Unit Test (Solutions): Health: The Ultimate Treasure | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
Q1: According to WHO, health is (1 Mark)
(i) the absence of disease only
(ii) complete physical, mental, and social well-being
(iii) physical fitness only
(iv) freedom from hospital visits
Ans: (ii)
Health includes physical, mental, and social well-being, not just “not being sick”; emotions, relationships, and functioning matter too.
Q2: Which of the following is a non-communicable disease? (1 Mark)
(i) Measles
(ii) Typhoid
(iii) Diabetes
(iv) Chickenpox
Ans: (iii)
Diabetes is linked to lifestyle, diet, hormones, and genetics and does not spread person-to-person.
Q3: Which measure most directly reduces transmission of diseases spread by air? (1 Mark)
(i) Boiling water
(ii) Using mosquito nets
(iii) Wearing masks in crowded places
(iv) Deworming tablets
Ans: (iii)
Masks, respiratory etiquette, and ventilation reduce droplet/aerosol spread of respiratory infections.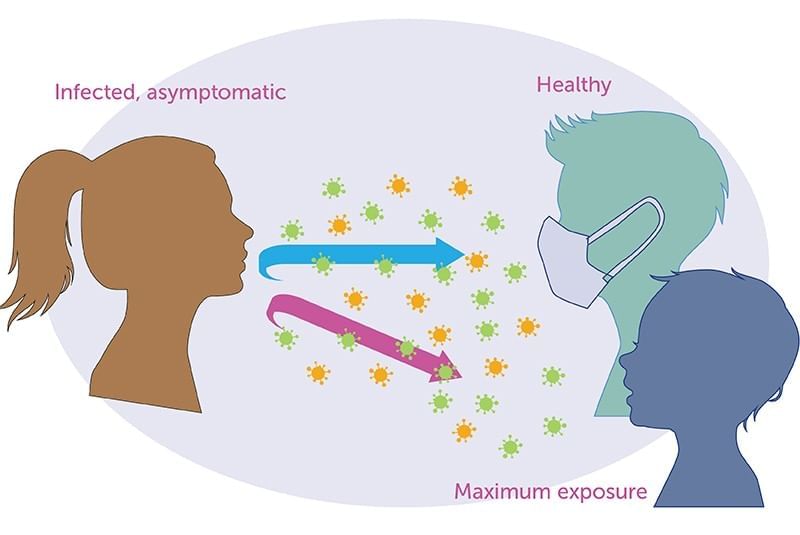
Q4: Which statement about antibiotics is correct? (1 Mark)
(i) They work against bacteria, not viruses
(ii) They cure viral colds
(iii) They replace vaccines
(iv) They prevent vector-borne diseases
Ans: (i)
Antibiotics target bacterial structures/processes; they do not treat viral illnesses like flu or common cold.
Q5: Which prevention is most relevant for dengue? (1 Mark)
(i) Boiling drinking water only
(ii) Using mosquito nets and eliminating stagnant water
(iii) Wearing woollens
(iv) Taking antibiotics
Ans: (ii)
Dengue spreads via Aedes mosquitoes; nets/repellents, covered tanks, and removing stagnant water interrupt transmission.
Q6: Distinguish between “signs” and “symptoms” with one example each. (2 Marks)
Ans: Symptoms are subjective experiences (e.g., headache, tiredness). Signs are observable/measurable findings (e.g., fever measured by thermometer, rash seen on skin). Both guide diagnosis.
Q7: List two daily habits that promote mental health in students. (2 Marks)
Ans: (i) Regular sleep schedule and screen-time limits,
(ii) Social connection through friends/family, relaxation/yoga/mindfulness. These lower stress, improve mood, focus, and resilience.
