Engineering Mathematics Exam > Engineering Mathematics Notes > Engineering Mathematics > Well-Formed Formulas
Well-Formed Formulas | Engineering Mathematics - Engineering Mathematics PDF Download
Well-formed Formulas (WFFs) of Propositional Logic
- Propositional logic uses a symbolic “language” to represent the logical structure, or form, of a compound proposition. Like any language, this symbolic language has rules of syntax—grammatical rules for putting symbols together in the right way. Any expression that obeys the syntactic rules of propositional logic is called a well-formed formula, or WFF.
Fortunately, the syntax of propositional logic is easy to learn. It has only three rules:
- Any capital letter by itself is a WFF.
- Any WFF can be prefixed with “~”. (The result will be a WFF too.)
- Any two WFFs can be put together with “•” (AND), “∨”(OR), “⊃”(SUBSET), or “≡”(EQUIVALENT) between them, enclosing the result in parentheses. (This will be a WFF too.)
Some logic textbooks add a 4th rule: Parentheses may be omitted when doing so doesn’t result in any ambiguity. This convention makes some formulas slightly easier to read and write, but complicates the rules of syntax. To avoid unnecessary complications, I’ll adhere to the stricter convention of keeping all parentheses.
Examples
Here are some examples of well-formed formulas, along with brief explanations how these formulas are formed in accordance with the three rules of syntax:
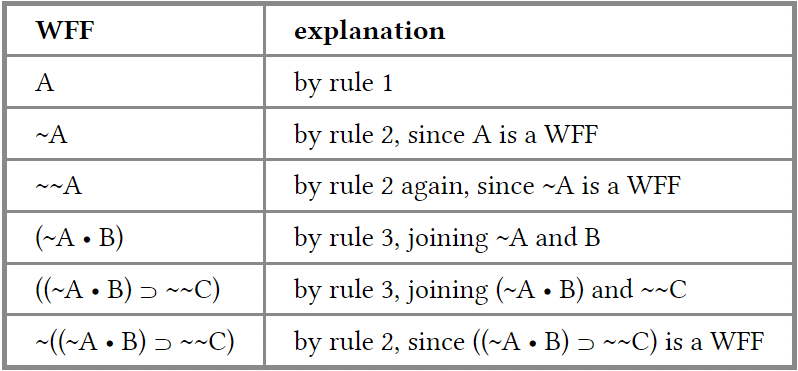
In contrast, here are a few formulas that are not well-formed:

- The last connective introduced by rule 2 or 3 is called the main connective of the WFF. The main connective represents the logical structure of the compound proposition as a whole. For example, if the main connective is a “~”, the proposition as a whole is a negation. If the main connective is a “•”, the proposition is a conjunction, and so on.
- Propositions joined by the main connective are called its components or component propositions. Components may themselves be compound propositions, made up of simpler components. Some components have special names. In a conjunction, the components joined by the “•” (dot) are called its conjuncts. In a disjunction, the propositions joined by the “∨” (wedge) are called disjuncts. In a conditional, the component to the left of the “⊃” (horseshoe) is called the antecedent and the component to the right is called the consequent.
Examples
- The proposition (A • ~B) is a conjunction because its main connective is the dot. The propositions A and ~B are its conjuncts.
- The proposition (~A ∨ (B ≡ C)) is a disjunction because its main connective is the wedge. The propositions ~A and (B ≡ C) are its disjuncts.
- The proposition ((A ∨ B) ⊃ (C • D)) is a conditional because its main connective is the horseshoe. The proposition (A ∨ B) is its antecedent and (C • D) is its consequent.
The document Well-Formed Formulas | Engineering Mathematics - Engineering Mathematics is a part of the Engineering Mathematics Course Engineering Mathematics.
All you need of Engineering Mathematics at this link: Engineering Mathematics
|
65 videos|133 docs|94 tests
|
FAQs on Well-Formed Formulas - Engineering Mathematics - Engineering Mathematics
| 1. What are some common tips for preparing for the French language exam? |  |
Ans. Some common tips for preparing for the French language exam include practicing regularly, immersing yourself in the language through listening to French music or watching French movies, and taking mock exams to familiarize yourself with the format.
| 2. How can I improve my French grammar skills for the exam? |  |
Ans. To improve your French grammar skills for the exam, you can practice conjugating verbs, learning common grammar rules, and doing exercises that focus on different grammar concepts such as verb tenses, pronouns, and sentence structure.
| 3. What are some effective strategies for expanding vocabulary before the French language exam? |  |
Ans. Effective strategies for expanding your vocabulary before the French language exam include reading French books or articles, using flashcards to memorize new words, and practicing speaking and writing in French to reinforce your vocabulary.
| 4. How important is cultural knowledge for the French language exam? |  |
Ans. Cultural knowledge is important for the French language exam as it helps you understand the context in which the language is used. Being familiar with French customs, traditions, and history can also enhance your understanding of the language and improve your overall performance on the exam.
| 5. Are there any online resources or apps that can help with studying for the French language exam? |  |
Ans. Yes, there are several online resources and apps available to help with studying for the French language exam. Some popular ones include Duolingo, Babbel, and FluentU, which offer interactive lessons, quizzes, and practice exercises to improve your French language skills.
Related Searches





















