Worksheet-1: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| True/False Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
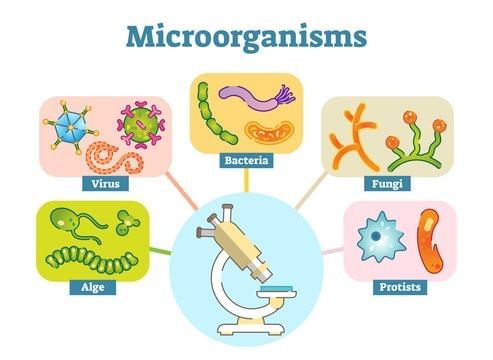
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
Q1. Who first used the term “cell” after observing thin slices of cork?
a) Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
b) Robert Hooke
c) Louis Pasteur
d) Ananda Mohan Chakrabarty
Q2. Which tool allows us to view objects too small to be seen with the naked eye?
a) Telescope
b) Periscope
c) Microscope
d) Binoculars
Q3. A round-bottom flask filled with water can act as:
a) A lens/magnifier
b) A telescope
c) A prism
d) A mirror
Q4. Which cell structure is present in plant cells but absent in animal cells?
a) Nucleus
b) Cell membrane
c) Cell wall
d) Cytoplasm
Q5. Which statement is true about cheek cells?
a) They are rectangular and have a cell wall.
b) They have a large central vacuole.
c) They contain chloroplasts.
d) They are polygon-shaped and lack a cell wall.
Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
Q1. The jelly-like substance inside a cell where life processes occur is the ______.
Q2. The thin, flexible boundary of a cell that controls entry and exit is the ______ ______.
Q3. In onion peel cells, staining with ______ helps make the cells visible.
Q4. Cheek cells are commonly stained with ______ ______.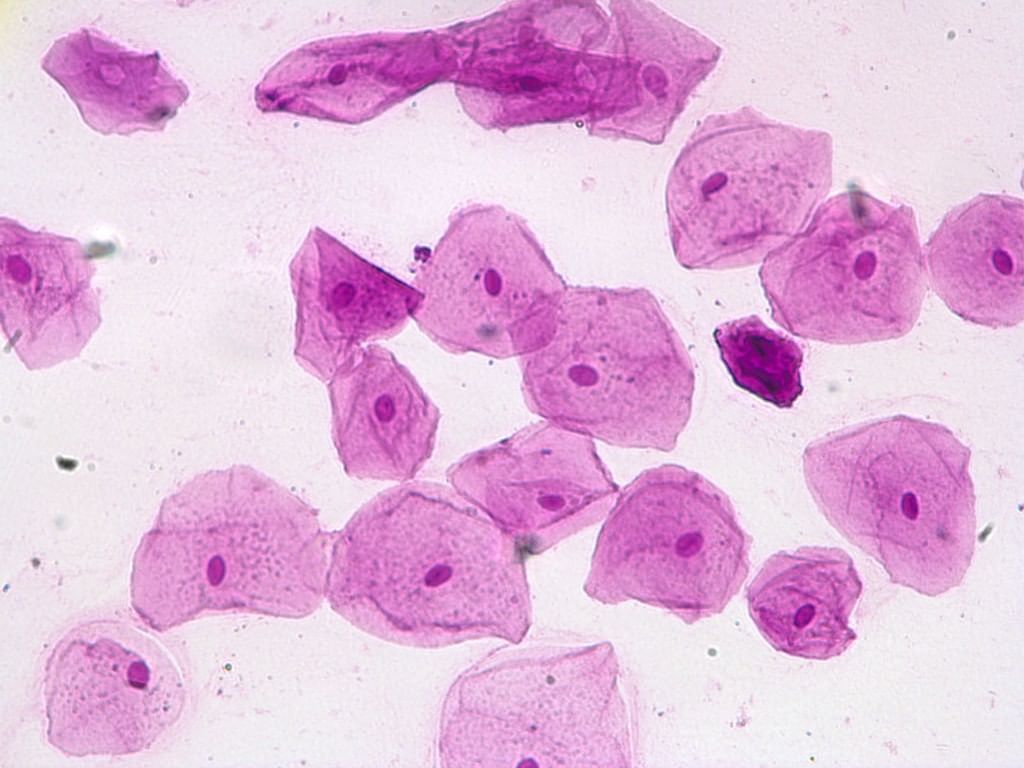 Cheek Cells
Cheek Cells
Q5. The bacteria that fix nitrogen in legume root nodules are called ______.