Q8: State two differences between communicable and non-communicable diseases. (2 Marks)
Ans: 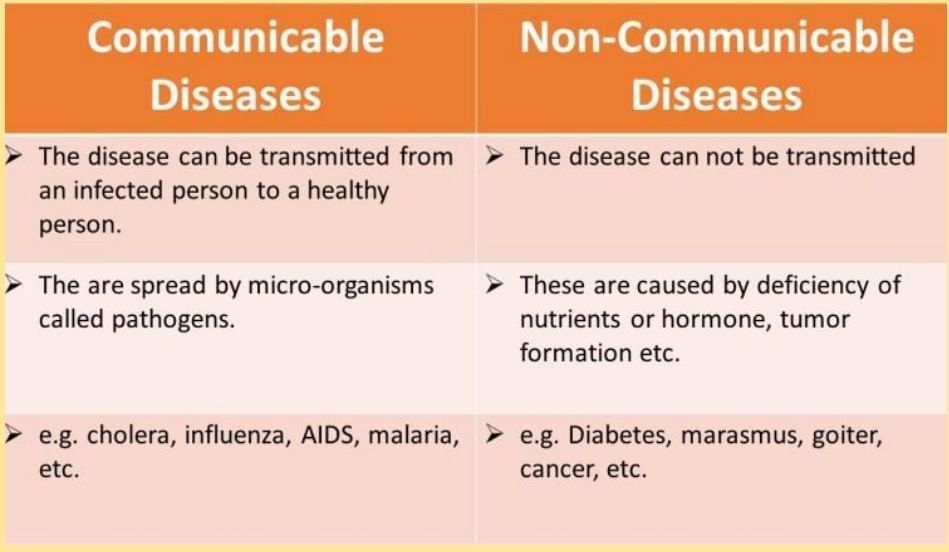
Q9: A classmate has a cold and is still attending school coughing and sneezing. What can the school and students do immediately to reduce spread? (3 Marks)
Ans: School: encourage the student to rest at home; ensure masks and tissues; improve ventilation; enhance cleaning of high-touch surfaces. Students: follow cough etiquette (elbow/tissue), wear masks in crowded spaces, handwashing with soap, avoid sharing bottles/towels; be kind and non-stigmatizing.
Q10: Explain why contaminated water increases risk of cholera and typhoid and list two preventive steps for each. (3 Marks)
Ans: Cholera (Vibrio cholerae) and typhoid (Salmonella typhi) are fecal-orally transmitted; pathogens in excreta can contaminate water/food and infect others. Prevention: safe water (boiling/filtration/chlorination), hygienic food handling, handwashing with soap, sanitation (toilets), and vaccination where applicable.
Q11: Why is prolonged screen time a health concern in children? Mention three possible effects and one mitigation each. (3 Marks)
Ans: Effects: (i) Dry eye/eye strain—20-20-20 rule, blink breaks;
(ii) Poor sleep/anxiety—digital curfew 1–2 hours before bed;
(iii) Obesity/sedentary risks—outdoor play, scheduled physical activity; plus posture problems—ergonomic setup and breaks.

Q12: (a) Explain how vaccines prevent disease.
(b) Why are vaccines called “preventive, not curative”?
(c) Give two examples of childhood vaccines and the diseases they prevent. (5 Marks)
Ans:
(a) Vaccines introduce weakened/killed pathogens or harmless parts (or instructions to make them) to train the immune system to recognize and rapidly neutralize the real germ later (acquired immunity, memory response).
(b) They work before exposure or early in exposure by priming immunity; they do not “treat” active illness (once sick, supportive/antimicrobial therapy is needed depending on cause).
(c) Examples: Measles vaccine prevents measles; Polio vaccine prevents poliomyelitis; Hepatitis B vaccine prevents hepatitis B; DPT prevents diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus.
Q13: (a) What is antibiotic resistance and how does it develop/spread?
(b) List four do’s/don’ts for responsible antibiotic use. (c) Why don’t antibiotics treat flu? (5 Marks)
Ans:
(a) Resistance is when bacteria survive antibiotics that previously killed them. It emerges via mutation/selection and spreads through misuse (unnecessary use, wrong dose/duration), use in animals, poor infection control, and horizontal gene transfer. It disseminates via people, food, water, and environments.
(b) Do use only with a doctor’s prescription; complete full course; follow dose/timing. Don’t use for viral colds/flu; don’t self-medicate or share antibiotics; don’t stop early when you “feel better”.
(c) Flu is viral; antibiotics target bacteria, not viruses. Misuse fuels resistance and side effects without benefit.
|
59 videos|235 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Health: The Ultimate Treasure - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the importance of maintaining good health? |  |
| 2. How can one achieve a balanced diet? |  |
| 3. What are some effective ways to manage stress? |  |
| 4. Why is regular physical activity important for health? |  |
| 5. What role does hydration play in maintaining health? |  |
















