Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animal Class 7 Notes Science
You may have experienced firsthand the importance of weather preparations, like remembering to pack an umbrella when the sky is cloudy before embarking on a trip to a hill station.

It's common for adults to engage in discussions about the weather before organizing family gatherings or outdoor activities, recognizing its significant impact on our plans and daily lives.
In this chapter, we'll delve into the fascinating world of weather and climate.
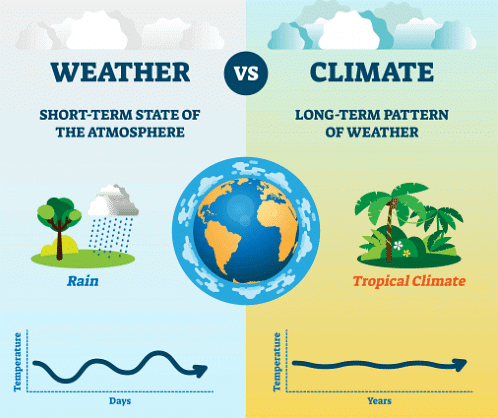 Weather & Climate
Weather & Climate
Further, we'll uncover the relationship between different forms of life and their adaptation to the climate of their habitats.
Weather
We often say, “today’s weather is too humid”, or “the weather was warm last week”. The weather varies each day, with changes in temperature, humidity, and rainfall.
 Different Types of Weather
Different Types of Weather
Weather refers to daily atmospheric conditions like temperature, humidity, and rainfall. It can change rapidly, for example, from sunny to rainy. Such rapid changes are common experiences. In short, Weather refers to the day-to-day conditions of the atmosphere, including temperature, humidity, rainfall, and wind speed.
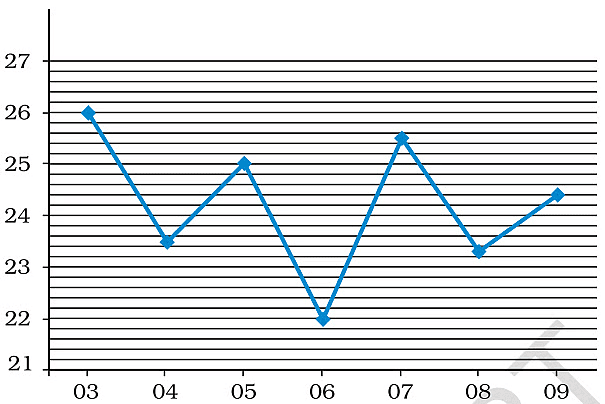 Shillong Weather Report
Shillong Weather Report
The graph given above shows the maximum temperature recorded from 03 August 2006 to 09 August 2006 at Shillong, Meghalaya .We can see from any weather report, that the maximum and minimum temperatures are recorded every day. 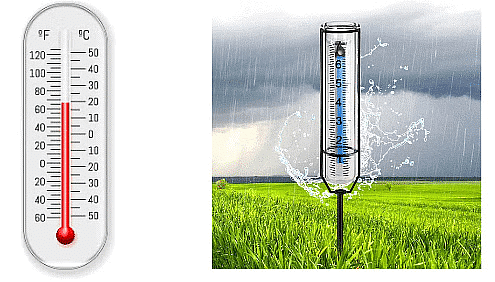 Weather Thermometer(left) & Rain Gauge(right)
Weather Thermometer(left) & Rain Gauge(right)
Special thermometers, called maximum and minimum thermometers, are used to record temperatures.Rainfall is measured by an instrument called the rain gauge. It is basically a measuring cylinder with a funnel on top to collect rainwater.