True/False Questions
Q1. The nucleus controls all cell activities like growth and division.
Q2. Spirulina is a fungus used in bread making.
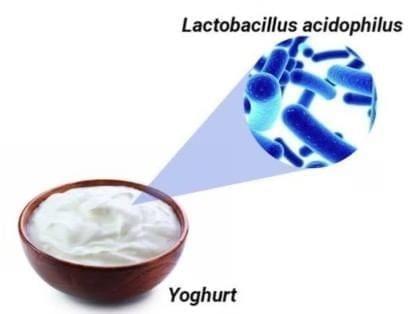
Q3. Lactobacillus is the microorganism responsible for converting milk into curd.
Q4. The process by which yeast releases carbon dioxide to make dough rise is called fermentation.
Q5. In bacteria, the genetic material is enclosed in a well-defined nucleus.
Very Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
Q1. Who is known as the Father of Microbiology?
Q2. What do chloroplasts contain that enables photosynthesis?
Q3. Name the large storage cavity commonly found in plant cells.
Q4. What shape are muscle cells typically described as?
Q5. Which organisms decompose waste to form manure?
Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.Q1. Why are some microorganisms invisible to the naked eye?
Q2. How does high salt or sugar preserve pickles and murabbas?
Q3. How do nerve cells (neurons) suit their function?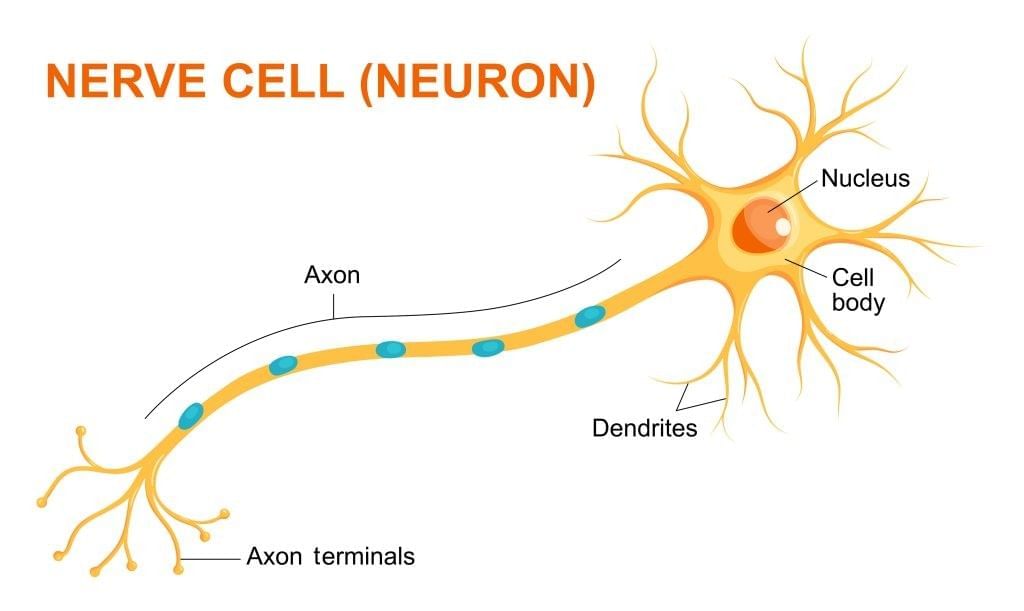
Q4. Why is warm milk preferred for curd formation?
Q5. What role do microalgae play in Earth’s oxygen supply?
Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.

Check worksheet solutions here.
FAQs on Worksheet-1: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What is the significance of microorganisms in our daily lives? |  |
| 2. How do microorganisms contribute to human health? |  |
| 3. What are some common types of microorganisms? |  |
| 4. How do scientists study microorganisms that are not visible to the naked eye? |  |
| 5. What role do microorganisms play in the ecosystem? |  |
















