Unit Test: Journey of a River | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 45 Minutes
M.M.: 20
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 6 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 7 to 9 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 10 carries 5 marks.
Q1. The Godavari River begins at which place?
(a) Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh
(b) Trimbakeshwar, Brahmagiri Hills, Maharashtra
(c) Gangotri, Uttarakhand
(d) Mahabaleshwar, Maharashtra
Q2. Fill in the blanks:
The Godavari is India’s __________-longest river and flows for about __________ km.
Q3. True or False:
The Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary lies in the Godavari delta near Kakinada and has mangrove forests.
Q4. Rivers like Manjira, Indravati, and Sabari that join the Godavari are called __________.
Q5. Match the following:
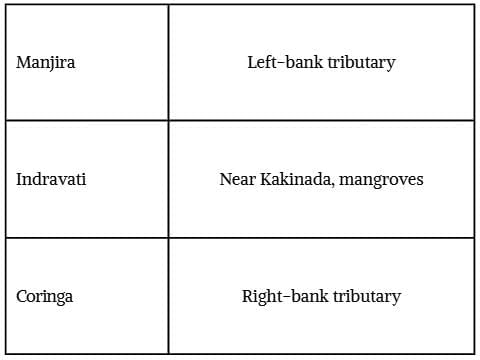
Q6. The Godavari is also called “Dakshina Ganga” because it is a major sacred river of southern India. This statement is:
(a) Always false
(b) True
(c) True only during monsoon
(d) True only in Maharashtra
Q7. List any three ways the Godavari supports human life and briefly explain each.
Q8. Explain how dams help people and also how they can cause problems. Give one point for each help and each problem.
Q9. Why is the Godavari delta around Coringa important for wildlife, and how do mangroves help during storms or floods?
Q10. A school near the Godavari plans an eco-club project to keep the river clean. Design a 5-point action plan that students can do without harming the environment. Include at least one awareness activity, one waste-reduction step, one monitoring step, and one community partnership.
Find Solutions of the Unit Test: Here
|
11 videos|211 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test: Journey of a River - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main stages in the journey of a river? |  |
| 2. How do rivers contribute to the ecosystem? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of rivers in human civilization? |  |
| 4. What are some common environmental issues faced by rivers? |  |
| 5. How can we protect rivers and their ecosystems? |  |
















