Very Short Answer Questions: Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1. What do you mean by pressure?
Ans. The force acting on a unit area of a surface is called pressure.
Pressure = Force/Area
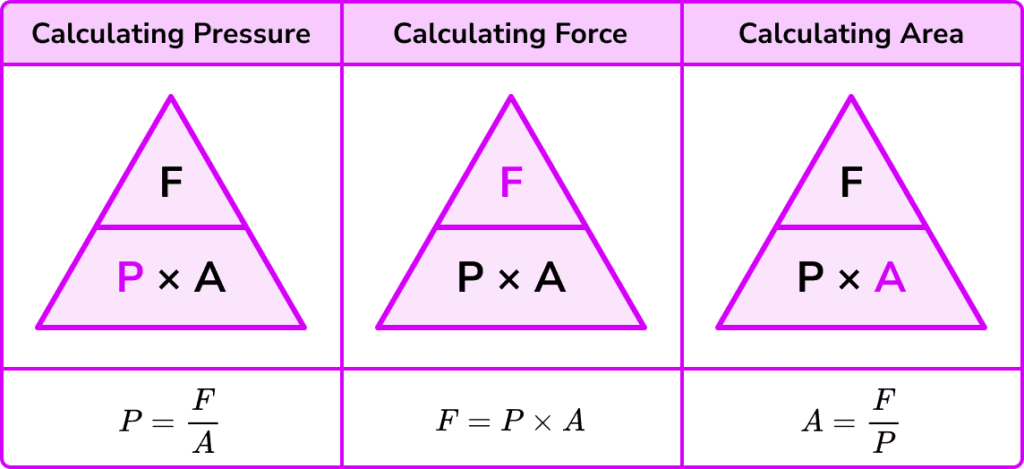
Q2. How can we increase the pressure by exerting same force?
Ans. To increase pressure we should exert the same force on a smaller area.
Q3. Do liquids and gases also exert pressure?
Ans. Yes, liquids and gases also exert pressure.
Q4. What is the site of the pressure exerted by a liquid on the container?
Ans. A liquid exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Q5. Do gases also exert pressure on the walls of containers?
Ans. Yes, gases also exert pressure on the walls of the containers.
Q6. Why do broad bag straps feel more comfortable than narrow ones?
Answer: Broad straps spread the same force over a larger area, reducing pressure on the shoulders.
Q7. Why does a sharp nail pierce wood more easily than a blunt one?
Answer: A sharp nail has a smaller area at the tip, creating higher pressure for the same force.
Q8. What is the SI unit of pressure?
Answer: The SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa), which is N/m².
Q9. How does the height of a water column affect liquid pressure at the bottom?
Answer: Greater height of the water column increases the liquid pressure at the bottom.
Q10. Do liquids exert pressure only downward?
Answer: No, liquids exert pressure in all directions, including sideways on container walls.
Q11. Why are dams built broader at the base?
Answer: Dams are broader at the base to withstand the higher water pressure at greater depths.
Q12. What is atmospheric pressure?
Answer: Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by the air in the atmosphere on all objects.
Q13. Why does a rubber sucker stick to a smooth surface?
Answer: It sticks because outside air pressure is greater than the pressure under the sucker.
Q14. Why aren’t we crushed by atmospheric pressure?
Answer: We aren’t crushed because the pressure inside our bodies balances the outside atmospheric pressure.
Q15. In which units is air pressure commonly reported in weather reports?
Answer: Air pressure is commonly reported in millibar (mb) or hectopascal (hPa).
Q16. In which direction does air move to form wind?
Answer: Air moves from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure.
Q17. What causes a sea breeze during the day?
Answer: A sea breeze occurs when cooler air from the sea moves toward warmer low-pressure air over land.
Q18. What causes a land breeze at night?
Answer: A land breeze occurs when cooler air from land moves toward the warmer low-pressure air over the sea.
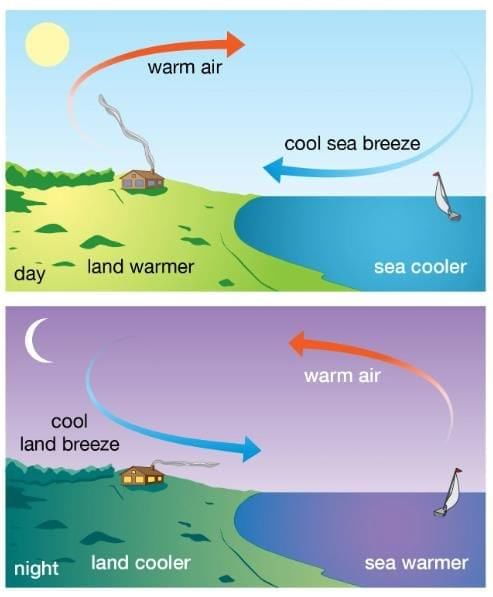 Land and Sea Breeze
Land and Sea Breeze
Q19. How do high-speed winds affect air pressure in an area?
