Unit Test: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
Q1: The basic unit of all living organisms is the (1 Mark)
(i) tissue
(ii) organ
(iii) cell
(iv) organ system
Q2: Which structure controls the activities inside a cell? (1 Mark)
(i) Cytoplasm
(ii) Nucleus
(iii) Cell membrane
(iv) Cell wall
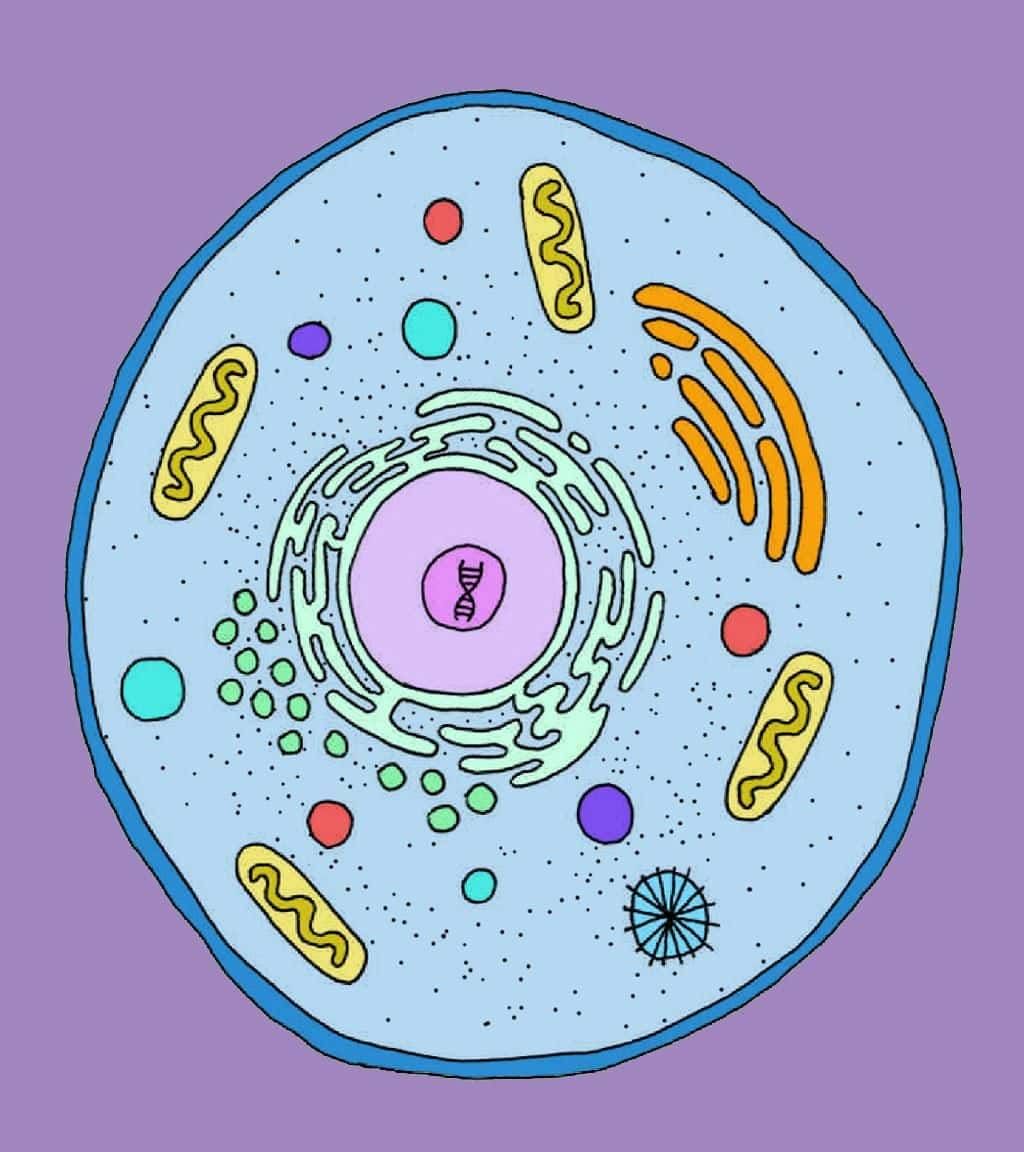 Cell
Cell
Q3: Onion peel cells appear rectangular and firm primarily because of the (1 Mark)
(i) nucleus
(ii) vacuole
(iii) chloroplast
(iv) cell wall
Q4: Which is a correct level-of-organisation sequence in organisms? (1 Mark)
(i) Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ system → Organism
(ii) Tissue → Cell → Organ → Organ system → Organism
(iii) Cell → Organ → Tissue → Organ system → Organism
(iv) Organism → Organ system → Organ → Tissue → Cell
Q5: Yeast makes dough rise mainly because it produces (1 Mark)
(i) oxygen
(ii) nitrogen
(iii) carbon dioxide
(iv) ammonia
 Rised Dough
Rised Dough
Q6: State two differences between plant cells and animal cells seen at this level of study. (2 Marks)
Q7: Define microorganisms. Give one example each of a unicellular microorganism and a multicellular microorganism. (2 Marks)
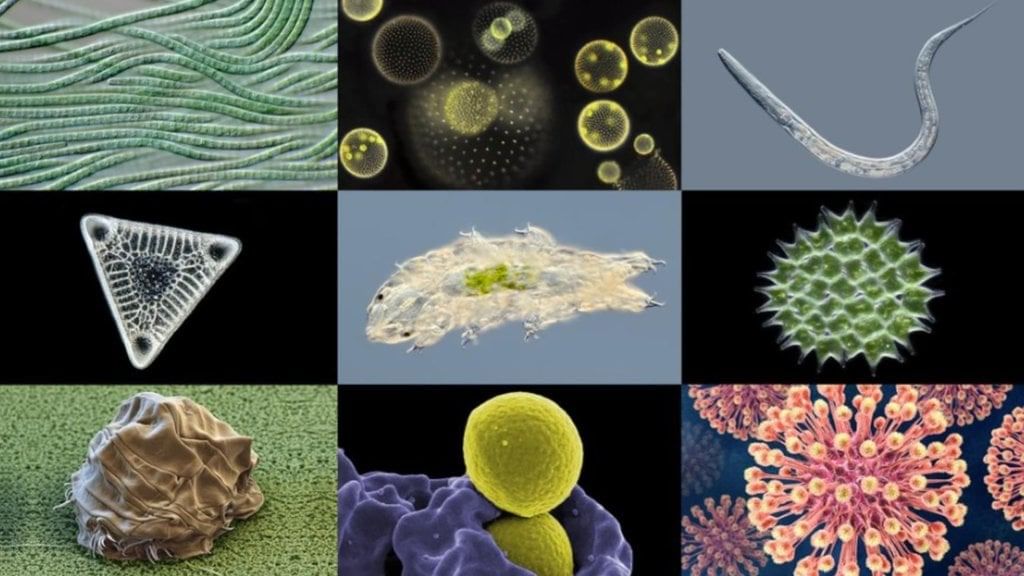 MicroorganismsQ8: What are root nodules and how do the bacteria in them benefit crops? (2 Marks)
MicroorganismsQ8: What are root nodules and how do the bacteria in them benefit crops? (2 Marks)
Q9: Explain how the structure of a nerve cell relates to its function. Contrast it briefly with a cheek cell. (3 Marks)
Q10: During the onion peel activity, why are stains (like safranin) and glycerin used? What would happen if a coverslip traps air bubbles? (3 Marks)
Q11: You observe pond water and soil suspension under a microscope. List two likely microorganisms from each and one short identifying feature. (3 Marks)
Q12: (a) Describe an investigation to show that yeast needs warmth and sugar to make dough rise.
(b) Explain the role of temperature and sugar in this process. (5 Marks)
Q13: Answer the following based on cells and microbes.
(a) Why is a cell called the basic unit of life?
(b) Distinguish bacteria from plant/animal cells in terms of the nucleus.
(c) Explain how microorganisms both “clean the environment” and “help in food”. (5 Marks)
|
59 videos|347 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the invisible living world and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How do microscopes help us study the invisible living world? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of beneficial microorganisms? |  |
| 4. How do harmful microorganisms affect human health? |  |
| 5. What techniques are used to study microorganisms in laboratories? |  |
















