes that dividends will continue to grow at a constant rate indefinitely.
Cost of Equity
- It represents the return that investors expect for investing in a company.
- Higher cost of equity indicates higher risk associated with the company’s equity.
Dividend Growth Rate
- This rate represents the expected annual rate at which dividends are projected to grow.
- It is a crucial component in determining the future value of dividends.
Q32: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Key Points
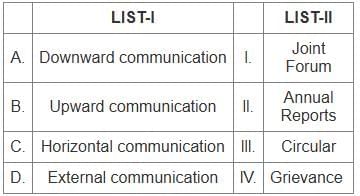
Downward communication
- Involves messages sent from higher levels to lower levels in the organizational hierarchy.
- Common methods include circulars, memos, and instructions.
Upward communication
- Refers to messages sent from lower levels to higher levels in the organizational hierarchy.
- Includes methods such as grievance mechanisms, feedback forms, and reports.
Horizontal communication
- Involves communication between peers or colleagues at the same hierarchical level.
- Often occurs in joint forums where collaboration and coordination are required.
External communication
- Includes communication that occurs between the organization and external entities.
- Examples are annual reports, press releases, and marketing materials.
Additional Information
Downward communication
- Ensures that employees receive clear and precise instructions.
- Helps in disseminating organizational goals and policies.
Upward communication
- Enables management to understand employee concerns and issues.
- Facilitates better decision-making by incorporating feedback from various levels.
Horizontal communication
- Enhances cooperation and teamwork among employees.
- Reduces misunderstandings and improves efficiency in project execution.
External communication
- Builds and maintains the organization’s image and reputation.
- Ensures transparency and accountability through public disclosures.
Q33: Which of the following are examples of Management Information system (MIS)?
A. Transaction Processing System (TPS)
B. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
C. Operating System Kernel (OSK)
D. Decision Support System (DSS)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) B and C only
(c) A and C only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A, B and D only
Key Points
Transaction Processing System (TPS)
- TPS is a type of Management Information System (MIS) that handles the collection, storage, and processing of transactional data.
- Examples include systems used in retail sales, banking, and order processing.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- ERP systems integrate various functions such as finance, HR, and inventory management into one complete system to streamline processes and information across the organization.
- It serves as a comprehensive Management Information System (MIS) by providing critical data to decision-makers.
Decision Support System (DSS)
- DSS are computer-based systems that support managerial decision-making by providing useful information and models.
- They are part of Management Information Systems (MIS) and help in analyzing complex data to aid in making strategic decisions.
Additional Information
Operating System Kernel (OSK)
- The OSK is the core component of an operating system that manages system resources and hardware.
- It is not a type of Management Information System (MIS) as it primarily deals with low-level system operations rather than organizational data management.
Q34: Which of the following is a disadvantage of the 'Critical Incident Method of Performance Appraisal'?
(a) Difficult to rate or rank employees relative to one another
(b) Time consuming
(c) Standards may be unclear
(d) Halo effect bias can be a problem
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Difficult to rate or rank employees relative to one another
Key Points
Difficult to rate or rank employees relative to one another
- In the Critical Incident Method, performance is evaluated based on specific incidents rather than overall performance, which can make comparative evaluations challenging.
- This method focuses on qualitative aspects of individual performance, complicating the process of establishing a clear, quantitative ranking.
- Relative comparisons are essential for decision-making in promotions and compensations, and this method does not provide a straightforward way to achieve this.
Additional Information
Time consuming
- The Critical Incident Method requires meticulous documentation of incidents, which can be time-consuming for managers.
- This detailed recording can be cumbersome and may not be feasible in fast-paced work environments.
Standards may be unclear
- Without clear standards, there can be inconsistencies in what is considered a critical incident, affecting the fairness of the evaluation.
- Managers may have different interpretations, leading to biased assessments.
Halo effect bias
- The Halo Effect can occur if a manager's overall impression of an employee influences their judgment of specific incidents.
- This bias can lead to either overly positive or overly negative evaluations, compromising the objectivity of the appraisal.
Q35: The vertical distance between the Total cost (TC) curve and the Total Variable cost (TVC) curve reflects:
(a) The law of diminishing returns
(b) The average fixed cost at each level of output
(c) Marginal cost at each level of output
(d) Average variable cost at each level of output
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - The average fixed cost at each level of output
Key Points
The average fixed cost at each level of output
- The vertical distance between the Total Cost (TC) and Total Variable Cost (TVC) curves is due to the presence of fixed costs.
- At any given level of output, the Total Fixed Costs (TFC) remain constant, and hence, the distance between the TC and TVC curves represents these fixed costs.
- The Average Fixed Cost (AFC) is calculated by dividing total fixed costs by the output level, which can be observed as the vertical distance between the TC and TVC curves divided by the quantity of output.
Additional Information
Total Cost (TC)
- Represents the sum of Total Fixed Costs (TFC) and Total Variable Costs (TVC) at each level of output.
- Formula: TC = TFC + TVC.
Total Variable Cost (TVC)
- Represents costs that vary with the level of output, such as raw materials, labor, etc.
- These costs increase as production increases.
Average Fixed Cost (AFC)
- Calculated by dividing Total Fixed Costs (TFC) by the quantity of output produced.
- Formula: AFC = TFC / Q, where Q is the quantity of output.
Q36: Arrange the steps involved in building data warehouse:
A. Data extraction from source system
B. Data transformation and cleaning
C. Data storage in the warehouse
D. Data presentation and reporting
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D
(b) A, C, D, B
(c) B, D, C, A
(d) D, C, B, A
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A, B, C, D
Key Points
Data extraction from source system (A)
- This is the first step where data is collected from various source systems.
- It involves identifying and capturing relevant data for the data warehouse.
Data transformation and cleaning (B)
- In this step, the extracted data is transformed into a suitable format.
- Data cleaning is done to remove errors and ensure data quality.
Data storage in the warehouse (C)
- The cleaned and transformed data is then loaded into the data warehouse.
- This step ensures that data is organized for efficient querying and analysis.
Data presentation and reporting (D)
- In the final step, the data is presented to users through reports and dashboards.
- This allows for data analysis and decision-making based on the stored data.
Additional Information
ETL Process
- ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load.
- It is a critical process for data warehousing and involves extracting data from various sources, transforming it to fit operational needs, and loading it into the target database.
Data Quality
- Ensuring data quality is crucial during the transformation and cleaning phase.
- Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate reports and decision-making.
Data Integration
- Data warehousing involves integrating data from multiple sources into a single repository.
- This integration helps in creating a unified view of the data for analysis.
Q37: Marketing logistics means.
(a) Managing upstream and downstream storage and warehousing facilities to meet consumer requirements
(b) Emphasizing teamwork both inside the company and among all the marketing channel organisations
(c) Planning implementation and controlling physical flow of materials, final goods and related information from points of origin to points of consumption to meet customer requirements at a profit
(d) Combining two or more modes of transportation of goods from place of production to place of distribution
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Planning implementation and controlling physical flow of materials, final goods and related information from points of origin to points of consumption to meet customer requirements at a profit
Key Points
Marketing logistics
- Refers to the planning, implementation, and control of the physical flow of materials, final goods, and related information.
- The goal is to move these from points of origin to points of consumption efficiently and effectively.
- This is done to meet customer requirements at a profit.
Additional Information
Components of Marketing Logistics
Order processing
- Involves the steps from the moment a customer places an order to the final delivery of the product.
Warehousing
- Includes storing goods until they are needed for production or consumption.
Inventory management
- Ensures that the right quantity of goods is available at the right time.
Transportation
- Involves the movement of goods from one location to another.
Importance of Marketing Logistics
- Enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely delivery of products.
- Helps in cost reduction through efficient logistics processes.
- Improves inventory management and reduces excess stock.
- Supports company profitability by optimizing logistics operations.
Q38: Which of the following statements pertaining to indifference curve is true?
A. The slope of the indifference curve represents the marginal rate of substitution between two goods
B. Indifference curve in case of perfect substitutes is a straight line with positive slope
C. Two indifference curves intersect with each other in case of perfectly complementary goods
D. Indifference curves intersect with each other at their mid point
E. In case of perfect substitutes, the indifference curves are linear
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and E only
(b) A and B only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) A, D, and E only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A and E only
Key Points
A
- The slope of the indifference curve represents the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) between two goods.
- The MRS indicates the rate at which a consumer is willing to substitute one good for another while maintaining the same level of satisfaction.
E
- In the case of perfect substitutes, the indifference curves are linear.
- Perfect substitutes have a constant MRS, which results in straight-line indifference curves.
Additional Information
Perfect Substitutes
- Perfect substitutes are goods that a consumer can replace with another good at a constant rate without affecting their utility.
- Examples include different brands of bottled water or different colors of the same model of a car.
Indifference Curves
- Indifference curves are used to represent consumer preferences graphically.They show combinations of two goods that give the consumer the same level of satisfaction.
- Indifference curves are typically convex to the origin, reflecting a diminishing MRS.
Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS)
- MRS measures the rate at which a consumer can give up some amount of one good in exchange for another good while maintaining the same level of utility.
- It is represented by the slope of the indifference curve at any given point.
Q39: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(d) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Key Points
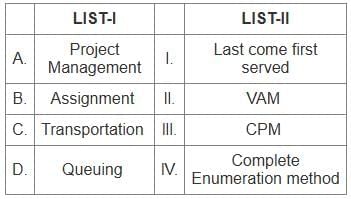
A - Project Management (III - CPM)
- CPM stands for Critical Path Method, a project management tool used to determine the longest sequence of tasks in a project.
B - Assignment (IV - Complete Enumeration method)
- The Complete Enumeration method is used in assignment problems to find the optimal assignment of tasks to resources.
C - Transportation (II - VAM)
- VAM stands for Vogel's Approximation Method, a technique used to find an initial feasible solution to a transportation problem.
D - Queuing (I - Last come first served)
- Last come first served (LCFS) is a queuing method where the most recently arrived entity is the first to be served.
Additional Information
Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Helps in identifying the most critical tasks that affect the project completion time.
- Ensures efficient scheduling and management of project activities.
Complete Enumeration Method
- A brute-force approach to find the optimal solution by evaluating all possible assignments.
- Ensures accuracy but can be computationally intensive for large problems.
Vogel's Approximation Method (VAM)
- Provides a good initial feasible solution which can be improved using other optimization techniques.
- Helps in minimizing the transportation cost effectively.
Queuing Theory
- Analyzes various queue configurations to optimize service efficiency.
- Common methods include FCFS (First Come First Served) and LCFS (Last Come First Served).
Q40: Which of the following are the execution styles for execution of advertising message?
A. Fantasy
B. Fashion
C. Slice of life
D. Testimonials
E. Life style
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C, D and E only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) A, B, D and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A, C, D and E only
Key Points
A, C, D and E only
- These execution styles are commonly used in advertising to effectively convey the advertising message.
- Fantasy involves using imaginative and often unrealistic elements to capture the audience's attention.
- Slice of Life depicts everyday situations that the target audience can easily relate to, making the advertisement more impactful.
- Testimonials use endorsements from real people or celebrities to build trust and credibility for the product or service.
- Lifestyle focuses on portraying the product in a setting that matches the lifestyle of the target audience, emphasizing how the product fits into their lives.
Additional Information
Fantasy
- Creates an escape for the audience, often using surreal settings or magical elements.
- Effective for products that benefit from a sense of wonder or aspiration.
Slice of Life
- Shows real-life scenarios that the average consumer faces, making the product appear as a solution to everyday problems.
- Highly relatable and can build a strong connection with the audience.
Testimonials
- Leveraging satisfied customers or influencers adds credibility.
- Can include before-and-after comparisons, enhancing trustworthiness.
Lifestyle
- Focuses on how the product enhances the consumer's lifestyle.
- Often used for products related to fashion, tech, or luxury items.
Q41: Theory given by McClelland emphasizes on which key factor related to entrepreneurship? Choose one option from the following:
(a) Innovation
(b) Political system
(c) Achievement
(d) Cultural values
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Achievement
Key Points
Achievement
- Mc Clelland's theory emphasizes the need for achievement as a key factor in entrepreneurship.
- Entrepreneurs are driven by a strong desire to accomplish challenging goals and attain a sense of personal fulfillment.
- This theory suggests that individuals with a high need for achievement are more likely to take calculated risks and innovate.
- The need for achievement motivates entrepreneurs to seek out opportunities for growth and success.
