Very Short Question Answers: Locating Places on the Earth | Short & Long Answer Questions for Class 6 PDF Download
Q1. What is a map?
Ans: A map is a visual representation of an area, illustrating its features and providing guidance on navigation.
Q2. What is an atlas?
Ans: An atlas is a collection of maps, typically organized by region or theme, used for reference or educational purposes.
Q3. What are physical maps?
Ans: Physical maps depict natural features such as mountains, rivers, and oceans.
Q4. What are political maps?
Ans: Political maps show boundaries, countries, cities, and other human-made features.
Q5. What are thematic maps?
Ans: Thematic maps focus on specific themes or subjects like population distribution or climate zones.
Q6. What are cardinal directions?
Ans: Cardinal directions refer to the main directions on a map: north, east, south, and west.
Q7. What are intermediate directions?
Ans: Intermediate directions are points between the cardinal directions, like northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest.
Q8. What do the arrows on a map indicate?
Ans: The arrows on a map indicate cardinal directions to help orientate the map.
Q9. What are symbols on a map?
Ans: Symbols on a map represent features such as buildings, roads, and natural elements, providing detailed information in a concise manner.
Q10. What is the scale of a map?
Ans: The scale of a map indicates the relationship between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground.
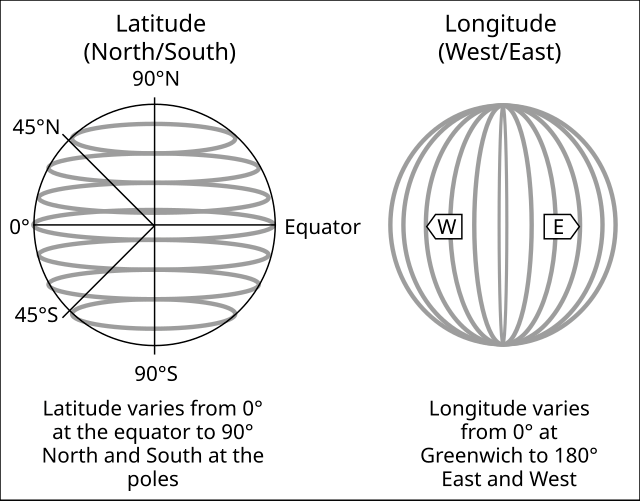
Q11. How are latitudes measured?
Ans: Latitudes are measured in degrees north or south of the Equator.
Q12. What is the Equator?
Ans: The Equator is an imaginary line around the middle of the Earth, equidistant from the North and South Poles.
Q13. How are longitudes measured?
Ans: Longitudes are measured in degrees east or west from the Prime Meridian.
Q14. What is the Prime Meridian?
Ans: The Prime Meridian is the line of 0° longitude, passing through Greenwich, England, serving as the starting point for measuring longitudes.
Q15. How does longitude affect time?
Ans: Longitudes determine time zones, with each 15° difference approximately equal to one hour of time difference.
Q16. What is Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)?
Ans: Greenwich Mean Time is the time at the Prime Meridian and serves as the standard time used worldwide.
Q17. What are time zones?
Ans: Time zones are regions of the Earth where the same standard time is used.
Q18. What is the International Date Line?
Ans: The International Date Line is the line approximately 180° longitude, where the date changes by one day when crossed.
Q19. How does crossing the International Date Line affect time?
Ans: Crossing eastward subtracts a day while crossing westward adds a day to the date.
Q20. What is a globe?
Ans: A globe is a spherical representation of the Earth's surface, providing a more accurate depiction of geographic features than flat maps.
Q21. How are maps and globes different?
Ans: Maps are flat representations, while globes are spherical representations of the Earth.
Q22. What are coordinates on a map?
Ans: Coordinates (latitude and longitude) pinpoint exact locations on Earth's surface.
Q23. How are coordinates similar to a chessboard?
Ans: Coordinates on a map resemble the grid system used in chess, enabling precise location identification.
Q24. Why do maps use symbols instead of detailed drawings?
Ans: Symbols on maps save space and simplify representation by using standardized icons to depict features.
Q25. What does a scale of 1 cm = 500 m mean on a map?
Ans: It means that each centimetre on the map represents a distance of 500 meters on the ground.
Q26. How do maps help with navigation?
Ans: Maps provide directions, distances, and landmarks to assist travellers in finding locations and navigating routes.
Q27. How do latitude and longitude help in locating places?
Ans: Latitude and longitude are coordinates that precisely identify any location on Earth's surface.
Q28. What is the purpose of the Equator in geography?
Ans: The Equator divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres and serves as a reference for latitude measurements.
Q29. Why are time zones necessary?
Ans: Time zones help synchronize time across regions, facilitating communication, travel, and international business.
Q30. Who decided on the Prime Meridian as the international standard?
Ans: The Prime Meridian was established by international agreement in 1884 to pass through Greenwich, England.
Q31. How does latitude affect climate?
Ans: Latitude influences climate; areas closer to the Equator generally experience warmer climates than those closer to the poles.
Q32. Why can't a globe be perfectly represented on a flat map?
Ans: The Earth's spherical shape causes distortion when flattened, making it impossible to perfectly represent all areas on a flat map.
Q33. What are the benefits of using thematic maps?
Ans: Thematic maps provide detailed information on specific subjects, such as population density or land use, offering insights beyond basic geographic features.
Q34. How do symbols vary on maps of different countries?
Ans: Different countries use unique sets of symbols on their maps to represent features such as buildings, roads, and landmarks.
Q35. What is the significance of the International Date Line?
Ans: The International Date Line marks where the date changes by one day when crossed, approximately along 180° longitude.
Q36. How do physical maps differ from political maps?
Ans: Physical maps emphasize natural features like mountains and rivers, while political maps show boundaries, cities, and administrative divisions.
Q37. What are the primary uses of an atlas?
Ans: An atlas is used for reference, education, and navigation, containing maps of various regions, countries, and thematic topics.
Q38. How do coordinates help in navigation?
Ans: Coordinates on maps provide precise locations, aiding in navigation by pinpointing specific points of interest or destinations.
Q39. What are the advantages of using a globe over a flat map?
Ans: A globe provides a more accurate representation of the Earth's surface and spatial relationships than flat maps.
Q40. How do time zones relate to longitude?
Ans: Time zones are based on lines of longitude, with each zone typically covering 15° of longitude and representing one hour of time difference.
FAQs on Very Short Question Answers: Locating Places on the Earth - Short & Long Answer Questions for Class 6
| 1. What are the main tools used for locating places on Earth? |  |
| 2. How do latitude and longitude help in locating places? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Equator in geography? |  |
| 4. What is a map scale and why is it important? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between physical and political maps? |  |

