Climate
Climate refers to the average weather conditions observed over an extended(longer) period, typically around 25 years. For instance, if a particular place consistently experiences high temperatures and frequent heavy rainfall over many years, it is characterized as having a hot and wet climate.
Comparison of Climates in different regions of India
(a) Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir:
- It exhibits a climate that is moderately hot and wet for a portion of the year.
- Temperatures and precipitation levels vary, but generally, the climate is milder compared to other regions.
(b)Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala:
- It features a climate that is significantly hotter and wetter compared to Srinagar.
- The weather tends to be consistently warm and experiences heavy rainfall throughout the year, indicating a tropical climate.
(c) Western Region (e.g., Rajasthan):
- Experiences high temperatures for most of the year, with notably cooler temperatures during the winter months.
- Precipitation levels are very low, contributing to the characteristic desert climate of the region, characterized by arid conditions and limited rainfall.
(d) Northeastern India:
- Receives substantial rainfall for a significant portion of the year, leading to a considerably wetter climate compared to other regions.
- The abundance of rainfall supports lush vegetation and diverse ecosystems characteristic of tropical rainforests.
Climate and Adaptation
Climate significantly impacts all living organisms. Animals adapt to their surroundings to survive, a process known as adaptation, which evolves over time. Polar Regions and Tropical Rainforests
Polar Regions and Tropical Rainforests
- Polar Regions:
- These are situated near the North and South Poles.
- Countries like Canada, Greenland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Alaska (USA), and Siberia (Russia) are part of these regions.
- Tropical Rainforests:
- They are found in countries such as India, Malaysia, Indonesia, Brazil, Republic of Congo, Kenya, Uganda, and Nigeria.
- These regions have hot, humid climates with abundant rainfall.
Animals in polar regions and tropical rainforests exhibit adaptations to cope with their respective climates. Understanding these adaptations helps us appreciate how animals survive in diverse environmental conditions.
- Weather: Day to day atmospheric condition.
- Climate: Average atmospheric condition for at least 25 years.
- Elements of weather: Temperature, Humidity, Rainfall, Wind-speed, etc.
- Rainforest: Dense forest near equator and tropical regions.
- Desert: A region with little rainfall, high temperature and full of sand.
- Polar Regions: Regions near poles, having very low temperature, area is covered with snow most of the parts of year.
- Adaptation: Special habits of animals which enable them to survive in particular climatic conditions.
- Camouflage: Special colour of animals because of which they can resemble with background of surrounding which hide themselves from predators.
(i) Polar Regions
The polar regions have extreme climates, with snow covering them for most of the year and very low temperatures, as low as -37°C in winter. Animals living in these regions have special adaptations to survive in such harsh conditions.
Polar Bears
 Polar Bears
Polar Bears
- Camouflage: Polar bears have white fur to blend with the snowy background, making them less visible to their prey and predators.
- Insulation: They have two thick layers of fur and a layer of fat under their skin to keep them warm in extreme cold.
- Swimming Abilities: Polar bears are excellent swimmers with streamlined bodies, webbed feet, and wide paws that help them move efficiently in water.
- Hunting Skills: They have a strong sense of smell to locate prey underwater and can stay submerged for long periods.
Penguins
 Penguins huddle together to keep themselves warm
Penguins huddle together to keep themselves warm
- Camouflage: Penguins are also white, blending with the snowy environment to avoid detection.
- Insulation: They have thick skin and a layer of fat to protect them from the cold.
- Group Huddling: Penguins huddle together to conserve body heat, similar to how people feel warmer in a crowded room.
Other Animals in Polar Regions
Many types of fish live in polar waters and can tolerate cold temperatures for extended periods. Musk Oxen, Reindeers, Foxes, Seals, Whales, Birds: These animals have different adaptations to survive in the polar environment. Birds migrate to warmer regions during winter and return when it's over.
Musk Oxen, Reindeers, Foxes, Seals, Whales, Birds: These animals have different adaptations to survive in the polar environment. Birds migrate to warmer regions during winter and return when it's over.(ii) The tropical rainforests
Tropical regions, located around the equator, have hot climates with temperatures above 15°C even in the coldest months and exceeding 40°C during summers. Rainforests, a prominent feature of these regions, receive abundant rainfall and support a diverse array of plants and animals.
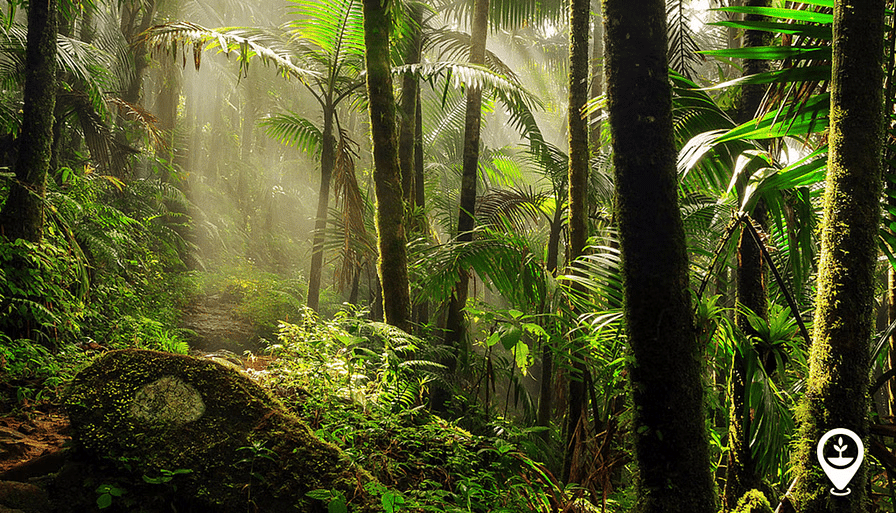

Characteristics of Tropical Rainforests
- Location: They are located in regions like Western Ghats, Assam, Southeast Asia, Central America, and Central Africa.
- Climate: They have hot and humid climate throughout the year, with plenty of rainfall.
- Biodiversity: They support a wide variety of plant and animal species due to continuous warmth and rain.
Animal Adaptations in Tropical Forests
Animals in tropical rainforests have evolved various adaptations to thrive in the hot, humid climate and compete for resources. These adaptations include specialized appendages, sensory adaptations, and behavioral strategies to ensure survival in this biodiverse ecosystem.
- Tree Dwellers: Many animals live in trees due to intense competition for food and shelter.
- Specialized Appendages: Animals like monkeys have long tails and specialized hands and feet for grasping branches.

