Worksheet: Organisms and Cells | Science for Grade 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): |

|
| Fill in the Blanks: |

|
| True/False: |

|
| Match the Column |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs):
Q1. What is the primary purpose of generating a hypothesis in scientific research?
A) To create a detailed report
B) To answer specific scientific questions
C) To find the best scientists
D) To make the research last longer
Ans: B
Explanation: A hypothesis is generated to propose a testable idea that answers specific scientific questions, guiding the research process.
Q2. Which process is not a life process necessary for survival?
A) Movement
B) Reproduction
C) Sensitivity
D) Photosynthesis
Ans: D
Explanation: While photosynthesis is critical for plants, it is not a universal life process necessary for the survival of all organisms.
Q3. Which organ is not paired in the human body?
A) Lungs
B) Kidneys
C) Heart
D) Eyes
Ans: C
Explanation: The heart is a single organ, unlike lungs, kidneys, and eyes, which are paired.
Q4. Which of the following is not one of the seven life processes discussed in the chapter?
A) Growth
B) Respiration
C) Excretion
D) Photosynthesis
Ans: D
Explanation: Photosynthesis is a process specific to plants and certain other autotrophic organisms to produce food. It is not considered one of the seven fundamental life processes necessary for the survival of all living organisms.
Q5. The ability to create new organisms similar to themselves is known as:
A) Nutrition
B) Movement
C) Reproduction
D) Sensitivity
Ans: C
Explanation: Reproduction is the life process where organisms create new organisms similar to themselves, called offspring.
Fill in the Blanks:
Q1. Predictions in scientific research are made based on the _______.
Ans: hypothesis
Explanation: Predictions are derived from the hypothesis to establish what the outcomes of the experiments might be if the hypothesis is correct.
Q2. The process by which organisms increase in size and maturity is called _______.
Ans: growth
Explanation: Growth is the process where organisms increase in size and advance in maturity over time.
Q3. The human organ responsible for oxygenating blood is the _______.
Answer: lungs
Explanation: The lungs are essential for oxygenating the blood and removing carbon dioxide through respiration.
Q4. The _______ system in plants helps in the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Ans: vascular
Explanation: In flowering plants, roots, stem, and leaves form the water transport system, absorbing, transporting, and distributing water throughout the plant. This refers to the vascular system.
Q5. Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665 while studying _______ bark under a microscope.
Ans: cork
Explanation: Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665 while studying cork bark under a microscope.
True/False:
Q1. Drawing conclusions in science involves ignoring the data collected.
Answer: False
Explanation: Drawing conclusions crucially involves analyzing the collected data to support or refute the hypothesis.
True/False:
Q2. A hypothesis does not need to be testable.
Answer: False
Explanation: A hypothesis must be testable; it is a fundamental requirement for it to serve its role in the scientific process.
Q3. All organisms perform photosynthesis.
Answer: False
Explanation: Not all organisms perform photosynthesis; this process is specific to plants and some bacteria.
Q4. The nervous system controls digestive processes.
Answer: False
Explanation: The nervous system primarily controls sensory and motor functions, although it does influence digestion indirectly through signaling.
Q5. The bladder's function is to filter blood.
Answer: False
Explanation: The bladder's function is to store urine, not filter blood; that function is performed by the kidneys.
Match the Column
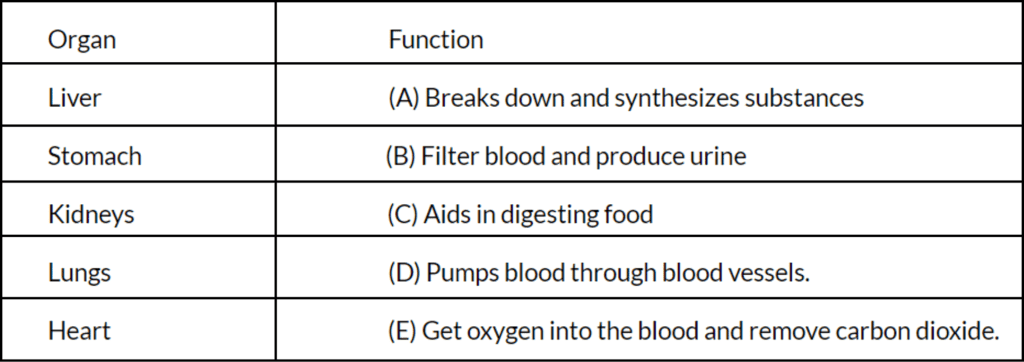
Answers: Liver - A, Stomach - C, Kidneys - B, Lungs - E, Heart - D
Explanation: Each organ has a specific function crucial for the body's overall health.
|
64 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Organisms and Cells - Science for Grade 7
| 1. What are some examples of unicellular organisms? |  |
| 2. How do multicellular organisms differ from unicellular organisms? |  |
| 3. What is the function of the cell wall in plant cells? |  |
| 4. How do animal cells differ from plant cells in terms of organelles? |  |
| 5. How do cells in a multicellular organism communicate with each other? |  |















