Units & Measurements: Basic Mathematics | Additional Study Material for JEE PDF Download
BASIC MATHEMATICS
(1) Quadratic Equations
A general quadratic equation represents a parabola.
y = ax2 + bx + c (a ≠ 0)
if a > 0 ; It will be a opening upwards parabola.
if a < 0 ; It will be a opening downwards parabola.
if c = 0 ; It will pass through origin.
y ∝ x2 or y = 2x2, etc. represents a parabola passing through origin as shown in figure shown.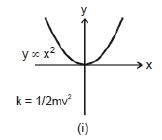
Example: y = 4 x2 + 3x
and
k = 1/2mv2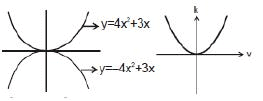
Note: That in the parabola y = 2x2 or y ∝ x2, if x is doubled, y will become four times.
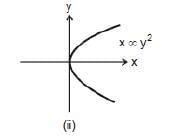
Graph x ∞ y2 or x = 4 y2 is again a parabola passing through origin as shown in figure shown. In this case if y is doubled, x will become four times.
y = x2 + 4 or x = y2 - 6 will represent a parabola but not passing through origin. In the first equation (y = x2 + 4), if x doubled, y will not become four times.
(2) Mensuration Formulas
r : radius ; d = diameter ;
V = Volume
S.A = surface area
(a) Circle
Perimeter: 2πr = πd,
Area : πr2 = 1/4 πd2
(b) Sphere
Surface area = 4πr2 = πd2,
Volume = 4/3 πr3 = 1/6 πd3
(c) Spherical Shell (Hollow sphere)
Surface area = 4πr2 = πd2
Volume of material used = (4πr2)(dr), dr = thickness
(d) Cylinder
Lateral area = 2πrh
V = πr2h
Total area = 2πrh + 2πr2 = 2πr (h + r)
(e) Cone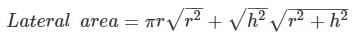
h = height
Total area = πr
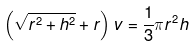
(f) Ellipse
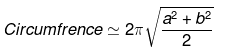
area = πaba = semi major axis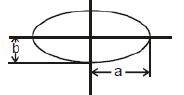
b = semi minor axis
(g) Parallelogram
A = bh = ab sin θ
a = side ; h = height; b = base
θ = angle between sides a and b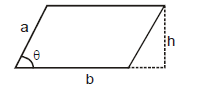
(h) Trapezoid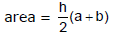
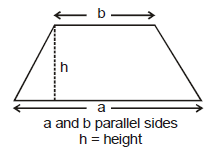
(i) Triangle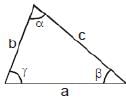
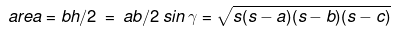
a, b, c sides are opposite to angles α, β, γ
b = base ; h = height
s = 1/2 (a + b + c)
(j) Rectangular container
lateral area = 2(ℓb + bh-hℓ)
V = lbh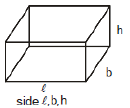
Mathematics is the language of physics. It becomes easier to describe, understand and apply the physical principles, if one has a good knowledge of mathematics.
(3) Logarithms
(i) e ≈ 2.7183
(ii) If ex = y, then x = loge y = ln y
(iii) If 10x = y, then x = log10y
(iv) log10y = 0.4343 loge y = 2.303 log10y
(v) log (ab) = log (a) + log (b)
(vi) log (a/b) = log(a) - log (b)
(vii) log an = n log (a)
(4) Trigonometric Properties
(i) Measurement of angle & relationship between degrees & radian
In navigation and astronomy, angles are measured in degrees, but in calculus it is best to use units called radians because of they simplify later calculations.
Let ACB be a central angle in circle of radius r, as in figure.
Then the angle ACB or q is defined in radius as -
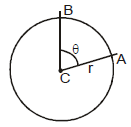
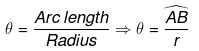
If r = 1 then θ = AB
The radian measure for a circle of unit radius of angle ABC is defined to be the length of the circular arc AB. since the circumference of the cirlce is 2π and one complete revolution of a circle is 360°, the relation between radians and degrees is given by the following equation.
