Unit & Measurement | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Measurement |

|
| Unit |

|
| The International System of Units |

|
| The Seven Base Units Of Measurement |

|
| Derived Units |

|
| Units of Long Distance |

|
| Units of Short Distance |

|
Measurement
Measurement is a technique in which the properties of an object are determined by comparing them to a standard.
- Measurement requires tools to provide scientists with a quantity. A quantity describes how much of something there is and how many there are.
- Scientists use a system of measurement still commonly referred to as the “metric system.”
- It was the first standardized system of measurement, developed in France in the 1790s. Today, this form is the standard form of measurement in every country except the United States.
Unit
A unit is a particular physical quantity, defined and adopted by the convention, with which other particular quantities of the same kind are compared to express their value.
The International System of Units
The International System of Units, abbreviated as SI from the French Système International d'Unités, is the modern form of the metric system and the most widely used system of measurement for all practical purposes, including science, technology, and everyday commerce globally.
Historical Context
Before the establishment of the SI, measurements varied significantly across the world, which led to confusion and inefficiencies in science, industry, and commerce. Key measurement systems prior to the SI included:
CGS System: Utilized the centimeter, gram, and second as base units for length, mass, and time, respectively. It was widely used in physics and had variations like the Gaussian units for electromagnetism.
FPS System: Stood for foot, pound, and second. It was primarily used in some English-speaking countries and is part of the broader category known as the imperial system.
MKS System: Based on the meter, kilogram, and second, this system was considered a precursor to the SI and was instrumental in shaping modern metric standards.
Formation and Adoption of SI
Recognizing the need for a unified system, the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) developed the SI, officially adopting it in 1971. This system not only simplified the existing systems but also aimed to create a universally consistent set of measurements based on fundamental physical properties.
The Seven Base Units Of Measurement
The SI system is built around seven base units from which all other units of measure are derived:
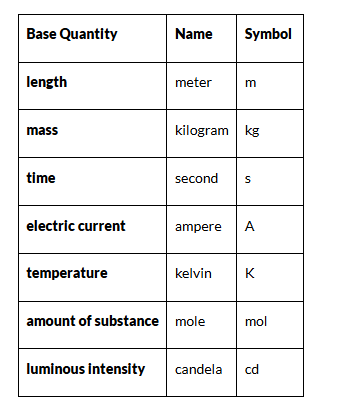
Length – Meter (m)
- It is defined as the length of the path traveled by light in an interval of exactly 1 / 299792458 s.
- It is based on the fundamental quantity, the speed of light in a vacuum which is c = 299,792,458 m/s.
Time – Second (s)
- The time taken by 9,192,631,770 periods of oscillations of the light emitted by a cesium -133 atoms corresponding to the transition between two hyper-fine levels of the ground state.
- This is determined by using highly precise atomic clocks.
Mass – Kilogram (kg)
- It is the mass of a prototype platinum-iridium cylinder kept at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in Paris, France.
- Copies of this cylinder are kept by many countries which use them to standardize and compare weights.
Electric current – Ampere (A)
- The constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length and negligible circular cross-section when placed 1 m apart in vacuum, would produce a force equal to 2×10−7 Newton per meter of length between these conductors.
- While, it may appear that electric charge should have been used as a base unit, measuring current is far easier and hence is chosen as the standard base unit.
Temperature – Kelvin (K)
- The SI unit of temperature is Kelvin. It is exactly 1273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.
- The triple point of water is a fixed temperature and pressure at which the solid, liquid and gaseous states can exist at the same time.
Amount of a substance – Mole (mol)
- The mole is the amount of substance which contains as many entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kg of carbon-12.
- A mole contains an Avogadro number of entities. Check out our chemistry articles to know more about the Avogadro number.
Luminous Intensity – Candela (cd)
- It is the luminous intensity of a source that emits radiation of a constant frequency of 540 × 1012Hz with a radiant intensity of 1683 Watt per steradian in any given direction.
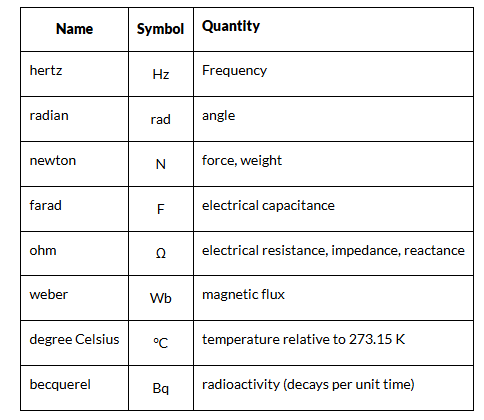
Derived Units
The units of measurement derived from the seven base units specified by the International System of Units is known as SI derived units.
- They are either dimensionless or can be expressed as a product of one or more of the base units, possibly scaled by an appropriate power of exponentiation.
- The names of SI-derived units, when written in full, are always in lowercase. However, the symbols for units named after persons are written with an uppercase initial letter.
- For example, the symbol for hertz is “Hz”, but the symbol for metre is “m.” In the table below, we have given a list of derived units.
Units of Long Distance
- Light Year: This is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one year, approximately equal to 15 meters. Light years are commonly used to express distances between stars and galaxies.
- Parsec: Defined as the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one arcsecond. A parsec is equivalent to about 3.26 light years. It is particularly useful in measuring distances of objects within our galaxy and nearby galaxies.
- 1 Parsec = 3.26 light year
Units of Short Distance
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Unit & Measurement - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the seven base units of measurement in the International System of Units (SI)? |  |
| 2. How do derived units differ from base units in measurement? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of units used for long-distance measurement? |  |
| 4. What units are typically used for short-distance measurement? |  |
| 5. How are mass and weight measured, and what is the difference between the two? |  |
















