Unit Test (Solution): Beyond Earth | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Attempt all questions.
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
- Question numbers 1 to 7 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 8 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 13 to 15 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 16 carries 4 marks each.
Q1: What are groups of stars that appear to form patterns like familiar shapes called? (1 Mark)
(i) Galaxies
(ii) Constellations
(iii) Planets
(iv) Satellites
Ans: (ii) Constellations
Constellations are regions of the sky defined by the International Astronomical Union, containing groups of stars that form recognizable patterns.
Q2: Which star appears stationary in the North direction and helps in locating the North in the Northern hemisphere? (1 Mark)
Ans: Pole Star
The Pole Star, or Polaris, is part of the Little Dipper constellation and remains fixed due to Earth's rotation.
Q3: The presence of excessive artificial light at night time is referred to as __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: light pollution
Light pollution reduces visibility of stars and affects night sky observation, especially in cities.
Q4: Which is the closest star to Earth and the main source of energy for our planet? (1 Mark)
(i) Sirius
(ii) Sun
(iii) Proxima Centauri
(iv) Betelgeuse
Ans: (ii) Sun
The Sun is a hot ball of gases that provides heat, light, and energy essential for life on Earth.
Q5: How many planets are there in our Solar System, in order of increasing distance from the Sun? (1 Mark)
Ans: Eight
The eight planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Q6: Objects that revolve around planets and are smaller in size than planets are called __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: satellites
Natural satellites, like the Moon, orbit planets, while artificial satellites are human-made.
Q7: What is the faint band of light visible across the moonless night sky from dark locations? (1 Mark)
(i) A comet
(ii) The Milky Way Galaxy
(iii) An asteroid belt
(iv) A constellation
Ans: (ii) The Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way Galaxy, or Ākāśha Gangā, is our home galaxy containing billions of stars, including our Solar System.
Q8: Why was Pluto reclassified as a dwarf planet? (3 Marks)
Ans: Pluto was once considered the ninth planet but is smaller than Earth's Moon. In 2006, the International Astronomical Union redefined planets, requiring them to clear their orbital path. With discovery of similar small objects, Pluto and others were reclassified as dwarf planets since they do not meet all criteria.
Q9: Why is the night sky better viewed from open dark areas away from cities? (2 Marks)
Ans: Open dark areas have less light pollution, smoke, and dust, allowing more stars to be visible. Tall buildings and trees in cities block views, while villages or reserves preserve clear skies for better observation.
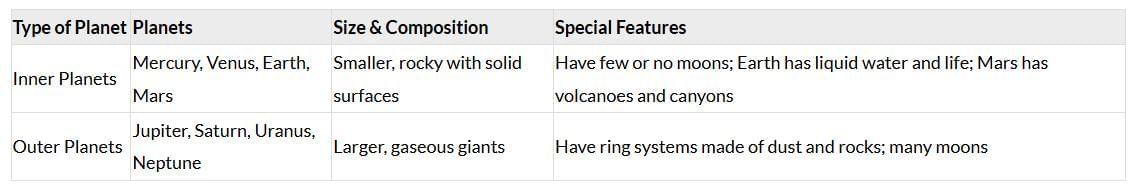
Q10: Distinguish between the inner and outer planets of the Solar System. (2 Marks)
Ans:
Q11: What causes the craters on the Moon's surface? (2 Marks)
Ans: Craters are formed by impacts from asteroids or rocks from space. Without atmosphere, water, or life, these features remain unchanged for a long time on the Moon.
Q12: Describe how comets form their tails. (2 Marks)
Ans: Comets are made of dust, gases, rocks, and ice. As they approach the Sun, the frozen material evaporates due to heat, forming a tail that points away from the Sun.
Q13: What are the Big Dipper and the Little Dipper, and how is the Pole Star important for navigation? Also, mention their Indian names. (3 Marks)
Ans: The Big Dipper and the Little Dipper are two distinct patterns of stars. The Big Dipper is part of the constellation Ursa Major, and the Little Dipper is part of the constellation Ursa Minor. The Pole Star, or Polaris, is part of the Little Dipper and appears stationary in the North direction, which helps in locating the North direction in the Northern Hemisphere. In India, the Big Dipper is called Saptaṛiṣhi, and the Pole Star is called Dhruva tārā.
Q14: What are constellations, how were they used in the past, and how can we identify some of them in the night sky today? (3 Marks)
Ans: Constellations are groups of stars that appear to form patterns, often resembling animals, objects, or characters from stories. Long ago, people used these patterns for navigation, especially sailors and travellers, before modern tools like the magnetic compass were invented. Different cultures gave names and stories to these star patterns. Today, constellations are defined as specific regions of the sky, with 88 officially recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). We can identify constellations in the night sky by observing clear dark areas away from light pollution, using images of constellations, or mobile apps like Sky Map and Stellarium. Familiar patterns, such as the Big Dipper, Little Dipper, and Orion, can be located by identifying key stars and using imaginary lines to guide us.
Q15: Describe India’s Chandrayaan missions to the Moon and their significance. (3 Marks)
Ans: India launched its first Moon mission, Chandrayaan-1, in 2008, followed by Chandrayaan-2 in 2019. Chandrayaan-3 was launched in July 2023, and its Vikram lander with the Pragyan rover successfully soft-landed on 23 August 2023 near the Moon’s south pole, making India the first country to achieve a landing in this less-explored region. To celebrate this achievement, 23 August was declared as ‘National Space Day’ in India. A fourth mission, Chandrayaan-4, is being planned to bring back soil and rock samples from the Moon.
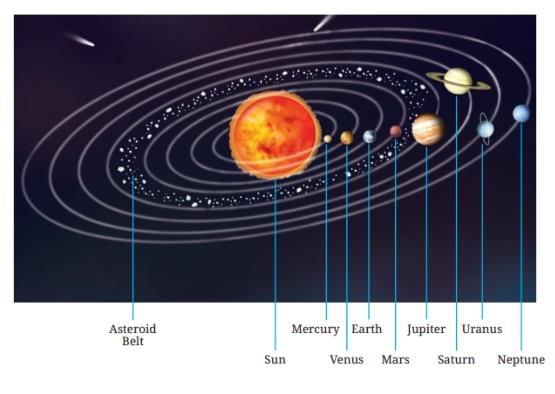
Q16: Describe the structure of our Solar System, including key components and their characteristics. (4 Marks)
Ans:
- The Solar System consists of the Sun at the center, a star providing energy, around which eight planets revolve: inner rocky planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) and outer gaseous giants (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) with rings. Earth has one natural satellite, the Moon, which revolves in 27 days and has craters from impacts.
- Between Mars and Jupiter lies the asteroid belt, containing numerous rocky objects called asteroids.
- Comets from outer regions have icy tails when near the Sun.
- Meteoroids are smaller rocky or metallic objects moving through space, some of which enter Earth’s atmosphere as meteors.
- All these objects together form part of the Milky Way Galaxy, with the Sun as the largest object reflecting light off others.
|
70 videos|367 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solution): Beyond Earth - Science for Class 6
| 1. What is the significance of space exploration in understanding our universe? |  |
| 2. What are some of the major achievements in space exploration? |  |
| 3. How does studying other planets help us understand Earth? |  |
| 4. What role do satellites play in modern space exploration? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced in space exploration? |  |





