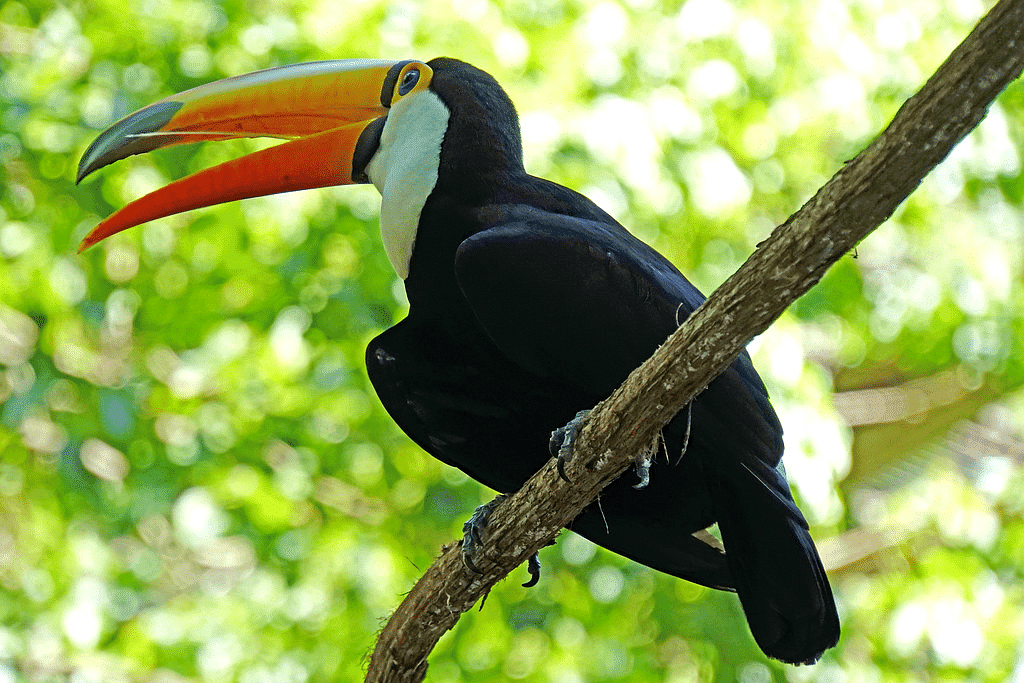
- Long Beaks: Birds like the Toucan have long, large beaks to reach fruits on weak branches.
- Sensory Adaptations: Animals have sensitive hearing, sharp eyesight, and camouflage to protect themselves from predators. For example, big cats have thick skin and sensitive hearing.
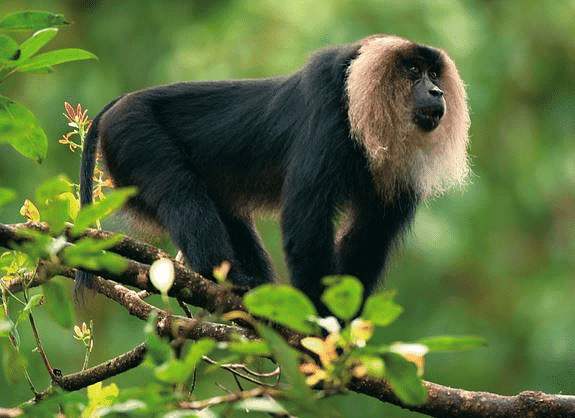
- Lion-Tailed Macaque: This species lives in Western Ghats and has a silver-white mane. It is a good climber and mainly feeds on fruits and insects found in trees.

- Elephant: Elephants have adapted in remarkable ways, such as using their trunks for smelling and picking food, and their tusks for tearing bark. Large ears help them hear soft sounds and regulate body temperature in the hot, humid climate.
FAQs on Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animal Class 7 Notes Science
| 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? |  |
| 2. How does weather affect animals? |  |
| 3. What are some adaptations of animals to different climates? |  |
| 4. How do animals adapt to changes in climate? |  |
| 5. How does climate change affect animal populations? |  |























