Wren and Martin Summary: Verbs | Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Verb? |

|
| The Verb: Person and Number |

|
| The Infinitive |

|
| The Participle |

|
| Tenses |

|
What is a Verb?
A verb is a doing word that shows an action, an event or a state. A sentence may either have a main verb, a helping verb or both. In other words, a verb is a word that informs about an action, an existence of something or an occurrence. No sentence can be completed without a verb.

- The word ‘verb’ derived from the Latin word ‘verbum‘
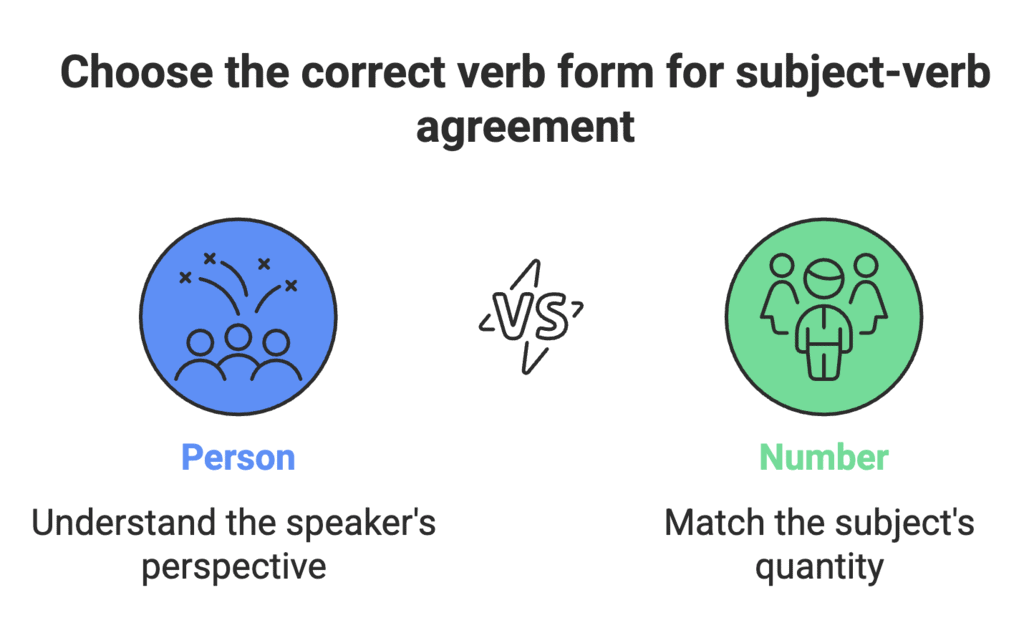
The Verb: Person and Number
What is Person and Number?
Verbs have three persons:
- First Person: I or we (the speaker).
- Second Person: You (the person spoken to).
- Third Person: He, she, it, or they (the person or thing spoken about).
Verbs also have two numbers:
- Singular: One person or thing.
- Plural: More than one person or thing.
Key Rule:
The verb must match its subject in person and number. This is called an agreement.
Examples of Person:
- First Person: I speak. (Subject "I" is first person, so the verb "speak" is too.)
- Second Person: You speak. (In Old English: "Thou speakest.")
- Third Person: He speaks. (The verb adds -s for third person singular.)
Examples of Number:
- Singular: He speaks. (One person, so the verb is singular.)
- Plural: They speak. (More than one, so the verb is plural.)
How It Works:
- If the subject is singular and first person, the verb is too: I am here.
- If the subject is singular and third person, the verb matches: He is here.
- If the subject is plural and third person, the verb matches: They are here.
Special Notes:
In modern English, most verbs only change for third person singular (add -s or -es).
- I speak, you speak, we speak, they speak (no change).
- He speaks (adds -s).
The verb "to be"is different and changes more:
- I am, you are, he is, we are, they are.
Why It Matters:
- The verb shows who is doing the action (person) and how many (number).