Additional Information
McClelland's Theory of Needs
- McClelland's Theory of Needs, also known as the Three Needs Theory, identifies three primary drivers: achievement, affiliation, and power.
- Achievement- The desire to excel and succeed.
- Individuals motivated by achievement seek challenging tasks and strive for excellence.
- Affiliation- The need for friendly and close interpersonal relationships.
- People driven by affiliation seek harmony and prefer cooperative situations over competitive ones.
- Power- The need to influence or control others.
- Individuals with a high need for power desire to impact and direct others and can thrive in leadership positions.
Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurship involves the process of designing, launching, and running a new business.
- Entrepreneurs are characterized by their innovation, risk-taking, and proactive approach to identifying and exploiting business opportunities.
- McClelland's theory helps understand the intrinsic motivations that drive entrepreneurs to pursue and achieve their business goals.
Q42: Outstanding wages is which type of Account?
(a) Personal Account
(b) Real Account
(c) Nominal Account
(d) Nominal and Real Account
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Personal Account
Key Points
Personal Account
- Outstanding wages refer to the wages that are due but have not yet been paid.
- In accounting, outstanding wages are considered a liability.
- Liabilities are classified under Personal Accounts because they represent amounts owed to other parties (i.e., employees in this case).
- Personal Accounts deal with accounts of persons, firms, companies, etc.
Additional Information
Types of Accounts
- Personal Accounts: These include accounts related to individuals, firms, companies, etc. They are used to record transactions related to entities with whom the business has direct dealings.
- Real Accounts: These accounts relate to assets and liabilities, such as land, buildings, machinery, etc. Real accounts are also known as permanent accounts as they are not closed at the end of the accounting year.
- Nominal Accounts: These are related to expenses, losses, incomes, and gains. They are temporary accounts that are closed at the end of the accounting period.
Golden Rules of Accounting
- Personal Account: Debit the receiver, credit the giver.
- Real Account: Debit what comes in, credit what goes out.
- Nominal Account: Debit all expenses and losses, credit all incomes and gains.
Q43: Which of the following is the pre-testing technique of measuring advertisement effectiveness.
(a) Portfolio tests
(b) Aided Recall test
(c) Attitude tests
(d) Inquiry test
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Portfolio tests
Key Points
Portfolio tests
- These are used to measure the effectiveness of advertisements before they are launched.
- In this technique, a portfolio of test and control advertisements is presented to a sample of the target audience.
- Participants are asked to evaluate the advertisements, typically through recall and recognition measures.
- The responses are analyzed to determine which advertisements are most effective in conveying the intended message.
Additional Information
Other Advertisement Effectiveness Techniques
Aided Recall test
- Participants are shown an advertisement and then asked specific questions to gauge their recall ability.
- This test helps in understanding how well the advertisement is remembered by the audience.
Attitude tests
- These tests measure the change in the audience's attitude towards a product or brand after being exposed to an advertisement.
- They help in understanding the persuasive power of the advertisement.
Inquiry test
- This technique measures the number of inquiries or responses generated by an advertisement.
- It is often used in direct marketing and sales promotion campaigns.
Q44: From the following options, choose the correct sequence of parts of a business plan that ideally come after one another.
A. Executive summary
B. Management and organization plan
C. Description of Business
D. Financial plan
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, B, D, A
(b) A, B, C, D
(c) A, C, B, D
(d) C, B, A, D
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A, C, B, D
Key Points
Executive summary (A)
- The Executive summary is typically the first section of a business plan, providing an overview of the key points.
- It includes essential information like the business concept, financial features, and current business position.
Description of Business (C)
- The Description of Business follows the executive summary and provides a detailed explanation of what the business does.
- This section covers the business model, products/services, market, and competitive advantage.
Management and organization plan (B)
- The Management and organization plan outlines the business structure, ownership, and management team.
- It includes information about the roles and responsibilities of key team members.
Financial plan (D)
- The Financial plan is the final section of the business plan, detailing financial projections and funding requirements.
- This includes income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets.
Additional Information
Importance of a Business Plan
- A business plan is a crucial document for outlining the strategy and direction of a business.
- It helps in securing funding from investors and lenders by providing a clear roadmap for growth and profitability.
Components of a Business Plan
- Other important sections can include market analysis, marketing and sales strategy, and product line description.
- Each section plays a critical role in demonstrating the viability and potential success of the business.
Q45: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
Ans: c
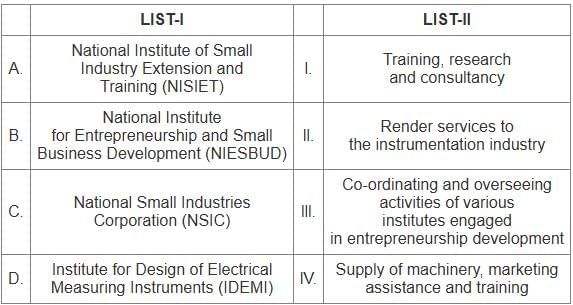
Sol: The correct answer is - A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
Key Points
National Institute of Small Industry Extension and Training (NISIET) - Training, research and consultancy
- NISIET focuses on training and development of small industries through research and consultancy services.
National Institute for Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development (NIESBUD) - Co-ordinating and overseeing activities of various institutes engaged in entrepreneurship development
- NIESBUD works to coordinate and oversee the activities of different organizations involved in entrepreneurship development.
National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) - Supply of machinery, marketing assistance and training
- NSIC provides machinery on hire-purchase basis, gives marketing assistance and conducts training for small industries.
Institute for Design of Electrical Measuring Instruments (IDEMI) - Render services to the instrumentation industry
- IDEMI offers specialized services to the instrumentation industry, including design and development.
Additional Information
Small Industries Development
- Organizations like NISIET and NIESBUD are crucial for the development of small industries through focused training and entrepreneurship programs.
- These institutes help in promoting and supporting small businesses by providing necessary skills and resources.
Instrumentation Industry
- IDEMI plays a significant role in the instrumentation industry by offering design and development services, which are essential for technological advancement.
- It helps in upgrading the skills of professionals in the field through various training programs.
Q46: Which of the following has increased the importance of strategic planning due to the liberalization of the economy?
(a) Change in the technological environment
(b) Change in the career expectations of people at house hold level
(c) Rapid change in competitive forces in the business environment due to the entry of multinational corporations
(d) Growing cases of labour regulations and laws
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Rapid change in competitive forces in the business environment due to the entry of multinational corporations
Key Points
Rapid change in competitive forces in the business environment due to the entry of multinational corporations
- The liberalization of the economy has led to the entry of multinational corporations into various markets.
- This entry has resulted in a significant increase in competition among businesses.
- Companies are now required to engage in strategic planning to maintain their competitive edge and adapt to the dynamic market conditions.
- Strategic planning helps businesses to identify opportunities and threats posed by the new entrants and to develop strategies to leverage their strengths and mitigate weaknesses.
Additional Information
Globalization
- Globalization has made it easier for companies to expand internationally and access new markets.
- This expansion necessitates the development of strategic plans that consider global competitive dynamics.
- Firms must adapt to different regulatory environments, cultural differences, and local market needs.
Technological Advancements
- Rapid technological changes require businesses to continuously update their strategic plans.
- Technological innovation can create new opportunities and disrupt existing business models.
- Companies must invest in research and development to stay ahead of technological trends.
Market Deregulation
- Deregulation in various industries has increased the level of competition.
- Businesses must be agile and develop strategic plans that allow them to navigate deregulated environments.
- Deregulation can lead to price competition, innovation, and the entry of new players in the market.
Q47: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - IV, B - II, C - I, D - III
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Key Points
Coaching
- Involves educating, instructing, and training subordinates to improve their performance.
Career
- The occupational positions a person has had over many years, reflecting their professional journey.
Mentoring
- Involves advising, counseling, and guiding individuals to help them grow professionally.
Career anchors
- The pivots around which a person's career swings, representing their core values and preferences.
Additional Information
Coaching vs. Mentoring
- Coaching is typically task-oriented and short-term, focusing on improving specific skills.
- Mentoring is relationship-oriented and long-term, focusing on overall professional development and career growth.
Importance of Career Anchors
- Understanding one's career anchors can help in making career decisions that align with personal values and strengths.
- Common career anchors include technical competence, managerial competence, autonomy, and security.
Career Development
- Effective career development involves a combination of coaching, mentoring, training, and self-assessment.
- Organizations often provide career development programs to support employee growth and retention.
Q48: Choose the option that represents the sequence of steps involved in capital budgeting analysis?
A. Identification of investment / project
B. Application of capital budgeting technique
C. Forecasting the cash flows
D. Accept/reject decision
E. Calculation of cash flow after tax
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, B, D, E
(b) A, C, E, D, B
(c) A, E, C, B, D
(d) A, C, E, B, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A, C, E, B, D.
Key Points
Option 4: A, C, E, B, D
- Identification of investment/project (A): The first step in capital budgeting is identifying potential investment opportunities or projects.
- Forecasting the cash flows (C): After identifying the project, the next step is to forecast the cash flows that the project will generate over its lifetime.
- Calculation of cash flow after tax (E): Once the cash flows are forecasted, they need to be adjusted for taxes to get the net cash flows.
- Application of capital budgeting technique (B): Various capital budgeting techniques like Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Payback Period are then applied to evaluate the project.
- Accept/reject decision (D): Based on the results of the capital budgeting techniques, a decision is made to either accept or reject the project.
Additional Information
Capital Budgeting Techniques
- Net Present Value (NPV): Calculates the present value of cash inflows minus the present value of cash outflows. A positive NPV indicates a good investment.
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): The discount rate at which the NPV of all the cash flows from a project is zero. Projects with an IRR higher than the cost of capital are generally considered good investments.
- Payback Period: The amount of time it takes for an investment to generate an amount of cash flows to recover its initial cost. Shorter payback periods are preferred as they indicate quicker recovery of the investment.
Importance of Tax Adjustments
- Tax adjustments are crucial as they affect the net cash flows, and hence the valuation of the project.
- Ignoring taxes can lead to overestimating the profitability and feasibility of the project.
Q49: Which of the following options is related to training for developmental strategy of rural entrepreneurship?
(a) Skill enhancement
(b) Construction of modern infrastructure
(c) Credit Assistance
(d) Integrating Government Efforts
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Skill enhancement
Key Points
Skill enhancement
- Essential for the development of entrepreneurial capabilities in rural areas.
- Involves training programs aimed at improving technical and managerial skills.
- Enables rural entrepreneurs to effectively manage and grow their businesses.
- Facilitates the adoption of modern techniques and innovations in agriculture and rural industries.
Additional Information
Construction of modern infrastructure
- While important for rural development, it is more related to providing facilities rather than directly enhancing skills.
- Includes development of roads, electricity, and internet connectivity, which are supportive but not primary training activities.
Credit Assistance
- Focuses on providing financial support to rural entrepreneurs.
- Includes loans, subsidies, and grants, but does not directly address skill development.
Integrating Government Efforts
- Involves coordination of various government schemes and policies.
- Aims to ensure comprehensive support for rural entrepreneurship but not specifically focused on training.
Q50: Which of the following is part of corporate level strategies?
A. Concentration strategies
B. Retrenchment strategies
C. Simultaneous and sequential
D. Stakeholder analysis map
E. Stability strategies
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C and D only
(b) A, B, C and E only
(c) B, C, D and E only
(d) A and B only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A, B, C and E only
Key Points
Corporate level strategies
- These strategies are designed for the overall scope and direction of the entire organization.
- They include decisions regarding which industries or markets the firm will compete in, and how resources will be allocated among the different businesses.
Concentration strategies
- Focus on a single product or market.
- Aim to achieve growth by concentrating resources in a specific area.
Retrenchment strategies
- Involve reducing the company’s level of activities.
- These strategies can include downsizing or divesting parts of the business.
Simultaneous and sequential
- Refer to the methods of implementing strategies.
- Simultaneous implementation means executing multiple strategies at the same time.
- Sequential implementation involves executing strategies one after the other.
Stability strategies
- Focus on maintaining the current status quo.
- Aim to sustain current levels of performance and market position.
Additional Information
Stakeholder analysis map
- It is not typically categorized as a corporate-level strategy.
- This tool is used to identify and analyze stakeholders' needs and expectations.
- Helps in understanding the influence and interest of various stakeholders on the organization's activities.
Resource allocation
- Critical to the success of corporate-level strategies.
