Worksheet: Determination of Income and Employment- 1 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are two alternative ways of determining equilibrium level of income ? How are these related ?
Q2: An economy is in equilibrium. Calculate the Marginal Propensity to Save from the following : National Income = 1,000 Autonomous Consumption = 100 Investment= 120
Q3: Calculate Marginal Propensity to Consume from the following data about an economy which is in equilibrium:
National Income = 1,500
Autonomous Consumption Expenditure = 300 Investment Expenditure = 300
Q4: What is ex-Ante consumption? Distinguish between autonomous consumption and induced consumption
Q5: Calculate equilibrium level of income : (i) Autonomous consumption = 200 (ii) Marginal propensity to consume = 0.9 (iii) Investment expenditure = 1,000A
Q6: An economy is in equilibrium. From the following data calculate investment expenditure :
(i) Marginal propensity to consume = 0·9
(ii) Autonomous consumption = 200
(iii) Level of income = 10000
Q7: Calculate Autonomous Consumption Expenditure from the following data about an economy which is in equilibrium : National Income = 900
Marginal Propensity to Save = 0.10 Investment Expenditure = 80
Q8: Calculate “Investment Expenditure” from the following data about an economy which is in equilibrium :
National Income = 700
Marginal Propensity to Consume = 0.8 Autonomous Consumption Expenditure = 70
Q9: An economy is in equilibrium. Find ‘autonomous consumption’ from the following : National Income= 1,000 Marginal Propensity to Consume = 0.8 Investment Expenditure= 100
Q10: S = – 100 + 0.2 Y is the saving function in an economy. Investment expenditure is 5,000. Calculate the equilibrium level of income.
Q11: An economy is in equilibrium. Find Marginal Propensity to Consume from the following : National Income= 2,000 Autonomous Consumption = 400 Investment Expenditure=200
Q12: An economy is in equilibrium. Calculate the Investment Expenditure from the following : National Income = 800 Marginal Propensity to Save = 0.3 Autonomous Consumption = 100
Q13: Calculate “Investment Expenditure” from the following data about an economy which is in equilibrium :
National Income = 700
Marginal Propensity to Consume = 0.8 Autonomous Consumption Expenditure = 70
Q14: Calculate Marginal Propensity to Consume from the following data about an economy which is in equilibrium :
National Income = 2,000
Autonomous Consumption Expenditure = 200 Investment Expenditure = 100
Q15: Shouldn’t greater saving imply greater investment and greater flow of goods and services?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the Consumption Function and Saving Function.
Q2: Given Saving Curve, derive Consumption Curve and state the steps in doing so. Use diagram.
OR
Outline the steps required to be taken in deriving the consumption curve from given saving curve. Use diagram.
Q3: Given Consumption Curve, derive Saving Curve and state the steps taken in the process of derivation.
OR
Outline the steps required to be taken in deriving saving curve from the given consumption curve.
OR
Given a consumption curve, outline the steps required to be taken in deriving a saving curve from it. Use diagram.
Q4: Giving reason state whether the following statements are true or false:
(i) Average propensity to save cannot be negative.
(ii) Value of marginal propensity to consume can be greater than one.
(iii) Average propensity to consume can be greater than one.
Q5: Derive a straight line saving curve using the following consumption saving on function: C = 20 + 0.6Y. Presuming the income levels to be ₹ 100, ₹ 200 and ₹ 300 crore. Calculate that level of income where consumption is equal to income.
Q6: Complete the following table :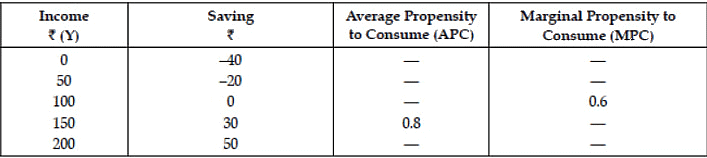
Q7: In an economy, investment increased by 1,100 and as a result of it income increased by 5,500. Had the marginal propensity to save been 25 percent, what would have been the increase in income?
Q8: When is an Economy in Equilibrium ? Explain with the help of saving and investment functions.
Also explain the changes that take place in an economy when the economy is not in equilibrium.
OR
Explain the determination of equilibrium level of national income using ‘saving and investment’ approach. Use diagram. Also explain the effects if savings is greater than investment.
Q9: Explain the changes that take place when Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply are not equal.
Q10: In an economy planned spending is greater than planned output. Explain all the changes that will take place in the economy.
Q11: (i) Define Aggregate Demand. What are its component ?
(ii) From the following data about an economy, calculate its equilibrium level of income.
(a) Marginal Propensity to Consume = 0.75
(b) Autonomous Consumption = 200
(c) Investment = 6,000
Q12: (i) Distinguish between Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply.
(ii) From the following data about an economy calculate its equilibrium level of income.
(a) Marginal Propensity to Consume = 0.8
(b) Investment = 5,000
(c) Autonomous Consumption = 500
Q13: (i) Distinguish between Autonomous Invest-ment and Induced Investment.
(ii) On the basis of the following information about an economy, calculate its equilibrium level of income.
(a) Autonomous Consumption = 100
(b) Marginal Propensity to Consume = 0.75
(c) Investment = 5,000
Q14: (i) Distinguish between Autonomous Consumption and Induced Consumption.
(ii) From the following data about an economy, Calculate its equilibrium level of income.
(a) Marginal Propensity to Consume = 0.5
(b) Autonomous Consumption = 300
(c) Investment = 6,000
Q15: Explain the working of the Investment Multiplier with the help of a Numerical example.
Q16: What is the range of values of investment multiplier ? Clarify the relation of investment multiplier with marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and with marginal propensity to save (MPS).
Q17: Assuming that increase in investment is ₹ 1000 crore and marginal propensity to consume is 0.9, explain the working of multiplier.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Determination of Income and Employment- 1 - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the meaning of income? |  |
| 2. How is income determined in an economy? |  |
| 3. What factors determine the level of employment in an economy? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to measure income and employment in an economy? |  |
| 5. What are the different methods used to calculate national income? |  |
