The Infinitive
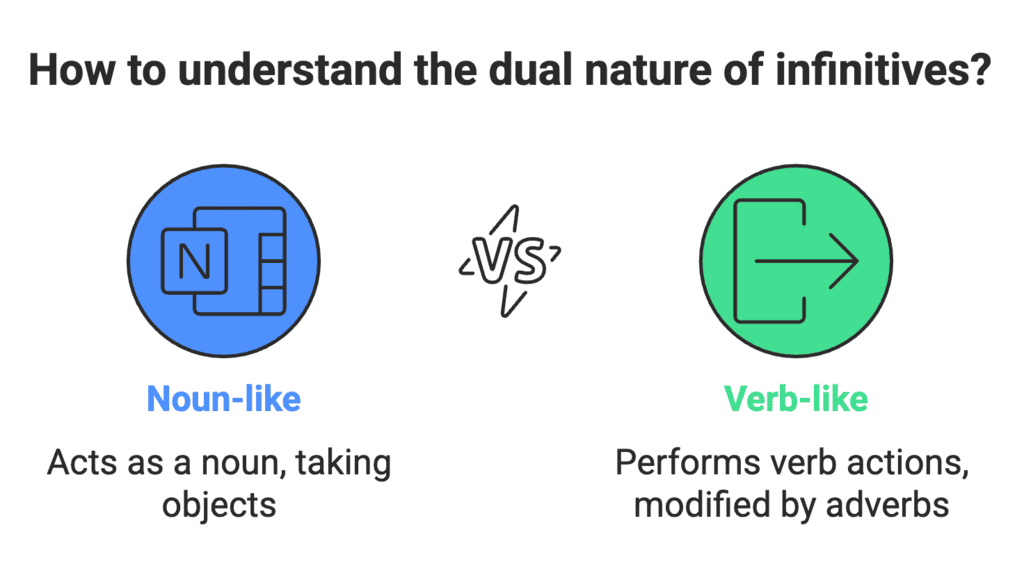
What is an Infinitive?
- The infinitive is the basic form of a verb, usually with "to" (e.g., to go, to sing).
- It acts like a noun but can also do verb things, like take an object or be modified by an adverb. It’s called a Verb-Noun.
Examples:
- I want to go. (To go is the infinitive.)
- They tried to find fault. (To find is the infinitive.)
Uses of the Infinitive:
- As a Subject: To err is human. (It’s what the sentence is about.)
- As an Object: Birds love to sing. (It’s what the birds love.)
- As a Complement: Her pleasure is to sing. (It completes the idea.)
- As an Object of a Preposition: He had no choice but to obey. (Follows "but.")
- As an Objective Complement: I saw him go. (Describes what I saw.)
- To Show Purpose: He came to help. (Why he came.)
- To Describe an Adjective: Figs are good to eat. (Tells about "good.")
- To Describe a Noun: This is the time to play. (Tells about "time.")
- To Start a Sentence: To tell the truth, I forgot. (Sets up the sentence.)
Infinitive Without "To":
After some verbs like bid, let, make, see, hear, need, dare:
- Let him sit. (Not to sit.)
- I saw him run.
After modal verbs like will, can, must:
- I will go. (Not to go.)
- He can sing.
After phrases like had better, would rather:
- You had better ask.
Forms of the Infinitive:
- Active: to love (present), to have loved (perfect).
- Passive: to be loved (present), to have been loved (perfect).
Why It’s Useful:
- Infinitives let us use verbs in many ways, like nouns or to explain why something happens.
The Participle
What is a Participle?
- A participle is a verb form that acts like an adjective. It’s called a Verbal Adjective.
- It describes a noun and can also act like a verb by taking an object or being modified by an adverb.
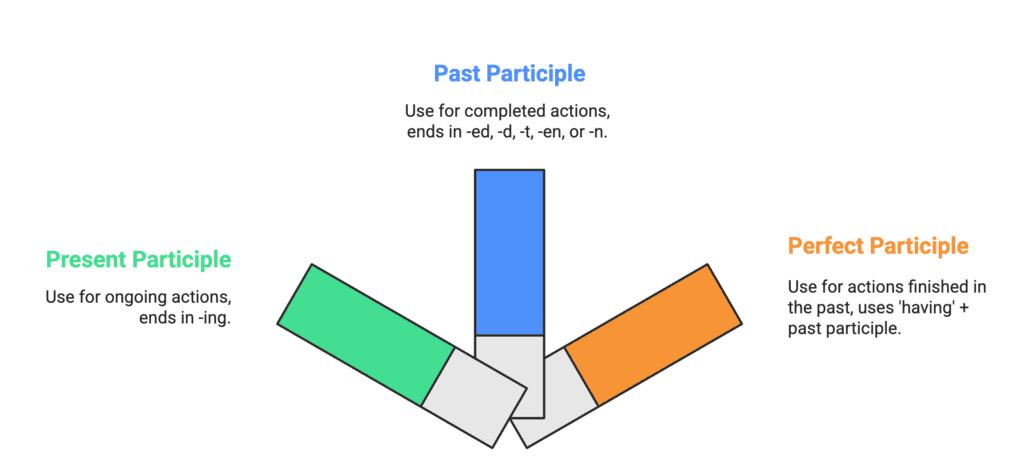
Types of Participles:
- Present Participle:
- Ends in -ing (e.g., hearing, carrying).
