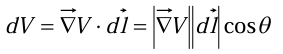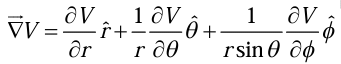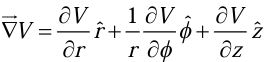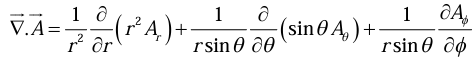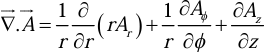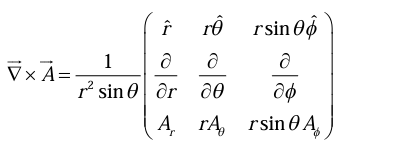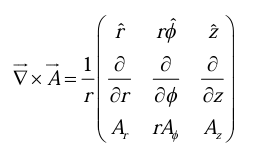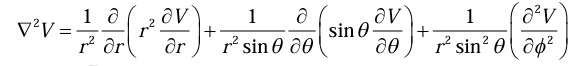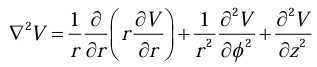Vector Calculus - Mathematical Methods of Physics | Physics for IIT JAM, UGC - NET, CSIR NET PDF Download
Introduction
Imagine you’re exploring the invisible forces of nature—how does electricity move through a circuit, how do planets follow their curved paths, or how do fluids flow effortlessly through pipes?
The answer lies in vector calculus, the language of physics that reveals the hidden patterns in the universe.
Vector Calculus equips you with tools like the gradient to find steepest climbs, the divergence to measure spreading flows, and the curl to detect swirling motions. Whether you're decoding Maxwell's equations in electromagnetism or analyzing fluid dynamics, vector calculus is your key to unlocking the mysteries of the physical world!
Gradient of a Vector
Suppose that we have a function of three variables-say, V (x, y, z) in a 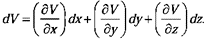
This tells us how V changes when we alter all three variables by the infinitesimal amounts dx, dy, dz. Notice that we do not require an infinite number of derivatives-three will suffice the partial derivatives along each of the three coordinate directions.
Thus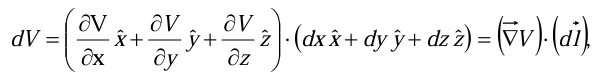 where
where 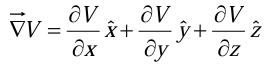 is the gradient of V.
is the gradient of V.
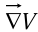 is a vector quantity with three components.
is a vector quantity with three components.
Geometrical Interpretation of the Gradient
Like any vector, the gradient has magnitude and direction. To determine its geometrical meaning, let’s rewrite:
where
is the angle between
and
Now, if we fix the magnitude  and search around in various directions (that is, vary
and search around in various directions (that is, vary  ), the maximum change in V evidently occurs when
), the maximum change in V evidently occurs when 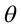 = 0 (for then cos
= 0 (for then cos 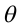 = 1). That is, for a fixed distance
= 1). That is, for a fixed distance 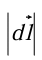 , dT is greatest when one move in the same direction as
, dT is greatest when one move in the same direction as 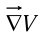 .
.
Thus, the gradient 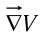 points in the direction of maximum increase of the function V.
points in the direction of maximum increase of the function V.
Moreover, the magnitude  gives the slope (rate of increase) along this maximal direction.
gives the slope (rate of increase) along this maximal direction.
Gradient in Spherical polar coordinates 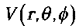
Gradient in cylindrical coordinates 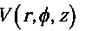
Example 1:Find the gradient of a scalar function of position V where 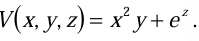 Calculate the magnitude of gradient at point
Calculate the magnitude of gradient at point 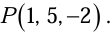
Example 2: Find the unit vector normal to the curve y = x2 at the point (2, 4, 1).
Solution:The equation of curve in the form of surface is given by 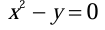
A constant scalar function V on the surface is given by V (x, y, z) = x2 - y
Taking the gradient
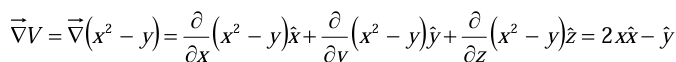 The value of the gradient at point (2, 4, 1),
The value of the gradient at point (2, 4, 1), 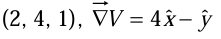
The unit vector, as required 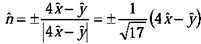
Example 3: In electrostatic field problems, the electric field is given by 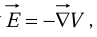 where V is the scalar field potential. If
where V is the scalar field potential. If 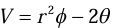 in spherical coordinates, then find
in spherical coordinates, then find 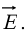 .
