Whole Numbers- 2 Class 6 Worksheet Maths
MCQs
Q1: Counting numbers are called:
(a) Whole numbers
(b) Integers
(c) Natural numbers
(d) None of these
Ans: (c) Natural numbers
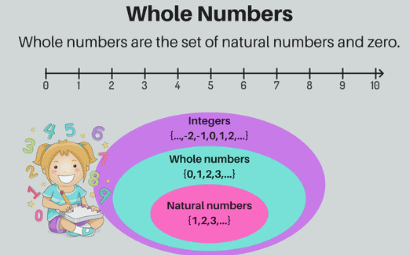
Counting numbers are the numbers we use to count things, starting from 1 (1, 2, 3, ...). These are called natural numbers. Whole numbers, on the other hand, include all natural numbers plus 0. Hence, the correct answer is Natural numbers.
Q2: The sum of two whole numbers is always:
(a) a whole number
(b) an odd number
(c) a natural number
(d) an even number
Ans: (a) a whole number
When you add two whole numbers, the result is always another whole number. For example, 2 + 3 = 5, and 4 + 6 = 10. Both 5 and 10 are whole numbers. So, the correct answer is a whole number.
Q3: The sum of a natural number with a whole number is always:
(a) an even number
(b) a natural number
(c) 0
(d) an odd number
Ans: (b) a natural number
If you add a natural number (like 1, 2, 3, etc.) to a whole number, the result is always another natural number. For example, 3 + 2 = 5, and 4 + 0 = 4. Both 5 and 4 are natural numbers. Hence, the correct answer is a natural number.
Q4: Which one of the following is the smallest whole number?
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) -2
Ans: (a) 0
Whole numbers start from 0 and include all positive integers (0, 1, 2, 3, ...). The smallest whole number is 0. Therefore, the correct answer is 0.
Match the Following
Q5: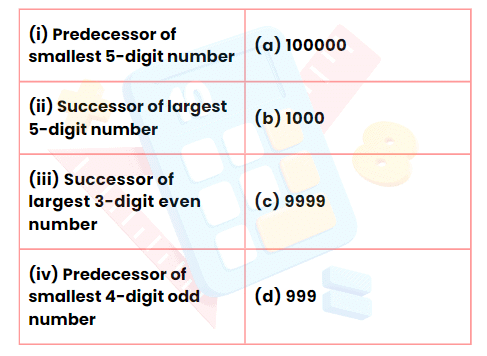
Ans:
(i) ↔ (c)
(ii) ↔ (a)
(iii) ↔ (d)
(iv) ↔ (b)
Answer the following questions
Q6: A boy is moving from one tree to another find the position of the boy from the number line?
(i) 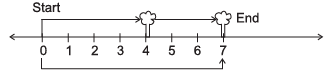
(ii) 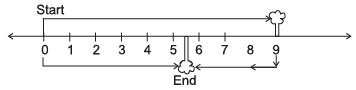
(iii) 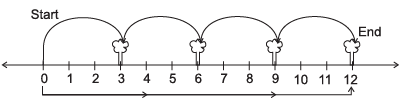
Ans:
(i) Position of boy is 7 units (4 + 3 = 7)
(ii) Position of boy is 9 – 3 = 6 units
(iii) Position of boy is 4 × 3 = 12 units
Q7: Represent the following on a number line:
(i) 5 + 3
(ii) 10 – 6
(iii) 2 × 5
Ans.
(i) 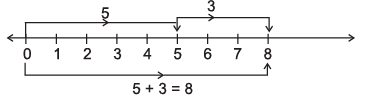
(ii)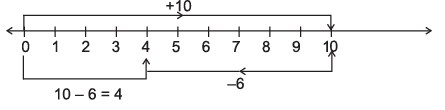
(iii)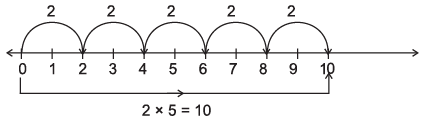
Q8: Predecessor of:
(a) 2340 is __________
(b) 25621 is __________
Ans: (a) 2339
(b) 25620
Q9: Successor of:
(a) 21029 is __________
(b) 7810 is __________
Ans: (a) 21030
(b) 7811
Q10: Write the smallest 3-digit number which will not change on reversing the digits.
Ans: 101
Q11: The difference of the smallest 3-digit number and its predecessor is __________.
Ans: 1
Assertion Reason Questions
Q12: Assertion (A): The successor of a two-digit number is always a two-digit number.
Reason (R): Given any natural number, you can add 1 to that number and get the successor.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (d) A is false but R is true.
The successor of a two-digit number is not always a two-digit number. For example, the successor of 99 is 100, which is a three-digit number. The reason (R) is true because adding 1 to any natural number will give its successor, but it doesn't correctly explain the assertion. Thus, the correct answer is d) A is false but R is true.
Q13: Assertion (A): 135 will be to the left of 150 on the number line.
Reason (R): The smaller whole number is on the left of the larger number on the number line.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
On a number line, smaller numbers are always to the left of larger numbers. Since 135 is smaller than 150, it will be to the left of 150 on the number line. The reason (R) correctly explains the assertion (A). Therefore, the correct answer is a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Q14: Assertion (A): To add 5 and 4, we start from 5, then we make 4 jumps to the right.
Reason (R): To add two numbers, we start from the first number, then we make jumps equal to the second number.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
When adding two numbers on a number line, you start at the first number (in this case, 5) and make jumps equal to the second number (in this case, 4). This method correctly explains how to add 5 and 4 by making 4 jumps to the right from 5. So, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. The correct answer is a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Q15: Assertion (A): Starting from 0, moving 4 units at a time to the right, and making 5 such moves will bring us to 20.
Reason (R): 4 x 5 = 20.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
When you move 4 units at a time to the right and make 5 moves, you move a total of 4 × 5 = 20 units. Therefore, you will end up at 20. The reason correctly explains the assertion, so the correct answer is a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
FAQs on Whole Numbers- 2 Class 6 Worksheet Maths
| 1. What are the basic operations performed with whole numbers? |  |
| 2. How do I add whole numbers? |  |
| 3. Can whole numbers be negative? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of zero in whole numbers? |  |
| 5. How can I multiply whole numbers? |  |

