- Shows an action that’s ongoing.
- Example: We met a girl carrying a basket. (Carrying describes "girl" and takes "basket" as an object.)
- Past Participle:
- Ends in -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n (e.g., blinded, lost).
- Shows a completed action.
- Example: Deceived by his friends, he lost hope. (Deceived describes "he.")
- Perfect Participle:
- Uses having + past participle (e.g., having rested).
- Shows an action finished in the past.
- Example: Having rested, we continued. (Having rested describes "we.")
How Participles Are Used:
- Attributively(before a noun):
- A rolling stone gathers no moss. (Rolling describes "stone.")
- Predicatively(after a verb):
- The man seems worried. (Worried describes "man.")
- He kept me waiting. (Waiting describes "me.")
- Absolutely(with a noun, separate from the main sentence):
- The weather being fine, I went out. (Called a Nominative Absolute.)
Special Features:
- Present participles are active (e.g., rolling = something that rolls).
- Past participles are passive (e.g., painted = something that was painted).
- Participles can form tenses:
- I am loving (present participle + be).
- I have loved (past participle + have).
- I am loved (past participle + be).
Common Mistake:
- Don’t leave a participle without a clear subject (dangling participle).
- Wrong: Standing at the gate, a scorpion stung him. (Sounds like the scorpion was standing.)
- Right: Standing at the gate, he was stung by a scorpion.
Why It’s Important:
- Participles help describe things and actions together, making sentences shorter and clearer.
Tenses
- A tense may be defined as that form of a verb which indicates the time and the state of an action or event.
- A tense is a form of a verb which shows the time at which an action happens. (Latin word tempus = time).
- Tenses on the basis of time can be divided into 3 parts, viz. past tense, present tense, and future tense.

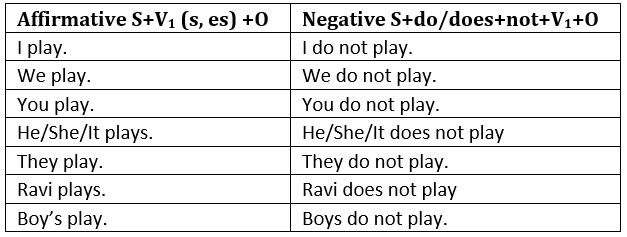
Indefinite/Simple Tense
1. Simple PresentSimple Present Tense is used:
- To express habitual action.
He smokes.
I always take my tea without sugar.
It is used with the adverbs usually, generally, occasionally, rarely, always, often, sometimes on Sundays, once a week/month/year, etc.
- To express general or universal truths.
The sun rises in the east.
Water boils at 100°C. - To express a fact or something which is true at present.
All trains stop at this station.
She teaches English in a school. - To express future actions planned in advance, especially concerning a journey or programme.
The train leaves at six in the morning.
Schools close in May for summer vacation and reopen in June. - To introduce quotations with the verb ‘say’.
The notice says, “No parking.”
Keats says, “A thing of beauty is a joy forever.” - In running commentaries on sporting events.
Ajit passes the ball to Mohinder who kicks it past the goalkeeper. - In exclamatory sentences beginning with ‘here’ and ‘there’.
There goes the bell!
Here comes the train! - In ‘Time Clauses’ and ‘Conditional Clauses’ in place of future tense.
We shall start when the sun rises.
If you work hard, you will succeed.