- Involves distributing resources among different business units to achieve strategic objectives.
Q51: If Current Ratio is 3.5 : 1 and Quick Ratio is 2 : 1. If excess of current assets over quick assets represented by inventories is Rs 24000. Calculate current assets.
(a) 32000
(b) 16000
(c) 48000
(d) 56000
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - 56000
Key Points
Current Ratio
- The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures a company's ability to pay short-term obligations or those due within one year.
- It is calculated as Current Assets divided by Current Liabilities. In this case, the current ratio is given as 3.5 : 1.
Quick Ratio
- The quick ratio is a measure of a company's short-term liquidity position and its ability to meet its short-term obligations with its most liquid assets.
- It is calculated as (Current Assets - Inventory) / Current Liabilities. In this case, the quick ratio is given as 2 : 1.
Calculation
- Let Current Liabilities be Rs X.
- Current Assets = 3.5X.
- Quick Assets = 2X.
- Excess of Current Assets over Quick Assets = Inventory = 3.5X - 2X = Rs 24000.
- Therefore, 1.5X = 24000, which gives X = 24000 / 1.5 = 16000.
- Current Assets = 3.5X = 3.5 * 16000 = Rs 56000.
Additional Information
Liquidity Ratios
- Liquidity ratios are financial metrics used to determine a company's ability to pay off its short-term debts obligations.
- Common liquidity ratios include the current ratio and the quick ratio.
Importance of Inventory in Liquidity Ratios
- Inventory is included in the current ratio but excluded in the quick ratio because it is not considered as liquid as other current assets.
- Companies with high inventory levels might have a strong current ratio but a weak quick ratio.
Practical Applications
- These ratios are used by investors and creditors to gauge the liquidity and financial health of a business.
- Maintaining an appropriate balance between current and quick assets is crucial for ensuring sufficient liquidity without holding excessive non-liquid assets.
Q52: Which of the following options indicates that the small industrial unit is sick?
A. The unit's borrowing account remains below the standard level.
B. Accumulated losses lead to erosion of capital
C. The unit has been in commercial production for at least two years
D. Lack of commitment from management
E. Competitors are thriving
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Only A, B and C
(b) Only B, C and D
(c) Only A, C, D and E
(d) Only A, B और D
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Only A, B, and D
Key Points
Accumulated losses lead to erosion of capital
- This indicates that the unit has been operating at a loss for an extended period, leading to the depletion of its financial resources.
- Such financial erosion is a clear sign of a sick industrial unit.
The unit's borrowing account remains below the standard level
- When a unit continuously fails to meet its borrowing obligations, it signifies financial instability.
- This is a strong indicator that the unit is struggling and likely in a sick state.
Lack of commitment from management
- Effective management is crucial for the success of any business.
- A lack of managerial commitment can lead to poor decision-making and operational inefficiencies, contributing to the unit's sickness.
Additional Information
Commercial production for at least two years
- This criterion is typically used to assess the performance of a unit over a reasonable period.
- However, it alone does not indicate sickness; it must be considered alongside financial and managerial indicators.
Competitors are thriving
- While this can be a concern, it is not a direct indicator of a unit's sickness.
- Thriving competitors may indicate market opportunities or threats, but they do not necessarily reflect the internal health of a unit.
Q53: In which of the following cases there will be flow of fund?
A. Purchase of furniture for cash
B. Payment of outstanding wages for cash
C. Purchase of building by issue of shares
D. Payment of creditor by issue of debenture
E. Cash collection from debtors
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) A, D, E only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) A and D only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A and D only
Key Points
Flow of funds
- Flow of funds refers to the movement of money or financial resources from one account to another.
- It typically involves a change in the financial position of the business.
Purchase of furniture for cash (Option A)
- Involves a cash outflow and an increase in the asset (furniture).
- This transaction reflects a flow of funds because it affects the cash balance.
Payment of creditor by issue of debenture (Option D)
- Involves issuing debentures to settle a liability (creditor).
- This transaction reflects a flow of funds as it changes the nature of the liability.
Additional Information
Non-flow of funds
- Payment of outstanding wages for cash (Option B): This involves a decrease in cash and a corresponding decrease in liability (outstanding wages). It does not reflect a flow of funds as it is merely a settlement of an existing liability without affecting the overall financial position.
- Purchase of building by issue of shares (Option C): This involves issuing shares in exchange for a building. There is no movement of cash or other financial resources; hence, it does not reflect a flow of funds.
- Cash collection from debtors (Option E): This involves receiving cash from debtors, which increases cash and decreases receivables. This does not reflect a flow of funds as it is just a conversion of one asset into another.
Q54: Which of the following factors are based on situation in the process of perception?
A. Similarity
B. Time
C. Work setting
D. Experience
E. Social setting
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) A, B and D only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - B, C and E only
Key Points
Factors based on situation
- The process of perception can be influenced by various situational factors.
- Time (B) is a situational factor as it affects how we perceive events depending on when they occur.
- The work setting (C) also influences perception, as the environment and context in which one works can alter their perception.
- Additionally, the social setting (E) plays a significant role in perception, as social contexts and interactions can shape how one perceives situations and individuals.
Additional Information
Other Influencing Factors
- Similarity (A) is more related to the characteristics of the stimuli rather than the situational context.
- Experience (D) impacts perception through past knowledge and learning, rather than the immediate situational factors.
Q55: 'Strategic Drift' occurs when:
(a) Organizations deliberately move towards innovation
(b) There is a mismatch between the organisation strategy and its external environment over time
(c) Organizations implement successful strategies consistently
(d) Firms experience rapid growth and expansion
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - There is a mismatch between the organisation strategy and its external environment over time
Key Points
Strategic Drift
- Occurs when there is a misalignment between an organization's strategy and its external environment over time.
- This misalignment can lead to the organization becoming less effective in achieving its goals and maintaining competitiveness.
- It often happens gradually, making it difficult to identify and address in its early stages.
Additional Information
Causes of Strategic Drift
- Changes in the external environment, such as new technologies, market conditions, or regulatory changes.
- Internal factors like organizational inertia and resistance to change.
- Lack of strategic vision or foresight by leadership.
Consequences of Strategic Drift
- Decline in organizational performance and effectiveness.
- Loss of competitive advantage in the market.
- Potential need for major strategic change or turnaround efforts to realign with the external environment.
Preventing Strategic Drift
- Regularly reviewing and updating the organizational strategy to ensure alignment with the external environment.
- Encouraging a culture of innovation and adaptability within the organization.
- Maintaining strong leadership that can foresee changes and make necessary adjustments proactively.
Q56: Amongst the following options what are inclusive of opportunity recognition process?
A. Risk taking ability
B. Prior knowledge of markets and customer problems
C. Entrepreneurial alertness
D. Networks
E. Availability of job opportunities
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) A, B, D and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - B, C and D only
Key Points
Prior knowledge of markets and customer problems
- Essential for identifying unmet needs and potential opportunities.
- Helps in creating solutions that are relevant and have a higher success probability.
Entrepreneurial alertness
- Involves being aware of and responsive to new business opportunities.
- Allows entrepreneurs to spot opportunities that others might miss.
Networks
- Provide access to resources, information, and support.
- Enable entrepreneurs to leverage relationships for business development.
Additional Information
Risk taking ability
- While crucial for entrepreneurship, it is not specific to the opportunity recognition process.
Availability of job opportunities
- This factor is more related to employment markets and does not directly impact the process of recognizing entrepreneurial opportunities.
Q57: Which of the following are the types of surface level diversity in an organisation?
A. Age
B. Sexual orientation
C. Number aptitude
D. Physical Disability
E. Length of Tenure
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, and D only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) A, D and E only
(d) B, D and E only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A, D, and E only
Key Points
Surface-level diversity
- Refers to the observable attributes such as age, physical disability, and length of tenure in an organization.
- These attributes are easily identifiable and often used in initial impressions.
Age
- It is a visible characteristic that can influence interactions within the workplace.
Physical Disability
- It refers to observable physical conditions that can impact workplace dynamics.
Length of Tenure
- Refers to the duration an individual has been with the organization, which is a surface-level attribute.
Additional Information
Deep-level diversity
- Refers to attributes that are not immediately observable, such as values, personality, and work preferences.
- These characteristics become apparent over time through interactions and communication.
Sexual Orientation
- While significant, it is often considered a deep-level attribute as it is not immediately visible.
Number Aptitude
- Refers to cognitive abilities and is considered a deep-level attribute.
Q58: Which queuing model represents a situation in which a customer comes to a bank counter every five minutes and it takes exactly five minutes for a banker to serve a customer?
(a) Poisson- Exponential Single Server
(b) Poisson- Exponential Multi Server
(c) Poisson Exponential Binary Server
(d) Determinant
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Determinant
Key Points
Determinant
- Deterministic models assume that all events occur at exact intervals, with no randomness.
- In the given situation, a customer arrives every five minutes, and it takes exactly five minutes to serve them, indicating a predictable and fixed pattern.
- This type of model is suitable for systems where the timing of arrivals and service is known and constant.
Additional Information
Poisson-Exponential Models
- These models are used in queuing theory to describe systems where arrivals and service times are random.
- In a Poisson process, arrivals are random and follow a Poisson distribution.
- The service times in an Exponential model are also random and follow an exponential distribution.
Single Server vs. Multi Server
- A Single Server model has only one server attending to customers, suitable for small-scale systems.
- A Multi Server model involves multiple servers, useful for larger systems with higher traffic.
Q59: Arrange the organisational change in proper sequence :
A. Diagnosis
B. Implementation
C. Information gathering
D. Discuss
E. Work proposal
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, C, A, E
(b) A, C, D, E, B
(c) A, D, E, C, B
(d) A, B, C, D, E
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A, C, D, E, B
Key Points
Diagnosis
- The process begins with identifying the problem or areas for improvement within the organization.
- Diagnosis involves understanding the current state and what needs to change.
Information Gathering
- Collecting relevant data and information to understand the context and specifics of the issue.
- This step helps in forming a clear picture and sets the foundation for the next steps.
Discuss
- Engaging stakeholders to discuss findings and potential solutions.
- Involves collaboration and input from various parts of the organization to ensure all perspectives are considered.
Work Proposal
- Formulating a detailed plan or proposal based on the diagnosis and discussions.
- This proposal outlines the steps to be taken, resources needed, and expected outcomes.
Implementation
- Executing the proposed changes to achieve the desired improvements.
- Involves putting the plan into action and monitoring progress.
Additional Information
Organizational Change Management
- It is a structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from a current state to a desired future state.
- The goal is to implement strategies for effecting change, controlling change, and helping people to adapt to change.
Key Components
- Readiness Assessments: Evaluate the organization's readiness for change.
- Communication Plan: Ensure clear, consistent messaging to all stakeholders.
- Training and Support: Provide necessary training and support to facilitate the change.
- Resistance Management: Identify and manage resistance to change.
Success Factors
- Strong Leadership: Effective leadership is critical to driving and sustaining change.
- Employee Involvement: Involving employees at all levels ensures buy-in and reduces resistance.
- Clear Vision: A clear vision helps to align efforts and provide direction throughout the change process.
Q60: Which one of the following is the standard deviation of the first 'n' natural number?
(a) 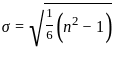
(b) 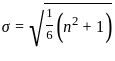
(c) 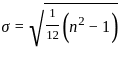
(d) 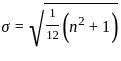
Ans: c
Sol: To determine the standard deviation $$\sigma$$σ of the first $$N$$N natural numbers, we can follow a structured approach to derive the formula.
Understand the definition of standard deviation. The standard deviation is defined as the square root of the variance. The variance σ2 is calculated using the formula:
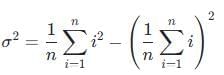
Calculate the first term, which is the mean of the squares of the first N natural numbers. The formula for the sum of squares is:
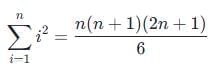
Thus, the first term becomes:
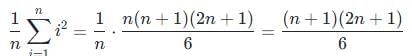
Calculate the second term, which is the square of the mean of the first $$N$$N natural numbers. The formula for the sum of the first $$N$$N natural numbers is:
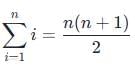
Thus, the mean is:
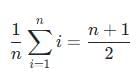
Therefore, the square of the mean is:
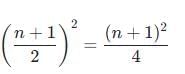
Substitute both terms back into the variance formula:
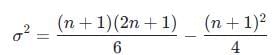
Simplify the expression to find the variance:
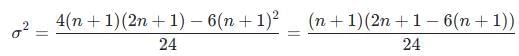
After simplification, we find:
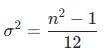
Finally, take the square root to find the standard deviation:
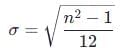
Q61: Which of the following are Positional Average?
