Worksheet: Exploring the Investigative World of Science | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
Q1. According to this chapter, what starts every good scientific investigation?
a) Expensive lab equipment
b) Memorising facts
c) Asking focused “Why?” and “How?” questions
d) Copying others’ experiments
Q2. What does “controlling variables” mean in an experiment like puffing a puri?
a) Changing many things at once
b) Changing nothing at all
c) Changing only one factor while keeping others the same
d) Ignoring measurements
Q3. In the “roots and kites” symbol, roots mainly remind us to:
a) Fly kites higher
b) Rely only on imagination
c) Stay grounded in careful observations and facts
d) Ignore data Roots and Kites
Roots and Kites
Q4. Which topic best illustrates “the invisible world”?
a) Moon phases
b) Microbes in a drop of water
c) Cyclones
d) Mirrors and lenses
Q5. Which is NOT a correct match of topic to key idea?
a) Health — immunity and vaccines help prevent disease
b) Electricity — only lighting bulbs, not heating
c) Forces — change speed/direction of objects
d) Pressure and winds — air moves from high to low pressure
Q6. What is the main reason for doing “one change at a time” in an experiment?
a) To finish faster
b) To make it more exciting
c) To clearly link cause and effect
d) To avoid writing observations
Q7. Which tool of science is most directly used when you record time to puff a puri?
a) Classifying
b) Measuring
c) Predicting without testing
d) Guessing
Q8. Why do we learn about Moon phases and eclipses under “keeping time with the skies”?
a) For decoration
b) To ignore calendars
c) Because celestial motions helped humans define days, months, years
d) To stop using watches
Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
Q1. Writing down what you see is called __________.
Q2. Health is complete physical, mental, and __________ well-being.
Q3. Air moves from high pressure to __________ pressure to form winds.
Q4. All matter is made of tiny __________ that behave differently in solids, liquids, and gases.
Q5. Light can __________ from mirrors and __________ through lenses.
Q6. Watching the Sun and Moon helped humans create __________ to track days and months.
Q7. Science balances careful observation with __________ thinking.

Very Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
Q1. What two words best start a scientific investigation?
Q2. In an experiment, what do we call the factor we deliberately change?
Q3. Name one measurement you could take in the puri experiment.
Q4. Give one reason to keep a science notebook.
Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
Q1. Why is changing only one variable at a time important?
Q2. How does this chapter connect small observations to big ideas?
Q3. What skills are highlighted as core to doing science well?
Q4. Give two example variables for the puri activity.
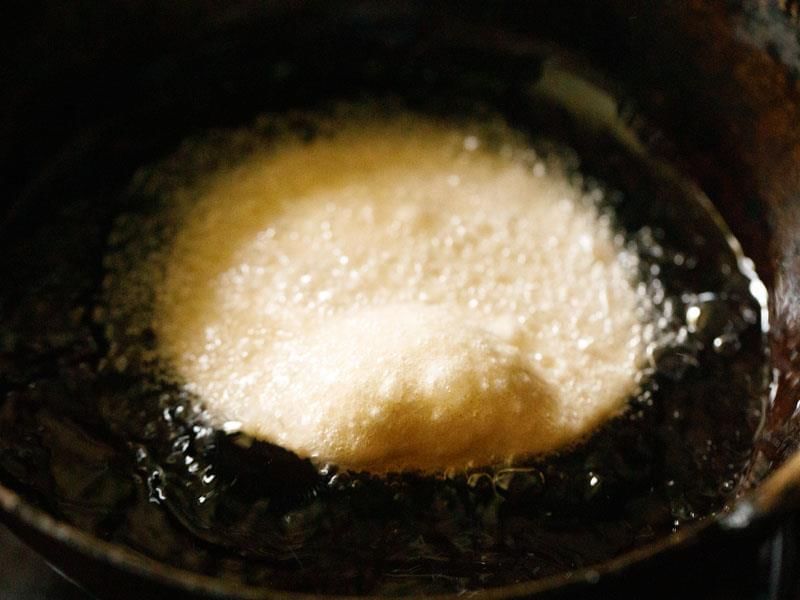 Poori puffing up in Oil
Poori puffing up in Oil
Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.

Check the solutions of worksheet here.
FAQs on Worksheet: Exploring the Investigative World of Science - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What are the key components of the investigative process in science? |  |
| 2. How does the scientific method contribute to investigations in science? |  |
| 3. What role does observation play in scientific investigations? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to document findings during scientific investigations? |  |
| 5. How do experiments differ from observations in the context of scientific investigations? |  |
















