Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Question Answers - Gravitation
Q1: Write SI unit of G.
Ans:
We know,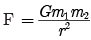
or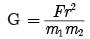
In SI system, force F is measured in N, distance r in m and masses m1 and m2 in kg, therefore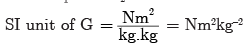
Q2: Why should we be sent flying in space if the force of gravity somehow vanishes today?
Ans: The centripetal force required to keep us rotating along with the Earth would not be available in the absence of force of gravity. We would then fly off along the tangent to the Earth into the space.
Q3: A ball moving on a table reaches the edge and falls. Sketch the path it will follow while falling.
Ans: As the ball falls, it has a horizontal velocity and a vertical downward acceleration due to gravity. Under the combined effect of these two motion the ball moves along a parabolic trajectory as shown in figure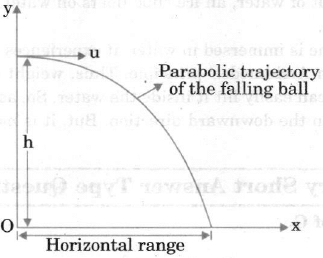
Q4: Is value of “g” same at all places on the Earth? Give reason for your answer.
Ans: No, the value of “g” is maximum at the poles and minimum at equator. This variation is because to the oblong shape of the Earth and its rotation about its own axis.
Q5: What is the relation between gravitational force of the Moon with the Earth.
Ans: The gravitational force of the Moon is about one-sixth of what it is on the Earth.
Q6: Why does a mug full of water feel lighter inside water?
Ans: A mug of water appears lighter inside the water because a buoyant force acts on the mug when placed inside the water.
Q7: Name the force which accelerates a body in free fall.
Ans: Gravitational force of Earth.
Q8: Why value of “g” more or less constant on or near the Earth?
Ans: Radius of Earth does not change much; “g” is more or less constant on or near the Earth.
Q9: What is the unit of “g”?
Ans: The unit of “g” is ms–2.
Q10: What is the importance of universal law of gravitation?
Write four phenomenons which were successfully explained using universal law of gravitation.
Ans: Many unconnected phenomenon can be explained by gravitational law successfully.
(i) Force bind us with Earth
(ii) Motion of Moon around Earth
(iii) Motion of planet around Sun
(iv) Tides due to the Moon and Sun
Q11: Name the scientist in whose honor the SI unit of pressure is named.
Ans: The SI unit of pressure is named after Blaise Pascal.
Q12: Define the weight of an object on Moon.
Ans: The weight of an object on the Moon is the force with which the Moon attracts that object.
Q13: What is weightlessness?
Ans: A body is said to be in a state of weightlessness when the reaction of the supporting surface is zero or its apparent weight is zero.
Q14: Give difference between `g’ and ‘G’ in a tabular form.
Ans: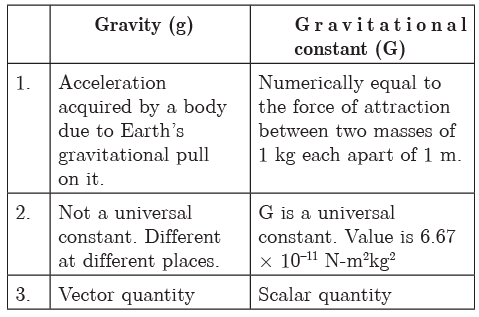
Q15: Why is G called ‘a universal gravitational constant’?
Ans: The value of G is same for any pair of objects in the universe. Also its value does not depend on the nature of the intervening medium. That is why constant G is called ‘universal gravitational constant’.
|
84 videos|541 docs|60 tests
|





















