Worksheet (Part - 2) - Tenses | English An Alien Hand Class 7 PDF Download
2. THE PAST TENSE
A. The Past Indefinite Tense Or The Simple Past Tense
(Subject + II form of the Verb…)
In the Simple Past (Past Indefinite) Tense the second form of the Verb is used; as—
→ He came here yesterday.
→ 'Did' is used in the Interrogative and Negative sentences. ‘Did’ is also used
to lay emphasis. Only the first form of the Verb is used with ‘did’.
(i) In Interrogative Sentences [‘did’ is placed before the subject and verb in first form after it ; as—]
(Did + Subject + I form of the Verb…?)
→ Did you show me your homework ?
(ii) In Negative Sentences [‘did not is put after the subject and first form of the verb is used thereafter : as—]
(Subject + did + not + I form of the Verb…)
→ I did not apply for leave.
→ Exception — I never told a lie.
(This sentence means — I did not ever tell a lie)
(iii) To lay emphasis
I did try to solve the question but was not able to solve it.
Uses of the Past Indefinite Tense
The Past Indefinite (Simple Past) Tense is used :
(a) To express an action completed in the past with reference to the time of speaking.
→ I saw many birds in the zoo.
(b) To express habitual or regular action in the Past.
→ Gandhiji always spoke the truth.
(c) To express an event which occurred at a particular point in the Past.
→ My father came back home yesterday.
(d) To express an action which occupied a period of time in the Past, but is now ended.
→ We lived in this house for ten years. (do not live now)
→ I stayed at the Green Hotel for two months. (not staying now)
(e) To express an action where some word, showing past action [yesterday, ago, last, etc.) is given in the sentence, as,
→ He received your message yesterday.
→ I passed the S.S.C. Examination last year.
Mark the correct use of the Past Indefinite Tense in the following sentences.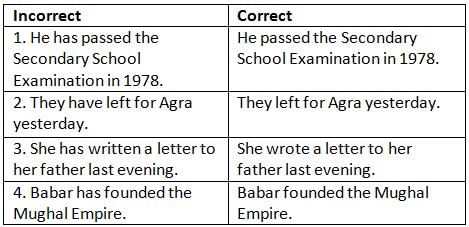
Note : The difference in the meaning of the following sentences :
(i) He has worked in this office for five years. (He is still working here)
(ii) He worked in this office for five years. (He is no longer working here)
Fill in the following blanks with correct past tense of the verbs given in brackets :
(i) I _______ your letter this morning.
Ans. Received
(ii) How many deer _______ you _______ in the zoo ?
Ans. Did, see
(iii) My father _______ a new house last month.
Ans. Bought
(iv) Prices _______ by forty percent last year.
Ans. Rose
(v) Columbus _______ America.
Ans. Discovered
(vi) Thousands of people _______ their lives in the earthquake.
Ans. Lost.
B. The Past Continuous Tense
(Subject + was/were + I form of the Verb + ing…)
(i) The Past Continuous Tense denotes an action going on in the past. In order to form Past Continuous Tense we add Present Participle to was or were ; as—
→ The train was running at full speed.
(ii) In Negative form [‘not is placed between the helping verb and the principal verb ; as—]
(Subject + was/were + not + Verb + ing…)
→ She was not weeping.
(iii) In Interrogative form [the helping verb is placed before the subject ; as— (Was/were + Subject + Verb + ing + … ?)
→ Were the sheep grazing in the field ?
Uses of the Past Continuous Tense
(i) The Past Continuous Tense is used to express an action that was happening in the Past at the time of speaking. The time of the action may or may not be mentioned.
Examples: The old lady was crying at the top of her voice.
→ They were not making a noise.
(ii) The use of this tense with Simple Past Tense denotes that the previous action was going on when the latter action took place ; as—
→ My mother was cooking the food when I reached home.
EXERCISE 7
Fill in the following blanks with correct Past Continuous Tense of the verbs given in brackets:
(i) The baby _______ in the room. (weep)
Ans. Was weeping
(ii) Children _______ a noise in the class. (make)
Ans. Were making
(iii) Why _______ you _______ at her ? (look)
Ans. Did, look, were, looking
(iv) We saw the aeroplane while it _______ . (take off)
Ans. Was taking off
(v) The students _______ their morning prayer when I reached their school. (say)
Ans. Were saying
(vi) I _______ my beard when the telephone bell rang. (shave)
Ans. Was shaving
(vii) My mother _______ when I returned home. (sleep)
Ans. Was sleeping
C. The Past Perfect Tense
(Subject + had + III form of the Verb)
We often make mistakes while using the Past Perfect Tense. We use ‘had! at random wherever we view ‘past action’ in a sentence in our mother-tongue.
→ I had gone to Delhi yesterday.
This sentence should be formed in Simple past.
→ I went to Delhi yesterday.
The structure of Past Perfect is—
In order to form the Past Perfect Tense we use ‘had’ before the Past Participle (III) form of the Verb.
(i) In Interrogative form [‘Had! is used before the subject]
(Had + Subject + Mform of the Verb + ?)
