Whole Numbers- 2 Class 6 Worksheet Maths
MCQs
Q1: Counting numbers are called:
(a) Whole numbers
(b) Integers
(c) Natural numbers
(d) None of these
Q2: The sum of two whole numbers is always:
(a) a whole number
(b) an odd number
(c) a natural number
(d) an even number
Q3: The sum of a natural number with a whole number is always:
(a) an even number
(b) a natural number
(c) 0
(d) an odd number
Q4: Which one of the following is the smallest whole number?
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) -2
Match the Following
Q5: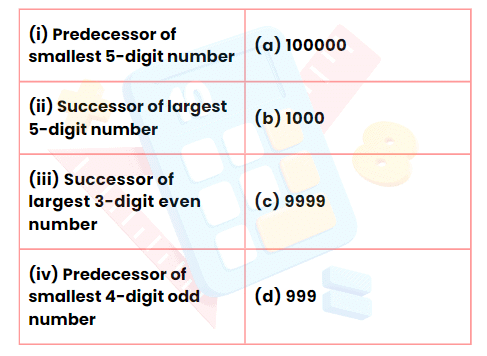
Answer the following questions
Q6: A boy is moving from one tree to another find the position of the boy from the number line?
(i) 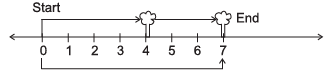
(ii) 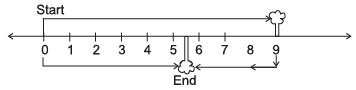
(iii) 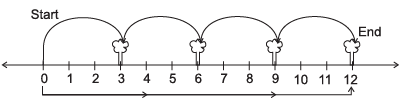
Q7: Represent the following on a number line:
(i) 5 + 3
(ii) 10 – 6
(iii) 2 × 5
Q8: Predecessor of:
(a) 2340 is __________
(b) 25621 is __________
Q9: Successor of:
(a) 21029 is __________
(b) 7810 is __________
Q10: Write the smallest 3-digit number which will not change on reversing the digits.
Q11: The difference of the smallest 3-digit number and its predecessor is __________.
 |
Download the notes
Worksheet: Whole Numbers- 2
|
Download as PDF |
Assertion Reason Questions
Q12: Assertion (A): The successor of a two-digit number is always a two-digit number.
Reason (R): Given any natural number, you can add 1 to that number and get the successor.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q13: Assertion (A): 135 will be to the left of 150 on the number line.
Reason (R): The smaller whole number is on the left of the larger number on the number line.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q14: Assertion (A): To add 5 and 4, we start from 5, then we make 4 jumps to the right.
Reason (R): To add two numbers, we start from the first number, then we make jumps equal to the second number.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q15: Assertion (A): Starting from 0, moving 4 units at a time to the right, and making 5 such moves will bring us to 20.
Reason (R): 4 x 5 = 20.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
92 videos|353 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on Whole Numbers- 2 Class 6 Worksheet Maths
| 1. What are whole numbers and how do they differ from other types of numbers? |  |
| 2. How can I teach whole numbers to young children effectively? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of whole numbers in real-life situations? |  |
| 4. How do you add and subtract whole numbers? |  |
| 5. Are whole numbers used in higher mathematics, and if so, how? |  |























