Unit Test (Solution): Living Creatures-Exploring their Characteristics | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Attempt all questions.
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
- Question numbers 1 to 7 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 8 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 13 to 15 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 16 carries 4 marks each.
Q1: Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of living beings? (1 Mark)
(i) Movement
(ii) Growth
(iii) Reproduction
(iv) Staying the same size forever
Ans: (iv) Staying the same size forever
Living beings grow and change size over time, unlike non-living things that remain unchanged.
Q2: What do plants excrete during photosynthesis? (1 Mark)
(i) Carbon dioxide
(ii) Oxygen
(iii) Water
(iv) Nutrients
Ans: (ii) Oxygen
During photosynthesis, plants release oxygen as a by-product, which is essential for most living organisms on Earth.
Q3: Plants show movement by opening flowers or trapping insects, as in the example of __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: Drosera
Drosera is an insectivorous plant that uses hair-like projections to trap insects, demonstrating plant movement.
Q4: The process of removal of waste products from the body is called __________. (1 Mark)
(i) Respiration
(ii) Excretion
(iii) Reproduction
(iv) Germination
Ans: (ii) Excretion
Excretion involves removing waste like sweat in humans or water droplets on plant leaves.
Q5: A stimulus is any event that prompts living beings to __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: respond
Stimuli like touch cause responses, such as the leaves of the touch-me-not plant folding.
Q6: For seed germination, seeds require water to soften the __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: seed coat
Water softens the seed coat, allowing the embryo inside to develop into a plant.
Q7: In the life cycle of a frog, the stage after tadpole with legs is the __________. (1 Mark)
(i) Spawn
(ii) Embryo
(iii) Froglet
(iv) Adult frog
Ans: (iii) Froglet
The froglet stage follows the tadpole with legs, where the tail begins to shorten.
Q8: List any three characteristics that distinguish living beings from non-living things. (2 Marks)
Ans: Living beings grow, respire, respond to stimuli, reproduce, and excrete. Non-living things do not show these characteristics, even if they can move (like a car).
Q9: Explain how the light requirements for germination differ among flowering plants. Give examples. (2 Marks)
Ans: Some seeds, like Coleus and Petunia, require light to germinate, so covering them with soil can prevent sprouting. Other seeds, such as Calendula and Zinnia, need darkness for germination and should be covered with sufficient soil to sprout successfully.
Q10: Give any two examples of movements in plants. (2 Marks)
Ans: Opening of flowers is one of the examples of movement in plants. Another example of movement in plants is seen in insectivorous plants. Drosera, which is an insectivorous plant, has saucer-shaped leaves with many hair-like projections of unequal length with sticky ends. Whenever an insect enters the saucer, hairs move inward and trap the insect with their sticky ends.
Q11: Differentiate between the pupa and larva stages in a mosquito's life cycle. (2 Marks)
Ans: The larva is a worm-like stage that lives in water and feeds actively, while the pupa is a non-feeding, comma-shaped stage that transforms into the adult mosquito. Both require air from the water surface.
Q12: Why is reproduction necessary for living beings? (2 Marks)
Ans: Reproduction is necessary for the continuity of life, as it produces new individuals of the same kind. Without it, species would end after death, as seen in the life cycles of plants and animals.
Q13: Which conditions are necessary for a seed to germinate, and how do water, air, and light affect the process of germination? (3 Marks)
Ans: 
Q14: How do plants respond to stimuli? Give two examples and explain the type of stimulus responsible. (3 Marks)
Ans: Plants respond to different types of stimuli from their environment. For example, the touch-me-not (Mimosa or Chhui-mui) folds its leaves when touched, which is a response to a mechanical or touch stimulus. Another example is the amla (Indian gooseberry) tree, whose leaves fold together after sunset, responding to changes in light intensity, a type of light stimulus. These responses help plants protect themselves, conserve water, or adjust to environmental conditions, showing that plants, like animals, are sensitive and react to stimuli around them.
Q15: Draw a diagram illustrating life cycle of a bean Plant. (3 Marks)
Ans: 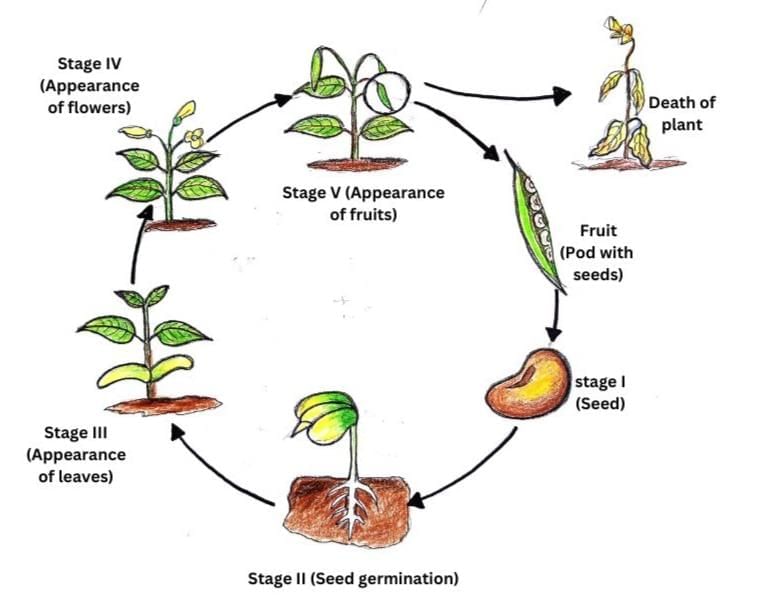
Q16: Compare the life cycles of a mosquito and a frog, highlighting significant changes and their importance. (4 Marks)
Ans:
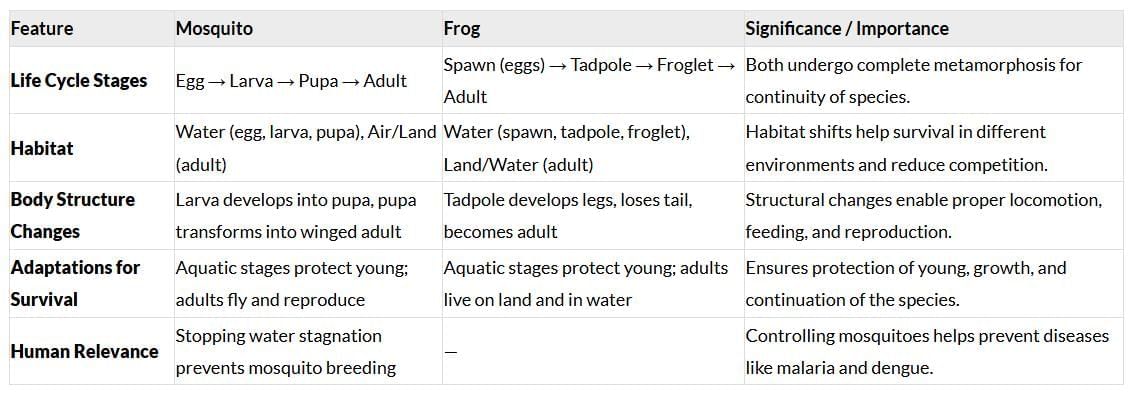
|
70 videos|367 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solution): Living Creatures-Exploring their Characteristics - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the main characteristics that define living creatures? |  |
| 2. How do living organisms differ from non-living things? |  |
| 3. Why is the classification of living organisms important? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of adaptation in living creatures? |  |
| 5. How do scientists study the characteristics of living organisms? |  |