π radians = 180°
ANGLE CONVERSION FORMULAS≈
1 degree = π/180° (= 0.02) radian Degrees to radians : multiply by = π/180°
1 radian = 57 degrees
Radians to degrees : multiply by = π/180°Example: Covert 45° to radians : 45 • π/180° = π/4 rad
Convert π/6 rad to degrees : π/6 • π/180° = 30°
Example 1. Convert 30° to radians:
Solution. 30° x (π/180°) = (π/6)rad
Example 2: Convert π/3 rad to degrees.
Solution.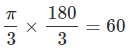
Standard values
(1) 30° = (π/6)rad
(2) 45° = (π/4)rad
(3) 60° = (π/3)rad
(4) 90° = (π/2)rad
(5) 120° = (2π/3)rad
(6) 135° = (3π/4)rad
(7) 150° = (5π/6)rad
(8) 180° = π rad
(9) 360° = 2π rad
(ii) Measurement of positive & Negative Angles:
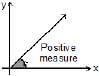
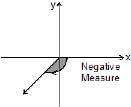
An angle in the xy-plane is said to be in standard position if its vertex lies at the origin and its initial ray lies along the positive x-axis (Fig). Angles measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis are assigned positive measures; angles measured clockwise are assigned negative measures.
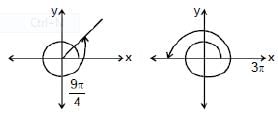
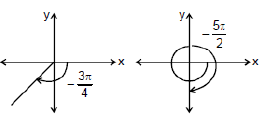
(iii) Six Basic Trigonometric Functions:
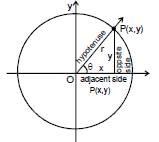
The trigonometric function of a general angle θ are defined in terns of x, y and r.Sine : sinθ = (opp/hyp) = (y/r)Cosecant : cosecθ = hyp/opp = r/y
Cosine: cosθ = adj/hyp = x/r Secant : secθ = hyp/adj = r/x
Tangent: tan θ = opp/adj = y/x Cotangent: cot θ = adj/opp = x/y
VALUES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
If the circle in (Fig. above) has radius r = 1, the equations defining sinθ and cosθ become cosθ = x, sinθ = y
We can then calculate the values of the cosine and sine directly from the coordinates of P.
Example 3. Find the six trigonometric ratios from given fig. (see above)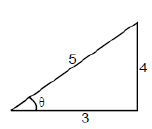
Solution. sinθ = opp/hyp = 4/5 cosθ = adj/hyp = 3/5
tanθ = opp/adj = 4/3 cotθ = adj/opp = 3/4
secθ = hyp/opp = 5/3 cosecθ = hyp/opp = 5/4
Example 4. Find the sine and cosine of angle 6 shown in the unit circle if coordinate of point p are as shown,
Solution.
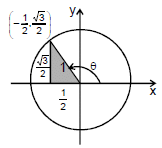
cos θ = x-coordinate of P = (-1/2) sin θ = y-coordinate of p = √3/2
Values of sinθ, cosθ and tanθ for some standard angles. 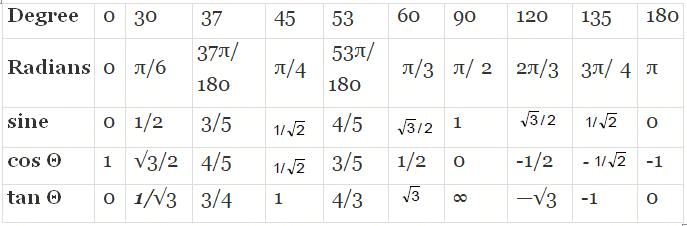
A useful rule for remembering when the basic trigonometric functions are positive and negative is the CAST rule. If you are not very enthusiastic about CAST. You can remember it as ASTC (After school to college)
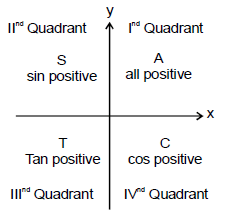
The CAST rule
RULES FOR FINDING TRIGONOMETRIC RATIO OF ANGLES GREATER THAN 90°.
Step 1 → Identify the quadrant in which angle lies.
Step 2 → (a) If angle = (nπ ± 6) where n is an integer. Then
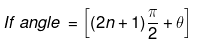
where n is in integer. Then trigonometric function of
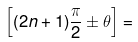
complimentary trigonometric function of Θ and sign will be decided by CAST Rule.
