Unit | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Physical Quantity |

|
| System of Units |

|
| Fundamental Quantities |

|
| Derived Quantities |

|
Physical Quantity

A physical quantity is a property of a body, substance, or phenomenon that can be quantified through measurement.
Measurement of a Physical Quantity
Measurement involves assigning a value to a physical quantity by comparing it with a standard or calibrated unit of that quantity. To determine the value or magnitude of a physical quantity, it is typically measured using different systems of units.
Errors in Measurement:
An error in measurement is the difference between the true value and the measured value of a quantity. There are three main types of measurement errors:
- Absolute Error: The difference between the true value and the measured value.
- Relative Error: The ratio of the absolute error to the mean value.
- Percentage Error: The relative error multiplied by 100.
System of Units
Physical quantities are measured using four main systems of units:
- CGS (Centimetre, Gram, Second)
- FPS (Foot, Pound, Second)
- MKS (Metre, Kilogram, Second)
- SI (International System of Units)
Fundamental Quantities
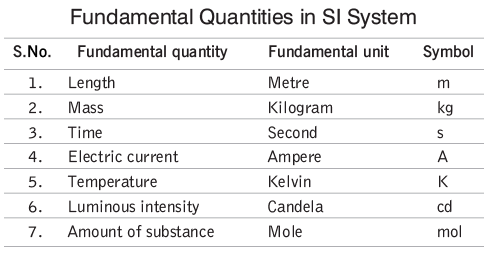
 Fundamental quantities are those that are independent of each other, and their units are called fundamental units. The most widely accepted system is the SI system, adopted in 1971 by the Conference of Weights and Measures held in Geneva. There are seven fundamental quantities in the SI system, along with two supplementary fundamental units:
Fundamental quantities are those that are independent of each other, and their units are called fundamental units. The most widely accepted system is the SI system, adopted in 1971 by the Conference of Weights and Measures held in Geneva. There are seven fundamental quantities in the SI system, along with two supplementary fundamental units:
- Radian (rad): Unit of plane angle.
- Steradian (sr): Unit of solid angle.
Derived Quantities
Derived quantities are those obtained using fundamental quantities, and their units are called derived units. Examples include velocity, force, work, density, and momentum.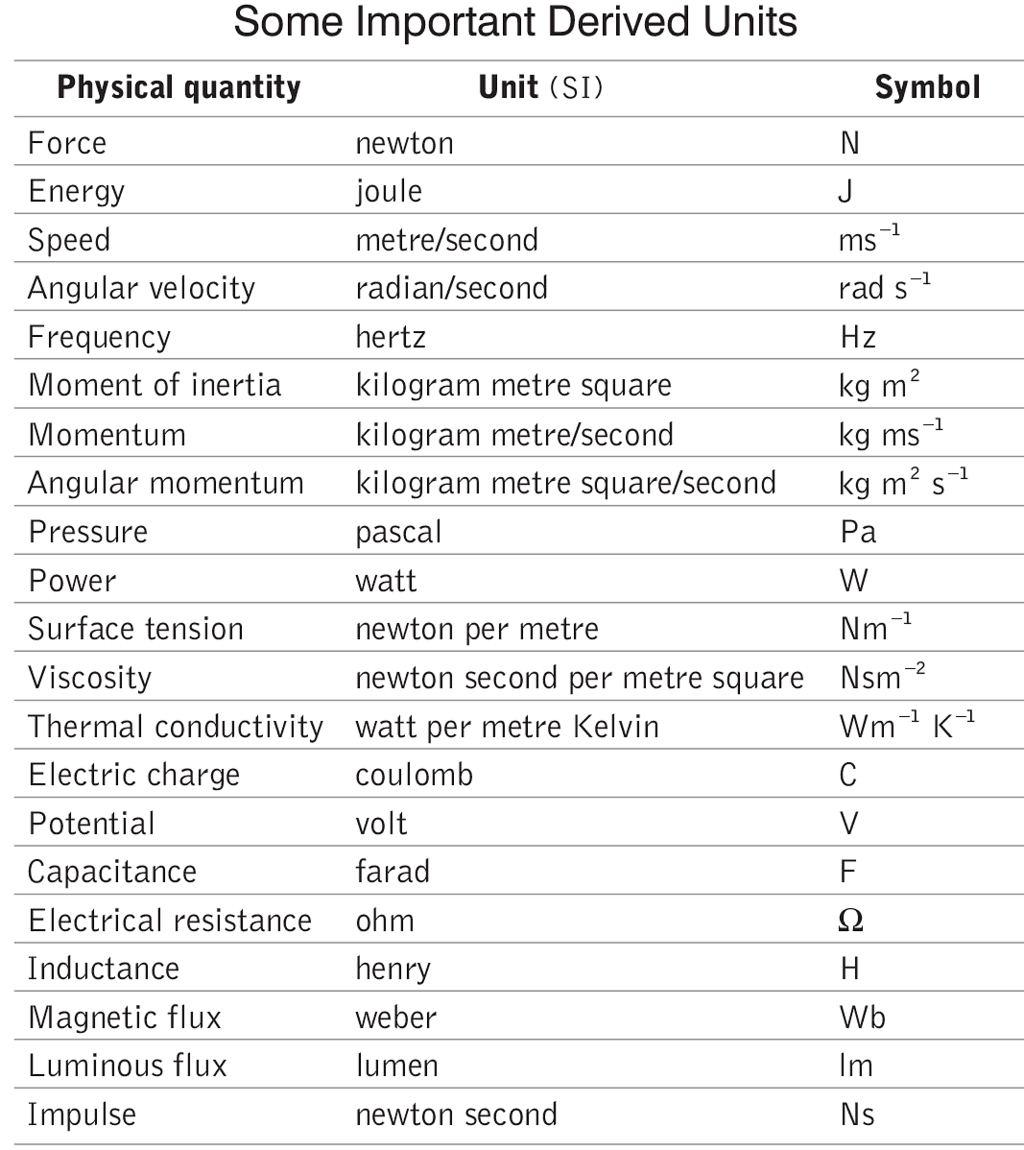