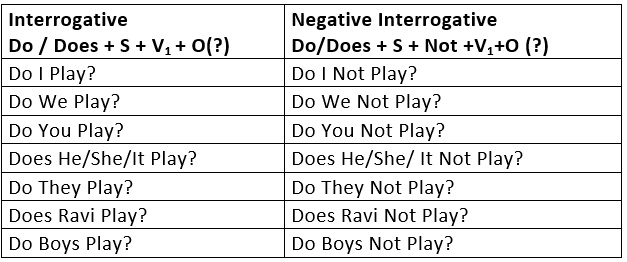
2. Simple Past
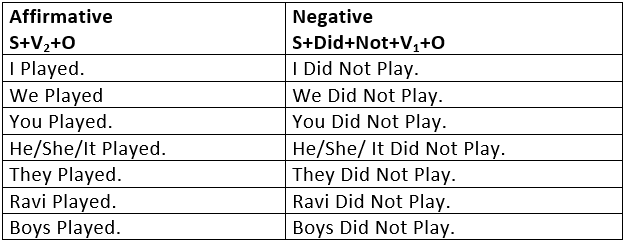
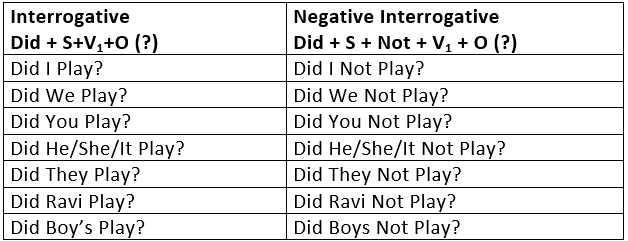
Simple Past Tense is used:
To express a past event or past action.
- The action is completely unrelated to the present.
It is therefore, used:
(i) When the time is given:
- I met him yesterday.
- She died in 1987.
(ii) When the time is not given, but it is implied and definite:
- I bought this pen in Bombay.
(iii) When the time is asked for:
- When did you meet him?
To express a past habit or regular action in the past.
- Every day he read a chapter of the Gita.
- He never smoked.
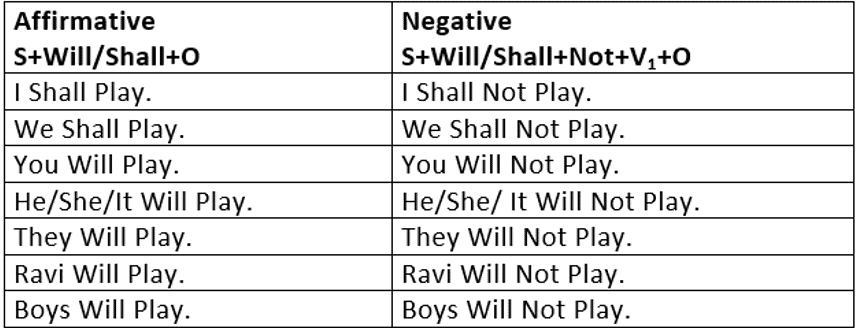
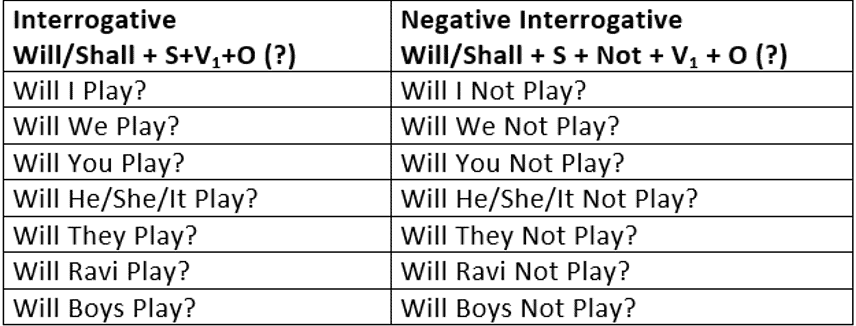
3. Simple Future
Simple Future Tense is used:
- To express an action that has still to take place.
He will play cricket tomorrow.
Continuous/ Progressive Tense
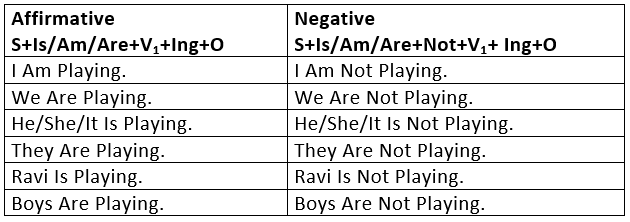
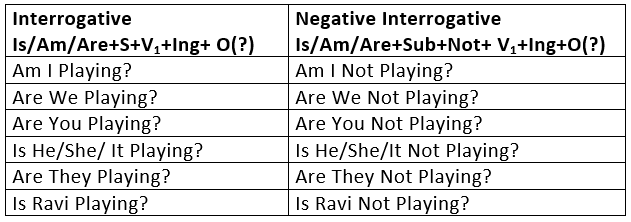
1. Present Continuous TenseThe Present Continuous is used:
- To express an action happening now at the time of speaking.