.
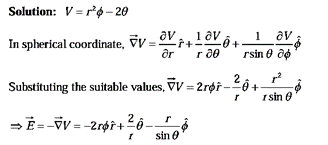
The Operator 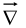
The gradient has the formal appearance of a vector 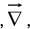 “multiplying” a scalar V:
“multiplying” a scalar V:
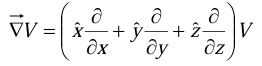
The term in parentheses is called “del”:
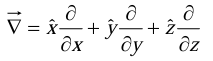 We should say that
We should say that 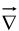 is a vector operator that acts upon V, not a vector that multiplies V.
is a vector operator that acts upon V, not a vector that multiplies V.
There are three ways the operator 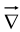 can act:
can act:
- On a scalar function V:
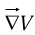 (the gradient);
(the gradient); - On a vector function
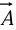 , via the dot product:
, via the dot product: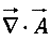 (the divergence);
(the divergence); - On a vector function
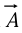 , via the cross product:
, via the cross product: 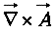 (the curl).
(the curl).
Divergence of a Vector
If
is a vector point function then
is called Divergence of
.
where
are the functions of x, y, z
Note:
1. Divergence of a vector is scalar.
2. Physically Divergence measures (outflow - inflow)
3. A vector whose divergence is zero then it is said to be divergence free vector (or) solenoid vector i.e. outflow = inflow = constant
Geometrical Interpretation
 is a measure of how much the vector
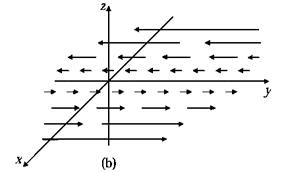
is a measure of how much the vector spreads out (diverges) from the point in question. For example, the vector function in figure (a) has a large (positive) divergence (if the arrows pointed in, it would be a large negative divergence), the function in figure (b) has zero divergence, and the function in figure (c) again has a positive divergence.
spreads out (diverges) from the point in question. For example, the vector function in figure (a) has a large (positive) divergence (if the arrows pointed in, it would be a large negative divergence), the function in figure (b) has zero divergence, and the function in figure (c) again has a positive divergence. 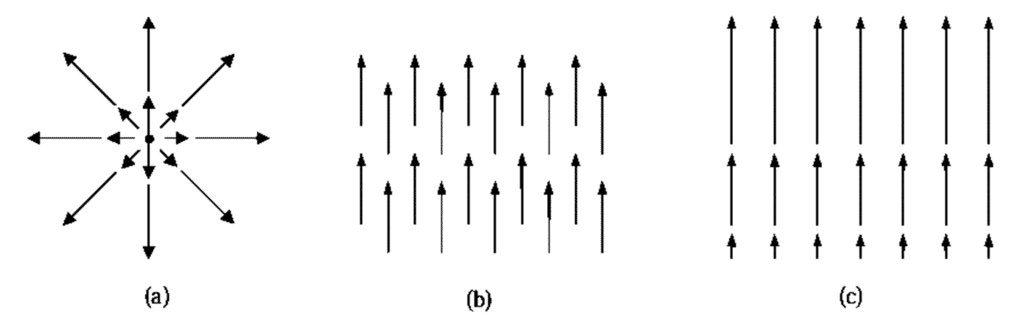
Divergence in Spherical polar coordinates
Divergence in cylindrical coordinates
The Curl of a Vector
From the definition of  we construct the curl
we construct the curl
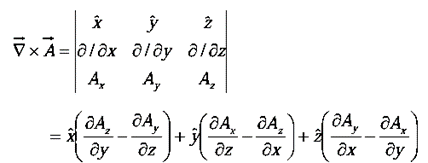
Geometrical Interpretation
 is a measure of how much the vector
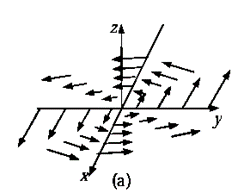
is a measure of how much the vector  “curls around” the point in question. Figure shown below have a substantial curl, pointing in the z-direction, as the natural right-hand rule would suggest.
