Unit Test (Solutions): Nature’s Treasures | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Attempt all questions.
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
- Question numbers 1 to 7 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 8 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 13 to 15 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 16 carries 4 marks each.
Q1: What is the main gas in air that living beings need for survival? (1 Mark)
(i) Nitrogen
(ii) Oxygen
(iii) Carbon dioxide
(iv) Argon
Ans: (ii) Oxygen
Oxygen is essential for the body to perform its functions, as shown in the breathing exercise where holding breath causes discomfort due to lack of oxygen.
Q2: Moving air is called __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: wind
Wind is observed when leaves rustle or clothes sway, and it powers devices like the firki and windmills.
Q3: Water covers about __________ of the Earth's surface. (1 Mark)
(i) One-third
(ii) Half
(iii) Two-thirds
(iv) Three-fourths
Ans: (iii) Two-thirds
Most of this water is saline in oceans and seas, unfit for domestic use, making freshwater precious.
Q4: The Sun is the main source of __________ on Earth. (1 Mark)
Ans: energy
All plants and animals depend on the Sun's energy; plants use it for food, and animals get it indirectly through plants.
Q5: Forests are large areas with dense growth of __________. (1 Mark)
(i) Rocks
(ii) Various types of plants
(iii) Minerals
(iv) Fossil fuels
Ans: (ii) Various types of plants
Forests provide food and shelter to wild animals, birds, and insects, supporting biodiversity.
Q6: Soil is formed by the __________ of rocks over a long time. (1 Mark)
(i) Growth
(ii) Disintegration
(iii) Melting
(iv) Freezing
Ans: (ii) Disintegration
This process involves actions of the Sun, water, and living organisms over thousands of years.
Q7: Fossil fuels like coal and petroleum are examples of __________ resources. (1 Mark)
(i) Renewable
(ii) Human-made
(iii) Non-renewable
(iv) Recyclable
Ans: (iii) Non-renewable
They take millions of years to form and are exhausted once used, leading to pollution when burnt.
Q8: Explain why air is considered a treasure of nature and Describe the composition of air. (2 Marks)
Ans: Air is a treasure because it contains oxygen essential for survival, refreshes us, and supports fertile soil and sunlight utilization. Without it, life on Earth is impossible, as most living beings need oxygen for functions.
Air is a mixture of gases: 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% argon, 0.03 - 0.04 % carbon dioxide, and others.
Q9: Why is ocean water not suitable for domestic use? (2 Marks)
Ans: Sea and ocean water contains large amounts of various salts. It is due to these salts the ocean water is salty and cannot be used for drinking, washing and for irrigation purposes.
Q10: How does the Sun provide energy to a cow indirectly? (2 Marks)
Ans: The Sun provides energy to the cow indirectly through grass. Sunlight helps grass leaves grow and prepare food, and the cow gets energy by eating the grass.
Q11: Name two products obtained from forests. (2 Marks)
Ans: Fruits like nellikai (Indian gooseberries) and medicinal herbs. Forests also provide timber for furniture and fuelwood.
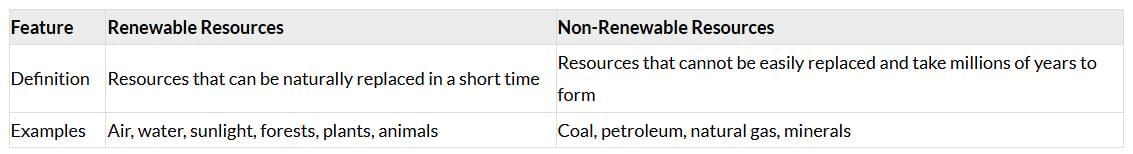
Q12: Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable resources with one example each. (2 Marks)
Ans:
Q13: Why is rainwater harvesting important in India? Give two reasons. (3 Marks)
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is important in India because it helps conserve the limited freshwater resources by collecting and storing rainwater for later use in homes, schools, and residential societies. It also prevents water shortage in dry regions like Rajasthan and Gujarat, where traditional stepwells (Bawadi or Vav) are built to store rainwater as well as water seeping from nearby lakes, ponds, and rivers. This practice ensures that clean water is available for drinking, irrigation, and other daily needs, while also reducing pollution and making water accessible to all living beings.
Q14: Explain how soil is formed and why it is important. Also, describe the uses of rocks and minerals in our daily life with examples. (3 Marks)
Ans: Soil is formed by the breaking down of rocks over thousands of years through the action of the Sun, water, and living organisms. It contains air, water, minerals, and decomposed matter, which provide space for roots to grow and support plant growth. Soil is important because it helps grow food, supports biodiversity, and is essential for life on Earth. Rocks are used in building houses, roads, temples, and dams, while minerals such as gold, copper, and iron are used to make tools, vehicles, jewellery, and electronic equipment like mobile phones. These resources are precious and should be used carefully.
Q15: Explain how forests prevent floods. (3 Marks)
Ans: Raindrops in a forest do not hit the ground directly. The uppermost layer of the forest canopy intercepts the raindrops, and most of the water comes down up to soil through the branches and the stems of the trees. From the leaves it drops slowly over the branches of the shrubs and herbs. Also forest trees have extensive deep roots that absorb and store rain water. Thus forests act as a natural absorber of rainwater and allows it to seep and therefore help in controlling floods.
Q16: Discuss the importance of conserving natural resources like forests and fossil fuels. Suggest three actions to achieve this. (4 Marks)
Ans: Conserving forests maintains biodiversity by providing food and shelter to animals, prevents soil erosion as roots hold soil, and enriches it through decaying leaves for new plant growth. It takes years for forests to regenerate, so large-scale cutting disrupts ecosystems. Fossil fuels like coal and petroleum are non-renewable, taking millions of years to form; overuse causes air pollution from smoke and exhausts supplies quickly. Conservation ensures resources for future needs without harming the environment.
Three actions:
(1) Plant trees during Van Mahotsav to increase green cover;
(2) Use public transport or cycle to reduce fossil fuel dependence;
(3) Follow traditions like not plucking fruits from trees, leaving them for wildlife.
|
86 videos|288 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Nature’s Treasures - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are some examples of natural treasures found in nature? |  |
| 2. How do natural treasures contribute to biodiversity? |  |
| 3. Why is it important to conserve natural treasures? |  |
| 4. What are some threats to natural treasures? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to the preservation of natural treasures? |  |
