I am writing a letter.
She is reading a book. - To express an action in progress at this time, but not necessarily at the time of speaking.
He is teaching English at the High School.
They are building a new house. - To express a definite arrangement in the near future.
I am going to London next week.
I am meeting her tonight.
The following verbs are not normally used in the present continuous tense:
- Verbs of senses: see, hear, smell, notice, recognise.
- Verbs of emotions: want, desire, love, hate, forgive, like, dislike, etc.
- Verbs of thinking: think, feel, know, mean, realise, understand, suppose, believe, remember, forget, expect, etc.
- Verbs expressing possession: have, own, belong, possess.
- Verbs like seem, appear, contain, consist, keep, etc.
These verbs are used in the simple present tense. They may, however, be used in the continuous tense with a changed meaning.
The headmaster is seeing the student in the afternoon. (meeting)
The judge is hearing the case tomorrow.Question for Wren and Martin Summary: VerbsTry yourself:Identify the tense used in the given sentence. “You are always working on your laptop.”View Solution
2. Past Continuous Tense
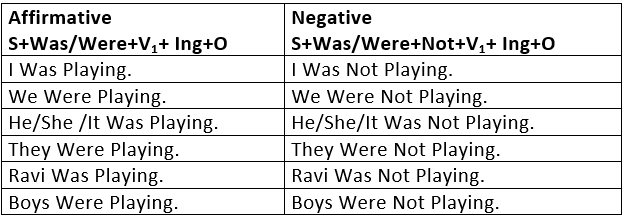
The Past Continuous Tense is used:
- To express an action that was in progress at some time in the past.
I was taking my bath at 8 o’ clock.
I was playing in the garden when he came. - To express two or more actions in progress at the same time.
While I was doing my homework, my brother was playing outside.
The students were talking when the teacher was writing on the black board. - To express an often repeated (undesirable) past action.
She was always taunting him.
He was always coming at odd hours.
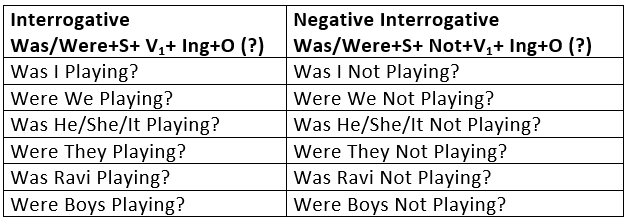
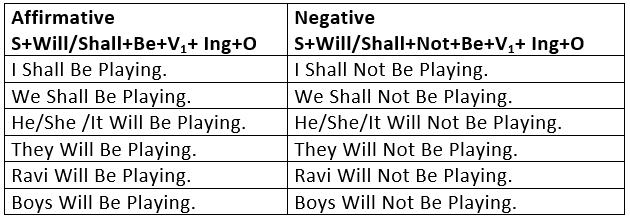
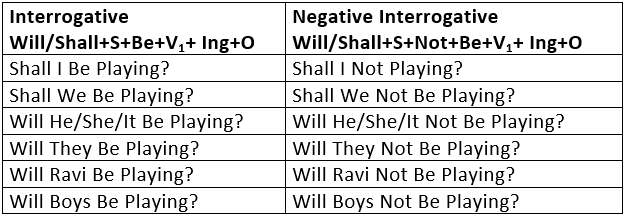
3. Future Continuous Tense
The Future Continuous is used:
- To express an action as going on at some time in future:
When I reach there, he will be reading a book. - To express future events that are planned:
He will be coming here for Diwali Puja.
|
111 videos|450 docs|90 tests
|
FAQs on Wren and Martin Summary: Verbs - Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT
| 1. What is a verb? |  |
| 2. How many tenses are there in verbs? |  |
| 3. Can a verb be used without a subject? |  |
| 4. What are the different forms of verbs? |  |
| 5. How can I identify a verb in a sentence? |  |





