A. Mean
B. Median
C. Mode
D. Quartiles
E. Harmonic Mean
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, D, E only
(b) B, C, E only
(c) A, B, C, D only
(d) B, C, D only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - B, C, D only
Key Points
Median
- The median is a positional average that represents the middle value in a sorted dataset.
- It is less affected by outliers and skewed data compared to the mean.
Mode
- The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a dataset.
- It can be used for both numerical and categorical data.
Quartiles
- Quartiles divide the dataset into four equal parts.
- They are essential for describing the spread and dispersion of the data.
Additional Information
Mean
- The mean, or average, is calculated by summing all values and dividing by the number of values.
- It is sensitive to outliers and skewed data.
Harmonic Mean
- The harmonic mean is used for datasets with rates or ratios.
- It is calculated as the reciprocal of the average of reciprocals of the data points.
Q62: Match List I with List II:
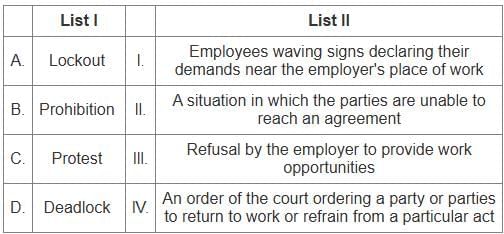
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - I, D - III
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Key Points
A - III
- Lockout is the refusal by the employer to provide work opportunities.
- This action is typically taken to exert pressure on employees during a labor dispute.
B - IV
- Prohibition refers to an order of the court ordering a party or parties to return to work or refrain from a particular act.
- This is often a legal measure to prevent actions that may disrupt industrial harmony.
C - I
- Protest involves employees waving signs declaring their demands near the employer's place of work.
- Such actions are common in industrial disputes to draw attention to employee grievances.
D - II
- Deadlock is a situation in which the parties are unable to reach an agreement.
- This often occurs during negotiations when neither side is willing to compromise.
Additional Information
Lockout
- It is a strategy used by employers to enforce terms of employment upon a group of employees during a dispute.
- During a lockout, employees are prohibited from entering the workplace.
Prohibition (Court Orders)
- Such orders are legally binding and must be adhered to by the parties involved.
- Non-compliance with court orders can result in legal consequences.
Protest Actions
- Protests are often organized by labor unions or worker groups to advocate for better working conditions.
- They are a form of collective action used to pressure employers to meet employee demands.
Deadlock in Negotiations
- Deadlocks can lead to prolonged disputes and may require mediation or arbitration to resolve.
- Understanding the causes of deadlocks can help in developing strategies to avoid them.
Q63: In the VRIO Framework a resource leads to sustained competitive advantage only if is:
(a) Valuable, widely available and flexible
(b) Valuable, rare, costly to imitate, and efficiently organized
(c) Rare, technologically advanced and easily substitutable
(d) Unique, non-valuable and adaptable
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Valuable, rare, costly to imitate, and efficiently organized
Key Points
Valuable
- A resource must provide value to the organization by exploiting opportunities or neutralizing threats in the market.
Rare
- If the resource is not widely available, it can provide a competitive edge over other firms.
Costly to imitate
- If competitors cannot easily duplicate the resource, the firm can sustain its competitive advantage.
Efficiently organized
- The firm must be organized to exploit the resource fully, ensuring that it can generate value from it.
Additional Information
VRIO Framework
- This framework is a tool used to analyze a firm's internal resources and capabilities to find out if they can be a source of sustained competitive advantage.
Competitive Advantage
- Competitive advantage occurs when a firm acquires or develops an attribute or combination of attributes that allows it to outperform its competitors.
Resource-Based View (RBV)
- RBV is a management tool used to identify the strategic resources available to a company.
- These resources can be tangible or intangible and must be valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable (VRIN).
Q64: Intermediate cash inflows are assumed to be reinvested at what rate under NPV method?
(a) IRR
(b) Cost of capital
(c) MIRR
(d) Repo rate
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Cost of capital
Key Points
Cost of capital
- In the Net Present Value (NPV) method, intermediate cash inflows are assumed to be reinvested at the cost of capital.
- This assumption is based on the premise that the firm can earn a return equivalent to its cost of capital on reinvested funds.
- The use of the cost of capital ensures that the reinvestment rate reflects the firm's required return for financing its operations and investments.
Additional Information
IRR (Internal Rate of Return)
- The IRR assumes that intermediate cash inflows are reinvested at the IRR itself, which is often considered optimistic and may not reflect the actual reinvestment opportunities available.
MIRR (Modified Internal Rate of Return)
- The MIRR assumes that positive cash flows are reinvested at the firm's cost of capital, while initial outlays are financed at the firm's financing cost. This provides a more realistic reinvestment rate than the IRR.
Repo Rate
- The repo rate is the rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks. It is not typically used as the reinvestment rate in capital budgeting methods like NPV.
Q65: Choose the correct sequence that represents the chronology of the international monetary system?
A. Bretton Woods System
B. Classical Gold Standard
C. Gold Exchange Standard
D. European union
E. Louvre Accord
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) E, D, C, B, A
(c) B, C, E, D, A
(d) B, C, A, E, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - B, C, A, E, D
Key Points
Classical Gold Standard
- The Classical Gold Standard system was the first international monetary system, established in the 19th century.
- Countries pegged their currencies to a specific amount of gold, facilitating stable international trade.
Gold Exchange Standard
- The Gold Exchange Standard followed the Gold Standard and was prevalent in the early 20th century.
- It allowed countries to hold currencies that were convertible to gold as reserves instead of gold itself.
Bretton Woods System
- The Bretton Woods System was established post-World War II in 1944.
- It created a system of fixed exchange rates where currencies were pegged to the US dollar, which was convertible to gold.
Louvre Accord
- The Louvre Accord was an agreement made in 1987 to stabilize the international currency markets.
- It aimed to halt the decline of the US dollar and manage exchange rates among major currencies.
European Union
- The formation of the European Union and the creation of the Euro in 1999 marked a significant development in the international monetary system.
- It established a single currency for many European countries, facilitating easier and more stable trade within the region.
Additional Information
Classical Gold Standard
- Introduced in the 1870s and lasted until World War I.
- Provided long-term price stability and reduced exchange rate risk.
Gold Exchange Standard
- Adopted in the 1920s after the collapse of the Gold Standard.
- Facilitated international trade and investments but was abandoned during the Great Depression.
Bretton Woods System
- Created institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank to oversee the new system.
- Collapsed in 1971 when the US suspended the convertibility of the dollar to gold.
Louvre Accord
- Followed the Plaza Accord of 1985, which aimed to devalue the US dollar.
- Involved major economies like the US, Japan, West Germany, France, and the UK.
European Union
- The Euro is used by 19 of the 27 EU member countries, known as the Eurozone.
- It promotes economic integration and eliminates the risks associated with exchange rate fluctuations within the Eurozone.
Q66: Which of the following are Probability Sampling Methods?
A. Quota sampling
B. Purposive sampling
C. Multistage sampling
D. Cluster sampling
E. Systematic sampling
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) B, D, A only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - C, D, E only
Key Points
Probability Sampling Methods
- Multistage Sampling (C)
- Involves selecting a sample in multiple stages, where each stage is a random sample of the previous stage.
- Commonly used in large-scale surveys.
- Cluster Sampling (D)
- The population is divided into clusters, and a random sample of these clusters is selected.All individuals within selected clusters are surveyed.
- Systematic Sampling (E)
- Involves selecting elements from an ordered sampling frame.
- Every nth element is selected after a random start.
Additional Information
Non-Probability Sampling Methods
- Quota Sampling (A)
- Involves selecting a sample that reflects the characteristics of the whole population.
- Selection is non-random, based on specific quotas.
Purposive Sampling (B)
- Also known as judgmental or expert sampling.
- Involves selecting individuals based on specific purposes or criteria.
Q67: Choose the correct option. Why employers are adopting Performance Management System in their organisations?
A. Adoption of total quality management philosophy
B. Introducing productive appraisal strategies
C. Aligning each employee in strategic planning
D. Managing conflict on day to day basis
E. Reduce diverse workforce
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) C, D and E only
(d) D, E and A only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - A, B and C only
Key Points
Adoption of total quality management philosophy
- Organizations adopt Total Quality Management (TQM) to enhance overall performance and efficiency.
- TQM emphasizes continuous improvement, which requires effective performance management systems.
- This ensures that quality standards are maintained and objectives are consistently met.
Introducing productive appraisal strategies
- Performance appraisals are used to evaluate employee performance and provide constructive feedback.
- This process helps in identifying strengths and areas for improvement, facilitating professional growth.
- Effective appraisal strategies align with organizational goals and enhance employee productivity.
Aligning each employee in strategic planning
- A performance management system helps in aligning employee goals with the strategic objectives of the organization.
- This ensures that every employee is working towards common organizational goals.
- It fosters a sense of purpose and direction among employees.
Additional Information
Conflict Management
- While managing day-to-day conflicts is important, it is not the primary reason for adopting a performance management system.
- Other mechanisms, such as conflict resolution strategies and communication frameworks, are more specifically designed for this purpose.
Diversity Management
- Reducing a diverse workforce is not a goal of performance management systems; rather, these systems aim to leverage diversity for better performance.
- Effective diversity management can lead to more innovative solutions and a broader range of perspectives.
Q68: Arrange the steps in their correct order for making use of artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analysis:
A. Develop an AI model with predictive capabilities
B. Collect and organize big data
C. Integrate the AI system with the company's software
D. Evaluate the performance of the model
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, A, D, C
(b) A, B, C, D
(c) B, C, D, A
(d) D, C, B, A
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - B, A, D, C
Key Points
Collect and organize big data
- Collecting and organizing big data is the first step in any AI project. Without data, the AI model has nothing to learn from.
- Big data refers to large and complex datasets that traditional data-processing software cannot handle efficiently.
Develop an AI model with predictive capabilities
- Once the data is collected and organized, the next step is to develop an AI model that can analyze this data and make predictions.
- This involves selecting the right algorithms, training the model, and refining it to improve accuracy.
Evaluate the performance of the model
- After developing the model, it is crucial to evaluate its performance to ensure it meets the desired accuracy and reliability.
- Evaluation metrics like precision, recall, and F1-score are commonly used to assess model performance.
Integrate the AI system with the company's software
- The final step is to integrate the AI model into the company's existing software systems for operational use.
- This step ensures that the predictive insights generated by the AI model are accessible and usable by the organization's stakeholders.
Additional Information
Importance of Data Quality
- The quality of the data collected directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the AI model.
- Data preprocessing steps like cleaning, normalization, and transformation are essential to ensure high-quality data.
Model Selection
- Choosing the right machine learning algorithm is critical for developing an effective predictive model.
- Common algorithms for predictive analysis include linear regression, decision trees, and neural networks.
Model Training and Testing
- Training the model involves using a portion of the data to teach the AI system to make predictions.
- Testing the model on unseen data helps evaluate its generalization capability and performance.
Continuous Improvement
- AI models require continuous monitoring and updating to maintain their predictive accuracy over time.
- Incorporating new data and refining the model parameters can help improve its performance.
Q69: Which of the following is not related to oligopoly markets?
(a) Paul M Sweezy
(b) Augustin Cournot
(c) Hall and Hitch
(d) J. K. Galbraith
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - J. K. Galbraith
Key Points
J. K. Galbraith
- J. K. Galbraith is a prominent economist known for his work on the American economy, power structures, and the role of technology in society.
- He is not specifically associated with the study or theories of oligopoly markets.
- His works primarily focus on broader economic themes rather than the specific market structures and dynamics of oligopolies.
Additional Information
Paul M Sweezy
- Paul M Sweezy is known for his work on monopoly and oligopoly markets.
- He co-authored the book "Monopoly Capital" which discusses the economic structure and dynamics of capitalism.
Augustin Cournot
- Augustin Cournot is a pioneer in the formal study of oligopoly through his model, which analyzes the behavior of firms in a duopoly setting.
- His work laid the foundation for the Cournot-Nash equilibrium in game theory.
