Unit Test(Solutions): The Fundamental Unit of Life | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each
Q1: Which of the following cellular structures contains its own DNA and is thought to be an ancient prokaryote symbiotically living in eukaryotic cells? (1 Mark)
(i) Lysosome
(ii) Mitochondria
(iii) Golgi apparatus
(iv) Endoplasmic reticulum
Ans: (ii)
Mitochondria contain their own DNA, which is circular like that of prokaryotes, supporting the endosymbiotic theory that they originated as free-living prokaryotes.
Q2: Fill in the blank: The semi-fluid substance inside the cell, which contains organelles and the cytoskeleton, is known as "________."
(1 Mark)
Ans: Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance within the cell that surrounds the organelles, providing a medium for cellular processes to occur.
Q3: Who discovered the cell while examining a thin slice of cork?
(i) Anton van Leeuwenhoek
(ii) Robert Hooke
(iii) Matthias Schleiden
(iv) Theodor Schwann
Ans: (ii)
Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665 when he observed the structure of cork through a self-designed microscope and noticed tiny, room-like compartments, which he called "cells."
Q4: True or False: The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for the synthesis of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells.(1 Mark)
Ans: False
The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for the synthesis of proteins and lipids, not ribosomes. Ribosomes are synthesized in the nucleolus of the nucleus.
Q5: Which of the following organelles plays a key role in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins for secretion or delivery to other organelles?(1 Mark)
(i) Nucleus
(ii) Mitochondria
(iii) Golgi apparatus
(iv) Ribosomes
Ans: (iii)
The Golgi apparatus is involved in the modification, sorting, and packaging of proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles, making it a crucial component of the cellular machinery.
Q6: Describe the function of the plasma membrane in a cell. (2 Marks)
Ans: The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that regulates the entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell. It allows essential nutrients and gases to enter the cell while removing waste products, thereby maintaining the cell's internal environment.
Q7: Differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of their nuclear region. (2 Marks)
Ans:
| Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|
| The nuclear region is not well-defined and is called a nucleoid. | The nuclear region is well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane. |
| No membrane-bound organelles are present. | Contains membrane-bound organelles, including a true nucleus. |
Q8: What would happen to an animal cell if placed in a hypotonic solution? (2 Marks)
Ans: In a hypotonic solution, the surrounding medium has a higher water concentration than inside the cell. Water enters the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to swell, and in extreme cases, it may burst (lyse) due to the influx of water.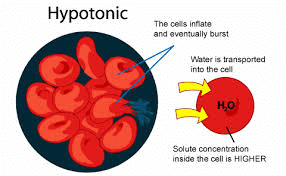
Q9: Explain the role of mitochondria in a cell. (3 Marks)
Ans: Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell because they generate ATP through the process of cellular respiration. They have a double membrane, with the inner membrane folded into cristae to increase the surface area for energy production. Mitochondria also have their own DNA, allowing them to produce some of their own proteins independently.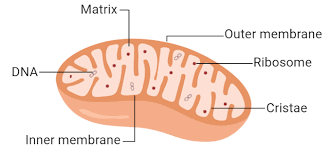
Q10: Describe the process of osmosis and its importance in the cell. (3 Marks)
Ans: Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. It is vital for maintaining cell turgidity, which is crucial for plant cells, and for the regulation of water balance in animal cells. It also plays a role in the absorption of water by plant roots and the removal of waste products from cells.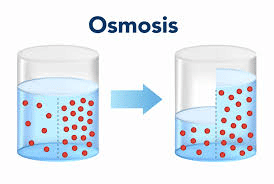
Q11: Discuss the structure and function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell. (3 Marks)
Ans: The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell's genetic material (DNA). It has a double-layered nuclear membrane with pores for material exchange between the nucleus and cytoplasm. The nucleus controls cellular activities by regulating gene expression and plays a crucial role in cell division by housing chromosomes that carry genetic information for inheritance.