Unit of Length
The SI unit of length is the metre (m). One metre is the distance light travels in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second.
Other Units of Length
- Light Year: The distance light travels in one year in a vacuum (1 light year = 9.46 × 1015 m).
- Parsec (Parallactic Second): The distance at which an arc of one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second (1 parsec = 3.085 × 1016 m).
- Micron (µm): 10-6 m.
- Astronomical Unit (AU): 1.49 × 1011 m.
- Angstrom (Å): 10-10 m.
- Nanometre (nm): 10-9 m.
- X-unit: 10-14 m.
- Fermi: 10-15 m.
- Yard: 0.9144 m.
Units of Area
Area is related to the square of length. Some units of area include:
- Barn: 10-28 m2.
- Acre: 4047 m2.
- Hectare: 10,000 m2.
Units of Volume
Volume is related to the cube of length. Some units of volume include:
- 10 millilitres (mL) = 1 centilitre (cL) = 0.018 pint (0.021 US pint).
- 100 centilitres (cL) = 1 litre (L) = 1.76 pints.
- 10 litres (L) = 1 decalitre (daL) = 2.2 gallons (2.63 US gallons).
- 1 cubic centimetre (cm3) = 1 millilitre (mL).
- 1 barrel = 159 litres.
Unit of Mass
The SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). One kilogram is defined as the mass of 5.0188 × 1025 atoms of carbon-12.
Other Units of Mass:
Unit of Time
The SI unit of time is the second. One second is defined as 1/86,400 of a mean solar day.
Other Units of Time:
- 1 microsecond = 10-6 s
- 1 picosecond = 10-12 s
- 1 Lunar month = 29.5 day
- 1 nanosecond = 10-9 s
- 1 shake = 10-8 s
Important Prefixes to Units

|
470 videos|570 docs|394 tests
|
FAQs on Unit - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are fundamental quantities in the system of units? |  |
| 2. Can derived quantities be expressed in terms of fundamental quantities? |  |
| 3. How are physical quantities measured in the system of units? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of derived quantities in the system of units? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to use a standardized system of units in scientific measurements? |  |





