Hall and Hitch
- Hall and Hitch are known for the development of the "kinked demand curve" theory, which explains pricing behavior in oligopoly markets.
- Their work highlighted the rigidity of prices in oligopolistic competition.
Q70: Arrange the following steps of Hypothesis testing in the proper sequence:
A. Formulate a decision rule to accept the null hypothesis
B. Select the suitable test of significance
C. State the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis
D. Establish critical or rejection region
E. State the level of significance
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) E, B, D, C, A
(b) A, B, C, D, E
(c) C, E, D, B, A
(d) A, E, C, D, B
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - C, E, D, B, A
Key Points
State the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis
- Clearly define the null hypothesis (H0) and the alternative hypothesis (H1).
- The null hypothesis often represents a statement of no effect or status quo.
- The alternative hypothesis represents a statement we are trying to find evidence to support.
State the level of significance
- Determine the alpha level (α), which is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true.
- Commonly used levels of significance are 0.05, 0.01, and 0.10.
Establish critical or rejection region
- Define the critical value(s) that separate the rejection region from the non-rejection region.
- The rejection region is the range of values for which the null hypothesis is not probable.
Select the suitable test of significance
- Choose an appropriate statistical test (e.g., t-test, chi-square test) based on the data type and distribution.
- The choice of test impacts the ability to detect a true effect.
Formulate a decision rule to accept or reject the null hypothesis
- Based on the test statistic and critical value, decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis.
- This decision is informed by the level of significance and the established critical region.
Additional Information
Hypothesis Testing Steps
- Hypothesis Formulation: Establishing H0 and H1 is the foundation of the testing process.
- Significance Level: The alpha level controls the Type I error rate.
- Critical Region: Based on the distribution of the test statistic, defines the threshold for rejection.
- Test Selection: Different tests are suitable for different data types and distributions.
- Decision Rule: Determines the conclusion based on the comparison of the test statistic with the critical value.
Types of Errors
- Type I Error: Incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis (false positive).
- Type II Error: Failing to reject a false null hypothesis (false negative).
Q71: Which one of the following is correct when a null hypothesis is accepted?
(a) χ2 cal ≤ χ2 table
(b) χ2 cal > χ2 table
(c) χ2 cal < χ2 table
(d) χ2 cal = χ2 table
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - χ2 cal < χ2 table
Key Points
χ2 cal < χ2 table
- When the calculated chi-square value (χ2 cal) is less than the table value of chi-square (χ2 table), the result is not statistically significant at the chosen significance level.
- This implies that there is no sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis (H0).
- The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or no difference, and the data observed is consistent with the expected data under this hypothesis.
Additional Information
Chi-Square Test
- The chi-square test is a statistical test used to determine whether there is a significant association between two categorical variables.
- The test compares the observed frequencies in each category of the contingency table to the frequencies expected under the null hypothesis of no association.
Degrees of Freedom
- The degrees of freedom in a chi-square test are calculated based on the number of categories minus one for each variable being tested.
- For a contingency table, it is calculated as (number of rows - 1) * (number of columns - 1).
Significance Level
- The significance level (alpha) is the threshold for determining whether the observed data is significantly different from the expected data.
- Common alpha levels are 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, which correspond to 95%, 99%, and 99.9% confidence levels, respectively.
Q72: Premium is payable by a person who _______?
A. Sells a call option
B. Purchases a call option
C. Sells futures contract
D. Purchases a put option
E. Purchases a futures contract
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and E only
(b) A, B and D only
(c) C and D only
(d) B and D only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - B and D only
Key Points
Premium Payment in Options
- A call option buyer pays a premium to acquire the right to buy the underlying asset at a specified price.
- A put option buyer pays a premium to acquire the right to sell the underlying asset at a specified price.
Additional Information
Options Contracts
- An option is a financial derivative that represents a contract sold by one party (option writer) to another party (option buyer).
- The contract offers the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an asset at an agreed-upon price before the expiration date.
- The price paid for this right is known as the premium.
Futures Contracts
- A futures contract is a standardized legal agreement to buy or sell something at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future.
- Futures contracts do not involve the payment of a premium, but they may require a margin deposit.
Q73: Arrange the five-stage model of group development, first to last
A. Forming
B. Adjourning
C. Storming
D. Performing
E. Norming
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) C, B, A, E, D
(c) B, D, C, B, A
(d) A, C, E, D, B
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A, C, E, D, B
Key Points
Forming
- This is the first stage where the group comes together and gets to initially know one another.
- Characterized by dependence on the leader for guidance and direction.
Storming
- The second stage where group members start to push against the boundaries established in the forming stage.
- Characterized by conflict and competition as individuals try to assert their opinions.
Norming
- The third stage where the group starts to come together and establish a norm or routine.
- Conflict is resolved, and the group starts to work more cohesively.
Performing
- The fourth stage where the group is fully functional and works towards achieving the group goals.
- Characterized by high productivity and strong collaboration among members.
Adjourning
- The final stage where the group disbands after achieving its goals.
- Characterized by reflection on the group's accomplishments and potential future collaborations.
Additional Information
Tuckman's Model
- Developed by Bruce Tuckman in 1965, this model outlines the phases groups typically go through as they develop and mature.
- Understanding these stages helps in diagnosing group issues and applying appropriate interventions.
Group Dynamics
- Refers to the behavioral and psychological processes that occur within a social group.
- Effective management of group dynamics can lead to better group performance and satisfaction.
Role of Leadership
- Leadership is crucial in guiding the group through these stages.
- Different leadership styles may be required at different stages to effectively manage group development.
Q74: What occurs through the interplay of drives, stimulus, responses and reinforcement?
(a) Attitude
(b) Belief
(c) Learning
(d) Perception
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Learning
Key Points
Learning
- Occurs through the interplay of drives, stimulus, responses, and reinforcement.
- Involves acquiring new knowledge, skills, or behaviors.
- Is a continuous and dynamic process that can occur in various contexts.
- Requires active participation and is influenced by both internal and external factors.
Additional Information
Drives
- Are internal states that motivate behavior.
- Can be physiological (e.g., hunger) or psychological (e.g., curiosity).
Stimulus
- Is any event or change in the environment that elicits a response.
Responses
- Are the reactions to a stimulus.
- Can be observable behaviors or internal processes.
Reinforcement
- Is a consequence that strengthens or weakens a response.
- Can be positive (adding a desirable stimulus) or negative (removing an aversive stimulus).
Q75: Out of the following alternatives, which one is a tool for allocating resources, linking business growth rate with relative competitive position of the firm.
(a) Strategy
(b) Delphi technique
(c) Tows matrix
(d) Portfolio Matrix
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Portfolio Matrix
Key Points
Portfolio Matrix
- It is a strategic management tool used for allocating resources among different business units or products.
- The matrix helps in linking business growth rates with the relative competitive position of the firm.
- Examples include the BCG Matrix and the GE-McKinsey Matrix, which classify business units or products based on factors like market share and market growth.
Additional Information
BCG Matrix
- Developed by the Boston Consulting Group, the BCG Matrix is a popular tool for portfolio analysis.
- It categorizes business units into four categories: Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs, based on market growth and market share.
GE-McKinsey Matrix
- Developed by General Electric and McKinsey & Company, this matrix is more detailed than the BCG Matrix.
- It evaluates business units on multiple factors, including industry attractiveness and competitive strength, and categorizes them into nine cells.
Strategic Management
- Involves the formulation and implementation of major goals and initiatives taken by a company's top management on behalf of owners.
- These decisions are based on the consideration of resources and an assessment of the internal and external environments in which the organization competes.
Q76: Which of the following are the steps in the business purchasing process?
A. Identifying the problem
B. Common routine specification
C. Supplier Selection
D. Offer request
E. Post-purchase behavior
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Only A, B, C and D
(b) A, B, C, D and E
(c) Only B, C and D
(d) Only B, C, D and E
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - Only A, B, C and D
Key Points
Identifying the problem
- This is the first step where businesses recognize a need or a problem that requires a purchase.
Command-routine specification
- This involves defining the requirements or specifications for the needed product or service.
Supplier Selection
- In this step, businesses evaluate and choose suppliers based on criteria such as price, quality, and reliability.
Offer request
- Businesses solicit bids or proposals from potential suppliers to fulfill their requirements.
Additional Information
Post-purchase behavior
- This step involves evaluating the performance of the purchased product or service and the supplier.
- It is important for future purchasing decisions but is not part of the initial purchasing process steps.
Understanding the Business Purchasing Process
- The business purchasing process typically follows a structured series of steps to ensure that the right products or services are acquired.
- It is designed to maximize value while minimizing costs and risks.
Q77: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Key Points
A - Short term deposit (IV - Cash and cash equivalents)
- A short-term deposit is considered a part of cash and cash equivalents as it can be converted into cash quickly.
- It is not related to operating, investing, or financing activities directly.
B - Proceeds from issue of equity shares (III - Financing Activities)
- Issuing equity shares is a method of raising funds, hence it falls under financing activities.
- It involves inflow of cash through the issuance of ownership stakes in the company.
C - Purchase of Machinery (II - Investing Activities)
- Purchasing machinery is an investment in long-term assets, so it is classified under investing activities.
- This involves outflow of cash for acquiring or upgrading physical assets.
D - Employee benefits expenses paid (I - Operating Activities)
- Paying employee benefits is part of the day-to-day operations of the business, therefore it is an operating activity.
- It includes cash outflows related to salaries, wages, and other employee-related expenses.
Additional Information
Cash and Cash Equivalents
- These include cash on hand, demand deposits, and highly liquid short-term investments.
- They are crucial for assessing the liquidity position of a company.
Financing Activities
- These activities include transactions that result in changes in the size and composition of the equity capital or borrowings of the company.
- Examples include issuing shares, borrowing loans, and repaying debt.
Investing Activities
- Investing activities involve the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents.
- Examples include purchasing machinery, selling property, or acquiring other businesses.
Operating Activities
- Operating activities are the principal revenue-producing activities of the entity and other activities that are not investing or financing activities.
- Examples include receipts from sales of goods and services, payments to suppliers, and payments to employees.
Q78: 'A system of shared meaning held by an organizations' members that distinguishes the organisation from others', the above statement describes which of the following?
(a) Organisational learning
(b) Organisational culture
(c) Organisational supremacy
(d) Organisational cohesiveness
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Organisational culture
Key Points
Organisational culture
- The statement describes a system of shared meaning held by an organization’s members.
- This shared meaning helps to distinguish the organization from others.
- Organisational culture encompasses the values, beliefs, and norms that are shared by the members of an organization.
- It influences how employees interact with each other and how the organization interacts with external stakeholders.
Additional Information
Components of Organisational Culture
- Values: Core beliefs and ideals that guide the behavior of members within the organization.
- Norms: Unwritten rules and expectations about how members should behave.
- Symbols: Objects, actions, or events that convey meaning within the organization.
- Language: The specific jargon, slang, and language used by members to communicate.
Importance of Organisational Culture
- Shapes employees' attitudes and behaviors.
- Enhances organizational identity and cohesion.
- Facilitates communication and decision-making processes.
- Helps in adaptation to external changes and challenges.
Q79: Data Mining is the process of:
(a) Cleaning and storing data in a database
(b) Extracting patterns and knowledge from large datasets
(c) Structuring unorganised data into relational formats
(d) Creating storage schemas for raw data
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Extracting patterns and knowledge from large datasets
Key Points
Extracting patterns and knowledge from large datasets
- Data Mining involves the process of identifying patterns and extracting meaningful information from large volumes of data.
- This process helps in discovering hidden patterns that are not immediately obvious, providing valuable insights for decision-making.
- It employs various techniques like classification, clustering, and association rule learning to analyze the data.
- The ultimate goal of data mining is to transform the data into an understandable structure, facilitating effective analysis.
Additional Information
Data Cleaning
- Data cleaning involves removing inaccurate, incomplete, or irrelevant data from the dataset to improve its quality.
- This step is crucial before performing data mining as it ensures the reliability of the results.
Data Storage
- Data storage refers to the process of storing data in a structured format, such as databases or data warehouses.
- It provides the infrastructure needed to manage and retrieve large volumes of data efficiently.
Data Structuring
- Data structuring involves organizing unstructured data into a relational format, making it easier to access and analyze.
- This step is often a precursor to data mining, as it prepares the data for further analysis.
Storage Schemas
- Creating storage schemas involves designing the blueprint for how data is stored, including the tables, relationships, and indexes.
