Viruses: Structure, Replication and Diagnosis | Biology and Biochemistry for MCAT PDF Download
Structure of Virus
Lipid Envelope
- Usually formed from a lipid bilayer taken from their host, into which the virus inserts its own glycoproteins (enveloped virus).
- Not all viruses have envelopes (naked virus).
- Viruses without envelopes are less prone to damage by external factors, such as pH, than those with envelopes.
- The lipid envelope also determines how viruses enter their host cells.
Glycoproteins
- Either function as transport channels or form viral antigens
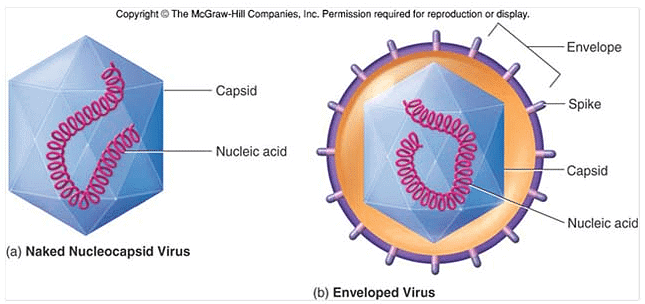
Capsid
- Capsids are proteins that form a coat around the nucleic acid.
- The capsid and genetic information are grouped together and are collectively known as the nucleocapsid.
- Often the whole virus is actually just a nucleocapsid, without a membrane or envelope.
Genetic Material
- The genetic material within viruses can be single- or double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA).
- A protein coating often protects the genome from external factors.
Replication of Virus
Adsorption
- Glycoproteins in the viral lipid envelope or molecules on the nucleocapsid (naked viruses) attach to specific receptor molecules on the host cell.
- This viral-host receptor molecule relationship is often highly specific. Accordingly, many viruses can only infect a limited range of cells.
- For example, the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) preferentially infects T-helper cells as they express CD4 and CXCR4 receptor molecules on their cell membrane. The glycoprotein 120 molecule found in the lipid envelope of the HIV is able to bind with these receptor molecules.
Entry
The mechanism by which viruses gain entry to their host cells is dependent upon their structure; in particular, whether a lipid membrane is present.
- Enveloped virus: Cytoplasmic membrane fusion: the virus fuses with the host cell cytoplasmic membrane and the viral contents are then released into the cytoplasm.
Endocytosis: the virus is engulfed by the host cell cytoplasmic membrane. - Naked virus: Direct: the virus passes directly across the host cell cytoplasmic membrane.
Endocytosis.
Un-Coating
- Once inside the host cell, the viral lipid envelope or capsid is shed and the viral nucleic acids are released.
- At this stage, the virus ceases to be infective and will only regain infectivity after new virions have been formed (eclipse phase).
Replication
- Viral replication is broadly a two-stage process; both viral proteins and nucleic acid must be replicated to form new virus particles.
(A) Viral Protein Production
- Viruses must first transcribe their genetic material into messenger RNA (mRNA) in order to use host ribosomes to produce new viral proteins.
- This process varies depending on the form and sense of the viral genetic material.
Forms:
- RNA: single-stranded (ssRNA) or double-stranded (dsRNA).
- DNA: double-stranded (dsDNA).
Sense:
- Sense (positive sense, +ve): genetic material is ready for translation, and is already equivalent to mRNA.
- Anti-sense (negative sense, -ve): genetic material requires transcription to mRNA before translation can occur.
RNA:
- -ve dsRNA and -ve ssRNA: use viral RNA polymerase to form +ve ssRNA, which is equivalent to mRNA.
- +ve ssRNA: already equivalent to mRNA.
DNA:
- DNA viruses have the equivalent of a positive and negative sense single strand.
- They use host cell RNA polymerase to transcribe the negative sense strand into + ve ssRNA, which is equivalent to mRNA.
Retroviruses
- retroviruses contain +ve ssRNA;
- this is transcribed by viral reverse transcriptase into -ve ssRNA;
- this is then used to form dsDNA, which is integrated into the host genome;
- the negative sense strand is then transcribed by the host RNA polymerase to form mRNA (similar to the DNA process);
- after mRNA or the +ve ssRNA has been formed, the host cell ribosomes are used as a site of viral protein synthesis.
(B) Viral Nucleic Acid Production
The mechanism of this process is also determined by the form and sense of the viral genetic material.
RNA:
- + ve ssRNA and dsRNA: viral polymerase produces multiple – ve ssRNA, which is transcribed into + ve ssRNA. With dsRNA, only the negative sense strand is converted into + ve ssRNA.
- – ve ssRNA: the inverse of the above process- viral polymerase produces multiple + ve ssRNA, which is then transcribed into – ve ssRNA.
DNA:
- The viral genetic material is transcribed by viral DNA polymerase and then incorporated into the host genome.
- Host or viral DNA polymerase is then used to produce multiple viral genetic material.
Retroviruses:
- Following integration into the host genome by viral reverse transcriptase, host RNA polymerase transcribes the viral DNA into RNA.
Assembly
- Viral progeny are formed by integrating the new viral proteins and genetic material.
Release
- Viruses are released from their host cell either by host cell lysis or by a process called budding, in which the virus forms an envelope from the host cell cytoplasmic membrane.
Diagnosis of Virus
There are two broad approaches to detecting and diagnosing a viral infection in the laboratory: viral detection and host response.
Viral Detection
Viruses must be cultured in medium that contains living cells such as monkey kidney.
Viral growth can be identified by observing:
- Cytopathic effect: a characteristic cellular change due to viral growth (e.g. respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) culture leads to multinucleated giant cells).
- Haemadsorption: the envelope protein haemagglutinin (HA) causes added red blood cells to attach to the viral infected cell. Examples include influenza and mumps virus.
- Viral antibody: a positive response to the addition of viral antibody is detected by a range of methods, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence.
Microscopic Techniques
Light microscopy: detects inclusion bodies (collections of viral particles) within the infected cell. Some have a characteristic appearance such as Negri bodies with rabies infection.
Electron microscopy: detects viruses and viral particles.
Viral antigen detection
- ELISA and immunofluorescence
Viral nucleic acid
- The sequencing of viral nucleic acids has enabled the creation of highly sensitive diagnostic tests.
- A complementary DNA or RNA probe to the viral nucleic acid labelled with a marker will identify viral nucleic acid.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can amplify small amounts of nucleic acid.
Host Response
Antibody detection
Interpretation: Immunoglobulin (Ig) M: levels rise early and suggest recent or current infection. IgG: must rise fourfold over a 2 week period to be diagnostic of a recent or current infection. Can also suggest previous infection.
Elisa
Western blot
- Electrophoresis is used to separate viral proteins in a gel solution.
- These proteins are subsequently transferred (blotted) onto filter paper.
- The sample serum is added to the paper; if viral antibodies are present, they will bind to the antigen.
- This complex can be detected by adding a labelled antibody to human IgG and visualized in a similar manner to ELISA or immunofluorescence.
|
129 videos|60 docs|24 tests
|
