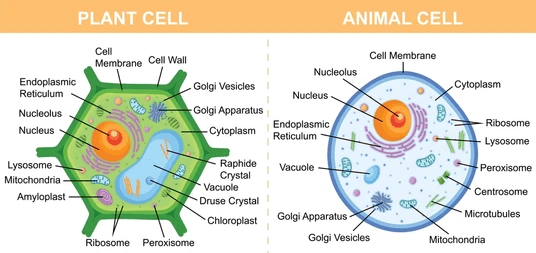
Q12: Compare and contrast plant cells and animal cells based on their structure and organelles. (5 Marks)
Ans: 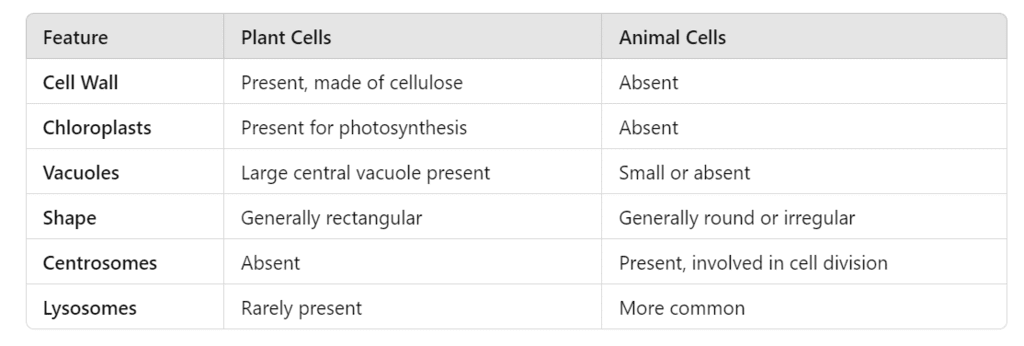
- Plant cells have a rigid cell wall that provides structural support, while animal cells lack a cell wall.
- Chloroplasts in plant cells are responsible for photosynthesis, a process absent in animal cells.
- Vacuoles in plant cells are large and central, storing nutrients and waste products, whereas vacuoles in animal cells are smaller and may not be present.
- Additionally, plant cells generally have a more regular, rectangular shape, while animal cells are more flexible in shape.
- Centrosomes, involved in cell division, are found in animal cells but not in plant cells.
- Lysosomes, responsible for waste digestion, are more commonly found in animal cells.
Q13: Explain the process of cell division and its importance in growth and reproduction. (5 Marks)
Ans: Cell division is the process by which a single cell divides into two or more daughter cells. Cell division is fundamental for the survival of organisms, as it enables growth, repair of damaged tissues, and reproduction, thereby ensuring the continuity of life. There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis: This process involves the division of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells, each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Mitosis is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in organisms. It ensures that each new cell has the same genetic material as the original cell.
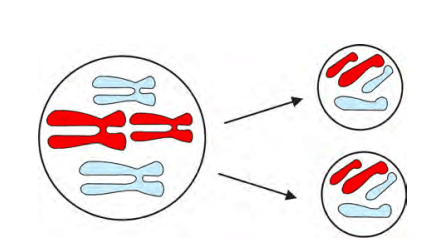 Mitosis
MitosisMeiosis: This type of cell division reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse daughter cells. Meiosis occurs in the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells) and is essential for sexual reproduction. It introduces genetic variation through the recombination and segregation of chromosomes.
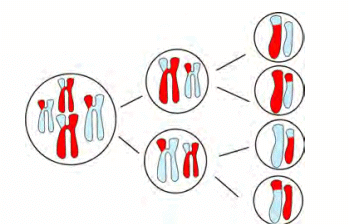 Meiosis
Meiosis
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test(Solutions): The Fundamental Unit of Life - Science Class 9
| 1. What is the structure of a typical cell ? |  |
| 2. What is the function of the cell membrane ? |  |
| 3. How do plant cells differ from animal cells ? |  |
| 4. What are organelles and why are they important ? |  |
| 5. What role does the nucleus play in a cell ? |  |
