Example 5. Evaluate sin 120°
Solution. sin 120° = sin (90° + 30°)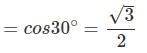
Alter sin 120° = sin (180° - 60°)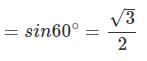
Example 6. Evaluate cos 210°
Solution.
cos 210° = cos (180° + 30°)
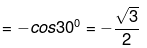
Example 7. tan 210° - tan (180° + 30°) = tan 300 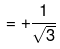
5. IMPORTANT FORMULAS
(i) sin2θ + cos2θ = 1
(ii) 1 + tan2θ = sec2θ
(iii) 1 + cot2θ = cosec2θ
(iv) sin2θ = 2 sin θ cos θ
(v) cos 2θ = 2 cos2θ -1 = 1-2 sin2θ = cos2θ - sin2θ
(vi) sin (A ± B) = sin A cos B ± cos A sin B
(vii) cos (A ± B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
(viii) sin C + sin D = 2sin((C+D)/2)cos((C-D)/2)
(ix) sin C + sin D = 2sin((C-D)/2)cos((C+D)/2)
(x) cos C + cos D = 2cos((C+D)/2)cos((C-D)/2)
(xi) cos C - cos D = 2sin((D-C)/2)sin((C+D)/2)
(xii) tan 2θ - ((2tanθ)/1-tan2θ)
(xiii) 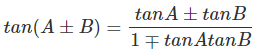
(xiv) sin(90° + θ) = cos θ
(xv) cos (90° + θ) = - sin θ
(xvi) tan (90° + θ) = - cot θ
(xvii) sin(90° - θ) = cos θ
(xviii) cos{90° - θ) = sin θ
(xix) cos (180° - θ) = - cos θ
(xx) sin(180° - θ) = sin θ
(xxi) cos (180° + θ) = - cos θ
(xxii) tan (180° + θ) = tan θ
(xxiii) sin(- θ) = - sin θ
(xxiv) cos (-θ) = cos θ
(xxv) tan (-θ) = - tan θ
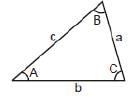
Sine Rule (sinA/a)=(sinB/b)= (sinC/c)
Cosine rule a2 = b2 + c2 - 2bc cosA
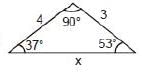
Find x:
Solution.
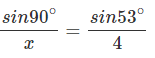
x = 5
6. small angle approximation
It is a useful simplification which is only approximately true for finite angles. It involves linearization of the trigonometric functions so that, when the angle q is measured in radians.
sinθ  θ
θ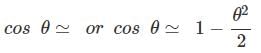
for the second order approximation tanθ  q
q
Geometric justification 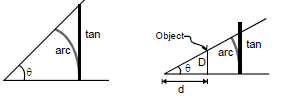
Small angle approximation. The value of the small angle X in radians is approximately equal to its tangent.
- When one angle of a right triangle is small, is hypotenuse in approximately equal in length to the leg adjacent to the small angle, so the cosine is approximately 1.
The short leg is approximately equal to the arc from the long leg to the hypotenuse, so the sine and tangent are both approximated by the value of the angle in radians.
7. Binomial theorem
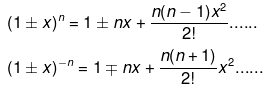
If x << 1 ; then(1 ± x)n = 1 ± nx (neglecting higher terms)
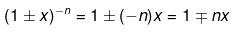
(1 + x)2 = 1 + 2x+ x2
(1 + x)3 = 1 + 3x + x3 - 3x2
(1 + x)n = 1 + nx
if x << I
Note:
(1) When n is a positive integer, then expansion will have (n + 1) terms
(2) When n is a negative integer, expansion will have infinite terms.
(3) When n is a fraction expansion will have infinite terms.
Example 8. Calculate (1001)1/3.
Solution.
We can write 1001 as : 1001 = 1000(1+(1/1000), so that we have
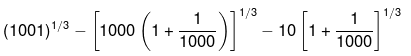
= (10(1+0.001)1/3
=10(1+(1/3) x 0.001)
= 10.003333
Example 9. Expand (1 +x)-3
Solution.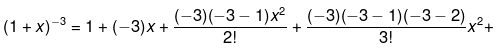
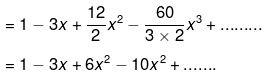
8. Graphs
Following graphs and their corresponding equations are frequently used in Physics.