Had he left when you came ?
(ii) In Negative form [‘nof is used after ‘had’]
(Subject + had + not + III form of the Verb +)
I had not seen you before.
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
(a) The Past Perfect Tense is used to express an action completed before another action took place ; as—
→ When he came to me, I had posted the letter.
(b) (i) It is also used to express an unfulfilled action in the past; as—
→ If she had worked hard she would have passed.
(ii) It is also used to express an unfulfilled wish in the past; as—
→ I wish I had won the election.
(c) To denote the action or event which has been completed before some point of time.
By afternoon he had completed much work.
Use of Past Indefinite and Past Perfect Tenses in Time Clauses
We can express time by using some ‘time-denoting’ Adverbs or through Adverbial clauses of Time. The combination of two past actions depends upon their mutual relevance.
Examples :
→ I had waited for my friend until he arrived.
→ After he had sailed many days, the mariner reached the coast.
EXERCISE 8
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given in brackets. (Past Tense)
(i) Mohan ______ already ______ his breakfast. (take)
Ans. Had,taken
(ii) If she ______ for the examination she would not have failed. (prepare)
Ans. Had prepaired
(iii) The bell ______ before I reached the school. (go)
Ans. Had gone
(iv) The patient ______ before the doctor arrived. (die)
Ans. Had died
(v) She ______ not ______ the place before her husband permitted her. (leave)
Ans. Had, left
(vi) ______ the child before his mother returned from office ? (sleep)
Ans. Had, slept
(vii) The rain ______ when we stepped out of our house. (stop)
Ans. had stopped.
D. The Past Perfect Continuous Tense
(Subject + had + been + Present Participle..
(a) The Past Perfect Continuous Tense expresses an action that had been going on for some time in the past. In order to use this tense we use had been with Present Participle (ing) form of the verb.
Examples :
→ Children had been playing since morning.
(b) The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is also used to express an action that had been going on for some time before another action took place in the past ; as—
Examples :
→ They had been playing chess for two hours when I joined them.
(i) In Interrogative form, ‘had’ precedes the subject and ‘been’ comes after the subject; as—
→ Had he been quarrelling with you for some time ?
(ii) In negative form, ‘not’ is placed after ‘had’ and before ‘been’ ; as—
→ They had not been working on this project for many years.
3. THE FUTURE TENSE
A. The Simple Future/Future Indefinite Tense
(Shall/ will + Verb)
The Future Indefinite Tense is used to express the action or event which is likely to happen in Future. In this tense we use shall/ will between the subject and the first form of the verb. Normally we use ‘shall with pronouns of first person (I, We). In the same way, we use ‘will’ with the pronouns of second person (you) and third person (he, she, it, they).
(i) In Negative sentences ‘not is added after ‘shall’/‘wilt as the case may be; as—
→ We shall not see the picture today.
(ii) In Interrogative sentences ‘will’/‘shall’ is placed before the subject and first form of the verb after it; as—
→ Will you go to college today ?
B. The Future Continuous Tense
(Will/shall + be + Verb + ing)
The Future Continuous Tense is used to express an event that is expected to take place in the normal course or at some time in the future ; as—
→ We shall be playing a football match on Sunday.
→ The new edition of this book will be coming out shortly.
→ When I reach Calcutta, it will be raining heavily there.
→ Will you be taking part in the debate ? (Interrogative)
→ The farmers will not be watering the plants at this time. (Negative)
C. The Future Perfect Tense
(Shall/ will + have + III form of the Verb)
(i) The Future Perfect Tense expresses an action which is expected to be completed by a certain time in the Future ; as—
→ She will have covered half of her journey by Monday next.
(ii) The Future Perfect Tense sometimes expresses the speaker’s belief that something has taken place. In such sentences it does not express the Future ; as—
→ “You will have discussed the plans how to celebrate the function”, said my mother.
(iii) It is also used for an action which at a given future time will be in the past; as—
→ In two years’ time (i.e., two years from now) I shall have taken my degree.
EXERCISE 9
Q.1. Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given in brackets : (Future Perfect Tense)
(i) The picture ______ by the time we reach the hail. (start)
Ans. Will have started
(ii) ______ you ______ your studies by 2009 ? (finish)
Ans. Will, have finished
(iii) The farmers ______ not ______ the harvest before September. (reap)
Ans. Will, have reapted
(iv) I ______ exercise before the sun rises. (take)
Ans. Shall have taken
(v) He ______ his lesson by next week. (learn)
Ans. Will have learnt.
D. The Future Perfect Continuous Tense
(Shall/ will + have been + Verb + ing)
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to express an action that will have been going on at or before some point of time in the Future ; as—
→ We shall have been waiting for you for a long time.
|
7 videos|128 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet (Part - 2) - Tenses - English An Alien Hand Class 7
| 1. What are the different tenses in English grammar? |  |
| 2. How do you form the past tense in English? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between simple present and present continuous tense? |  |
| 4. How do you form the future tense in English? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my understanding and usage of tenses in English? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|

















