Unraveling the Intricate Process: Biological Oxidation of Alcohols | Organic Chemistry for MCAT PDF Download
Introduction
Have you ever experienced the unpleasant consequences of consuming alcohol, such as a pounding headache and feeling like a zombie? While dehydration plays a role, there is more to the story. To fully understand what happens to your body when you drink, we need to delve into the process known as the biological oxidation of alcohols. In this article, we will explore the fascinating journey of alcohol through our bodies, examining the structure of alcohol molecules, the solubility of ethanol, the metabolism of alcohol in the liver, the role of enzymes and coenzymes, and the toxicity of methanol. Get ready for an insightful journey into the inner workings of alcohol metabolism!
Understanding Alcohol Molecules
Alcohols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl functional group (-OH) bound to a carbon atom. This section will explain the general structure of alcohols, highlighting their significance in scientific, medical, and industrial applications. By focusing on ethanol, the primary alcohol found in beer, wine, and spirits, we will uncover the distinct carbon/hydrogen chains that differentiate various alcohols.
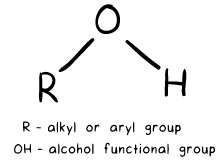
The Solubility of Ethanol
Have you ever wondered why alcohol mixes so effortlessly with water? This section explores the solubility of ethanol, explaining how it readily dissolves in water and becomes uniformly distributed throughout our bodies. By drawing a comparison with the separation of oil and vinegar in salad dressing, we shed light on the unique solubility properties of ethanol that allow it to seamlessly integrate into our bloodstream and affect the brain.
Metabolism of Ethanol in the Liver
The liver plays a vital role in the breakdown of ethanol. In this section, we delve into the two-step process of alcohol metabolism. We first witness the conversion of ethanol into acetaldehyde, a toxic aldehyde. Next, we witness the transformation of acetaldehyde into acetic acid, a harmless carboxylic acid. This section clarifies the biochemical oxidation that occurs during this process and its significance in understanding the effects of alcohol on our bodies.
Enzymes and Coenzymes in Oxidation
Enzymes and coenzymes act as catalysts to expedite the oxidation of alcohols. This section explores the critical role of coenzymes, specifically NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADH (the reduced form of NAD), in the oxidation process. By facilitating the removal of hydrogens and electrons, these coenzymes serve as the biological oxidizing agents. Furthermore, we shed light on how enzymes contribute to accelerating this process.
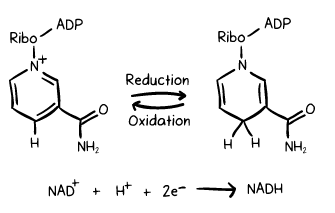
Hangover: The Role of Acetaldehyde
Ever wondered why hangovers occur? In this section, we uncover the role of acetaldehyde, the intermediary product between ethanol and acetic acid, in contributing to hangover symptoms. By explaining the toxic effects of acetaldehyde on our bodies, such as vasodilation and unpleasant side effects, we emphasize the importance of swiftly metabolizing acetaldehyde into acetic acid to mitigate hangover severity.
Enzymatic Variations and Genetic Influence
This section highlights the significance of enzymes in alcohol oxidation by focusing on two specific hepatic enzymes: Alcohol dehydrogenase IB (class I) - ADH1B and Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 - ALDH2. We explore the crucial role of ALDH2 in swiftly converting acetaldehyde into acetic acid, reducing the build-up of toxic substances in the body. Additionally, we address the genetic variations in ALDH2 and its impact on individuals, particularly those of East Asian descent.
Biological Oxidation of Methanol
Not all alcohols undergo the same harmless transformation as ethanol. This section uncovers the exceptional toxicity of methanol, explaining how its oxidation process leads to the formation of formaldehyde and formic acid. We delve into the devastating consequences of these substances on our body, emphasizing why methanol consumption should be avoided at all costs.
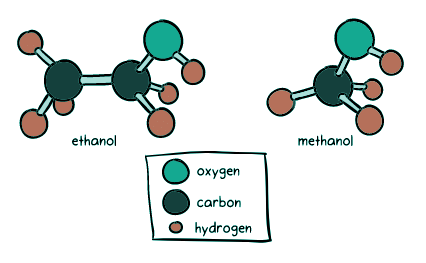
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of the biological oxidation of alcohols, we invite readers to reflect on the chemical reactions that occur within their bodies when consuming alcohol. From the solubility of ethanol to the metabolism in the liver, the role of enzymes and coenzymes, and the differences between ethanol and methanol, we gain a deeper understanding of the intricate processes that underpin alcohol metabolism. Armed with this knowledge, we can approach alcohol consumption with a heightened awareness of its effects on our bodies.
|
140 videos|5 docs|15 tests
|