- This is a critical step in database management, ensuring the data is stored efficiently and can be accessed quickly.
Q80: One advantage that advertising enjoys over publicity is:
(a) Credibility
(b) Selectivity
(c) Control
(d) Timing
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Control
Key Points
Control
- Advertising provides a high degree of control over the message content, timing, and placement.
- In advertising, businesses can precisely target their desired audience through various channels.
- Advertising allows for consistent messaging, ensuring the company’s branding and key points are communicated effectively.
- Unlike publicity, which is often managed by third parties, advertising is fully controlled by the advertiser, allowing for strategic planning and execution.
Additional Information
Credibility
- Publicity often has higher credibility because it is earned media, which is generally perceived as more trustworthy.
- Examples include news articles, reviews, and word-of-mouth recommendations.
Selectivity
- Advertising allows for selectivity in terms of reaching specific demographic groups and market segments.
- Tools such as targeted ads and market research help in precisely hitting the intended audience.
Timing
- Advertising offers control over timing, allowing businesses to schedule their messages for maximum impact.
- However, publicity timing is often less predictable, as it depends on external media outlets.
Q81: Identify the key aspects of Business Process Engineering from the following:
A. Radical Redesign
B. Operational Redesign
C. Fundamental Rethinking
D. Dramatic Results
E. Operational Transformation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) A, C, D only
(c) A, B, D only
(d) A, C, E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - A, C, D only
Key Points
Radical Redesign
- This involves a complete overhaul of existing processes to achieve significant improvements.
- It is essential to focus on making fundamental changes rather than incremental improvements.
Fundamental Rethinking
- Requires organizations to question and rethink the way they conduct their business processes.
- It emphasizes the need to start from scratch to create more efficient and effective workflows.
Dramatic Results
- The goal is to achieve substantial improvements in performance metrics such as cost, quality, service, and speed.
- These results are often achieved by implementing innovative solutions and leveraging new technologies.
Additional Information
Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
- BPR aims to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the processes that exist within and across organizations.
- It often involves the use of information technology to enable new forms of organizing and working.
Steps in BPR
- Identify Processes: Recognize and prioritize the processes that need reengineering.
- Analyze Processes: Examine current processes to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Design New Processes: Develop new processes that eliminate the identified inefficiencies and create value.
- Implement Changes: Apply the new processes and ensure they are integrated into the organizational workflow.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously measure the performance of the new processes and make adjustments as needed.
Challenges of BPR
- Resistance to change within the organization.
- High initial costs and resource investment.
- Complexity in redesigning processes and integrating new technologies.
Q82: Arrange the steps of New Product Development process.
A. Commercialization
B. Market strategy development and business analysis
C. Product development and test marketing
D. Idea generation and screening
E. Concept development and testing
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) E, C, B, A, D
(b) D, E, B, C, A
(c) D, B, E, C, A
(d) E, D, B, C, A
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - D, E, B, C, A
Key Points
New Product Development Process
- The process starts with Idea Generation and Screening (D), where potential product ideas are created and evaluated.
- Next is Concept Development and Testing (E), which involves developing the product concept and testing it with a target audience.
- Then comes Market Strategy Development and Business Analysis (B), where the market strategy is formulated and the business potential is analyzed.
- Following that is Product Development and Test Marketing (C), where the product is developed and tested in the market.
- Finally, the product goes through Commercialization (A), where it is launched in the market.
Additional Information
Idea Generation and Screening
- Involves brainstorming sessions, market research, and feedback collection.
- Screening is done to eliminate ideas that are not feasible.
Concept Development and Testing
- Detailed version of the new product idea is developed.
- Concept is tested with potential customers to gather feedback.
Market Strategy Development and Business Analysis
- Marketing strategy includes defining target market, value proposition, and marketing mix.
- Business analysis involves estimating sales, costs, and profits.
Product Development and Test Marketing
- Product is developed in prototype form.
- Test marketing involves introducing the product in a limited market to gauge consumer response.
Commercialization
- Product is launched on a large scale in the target market.
- Involves full-scale production, distribution, and marketing efforts.
Q83: In HRM, 'Line' and 'Staff' (respectively) are based on which type of relationship?
(a) Formal and informal (respectively)
(b) Responsibility and status (respectively)
(c) Commanding and supporting (respectively)
(d) Job and Role (respectively)
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Commanding and supporting (respectively)
Key Points
Commanding and supporting
- In Human Resource Management (HRM), the term 'Line' refers to positions that have direct responsibility for achieving the basic objectives of the organization, typically involving commanding roles.
- The term 'Staff' refers to positions that provide support, advice, and specialized services to the line functions, hence supporting roles.
- Understanding the distinction between line and staff roles is crucial for effective organizational structure and management.
Additional Information
Line Functions
- These are the core activities of the organization that directly contribute to achieving its objectives, such as production, sales, and marketing.
- Individuals in line roles typically have decision-making power and are accountable for the performance of their units.
Staff Functions
- These functions provide specialized expertise and support to line functions, including departments like HR, finance, and legal.
- Staff roles are advisory in nature and do not have direct control over the core activities, but they play a vital role in facilitating the success of line functions.
Effective Coordination
- For an organization to function efficiently, there must be effective coordination between line and staff roles.This involves clear communication channels, defined responsibilities, and mutual respect for each other's contributions.
Q84: Which of the following theories explain the parity conditions in the forex markets?
A. Lintner Model
B. Purchasing Power Parity
C. The International Fisher effect
D. Sharpe Model
E. Interest Rate Parity
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C and D only
(b) B, C and E only
(c) B, D and E only
(d) A, D and E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - B, C and E only
Key Points
Purchasing Power Parity
- This theory suggests that in the long run, exchange rates should move towards the rate that would equalize the prices of an identical basket of goods and services in any two countries.
The International Fisher Effect
- This theory states that the expected difference in the nominal interest rates between two countries is equal to the expected change in their exchange rates.
Interest Rate Parity
- This theory asserts that the difference in interest rates between two countries will be equal to the difference between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange rate.
Additional Information
Lintner Model
- This model is related to dividend policy and not directly relevant to forex markets.
Sharpe Model
- This model is associated with the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and is not directly relevant to forex markets.
Q85: Which of the following is not an assumption of the MM theory for Irrelevance of dividends?
(a) No transaction costs
(b) No floatation cost
(c) Irrational investors
(d) No tax discrimination on capital gains and dividends
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - Irrational investors
Key Points
Irrational investors
- The MM theory assumes that investors are rational and make decisions based on logical and consistent criteria.
- Rational investors will value dividends and capital gains equivalently if there is no tax preference, transaction costs, or other market frictions.
- This assumption allows the theory to argue that the dividend policy of a firm is irrelevant to its valuation.
Additional Information
No transaction costs
- The MM theory assumes that there are no transaction costs involved in buying or selling shares.
- This assumption simplifies the analysis by removing any friction that could influence investor behavior.
No flotation cost
- Flotation costs refer to the costs incurred when a company issues new securities. The MM theory assumes these costs are zero.
- This assumption ensures that the market value of the firm is not affected by the costs of issuing new stock.
No tax discrimination on capital gains and dividends
- The theory assumes that there is no tax advantage or disadvantage to receiving dividends versus capital gains.
- This means that investors are indifferent to whether they receive returns in the form of dividends or capital gains, as their after-tax income remains the same.
Q86: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is - A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
Key Points
Price elasticity of demand
- Calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by percentage change in price.
Income elasticity of demand
- A measure of how demand changes in response to changes in consumer income.
Perfectly inelastic demand
- Demand remains unchanged regardless of price changes.
Perfectly elastic demand
- Demand drops to zero with even the slightest increase in price.
Additional Information
Elasticity of Demand
- It is a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good.
- Understanding elasticity helps businesses and policymakers determine how changes in pricing or income levels can impact market demand.
Types of Elasticity
- Price Elasticity: Reflects the responsiveness of quantity demanded to price changes.
- Income Elasticity: Measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in consumer income.
- Cross-Price Elasticity: Measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded for one good to price changes of another good.
Q87: Which is the correct sequence of consumer research process out of the following.
A. Choosing sampling technique
B. Analyzing the data
C. Developing Research Design
D. Collecting data
E. Defining the objectives of research
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, E, D, B
(b) E, C, A, B, D
(c) E, D, A, C, B
(d) E, C, A, D, B
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - E, C, A, D, B
Key Points
Defining the objectives of research
- The first step is to clearly identify and define the objectives of the research.
- This involves understanding the problem that needs to be addressed and setting specific goals for the research study.
Developing Research Design
- Once the objectives are defined, the next step is to develop a research design.
- This includes determining the type of research, data collection methods, and the overall strategy for conducting the study.
Choosing sampling technique
- After the research design is developed, a sampling technique must be chosen.
- This involves selecting the appropriate sample size and method to ensure the data collected is representative of the population.
Collecting data
- With the sampling technique in place, the next step is data collection.
- This involves gathering the necessary information using the methods outlined in the research design.
Analyzing the data
- Finally, the collected data is analyzed to draw conclusions and insights.
- This step involves using statistical methods and tools to interpret the data and answer the research questions.
Additional Information
Research Design Types
- Exploratory Research: Used to explore a problem or situation when there are no or few earlier studies to refer to.
- Descriptive Research: Used to describe characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied.
- Explanatory Research: Used to understand the cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
Sampling Techniques
- Random Sampling: Every individual has an equal chance of being selected.
- Stratified Sampling: The population is divided into strata and random samples are taken from each stratum.
- Cluster Sampling: The population is divided into clusters, some of which are randomly selected for the study.
Data Analysis Methods
- Quantitative Analysis: Involves the use of statistical methods to analyze numerical data.
- Qualitative Analysis: Involves analyzing non-numerical data such as text, video, or audio to identify patterns and themes.
Q88: Which of the following is the quality of an entrepreneur that harnesses the power of the relationships and puts people first and enables them to take challenges?
(a) Creativity
(b) Leadership
(c) Achievement motivation
(d) Administration
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is - Leadership
Key Points
Leadership
- Leadership involves inspiring and motivating team members.
- Entrepreneurs with leadership qualities can harness the power of relationships.
- Such entrepreneurs put people first and enable them to take on challenges.
- Leadership is crucial for building a cohesive and effective team.
Additional Information
Creativity
- While creativity is important for innovation, it does not specifically focus on harnessing relationships or putting people first.
Achievement motivation
- This quality drives entrepreneurs to reach goals and achieve success but does not necessarily involve empowering others.
Administration
- Administration focuses on managing and organizing tasks rather than leading and inspiring a team.
Q89: The 5P model of Strategic Human Resource Management clearly identifies the various HR activities that must be aligned with the strategic needs of the business to gain competitive advantage. These 5 Ps are philosophy, programs, practices, process and __________.
(a) People
(b) Product
(c) Politics
(d) Price
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is - People
Key Points
People
- The 5P model of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) includes five key elements: Philosophy, Programs, Practices, Process, and People.
- People refers to the workforce of the organization, including their skills, competencies, and alignment with the company's strategic goals.
- Aligning HR activities with the strategic needs of the business involves focusing on People to ensure they contribute effectively to achieving a competitive advantage.
Additional Information
Philosophy
- Refers to the underlying beliefs and values that guide HR policies and practices within an organization.
- Includes the company's approach to employee management, development, and engagement.
Programs
- Encompass the specific HR initiatives and strategies designed to support the organization's goals.
- Examples include training and development programs, recruitment strategies, and employee retention plans.
Practices
- Refers to the day-to-day HR activities and processes that are implemented to manage the workforce effectively.
- Includes performance management, employee relations, and compensation management.
Process
- Describes the systems and procedures used to deliver HR services and support the organization's strategic objectives.
- Includes workflows, communication channels, and decision-making processes within the HR function.
Q90: Bad Debts associated with extension of credit to customers represented which category of cost?
(a) Collection costs
(b) Capital costs
(c) Delinquency costs
(d) Default costs
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is - Default costs
Key Points
Default costs
- These are costs incurred when customers fail to repay their credit obligations.
- These costs may include the direct financial loss from the unpaid debt, as well as administrative costs related to managing the default.
- Bad debts are a direct result of customer defaults, making them part of default costs.
Additional Information
Collection costs
- Costs associated with efforts to collect overdue payments from customers.
- These can include costs for collection agencies, legal fees, and in-house collection efforts.
Capital costs
- Refers to the cost of funds used for financing a business.
