Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE > Using Liquidity Ratios to Analyse Performance
Using Liquidity Ratios to Analyse Performance | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
The Current Ratio
- Liquidity refers to the cash and other current assets businesses have available to quickly pay bills and meet short-term financial obligations.
- The liquidity of a business can be measured using two ratios: Current ratio and Acid test ratio.
- The Current Ratio serves as a rapid gauge of liquidity.
- It is presented as a ratio.
- All categories of current assets are considered in its computation.
- The ratio reveals the amount of currency units of current assets available to offset each currency unit of short-term debt.
- It is determined using the formula:
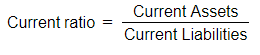
The acid test ratio
The acid test ratio serves as a precise and pragmatic method for assessing liquidity, particularly applicable to businesses with substantial stock holdings.
- Presented as a ratio.
- Also referred to as the liquid capital ratio.
- By deducting the least liquid current asset (stock), the acid test ratio offers a more realistic evaluation of the business's capability to promptly fulfill short-term debts.
- Given the time required to sell stock, it is excluded from the calculation.
- Calculated using the formula:
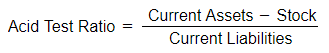
Question for Using Liquidity Ratios to Analyse PerformanceTry yourself: What is the purpose of the Current Ratio?View Solution
Improving Liquidity Ratios
Enhancing liquidity is most effectively achieved through improved business management:
- Employ cash flow forecasts to preempt potential cash flow challenges and implement suitable measures in advance.
- Practice effective budgeting and contemplate adopting zero-based budgeting to meticulously regulate expenditures.
- Establish distinct financial objectives and explore avenues to curtail costs and augment revenue whenever feasible.
Methods to Improve Liquidity

The document Using Liquidity Ratios to Analyse Performance | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
70 videos|94 docs|26 tests
|
FAQs on Using Liquidity Ratios to Analyse Performance - Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the current ratio and how is it calculated? |  |
Ans. The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures a company's ability to cover its short-term liabilities with its short-term assets. It is calculated by dividing a company's current assets by its current liabilities.
| 2. What is the acid test ratio and why is it important for analyzing liquidity? |  |
Ans. The acid test ratio, also known as the quick ratio, is a liquidity ratio that measures a company's ability to pay off its current liabilities without relying on the sale of inventory. It is important for analyzing liquidity because it provides a more stringent measure of a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations.
| 3. How can a company improve its liquidity ratios? |  |
Ans. A company can improve its liquidity ratios by increasing its current assets, such as cash and accounts receivable, while reducing its current liabilities, such as accounts payable and short-term debt. This can be achieved through better cash flow management, efficient inventory management, and timely collection of receivables.
| 4. How can liquidity ratios be used to analyze a company's performance? |  |
Ans. Liquidity ratios can be used to analyze a company's performance by providing insights into its ability to meet its short-term obligations. A high current ratio and acid test ratio indicate strong liquidity and financial health, while a low ratio may signal potential liquidity problems. By comparing liquidity ratios over time or against industry benchmarks, investors and analysts can assess a company's financial stability.
| 5. What are some common pitfalls to avoid when interpreting liquidity ratios? |  |
Ans. Some common pitfalls to avoid when interpreting liquidity ratios include solely relying on one ratio to assess a company's liquidity, not considering the industry norms for liquidity ratios, and failing to take into account the specific circumstances of the company. It is important to use liquidity ratios in conjunction with other financial metrics and to consider the overall financial health of the company.
Related Searches




















