Unit Test (Solutions): The Frog | English Santoor Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. Where does the frog often sit?
(a) In the desert
(b) In ponds and in the rain
(c) On mountain tops
(d) In hot sand
Ans: (b) The frog often sits in ponds and in the rain.
Frogs like wet places, so they are found in ponds and when it rains.
Q2. True / False:
Frogs live only on land and never in water.
Ans: False.
The poem says the frog lives on land and water, and swims as a tadpole too.
Q3. Fill in the blank:
As a young tadpole the frog swims like a ______.
Ans: As a young tadpole, the frog swims like a tiny fish.
Q4. What helps the frog to catch food quickly?
(a) Sharp claws
(b) Long ears
(c) Flicking its tongue
(d) Big teeth
Ans: (c) Flicking its tongue helps the frog catch food quickly.
The frog’s tongue moves fast to catch insects.
Q5. Fill in the blank:
The frog’s colours help it to ______.
Ans: The frog’s colours help it to hide among plants and leaves.
Matching colours makes the frog hard for predators to see.
Q6. Why must the frog beware of snakes?
Ans: The frog must beware of snakes because snakes can catch and eat it.
Snakes are predators that hunt frogs.
Q7. How do webbed feet help the frog?
Ans: Webbed feet help the frog to swim with ease and move quickly in water.
The webbing between the toes gives the frog more surface to push water.
Q8. What do the frog’s croaks tell us about its feelings?
Ans: The frog’s loud croaks show that it is proud and happy in its pond.
The poem describes the frog croaking loudly and feeling proud of its pond.
Q9. Match the following (3 marks)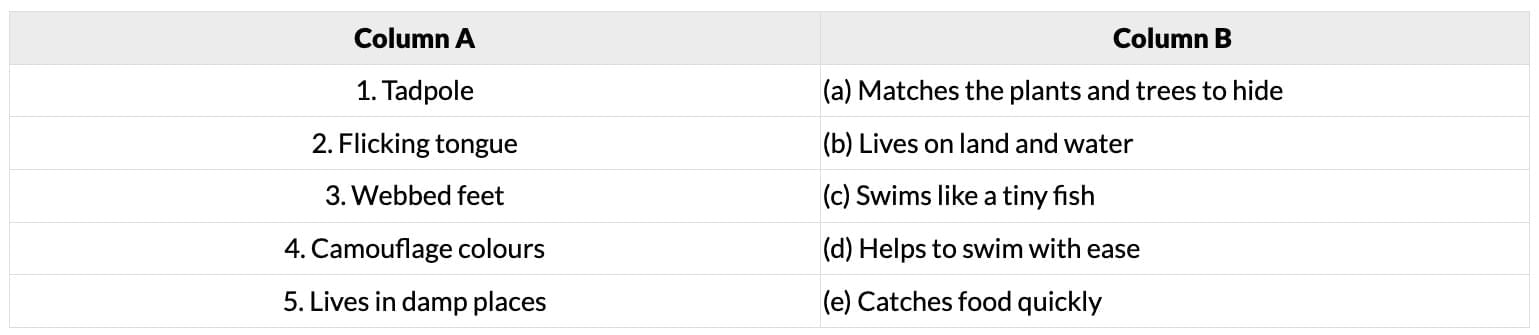
Ans: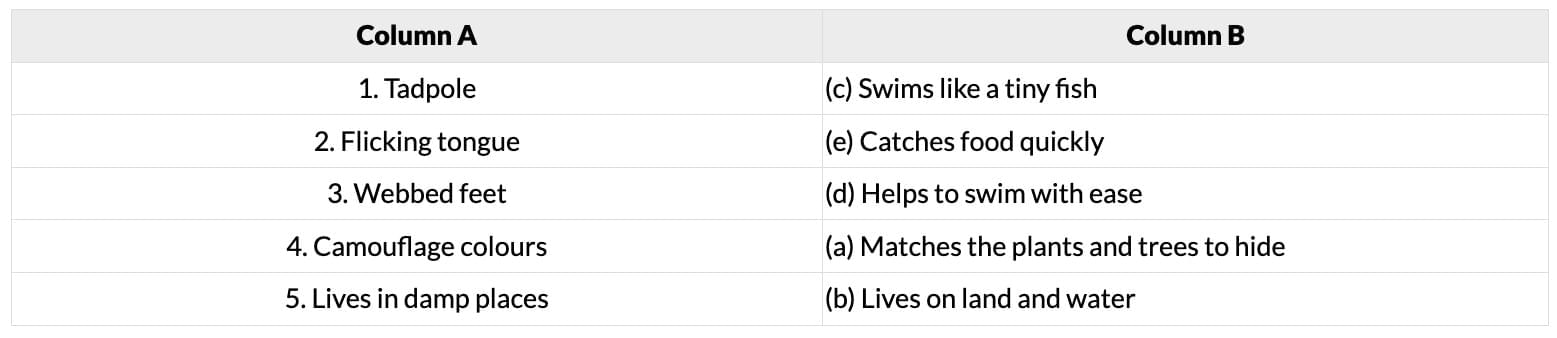
Q10. Describe three ways the poem shows that the frog is suited to both land and water.
Ans:
- The frog is first a tadpole that swims like a tiny fish, which shows it is suited to water.
- The frog has webbed feet that make swimming easy, which helps it move well in water.
- The frog also hops on land and hides in grass and leaves, which shows it lives comfortably on land, too.
Q11. Explain why the frog’s colours are important for its safety.
Ans: The frog’s colours help it to blend with plants and trees so that predators cannot see it easily, and this hiding keeps the frog safe.
Brief explanation: Camouflage makes it hard for enemies like snakes to spot the frog.
Q12. How does the poem show the frog’s joy in its life? Give two examples and explain them.
Ans:
- The poem says the frog “croaks” loudly and feels proud in its pond, which shows the frog is happy and confident about its home.
- The frog “hops around” and “leaps so high,” which shows that it enjoys jumping and playing.
- Together, these actions and sounds describe a lively, joyful life in the pond.
Q13. Why is it important for children to learn about animals like the frog from poems and short passages? Give three reasons.
Ans:
- Learning about animals helps children understand different kinds of life and how animals live in nature.
- Poems make learning fun and help children remember facts like where animals live and how they move.
- Understanding animals also teaches children to respect and protect nature and the habitats where animals live.
|
40 videos|659 docs|63 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): The Frog - English Santoor Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the life cycle of a frog and how does it differ from other amphibians? |  |
| 2. Why are frogs considered important indicators of environmental health? |  |
| 3. What are the primary threats to frog populations worldwide? |  |
| 4. How do frogs adapt to their environments? |  |
| 5. What role do frogs play in their ecosystems? |  |
