- This is not directly related to bad debts but rather the cost of raising capital.
Delinquency costs
- Costs incurred due to late payments by customers.
- These may include late fees and the cost of additional collection efforts.
Q91: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows. Its main objective is improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It was one of the earliest attempts to apply science of engineering processes to management. Scientific Management is also known as Taylorism after its pioneer, Frederick Winslow Taylor.
Taylor began the theory's development in the United states during the 1880 s and 1890 s within manufacturing industries, especially steel. Its peak of influence came in the 1910s. Although Taylor died in 1915, by the 1920s scientific management was still influential but had entered into competition and syncretism with opposing or complementary ideas.
The Midvale Steel Company, "one of America's great armor plate making plants," was the birthplace of scientific management. In 1877, Frederick W. Taylor started as a clerk in Midvale, but advanced to foreman in 1880 . As foreman, Taylor was constantly impressed by the failure of team members to produce more than about one-third of what he deemed a good day's work. Taylor determined to discover, by scientific methods, how long it should take men to perform each given piece of work; and it was in the fall of 1882 that he started to put the first features of scientific management into operation. Although scientific management as a distinct theory or school of thought was obsolete by the 1930s, most of its themes are still important parts of industrial engineering and management today.
Fredrick Winslow Taylor started his career in the Midvale Steel Company during:
(a) 1860 s
(b) 1870 s
(c) 1880 s
(d) 1890 s
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 1870s
Explanation
Frederick Winslow Taylor started his career at Midvale Steel Company in the 1870s:
- The passage states that Taylor began as a clerk in Midvale in 1877, which clearly places the beginning of his career in the 1870s.
- Understanding timelines is important in evaluating a company or theory’s growth in a financial enterprise — recognizing that management principles like Taylorism emerged in a specific industrial era can inform modern applications in corporate efficiency and workflow optimization.
- In a financial enterprise context, Taylor’s early experiences reflect how systematic workflow analysis and time studies became foundational in cost control and budgeting techniques, still vital in corporate finance today.
Other Related Points
1860s:
- This is incorrect as Taylor would have been too young to start a professional career in the 1860s. The passage specifies he joined Midvale in 1877.
1880s:
- Although Taylor became a foreman in 1880 and began implementing his management methods in 1882, his career at Midvale had already begun earlier in the 1870s.
1890s:
- This is inaccurate as Taylor's foundational work in scientific management began well before the 1890s, including his early experimentation in the 1880s.
Q92: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows. Its main objective is improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It was one of the earliest attempts to apply science of engineering processes to management. Scientific Management is also known as Taylorism after its pioneer, Frederick Winslow Taylor.
Taylor began the theory's development in the United states during the 1880 s and 1890 s within manufacturing industries, especially steel. Its peak of influence came in the 1910s. Although Taylor died in 1915, by the 1920s scientific management was still influential but had entered into competition and syncretism with opposing or complementary ideas.
The Midvale Steel Company, "one of America's great armor plate making plants," was the birthplace of scientific management. In 1877, Frederick W. Taylor started as a clerk in Midvale, but advanced to foreman in 1880 . As foreman, Taylor was constantly impressed by the failure of team members to produce more than about one-third of what he deemed a good day's work. Taylor determined to discover, by scientific methods, how long it should take men to perform each given piece of work; and it was in the fall of 1882 that he started to put the first features of scientific management into operation. Although scientific management as a distinct theory or school of thought was obsolete by the 1930s, most of its themes are still important parts of industrial engineering and management today.
Which of the following is not correct statement?
(a) Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflow.
(b) By the 1920 s, scientific management was still influential but had entered into competition and syncretism with opposing or complementary ideas
(c) Frederick W. Taylor started as a clerk in Midvale, but advanced to a senior supervisor in 1880
(d) Taylor began his Theory's development within manufacturing industries
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Frederick W. Taylor started as a clerk in Midvale, but advanced to a senior supervisor in 1880
Frederick W. Taylor advanced to foreman, not senior supervisor, in 1880:
- The passage clearly states that Taylor became a "foreman" in 1880. The term "senior supervisor" does not appear and is not equivalent in context.
- This distinction matters in financial enterprises, as titles represent levels of responsibility and hierarchy, which affect pay scales, budgeting for human resources, and operational decision-making.
- Accurate designation of roles ensures proper workflow documentation and helps in labor cost analysis — a key component of efficient enterprise resource planning.
Other Related Points
Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflow:
- This statement is accurate. It directly aligns with the passage, which introduces scientific management as a theory focused on improving workflow and efficiency.
By the 1920s, scientific management was still influential but had entered into competition and syncretism with other ideas:
- This is correct. The passage clearly mentions that scientific management remained influential in the 1920s but was integrating or competing with other management theories.
Taylor began his theory’s development within manufacturing industries:
- This is true. The text mentions he developed his theory in the steel industry, a key part of manufacturing during that era.
Q93: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows. Its main objective is improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It was one of the earliest attempts to apply science of engineering processes to management. Scientific Management is also known as Taylorism after its pioneer, Frederick Winslow Taylor.
Taylor began the theory's development in the United states during the 1880 s and 1890 s within manufacturing industries, especially steel. Its peak of influence came in the 1910s. Although Taylor died in 1915, by the 1920s scientific management was still influential but had entered into competition and syncretism with opposing or complementary ideas.
The Midvale Steel Company, "one of America's great armor plate making plants," was the birthplace of scientific management. In 1877, Frederick W. Taylor started as a clerk in Midvale, but advanced to foreman in 1880 . As foreman, Taylor was constantly impressed by the failure of team members to produce more than about one-third of what he deemed a good day's work. Taylor determined to discover, by scientific methods, how long it should take men to perform each given piece of work; and it was in the fall of 1882 that he started to put the first features of scientific management into operation. Although scientific management as a distinct theory or school of thought was obsolete by the 1930s, most of its themes are still important parts of industrial engineering and management today.
Which one of the following periods is associated with the evolution of Scientific Management Concept?
(a) 20th Century
(b) 21st Century
(c) 1880 s and 1890 s
(d) 1890 s and 1900 s
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 1880 s and 1890 s
1880s and 1890s marked the evolution of Scientific Management:
- The passage states that Frederick W. Taylor began developing the theory of Scientific Management during the 1880s and 1890s, particularly in steel manufacturing industries in the United States.
- This period marks the foundational phase of industrial engineering practices, a concept crucial for modern financial enterprises that rely on structured workflow, efficiency, and cost optimization.
- In financial enterprises, adopting similar systematic approaches aids in enhancing productivity, reducing redundancy, and increasing overall profitability—principles rooted in Taylor’s management theory.
Other Related Points
20th Century:
- This is too broad and slightly misleading. While Scientific Management continued to influence practices in the early 20th century, its actual development began in the 1880s and 1890s.
- In finance, using correct historical context helps understand how evolving theories were applied to capital planning and labor management across industrial eras.
21st Century:
- This is incorrect. By the 21st century, Scientific Management as a standalone theory was long considered outdated, though its concepts are embedded in modern management practices.
- Financial systems today utilize more integrated technologies and agile methodologies, moving beyond the rigid structures of early Scientific Management.
1890s and 1900s:
- This range only partially overlaps with the correct timeline. The theory was already in development by the 1880s, and limiting its start to the 1890s overlooks important early contributions.
- Accurate timelines are vital in financial planning, particularly when assessing long-term trends or historical performance of managerial practices.
Q94: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows. Its main objective is improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It was one of the earliest attempts to apply science of engineering processes to management. Scientific Management is also known as Taylorism after its pioneer, Frederick Winslow Taylor.
Taylor began the theory's development in the United states during the 1880 s and 1890 s within manufacturing industries, especially steel. Its peak of influence came in the 1910s. Although Taylor died in 1915, by the 1920s scientific management was still influential but had entered into competition and syncretism with opposing or complementary ideas.
The Midvale Steel Company, "one of America's great armor plate making plants," was the birthplace of scientific management. In 1877, Frederick W. Taylor started as a clerk in Midvale, but advanced to foreman in 1880 . As foreman, Taylor was constantly impressed by the failure of team members to produce more than about one-third of what he deemed a good day's work. Taylor determined to discover, by scientific methods, how long it should take men to perform each given piece of work; and it was in the fall of 1882 that he started to put the first features of scientific management into operation. Although scientific management as a distinct theory or school of thought was obsolete by the 1930s, most of its themes are still important parts of industrial engineering and management today.
Scientific Management is also known as:
(a) Managerial Rationalism
(b) Fayolism
(c) Taylorism
(d) Functional Organization
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Taylorism
Taylorism refers to Scientific Management pioneered by Frederick Winslow Taylor:
- The passage clearly states that Scientific Management is also known as Taylorism, named after Frederick W. Taylor, who developed this theory in the late 19th century.
- This method aimed at improving efficiency and labor productivity through scientific study of workflows — a principle that is still crucial in financial enterprises for optimizing operations and resource allocation.
- In the context of financial enterprises, adopting Taylorism-inspired methods can lead to improved process standardization, reduced operational waste, and increased profitability through data-driven performance metrics.
Other Related Points
Managerial Rationalism:
- This is not a recognized synonym for Scientific Management. While it may refer to logical or rational approaches to management, it does not specifically denote the methodology developed by Taylor.
- In finance, clarity in terminology is essential to avoid misinterpretation of management principles or practices.
Fayolism:
- This term is associated with Henri Fayol, a different management theorist who introduced administrative management theory — distinct from Taylor’s focus on labor productivity and scientific workflow.
- Confusing these schools of thought can mislead professionals trying to implement the appropriate method in financial planning or strategy design.
Functional Organization:
- This is an organizational structure, not a theory of management. It describes how work is divided within an enterprise, typically by specialized functions, but does not encapsulate the methodology or principles of Scientific Management.
- In financial enterprises, functional organization might be an output of management theories like Taylorism, but it is not synonymous with the theory itself.
Q95: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows. Its main objective is improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It was one of the earliest attempts to apply science of engineering processes to management. Scientific Management is also known as Taylorism after its pioneer, Frederick Winslow Taylor.
Taylor began the theory's development in the United states during the 1880 s and 1890 s within manufacturing industries, especially steel. Its peak of influence came in the 1910s. Although Taylor died in 1915, by the 1920s scientific management was still influential but had entered into competition and syncretism with opposing or complementary ideas.
The Midvale Steel Company, "one of America's great armor plate making plants," was the birthplace of scientific management. In 1877, Frederick W. Taylor started as a clerk in Midvale, but advanced to foreman in 1880 . As foreman, Taylor was constantly impressed by the failure of team members to produce more than about one-third of what he deemed a good day's work. Taylor determined to discover, by scientific methods, how long it should take men to perform each given piece of work; and it was in the fall of 1882 that he started to put the first features of scientific management into operation. Although scientific management as a distinct theory or school of thought was obsolete by the 1930s, most of its themes are still important parts of industrial engineering and management today.
Which of the following is the birthplace of Scientific Management?
(a) Bethlehem Steel Corporation
(b) Midvale Steel Corporation
(c) Bethlehem Steel Incorporation
(d) Midvale Steel Company
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Midvale Steel Company
Midvale Steel Company is the birthplace of Scientific Management:
- The passage states that Midvale Steel Company was where Frederick W. Taylor first began implementing his ideas on Scientific Management in the early 1880s.
- This historical fact marks it as the origin of this influential management theory which emphasized measuring work scientifically to improve productivity.
- For financial enterprises, the legacy of Scientific Management still resonates today in the use of analytics, performance benchmarking, and operational efficiency strategies that ensure optimal resource utilization and productivity.
- By studying work processes scientifically, modern financial institutions can reduce overheads, improve turnaround times, and deliver services more efficiently — a principle rooted in Taylor's early experiments at Midvale.
Other Related Points
Bethlehem Steel Corporation:
- This was another company where Taylor worked later in his career, but it was not the birthplace of Scientific Management. His initial development of the theory occurred at Midvale Steel.
- In financial management, accurate attribution of historical methods ensures the right application of strategies in process optimization and business planning.
Bethlehem Steel Incorporation:
- This is an incorrect variant of the name and not mentioned in the passage. It appears to be a distractor or a misnaming of Bethlehem Steel Corporation.
Midvale Steel Corporation:
- This is an incorrect name; the correct term used in the passage is “Midvale Steel Company.” Even though it sounds similar, precision in naming is crucial in historical and academic contexts.