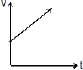
(i) y = mx, represents a straight line passing through origin. Here, m = tanθ is also called the slope of line, where θ is the angle which the line makes with positive x-axis, when drawn in anticlockwise direction from the positive x-axis towards the line.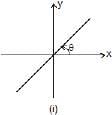
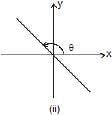
The two possible cases are shown in figure 1.1 (i) θ< 90°. Therefore, tanθ or slope of line is positive. In fig. 1.1 (ii), 90° < θ < 180°. Therefore, tanθ or slope of line is negative.
Note: That y = mx of y ∝ x also means that value of y becomes 2 time if x is doubled. Or it becomes 1/4th if x becomes x/4, and c the intercept on y-axis.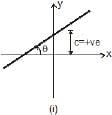
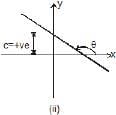
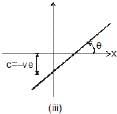
In figure (i): slope and intercept both are positive.
In figure (ii): slope is negative but intercept is positive and
In figure (iii): slope is positive but intercept is negative.
Note: That in y = mx + c, y does not become two times if x is doubled
Example 10. v = u + at
Example 11. ρ = mv
Example 12. Draw the graph for the equation : 2y = 3x + 2
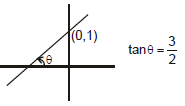
Solution. 2y = 3x + 2 ⇒ y = 3/2(x) + 1
m = 3/2 > 0 ⇒ θ < 90°
c = +1 > 0
⇒ The line will pass through (0, 1)
Example 13. Draw the graph for the equation : 2y + 4x + 2 = 0
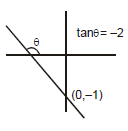
Solution.
2y + 4x + 2 = 0
⇒ y = - 2x - 1
m = - 2 < 0
i.e., θ > 90°
c = - 1 i.e.,
line will pass through (0, -1)
(a) If c = 0 line will pass through origin.
(b) y = c will be a line parallel to x axis.
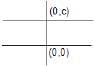
(c) x = c will be a line perpendicular to y axis

(ii) Parabola
A general quadratic equation represents a parabola.
y = ax2 + bx + c a ¹ 0
if a > 0 ; It will be a opening upwards parabola.
if a < 0 ; It will be a opening downwards parabola.
if c = 0 ; It will pass through origin.
y ∝ x2 or y = 2x2, etc. represents a parabola passing through origin as shown in figure
shown.
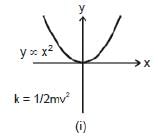
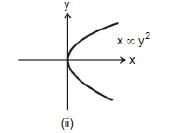
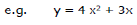
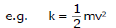
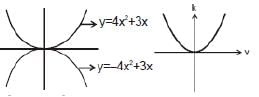
Note: That in the parabola y = 2x2 or y ∝ x2, if x is doubled, y will become four times.
Graph x ∞ y2 or x = 4 y2 is again a parabola passing through origin as shown in figure shown. In this case if y is doubled, x will become four times.
y = x2 + 4 or x = y2 - 6 will represent a parabola but not passing through origin. In the first equation
(y = x2 + 4), if x doubled, y will not become four times.
9. Similar Triangle
Two given triangle are said to be similar if
(1) All respective angle are same
or
(2) All respective side ratio are same.
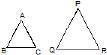
As example, ABC, PQR are two triangle as shown in figure.If they are similar triangle then
(1) ∠A = ∠P
∠B = ∠Q
∠C = ∠R
OR
(2) AB/PQ = BC/QR = AC/PR
|
22 videos|163 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Units & Measurements: Basic Mathematics - Additional Study Material for JEE
| 1. What are units and measurements in basic mathematics? |  |
| 2. How are units and measurements important in JEE (Joint Entrance Examination)? |  |
| 3. What are the SI units commonly used in JEE for different physical quantities? |  |
| 4. How can one convert between different units in JEE? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when dealing with units and measurements in JEE? |  |






















