Unit Test(Solutions): Structure of the Atom | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. What are canal rays? (1 Mark)
Ans: Canal rays are positively charged radiations discovered by E. Goldstein in 1886, which led to the discovery of protons.
Q2. What is the charge of an atom with one electron and one proton? (1 Mark)
Ans: Neutral, as the negative charge of the electron balances the positive charge of the proton.
Q3. Which subatomic particle was discovered by J. Chadwick? (1 Mark)
Ans: Neutron.
Q4. What is the maximum number of electrons in the K-shell? (1 Mark)
Ans: 2.
Q5. Which model of the atom compares it to a Christmas pudding? (1 Mark)
Ans: Thomson’s model of the atom
Q6. State two features of Rutherford’s model of the atom. (2 Marks)
Ans:
There is a positively charged centre in the atom called the nucleus.
The electrons revolve around the nucleus in well-defined orbits.
Q7. How is the valency of fluorine determined? (2 Marks)
Ans: Fluorine has 7 electrons in its outermost shell. It gains one electron to achieve an octet, so its valency is 1 (8 - 7 = 1).
Q8. Differentiate between atomic number and mass number. (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Atomic number (Z): Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Mass number (A): Sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Q9. Explain the limitations of Thomson’s model of the atom. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- It could not explain results of experiments like Rutherford’s alpha-particle scattering.
- It did not account for the presence of a nucleus or the arrangement of electrons.
- It failed to explain the stability and spectral properties of atoms.
Q10. Describe Bohr’s model of the atom with its postulates. (3 Marks)
Ans: Bohr’s model: Electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed energy orbits or shells.
Postulates:
Electrons revolve in fixed orbits without radiating energy.
Each orbit has a fixed amount of energy.
Energy is absorbed or emitted when an electron moves from one orbit to another.
Q11. What are isotopes? Explain with two examples. (3 Marks)
Ans: Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to varying neutrons.
Example:
1. Carbon-12 (¹²C) and Carbon-14 (¹⁴C) – both have 6 protons, but Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons while Carbon-14 has 8 neutrons.2. Hydrogen Isotopes:
Protium (¹H): 1 proton, 0 neutrons
Deuterium (²H): 1 proton, 1 neutron
Tritium (³H): 1 proton, 2 neutrons
All three are isotopes of hydrogen.
Q12. Explain Rutherford’s alpha-particle scattering experiment and its conclusions. (5 Marks)
Ans: Rutherford’s experiment involved firing fast-moving alpha particles at a thin gold foil. Observations:
1. Most alpha particles passed through the foil.
2. Some were deflected by small angles.
3. Very few were deflected back.Scattering of α-particles by a gold foilConclusions:
1. Most of the space in an atom is empty.
2. The atom has a small, dense, positively charged nucleus.
3. Electrons revolve around the nucleus.
4. The size of the nucleus is very small compared to the atom.
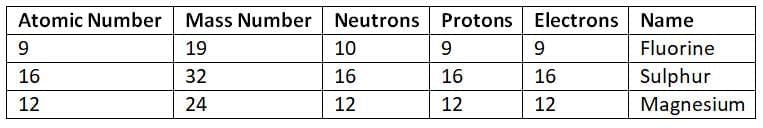
Q13. Complete the table for the given atomic species and identify their relationship. (5 Marks)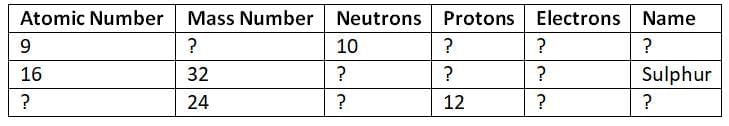
Ans:Relationship:
All three are neutral atoms (electrons = protons).
They do not have the same atomic number or mass number, so they are not isotopes or isobars.
They are different elements with different atomic structures.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test(Solutions): Structure of the Atom - Science Class 9
| 1. What is the structure of an atom and what are its main components? |  |
| 2. How did early scientists contribute to our understanding of atomic structure? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the atomic number and mass number in an atom? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of isotopes and give examples? |  |
| 5. What is the role of electrons in atomic structure and chemical bonding? |  |