“curls around” the point in question. Figure shown below have a substantial curl, pointing in the z-direction, as the natural right-hand rule would suggest.
Curl in Spherical polar coordinates
Curl in cylindrical coordinates
Angle between Two Surfaces
Let ϕ1(x,y,z) = C, ϕ2(x,y,z) = C be given equations of two level surfaces and angle between these two surfaces are given as θ then cos θ
Note:
The angle between two surfaces is nothing but the angle between their normal.
then they are said to be orthogonal surfaces.
Example 4:The angle between the two surfaces x2 + y2+ z2 = 9 and z = x2 + y2 − 3 at the point (2, −1, 2) is
Solution:
Example 5: Find the curl of the vector 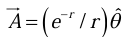
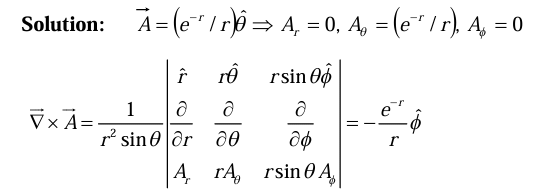
Directional Derivatives of a Scalar Function
The directional derivative of a scalar function ϕ (x, y, z) in the direction of a vector
given as
ve then it is in the opposite direction.
Example 6: The Directional derivative of f(x, y, z) = x2yz + 4xz2 at (1, −2, −1) along (2i – j − 2k) is
Solution:
Directional Derivative =
At (1, −2, −1) we have
Example 7: The values of a, b, c so that the vector,
is irrotational.
Solution:
Given, that vector V is irrotational
⇒ c = −1, a = 4, b = 2
∴ a = 4, b = 2, c = −1
Second Derivatives
The gradient, the divergence, and the curl are the only first derivatives we can make with 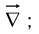 by applying
by applying 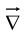 twice we can construct five species of second derivatives. The gradient
twice we can construct five species of second derivatives. The gradient 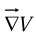 is a vector, so we can take the divergence and curl of it:
is a vector, so we can take the divergence and curl of it:
Divergence of gradient: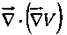
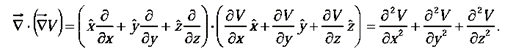
This object, which we write 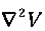 for short, is called the Laplacian of V. Notice that the Laplacian of a scalar V is a scalar.
for short, is called the Laplacian of V. Notice that the Laplacian of a scalar V is a scalar.
Laplacian in Spherical polar coordinates
Laplacian in cylindrical coordinates
Occasionally, we shall speak of the Laplacian of a vector, 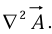 . By this we mean a vector quantity whose x-component is the Laplacian of Ax, and so on:
. By this we mean a vector quantity whose x-component is the Laplacian of Ax, and so on: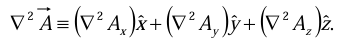
- Curl of gradient:
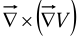
The divergence 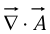 is a scalar-all we can do is taking its gradient.
is a scalar-all we can do is taking its gradient.
The curl of a gradient is always zero: 
- Gradient of divergence:
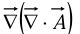
The curl 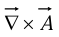 is a vector, so we can take its divergence and curl.
is a vector, so we can take its divergence and curl.
Notice that 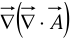 is not the same as the Laplacian of a vector:
is not the same as the Laplacian of a vector:
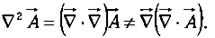
- Divergence of curl:
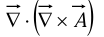
The divergence of a curl, like the curl of a gradient, is always zero: 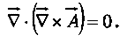
- Curl of curl:
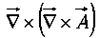
As you can check from the definition of 
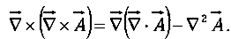
So curl-of-curl gives nothing new; the first term is just number (3) and the second is the Laplacian (of a vector).
FAQs on Vector Calculus - Mathematical Methods of Physics - Physics for IIT JAM, UGC - NET, CSIR NET
| 1. What is the gradient of a vector field, and how is it calculated? |  |
| 2. What is the divergence of a vector field and what does it signify? |  |
| 3. How do you compute the curl of a vector field? |  |
| 4. How do you find the angle between two surfaces using their gradients? |  |
| 5. What are directional derivatives, and how are they calculated for a scalar function? |  |