Answer: High-speed winds lower the air pressure in the area where they flow rapidly.
Q20. Why can strong winds blow off a weak roof?
Answer: Strong winds create low pressure above the roof, and higher inside pressure can push the roof up.
Q21. What is a thunderstorm?
Answer: A thunderstorm is a storm with lightning and thunder caused by charged clouds and rapid air movement.
Q22. How is lightning formed in a cloud?
Answer: Lightning forms when charge buildup breaks air’s resistance, causing a sudden flow of charges as a bright flash.
Q23. What safety action should you take during lightning outdoors?
Answer: You should avoid tall objects and crouch in a low, open area without lying flat.
Q24. What is the function of a lightning conductor on a building?
Answer: A lightning conductor safely carries electric charges from lightning into the ground.
Q25. What is a cyclone?
Answer: A cyclone is a large spinning storm over warm oceans with very low pressure at the center and high-speed winds.
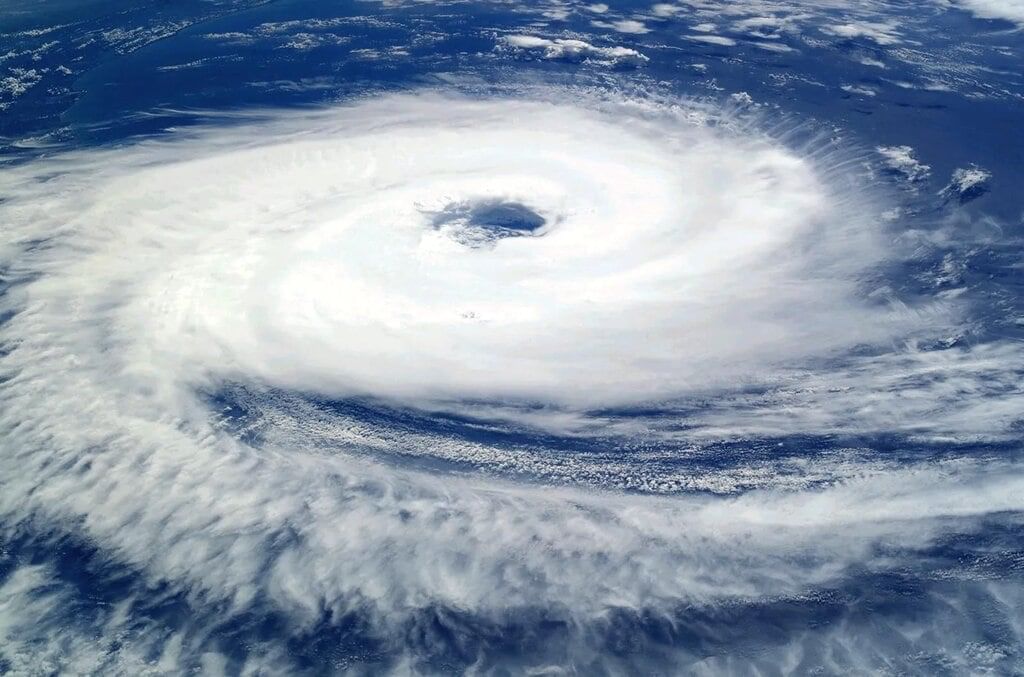 Cyclone
Cyclone
Q26. What provides energy to a cyclone over the ocean?
Answer: Warm, moist air and heat released during condensation provide energy to a cyclone.
Q27. What is a storm surge?
Answer: A storm surge is a high wall of seawater pushed toward land by strong cyclone winds, causing coastal flooding.
Q28. Why do cyclones weaken after landfall?
Answer: Cyclones weaken after landfall because they lose their supply of warm, moist air from the ocean.
|
54 videos|262 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Very Short Answer Questions: Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is atmospheric pressure and how is it measured? |  |
| 2. How do winds form and what factors influence their direction? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of a cyclone? |  |
| 4. How do thunderstorms develop and what are their typical features? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a tropical cyclone and an extratropical cyclone? |  |
















