Whose Forests? - 1 Class 5 Worksheet EVS Chapter 20
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions.
(i) To which community did Suryamani belong?
(a) Kuduk
(b) Baiga
(c) Bhils
(d) Khasis
Ans: Kuduk
(ii) Suryamani was associated with which movement?
(a) Chipko Movement
(b) Jharkhand Jungle Bachao Andolan
(c) Appiko Movement
(d) Narmada Bachao Andolan
Ans: Jharkhand Jungle Bachao Andolan
(iii) To which state did Suryamani belong?
(a) Chhattisgarh
(b) Orissa
(c) Jharkhand
(d) Mizoram
Ans: Jharkhand
(iv) What was the name of Suryamani's center?
(a) Kuduk
(b) Torang
(c) Jungle Bachao
(d) Cheraw
Ans: Torang
(v) Which crop is major in Mizoram?
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Tea
(d) Bajra
Ans: Rice
Q2: Fill in the blanks
(i) The cut weeds are burned and their __________ is mixed with the soil to make it ready for sowing.
(ii) Suryamani studied hard and passed her BA after receiving a _______
(iii) __________ cut down forests.
(iv) Forest __________ have a right on the forest.
(v) Baskets are woven from __________ and leaf plates are made from __________ leaves.
Ans: (i) Ash
(ii) Scholarship
(iii) Developers
(iv) Adivasis
(v) Bamboo, fallen
Q3: True or False.
(i) Children were going to shopping mall with Suryamani didi.
(ii) Children enjoy a special class in the forest.
(iii) Suryamani’s family used to sell the leaves and herbs collected from forest.
(iv) Cheraw dance is performed in Punjab.
(v) Forest is called a 'Collective Bank’.
Ans: (i) False
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) False
(v) True
 Cheraw Dance
Cheraw DanceQ4: Short Answer Type Questions
(i) What do you think is a forest?
Ans: A large area covered by trees and undergrowth is called as Forest.
(ii) Other than trees what all is there in a forest?
Ans: A forest is made up of abiotic and biotic components including animals, birds insects etc.
(iii) What is the web of relationships in forest?
Ans: Plants, trees, and animals in a forest depend on each other for food, security and habitat. This is called the web of relationship in a forest.
(iv) Suryamani says, “If the forests are not there, we too will not remain.” Why so?
Ans: Forests provide us wood, medicines, fresh air and many other materials. They also cause rain, keep the climate cold and maintain balance in nature. Therefore, if forests are not there, we too will not remain.
(v) Why did Suryamani’s father move to town?
Ans: After the arrival of the contractor, it was not possible to pick a single leaf from the forest. Suryamani’s father could no longer support the family on the small land. So he moved to the town in search of work.
Q5: Long Answer Type Questions
(i) Why is learning from forests considered as important as learning from books?
Ans: As learning from books cannot teach a student well and it can happen that the student doesn't understand properly but in the forest, students can learn practically can clear their doubts properly.
(ii) Why are forests are called collective banks?
Ans: Forest is our collective bank. We should take from it only as much as we need. We should not use up all our wealth.
(iii) What is the importance of education in relation to saving forests?
Ans: Education on the environment helps students to understand the causes of environmental destruction and ways to deal with them. Today, pollution, plastic waste, etc. have become a threat and are responsible for global warming. So education is necessary to overcome these and ensure a healthy environment that is worth living for us and the coming generations.
(iv) Write about the “Right to Forest Act 2007?”
Ans: People who have been living in the forests for at least 25 years, have the right over the forest land and what is grown on it. They should not be removed from the forest. The work of protecting forests should be done by their Gram Sabha.
(v) Write a few lines about “Cheraw Dance?”
Ans: Cheraw is a special dance performed after harvest in Mizoram. In this dance, people sit in pairs in front of each other, holding bamboo sticks on the ground. As the drum beats, the bamboos are beaten to the ground. Dancers step in and out of the bamboo sticks, and dance to the beat.
(vi) Look at the below India map and answer the following questions.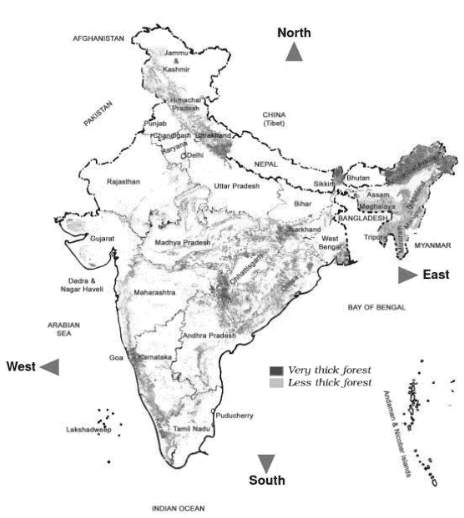 (a) Name any two states that have “thick forests.”
(a) Name any two states that have “thick forests.”
(b) Name any two states that have “thin forests.”
(c) Name a state in South India that has thick forests.
(d) Name any one state that doesn’t have any forest.
Ans:
(a) Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim
(b) Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan
(c) Andhra Pradesh
(d) There are different kinds of forests present in each state. Hence, no state of India lacks forest.
|
37 videos|244 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Whose Forests? - 1 Class 5 Worksheet EVS Chapter 20
| 1. What are the main causes of deforestation? |  |
| 2. How does deforestation affect the environment? |  |
| 3. What are the consequences of deforestation for local communities? |  |
| 4. How can we prevent deforestation? |  |
| 5. What is the role of international cooperation in addressing deforestation? |  |

