- In financial records or historical referencing, such mislabeling can lead to confusion or misinterpretation of legacy practices and their relevance to modern systems.
Q96: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1999 set up a committee under Shri Kumar Mangalam Birla, member SEBI Board, to promote and raise the standards of good corporate governance. The primary objective of the committee was to view corporate governance from the perspective of the investors and shareholders and to prepare a 'Code' to suit the Indian corporate environment.
The mandatory recommendations apply to the listed companies with paid up share capital of Rs. 3 crore and above. The composition of board of directors should be a combination of executive and non-executive directors. Audit committee should contain 3 independent directors with one having financial and accounting knowledge. The Board should hold at least 4 meetings in a year with a maximum gap of 4 months between 2 meetings to review operational plans, capital budgets, quarterly results, minutes of committee meetings. The director shall not be member of more than 10 committee and shall not act as chairman of more than 5 committees across all companies.
The non-mandatory recommendations were to apply to all the listed private and public sector companies, their directors, management, employees and professionals associated with such companies. The committee recognizes that compliance with the recommendations would involve restructuring the existing boards of companies. It also recognizes that smaller ones will have difficulty in immediately complying with these conditions.
Which one of the following is not a part of mandatory recommendations?
(a) Audit committee should contain 3 independent directors with one having financial and accounting knowledge
(b) The Board should hold at least 4 meetings in a year with maximum gap of 4 months between 2 meetings to review operational plans
(c) Director shall not be a member of more than 10 committees and shall not act as chairman of more than 5 committees across all companies
(d) Auditor of the company must have experience of 10 years
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Auditor of the company must have experience of 10 years
Auditor of the company must have experience of 10 years:
- This is not mentioned as a mandatory recommendation by the Kumar Mangalam Birla Committee in the passage.
- The committee focused on board structure, audit committee composition, and meeting frequency, not specific auditor qualifications or years of experience.
- In the context of financial enterprises, while auditor experience is important for accuracy and compliance, this criterion was not part of SEBI’s mandated governance reforms.
- Mandatory guidelines emphasize oversight and independence over tenure-based eligibility, promoting transparency and investor confidence through board governance mechanisms rather than focusing on professional experience thresholds.
Other Related Points
Audit committee should contain 3 independent directors with one having financial and accounting knowledge:
- This is a correct mandatory recommendation according to the committee. It ensures financial expertise and independence in internal control, especially relevant for financial institutions where audit transparency is critical.
The Board should hold at least 4 meetings in a year with maximum gap of 4 months between 2 meetings to review operational plans:
- Also a correct mandatory recommendation. Regular board meetings ensure continuous oversight and timely decision-making, vital in fast-changing financial markets.
Director shall not be a member of more than 10 committees and shall not act as chairman of more than 5 committees across all companies:
- This is part of the mandatory norms to avoid overcommitment and ensure effective participation. It is crucial in financial enterprises where governance and risk management responsibilities are complex and demanding.
Q97: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1999 set up a committee under Shri Kumar Mangalam Birla, member SEBI Board, to promote and raise the standards of good corporate governance. The primary objective of the committee was to view corporate governance from the perspective of the investors and shareholders and to prepare a 'Code' to suit the Indian corporate environment.
The mandatory recommendations apply to the listed companies with paid up share capital of Rs. 3 crore and above. The composition of board of directors should be a combination of executive and non-executive directors. Audit committee should contain 3 independent directors with one having financial and accounting knowledge. The Board should hold at least 4 meetings in a year with a maximum gap of 4 months between 2 meetings to review operational plans, capital budgets, quarterly results, minutes of committee meetings. The director shall not be member of more than 10 committee and shall not act as chairman of more than 5 committees across all companies.
The non-mandatory recommendations were to apply to all the listed private and public sector companies, their directors, management, employees and professionals associated with such companies. The committee recognizes that compliance with the recommendations would involve restructuring the existing boards of companies. It also recognizes that smaller ones will have difficulty in immediately complying with these conditions.
Non-Mandatory Recommendations were to apply to:
A. Listed private
B. Listed public sector companies
C. Shareholders
D. Professionals associated
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C
(b) A, B and D
(c) B, C and D
(d) A, C and D
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and D
Non-mandatory recommendations were to apply to listed private companies, listed public sector companies, and professionals associated:
- The passage clearly mentions that these recommendations apply to listed private and public sector companies, along with their directors, management, employees, and professionals associated with them.
- This ensures that voluntary compliance with governance standards is encouraged not just among large public entities, but also across smaller or privately held listed firms.
- For financial enterprises, professionals such as auditors, compliance officers, and governance advisors are critical in applying such recommendations and fostering transparency and accountability.
- Applying these recommendations to a broader range of participants ensures a culture of corporate ethics, especially vital in sectors dealing with public funds and investments.
Other Related Points
Shareholders are not included under non-mandatory recommendations:
- The passage does not state that shareholders are part of the target audience for non-mandatory recommendations.
- Shareholders benefit from corporate governance practices, but the application of these recommendations is focused on the internal structure of companies and associated professionals.
- Therefore, including shareholders in the list is incorrect, making any answer option containing “C” invalid.
The recommendations aim to improve internal governance rather than investor behavior:
- While good governance indirectly protects investors, the non-mandatory code is about improving the conduct and structure within corporations, not imposing standards on shareholders themselves.
Q98: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1999 set up a committee under Shri Kumar Mangalam Birla, member SEBI Board, to promote and raise the standards of good corporate governance. The primary objective of the committee was to view corporate governance from the perspective of the investors and shareholders and to prepare a 'Code' to suit the Indian corporate environment.
The mandatory recommendations apply to the listed companies with paid up share capital of Rs. 3 crore and above. The composition of board of directors should be a combination of executive and non-executive directors. Audit committee should contain 3 independent directors with one having financial and accounting knowledge. The Board should hold at least 4 meetings in a year with a maximum gap of 4 months between 2 meetings to review operational plans, capital budgets, quarterly results, minutes of committee meetings. The director shall not be member of more than 10 committee and shall not act as chairman of more than 5 committees across all companies.
The non-mandatory recommendations were to apply to all the listed private and public sector companies, their directors, management, employees and professionals associated with such companies. The committee recognizes that compliance with the recommendations would involve restructuring the existing boards of companies. It also recognizes that smaller ones will have difficulty in immediately complying with these conditions.
The Kumar Mangalam Birla Committee's recommendations are given in:
(a) Two categories
(b) Three categories
(c) Four categories
(d) Five categories
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Two categories
Kumar Mangalam Birla Committee's recommendations are divided into two categories:
- The passage states that the recommendations are categorized into mandatory and non-mandatory guidelines.
- Mandatory recommendations are binding for listed companies with paid-up capital of ₹3 crore and above, focusing on board composition, audit committees, board meetings, and limits on committee memberships.
- Non-mandatory recommendations are intended for all listed private and public sector companies, aiming to promote good governance practices but without enforcement obligations.
- This two-tier structure allows flexibility for smaller firms while ensuring essential governance standards are maintained for larger ones in financial enterprises.
Other Related Points
Three categories:
- No mention in the passage of recommendations being split into three distinct categories.
- This would be inaccurate as the text clearly highlights only mandatory and non-mandatory types.
Four categories:
- Incorrect assumption. The committee does not subdivide recommendations further into four sections such as audit, board structure, shareholders’ rights, etc.
Five categories:
- This is incorrect as there is no evidence or mention in the text supporting five separate recommendation types. The bifurcation is clearly limited to two.
Q99: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1999 set up a committee under Shri Kumar Mangalam Birla, member SEBI Board, to promote and raise the standards of good corporate governance. The primary objective of the committee was to view corporate governance from the perspective of the investors and shareholders and to prepare a 'Code' to suit the Indian corporate environment.
The mandatory recommendations apply to the listed companies with paid up share capital of Rs. 3 crore and above. The composition of board of directors should be a combination of executive and non-executive directors. Audit committee should contain 3 independent directors with one having financial and accounting knowledge. The Board should hold at least 4 meetings in a year with a maximum gap of 4 months between 2 meetings to review operational plans, capital budgets, quarterly results, minutes of committee meetings. The director shall not be member of more than 10 committee and shall not act as chairman of more than 5 committees across all companies.
The non-mandatory recommendations were to apply to all the listed private and public sector companies, their directors, management, employees and professionals associated with such companies. The committee recognizes that compliance with the recommendations would involve restructuring the existing boards of companies. It also recognizes that smaller ones will have difficulty in immediately complying with these conditions.
The Kumar Mangalam Birla Committee report is on:
(a) Investors' Protection
(b) Investors and Shareholders Awareness
(c) Corporate Governance
(d) SEBI Guidelines on Market Operations
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Corporate Governance
Kumar Mangalam Birla Committee focused on Corporate Governance:
- The passage clearly states that SEBI set up the committee to promote and raise the standards of good corporate governance.
- The committee's objective was to develop a code tailored to the Indian corporate environment, ensuring accountability, transparency, and investor protection within corporate structures.
- Corporate governance involves a set of systems, principles, and processes by which companies are directed and controlled to enhance stakeholder trust and long-term value.
- For financial enterprises, sound corporate governance ensures operational integrity, promotes investor confidence, and mitigates risk by improving oversight and decision-making structures.
Other Related Points
Investors' Protection:
- Although investor protection is an indirect goal, the report's direct and central theme was governance frameworks, not specific laws or measures focused solely on protecting investors’ rights.
Investors and Shareholders Awareness:
- This is inaccurate because the committee's mandate was not about conducting awareness campaigns or educational efforts for investors, but about improving the governance mechanisms within companies.
SEBI Guidelines on Market Operations:
- This option refers to the broader regulatory functions of SEBI concerning market conduct, trading mechanisms, etc. The Birla Committee’s focus was limited to governance issues within companies, not operational market guidelines.
Q100: Read the following passage carefully, and answer the questions.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1999 set up a committee under Shri Kumar Mangalam Birla, member SEBI Board, to promote and raise the standards of good corporate governance. The primary objective of the committee was to view corporate governance from the perspective of the investors and shareholders and to prepare a 'Code' to suit the Indian corporate environment.
The mandatory recommendations apply to the listed companies with paid up share capital of Rs. 3 crore and above. The composition of board of directors should be a combination of executive and non-executive directors. Audit committee should contain 3 independent directors with one having financial and accounting knowledge. The Board should hold at least 4 meetings in a year with a maximum gap of 4 months between 2 meetings to review operational plans, capital budgets, quarterly results, minutes of committee meetings. The director shall not be member of more than 10 committee and shall not act as chairman of more than 5 committees across all companies.
The non-mandatory recommendations were to apply to all the listed private and public sector companies, their directors, management, employees and professionals associated with such companies. The committee recognizes that compliance with the recommendations would involve restructuring the existing boards of companies. It also recognizes that smaller ones will have difficulty in immediately complying with these conditions.
In the light of the recommendations:
(a) Existing company boards will be restructured
(b) Foreign company can be listed on Indian stock exchanges
(c) There will be only two categories of companies
(d) Directors will have to be re-elected
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Existing company boards will be restructured
Existing company boards will be restructured:
- The passage clearly states that the committee recognized that complying with the recommendations would involve restructuring the existing boards of companies.
- This restructuring includes changes such as increasing the number of independent directors, forming audit committees, and adhering to board meeting requirements.
- For financial enterprises, restructuring improves governance mechanisms, which in turn enhances transparency, reduces risks of mismanagement, and boosts investor confidence.
- It ensures that companies are managed in a more accountable and professionally sound manner, aligning their interests with those of stakeholders.
Other Related Points
Foreign company can be listed on Indian stock exchanges:
- This is incorrect. The passage does not mention anything about foreign companies or cross-border listings. It focuses solely on improving governance in Indian listed companies.
There will be only two categories of companies:
- While the committee made both mandatory and non-mandatory recommendations, the passage does not classify companies into only two distinct legal categories. The focus is more on governance norms than company categorization.
Directors will have to be re-elected:
- This is not mentioned in the recommendations. The committee’s guidelines relate more to composition and functioning of the board rather than election processes for directors.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Management 9th Jan 2025 Shift 2 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam, and what subjects does it cover? |  |
| 2. What is the structure of the UGC NET Paper 2 for Management? |  |
| 3. How can candidates prepare effectively for the UGC NET Management exam? |  |
| 4. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET exam for Management? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the UGC NET certificate for management professionals? |  |
















