Electoral Politics Class 9 Worksheet Civics Chapter 1
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
Q1: Who appoints the Chief Election Commissioner of India?
(a) The Chief Justice of India
(b) The Prime Minister of India
(c) The President of India
(d) The Law Minister of India
Q2: Constituencies called ‘wards’ are made for the election to
(a) Parliament
(b) State Legislative Assembly
(c) State Legislative Council
(d) Local bodies such as Panchayats and Municipalities
Q3: Which of these is not a part of the district and local level bodies?
(a) Panchayats
(b) Municipalities
(c) Corporations
(d) Lok Sabha
Q4: When on election duty, under whose control do the government officers work?
(a) Central Government
(b) Election Commission
(c) District Magistrate
(d) District Court
Q5: Which document must a candidate submit before elections?
(a) Identity Card
(b) Nomination Form
(c) Proof of citizenship only
(d) School certificate
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: In India, Lok Sabha and Vidhan Sabha elections are held regularly after every _______ .
Q2: The party that does not form the government is called the _______.
Q3: The list of those people who are eligible to vote is officially called the Electoral Roll and is commonly known as the _______ .
Q4: _______ is the term used for fake voting or misuse of polling process.
Q5: A person must be at least _______ years old to vote in India.
Match the Following
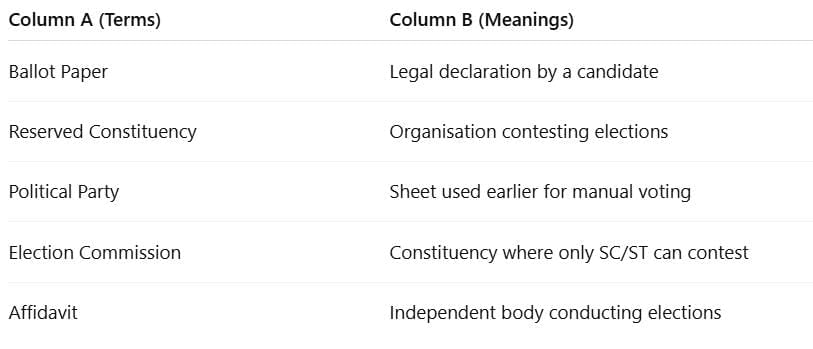
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1. Who formed the new party named Lok Dal?
Q2. How many Lok Sabha Constituencies are there in the Indian Parliament?
Q3. What is an Electoral Roll?
Q4. What is a party ticket?
Q5. What do you mean by Turn Out?
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Electoral Politics Class 9 Worksheet Civics Chapter 1
| 1. What is electoral politics? |  |
| 2. How does the electoral politics system work? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of electoral politics in a democracy? |  |
| 4. What are some challenges faced in electoral politics? |  |
| 5. How can citizens actively engage in electoral politics? |  |
















